Doppler Frequency Estimation of Point Targets in the Single-Channel SAR Image by Linear Least Squares
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Linear Least Squares for Doppler Frequency Estimation
2.2. Azimuth Subsamples
3. Application Results
3.1. SAR SLC Data Used for Evaluation and Validation
3.2. On-Land Application Results
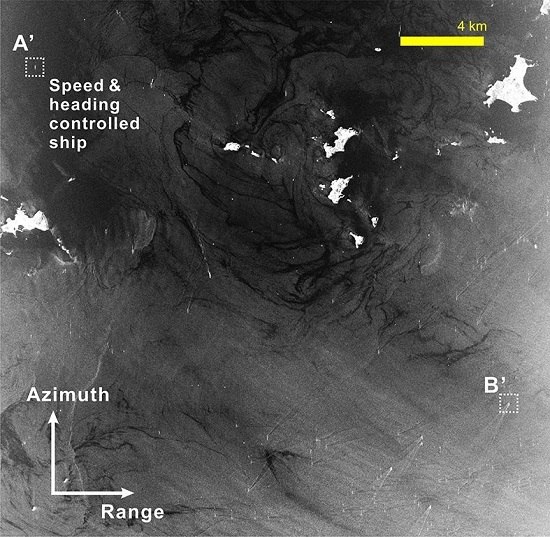
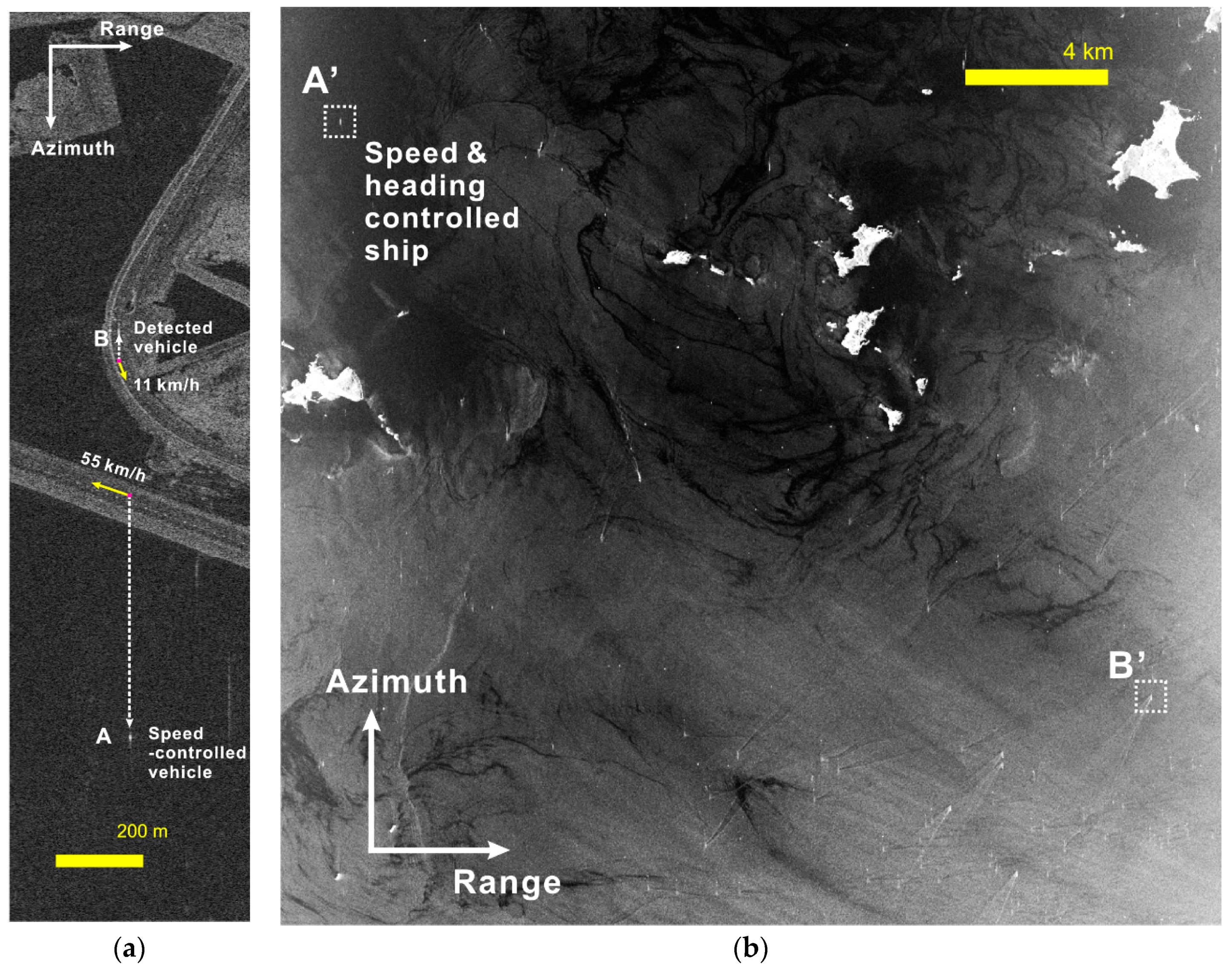
3.3. Application Results in Coastal Areas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Interferometric radar measurement of ocean surface currents. Nature 1987, 328, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.R.; Jensen, J.R. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry applied to ship-generated waves in the 1989 Loch Linnhe experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 981, 10259–10269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, C.; Sikaneta, I.; Gierull, C.H.; Chiu, S.; Beaudoin, A.; Campbell, J.; Beaudoin, J.; Gong, S.; Knight, T. An airborne SAR experiment to support RADARSAT-2 ground moving target indication (GMTI). Can. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 28, 749–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breit, H.; Eineder, M.; Holzner, J.; Runge, H.; Bamler, R. Traffic monitoring using SRTM along-track interferometry. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003: 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 1187–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Gierull, C.H. Ground moving target parameter estimation for two-channel SAR. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2006, 153, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchandt, S.; Runge, H.; Breit, H.; Steinbrecher, U.; Kotenkov, A.; Balss, U. Automatic extraction of traffic flows using TerraSAR-X along-track interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.; Dragosevi, M.V. Moving target indication via RADARSAT-2 multichannel synthetic aperture radar processing. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2010, 2010, 740130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K. Synthetic aperture imaging radar and moving targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1971, 7, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, F.R.; Labitt, M.; Staudaher, F.M. Development of airborne moving target radar for long range surveillance. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1991, 27, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnitkin, H. Joint stars phased array radar antenna. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 1994, 9, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.; Livingstone, C.E. A comparison of displaced phase centre antenna and along-track interferometry techniques for RADARSAT-2 ground moving target indication. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 31, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti-Maori, D.; Sikaneta, I. Generalization of DPCA processing for multichannel SAR/GMTI radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, J.H.G. Space-time processing for multichannel synthetic aperture radar. Electron. Commun. Eng. J. 1999, 11, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, W.L. A STAP overview. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2004, 19, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti-Moari, D.; Gierull, C.H.; Ender, J.H.G. Experimental verification of SAR-GMTI improvement through antenna switching. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.D.; Hawes, C.M.; Nord, M.E. Target motion ambiguities in single-aperture synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, P.R.; Topokov, J.V.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Sletten, M.A.; Jansen, R.W. Estimating surface water speeds with a single-phase center SAR versus an along-track interferometric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3638–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Andrews, H.C. Target motion induced radar imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1980, 16, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, S. Detection and imaging of moving objects with synthetic aperture radar—Part I: Optimal detection and parameter estimation theory. IEE Proc. F Radar Signal Process. 1992, 139, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petterson, M.I.; Sjogren, T.K.; Vu, V.T. Performance of moving target parameter estimation using SAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Kim, J.H.; Won, J.-S. Fast and efficient correction of ground moving targets in a synthetic aperture radar, single-look complex image. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statman, J.I.; Rodemich, E.R. Parameter estimation based on Doppler frequency shifts. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1987, 23, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Currie, A. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images of moving targets. GEC J. Res. 1987, 5, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Barbarossa, S.; Farina, A. Space-time-frequency processing of synthetic aperture radar signals. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, P.R.; Jansen, R.W.; Luc, K.; Ainsworth, T.L. Motion analysis in SAR images of unfocused objects using time-frequency methods. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparr, T. Moving target motion estimation and focusing in SAR images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 9–12 May 2005; pp. 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-K.; Held, D.N.; Curlander, J.C.; Wu, C. Doppler parameter estimation for spaceborne synthetic-aperture radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 23, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, S.N. Estimating the Doppler centroid of SAR data. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1989, 25, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bamler, R. Doppler frequency estimation and the Cramer-Rao bound. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1991, 29, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.; Cumming, I.G. A combined SAR Doppler centroid estimation scheme based upon signal phase. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G. A spatially selective approach to Doppler estimation for frame-based satellite SAR processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Kam, P.Y. An improved Doppler parameter estimator for synthetic aperture radar. PIERS Online 2008, 4, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y. Improved Doppler parameter estimation of squint SAR based on slope detection. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 1417–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.A.C.; Dias, J.M.B. Velocity estimation of moving targets using a single SAR sensor. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Won, J.