Focusing High-Resolution Highly-Squinted Airborne SAR Data with Maneuvers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling and Motivation
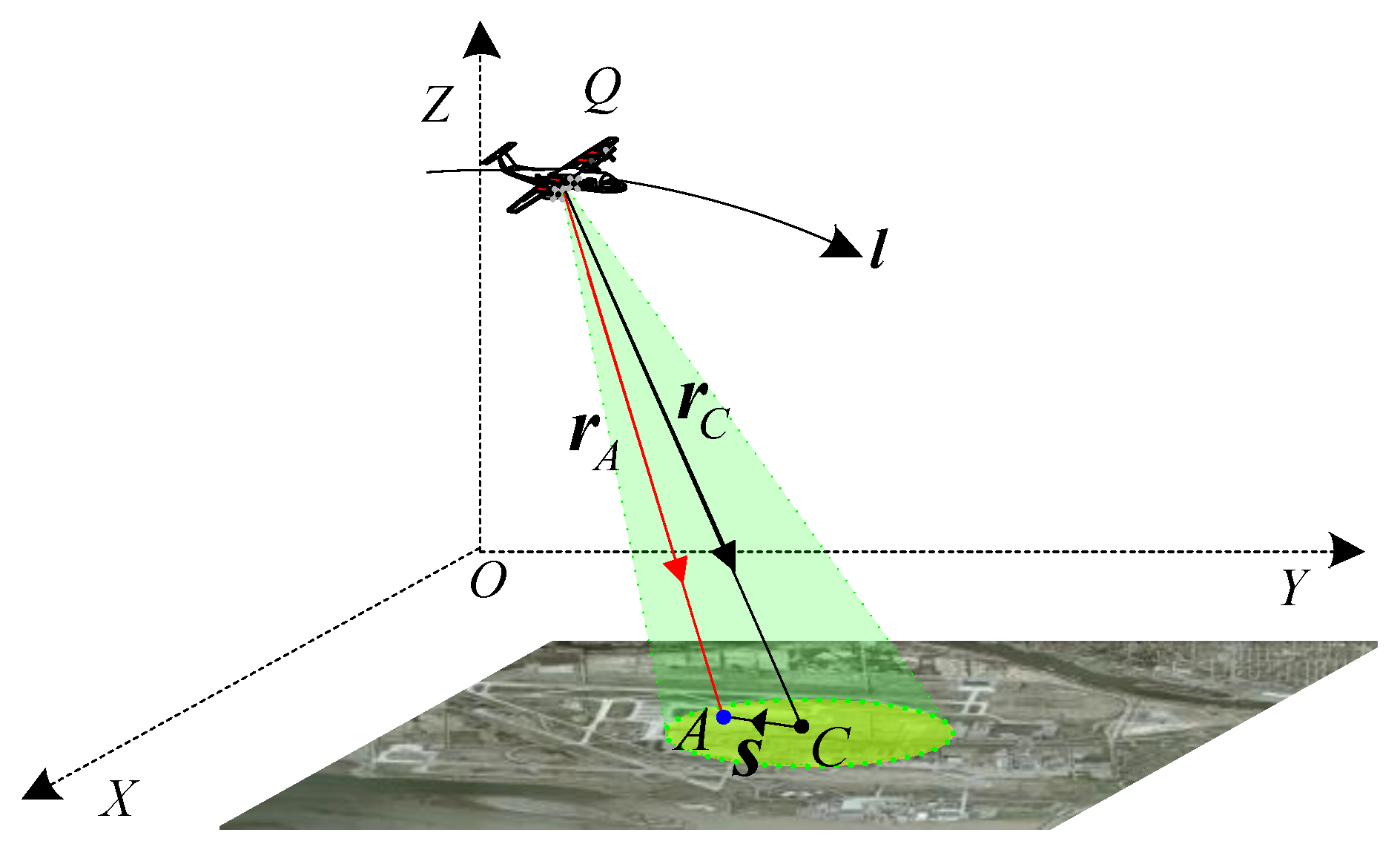
2.1. Modeling
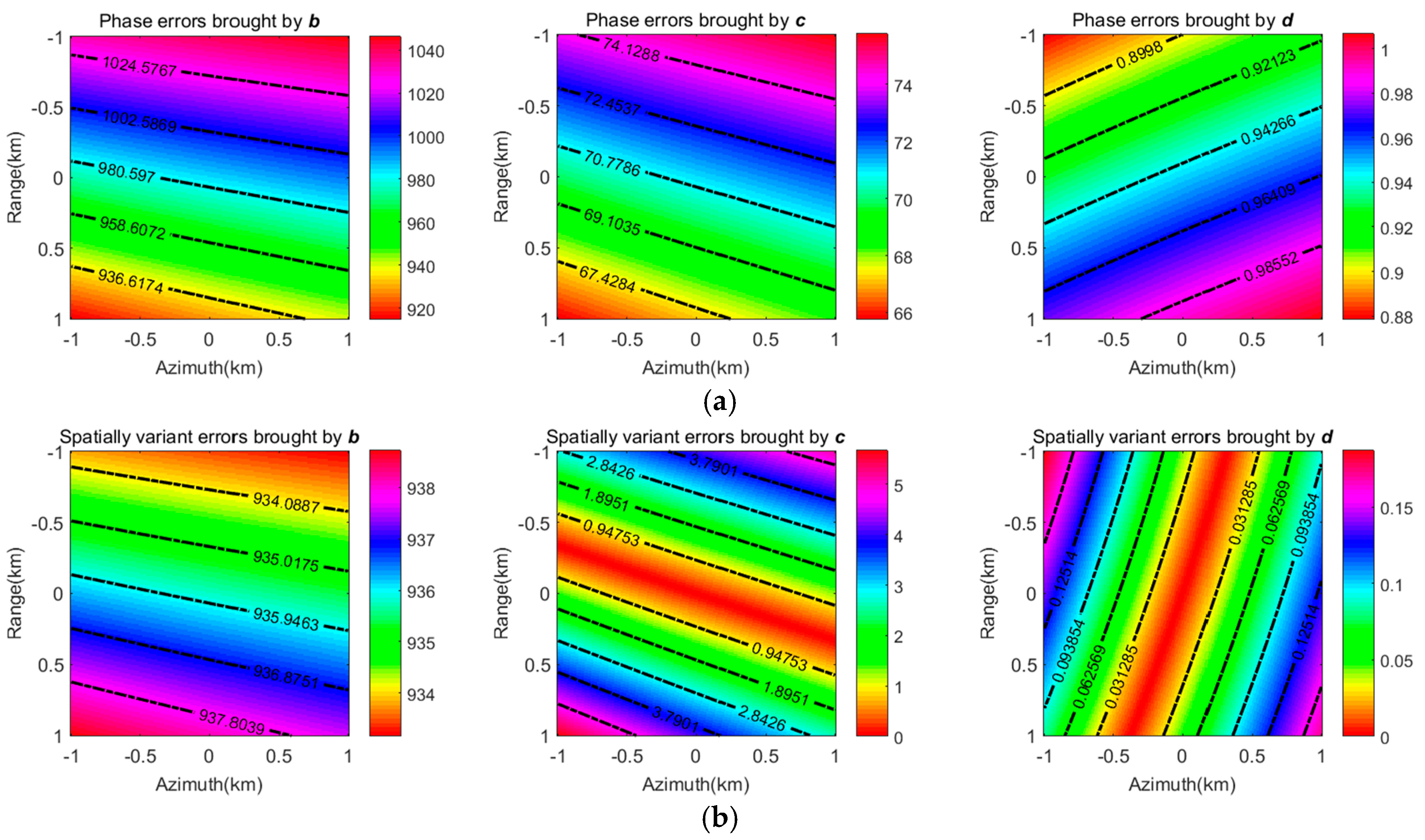
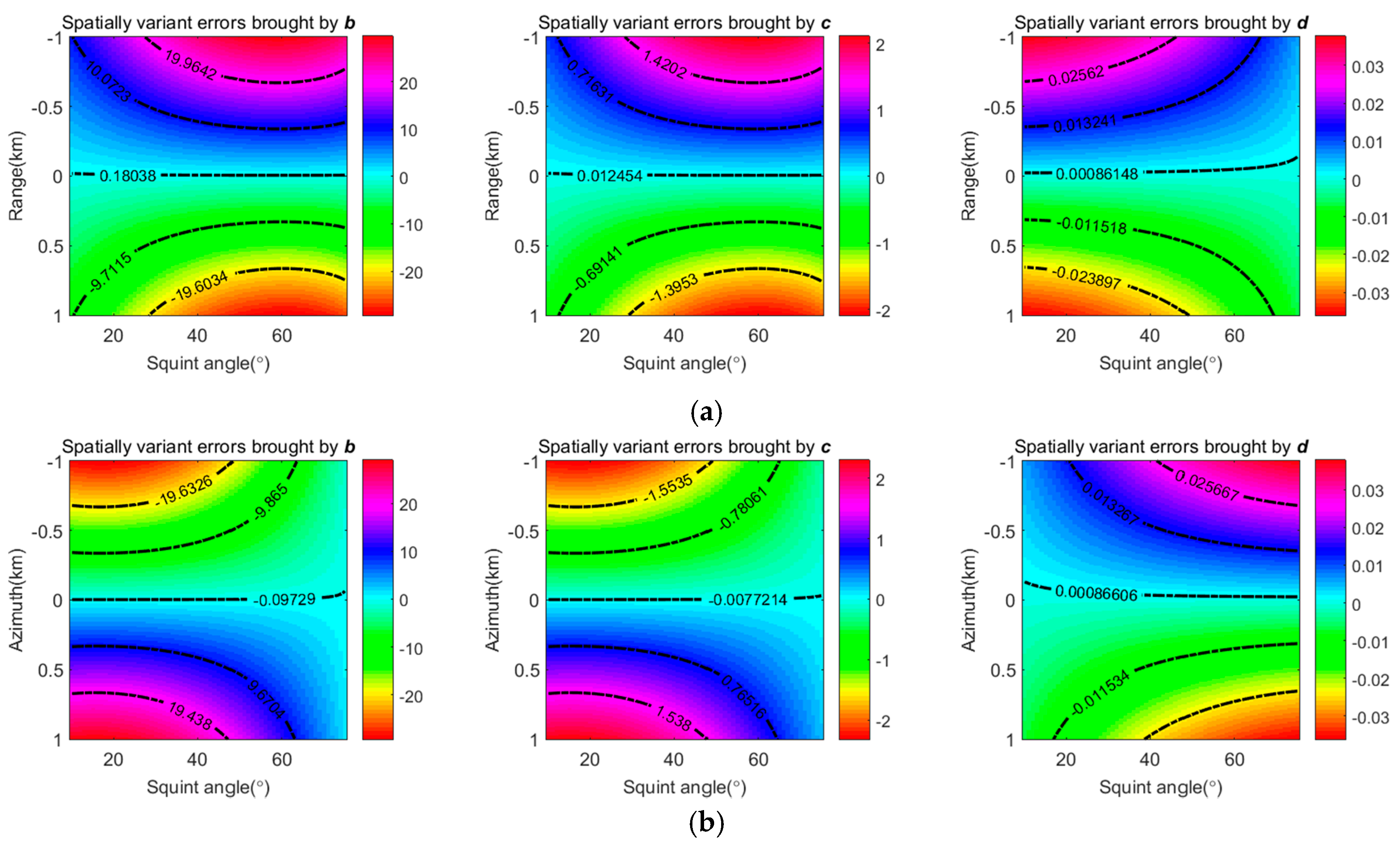
2.2. Motivation
3. Imaging Approach
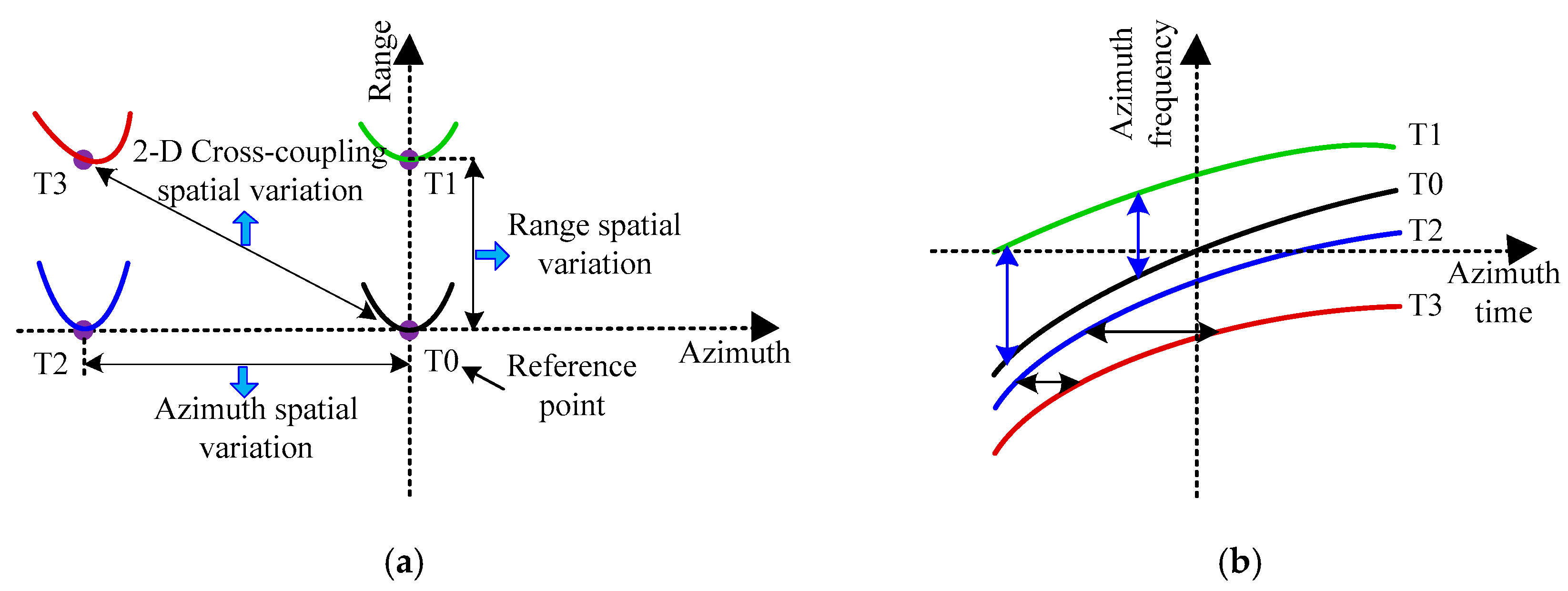
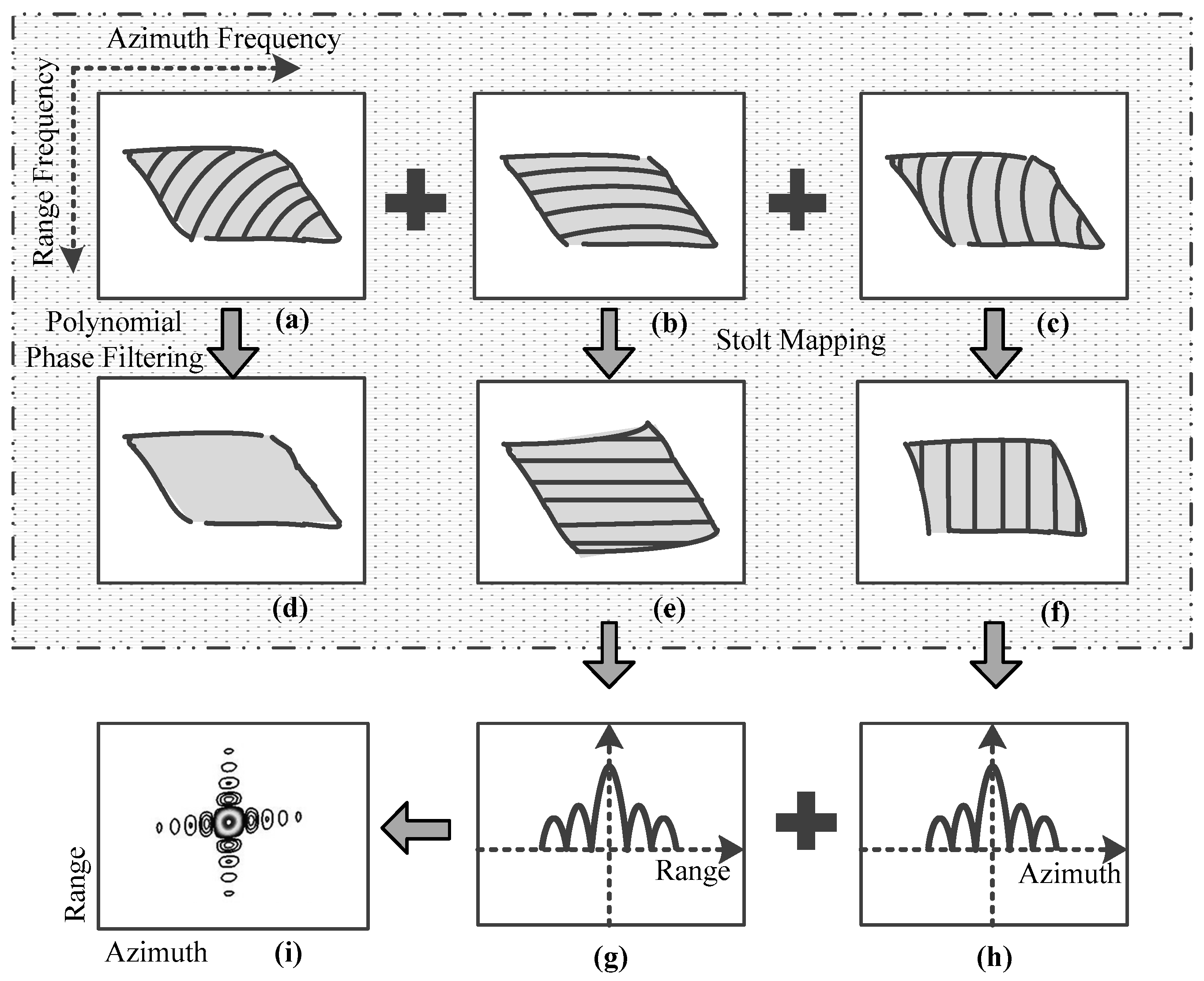
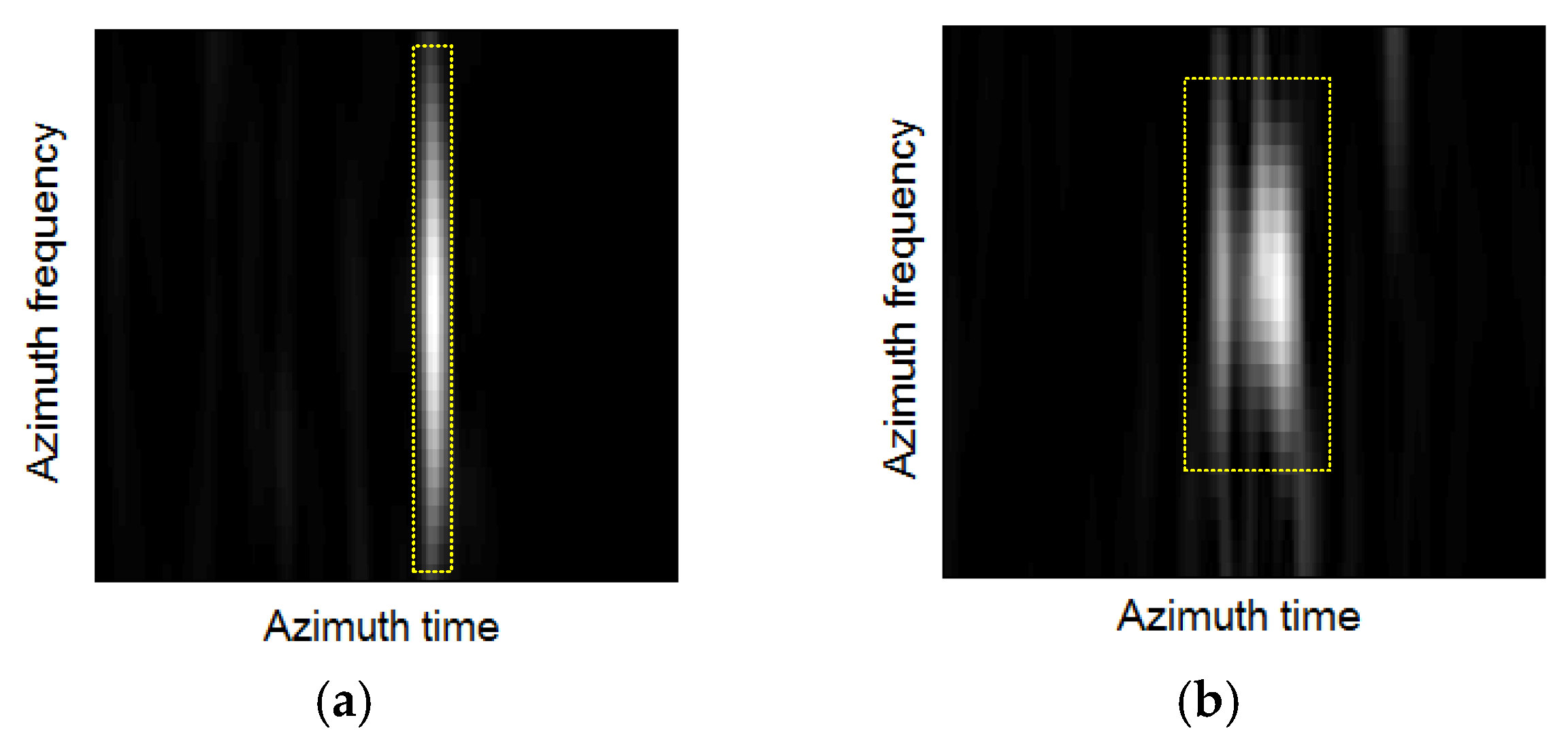
3.1. 2-D Cross-Coupling Spatial Variation Elimination
3.2. Range and Azimuth Spatial Variation Elimination
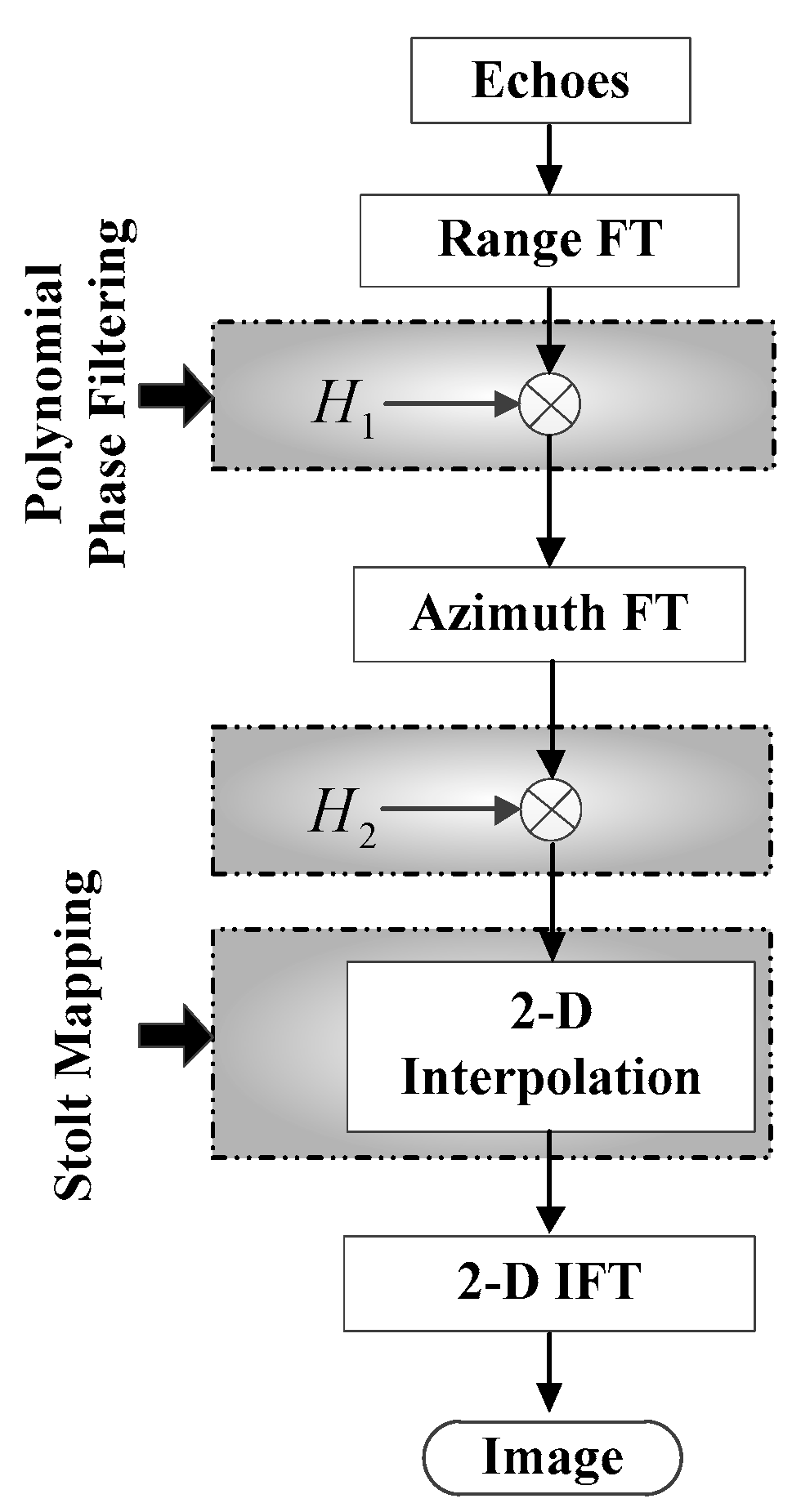
3.3. Flowchart of Imaging Algorithm
4. Implementation and Discussion
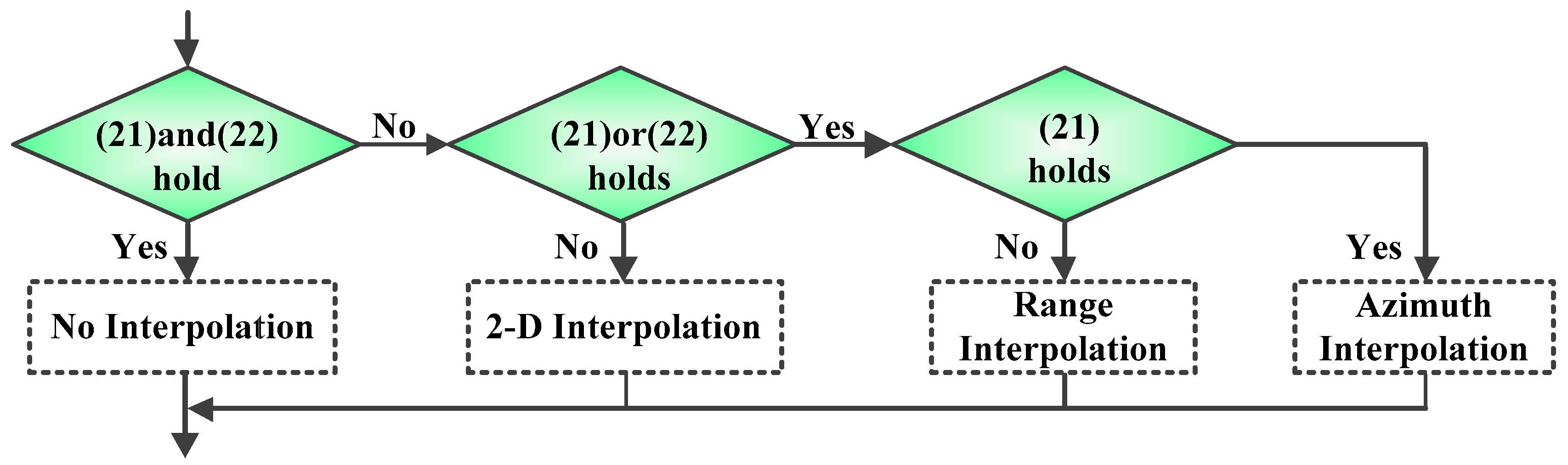
4.1. Simplified Processing
4.2. Constraint on Scene Extent
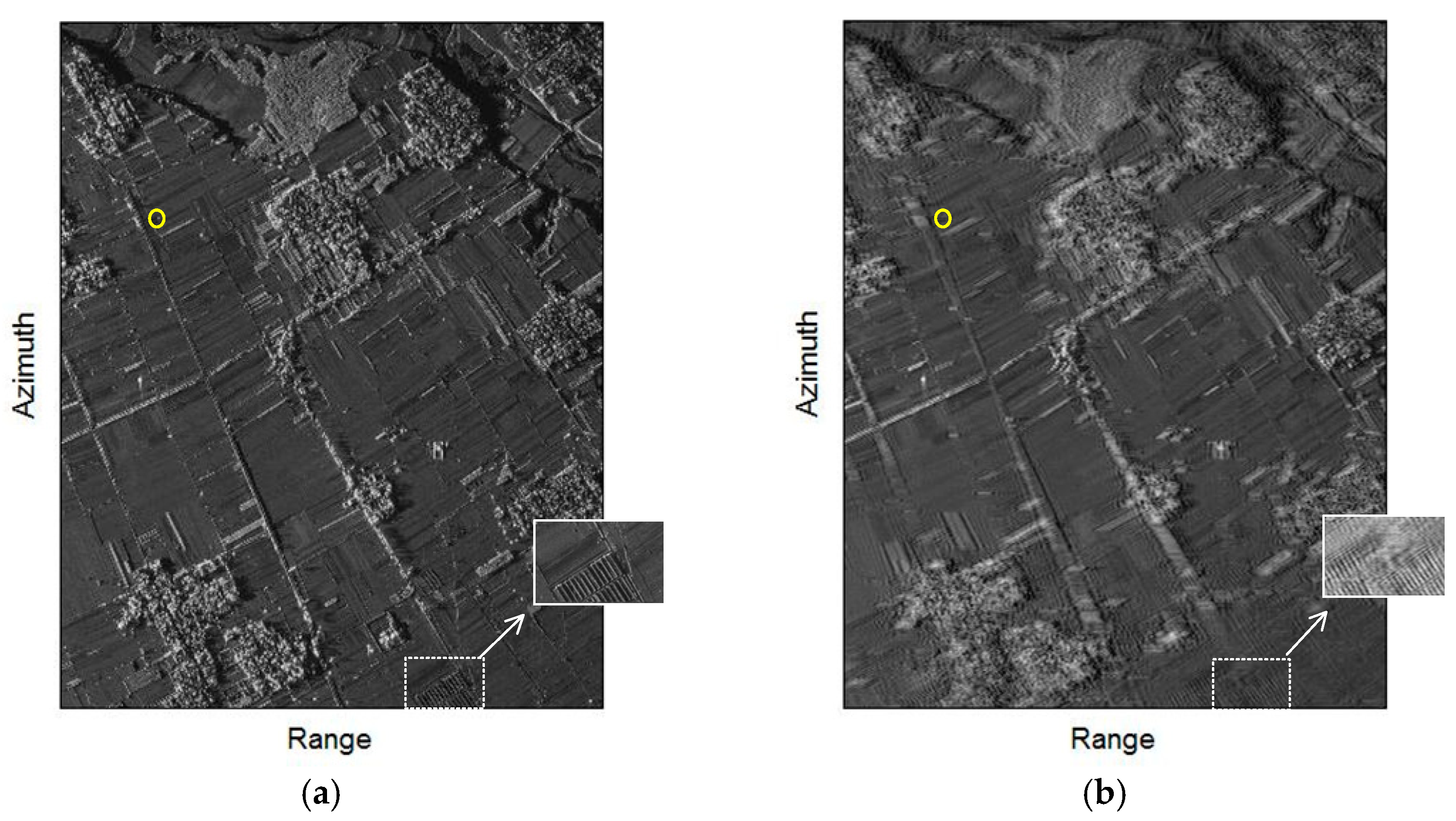
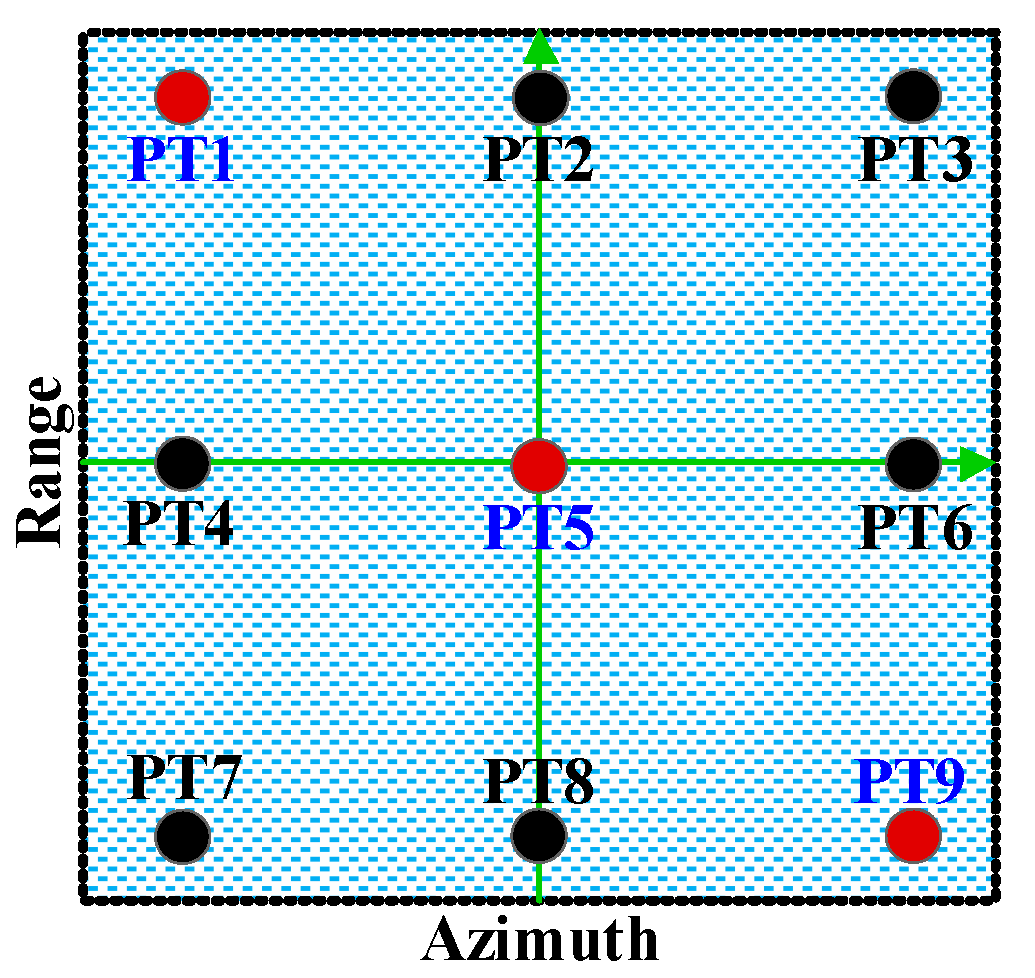
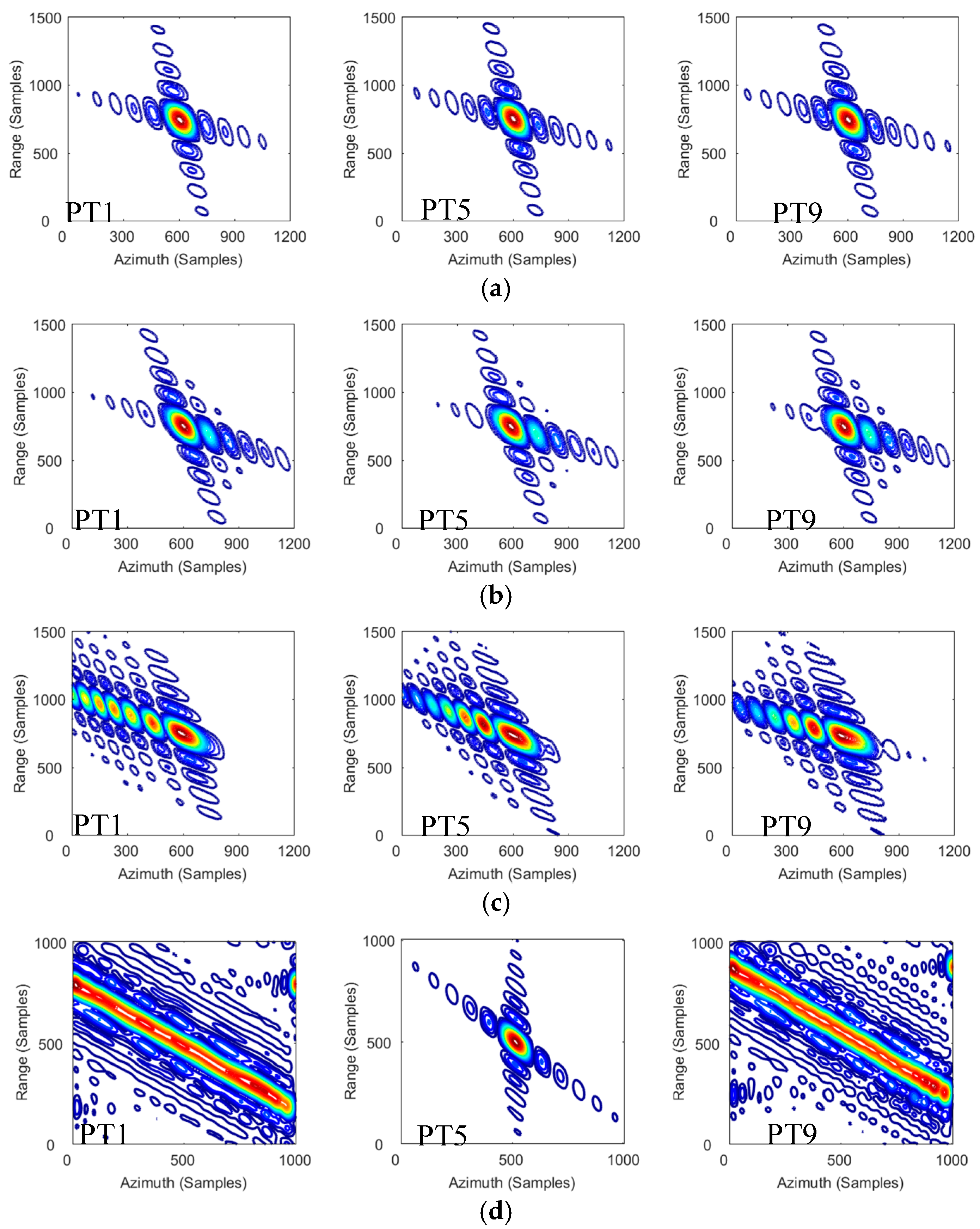
5. Simulation Results
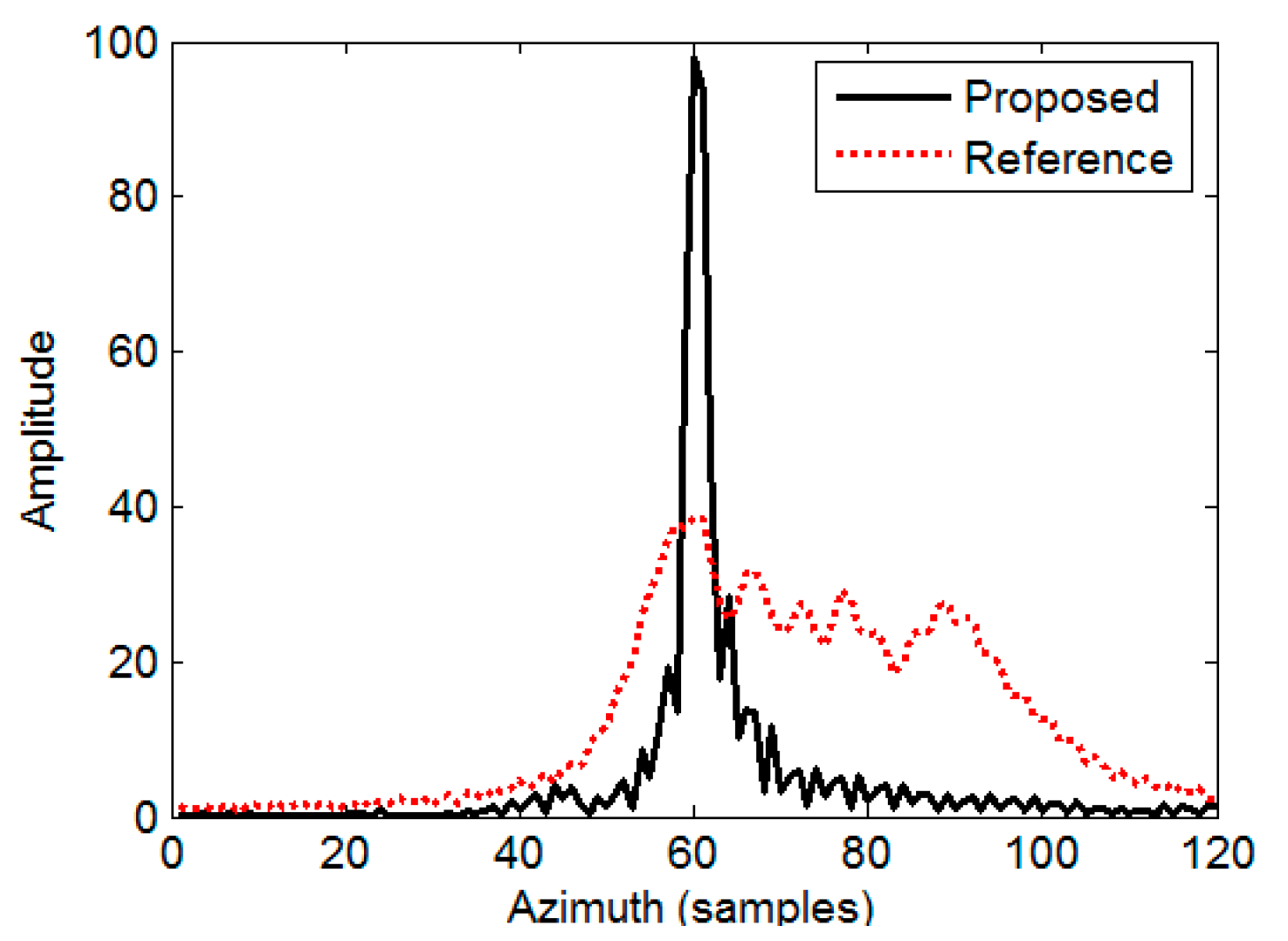
5.1. Experiment 1
5.2. Experiment 2
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.-C.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Bao, Z. A Unified Focusing Algorithm for Several Modes of SAR Based on FrFT. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3139–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, Y.; Hong, W.; Wu, Y. Autonomous Navigation Airborne Forward-Looking SAR High Precision Imaging with Combination of Pseudo-Polar Formatting and Overlapped