Evaluation of Three-Hourly TMPA Rainfall Products Using Telemetric Rain Gauge Observations at Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Datasets, and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Telemetric Rain Gauge Observations
2.3. TMPA
2.4. Methodology
3. Analysis and Results
3.1. TMPA Products Evaluation for Entire Study Period
3.1.1. TMPA Performance Assessment Using Categorical Indices
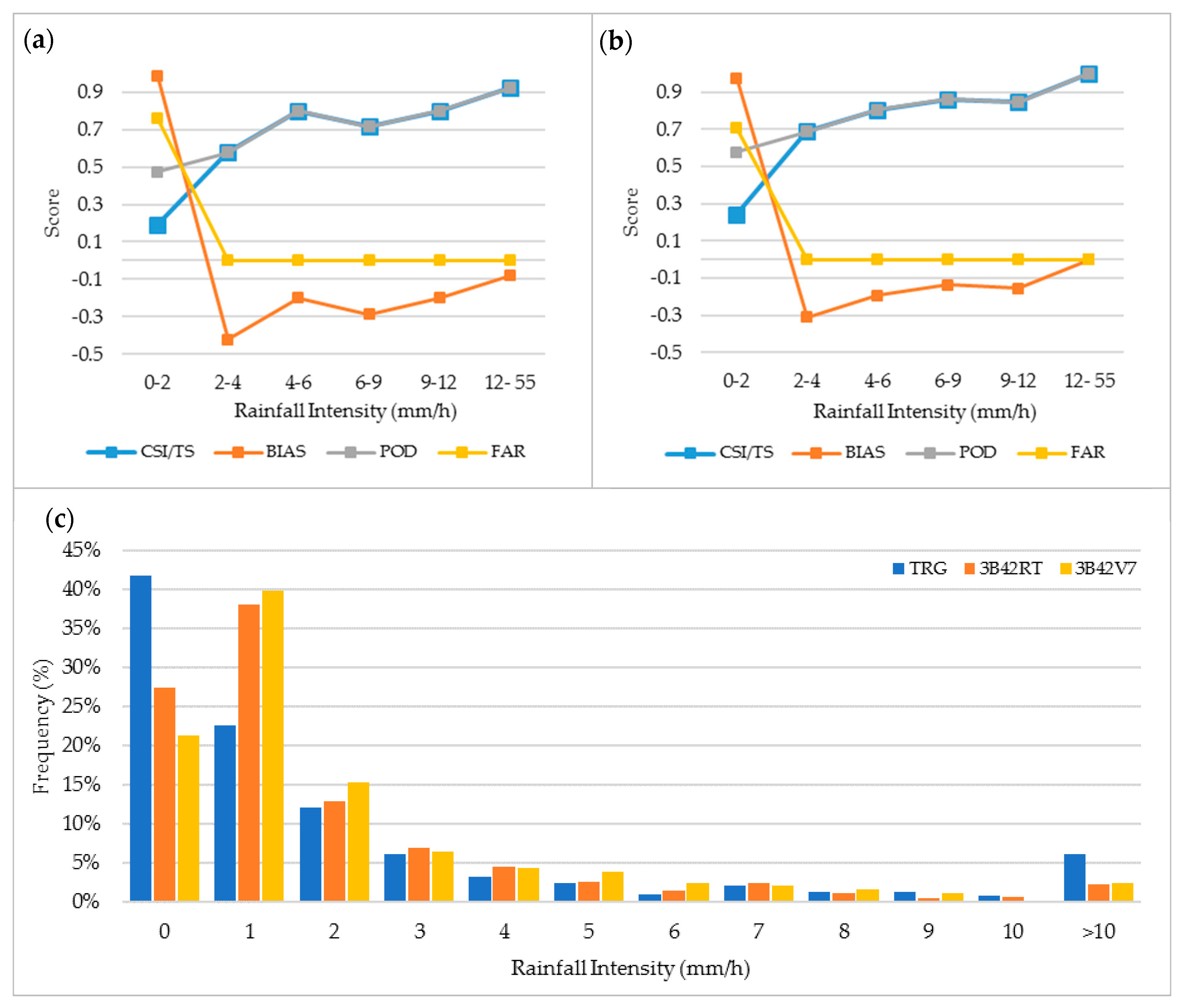
3.1.2. TMPA Performance as a Function of Rainfall Intensity
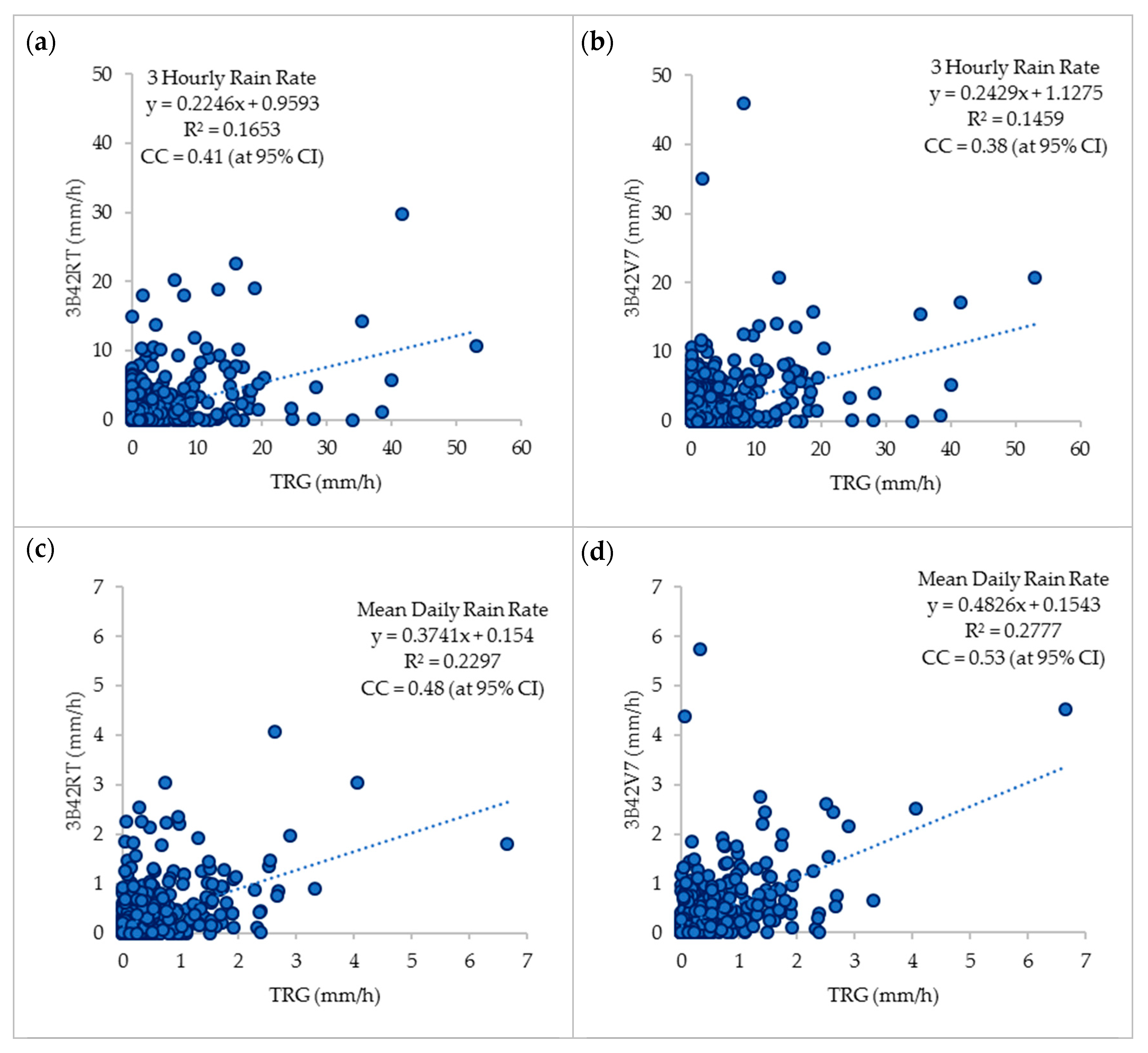
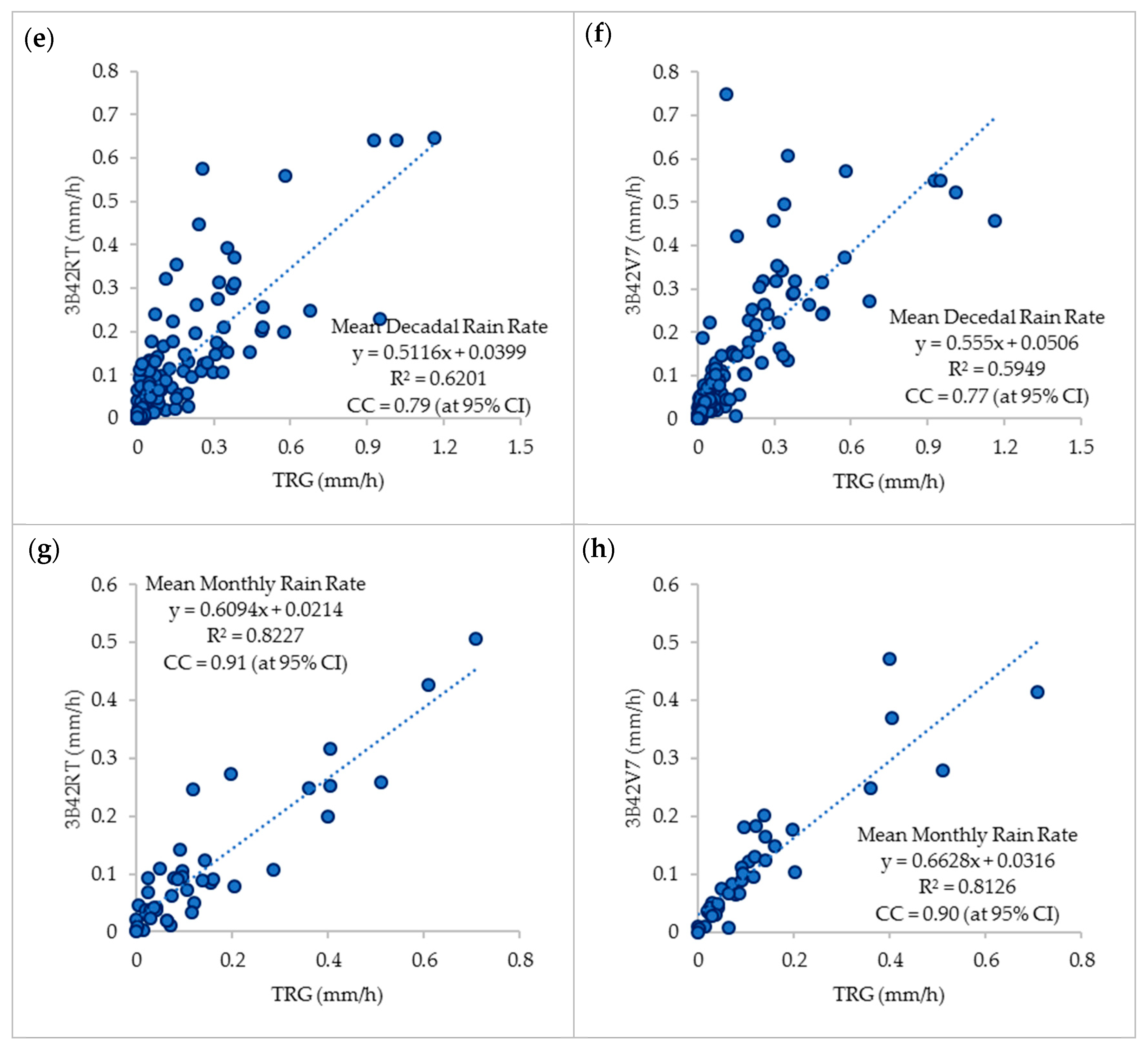
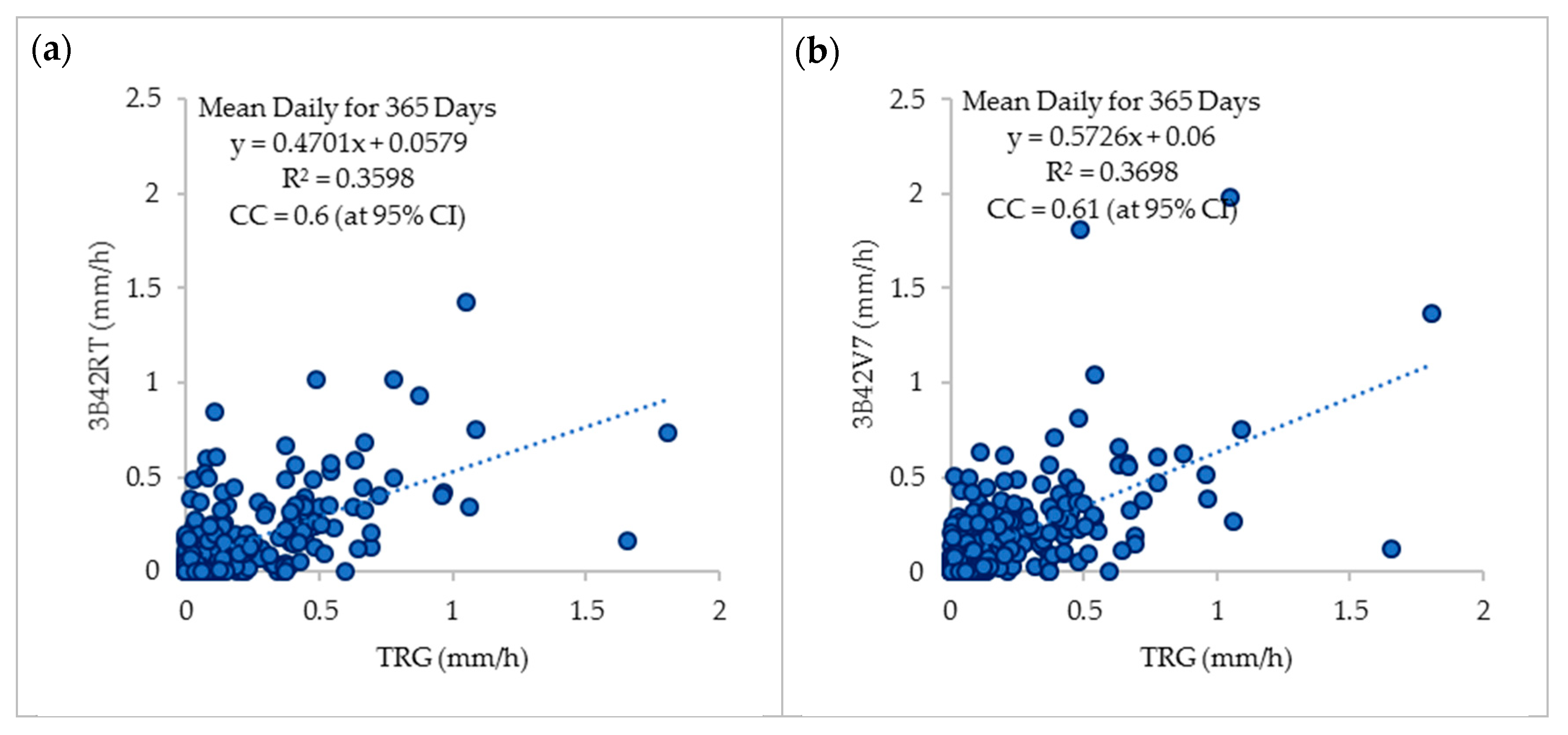
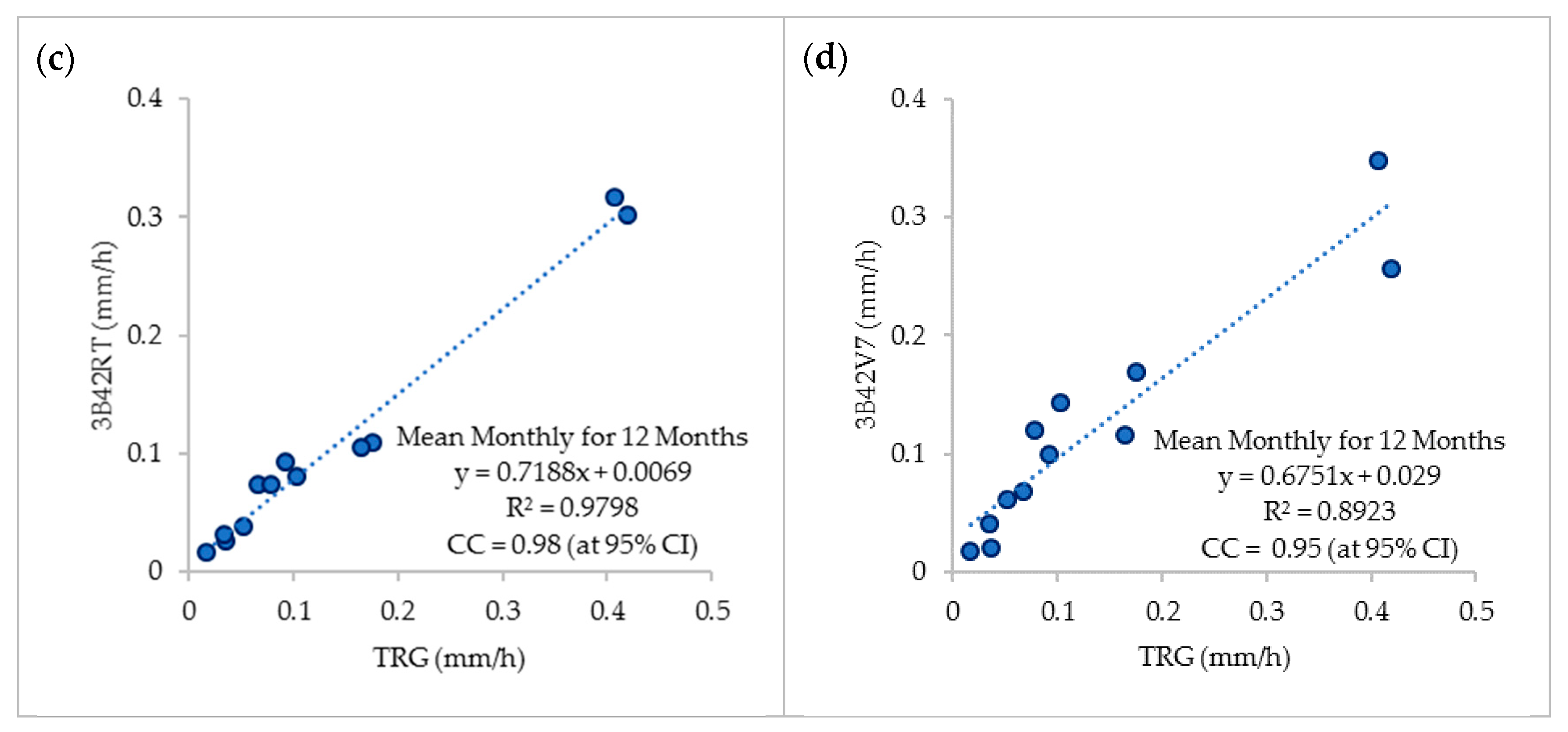
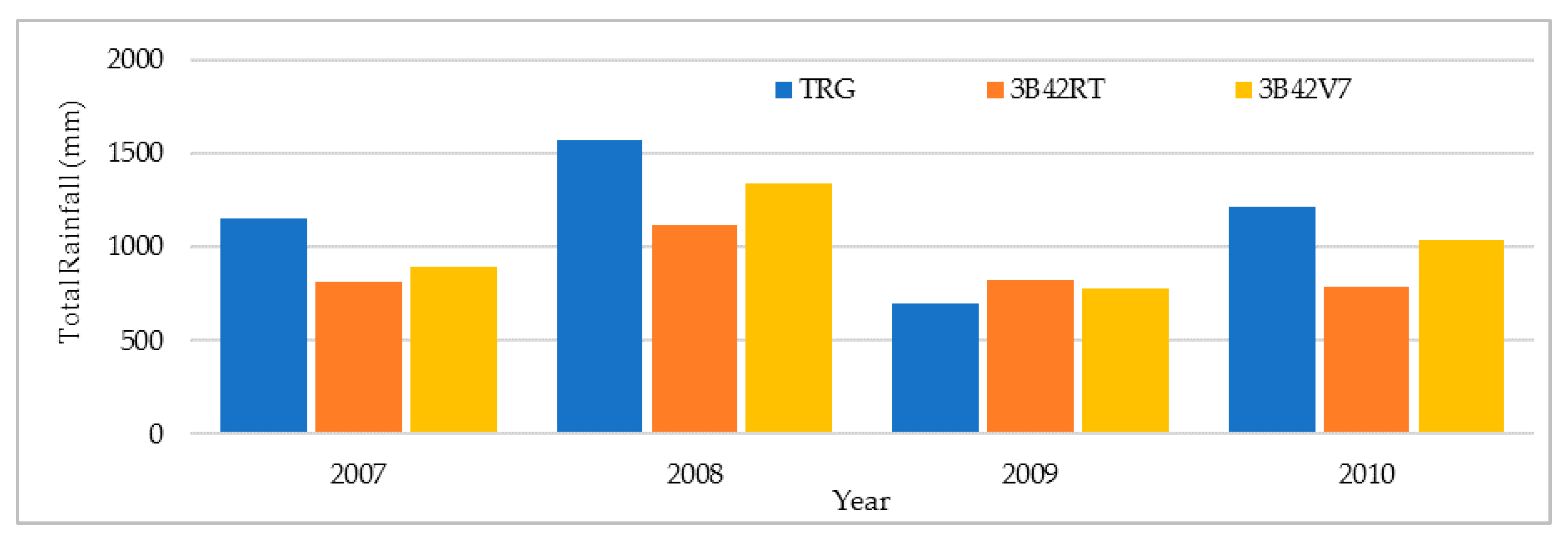