-S. An efficient method of Doppler parameter estimation in the time–frequency domain for a moving object from TerraSAR-X data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4771–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renga, A.; Moccia, A. Use of Doppler parameters for ship velocity computation in SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 3995–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Paulraj, A.; Kailath, T. ESPRIT—A subspace rotation approach to estimation of parameters of cisoids in noise. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1986, 34, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Kailath, T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Moses, R.L. Spectral Analysis of Signals, 1st ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-13-113956-8. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria, I.; Pantaleon, C.; Ibanez, J. A comparative study of high-accuracy frequency estimation methods. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2010, 14, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, G.; Gebert, N.; Moreira, A. Unambiguous SAR signal reconstruction from nonuniform displaced phase center sampling. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of 2 × 2 Matrices. Available online: http://www.math.harvard.edu /archive/21b_fall_04 /exhibits/2dmatrices/index.html (accessed on 23 May 2018).
- Graziano, M.D.; D’Errico, M.; Rufino, G. Wake component detection in X-Band SAR images for ship heading and velocity estimation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panico, P.; Graziano, M.D.; Renga, A. SAR-based vessel velocity estimation from partially imaged Kelvin pattern. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Linear Least Squares Algorithm Pseudocode |
|---|
| Input: Output: Initialize the accumulator to zero Define a total of (2N + 1) time symmetric ← FFT of for all do ← Multiply to ← IFFT of Estimate by ESPRIT method ← end for Compute ← diving by sum of squares , Equation (12) return |
| Parameter | TerraSAR-X | KOMPSAT-5 |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 3.1 cm | 3.1 cm |
| Polarization | HH | HH |
| PRF | 3815.5 Hz | 3787.9 Hz |
| Antenna velocity | 7686.5 m/s | 7664.5 m/s |
| Antenna size | 4.8 m | 4.5 m |
| Incidence angle | 39.25° | 33.55° |
| Altitude | 513.1 km | 557.5 km |
| Area | Target ID | Reference Range Velocity [km/h] | Range Velocity by Proposed Method [km/h] | Error [km/h] | Doppler Freq./RMSE Ratio | Range Velocity by ESPRIT [km/h] | Error [km/h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land | A | −49.6 | −51.4 ± 1.20 | 1.8 | 42.8 | −55.8 | 6.2 |
| B | 5.9 1 | 5.1 ± 0.91 | 0.9 | 5.6 | 12.3 | 6.4 | |
| Sea | A’ | −2.9 | −2.85 ± 0.15 | 0.05 | 19.2 | −4.4 | 1.5 |
| B’ | 18.1 1 | 18.3 ± 0.72 | 0.2 | 25.4 | 20.9 | 2.8 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Won, J.-S. Doppler Frequency Estimation of Point Targets in the Single-Channel SAR Image by Linear Least Squares. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071160
Won J-S. Doppler Frequency Estimation of Point Targets in the Single-Channel SAR Image by Linear Least Squares. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(7):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071160
Chicago/Turabian StyleWon, Joong-Sun. 2018. "Doppler Frequency Estimation of Point Targets in the Single-Channel SAR Image by Linear Least Squares" Remote Sensing 10, no. 7: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071160
APA StyleWon, J.-S. (2018). Doppler Frequency Estimation of Point Targets in the Single-Channel SAR Image by Linear Least Squares. Remote Sensing, 10(7), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071160