Sub-Aperture Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6063–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroppiana, D.; Azar, R.; Calò, F.; Pepe, A.; Imperatore, P.; Boschetti, M.; Silva, J.M.N.; Brivio, P.A.; Lanari, R. Integration of Optical and SAR Data for Burned Area Mapping in Mediterranean Regions. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1320–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, W.G.; Goodman, R.S.; Majewski, R.M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ausherman, D.A.; Kozma, A.; Walker, J.L.; Jones, H.M.; Poggio, E.C. Developments in Radar Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1984, AES-20, 363–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.L.; Mims, J.H.; Sorrell, A. Effects of Navigation Errors in Maneuvering SAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1973, AES-9, 758–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.N. Depth of Field for SAR with Aircraft Acceleration. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1984, AES-20, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, S.R.J. Mapping Performance of Curved-path SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2224–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Xing, M.; Xiong, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. A Variable-decoupling- and MSR-based Imaging Algorithm for a SAR of Curvilinear Orbit. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldhuset, K. A New Fourth-order Processing Algorithm for Spaceborne SAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1998, 34, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldhuset, K. Ultra High Resolution Spaceborne SAR Processing with EETE4. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2011, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 2689–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, B.; Han, X.; Wang, R.; Song, H.; Deng, Y. A Novel High-order Range Model and Imaging Approach for High-resolution LEO SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3473–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Niu, M.; Yang, W. A High-order Imaging Algorithm for High-resolution Spaceborne SAR Based on a Modified Equivalent Squint Range Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.J.; Qiu, X.L.; Hu, D.H.; Han, B.; Ding, C.B. Medium-earth-orbit SAR Focusing using Range Doppler Algorithm with Integrated Two-step Azimuth Perturbation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, P.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Gu, Y.; Lin, C. Processing of Monostatic SAR Data with General Configurations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6529–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xing, M.; Xing, W.; Liang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Dai, B.; Hu, L.; Bao, Z. A Modified Equivalent Range Model and Wavenumber-domain Imaging Approach for High-resolution-high-squint SAR with Curved