Abstract
In the last few decades the magnitude and impacts of planetary urban transformations have become increasingly evident to scientists and policymakers. The ability to understand these processes remained limited in terms of territorial scope and comparative capacity for a long time: data availability and harmonization were among the main constraints. Contemporary technological assets, such as remote sensing and machine learning, allow for analyzing global changes in the settlement process with unprecedented detail. The Global Human Settlement Layer (GHSL) project set out to produce detailed datasets to analyze and monitor the spatial footprint of human settlements and their population, which are key indicators for the global policy commitments of the 2030 Development Agenda. In the GHSL, Earth Observation plays a key role in the detection of built-up areas from the Landsat imagery upon which population distribution is modelled. The combination of remote sensing imagery and population modelling allows for generating globally consistent and detailed information about the spatial distribution of built-up areas and population. The GHSL data facilitate a multi-temporal analysis of human settlements with global coverage. The results presented in this article focus on the patterns of development of built-up areas, population and settlements. The article reports about the present status of global urbanization (2015) and its evolution since 1990 by applying to the GHSL the Degree of Urbanisation definition of the European Commission Directorate General for Regional and Urban Policy (DG-Regio) and the Statistical Office of the European Communities (EUROSTAT). The analysis portrays urbanization dynamics at a regional level and per country income classes to show disparities and inequalities. This study analyzes how the 6.1 billion urban dwellers are distributed worldwide. Results show the degree of global urbanization (which reached 85% in 2015), the more than 100 countries in which urbanization has increased between 1990 and 2015, and the tens of countries in which urbanization is today above the global average and where urbanization grows the fastest. The paper sheds light on the key role of urban areas for development, on the patterns of urban development across the regions of the world and on the role of a new generation of data to advance urbanization theory and reporting.
1. Introduction
The understanding that the majority of the global population lives in urban areas is now a decade old [1,2,3]. The share of population settled in urban areas is referred as the Degree of Urbanisation, and it is determined by the ratio between the urban population and the total population of a spatial entity, following a classical approach to urbanization theory [4]. However, detailed knowledge about human presence on Earth and the degree of planetary urbanization remains limited due to data shortcomings [5].
The recent surge in urbanization is a challenge at the world polity level and the consolidation of specific goals and indicators for sustainable urban development leave no room for gaps in urbanization knowledge, information and reporting. The Post 2015 Development Agenda process (the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, the Sustainable Development Goals, the Paris Climate Agreement and the New Urban Agenda) has further stressed the salience of geospatial information for assessing and explaining global development patterns and for monitoring policy objectives through indicators [6].
Urbanization is generally analyzed with two principal foci: one on the spatial manifestation of urban expansion, the other on the dynamics of demography. Spatial data from remote sensing have mostly been based on case study applications at local and regional level [7], whereas studies with wider geographical scope relied on moderate or coarse spatial resolution sensors [8] or captured only thematic manifestations of human presence [9]. Nevertheless, the measurements of observable human presence on Earth can provide a basis for spatially explicit definition of urban surfaces. To this end, one product generally used is the global urban map created from the moderate resolution imaging (MODIS) data circa 2001–2002 [10]. This product maps the very high-density built-up environment, which allows us to identify major cities and delineate their high-density built-up areas. It overcomes some gaps observed in earlier global maps derived from other sources [11], such as inconsistencies in urban definition, scale, and data quality; however, this product offers a single-epoch perspective on human settlements [8].
The availability of open and free Earth Observation data (such as MODIS, Sentinel-1/2 data, Landsat imagery), robust algorithms and high-performance computing systems (for example, Google Earth Engine) are enabling the creation of high-resolution datasets depicting the built-up environment. Over the past decade, several initiatives have successfully produced continental and global maps of built-up areas [12,13,14,15,16,17]. The most relevant global products providing a static snapshot of the status on human settlement presence (and therefore built-up areas) at a decametric scale are GlobeLand30 [16] and Global Urban Footprint (GUF) [17]. The former is the first global product derived from Landsat data, mapping several land cover classes including artificial surfaces at 30-m spatial resolution, while the latter is a global thematic map of settlement mask produced from TerraSAR-X data at 12-m spatial resolution (available for the scientific community, and at 84-m for non-profits).
The demographic motives (population statistics) driving urbanization studies are most often derived from the information compiled by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA). UNDESA periodically reports global urbanization figures in the World Urbanization Prospects (WUP) based on member states input. This information relies on heterogeneous data sources as different ways of defining urban areas exist worldwide [18]. Despite its shortcomings [5,19], UNDESA statistics have become the main source for urbanization analysis due to the scarcity of alternative sources.
Nevertheless, with new approaches to georeferenced population data, it is possible to achieve advances in urbanization analysis [20]. Insights into the process of urbanization can be approximated using population density grids, such as census-based multi-temporal Gridded Population of the World (GPW) data [21], or more advanced products that combine multiple information sources, such as GRUMP [22] and WorldPop [23]. The Global Rural Urban Mapping Project (GRUMP) offers spatially explicit delineation of urban areas by combining population statistics and nightlights [22], which biases the detection and representation of settlements towards those with a strong illumination footprint, typical of more developed countries. GRUMP offers a series of multi-temporal grids (1990–1995–2000) at near 1-km spatial resolution representing estimated population counts and density. It differs from GPW by incorporating urban–rural designations, primarily derived from nighttime satellite imagery, in the spatial reallocation of population. WorldPop combines census data with remotely sensed layers (night lights, land cover, elevation models, etc.) and other ancillary data available at a national level. Currently, multi-temporal data are available for countries in Africa, South America, and Asia at 100-m spatial grid. However, high spatial resolution of population estimates should be produced by a globally consistent model for spatial distribution of the population in order to support the analyses of the urbanization processes occurring across the globe.
While there is an improvement in the availability of global geospatial data on human settlements and in their spatial resolution, most of these data remain limited in multi-temporal data records or do not offer comparative capabilities. Advances in the understanding of the urban connotation of human development can be achieved by refining global information on the spatial and demographic traits of human settlements and introducing the temporal domain in the analysis.
A new generation of products derived from Earth Observation (i.e., spatially consistent, with multi-temporal coverage, open, and free) could overcome traditional limitations like data gaps, or factors making comparison impossible. With this purpose, the European Commission-Joint Research Centre has made the multi-temporal geospatial data on human settlements open and freely available to all at the Habitat III conference with the release of the Global Human Settlement layer (GHSL) data suite (GHS P2016). GHS P2016 consists of harmonized global geospatial information on human settlements composed of built-up areas (GHS-BUILT), population density (GHS-POP) and a settlement model (GHS-SMOD) for the epochs 1975–1990–2000–2015. The GHSL exploits the availability of global data from remote sensing (Landsat imagery) and applies open automatic machine learning workflows to extract information on built-up presence. Built-up presence and density are used to disaggregate the best available global census data, originating from CIESIN’s GPW project [21]. The combination of built-up and demographic information with the multi-temporal component, allows the generation of GHS-SMOD, which globally classifies and maps settlements and populated areas. With GHS-SMOD it is possible to quantify and compare the process of urbanization through epochs and across the globe in a consistent way. The settlement model is based on the globally harmonized definition of cities (defining urban areas with a combination of spatial and population criteria) [24]. These features allow for carrying out multi-temporal analyses of the status and process of urbanization, urban development and the monitoring of indicators adopted by international frameworks. Furthermore, the GHSL complies with the European Commission’s open and free data policy that makes data available to all, promoting the engagement of stakeholders, transparency, and equal access to information.
In this article, we present and discuss the main results of extended analytics on human settlements based on the integration of Earth Observation-derived information (GHS-BUILT) with harmonized population statistics (GHS-POP) classified in a global settlement model (GHS-SMOD). It assesses the process of global urbanization in the period 1990–2015 and should be framed as a remote sensing-derived analysis of the research strand conceptualized by reference urbanization scholars on planetary urbanization [19,25,26,27,28]. In particular, the contribution focuses on the combination of the spatial and demographic components of human settlements, which remained often unaccounted at global level. The analysis concentrates on functional aggregations of data extracted at national level, per region of the world and by country’s income classes. The study reveals the different trajectories and extents of urbanization patterns around the globe. In the article, we elaborate on the following: first, we applied to the GHSL the people-based definition of the “Degree of Urbanisation” [24] that allowed to define the spatial dimension of urban areas and to capture their demography and built-up areas. The results of our analysis, enabled by the synoptic capabilities of remote sensing in space and time, shed new lights on the planetary urbanization narrative, and provide additional evidence suggesting that: (i) the globe is more urbanized than previously thought; (ii) the pace and size of spatial and demographic development in urban areas show different patterns across the regions of the world; (iii) built-up areas tend to slightly disperse out of urban areas; (iv) and fastest urbanization occurs in Low Income Countries of Asia. In the article we propose a deeper and more thematic analysis with GHSL data explicitly focusing on the urban component of the GHSL data (Urban Centres and Urban Clusters) elaborating further on the broad policy messages on human settlements derived from GSHL data contained in The Atlas of the Human Planet 2016 [29].
2. Materials and Methods
The narratives on urbanization have long remained subject to data limitations. Traditional research has been strongly rooted in a purely demographic approach [4] and has been fed with data that were largely inconsistent, unreliable, and incompatible [5]. The opportunities offered by remote sensing and Earth Observation can provide a renewed source of reliable periodically updated information capturing the spatial and demographic component of the urbanization process to offer support for analysis and policy decisions.
The GHSL data were released in 2016, as an open and free data package (GHS P2016). This data package (Table 1 and Figure 1) consists in several thematic grids reporting on (i) density of built-up area (GHS-BUILT); (ii) density of population (GHS-POP) and (iii) the classification of each grid cell into one of the settlement model classes (GHS-SMOD), which is an application of the Degree of Urbanization model to the GHSL baseline data. The GHSL was produced between 2014 and 2016 using 40 years of Landsat imagery archives to document changes to the global built environment. The global imagery was sourced from three Global Land Survey (GLS) collections [30] and one ad-hoc Landsat 8 collection (gathered for the purpose of this product). These collections consists in 32,808 scenes acquired by heterogeneous sensors, that are Multispectral Scanner (7588 scenes from GLS 1975), Thematic Mapper (7375 Landsat 4–5 scenes from GLS 1990), Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (8756 Landsat 7 scenes from GLS 2000), and Operational Land Imager (9089 Landsat 8 scenes).

Table 1.
Datasets that constitute the GHS P2016.
