COMS Visible Channel Calibration Using Moon Observation Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Moon Observation Data of COMS MI
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Computation of the ROLO Irradiance
2.2.2. Instrument Irradiance
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Trends
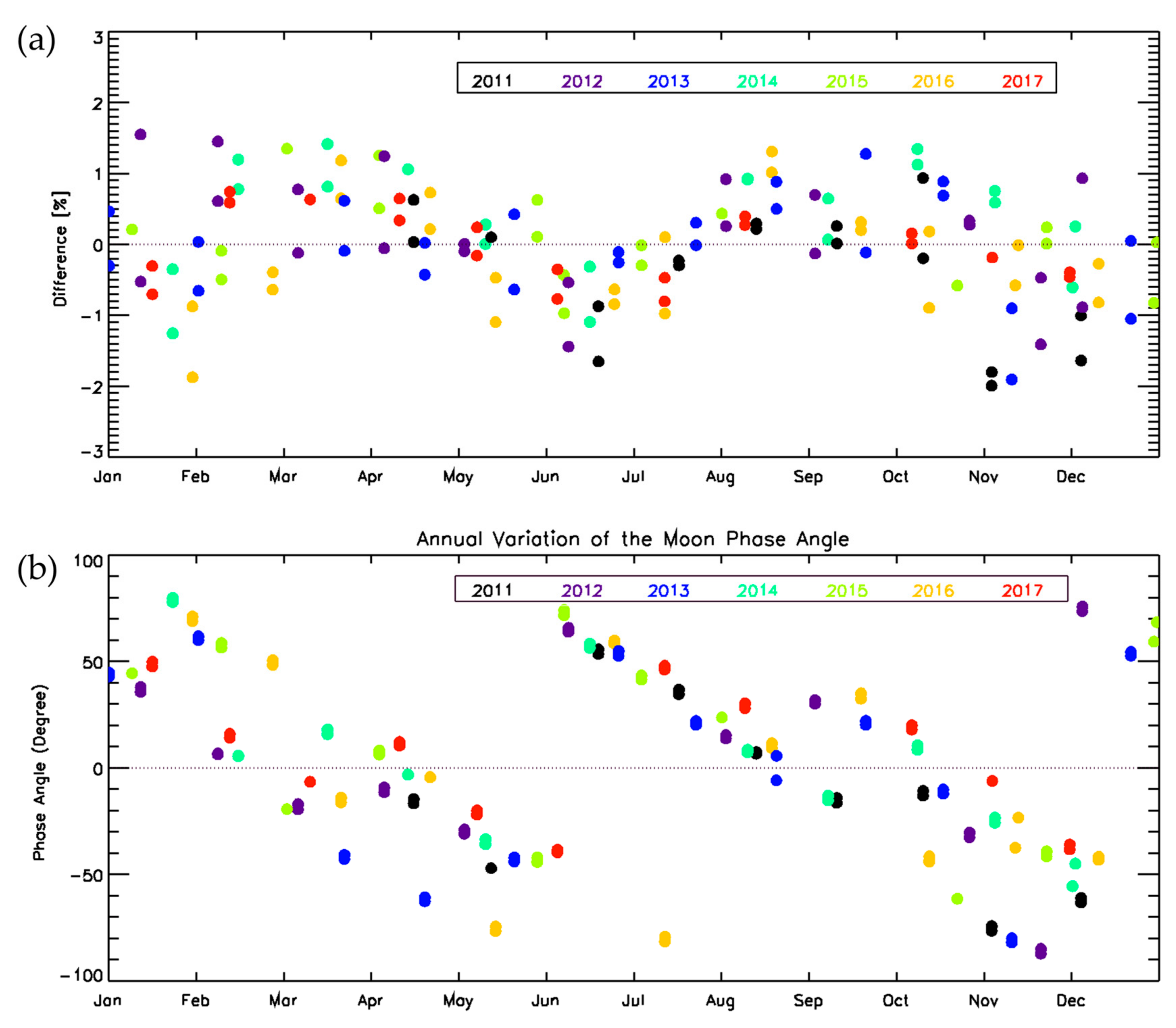
3.2. Seasonal Variation
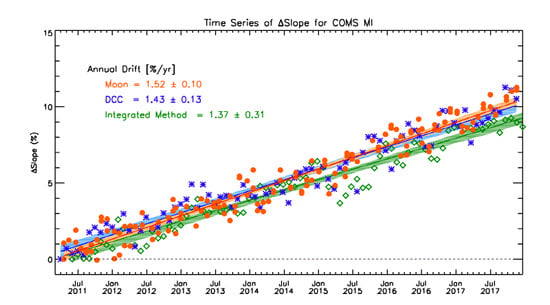
3.3. Comparison with Other Methods
3.4. Uncertainty Assessments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
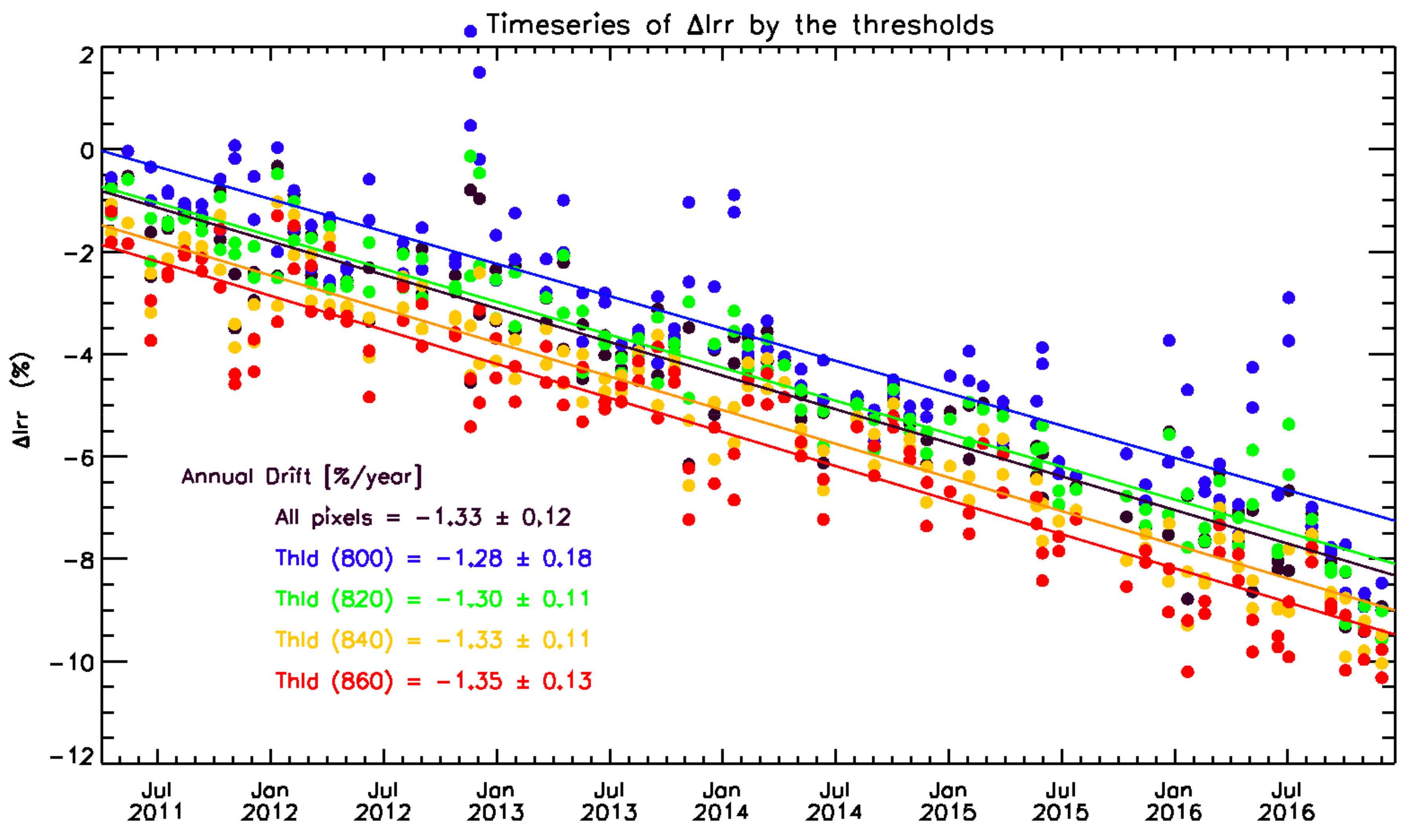
Appendix A.1. Sensitivity Test
Appendix A.1.1. Defining on-Moon Pixels
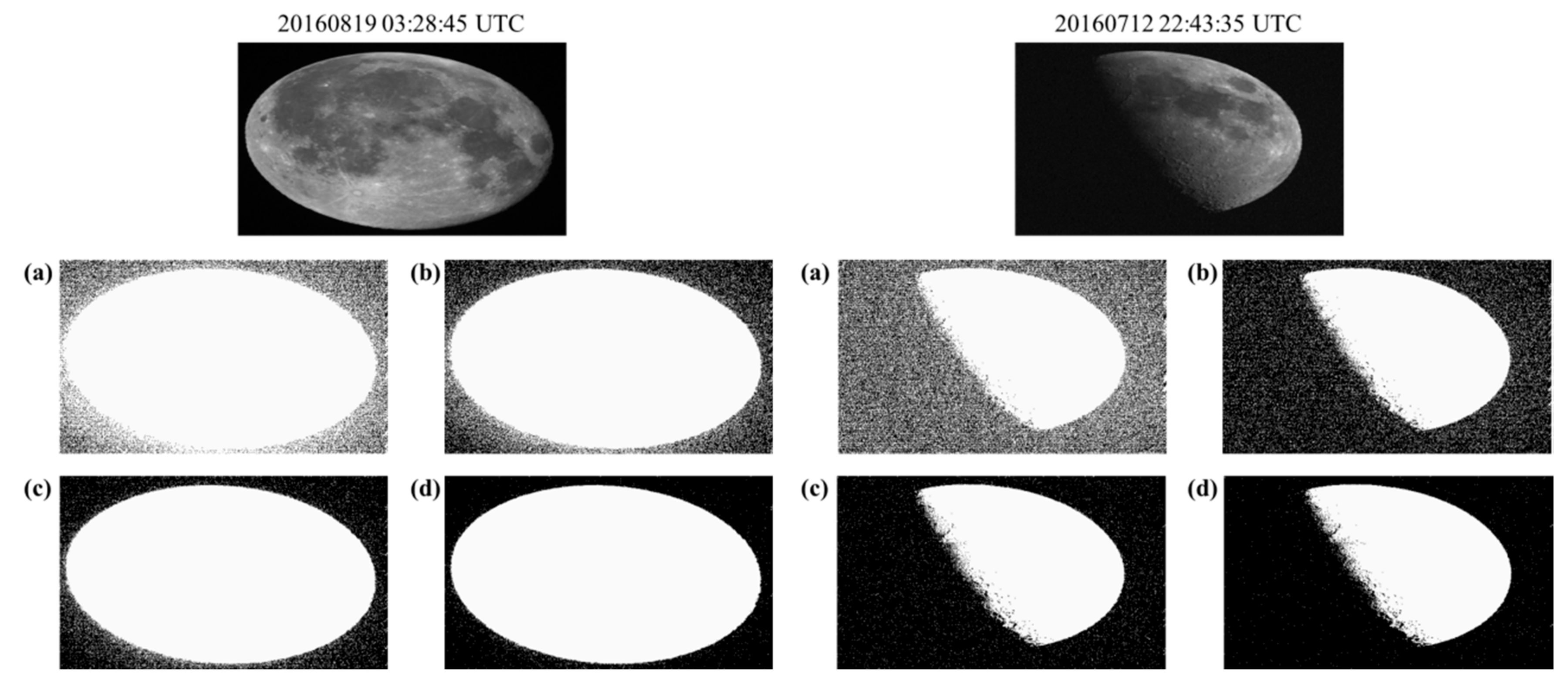
Appendix A.1.2. Phase Angle Dependence
| Absolute Phase Angle Range (Degree) | Observation Time (UTC) | Moon Images | Phase Angle (Degree) |
|---|---|---|---|
| |phase angle| ≤ 30 | 2016-08-1903:28:45 |  | 9.3 |
| 30 < |Phase angle| ≤ 60 | 2016-10-1301:13:34 |  | −41.5 |
| 60 < |phage angle| | 2016071221:28:45 |  | −81.5 |
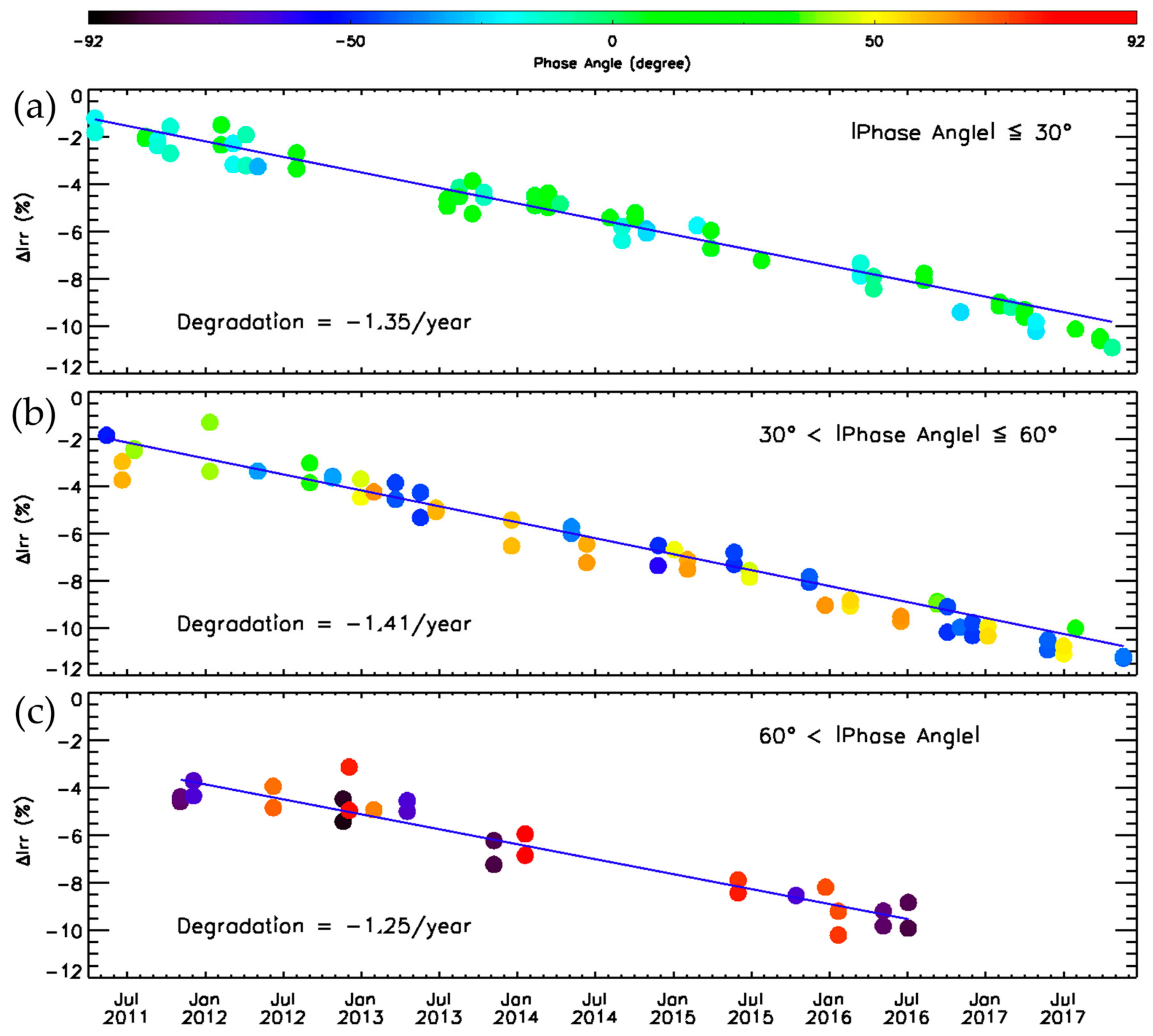
| Absolute Phase Angle Range (Degree) | No. of Moon Observation Data | Degradation Ratio (%/year) |
|---|---|---|
| |phase angle ≤ 30| | 60 | −1.35 ± 0.09 |
| |30 < Phase angle ≤ 60| | 59 | −1.41 ± 0.11 |
| |60 < phage angle| | 27 | −1.25 ± 0.27 |
| All phase angle | 146 | −1.35 ± 0.10 |