Trajectory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3721–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Jiang, X.; Wu, R.; Zhou, F.; Bao, Z. Motion Compensation for UAV SAR Based on Raw Radar Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2870–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M. A New Approach to Range-Doppler SAR Processing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K.; Runge, H.; Bamler, R.; Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Precision SAR Processing using Chirp Scaling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafforio, C.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. SAR Data Focusing using Seismic Migration Techniques. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1991, 27, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, P.; Liu, G.; Sun, G.-C. Acceleration Model Analyses and Imaging Algorithm for Highly Squinted Airborne Spotlight Mode SAR with Maneuvers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xing, M.; Liang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Huai, Y.; Zeng, L.; Sun, G.-C.; Bao, Z. A Frequency-domain Imaging Algorithm for Highly Squinted SAR Mounted on Maneuvering Platforms with Nonlinear Trajectory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4023–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, P.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L. Focusing Highly Squinted Data with Motion Errors Based on Modified Non-linear Chirp scaling. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2013, 7, 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, X.; Yang, J.M. A Three-Dimensional Localization Method for Multistatic SAR Based on Numerical Range-Doppler Algorithm and Entropy Minimization. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Lin, C.; Zhou, Y.; So, H.C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z. Processing of Long Integration Time Spaceborne SAR Data with Curved Orbit. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 888–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, K.Y.; Jin, M. Modeling and a Correlation Algorithm for Spaceborne SAR Signals. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1982, AES-18, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, L.; Xing, M. Coherent Auto-Calibration of APE and NsRCM under Fast Back-Projection Image Formation for Airborne SAR Imaging in Highly-Squint Angle. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, D.; O’Brien, J.; Jenkins, W. A Tomographic Formulation of Spotlight-mode Synthetic Aperture Radar. Proc. IEEE 1983, 71, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulander, L.M.H.; Hellsten, H.; Stenström, G. Synthetic Aperture Radar Processing using Fast Factorized Back-projection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 760–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.-L.; Qiao, Z.-J.; Xu, Z.