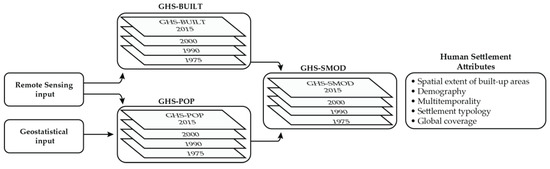
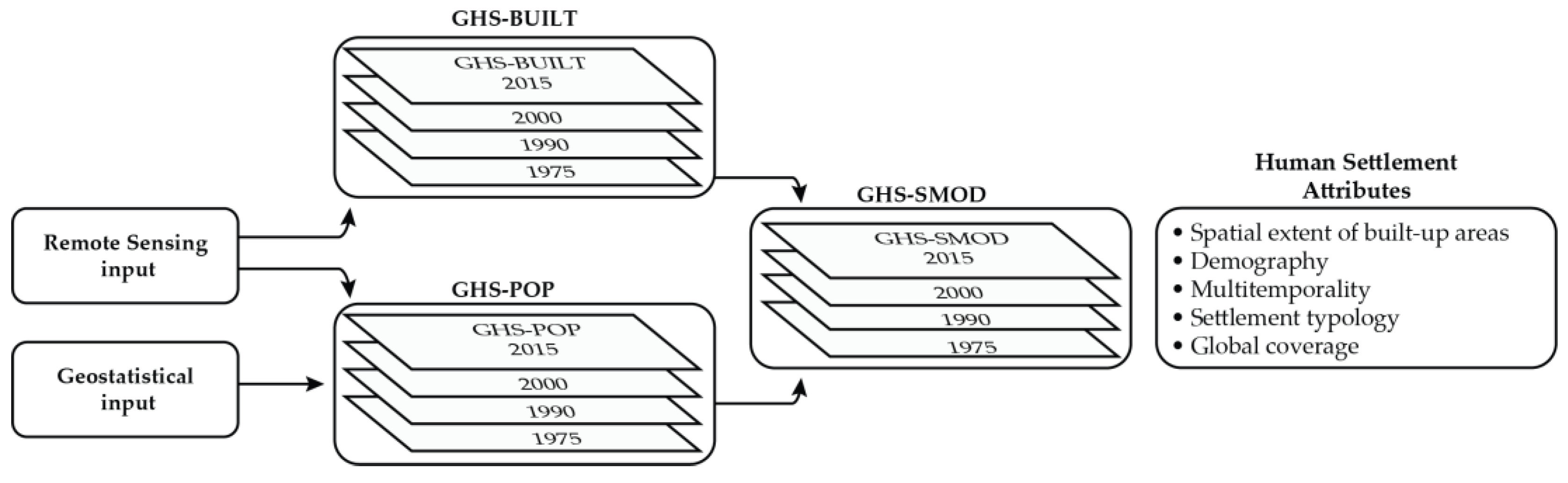
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the GHS-SMOD input data: the spatial extent component (GHS-BUILT) is derived from remote sensing sources; the demographic component (GHS-POP) is a combination of GHS-BUILT with geostatistical information of population abundance. Spatial statistics operations applied to the GHS-SMOD return data on human settlements suitable for multi-temporal, spatial, demographic, and global sustainable urban development studies and applications.
The processing of the image data was based on a Symbolic Machine Learning approach [31,32]. This approach relies on a reference layer, which is a high abstraction semantic information layer of the targeted class derived from ancillary sources. Here, a number of information layers with different scales and diverse thematic definitions, completeness and reliability were combined into a reference built-up layer used for training the algorithm [33] including MERIS Globe Cover artificial surfaces [34], LandScan population grids [35], Open Street Map (OSM) [6], GeoNames, MODIS 500 global urban extents [8]. The final product is a multi-temporal classification grid that for each cell (approx. 38-m resolution) reports the earliest epoch for which the built-up area presence was detected. This classification grid was later aggregated to 250-m and 1-km density grids for analysis (and in an appropriate projection for calculating area-related estimates). These datasets can be applied to characterize the manifestation of urban change, including urban sprawl, urban expansion, and also more complex patterns of change [27,29,36].
The GHS-BUILT grids were combined with multi-temporal census data from Gridded Population of the World-GPW [21] to produce population grids [37] depicting globally the population distribution and density at 250 m spatial resolution, then aggregated at 1 km. Built-up areas and population density grids are as much as possible globally consistent in space and time and report on human presence independently of administrative divisions. Both the methodological approach and these specific datasets were validated using independent reference data [31,38,39], with results suggesting GHSL to be one of the most reliable global, open and free data available to estimate built-up area, and with the accuracy of the layers to increase over time and with growing development intensity [39]. Given the availability of the GHS-BUILT and GHS-POP layers, it was possible to apply globally the EC-OECD harmonized definition of cities and settlements Degree of Urbanisation model [24,40].
The grid based model classifies land mass at 1-km resolution into one of the following classes (Table 2): (1) Urban Centres, (2) Urban Clusters, and (3) Rural Areas. This classification method relies on population thresholds, which makes it a people-based definition. The applied thresholds are: (i) the population density thresholds on the 1-km cells to identify potential settlements as a group of contiguous cells (i.e., cell clusters with a minimal population density); and (ii) the total population size to classify each cell cluster as one of the three classes. Before step (ii), additional connectivity analysis and morphological operations were performed to derive the cell clusters (more details in [29]). Within the GHSL framework, the application of the cities and settlements definition to the 1-km grids resulted in a set of multi-temporal layers, called a GHS Settlement MODel (GHS-SMOD) grids (Figure 2) [37,40,41].

Table 2.
Degree of Urbanization and GHS-SMOD criteria.
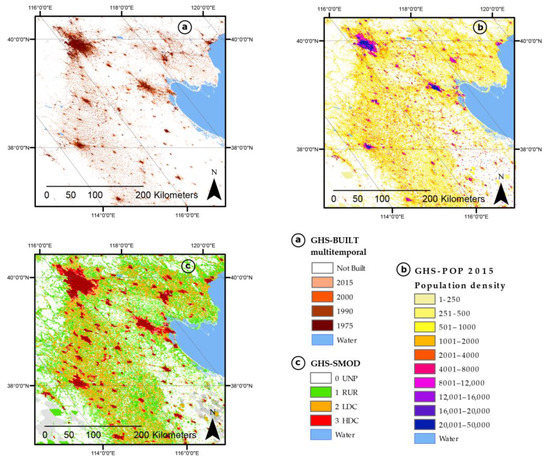
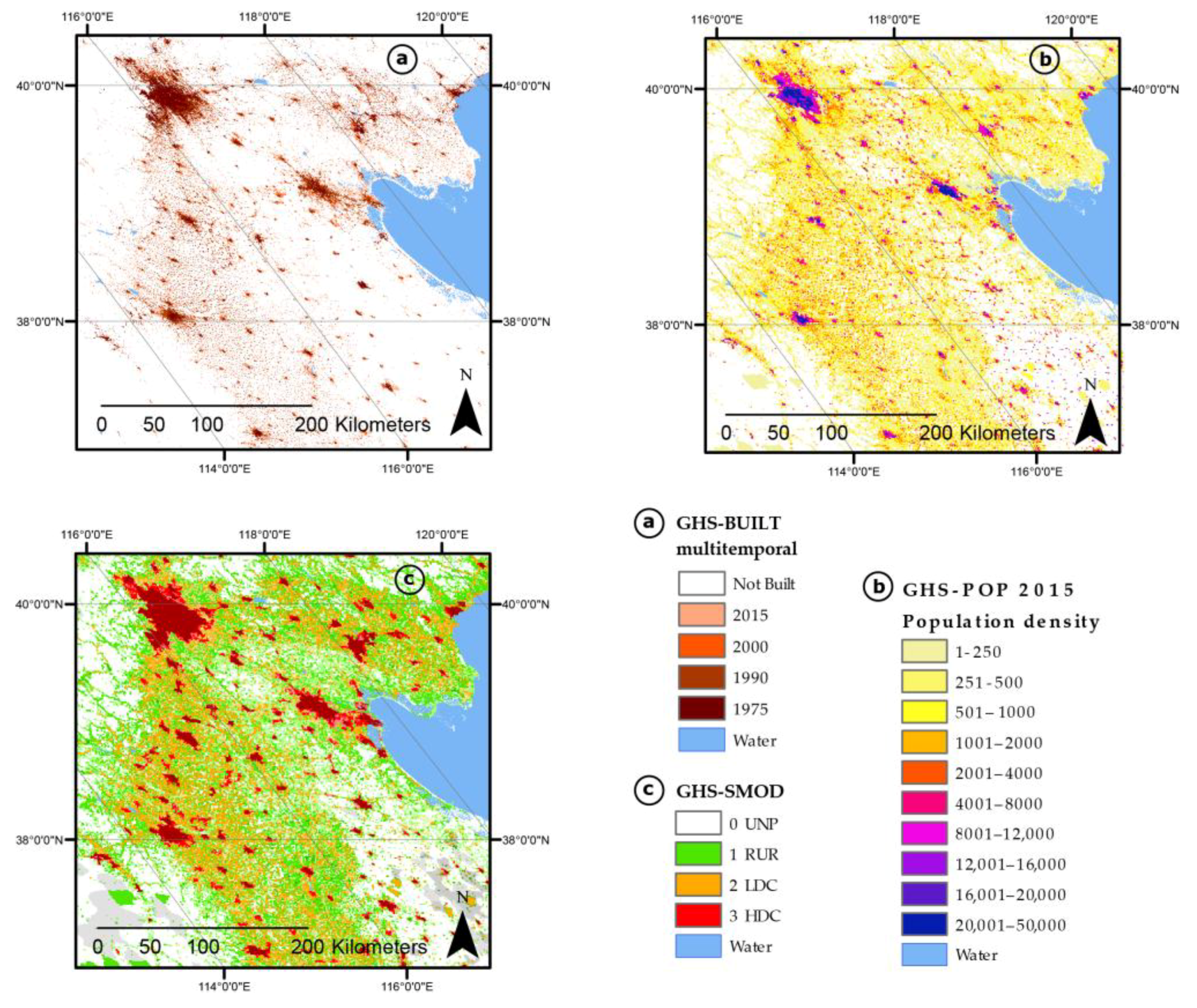
Figure 2.
Extract of GHS P2016 dataset displayed in parts of North and East China (World Mollweide projection): (a) GHS-BUILT multi-temporal; (b) GHS-POP at the reference year 2015; (c) GHS-SMOD at the reference year 2015.
The multi-temporal GHS-SMOD grids offer an analytical framework to analyze the urbanization dynamics over the past 40 years (Figure 1). Using standard geostatistical tools with the GHS-SMOD grid together with the multi-temporal GHS-BUILT and GHS-POP grids as the input data, we derived the statistical dataset. For the sake of simplicity, in this work we use conventional dichotomy (i.e., urban area and rural area) by aggregating the Urban Centres and Urban Clusters into one class: “urban area.” The Degree of Urbanisation model is applied at 1 km grid and it is spatially explicit, i.e., a Degree of Urbanization of a given spatial entity is the share of population summed in the in urban area over the total population of the spatial entity. In the paper, we propose analyses at multiple scales: global, continental, and national. This operation was performed with input data in grid format. The grid were grouped according to the country classification following the GADM database of Global Administrative Areas version 2.8 (http://gadm.org/). First, we calculated national estimates, which are later aggregated to global estimates (inspired by the UN country classification per region of the world and income classes).
The urbanization analysis was implemented with the GHSL data due to the following reasons:
- (a)
- The GHSL offers global coverage, and the possibility to aggregate data at multiple levels (from global and continental to subnational levels);
- (b)
- It is possible to observe the socio-spatial dimension of the urbanization process by capturing the demographics (population) and built-up areas;
- (c)
- The GHSL contains multi-temporal data for the epochs 1975–1990–2000–2015 to allow monitor human settlements and their process of change;
- (d)
- The application of the Degree of Urbanisation model [24] to the layer returns a globally consistent classification of human settlements, from which harmonized population and built-up statistics were generated.
The statistical dataset used for the experiments is released as Supplementary Materials. Compared to the Atlas of the Human Planet 2016 [29] this research proposes a perspective on the multi-temporal changes in the national degrees of urbanization, a socio-spatial analysis of the changes in the sole urban areas, and a new approach for the estimation of the degree of agglomeration (share of built-up areas in urban areas).
3. Results
This section presents the results of the analysis of the process of urbanization carried out with the GHSL data. The analysis is organized in six thematic areas: in the first, we track the spatial expansion of built-up areas and the demographic change in urban areas per region of the world; in the second we provide figures about the planetary reach of the process of urbanization; in the third, we report on the concentration of people in urban areas and the dispersion of built-up areas; in the fourth, we combine the degree of urbanization and agglomeration at national level; in the fifth, we present the different paces of urbanization disaggregating countries in income classes; in the last section we present key uneven aspects of urbanization.
