Real-Time Phase Bias Estimation for BeiDou Satellites Based on Consideration of Orbit Errors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Effects of Orbit Error on FCB Estimation
2.2. FCB and Orbit Error Estimation Algorithm
- (a)
- Add a loose zero-value constraint to all the orbit error and FCB parameters to eliminate the singular values in Equation (7). The variance of this constraint is set at 10 m in this study.
- (b)
- Generate independent baselines among all the reference stations. For each baseline, assuming the initial satellite orbit error to be zero, form double-differenced (DD) NL ambiguities and then attempt to fix these DD ambiguities by rounding.
- (c)
- Solve Equation (7) to obtain the updated satellite orbit error. Take this updated orbit error into account and then repeat procedure (b) until no more of the DD ambiguities can be fixed.
- (d)
- Now that the satellite orbit error has been recovered, the undifferenced NL ambiguities can be fixed by following the procedures that were proposed by Laurichesse et al. [8]. The satellite orbit error and the satellite and receiver FCBs can then be updated using the LSQ to obtain the final estimates.
3. Data and Processing Strategy
4. Results
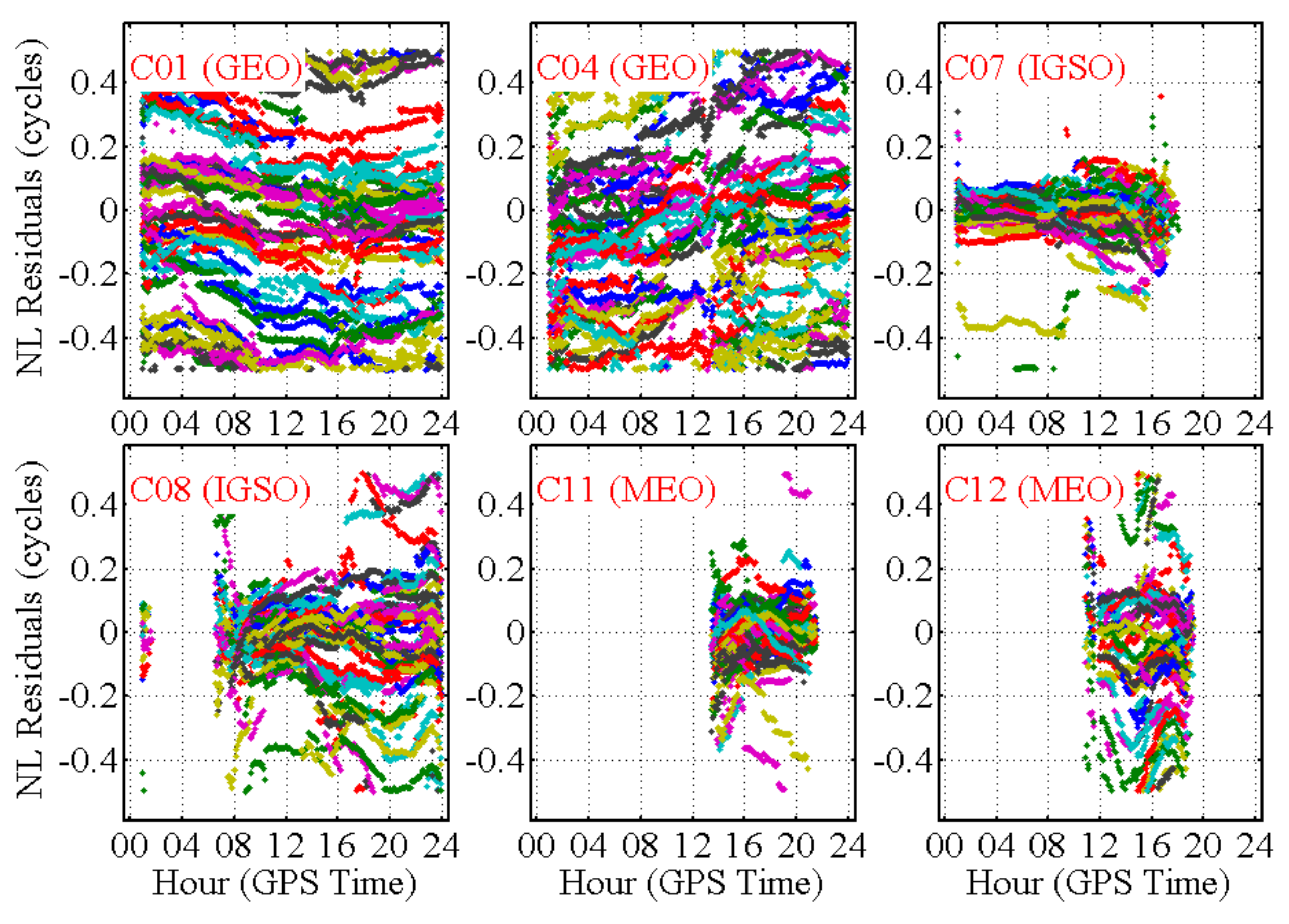
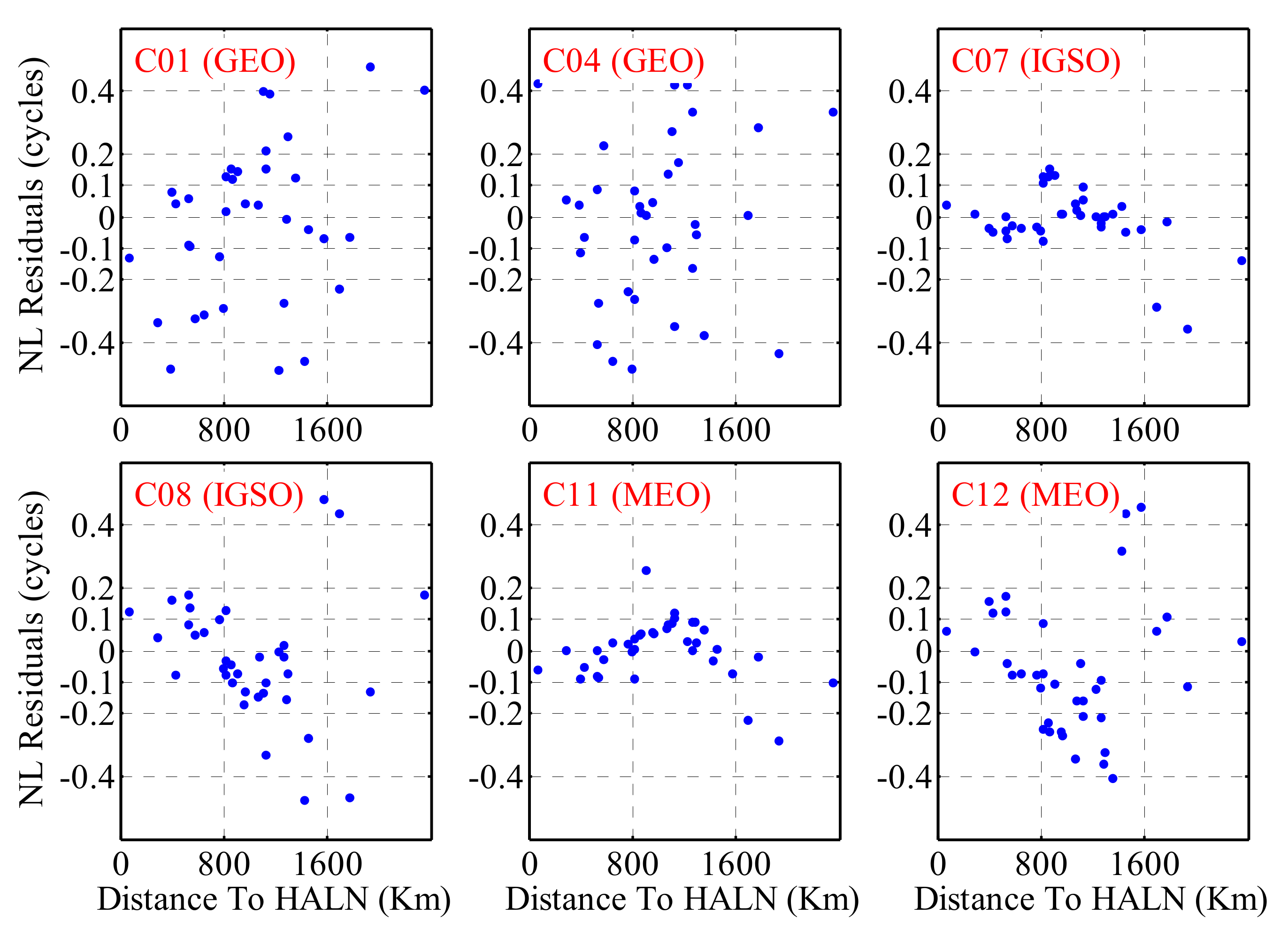
4.1. Effects of Orbit Errors on FCB Estimation
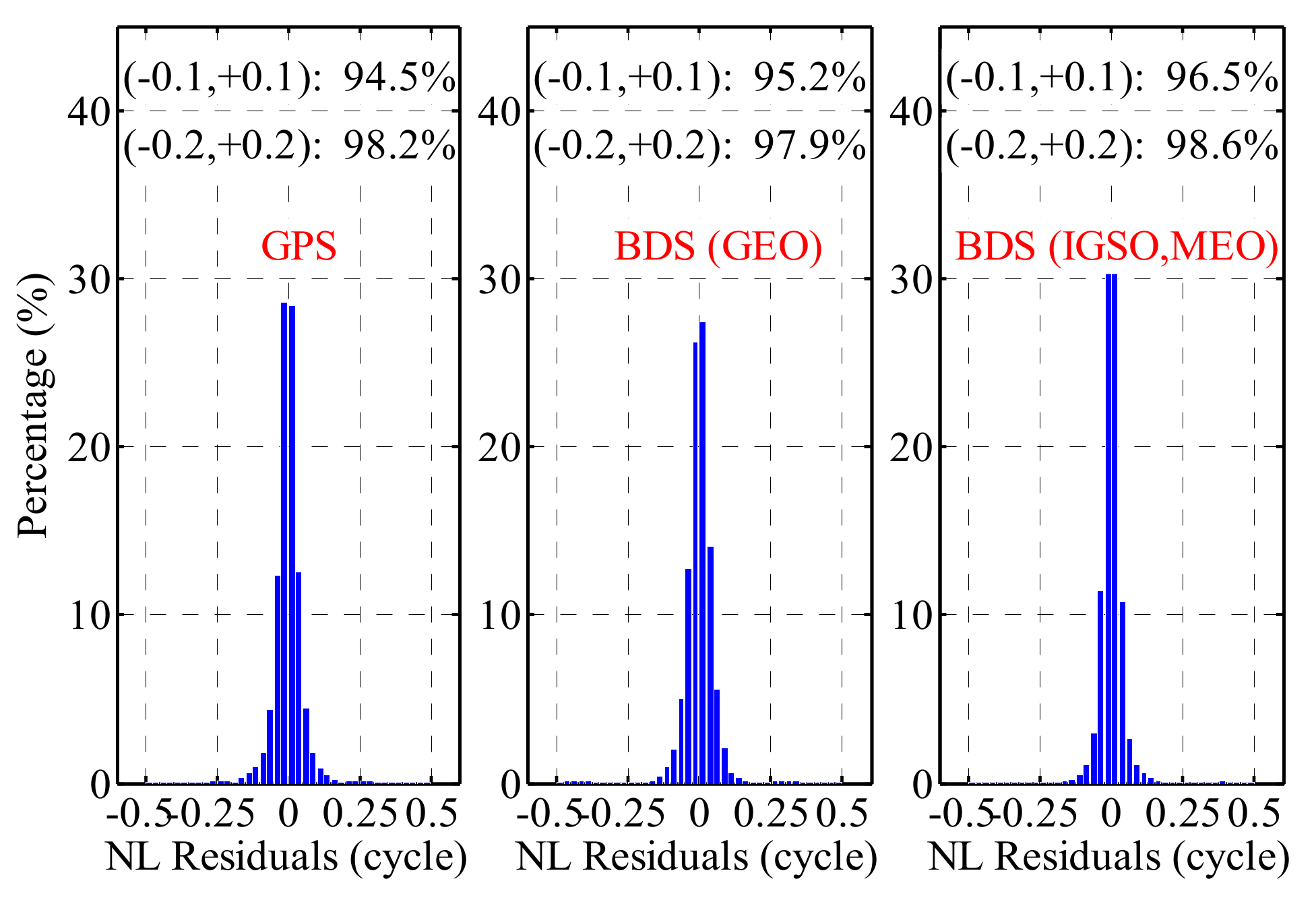
4.2. NL FCB Estimation When Considering Orbit Errors
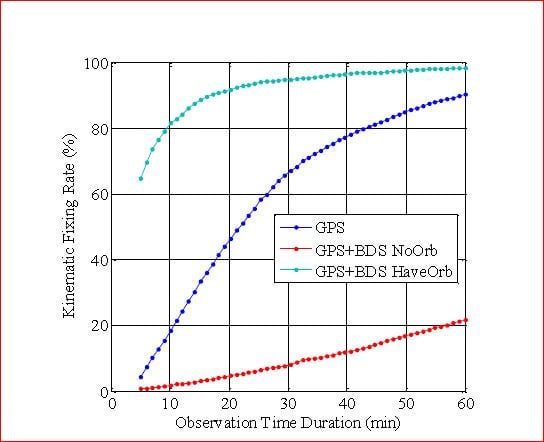
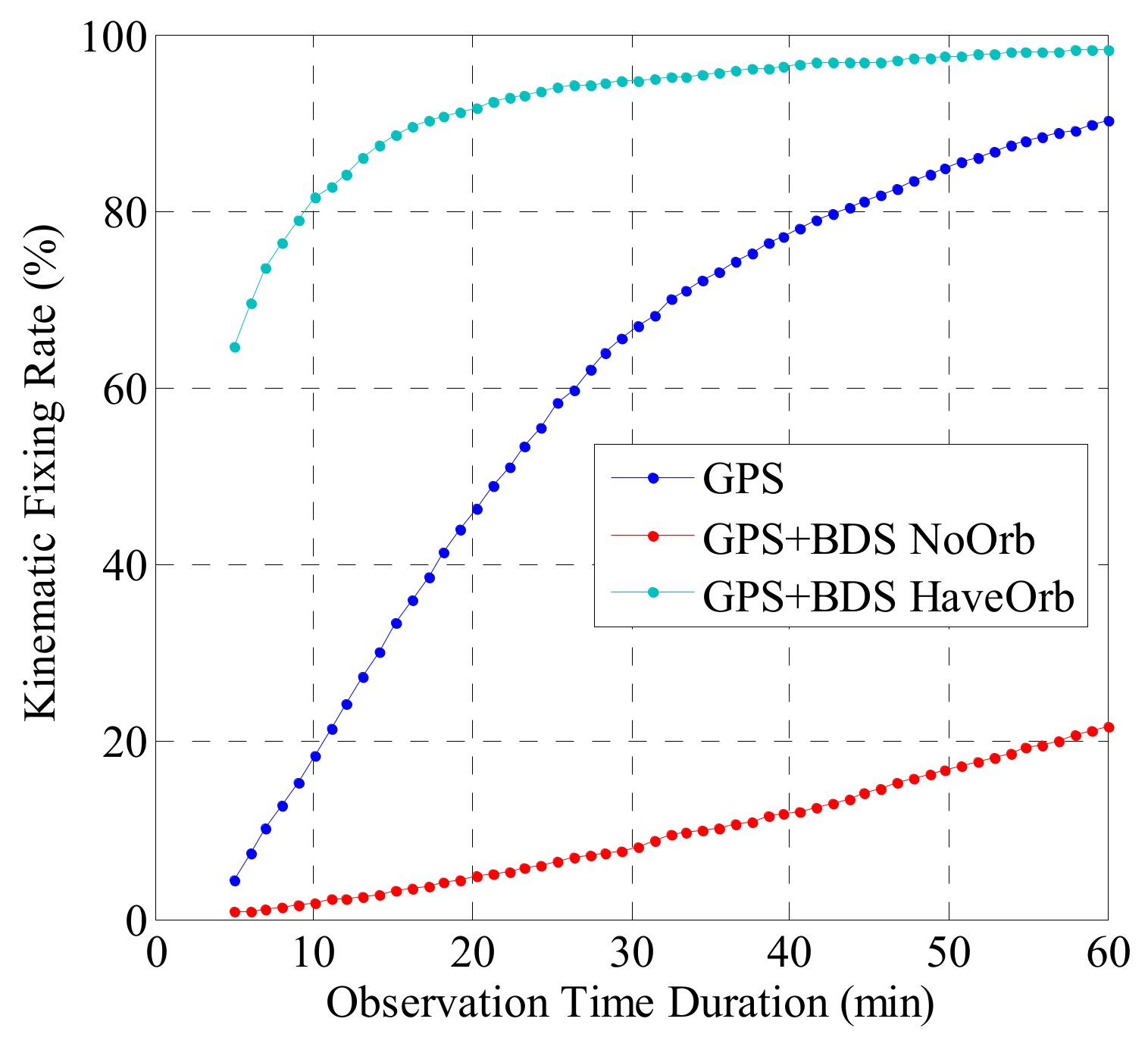
4.3. PPP-IAR Performance Analysis
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zumberge, J.; Heflin, M.; Jefferson, D.; Watkins, M.; Webb, F. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophy. Res. 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisnath, S.; Gao, Y. Current state of precise point positioning and future prospects and limitations. In Observing our Changing Earth; IAG Symposium Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 133, pp. 615–624. [Google Scholar]