-W. A Fast BP Algorithm with Wavenumber Spectrum Fusion for High-resolution Spotlight SAR Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokowartz, C.V.; Wahl, D.E.; Eichel, P.H.; Ghiglia, D.C.; Thompson, P.A. Spotlight-Mode Synthetic Aperture Radar: A Signal Processing Approach; Kluwer: Norwell, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, A.E.; Mann, W.R. Advanced Calculus, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Jankech, A. Using Vluster Multifunctions for Fecomposition Theorems. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2008, 46, 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, F.H.; Yeo, T.S. New Application of Nonlinear Chirp Scaling in SAR Data Processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Huang, X.; Jin, T.; Zhou, Z. Extended Nonlinear Chirp Scaling Algorithm for High-resolution Highly Squint SAR Data Focusing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3595–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xing, M.; Zhang, L.; Bao, Z. Robust Autofocusing Approach for Highly Squinted SAR Imagery using the Extended Wavenumber Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 5031–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sheng, J.; Xing, M.; Qiao, Z.; Xiong, T.; Bao, Z. Wavenumber-domain Autofocusing for Highly Squinted UAV SAR Imagery. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, Y.L.; Wong, F.; Cumming, I.G. A Two-dimensional Spectrum for Bistatic SAR Processing using Series Reversion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, Y.L.; Wong, F.; Cumming, I.G. Processing of Azimuth Invariant Bistatic SAR Data using the Range Doppler Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Long, T. An Improved CS Algorithm Based on the Curved Trajectory in Geosynchronous SAR. IEEE J. STARS 2012, 5, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Motion Parameter | Value | System Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radar Position at ACM | (0, 0, 10) km | Carrier Frequency | 17 GHz |
| Reference Position | (12.68, 26, 0) km | Pulse Bandwidth | 500 MHz |
| Velocity | (0, 170, −10) m/s | Sampling Frequency | 620 MHz |
| Acceleration | (1.2, 1.73, −1.4) m/s2 | Squint Angle | 60° |
| Third-order Parameter | (−0.09, 0.11, −0.14) m/s3 | Azimuth Resolution | 0.242 m |
| Fourth-order Parameter | (0.005, 0.007, 0.003) m/s4 | Scene Size (Range×Azimuth) | 1.6 × 1.6 km |
| Range | Azimuth | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Target | IRW (m) | PSLR (dB) | ISLR (dB) | IRW (m) | PSLR (dB) | ISLR (dB) |
| Proposed | PT1 | 0.266 | −13.21 | −9.99 | 0.247 | −13.17 | −9.92 |
| PT5 | 0.265 | −13.23 | −10.01 | 0.243 | −13.22 | −10.03 | |
| PT9 | 0.266 | −13.19 | −9.98 | 0.241 | −13.15 | −9.95 | |
| FDA | PT1 | 0.266 | −13.24 | −9.96 | 0.893 | −6.02 | −4.49 |
| PT5 | 0.266 | −13.25 | −10.09 | 0.242 | −13.23 | −10.07 | |
| PT9 | 0.267 | −13.17 | −10.01 | 1.302 | −4.74 | −3.56 | |
| Method | Target | IRW (m) | PSLR (dB) | ISLR (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed | PT1 | 0.367 | −13.16 | −9.87 |