3.1. Spatial Expansion and Demographic Growth of Urban Areas
The first thematic exploration of the process of urbanization is that of the spatial expansion of the built-up footprint and demographic growth in urban areas. Monitoring of the process of urbanization with the GHSL allows portraying the dynamics of demographic change and spatial expansion in urban areas simultaneously and with a single, homogeneous dataset. This section focuses on figures on urban areas only (aggregating Urban Centres and Urban Clusters).
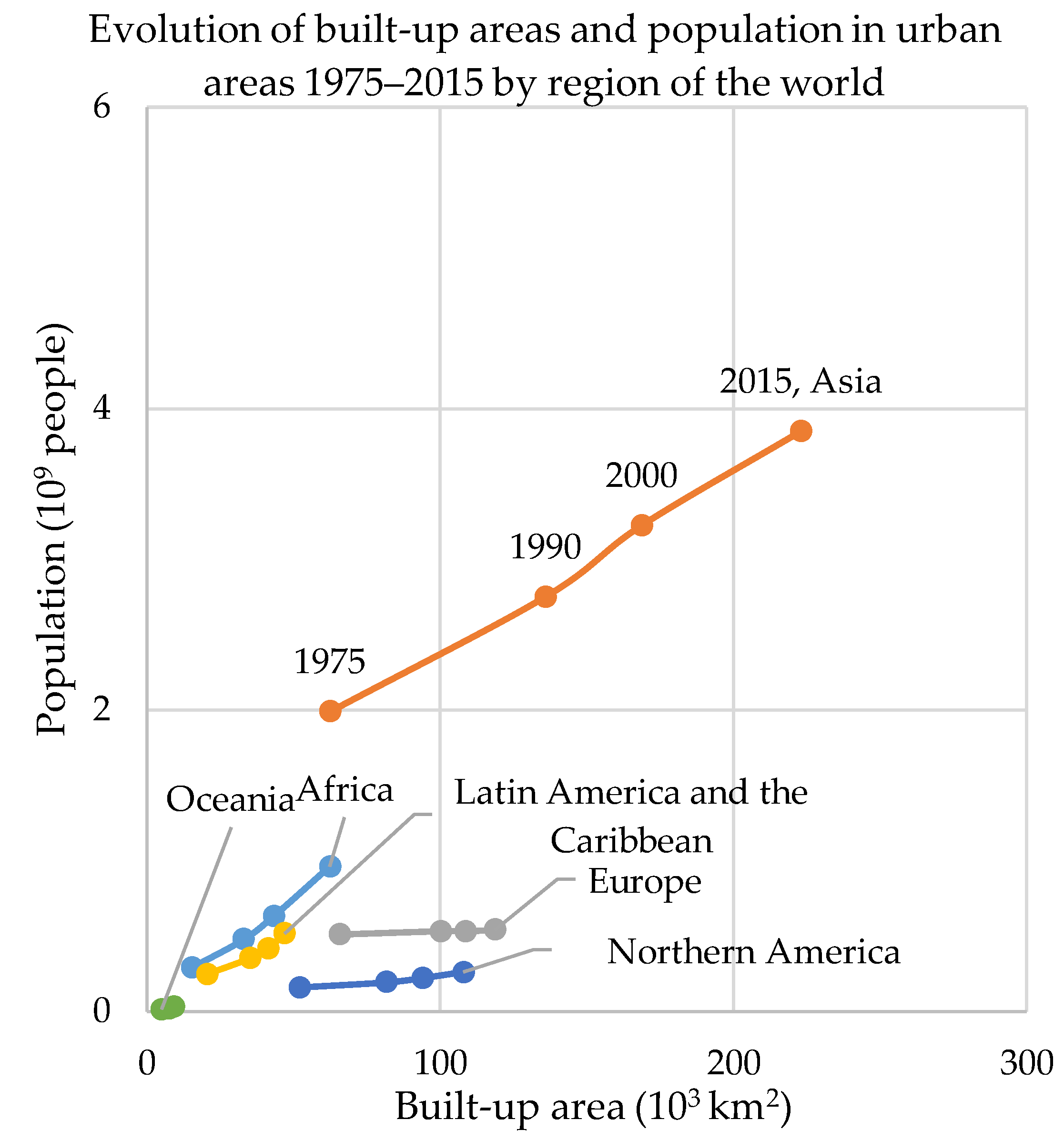
Between 1975 and 2015 the urban population almost doubled and built-up areas in urban areas increased 2.5-fold. According to GHSL data, urban areas host in 2015 more than 6.1 billion inhabitants, nearly twice the urban population in 1975, and their built-up footprint exceeds half a million square kilometers (expanded by more than 20% since 2000). However, the patterns of socio-spatial growth of urban areas are subject to strong regional connotations (Figure 3 and Table 3). Two major trends are observed. In Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean, and Africa, urban population increased in relative terms more than urban built-up areas, while in Europe and Northern America the spatial growth of urban areas has exceeded the pace of demographic one.
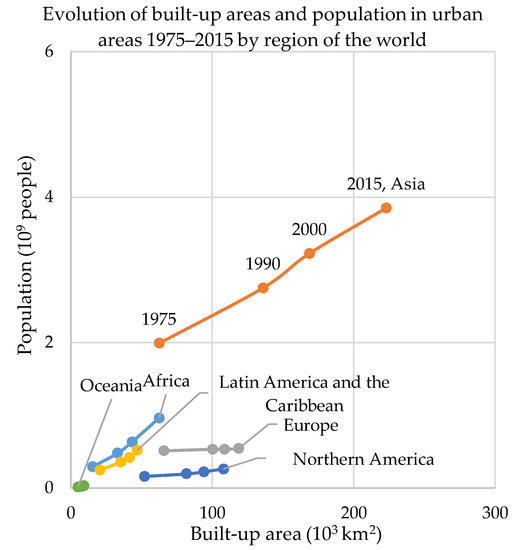
Figure 3.
Evolution of built-up area and population between 1975 and 2015 within urban areas (Urban Centres and Urban Clusters) by world region. Built-up area is expressed in thousands of square kilometers and population in billions of people.

Table 3.
Global urban built-up areas and population per epoch and region of the world.
Cities in Asia have 1 billion people more in 2015 than in 1990 (equivalent to a 40% increase); in Africa the urban population has doubled (equivalent to more than 480 million new urban dwellers in 25 years), and in Latin America and the Caribbean it increased by more than 164 million (+47%). The spatial component of urban development in these three regions has also been very strong: the built-up footprint of urban areas in Africa expanded by nearly 90%, in Asia by 65% and in Latin America and the Caribbean it increased by more than 1/3. The most relevant expansion of human settlements is concentrated in Africa and Asia: nearly 40% of overall global spatial expansion of built-up areas and nearly 80% of demographic increase took place in urban areas in these two regions of the world.
Europe and Northern America present a trajectory of change in which the spatial growth of urban areas is extensive although it is not consistently accompanied by population growth. Built-up areas in urban areas increased in Europe by 18%, while population growth has been very limited (1.5%). Urban areas in 2015 had only 8 million more inhabitants compared to 1990, despite the additional 18,500 km2 of urban built-up areas. In North America both urban population and built-up areas increased by around 1/3: urban population grew by around 70 million and urban built-up areas by 26,000 km2. In Europe, between 1990 and 2000, extensive spatial expansion of built-up areas resulted in 2.2 km2 being added for each new urban dweller, on average. During the same period, for each square kilometer of urban built-up areas expansion there were more than 16,500 new urban dwellers in Africa, 13.8 in Latin America, and 12,500 in Asia.
In sum, urban areas account for 90% of the global demographic change and 72% of the spatial expansions of built-up areas. Urban areas grow with distinct characteristics across regions of the world. The alternative development trajectories imply considerable imbalances in the availability of built-up surface per inhabitant and in the efficient use of land, causing us to question whether all trajectories bolster sustainable urban development.
3.2. Planetary Reach of the Urbanization Process
The share of the global population settled in urban areas topped 85 in 100 people in 2015; however, this global figure is determined by rather different regional profiles. The degree of urbanization in Europe and Northern America is lower (around 73%), while it is above 80% in Africa, Asia, and Latin America and the Caribbean. Moreover, changes in the degree of urbanization have been different across regions of the world: in Africa, the degree of urbanization increased in 25 years by more than 5%, in Latin America and the Caribbean it increased by 2.6%, in Asia it increased by around 2%, and it remained nearly constant in Europe (−0.6%).
The degree of urbanization in 2015 was above the global average (85%) in 51 countries, nearly half of which were in Asia. In these, the average degree of urbanization reached 89%.
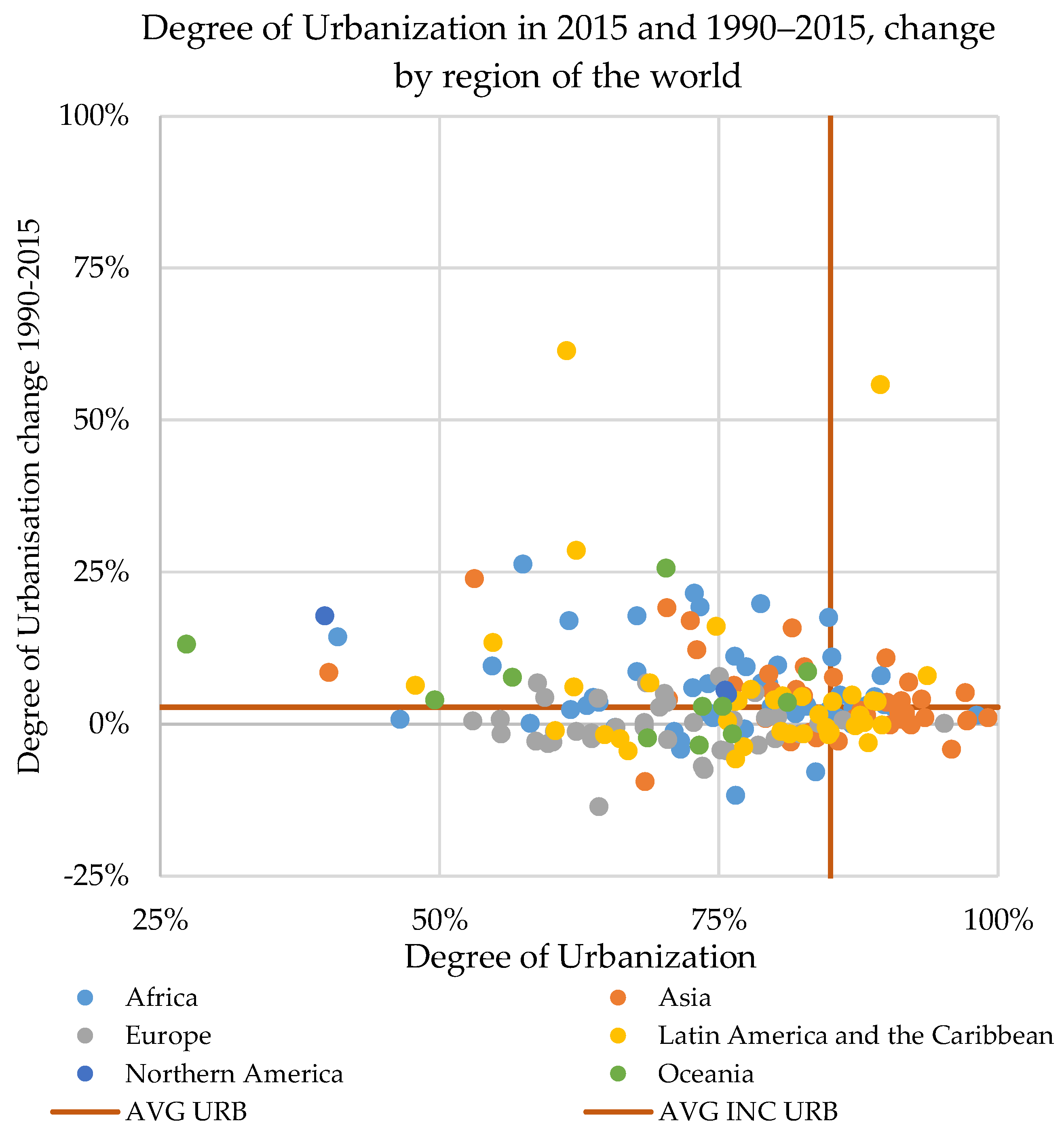
Considering the degree of urbanization in 2015 and its change between 1990 and 2015, countries can be grouped into four principal urbanization processes (Figure 4):
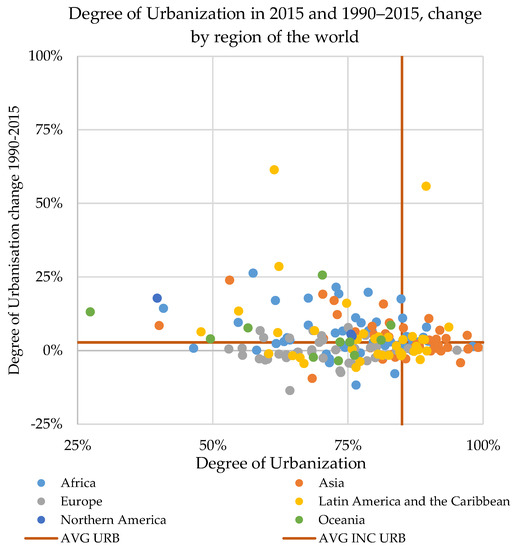
Figure 4.