3.1.3. TMPA Rainfall Validation
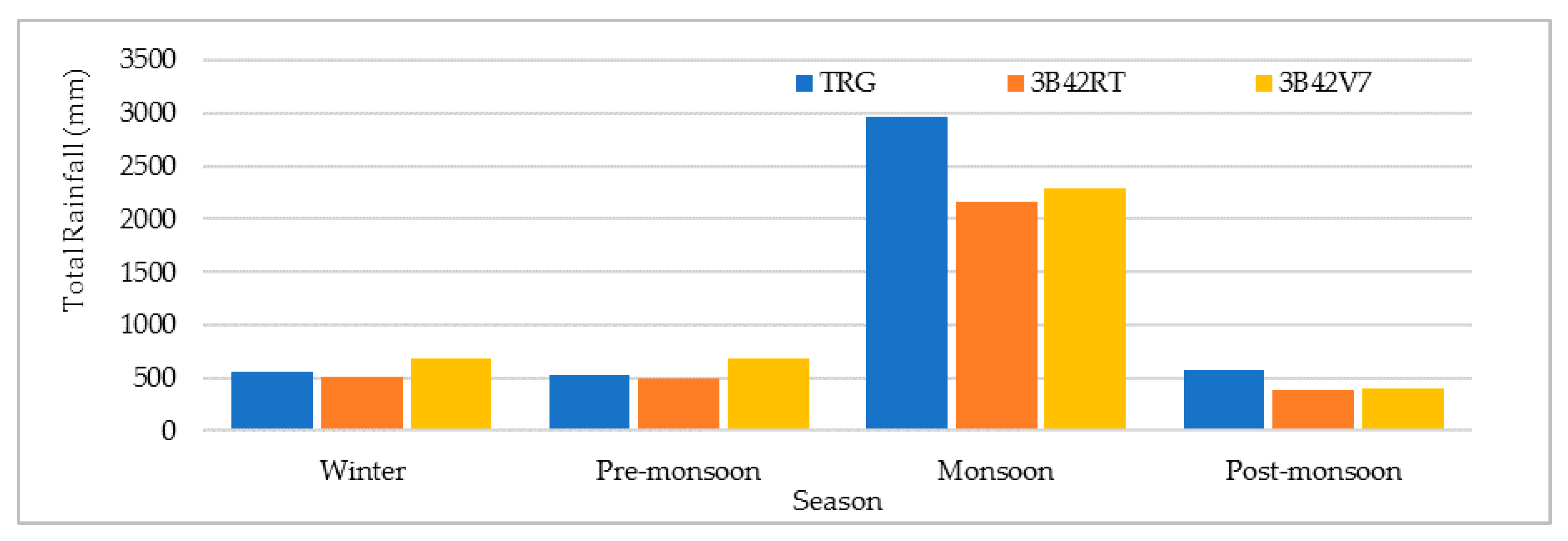
3.2. TMPA Products Evaluation for Different Seasons
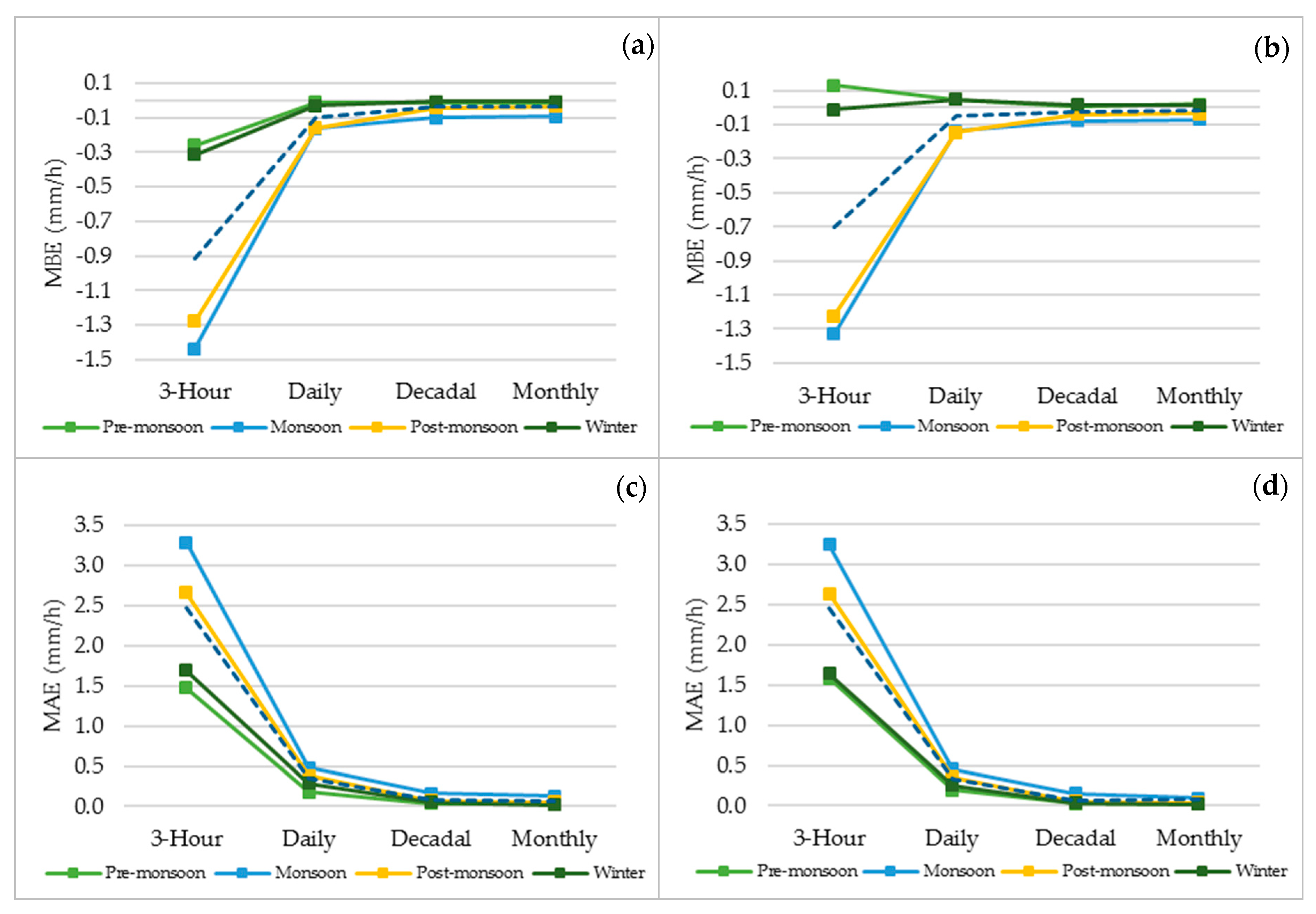
3.2.1. Seasonal Performance Assessment
3.2.2. TMPA Validation across Different Seasons
3.3. Diurnal Rainfall Analysis
3.3.1. Diurnal Rainfall Analysis for Entire Study Period
3.3.2. Seasonal Diurnal Rainfall Analysis
3.3.3. Case Study: Heavy Rainfall Event—July 2008
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Lu, H.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, L.; Shi, J. Evaluation and comparison of daily rainfall from latest gpm and trmm products over the mekong river basin. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, Z.; Zeeshan, M. Environmental hazards faced by inhabitants of Nala Lai. Pak. Assoc. Anthropol. 2015, 27, 781–784. [Google Scholar]
- Shamim, N. Climate change, flood disasters, human displacement and changing lives and food patterns of marginalized people living in tributeries of Nullah Lai Rawalpindi. Explor. Islam. J. Soc. Sci. 2016, 2, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, A. Flash flood forecasting system for Lai Nullah basin (a case study of March 19, 2007 rainfall event). Pak. J. Meteorol. 2007, 4, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Kazmi, S.F.; Pervez, T. Human response to hydro-meteorological disasters: A case study of the 2010 flash floods in Pakistan. J. Geogr. Reg. Plan. 2011, 4, 518–524. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, M. A view from Pakistan: Recurrent flash floods in areas surrounding Nullah Lai, Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Middle East J. Bus. 2014, 9, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, H.N.; Siddiqui, Q.T.M.; Ghumman, A.R.; Kamal, M.A.; Mughal, H.R. A critical analysis of 2010 floods in Pakistan. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Paulikas, M.J.; Rahman, M.K. A temporal assessment of flooding fatalities in Pakistan (1950–2012). J. Flood Risk Manag. 2015, 8, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia Lai Nullah. 2017. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lai_Nullah (accessed on 21 January 2018).
- Ahmad, B.; Kaleem, M.S.; Butt, M.J.; Dahri, Z.H. Hydrological modelling and flood hazard mapping of Nullah Lai. Proc. Pak. Acad. Sci. 2010, 47, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, A. Pakistan: Lai Nullah Basin Flood Problem Islamabad—Rawalpindi Cities; World Meteorological Organization: Geneve, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Japan International Cooperation Agency. Basic Design Study Report on the Lai Nullah Flood Forecasting and Warning System Project in the Islamic Republic of Pakistan; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2005.
