Opium Poppy Detection Using Deep Learning
Abstract
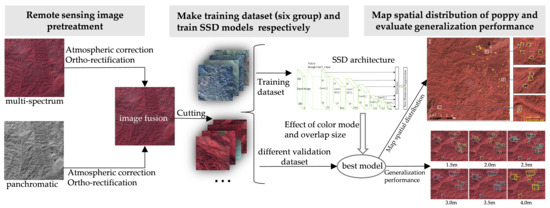
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Images
2.2.2. Ground Truth Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Training Datasets
2.3.2. Training Strategy
- random changes in saturation, brightness, and contrast ratio;
- flip horizontally and vertically;
- cut to random size.
2.3.3. Post-Processing
2.3.4. Accuracy Assessment
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Effect of Different Sliding Window Size
3.2. Effect of Band Combinations
3.3. Poppy Parcel Mapping Using Optimal Results
3.4. Application to Different Spatial Resolutions
3.5. Application to Other Satellite Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Unique Poppy Parcel Detection with Deep Learning-Based Object Detection
4.2. Uncertainty Analysis and Scope for Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UNODC | United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime |
| CNNCC | Chinese National Narcotics Control Commission |
| RGB | Red–Green–Blue |
| NRG | Near infrared-Red-Green |
| VGG | Visual Geometry Group |
| DCNN | Deep Convolutional Neural Network |
| SSD | Single Shot Multibox Detector |
References
- Agrawal, S.; Joshi, P.; Shukla, Y.; Roy, P. Spot vegetation multi temporal data for classifying vegetation in south central Asia. Curr. Sci. 2003, 84, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Sousa, W.; Gong, P. Integration of object-based and pixel-based classification for mapping mangroves with IKONOS imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 5655–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuinsiri, S.; Blasco, F.; Bellan, M.; Kergoat, L. A poppy survey using high resolution remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC. World Drug Report 2005. Available online: http://www.unodc.org /unodc/ en/data-and-analysis/WDR-2005.html (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Tian, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Jia, K.; Wen, M. Opium poppy monitoring with remote sensing in North Myanmar. Int. J. Drug Policy 2011, 22, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simms, D.M.; Waine, T.W.; Taylor, J.C. Improved estimates of opium cultivation in Afghanistan using imagery-based stratification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 3785–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms, D.M.; Waine, T.W.; Taylor, J.C.; Brewer, T.R. Image segmentation for improved consistency in image-interpretation of opium poppy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Wu, B.; Tian, Y.; Li, Q.; Du, X. Spectral discrimination of opium poppy using field spectrometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bussink, C. Unsupervised multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis-based detection of opium poppy fields from an EO-1 Hyperion image in Helmand, Afghanistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-J.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Bussink, C.; Zhang, J.; Ge, H. An unsupervised mixture-tuned matched filtering-based method for the remote sensing of opium poppy fields using EO-1 Hyperion data: An example from Helmand, Afghanistan. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennington, A.L. Application of Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing for Crop Discrimination in Afghanistan. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Bedfordshire, UK, March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Bischof, W.F.; Caelli, T. Road tracking in aerial images based on human–computer interaction and Bayesian filtering. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2006, 61, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Duan, H. Artificial bee colony (ABC) optimized edge potential function (EPF) approach to target recognition for low-altitude aircraft. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leninisha, S.; Vani, K. Water flow based geometric active deformable model for road network. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha, T.R.; Kerle, N.; van Westen, C.J.; Jetten, V.; Kumar, K.V. Segment optimization and data-driven thresholding for knowledge-based landslide detection by object-based image analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 49, 4928–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.A.; Warner, T.A.; Conley, J.F.; McNeil, B.E. Does spatial resolution matter? A multi-scale comparison of object-based and pixel-based methods for detecting change associated with gas well drilling operations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1633–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, D.; Blaschke, T.; Tiede, D.; Jilge, M. Monitoring recovery after earthquakes through the integration of remote sensing, GIS, and ground observations: the case of L’Aquila (Italy). Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 43, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembhavi, A.; Harwood, D.; Davis, L.S. Vehicle detection using partial least squares. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytekin, Ö.; Zöngür, U.; Halici, U. Texture-based airport runway detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Q.; Yang, J. Hyperspectral image denoising via sparse representation and low-rank constraint. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 53, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J. A survey on object detection in optical remote sensing images. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 117, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1409.1556. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556 (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Costante, G.; Ciarfuglia, T.A.; Biondi, F. Towards Monocular Digital Elevation Model (DEM)Estimation by Convolutional Neural Networks—Application on Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 4–7 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xia, G.