National degrees of urbanization in 2015 by country (colored by regional group) and change between 1990 and 2015.
- (A)
- The upper-left part shows where the degree of urbanization in 2015 was below the global average (85%) but the area had urbanized fast (the 1990–2015 degree of urbanization change was above the global average of 2.3%);
- (B)
- The lower-right part of the chart shows where the degree of urbanization in 2015 was above the global average but the urbanization process had been less vibrant (the change between 1990 and 2015 was below the global average);
- (C)
- In the upper right are countries that are more urbanized in 2015 and that since 1990 have urbanized faster than the global average;
- (D)
- In the lower left are those without a distinctive urban character and where the process of urbanization is not considerably relevant.
The first case, A, describes a pattern in which the present urbanization is below the global average but rapid changes have occurred since 1990. More than 50 countries experienced a change in the degree of urbanization at least four times the global average, including Tanzania and Malawi (exceeding +20%), Cambodia, Equatorial Guinea, Mauritania, Kenya, and Mongolia (between +15% and +20%). In another 40 countries the change in the degree of urbanization was twice the global average, including Mali, Bhutan, Ghana, Norway, Niger and Peru (between +6% and +8%), and, Albania, Canada, Uruguay, Malaysia, Rwanda, Ecuador, and Mexico (between +5% and 4%). The urbanization process in the above countries has been especially vibrant. In particular, despite these countries remaining below the global urbanization average, in 25 years some of these countries transitioned to a clear urban connotation. Countries like Malawi, Equatorial Guinea, Honduras, and Liberia, transitioned from a degree of urbanization below 45% in 1990 to a predominantly urban population in 2015, with degrees of urbanization ranging between 54% (Liberia) and 61% (Equatorial Guinea). In Western Sahara, Mauritania, Kenya, Tanzania, Cambodia, and Mongolia, the degree of urbanization was above 70% in 2015, while in 1990 it was around 50%. Another case is Malawi, where around 30 in 100 inhabitants were urban dwellers in 1990, and in 2015 more than half of the population lived in urban areas. The last case in group A is Namibia, which was a predominantly rural country in 1990, with more than 70% of its population accounted in rural settlements; despite an increase in the degree of urbanization of more than 14%, it remains a ‘rural’ country (with a share of urban population around 40%). However, in Namibia urban areas report a considerable population growth (+65%) and rural areas face a net demographic decline.
The second group (B) includes countries that were more urbanized in 2015 than the global average but whose change in degree of urbanization was below the global average (<2.3%). Most of these countries are located across Central, Western, Eastern, and Southeastern Asia. The average degree of urbanization in these 37 countries is above 92% and in six the entire population is settled in urban areas (entities like Singapore, Macao, Monaco, and Gibraltar). In one-third of the countries in this group, the degree of urbanization remained stable (between −0.5% and +0.5%), and in six it increased by between 1% and 2%. Most of the group B countries were already predominantly urban in 1990: in 20 of them, the degree of urbanization was already above 90% (i.e., Japan, Egypt, South Korea, Vietnam, and Venezuela).
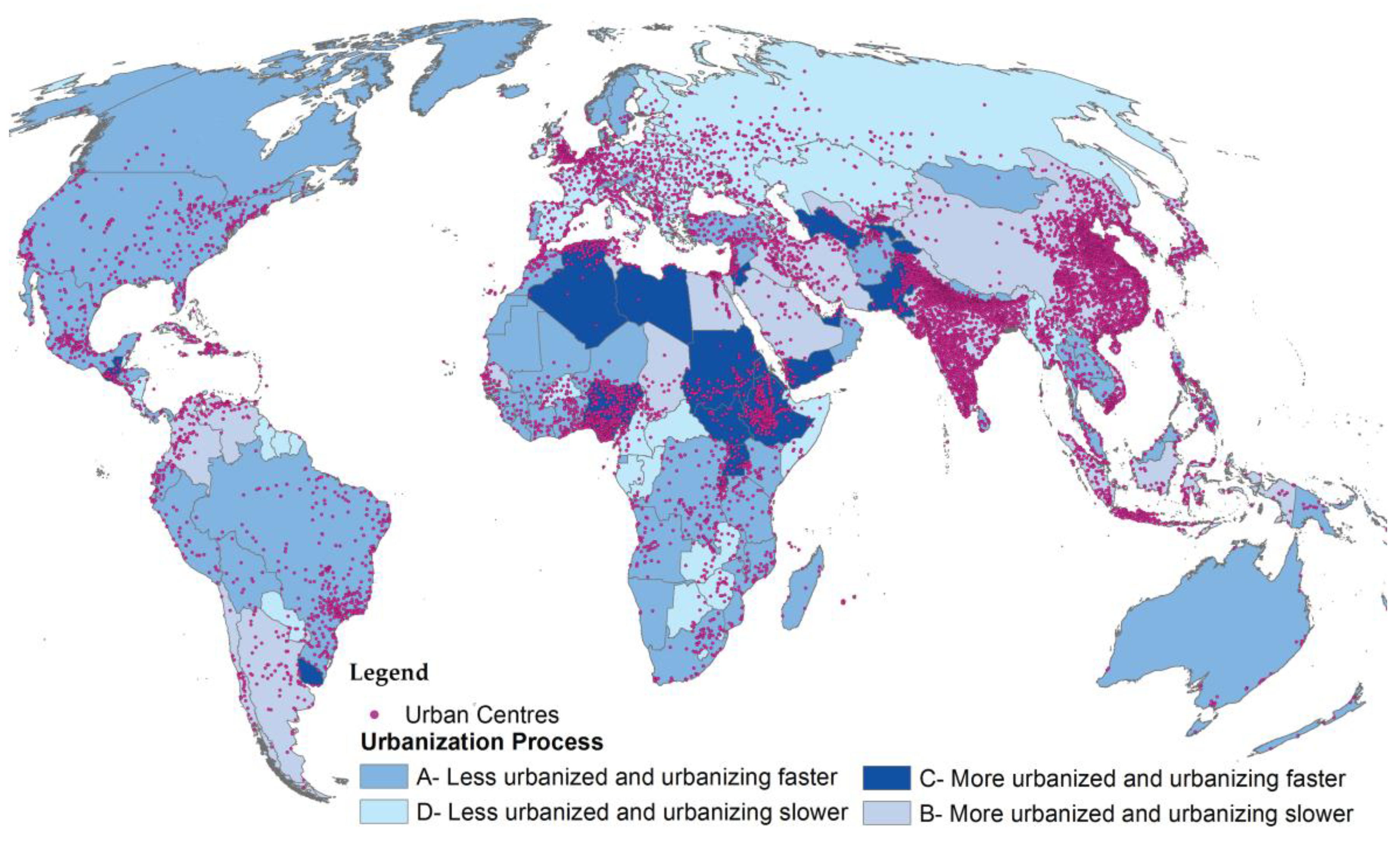
Figure 5 shows the spatial distribution of the four principal urbanization dynamics. In group C are those urbanization champions in which the present degree of urbanization is above the global average and where the transition over the past 25 years has been faster than the global average. Within this cluster of 33 countries, we identified two subsets. The first, with 17 cases, contains countries where the degree of urbanization in 1990 was below the current global average, but due to an intense process of urbanization they were more urbanized than the global average by 2015; the second subset includes 16 countries where the degree of urbanization was already above 85% in 1990 but a dynamic urbanization process continued. Examples of the first subset include Yemen and Lebanon, where the degree of urbanization in 1990 was below 80% and increased by more than 7%; and Guatemala, Algeria, and Uruguay, where the share of the urban population changed from approximately 80% to 85%, 86%, and 87%, respectively, a change of around 4% (nearly twice the average global growth rate). The second subset comprises countries like Pakistan, the United Arab Emirates, and Tajikistan, where the present degree of urbanization is generally 90% and where the share of urban population has increased by around 4%.
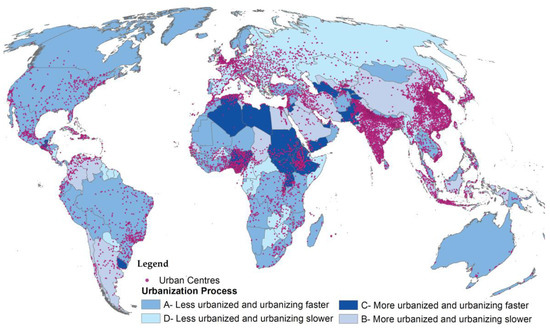
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of the four principal urbanization processes (World Mollweide projection). Countries are classified according to their 2015 Degree of Urbanization and their Degree of Urbanization variation between 1990 and 2015. ‘More’ or ‘Less’ classification refers to the mean Degree of Urbanization in 2015, while ‘faster’ or slower’ refers to the mean Degree of Urbanization variation between 1990 and 2015 among all countries.
The last group (D) includes 83 countries where the urbanization process does not unfold fast. Twelve are in Africa, where on average 71 in 100 inhabitants are settled in urban areas. Europe has 29 of those countries with an average degree of urbanization in 2015 below 70%. Among them, in five the degree of urbanization in 2015 was below 60%. The change in the degree of urbanization in countries in this class is between 0% and 1% in 29 cases. There are, however, approximately 25 countries in which the degree of urbanization was above 80% in 1990 but where a decline in the degree of urbanization is observed. Among these are the Russian Federation, Latvia, and Paraguay.