- Siddiqui, Q.T.M.; Hashmi, H.N.; Ghumman, A.R.; Mughal, H.R. Flood Inundation Modeling for a Watershed in the Pothowar Region of Pakistan. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2011, 36, 1203–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Zaman, Q. Case study: Heavy rainfall event over Lai Nullah catchment area. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2010, 6, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, H.; Chaudhry, A.G.; Nasir, A. Nala Lai and urban ecology: A study of dwellers and disaster management. Pak. Assoc. Anthropol. 2015, 27, 617–619. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.F.; Hussain, A. Validation of satellite based precipitation over diverse topography of Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2018, 201, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuki, S.K.; Saghafian, B.; Moazami, S. Comprehensive evaluation of 3-hourly TRMM and half-hourly GPM-IMERG satellite precipitation products. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boegh, E.; Thorsen, M.; Butts, M.B.; Hansen, S.; Christiansen, J.S.; Abrahamsen, P.; Hasager, C.B.; Jensen, N.O.; van der Keur, P.; Refsgaard, J.C.; et al. Incorporating remote sensing data in physically based distributed agro-hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2004, 287, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J. Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multisatellite observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.E. Methods for verifying satellite precipitation estimates. In Measuring Precipitation from Space: EURAINSAT and the Future; Levizzani, V., Bauer, P., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 28, pp. 345–356. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauniyar, S.P.; Protat, A.; Kanamori, H. Uncertainties in TRMM-Era multisatellite-based tropical rainfall estimates over the Maritime Continent. Earth Space Sci. 2017, 4, 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Yen, H.; Collick, A.S.; Tilahun, S.A.; Langan, S.; Steenhuis, T.S. Evaluation of CFSR, TMPA 3B42 and ground-based rainfall data as input for hydrological models, in data-scarce regions: The upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Catena 2017, 152, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, W.; Satoh, M.; Nasuno, T. Improvement of a cloud microphysics scheme for a global nonhydrostatic model using trmm and a satellite simulator. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 74, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Adler, R.F.; Negri, A.; Huffman, G.J. Flood and landslide applications of near real-time satellite rainfall products. Nat. Hazards 2007, 43, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimot, S.; Amarnath, G. Applications of satellite-based rainfall estimates in flood inundation modeling—A case study in Mundeni Aru River Basin, Sri Lanka. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricko, M.; Carton, J.A.; Birkett, C. Climatic effects on lake basins. Part I: Modeling tropical lake levels. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 2983–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Adler, R.F.; Hong, Y.; Tian, Y.; Policelli, F. Evaluation of global flood detection using satellite-based rainfall and a hydrologic model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1268–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, D.; Adler, R.; Adler, D.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Huffman, G. Global distribution of extreme precipitation and high-impact landslides in 2010 relative to previous years. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1536–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, F.M.; Wang, X.X.; Li, X.D.; Fan, Y.Y.; Cai, S.X.; Ao, T.Q. Combining rainfall data from rain gauges and TRMM in hydrological modelling of Laotian data-sparse basins. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froidurot, S.; Diedhiou, A. Characteristics of wet and dry spells in the West African monsoon system. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2017, 18, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesús, A.; Breña-Naranjo, J.A.; Pedrozo-Acuña, A.; Yamanaka, V.H.A. The use of TRMM 3B42 product for drought monitoring in Mexico. Water (Switzerland) 2016, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Liu, D. Global view of real-time TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis: Implications for its successor global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Mitra, A.K.; AghaKouchak, A.; Pai, D.S. Error characterization of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA-3B42) products over India for different seasons. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Adler, R.F.; Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Real-time global flood estimation using satellite-based precipitation and a coupled land surface and routing model. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2693–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.T.-C.; McAneney, J.; Cheung, K.K.W. Case study of trmm satellite rainfall estimation for landfalling tropical cyclones: Issues and challenges. Trop. Cyclone Res. Rev. 2013, 2, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, S.; Mahesh, C.; Gairola, R.M.; Pal, P.K. Comparison of high-resolution TRMM-based precipitation products during tropical cyclones in the North Indian Ocean. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Space Development Agency. TRMM Data Users Handbook; National Space Development Agency of Japan: Saitama, Japan, 2001.
- Kidd, C.; Levizzani, V. Status of satellite precipitation retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moazami, S.; Golian, S.; Kavianpour, M.R.; Hong, Y. Comparison of PERSIANN and V7 TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) products with rain gauge data over Iran. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 8156–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M. Calibration of TRMM rainfall climatology over Saudi Arabia during 1998–2009. Atmos. Res. 2010, 99, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Das, S.; Uyeda, H. Calibration of TRMM derived rainfall over Nepal during 1998–2007. Open Atmos. Sci. J. 2010, 4, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Uyeda, H. Use of TRMM in determining the climatic characteristics of rainfall over Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, A.; Guan, D.; Wu, J.; Yuan, F.; Xu, L. Comprehensive precipitation evaluation of TRMM 3B42 with dense rain gauge networks in a mid-latitude basin, northeast, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, M.L.M.; Rohrer, M.; Huggel, C.; Villar, D.S.; Silvestre, E.; Huffman, G.J. Evaluation of TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) performance in the Central Andes region and its dependency on spatial and temporal resolution. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2649–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotsıfakıs, K.; Felonı, E.; Kotronı, V.; Baltas, E. Evaluation of the Version 7 TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) 3B42 product over Greece. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Rhodes, Greece, 31 August–2 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Yu, R. Intercomparison of summer rainfall diurnal features between station rain gauge data and TRMM 3B42 product over central eastern China. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, B.J.; Han, H.J.; Seo, E.K. Validation of satellite-based high-resolution rainfall products over the Korean Peninsula using data from a dense rain gauge network. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G. Evaluation of the research-version TMPA rainfall estimate at its finest spatial and temporal scales over the Rome metropolitan area. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 2591–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapiano, M.R.P.; Arkin, P.A. An intercomparison and validation of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates with 3-hourly gauge data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Y.; Sathe, F.; Hussain, M.B.; Martinez, H.E. Performance of CMORPH, TMPA, and PERSIANN rainfall datasets over plain, mountainous, and glacial regions of Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Ijaz, M.W.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite-based real-time and post-real-time precipitation estimates during 2010 extreme flood event in Swat River Basin, Hindukush Region. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Tahir, A.A.; Iqbal, M.; Adnan, M. Comparison of two successive versions 6 and 7 of TMPA satellite precipitation products with rain gauge data over Swat Watershed, Hindukush Mountains, Pakistan. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2016, 17, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.I.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Huelsing, H.K.; Khattak, M.U.; Vergara, H.J. Spatial and diurnal variability of monsoon systems assessed by TRMM rain rate over Indus Basin. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Khattak, M.U.K.; Yong, B.; Vergara, H.J. Evaluation of three high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates: Potential for monsoon monitoring over Pakistan. Adv. Sp. Res. 2014, 54, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Khan, S.J.; Aslam, I.; Khan, Z. Simulation of the impacts of land-use change on surface runoff of Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 102, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarraud, M. Measurement of precipitation. In Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation (WMO-No. 8), 7th ed.; World Meteorological Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z. Comparison of versions 6 and 7 3-hourly TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) research products. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. The TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA). In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, S.; Gairola, R.M. Validation of TRMM-3B42 precipitation product over the tropical Indian Ocean using rain gauge data from the RAMA buoy array. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcù, F.; Milani, L.; Petracca, M. On the uncertainties in validating satellite instantaneous rainfall estimates with raingauge operational network. Atmos. Res. 2014, 144, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Eder, B.; Dennis, R.; Chu, S.-H.; Schwartz, S.E. New unbiased symmetric metrics for evaluation of air quality models. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2006, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Long, D.; Guo, X. Statistical and hydrological comparisons between trmm and gpm level-3 products over a midlatitude basin: Is day-1 IMERG a good successor for TMPA 3B42V7? J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Gautam, A.K.; Palmate, S.S.; Pandey, A.; Suryavanshi, S.; Rathore, N.; Sharma, N. Evaluation of TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) against terrestrial measurement over a humid sub-tropical basin, India. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 129, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidas, H.; Porcu, F.; Puca, S.; Rinollo, A.; Lagouvardos, C.; Kotroni, V. Validation of the H-SAF precipitation product H03 over Greece using rain gauge data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 377–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Chen, D.; Xie, Y. Diurnal variations of precipitation during the warm season over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1154–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.H.; Walther, A.; Nikulin, G.; Chen, D.; Jones, C. Diurnal cycle of precipitation amount and frequency in Sweden: Observation versus model simulation. Tellus Ser. A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2011, 63, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifroth, U.; Trentmann, J.; Fink, A.H.; Ahrens, B. Evaluating satellite-based diurnal cycles of precipitation in the African tropics. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, K.; Khokhar, M.F.; Chishtie, F.; RazzaqKhan, W.; Hakeem, K.R. Identification and future description of warming signatures over Pakistan with special emphasis on evolution of CO2 levels and temperature during the first decade of the twenty-first century. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7617–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Xianfang, S.; Hussain, I.; Jianrong, L.; Mei, H.D.; Hu, Y.L.; Huang, W. Controlling factors of the stable isotope composition in the precipitation of Islamabad, Pakistan. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Khan, E.U.; Akhter, P.; Hussain, S. Wet depositional fluxes of 210Pb- and 7Be-bearing aerosols at two different altitude cities of North Pakistan. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5699–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, A.; Zaman, Q.; Afzal, M. Temporal trends in the peak monsoonal precipitation events over Northeast Pakistan. Pakistan J. Meteorol. Vol. 2013, 10, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Madhura, R.K.; Krishnan, R.; Revadekar, J.V.; Mujumdar, M.; Goswami, B.N. Changes in western disturbances over the Western Himalayas in a warming environment. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 44, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rain Measurement. 2018. Available online: http://wiki.sandaysoft.com/a/Rain_measurement (accessed on 10 March 2018).