Appendix B
ROLO Lunar Irradiance Model Coefficients of COMS MI
| Wavelength (nm) | a0 (Constant) | a1 (rad−1) | a2 (rad−2) | a3 (rad−3) | b1 (rad−1) | b2 (rad−3) | b3 (rad−5) | d1 (Exponent 1) | d2 (Exponent 2) | d3 (Cosine) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 544.0 | −2.13864 | −1.60613 | 0.27886 | −0.16426 | 0.03833 | 0.01189 | −0.00390 | 0.37190 | −0.10629 | 0.01428 |
| 549.1 | −2.10782 | −1.66736 | 0.41697 | −0.22026 | 0.03451 | 0.01452 | −0.00517 | 0.36814 | −0.09815 | 0.00000 |
| 553.8 | −2.12504 | −1.65970 | 0.38409 | −0.20655 | 0.04052 | 0.01009 | −0.00388 | 0.37206 | −0.10745 | 0.00347 |
| 665.1 | −1.88914 | −1.58096 | 0.30477 | −0.17908 | 0.04415 | 0.00983 | −0.00389 | 0.37141 | −0.13514 | 0.01248 |
| 693.1 | −1.89410 | −1.58509 | 0.28080 | −0.16427 | 0.04429 | 0.00914 | −0.00351 | 0.39109 | −0.17048 | 0.01754 |
| 703.6 | −1.92103 | −1.60151 | 0.36924 | −0.20567 | 0.04494 | 0.00987 | −0.00386 | 0.37155 | −0.13989 | 0.00412 |
| 745.3 | −1.86896 | −1.57522 | 0.33712 | −0.19415 | 0.03967 | 0.01318 | −0.00464 | 0.36888 | −0.14828 | 0.00958 |
| 763.7 | −1.85258 | −1.47181 | 0.14377 | −0.11589 | 0.04435 | 0.02000 | −0.00738 | 0.39126 | −0.16957 | 0.03053 |
| 774.8 | −1.80271 | −1.59357 | 0.36351 | −0.20326 | 0.04710 | 0.01196 | −0.00476 | 0.36908 | −0.16182 | 0.00830 |
References