In this section, we simultaneously analyzed the current degree of urbanization and the process that led countries to the present situation. With only a dozen countries with a degree of urbanization below 50% in 2015 (including islands), and with more than 80 countries where the degree of urbanization is increasing by more than double the global average, urbanization has attained a global reach. It has been reaffirmed by adopting a globally harmonized definition of urban areas and multi-temporal datasets with demographic information that the planet is more urbanized than was generally understood through other demographic datasets. Furthermore, the process of urbanization excludes only a very few countries. In more than 110 countries, the degree of urbanization has increased by at least 3% over the past 25 years. However, in contrast to this general pattern of continuous growth in urbanization, we identified more than 60 countries in which the degree of urbanization has declined.
3.3. Concentration of People and Diffusion of Built-Up Areas
Together with the process of urbanization that describes the dynamics of concentration of inhabitants in urban areas, GHSL allows us to analyze and map the process of spatial expansion of built-up areas. Agglomeration [29] refers to the concentration of built-up areas in cities, versus dispersion into rural areas. For the purposes of this analysis, the degree of agglomeration is calculated as the share of built-up surface accounted for in urban areas (including both Urban Centres and Urban Clusters) versus the total detected at a national level (whereas it was calculated solely on Urban Centrers in [29]).
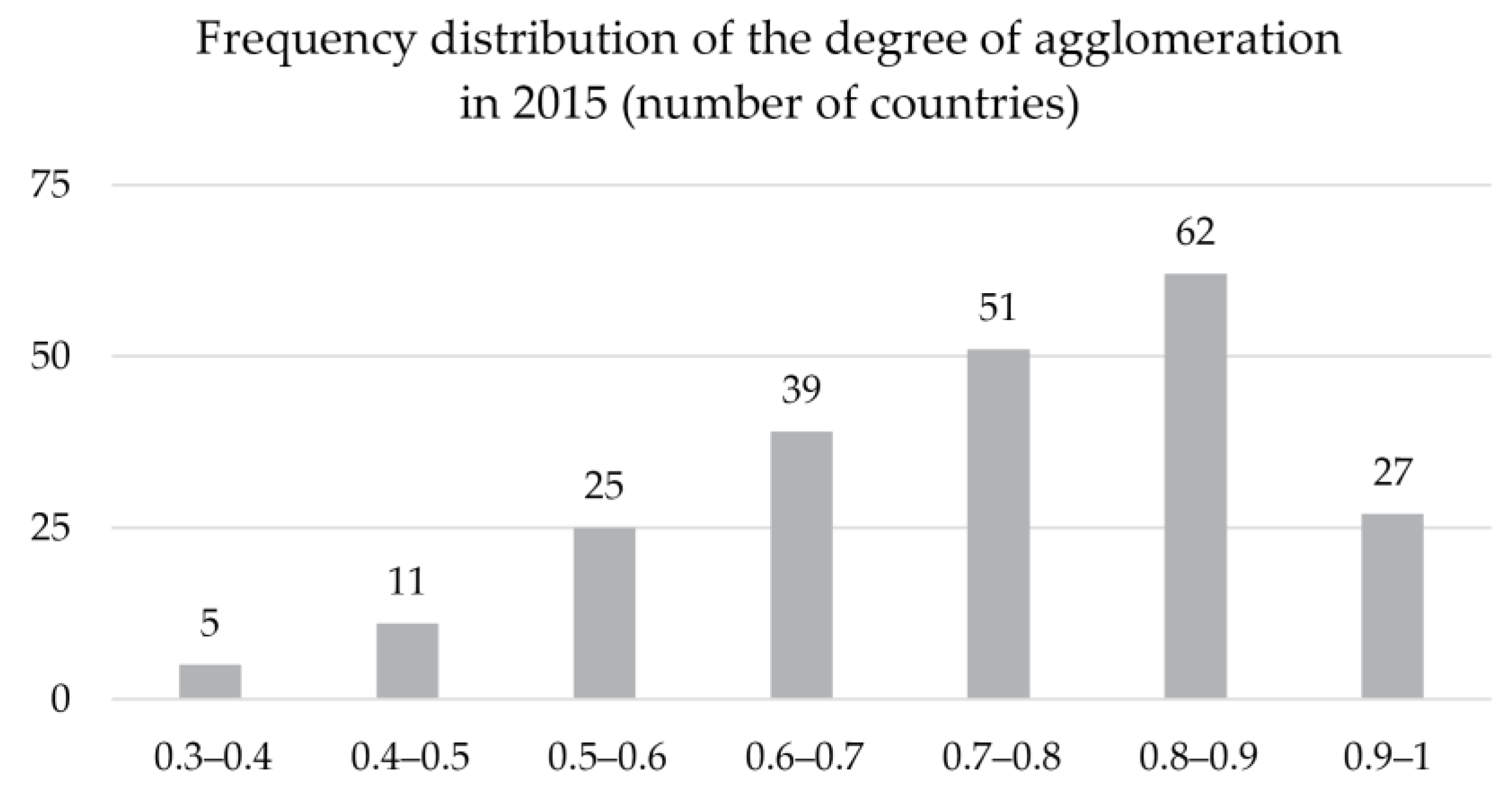
The global degree of agglomeration was 74% in 2015. In Asia, more than 87% of built-up areas were in urban areas, in Latin America and the Caribbean 78%, in Africa 73%, while in Northern America and Europe 66% and 61%, respectively. In 2015, there were nearly 90 countries where the degree of agglomeration was above 90%, and over 60 in which agglomeration was between 80% and 90% (Figure 6). Countries where agglomeration levels were highest include Bahrain, Bangladesh, the United Arab Emirates (all above 95%), Vietnam, Pakistan, Rwanda, Tajikistan, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka (between 90% and 95%). Excluding island states, the countries where the built-up areas were the least concentrated in urban areas included Namibia (11%), Norway (32%), and Romania (39%).
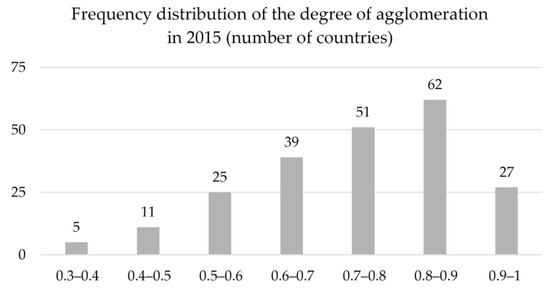
Figure 6.
Number of countries per degree of agglomeration (excluding the 19 countries below 30%).
Considering the multi-temporal evolution of the degree of agglomeration between 1990 and 2015, it emerges that at a global level agglomeration has marginally declined (−0.6%). A declining degree of agglomeration implies more intense growth of the built-up footprint in rural areas. At a global level, the degree of agglomeration has increased in 110 countries, while it has declined in 114 (and was not subject to variations in 12). The change in agglomeration is particularly subject to regional and national differences. The sharpest agglomeration decline took place in Europe (−5%). In Europe, the degree of agglomeration increased only in Andorra (+5%), Luxembourg, and Norway (+2%), with a marginal increase (<+2%) taking place in Malta and Switzerland. Considerable decline (>−10%) took place in Romania, and declines of between −9% and −5% in Croatia, Hungary, Albania, Bulgaria, and Ukraine, among others. In this last set of countries, the degree of agglomeration in 2015 remained below the global average.
Despite the overall global trajectory, in the circa 110 countries where the degree of agglomeration increased, distinct patterns were seen. In Afghanistan, for example, agglomeration increased by more than 25%, driven by the growth of built-up areas in urban areas of nearly 90%. Similar patterns were seen in Somalia (agglomeration +10% and urban built-up areas +90%), Venezuela (+16% and +57%), Madagascar (+14% and +74%), and Nepal (+12% and +77%).
Overall, the spatial footprint of urban expansion between 1990 and 2015 consists of more than 174,000 km2 of built-up areas newly detected in urban areas. While this figure corresponds to more than 70% of the total built-up footprint on Earth, built-up areas have slightly dispersed. Most of the spatial expansion within urban areas took place in Urban Centres.
3.4. Urbanization and Agglomeration
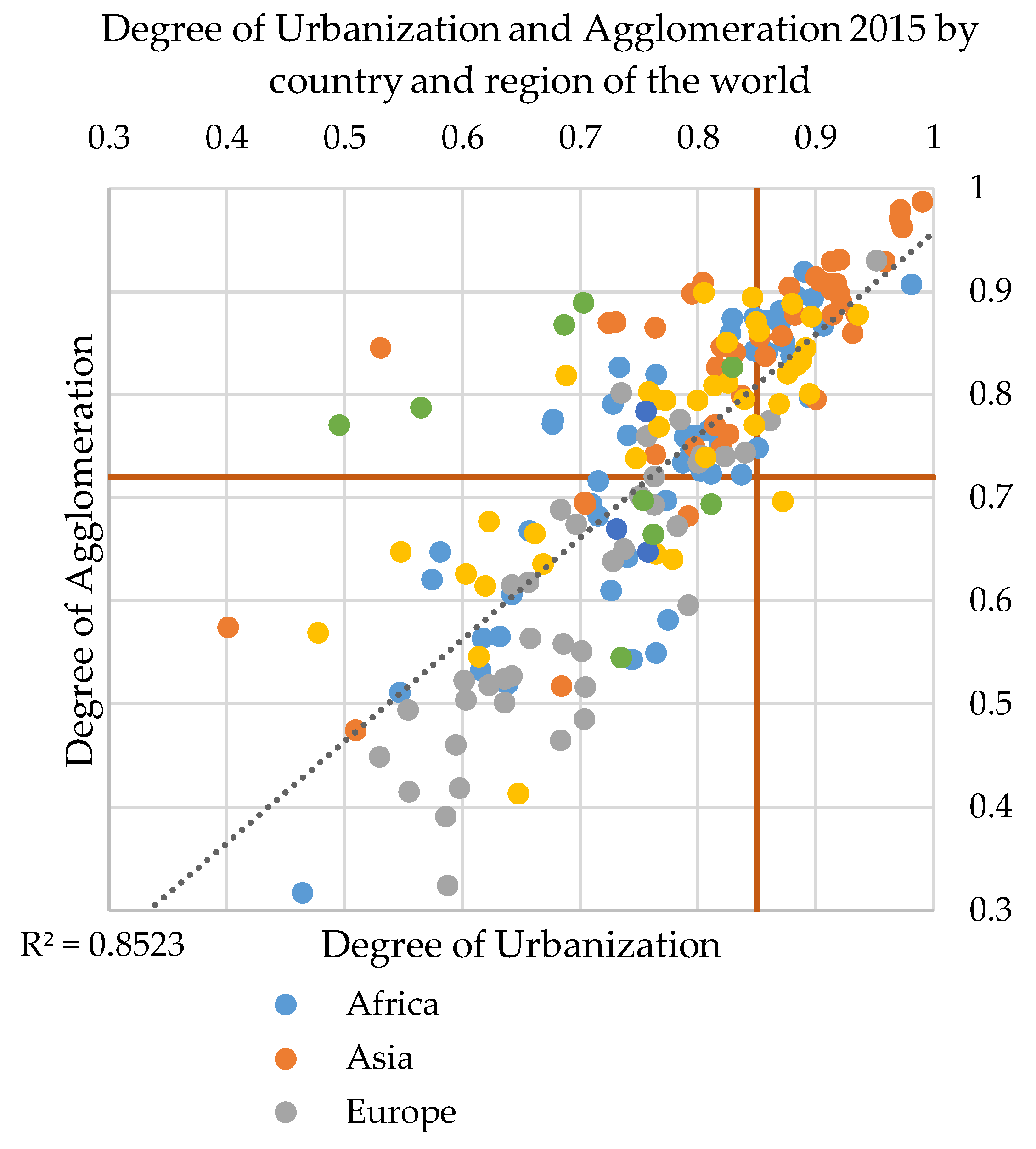
Our analysis of the process of spatial and demographic growth of human settlements is based on two main indicators: the degree of urbanization (based on population data), which generally increases; and the degree of agglomeration, for which on average a slight decrease has taken place globally. The combination of these two indicators (Figure 7) reveals 64 countries with a distinctive urban character where both the degree of urbanization and agglomeration is above the global average. The majority of these countries are in Asia (23) and Africa (15), two are in Europe (the United Kingdom and Malta), and 10 are in Latin America and the Caribbean. In these countries, urban areas host more than 74% of the national built-up areas and more than 85% of the national population. In particular, among the ones in Africa, three are upper-middle-income countries, five are lower-middle-income countries (e.g., Nigeria, where 87% of people are urban dwellers and 88% of built-up areas are in urban area; Sudan, 88% and 90%, respectively; and Senegal, 87% and 85%) and seven are low-income countries (e.g., Burundi, 87% and 88%; Ethiopia 88% and 84%, respectively; Chad, 86% and 87%). Among the ones in Asia, eight are high-income countries (e.g., Japan, where the degree of urbanization is 92%, and that of agglomeration is 92%; Israel, 93% and 86%; Saudi Arabia, 92% and 91%), six upper-middle-income countries (e.g., Lebanon, 90% and 80%; and Turkmenistan, 88% and 90%), and nine lower-middle-income countries (including Bangladesh with 97% and 98%, respectively; Indonesia with 90% and 91%, respectively; Pakistan, 91% and 93%; and Vietnam, 92% and 93%).