- Dow, J.; Neilan, R.; Rizos, C. The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier phase ambiguities in precise point positioning(PPP) with daily observations. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J. Rapid Integer Ambiguity Resolution in GPS Precise Point Positioning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 2010; p. 153. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, P.; Lahaye, F.; Héroux, P.; Bisnath, S. Precise point positioning with AR using the decoupled clock model. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS-2008, Savannah, GA, USA, 16–19 September 2008; pp. 1315–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Laurichesse, D.; Mercier, F.; Berthias, J.P.; Broca, P.; Cerri, L. Integer ambiguity resolution on undifferenced GPS phase measurements and its application to PPP and satellite precise orbit determination. Navigation 2009, 56, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor, M.J.; Nerem, R.S. GPS carrier phase AR using satellite-satellite single difference. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS-1999, Nashville, TN, USA, 14–17 September 1999; pp. 1569–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Teferle, F.N.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A.H. Towards PPP-RTK: Ambiguity resolution in real-time precise point positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokinen, A.; Feng, S.; Schuster, W.; Ochieng, W.; Hide, C.; Moore, T.; Hill, C. GLONASS aided GPS ambiguity fixed precise point positioning. J. Navig. 2013, 66, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X. Integrating GPS and GLONASS to accelerate convergence and initialization times of precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Shi, C. Rapid initialization of real-time PPP by resolving undifferenced GPS and GLONASS ambiguities simultaneously. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Gu, S.; Li, Q. Rapid PPP Ambiguity Resolution Using GPS+GLONASS Observations. J. Geod. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegedor, J.; Liu, X.; Jong, K.; Goode, M.; Øvstedal, O.; Vigen, E. Estimation of Galileo Uncalibrated Hardware Delays for Ambiguity-Fixed Precise Point Positioning. Navigation 2016, 63, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Gao, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhu, J. Precise point positioning with quad-constellations: GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS and Galileo. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Chen, D. Integrating GPS and BDS to shorten the initialization time for ambiguity-fixed PPP. GPS Solut. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhao, Q.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Hu, Z.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Niu, X.; Liu, J. Precise orbit determination of BeiDou Satellites with precise positioning. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Jia, X.; Song, S.; Wickert, L. What is achievable with the current COMPASS Constellations? In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2012, Institute of Navigation. Nashville, TN, USA, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. Orbit and clock analysis of compass GEO and IGSO satellites. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, M.; Qu, L.; Hu, Z.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Initial results of precise orbit and clock determination for COMPASS navigation satellite system. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ge, M.; Wang, J.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Experimental study on the precise orbit determination of the BeiDou navigation satellite system. Sensors 2013, 13, 2911–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, B.; Yao, X.; Zheng, F. Precise orbit determination of BeiDou constellation: Method comparison. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierski, K.; Sośnica, K.; Hadas, T. Quality assessment of multi-gnss orbits and clocks for real-time precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Lutz, S.; Bock, H.; Orliac, E.; Prange, L.; Thaller, D.; Mervart, L.; Jäggi, A.; Beutler, G.; et al. CODE Analysis Center Technical Report 2014; International GNSS Service: Technical Report 2014; Dach, R., Jean, Y., Eds.; IGS Central Bureau: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015; p. 2134. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Improving multi-GNSS ultra-rapid orbit determination for real-time precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Broadcast versus precise ephemerides: A multi-gnss perspective. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, L.; Beer, S. BeiDou satellite-induced code pseudorange variations: Diagnosis and therapy. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Gong, X.; Gu, S.; Zheng, F.; Feng, Y. Assessment of code bias variations of bds triple-frequency signals and their impacts on ambiguity resolution for long baselines. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Hajj, G.; Bertiger, W.; Lichten, S. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr. Geod. 1993, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A.; Teferle, F. Integer ambiguity resolution in precise point positioning: Method comparison. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Gao, Y. A comparison of three PPP integer ambiguity resolution methods. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, R. The synergism of GPS code and carrier measurements. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Satellite Doppler Positioning at Physical Sciences Laboratory of New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM, USA, 8–12 February 1982; Volume 2, pp. 1213–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Melbourne, W.G. The case for ranging in GPS-based geodetic systems. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Wübbena, G. Software developments for geodetic positioning with GPS using TI-4100 code and carrier measurements. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Song, W.; Li, Q. Estimating the orbit error of BeiDou GEO satellites to improve the performance of multi-GNSS PPP ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B.; Al, E. IERS Conventions; IERS Technical Note; IERS Central Bureau: Frankfurt am Main, Germany; 2010; Volume 36, pp. 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global mapping function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; de Jong, K.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Guo, J. Multipath analysis of code measurements for BeiDou geostationary satellites. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ge, M. PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2003, 8, 603–609. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, W.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Shi, C.; Yao, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, M.; Wu, J. Improved method to estimate undifferenced satellite fractional cycle biases using network observations to support PPP ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F. The multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS service (IGS)—Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, T.; Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Kaplon, J.; Paziewski, J.; Wielgosz, P.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Kazmierski, K.; Sosnica, K.; Kwasniak, D.; et al. Impact and implementation of higher-order ionospheric effects on precise gnss applications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 9420–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| GEO | IGSO | MEO | GPS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Along | 0.690 | 0.160 | 0.150 | 0.032 |
| Cross | 0.170 | 0.085 | 0.042 | 0.019 |
| Radial | 0.101 | 0.065 | 0.035 | 0.010 |
| 3D Error (m) | Scale Factor | NL FCB (m) | NL FCB (Cycle) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEO | 0.718 | 0.0835 | 0.0599 | 0.599 |
| IGSO | 0.193 | 0.0835 | 0.0161 | 0.161 |
| MEO | 0.160 | 0.1390 | 0.0222 | 0.222 |
| GPS | 0.039 | 0.1477 | 0.0057 | 0.057 |
| Observation or Parameter | Model | Constraint |
|---|---|---|
| Observations | Undifferenced ionosphere-free code and carrier-phase combination; 30-s interval; 7° elevation cutoff | 1 cm for carrier-phase and 1 m for pseudorange |
| Weight | Assign 100 times more weight for GPS in FCB estimation; equal weight for each system in PPP-IAR; elevation-dependent weighting | E > 30°, 1; else sin(E) |
| Phase center offset and variation of Satellite antenna | igs08_1899.atx for GPS and BDS | |
| Phase center offset and variation of Receiver antenna | igs08_1899.atx for GPS and use GPS values for BDS | |
| Phase rotation correction | Applied | |
| Site displacement | Solid Earth, pole tide, ocean loading [38] | |
| Troposphere | Saastamoinen model for wet and dry hydrostatic delay with global mapping function [39] | Initial model, 10 cm; random-walk process noise 2 cm |
| Satellite orbit | International GNSS Monitoring & Assessment System (iGMAS) ultra rapid products for GPS and BDS (www.igmas.org) | |
| Receiver clock offset | Estimated for each system | White noise process |