-S.; Wu, T.; Lin, L.; Tai, X.C. Deep learning for remote sensing image understanding. J. Sens. 2016, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Huo, H.; Zhu, T.; Fang, T. Harbor Detection in Large-Scale Remote Sensing Images Using Both Deep-Learned and Topological Structure Features. In Proceedings of the Computational International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design, Hangzhou, China, 9–10 December 2017; pp. 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Marcum, R.A.; Davis, C.H.; Scott, G.J.; Nivin, T.W. Rapid broad area search and detection of Chinese surface-to-air missile sites using deep convolutional neural networks. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 042614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Fu, Q. Combing Single Shot Multibox Detector with transfer learning for ship detection using Chinese Gaofen-3 images. In Proceedings of the Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, Toyama, Japan, 1–4 August 2017; pp. 712–716. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, K.; Sun, H.; Sun, X.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H. A multi-model ensemble method based on convolutional neural networks for aircraft detection in large remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese National Narcotics Control Commission (CNNCC). Opium Poppy Monitoring in Laos. (Interior Material), Beijing: CNNCC, 2017. Available online: http://www.nncc.org.cn/ (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Liu, X.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, L.; Li, P.; Liao, C.; Yang, Y.; You, Z. Rubber plantation and its relationship with topographical factors in the border region of China, Laos and Myanmar. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 1019–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapinmongkolkarn, P.; Thisayakorn, C.; Kattiyakulwanich, N.; Murai, S.; Kittichanan, H.; Vanasathid, C.; Okuda, T.; Jirapayooungchai, K.; Sramudcha, J.; Matsuoka, R. Remote sensing applications to land cover classification in northern Thailand [LANDSAT]. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 270, 10828–10832. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Xia, G.-S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Transferring deep convolutional neural networks for the scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14680–14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhao, B.; Song, Y. Urban land-use mapping using a deep convolutional neural network with high spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters a density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, OR, USA, 4–8 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. Airport target detection in remote sensing images: A new method based on two-way saliency. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, S.; Su, Y. Fast and accurate target detection based on multiscale saliency and active contour model for high-resolution SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5729–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karine, A.; Toumi, A.; Khenchaf, A.; EL Hassouni, M. Radar Target Recognition using Salient Keypoint Descriptors and Multitask Sparse Representation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















| Months | Climatic Seasons | Main Agricultural Activities |
|---|---|---|
| June–August | Almost continuous rain | Almost no poppy activity |
| September–October | End of rainy season | Slash and burn of small forest plots |
| November–February | Cool dry season, sometimes sunny | Drying the soil and sowing Weeding and thinning Blossoming Harvesting poppy capsules Burning the stubble |
| March–May | Scattered rains and beginning of the rainy season | End of harvesting season for late varieties |
| Satellite | Height | Incidence Angle | Sensor | Id-Image | Band | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZY3 | 506 km | 97.421° | MUX | ZY3_MUX_E102.5_N21.5_20161122_L1A0003584928 ZY3_MUX_E102.4_N21.1_20161122_L1A0003584929 | Near Infrared | 770–890 |
| Red | 630–690 | |||||
| Green | 520–590 | |||||
| Blue | 450–520 | |||||
| TLC | ZY3_NAD_E102.5_N21.5_20161122_L1A0003583973 ZY3_NAD_E102.4_N21.1_20161122_L1A0003583974 | Panchromatic | 500–800 | |||
| GF-2 | 631 km | 97.908° | PMS1 | GF2_PMS1_E102.1_N22.1_20171101_L1A0002729519 | Near Infrared | 770–890 |
| Red | 630–690 | |||||
| Green | 520–590 | |||||
| Blue | 450–520 |
| Color Mode | Overlap | Picture Samples | Poppy Parcels Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| false color (NRG) | 100 | 14,559 | 24,411 |
| false color | 150 | 6543 | 10,959 |
| false color | 200 | 3657 | 6087 |
| true color (RGB) | 100 | 14,559 | 24,411 |
| true color | 150 | 6543 | 10,959 |
| true color | 200 | 3657 | 6087 |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Batch size | 6 |
| Stochastic optimization method | Adam |
| Training epoch | 300 |
| Learning rate | epoch < 100: 0.004 epoch ∈ [100, 200): 0.0004 epoch ≥ 200: 0.00004 |
| Early stopping condition | valid-loss does not reduce for 60 epochs |
| Resolution (m) | Precision (%) | Prediction Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 56.7 | 88.88 |
| 2.0 | 95.1 | 50 |
| 2.5 | 88.2 | 32 |
| 3.0 | 88.0 | 22.22 |
| 3.5 | 64.1 | 16.32 |
| 4.0 | 64.4 | 12.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, F.; Yang, G. Opium Poppy Detection Using Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121886
Liu X, Tian Y, Yuan C, Zhang F, Yang G. Opium Poppy Detection Using Deep Learning. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(12):1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121886
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiangyu, Yichen Tian, Chao Yuan, Feifei Zhang, and Guang Yang. 2018. "Opium Poppy Detection Using Deep Learning" Remote Sensing 10, no. 12: 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121886
APA StyleLiu, X., Tian, Y., Yuan, C., Zhang, F., & Yang, G. (2018). Opium Poppy Detection Using Deep Learning. Remote Sensing, 10(12), 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121886