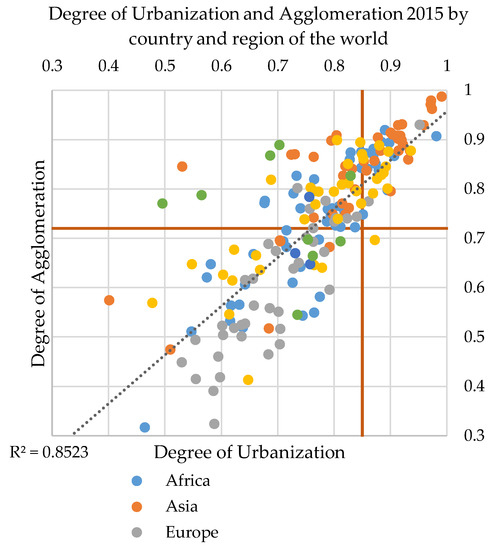
Figure 7.
Degrees of urbanization and agglomeration by country (colored by regional group).
The combination of the degree of urbanization and agglomeration helps to explain the dominance or primacy of urban areas in the different countries of the world. It is an index of spatial and demographic concentration of built-up areas and people in urban areas, and it has a rather strong correlation. The primacy of urban areas is more evident in Asia than in Europe (Figure 7).
3.5. Urban Growth and Pace of Urbanization
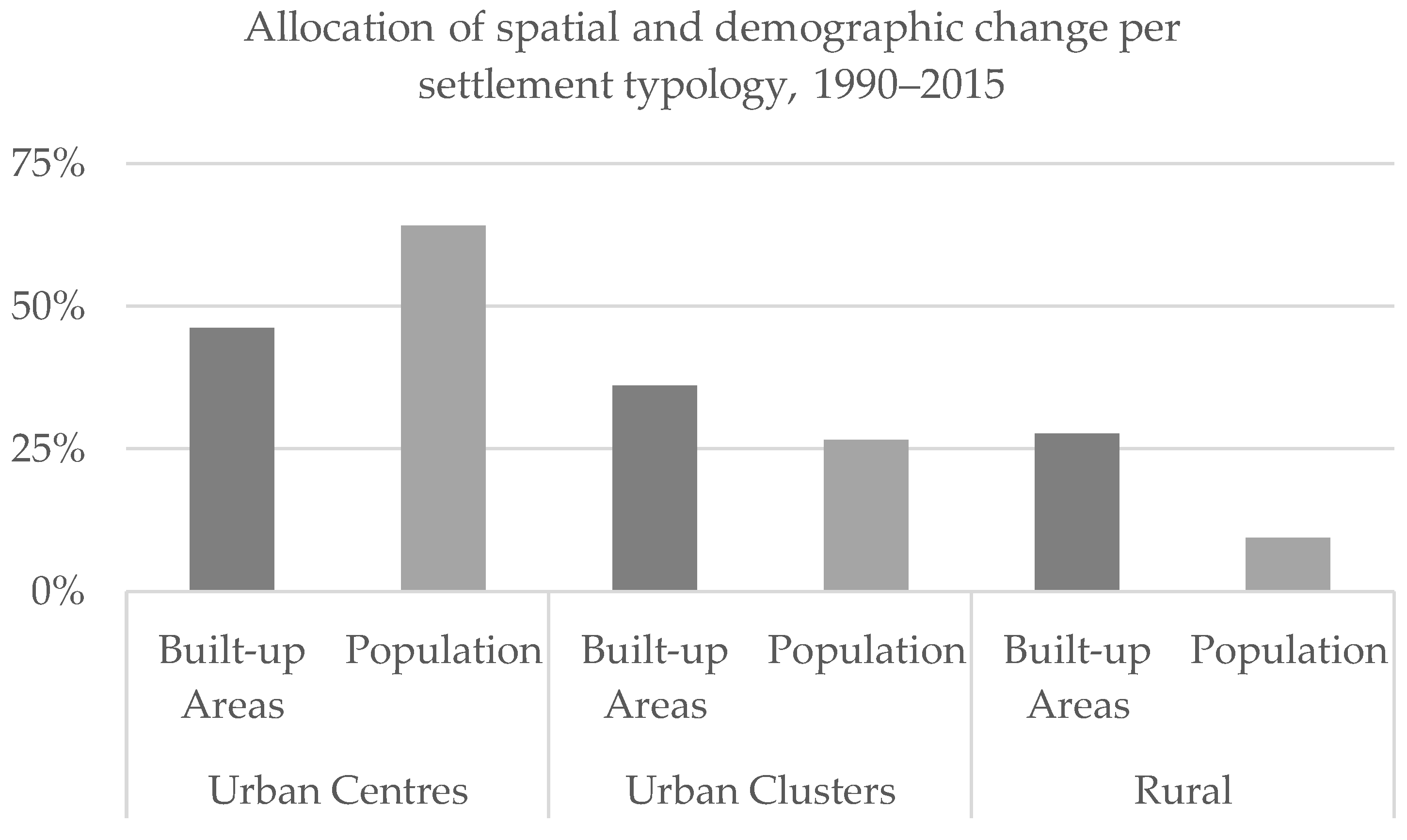
It was noted in Section 3.1 that 72% of the global expansion of built-up areas and more than 90% of the demographic growth between 1990 and 2015 took place in urban areas. In particular, it is important to determine which settlement class drives urban growth. Between 1990 and 2015, Urban Centres captured more than 40% of the expansion of built-up areas and 60% of population growth. At a regional level, this general trajectory is subject to variation. In Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean, and North America, Urban Centres hosted more than 50% of the built-up areas’ expansion. In Europe, more than 60% of urban built-up areas’ expansion took place in Urban Clusters, while built-up areas in Urban Centres grew by 15%. In Europe, more than 80% of total population growth took place in Urban Centres, while in Urban Clusters a net population decline was observed. Therefore, it emerges that while the population grows considerably more than built-up areas in Urban Centres, built-up areas increase in relative terms more than the population in Urban Clusters (Figure 8). In Africa and Asia, Urban Clusters have accommodated around one-third of the built-up areas newly detected in urban areas. The process of built-up areas’ dispersion in rural areas has been most evident in Europe, where more than 50% of the newly detected built-up areas between 1990 and 2015 are in rural areas.
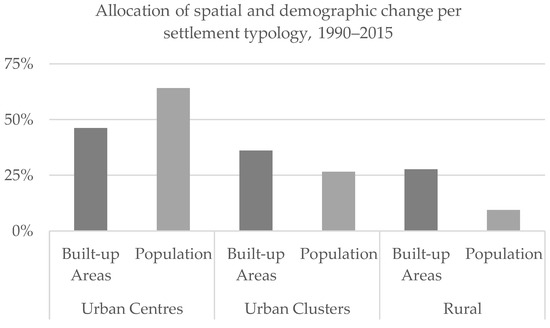
Figure 8.
Share of the total global built-up areas and population increase (1990–2015) captured by each SMOD settlement typology.
The disaggregation of the process of socio-spatial growth per settlement typology shows that the majority of spatial and demographic growth in urban areas took place in Urban Centres (which account for 64% of built-up areas and 70% of population changes). Figure 8 shows that, globally, Urban Centres have captured more population and built-up areas than Urban Clusters. Dense and highly populated urban areas tend to grow more than Urban Clusters; however, nearly 30% of the spatial growth took place in rural areas.
3.6. Uneven Aspects of Urbanization
The global distribution of global built-up areas and population in income classes is highly uneven. High-income countries (HIC) accounted for more than half of global built-up surfaces in 2015, but less than 18% of the population. In urban areas, this disparity is also present. Urban areas in HIC contain 47% of the global built-up area and 18% of the global population; upper-middle-income countries (UMC) contain 30% and 33%, respectively; lower-middle-income countries (LMC) 19% and 42%; low-income countries (LIC) 4% and 8%. Urban growth displays rather specific patterns of variation with income classes. Between 1990 and 2015, in LIC urban area has expanded by more than 11,000 km2 and the population has increased by more than 272 million new urban dwellers, essentially doubling their sizes.
However, it is in LMC urban areas that the highest absolute population change took place, corresponding to more than 930 million new inhabitants. In terms of spatial expansion of urban areas, the footprint of urban built-up areas in HIC expanded five times more than in LIC, but less than in UMC. In UMC, the urban built-up area has grown by 60% (64,000 km2).
