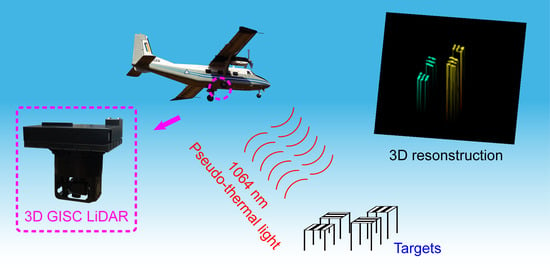
Airborne Near Infrared Three-Dimensional Ghost Imaging LiDAR via Sparsity Constraint
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
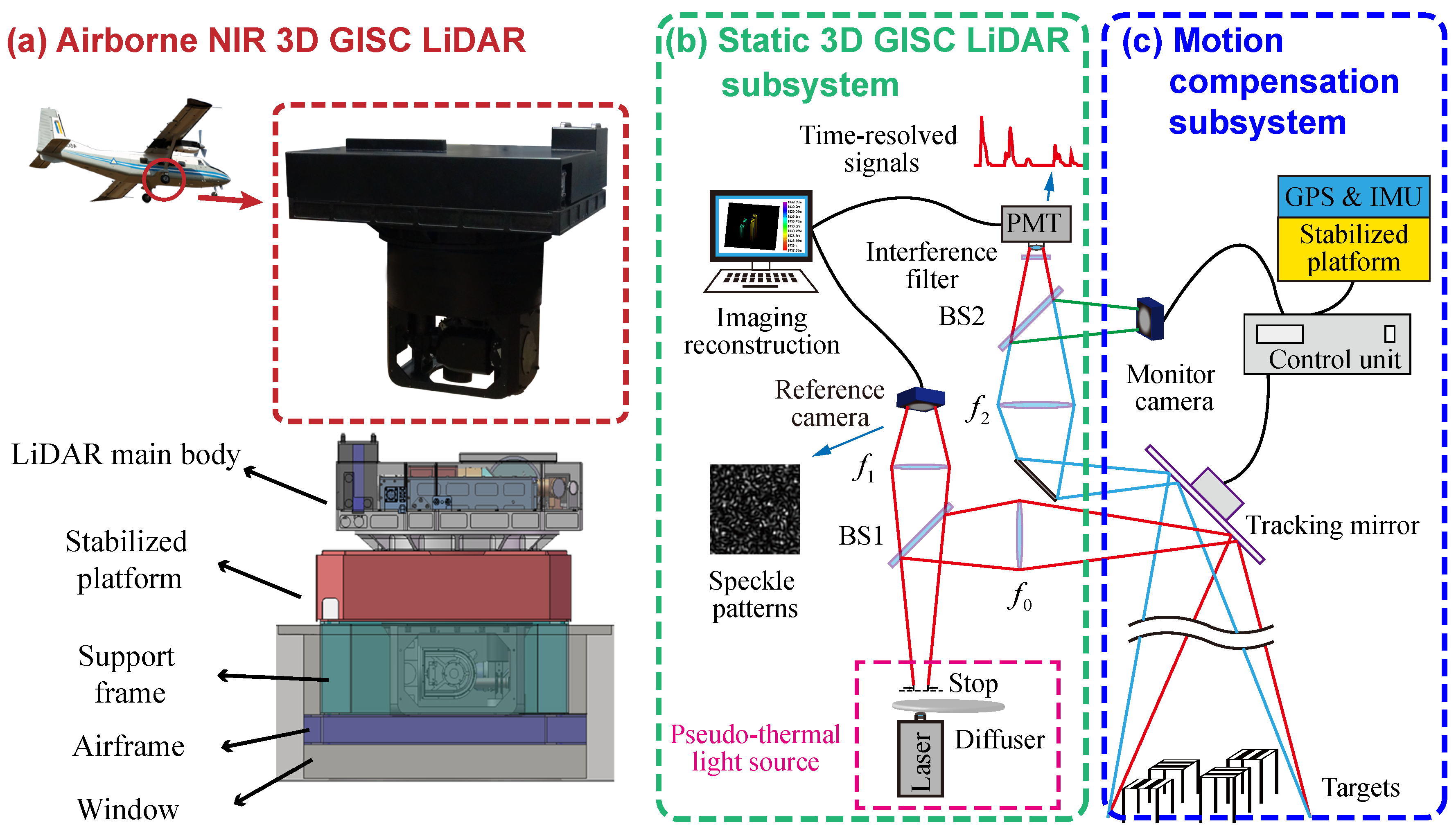
2.1. System Design
2.2. Structured 3D GISC Reconstruction
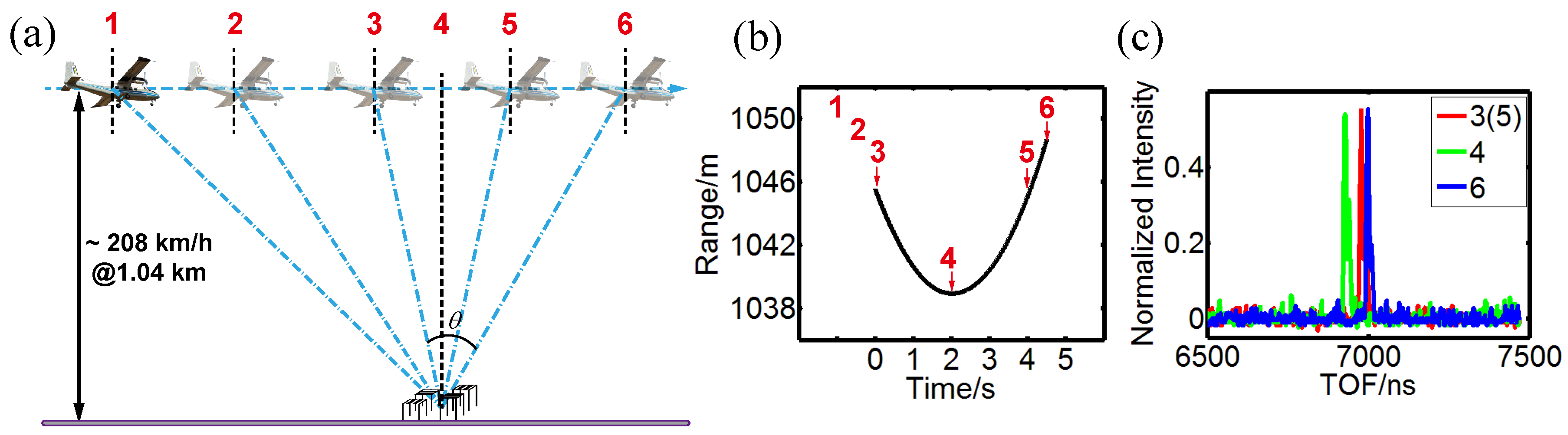
2.3. Experimental Section
2.4. Pre-Processing of the TOF Signals
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NIR | Near infrared |
| TOF | Time of flight |
| FOV | Field of view |
| RMS | Root mean square |
References
- Council, N.R. (Ed.) Laser Radar: Progress and Opportunities in Active Electro-Optical Sensing, 1st ed.; National Academies Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 6–106. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, C.; Bretar, F. Full-waveform topographic lidar: State-of-the-art. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Kambezidis, H.D.; Djepa-Petrova, V.; Adamopoulos, A.D. Radiative transfer. I. Atmospheric transmission monitoring with modeling and ground-based multispectral measurements. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 6976–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itzler, M.A.; Entwistle, M.; Wilton, S.; Kudryashov, I.; Kotelnikov, J.; Jiang, X.; Piccione, B.; Owens, M.; Rangwala, S. Geiger-Mode LiDAR: From Airborne Platforms To Driverless Cars. In Proceedings of the Applied Industrial Optics: Spectroscopy, Imaging and Metrology, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–29 June 2017; Optical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. ATu3A.3. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Wakin, M.B. An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O.; Bromberg, Y.; Silberberg, Y. Compressive ghost imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 131110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Edgar, M.P.; Sun, B.; Radwell, N.; Gibson, G.M.; Padgett, M.J. 3D single-pixel video. J. Opt. 2016, 18, 035203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gong, W.; Chen, M.; Li, E.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Han, S. Ghost imaging lidar via sparsity constraints. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 141123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhao, C.; Yu, H.; Chen, M.; Xu, W.; Han, S. Three-dimensional ghost imaging lidar via sparsity constraint. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, E.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Structured image reconstruction for three-dimensional ghost imaging lidar. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 14541–14551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Edgar, M.P.; Gibson, G.M.; Sun, B.; Radwell, N.; Lamb, R.; Padgett, M.J. Single-pixel three-dimensional imaging with time-based depth resolution. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, N.D.; Shapiro, J.H. Computational ghost imaging versus imaging laser radar for three-dimensional imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 023820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, B.I. Computational ghost imaging for remote sensing. JOSA A 2012, 29, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Pulse-compression ghost imaging lidar via coherent detection. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 25983–25994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xiong, J.; Zeng, G. Lensless ghost imaging for moving objects. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 127005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Wenlin, G.; Han, S. Ghost imaging for moving targets and its application in remote sensing. Chin. J. Lasers 2012, 12, 039. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Deng, C.; Chen, M.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Ghost imaging for an axially moving target with an unknown constant speed. Photonics Res. 2015, 3, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Statistical properties of laser speckle patterns. Laser Speckle Relat. Phenom. 1975, 9, 9–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, F.; Magatti, D.; Gatti, A.; Bache, M.; Brambilla, E.; Lugiato, L.A. High-resolution ghost image and ghost diffraction experiments with thermal light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 183602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics, 7th ed.; Cambridge University: London, UK, 2005; pp. 175–177. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, J.; Barth, M. The Global Positioning System and Inertial Navigation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 61, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Masten, M.K. Inertially stabilized platforms for optical imaging systems. IEEE Control Syst. 2008, 28, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Han, S. Multiple-input ghost imaging via sparsity constraints. JOSA A 2012, 29, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Mei, X.; Pan, L.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Gao, X.; Bo, Z.; Chen, M.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Airborne Near Infrared Three-Dimensional Ghost Imaging LiDAR via Sparsity Constraint. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050732
Wang C, Mei X, Pan L, Wang P, Li W, Gao X, Bo Z, Chen M, Gong W, Han S. Airborne Near Infrared Three-Dimensional Ghost Imaging LiDAR via Sparsity Constraint. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(5):732. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050732
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chenglong, Xiaodong Mei, Long Pan, Pengwei Wang, Wang Li, Xin Gao, Zunwang Bo, Mingliang Chen, Wenlin Gong, and Shensheng Han. 2018. "Airborne Near Infrared Three-Dimensional Ghost Imaging LiDAR via Sparsity Constraint" Remote Sensing 10, no. 5: 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050732
APA StyleWang, C., Mei, X., Pan, L., Wang, P., Li, W., Gao, X., Bo, Z., Chen, M., Gong, W., & Han, S. (2018). Airborne Near Infrared Three-Dimensional Ghost Imaging LiDAR via Sparsity Constraint. Remote Sensing, 10(5), 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050732