- Ali, A.F.; Xiao, C.; Anjum, M.N.; Adnan, M.; Nawaz, Z.; Ijaz, M.W.; Sajid, M.; Farid, H.U. Evaluation and comparison of TRMM multi-satellite precipitation products with reference to rain gauge observations in Hunza River Basin, Karakoram Range, Northern Pakistan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Ahmad, I.; Ijaz, M.W.; Farid, H.U.; Yagoub, Y.E.; Zaman, M.; Adnan, M. Performance evaluation of latest integrated multi-satellite retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (IMERG) over the northern highlands of Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2018, 205, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, W.; Yang, H.; Lei, H.; Muhammad, A.; Yang, D. Improving the Regional Applicability of Satellite Precipitation Products by Ensemble Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, R. Evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over the Chinese mainland. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11649–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Wolff, D.B.; Wolff, K.R.; Bashor, P. Rain gauge and disdrometer measurements during the Keys Area Microphysics Project (KAMP). J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1460–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
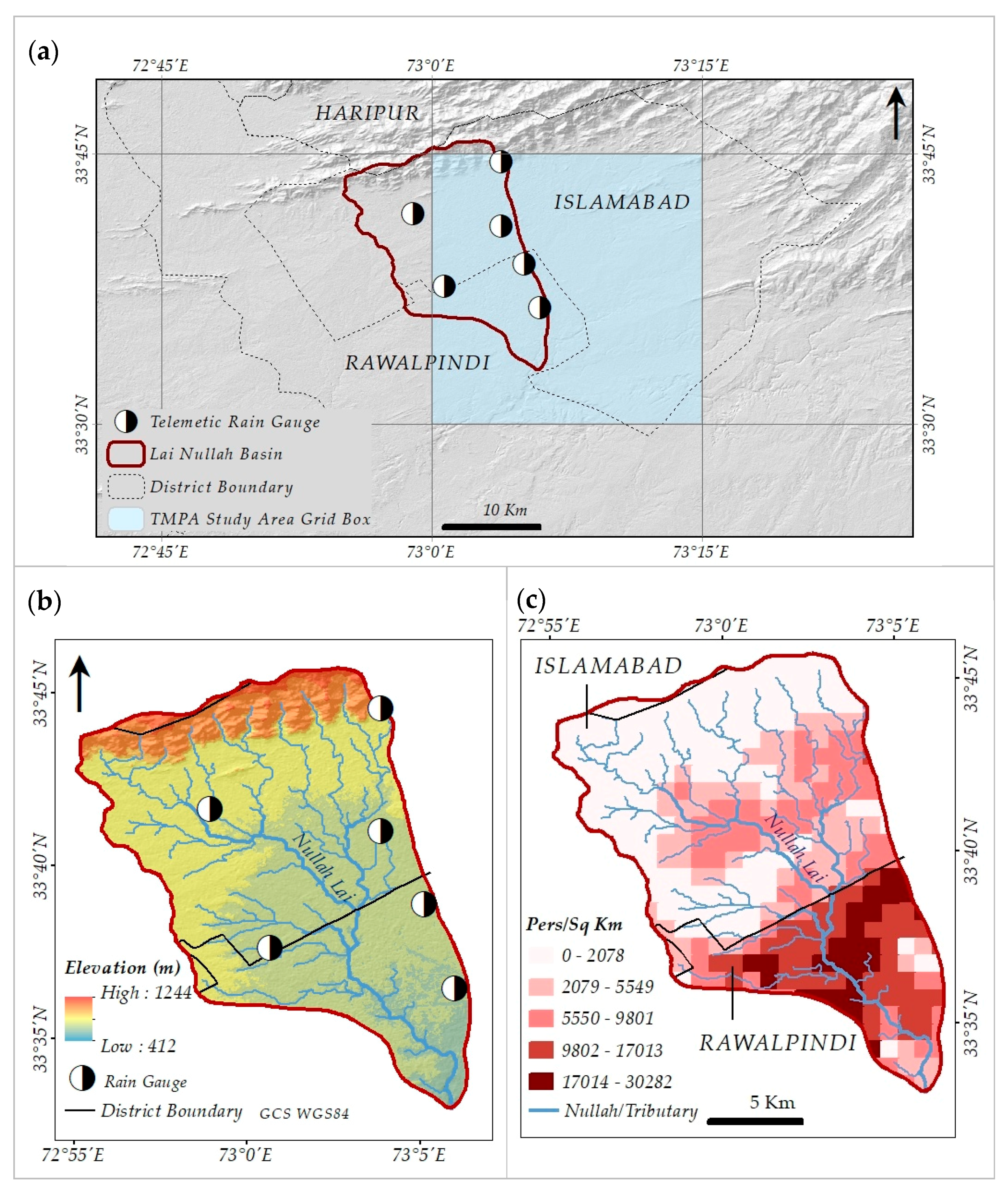











| SN | Name | District | Coordinates | Elevation (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) | ||||
| 1 | Saidpur | Islamabad | 73°03′51″ | 33°44′33″ | 668 |
| 2 | Golra | Islamabad | 72°58′55″ | 33°41′38″ | 556 |
| 3 | PMD | Islamabad | 73°03′51″ | 33°40′59″ | 531 |
| 4 | Bokra | Islamabad | 73°00′39″ | 33°37′38″ | 528 |
| 5 | RAMC | Rawalpindi | 73°05′07″ | 33°38′53″ | 508 |
| 6 | Chaklala | Rawalpindi | 73°05′60″ | 33°36′27″ | 506 |
| Type | Statistical Index | Equation | Perfect Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Categorical Statistical Measures | Bias | Bias = − 1 | 0 | H = hits (rain at both) FA = false alarms (rain at measured and no-rain at observed) M = misses (no-rain at measured and rain at observed) Z = zeros (no-rain at both) N = total events |
| Probability of Detection (POD) | POD = | 1 | ||
| False Alarm Ratio (FAR) | FAR = | 0 | ||
| Threat Score (TS) | TS = | 1 | ||
| Equitable Threat Score (ETS) | ETS = HRand = | |||
| Skill Score (SS) | SS = | 1 | ||
| Continuous Statistical Measures | Mean Bias Error (MBE) | MBE = | 0 | n = number of samples, M = measured value (TMPA) O = observed value (TRG), X = data element (X = M for TMPA products and X = O for TRG) Bar on variable shows mean value |
| Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | MAE = | 0 | ||
| Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | RMSE = | 0 | ||
| Correlation Coefficient (CC) | CC = | 1 | ||
| Standard Deviation (SD) | SD = | NA |
| SN | Rain Category | Threshold (mm/h) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Light rain | <1 |
| 2 | Moderate rain | 1–4 |
| 3 | Heavy rain | 4–16 |
| 4 | Very heavy rain | 16–50 |
| 5 | Extreme rain | >50 |
| Timescale | Rain Rate (mm/h) | SD (mm/h) | MBE (mm/h) | MAE (mm/h) | RMSE (mm/h) | CC | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRG | 3B42 | TRG | 3B42 | 3B42 | 3B42 | 3B42 | 3B42 | |||||||
| RT | V7 | RT | V7 | RT | V7 | RT | V7 | RT | V7 | RT | V7 | |||
| 3-h Interval | 2.42 | 1.50 | 1.72 | 5.18 | 2.86 | 3.30 | −0.92 | −0.70 | 2.47 | 2.46 | 4.88 | 5.01 | 0.41 | 0.38 |
| Mean Daily | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.60 | −0.10 | −0.05 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.48 | 0.53 |
| Mean Decadal | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.16 | −0.04 | −0.02 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.77 |
| Mean Monthly | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.12 | −0.03 | −0.02 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.91 | 0.90 |
| Timescale | Rain Rate (mm/h) | SD (mm/h) | MBE (mm/h) | MAE (mm/h) | RMSE (mm/h) | CC | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRG | 3B42 | TRG | 3B42 | 3B42 | 3B42 | 3B42 | 3B42 | ||||||||
| RT | V7 | RT | V7 | RT | V7 | RT | V7 | RT | V7 | RT | V7 | ||||
| Pre-monsoon | 3-h | 1.28 | 1.02 | 1.41 | 2.19 | 1.59 | 2.16 | −0.26 | 0.13 | 1.47 | 1.58 | 2.46 | 2.59 | 0.19 | 0.29 |
| Mean Daily | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.39 | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.58 | |
| Mean Decadal | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.11 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 0.95 | |
| Mean Monthly | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.06 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.46 | 0.92 | |
| Monsoon | 3-h | 3.44 | 2.00 | 2.11 | 6.80 | 3.57 | 4.14 | −1.44 | −1.33 | 3.28 | 3.24 | 6.31 | 6.54 | 0.44 | 0.40 |
| Mean Daily | 0.59 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.75 | −0.16 | −0.14 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.49 | 0.51 | |
| Mean Decadal | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.20 | −0.10 | −0.08 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 0.65 | |
| Mean Monthly | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.14 | −0.09 | −0.07 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.85 | 0.83 | |
| Post-monsoon | 3-h | 2.95 | 1.67 | 1.72 | 5.47 | 2.51 | 2.97 | −1.28 | −1.23 | 2.66 | 2.63 | 5.31 | 5.17 | 0.34 | 0.40 |
| Mean Daily | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.61 | 0.43 | 0.50 | −0.16 | −0.15 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.38 | 0.48 | |
| Mean Decadal | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.09 | −0.04 | −0.04 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.57 | 0.83 | |
| Mean Monthly | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.07 | −0.03 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 0.94 | |
| Winter | 3-h | 1.21 | 0.90 | 1.20 | 1.64 | 2.02 | 2.10 | −0.31 | −0.01 | 1.69 | 1.64 | 2.53 | 2.48 | 0.07 | 0.24 |
| Mean Daily | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.44 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.48 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.54 | |
| Mean Decadal | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.10 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.57 | 0.85 | |
| Mean Monthly | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.06 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.79 | 0.94 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, A.U.; Chishtie, F.; Qazi, W.A.; Ghuffar, S.; Shahid, I.; Fatima, K. Evaluation of Three-Hourly TMPA Rainfall Products Using Telemetric Rain Gauge Observations at Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122040
Rehman AU, Chishtie F, Qazi WA, Ghuffar S, Shahid I, Fatima K. Evaluation of Three-Hourly TMPA Rainfall Products Using Telemetric Rain Gauge Observations at Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(12):2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122040
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Asid Ur, Farrukh Chishtie, Waqas A. Qazi, Sajid Ghuffar, Imran Shahid, and Khunsa Fatima. 2018. "Evaluation of Three-Hourly TMPA Rainfall Products Using Telemetric Rain Gauge Observations at Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan" Remote Sensing 10, no. 12: 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122040
APA StyleRehman, A. U., Chishtie, F., Qazi, W. A., Ghuffar, S., Shahid, I., & Fatima, K. (2018). Evaluation of Three-Hourly TMPA Rainfall Products Using Telemetric Rain Gauge Observations at Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan. Remote Sensing, 10(12), 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122040