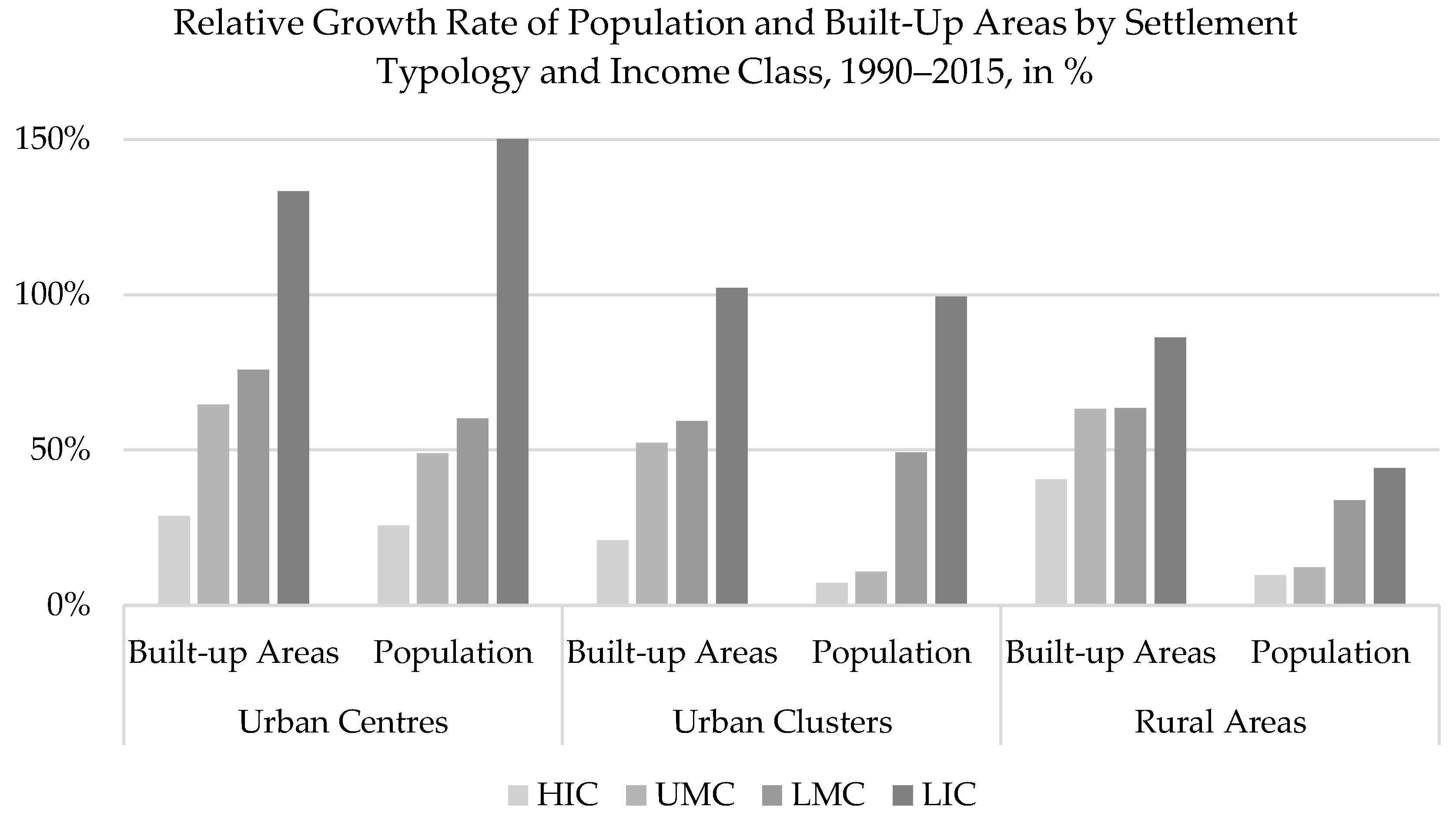
The dynamics of urban growth in LMC and LIC confirm that in relative terms these income classes have grown faster than others. In LMC urban built-up area has grown by 70% and population by 56%, while in LIC both indicators doubled in 25 years (Figure 9). The present degree of urbanization in LIC accounts for 78 in 100 people in urban areas, while it was 70% 25 years ago. Therefore, LIC are less urbanized than the global average but are urbanizing much faster than other countries. The process of urbanization has been considerably rapid in LIC: in 25 years the degree of urbanization increased by 8%. The speed of change remains below the global average in LMC (+1.6%).
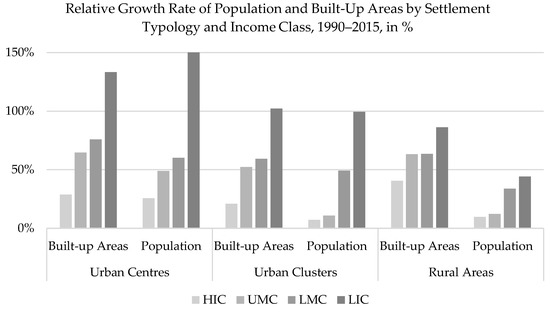
Figure 9.
Comparison of built-up and population change by income classes in the three SMOD settlement typologies.
The regional disaggregation of urban development patterns by income classes partially supports the global narrative of development that spotlights Africa and Asia [42]. It provides evidence of the vibrant relative growth of the urban population and built-up area in LMC and LIC in Africa and Asia. Moreover, it shows that urban areas in African LIC account for almost half the total population growth of the region (47%, equivalent to more than 230 million people), while African LMC account for more than 37% (more than 200 million). Indeed, the demographic growth in urban areas in African LIC represents more than 10% of the overall global population growth over the past 25 years. Demographic changes in urban areas in LMC in Asia account for 65% of total regional population change, and up to 35% of global population growth between 1990 and 2015. Demographic and spatial development evolves differently by settlement types, across income classes and regions of the world. More than half the spatial expansion (54%) and demographic growth (64%) of African LMC took place in Urban Centres. In African LIC, approximately 40% of both demographic and spatial growth occurred in Urban Centres, while Urban Clusters accounted for 32% of spatial growth and 42% of population increase. In Asia, rural areas shrank by more than 30% and built-up areas in both Urban Centres and cluster expanded by more than 60%.
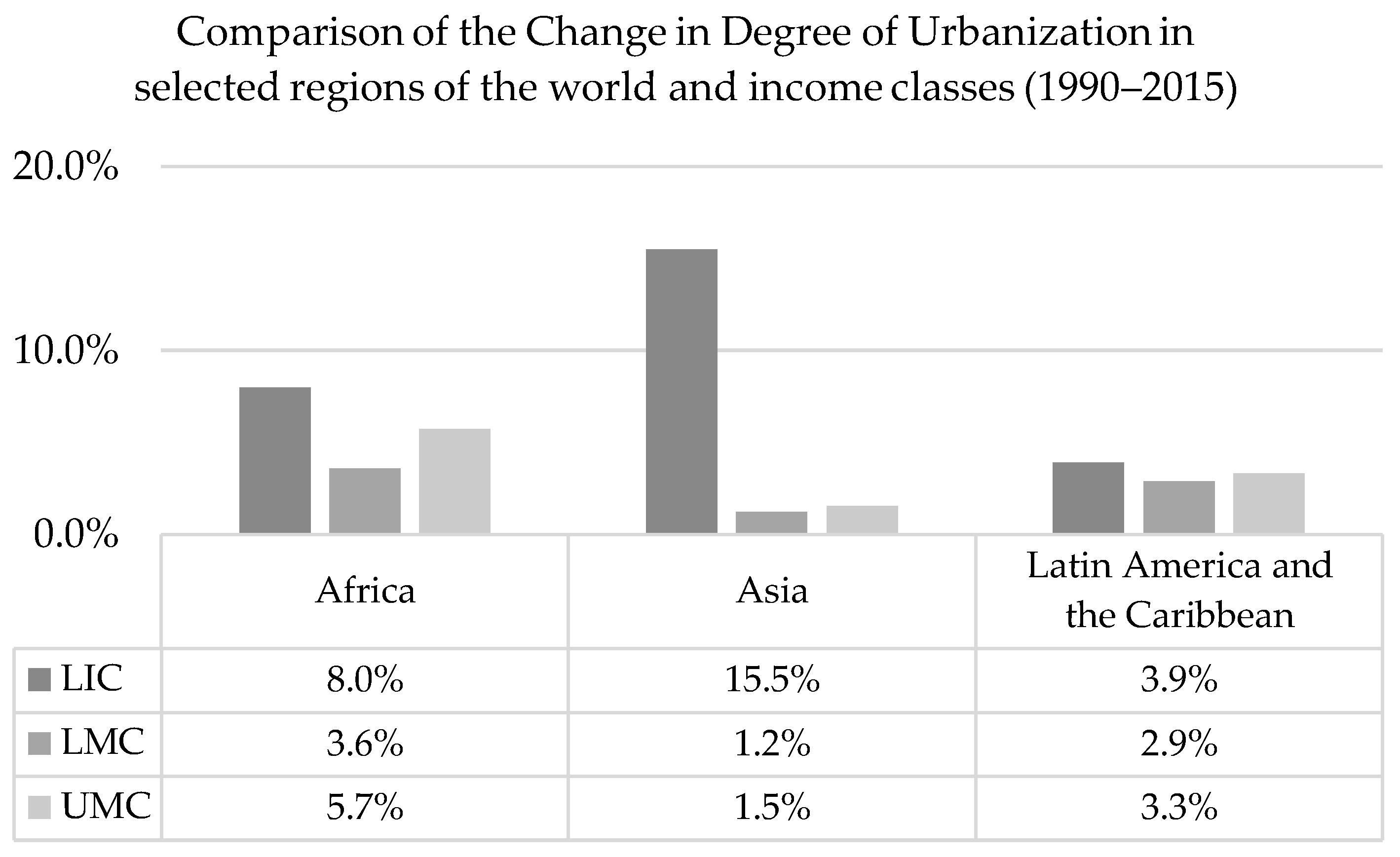
However, our results also demonstrate unevenness in terms of the change in degree of urbanization (Figure 10). Between 1990 and 2015, the degree of urbanization increased by 15% on average in LIC in Asia (Afghanistan, Cambodia, and Nepal), driven by very fast urbanization in Afghanistan (+16%) and Nepal (+12%). This was more than the average of LIC in Africa (8%) and the fastest global pace in the LIC income group. Figure 10 also shows that the most prominent changes in low- and middle-income country groups in the selected regions took place in Africa, where the degree of urbanization increased on average by 4% in LMC and 8% in UMC.
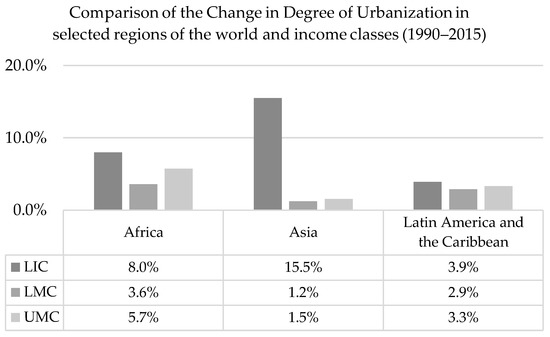
Figure 10.
Relative change of the degree of urbanization in selected regions of the world disaggregated by income class.
4. Discussion
The results of our analysis suggest that (i) urbanization has achieved a planetary reach; (ii) the population concentrates in cities and; (iii) built-up areas expand and marginally spread out of urban areas.
Our results shed light on the patterns of planetary urbanization from the perspective of the GHSL, identifying different degrees of intensity in specific areas of the world or specific income classes. Compared to thematic descriptors of urbanization (the spatial approach that captures the manifestations of urban expansion, and the other on the demography), GHSL supports a simultaneous analysis of socio-spatial patterns over a period of 25 years, and characterizes urban and rural dynamics in a consistent, globally comparable way by adopting the Harmonized Definition of Cities and Settlements [24]. The results we presented should be put in the framework of the epistemological guidelines for a new investigation of planetary urbanization, as proposed by Brenner and Schmidt [26]. In their article, the authors point out that there is a need for an understanding of the process of urbanization that a new generation of empirical evidence, tools, and methods should sustain.
Our research targets at least four of the epistemological guidelines proposed. In Section 3.1 we were able to quantify the process of socio-spatial urban development, analyzing it as a process over more than two decades to determine that urban areas have grown by more than 40% in terms of built-up footprint and population, with sound interdependence between the two factors across the regions of the world. In Section 3.2 we mapped the reach and pace of the urbanization process with evidence for this planetary phenomenon, and in Figure 5 we suggested an alternative “cognitive map” of urbanization. In Section 3.3 we tracked the process of concentration of people, and that of the extension and dispersion of built-up areas.