- Hewison, T.J.; Wu, X.; Yu, F.; Tahara, Y.; Hu, X.; Kim, D.; Koenig, M. GSICS Inter-Calibration of Infrared Channels of Geostationary Imagers Using Metop/IASI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ahn, M.H. Introduction to the in-orbit-test and its performance of the first meteorological imager of the Communication Ocean, and Meteorological Satellite. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2471–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Ohring, G.; Butler, J.; Cao, C.; Dalta, R.; Doelling, D.; Gaertner, V.; Hewison, T.; Iacovazzi, B.; Kim, D.; et al. The global space-based inter-calibration system (GSICS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Sun, J.; Espositio, J.; Guenther, B.; Barnes, W. MODIS reflective solar bands calibration algorithm and on-orbit performance. Proc. SPIE–Opt. Remote Sens. Atmos. Clouds III 2002, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; De Luccia, F.; Xiong, X.; Wolfe, R.; Weng, F. Early on-orbit performance of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) onboard the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (S-NPP) satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, B.-J.; Ham, S.H. Possibility of the visible-channel calibration using deep convective clouds overshooting the TTL. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 2271–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosnefroy, H.; Leroy, M.; Briottet, X. Selection and characterization of Saharan and Arabian desert sites for the calibration of optical satellite sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doelling, D.; Nguyen, L.; Minnis, P. On the use of deep convective clouds to calibrate AVHRR data. In Proceedings of the SPIE 49th Annual Meeting, Earth Observing Systems IX Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 2–6 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Doelling, D.; Minnis, P.; Nguyen, L. Calibration comparisons between SEVIRI, MODIS and GOES data. In Proceedings of the MSG RAO Workshop, Salzburg, Austria, 9–10 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fougnie, B.; Henry, P.; Morel, A.; Antoine, D.; Montagner, F. Identification and characterization of stable homogeneous ocean zones: Climatology and impact on in-flight calibration of space sensor over Rayleigh scattering. Proceedings of Ocean Optics XVI, Santa Fe, New Mexico, 18–22 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hagolle, O.; Nicolas, J.; Fougnie, B.; Cabot, F.; Henry, P. Absolute calibration of VEGETATION derived from an interband method based on the Sun glint over ocean. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 42, 1472–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Stone, T.C.; Yu, F.; Han, D. Vicarious calibration of GOES Imager visible channel using the Moon. Proc. SPIE Earth Obs. Syst. XI 2006, 6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wu, X. NOAA Operational Implementation of DCC Correction. In Proceedings of the GSICS Annual Meeting, Darmstadt, Germany, 10–14 March 2014; Available online: https://gsics.nesdis.noaa.gov/wiki/Development/20140324 (accessed on 2 May 2016).
- Doelling, D.; Morstd, D.; Bhatt, R.; Scarino, B. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) for Deep Convective Cloud (DCC), 2011. Available online: https://gsics.nesdis.noaa.gov/pub/Development/AtbdCentral/GSICS_ATBD_DCC_NASA_2011_09.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2016).
- Yu, F.; Wu, X. An integrated method to improve the GOES Imager visible radiometric calibration accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, H.H.; Wildey, R.L. Absolute calibration of Landsat instruments using the Moon. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1985, 51, 1391–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, H.H.; Wildey, R.L. Establishing the Moon as a spectral radiance standard. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Becker, K.J.; Kieffer, H.H.; Dodd, D.N. Real-time control of the Robotic Lunar Observatory telescope. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1996, 111, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Kieffer, H.H. New Views of the Moon II: Understanding the Moon through the Integration of Diverse Datasets; Gaddis, L., Shearer, C.K., Eds.; LPI: Houston, TX, USA, 1999; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, T.C.; Kieffer, H.H. Absolute Irradiance of the Moon for On-orbit Calibration. Proc. SPIE 2002, 4881, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, H.H.; Stone, T.C. The spectral irradiance of the Moon. Astron. J. 2005, 129, 2887–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.C.; Kieffer, H.H.; Anderson, J.M. Status of Use of Lunar Irradiance for On-orbit Calibration. Proc. SPIE 2002, 4483, 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, R.A.; Eplee, R.E., Jr.; Patt, F.S.; Kieffer, H.H.; Stone, T.C.; Meister, G.; Butler, J.J.; McClain, C.R. Comparison of SeaWiFS measurements of the Moon with the US Geological Survey lunar model. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 5838–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUMETSAT, High Level Description of the GIRO Application and Definition of the Input/Output Formats, 2015. Available online: http://gsics.atmos.umd.edu/bin/view/Development/LunarWorkArea (accessed on 2 February 2015).