| PT5 | 0.365 | −13.21 | −10.02 | |
| PT9 | 0.362 | −13.14 | −9.94 | |
| [17] | PT1 | 1.031 | −6.11 | −4.56 |
| PT5 | 0.364 | −13.24 | −10.06 | |
| PT9 | 1.135 | −5.78 | −4.12 | |
| BPA | PT1 | 0.365 | −13.24 | −10.04 |
| PT5 | 0.364 | −13.27 | −10.08 | |
| PT9 | 0.361 | −13.25 | −10.05 |
| Motion Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Velocity | (0, 110, −10) m/s |
| Acceleration | (1.21, 1.43, −0.74) m/s2 |
| 3rd-order Paramater | (−0.1, 0.2, 0.2) m/s3 |
| 4th-order Paramater | (0.007, −0.015, 0.004) m/s4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; So, H.C. Focusing High-Resolution Highly-Squinted Airborne SAR Data with Maneuvers. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060862
Tang S, Zhang L, So HC. Focusing High-Resolution Highly-Squinted Airborne SAR Data with Maneuvers. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(6):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060862
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Shiyang, Linrang Zhang, and Hing Cheung So. 2018. "Focusing High-Resolution Highly-Squinted Airborne SAR Data with Maneuvers" Remote Sensing 10, no. 6: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060862
APA StyleTang, S., Zhang, L., & So, H. C. (2018). Focusing High-Resolution Highly-Squinted Airborne SAR Data with Maneuvers. Remote Sensing, 10(6), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060862