| Relativistic effects | Applied | |
| WL and NL FCB | 1-day update interval for WL and 5 min for NL; 1200-s initialization time for NL FCB | |
| Orbit error | 15-min update interval with a 1200-s initialization time | |
| Receiver Coordinate | Fixed in satellite clock and FCB estimation while estimated in PPP | |
| Integer Ambiguity | Estimated as constant | Fixed for all GPS and BDS satellites |
| Time (min) | GPS Only (%) | GPS + BDS | GPS + BDS |
|---|---|---|---|
| NoOrb (%) | HaveOrb (%) | ||
| 05 | 4.27 | 0.78 | 64.56 |
| 10 | 18.33 | 1.78 | 81.53 |
| 20 | 46.25 | 4.77 | 91.73 |
| Time (min) | GPS Only (%) | GPS + BDS | GPS + BDS |
|---|---|---|---|
| NoOrb (%) | HaveOrb (%) | ||
| 05 | 10.33 | 0.91 | 68.17 |
| 10 | 42.44 | 2.49 | 84.01 |
| 20 | 77.29 | 6.05 | 93.48 |
| North | East | Up | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | 0.85 | 0.69 | 2.94 |
| GPS + BDS HaveOrb | 0.77 | 0.67 | 2.88 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ye, S.; Song, W. Real-Time Phase Bias Estimation for BeiDou Satellites Based on Consideration of Orbit Errors. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071009
Liu Y, Zhu J, Ye S, Song W. Real-Time Phase Bias Estimation for BeiDou Satellites Based on Consideration of Orbit Errors. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(7):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanyan, Jiasong Zhu, Shirong Ye, and Weiwei Song. 2018. "Real-Time Phase Bias Estimation for BeiDou Satellites Based on Consideration of Orbit Errors" Remote Sensing 10, no. 7: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071009
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhu, J., Ye, S., & Song, W. (2018). Real-Time Phase Bias Estimation for BeiDou Satellites Based on Consideration of Orbit Errors. Remote Sensing, 10(7), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071009