- Stone, T.C.; Rossow, W.B.; Ferrier, J.; Hinkelman, L.M. Evaluation of ISCCP multisatellite radiance calibration for geostationary imager visible channels using the Moon. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 51, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viticchie, B.; Wagner, S.C.; Hewison, T.J.; Stone, T.C.; Nain, J.; Gutierrez, R.; Muller, J.; Hanson, C. Lunar calibration of MSG/SEVIRI solar channels. In Proceedings of the EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, Vienna, Austria, 16–20 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Eplee, R.E.; Meister, G.; Patt, F.S.; Barnes, R.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; McClain, C.R. On-orbit calibration of SeaWiFS. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 8702–8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.B.; Yong, S.S. Moon ROLO irradiance calculation with coordinate transforms for detectors’ performance analysis of geostationary visible channel imagers. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Remote Sensing, Pusan, Korea, 16–18 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ledez, C. MI Radiometric Model, Astrium and KARI Proprietary Information; COMS.TN.00116.DP.T.ASTR; Astrium: Paris, France, 2011; pp. 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, M. Visible Channel Calibration of the JMA’s Geostationary Satellites Using the Moon Images. In Proceedings of the 2014 EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, Geneva, Switzerland, 22–26 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, S.-H.; Sohn, B.J. Assessments of the calibration performance of satellite visible channels using cloud targets: Application to Meteosat-8/9 and MTSAT-1R. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11131–11149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, B.A.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Yang, P.; Bedka, S.T. Bulk scattering models for the remote sensing of ice clouds. Part I: Microphysical data and models. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, B.; Yang, P.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Platnick, S.; King, M.D.; Hu, Y.-X.; Bedka, S.T. Bulk scattering models for the remote sensing of ice clouds. Part II: Narrowband models. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 1896–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Channel | Spectral Range (μm) | Central Wavelength (μm) | IFOV 1 (μrad) | Spatial Resolution (km) | Input Range | SNR 2 (VIS) and NEdT 3 (IR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIS | 0.55–0.8 | 0.675 | 28 × 28 | 1 | 0–115% albedo | 170:1 at 100% albedo 10:1 at 5% albedo |
| SWIR | 3.5–4.0 | 3.75 | 112 × 112 | 4 | 4–330 K | 0.10 K at 300 K 5.70 K at 220 K |
| WV | 6.5–7.0 | 6.75 | 112 × 112 | 4 | 4–330 K | 0.12 K at 300 K 0.85 K at 220 K |
| IR1 | 10.3–11.3 | 10.8 | 112 × 112 | 4 | 4–330 K | 0.12 K at 300 K 0.40 K at 220 K |
| IR2 | 11.5–12.5 | 12.0 | 112 × 112 | 4 | 4–350 K | 0.20 K at 300 K 0.48 K at 220 K |
| Satellite | Time Coverage | Moon Observations (Times) | Channel | Absolute Phase Angle Range (Degree) | Useful Observation for Calibration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMS MI | April 2011–December 2017 | 152 | Visible (0.6 μm) | 0–90 | 0–30 | 146 | 60 |
| 31–60 | 59 | ||||||
| 61–90 | 27 | ||||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, T.-H.; Kim, D. COMS Visible Channel Calibration Using Moon Observation Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050726
Oh T-H, Kim D. COMS Visible Channel Calibration Using Moon Observation Data. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(5):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050726
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Tae-Hyeong, and Dohyeong Kim. 2018. "COMS Visible Channel Calibration Using Moon Observation Data" Remote Sensing 10, no. 5: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050726
APA StyleOh, T.-H., & Kim, D. (2018). COMS Visible Channel Calibration Using Moon Observation Data. Remote Sensing, 10(5), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050726