We confirmed that urbanization generally increases yet negative changes in the degree of urbanization are rather frequent too. In 61 countries, in fact, the change in the degree of urbanization between 1990 and 2015 was negative. The decline can be rather marked, as in the Republic of Congo (−17%), Estonia (−14%), and Latvia (−7%), or moderate like in Nicaragua (−6%), Zimbabwe (−4%), Gabon (−3%), and France (−2%). These trajectories might be explained by economics, political science, and development studies, so our research calls for further and finer scale analysis of the alternative dynamics of urbanization change. Two main comparisons should be implemented (based on Figure 5). The first, between the countries in groups A and D, where despite the degree of urbanization (2015) being below the global average in both groups, in group A the process of urbanization was more vibrant, while in group D it was below the global average (or even negative). The regional collocation of countries in the two groups is very distinct. Group D (more urbanized but urbanizing slower) includes 29 countries in the European region, while group A (less urbanized but urbanizing faster) includes over 40 countries across Africa and Asia. The second comparison, between groups B and C, shows that, while in both the degree of urbanization in 2015 was above the global average, group C countries keep urbanizing fast, whereas in group D the urbanization is slower. In this case the regional distribution accounts for 12 group C countries (more urbanized and increasing faster) in Africa and eight in Asia, while in group B, five are in Africa and 15 are in Asia. The income class disaggregation adds that the majority of cluster B countries are HIC, while 15 in cluster C are LIC or LMC. This categorization could serve as a baseline for a next generation of national samples of cities, as currently proposed by UN‒Habitat and New York University (https://unhabitat.org/national-sample-of-cities/).
The findings emerging from this study help to characterize the scale, size, and growth of human settlements, and their regional and national differences.
In sum, we provided empirical evidence about the socio-spatial patterns of human settlement growth, the process of urbanization, the spatial concentration of built-up areas in cities, and the speed of the urbanization process that takes place in low- and middle-income countries.
The analysis of the urbanization process with a globally consistent dataset confirms that urbanization has attained a global reach: more than 1.8 billion new urban dwellers populate urban areas on the planet, and this figure accounts for more than 90% of the 2.2 billion people born since 1990. Between 1975 and 2015, urban areas grew by 40%, in terms of both population and built-up surface. Most of these changes took place in Africa and Asia, and in more than 110 countries worldwide the degree of urbanization has increased. Despite this overall trend, there are a fair number of countries where the degree of urbanization has declined, in some cases due to a net loss of urban population. The process of built-up areas’ concentration in urban areas is more diverse than that of population. The degree of agglomeration marginally declines as built-up areas tend to disperse outside urban areas. This process should be further analyzed as it might support an understanding of changes in land use efficiency (currently discussed as an indicator for the SDG 11.3). However, in some countries agglomeration grows fast, often due to the rapid spatial expansion of urban areas. The analysis of the process of urbanization by income classes has identified significant differences. First, it has been determined that the average degree of urbanization in LIC countries is below the global average, but also that these are urbanizing very fast, with a pace of change of +8% between 1990 and 2015. The change in LMC instead tends to be 1.6%, below the global average of 2.3%.
5. Conclusions
In this paper we analyzed the spatial and demographic changes that took place in human settlements over 25 years (1990–2015), proposing a global analysis of the present status and multi-temporal changes in the degree of urbanization at global, regional, and national levels. We provided examples of the manifestations of the urbanization process by analyzing its spatial and demographic manifestations over 25 years.
Following the theses of Brenner and Schmidt [26], our work has investigated salient thematic areas for urbanization theory, proving that the use of data based on remote sensing and earth observations overcomes the dependence on “state-centric” sources and permits the analysis of agglomeration, population distribution, and land cover dynamics.
The chief findings of this study are: (i) the planet is substantially more urbanized than what has been previously reported; (ii) although people concentrate in urban areas, built-up areas tend to disperse; (iii) the spatial expansion and the demographic growth of cities can be quantified; (iv) the concentration of people and built-up areas in urban areas is a proxy of urban dominance; and (v) we can account for the urban growth and urbanization pace of change. These results are derived from the Global Human Settlements Layer baseline data and the Settlement Model. The baseline data (built-up and population density layers), despite some data approximation due to built-up areas’ resolution and bidimensional representation, provide consistent, harmonized, and multi-temporal information that allows for global analyses of built-up areas and population. Moreover, the Settlement Model made it possible to classify human settlements in an urban vs. rural dichotomy (by aggregating the Urban Centres and Urban Clusters 1 km grid cells) with a standardized approach across national boundaries. Additional high-impact explorations may include the periodic update of GHSL datasets and eventually venturing into grids that spatialize population projections into the future.
The findings we presented support advances and quantification of the urbanization theory with spatial and demographic motives, to support policymakers and researchers in the understanding of the genesis of the global urbanization process. Being aware of data scarcity and quality in the past, and of the drawbacks to automatic built-up areas’ extraction with symbolic machine learning, we focused our study on 1990–2015, excluding the 1975 GHSL layer and obtaining more robust and reliable results. The analyses we presented can be replicated, detailed, or extended due to the provision of GHSL as open and free data. Moreover, it is possible to further process the GHSL and quantify additional indicators to monitor the process of urbanization and support international agreements such as the Sustainable Development Goals or the New Urban Agenda. GHSL is one of the core datasets of the Group on Earth Observation (GEO) Human Planet Initiative, a scientific and multi-stakeholder partnership committed to unleash a new generation of evidence mapping the human presence on Earth and to support the monitoring of the progress made in the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Supplementary Materials
The statistical dataset used to prepare the article is provided as supplementary material and it is available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/10/5/768/s1.
Author Contributions
M.M. wrote the paper, designed the study, led the research experiments and interpretation, and designed the statistical dataset; A.J.F. provided input on the manuscript, produced the data for the analysis, and helped with the analysis; S.F. gave advice on the research design, worked on data preparation, and revised the manuscript; M.S. revised the paper and gave advice on paper writing; T.K. and M.P. supported the review of the paper and offered guidance and support through the research.
Acknowledgments
This work has been carried out in the frame of the institutional work program of the Joint Research Centre (JRC, European Commission) and supported by the administrative arrangement No. 33994 between the JRC and the Directorate General for Regional and Urban Policies (DG REGIO, European Commission).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Martine, G.; Marshall, A. State of world population 2007: Unleashing the potential of urban growth. In State of World Population 2007: Unleashing the Potential of Urban Growth; UNFPA: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA). World Urbanization Prospects the 2007 Revision; United Nations: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Burdett, R.; Sudjic, D. (Eds.) The Endless City: The Urban Age Project by the London School of Economics and Deutsche Bank’s Alfred Herrhausen Society; Phaidon: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K. The Origin and Growth of Urbanization in the World. Am. J. Sociol. 1955, 60, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, D. Urban Myths and the Mis-Use of Data That Underpin Them; WIDER: Helsinki, Finland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- G.A. United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, S. Atlas of Urban Expansion; Lincoln Institute of Land Policy: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. A new map of global urban extent from MODIS satellite data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. A global analysis of urban reflectance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. Mapping global urban areas using MODIS 500-m data: New methods and datasets based on ‘urban ecoregions’. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Yeh, E.T.; Gong, P.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Validation of urban boundaries derived from global night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune-Lundberg, L.; Strand, G.-H. Corine Land Cover 2006: The Norwegian CLC2006 Project; Norsk Institutt for Skog og Landskap: Ås, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, S.; Syrris, V.; Florczyk, A.; Scavazzon, M.; Halkia, M.; Pesaresi, M. A new map of the European settlements by automatic classification of 2.5 m resolution SPOT data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1160–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakos, I.; Braun, M. (Eds.) Land Use and Land Cover Mapping in Europe; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Marconcini, M.; Felbier, A.; Roth, A.; Heldens, W.; Huber, M.; Schwinger, M.; Taubenböck, H.; Müller, A.; Dech, S. Urban Footprint Processor—Fully Automated Processing Chain Generating Settlement Masks From Global Data of the TanDEM-X Mission. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Blankespoor, B.; Deuskar, C.; Stewart, B. Urbanization and Development: Is Latin America and the Caribbean Different from the Rest of the World? The World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, N.; Schmid, C. Towards a new epistemology of the urban? City 2015, 19, 151–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, M.R. The Urban Transformation of the Developing World. Science 2008, 319, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for International Earth Science Information Network-CIESIN-Columbia University. Gridded Population of the World, Version 4 (GPWv4): Population Density; Palisades, NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Balk, D.L.; Deichmann, U.; Yetman, G.; Pozzi, F.; Hay, S.I.; Nelson, A. Determining Global Population Distribution: Methods, Applications and Data. In Advances in Parasitology; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 62, pp. 119–156. [Google Scholar]
- Tatem, A.J.; Noor, A.M.; von Hagen, C.; di Gregorio, A.; Hay, S.I. High Resolution Population Maps for Low Income Nations: Combining Land Cover and Census in East Africa. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, L.; Poelman, H. A Harmonised Definition of Cities and Rural Areas: The New Degree of Urbanisation; Publications Office of the European Union: Ispra, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, N. Theses on Urbanization. Public Cult. 2013, 25, 85–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N.; Schmid, C. The ‘urban age’ in question. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2014, 38, 731–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorri, M.; Siragusa, A. Analyzing Cities with the Global Human Settlement Layer: A Methodology to Compare Urban Growth Using Remote Sensing Data. In Smart and Sustainable Planning for Cities and Regions; Bisello, A., Vettorato, D., Stephens, R., Elisei, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soja, E.W. Beyond Postmetropolis. Urban Geogr. 2011, 32, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Siragusa, A.; Kemper, T. Atlas of the Human Planet 2016; EUR 28116 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Ispra, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, G.; Huang, C.; Chander, G.; Noojipady, P.; Masek, J. Assessment of the NASA-USGS Global Land Survey (GLS) datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Florczyk, A.; Freire, S.; Halkia, M.; Julea, A.; Kemper, T.; Soille, P.; Syrris, V. Operating Procedure for the Production of the Global Human Settlement Layer from Landsat Data of the Epochs 1975, 1990, 2000, and 2014; JRC Technical Report EUR 27741 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Ispra, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaresi, M.; Syrris, V.; Julea, A. A New Method for Earth Observation Data Analytics Based on Symbolic Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Huadong, G.; Blaes, X.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Gueguen, L.; Halkia, M.; Kauffmann, M.; Kemper, T.; Lu, L.; et al. A Global Human Settlement Layer from Optical HR/VHR RS Data: Concept and First Results. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2102–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arino, O.; Perez, J.J.R.; Kalogirou, V.; Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; van Bogaert, E. Global Land Cover Map for 2009 (GlobCover 2009); European Space Agency (ESA) & Université Catholique de Louvain (UCL): Frascati, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.A. Visualising world population density as an interactive multi-scale map using the global human settlement population layer. J. Maps 2017, 13, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Ehrlich, D.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Julea, A.; Kemper, T.; Syrris, V. The global human settlement layer from landsat imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 7276–7279. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, S.; MacManus, K.; Pesaresi, M.; Doxsey-Whitfield, E.; Mills, J. Development of New Open and Free Multi-Temporal Global Population Grids at 250 m Resolution; AGILE: Helsinki, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, M.; Kemper, T.; Geiß, C.; Esch, T.; Taubenböck, H. Mapping spatial settlement patterns on a global scale: Multi-scale cross-comparison of new and existing global urban maps. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Leyk, S.; Uhl, J.H.; Balk, D.; Jones, B. Assessing the accuracy of multi-temporal built-up land layers across rural-urban trajectores in the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 898–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesaresi, M.; Freire, S. GHS Settlement Grid Following the Regio Model 2014 in Application to GHSL Landsat and CIESIN GPW v4-Multitemporal (1975-1990-2000-2015); JRC Data Catalogue; European Commission, Joint Research Centre: Brussels, Belgium; Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, S.; Kemper, T.; Pesaresi, M.; Floczyk, A.; Syrris, V. Combining GHSL and GPW to improve global population mapping. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, B. Urbanization in developing countries: Current trends, future projections, and key challenges for sustainability. Technol. Soc. 2006, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).