Intercomparison of MODIS AQUA and VIIRS I-Band Fires and Emissions in an Agricultural Landscape—Implications for Air Pollution Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Emissions Estimation Using Agricultural Census Data
2.3. VIIRS I-Band Fire Product
2.4. MODIS Active Fire Products
2.5. Fire Radiative Power Products and Emissions
2.6. GFED Emissions Product
2.7. Temporal Emissions Integrating MODIS and VIIRS
3. Results
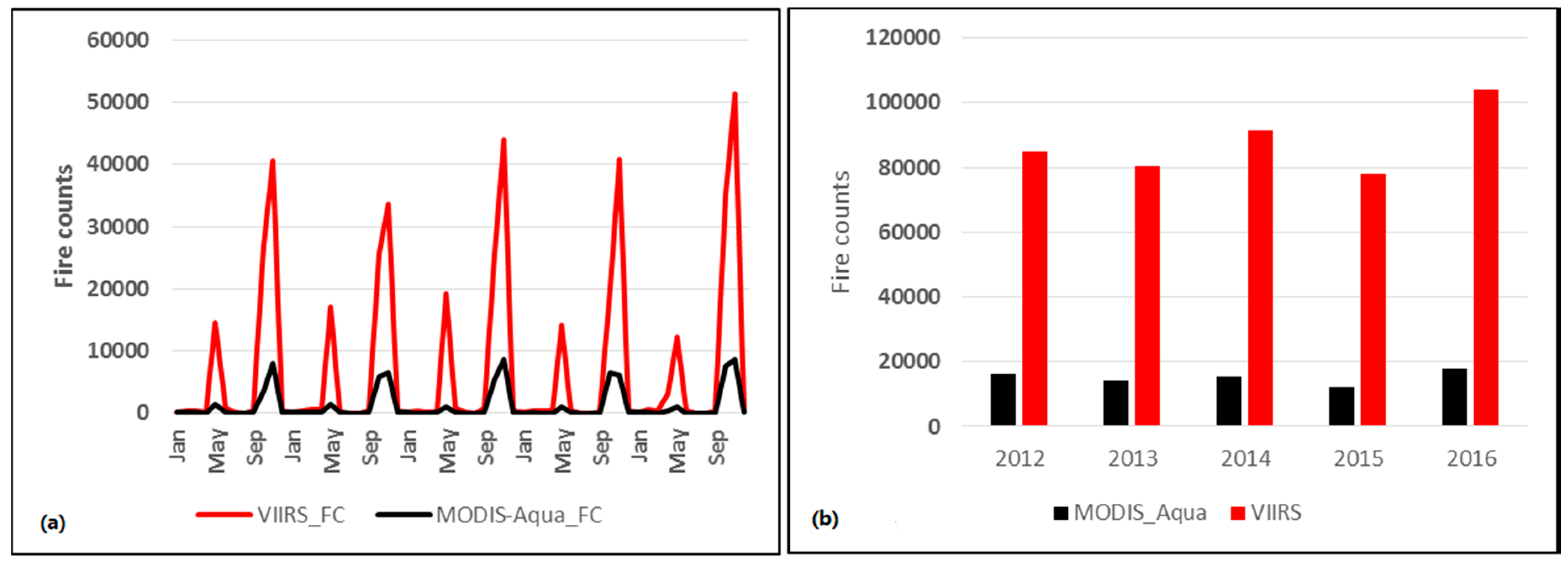
3.1. MODIS versus VIIRS Fire Counts
3.2. Agricultural Census Data Based Emissions
3.3. GFED Emissions
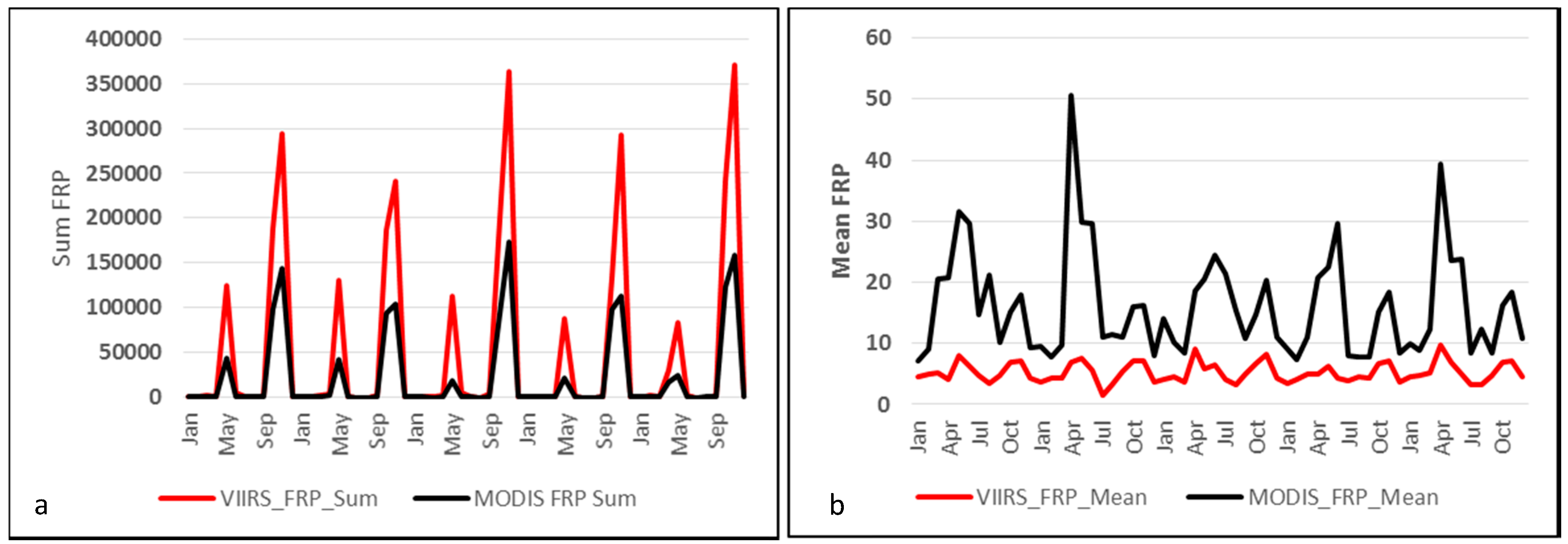
3.4. FRP-Based Emissions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreae, M.O.; Merlet, P. Emission of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Sidhu, H.S. Management of cereal crop residues for sustainable rice-wheat production system in the Indo-Gangetic plains of India. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2014, 80, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badarinath, K.V.S.; Kharol, S.K.; Sharma, A.R.; Prasad, V.K. Analysis of aerosol and carbon monoxide characteristics over Arabian Sea during crop residue burning period in the Indo-Gangetic Plains using multi-satellite remote sensing datasets. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2009, 71, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.K.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Anuradha, E.A. Biophysical and anthropogenic controls of forest fires in the Deccan Plateau. Indian J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 86, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.L. Biomass burning sources and their contributions to the local air quality in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itahashi, S.; Uno, I.; Irie, H.; Kurokawa, J.I.; Ohara, T. Impacts of biomass burning emissions on over tropospheric continental NO southeast 2 vertical Asia column density. In Land-Atmospheric Research Applications in South and Southeast Asia; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pochanart, P.; Akimoto, H.; Kajii, Y.; Sukasem, P. Carbon monoxide, regional-scale transport, and biomass burning in tropical continental Southeast Asia: Observations in rural Thailand. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.N.A.; Rafique, M.; Alaamer, A.S. Biomass fuel burning and its implications: Deforestation and greenhouse gases emissions in Pakistan. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2490–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.H.; Tsay, S.C.; Maring, H.B.; Yen, M.C.; Sheu, G.R.; Wang, S.H.; Chi, K.H.; Chuang, M.T.; Ou-Yang, C.F.; Fu, J.S.; et al. An overview of regional experiments on biomass burning aerosols and related pollutants in Southeast Asia: From BASE-ASIA and the Dongsha Experiment to 7-SEAS. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, P.V.; Reid, J.S.; Kotchenruther, R.A.; Ferek, R.J.; Weiss, R. Direct radiative forcing by smoke from biomass burning. Science 1997, 275, 1777–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Herman, J.R.; Tsay, S.C. Radiative impacts from biomass burning in the presence of clouds during boreal spring in southeast Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, Ö.; Kruså, M.; Zencak, Z.; Sheesley, R.J.; Granat, L.; Engström, E.; Praveen, P.S.; Rao, P.S.P.; Leck, C.; Rodhe, H. Brown clouds over South Asia: Biomass or fossil fuel combustion? Science 2009, 323, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Lin, N.H.; Chou, M.D.; Woo, J.H. Estimate of radiative forcing of Asian biomass-burning aerosols during the period of TRACE-P. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Lin, N.-H.; Chantara, S.; Wang, S.-H.; Khamkaew, C.; Prapamontol, T.; Janjai, S. Radiative response of biomass-burning aerosols over an urban atmosphere in northern peninsular Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 892–911. [Google Scholar]
- Kharol, S.K.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Sharma, A.R.; Mahalakshmi, D.V.; Singh, D.; Prasad, V.K. Black carbon aerosol variations over Patiala city, Punjab, India—A study during agriculture crop residue burning period using ground measurements and satellite data. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 84, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; Zheng, F. Investigation on emission factors of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from crop residue burning. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumaty, K.C.; Rodda, S.R.; Singhal, J.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Jha, C.S.; Parsi, G.D.; Dadhwal, V.K. Spatio-temporal characterization of agriculture residue burning in Punjab and Haryana, India, using MODIS and Suomi NPP VIIRS data. Curr. Sci. 2015, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundeep, S.; Barnes, P.J. Is exposure to biomass smoke the biggest risk factor for COPD globally? Chest 2010, 138, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-H.; Jahan, S.A.; Kabir, E. A review of diseases associated with household air pollution due to the use of biomass fuels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badarinath, K.V.S.; Chand, T.K.; Prasad, V.K. Agriculture crop residue burning in the Indo-Gangetic Plains–a study using IRS-P6 AWiFS satellite data. Curr. Sci. 2006, 91, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Ellicott, E.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Vermote, E. MODIS derived fire characteristics and aerosol optical depth variations during the agricultural residue burning season, north India. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.N.; Pattnaik, A.; Dey, S. Aerosol indirect effect over Indo-Gangetic plain. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7037–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, S.; Sharma, C.; Singh, D.P.; Dixit, C.K.; Singh, N.; Sharma, P.; Singh, K.; Bhatt, S.; Ghude, S.; Gupta, V.; et al. A study for development of emission factors for trace gases and carbonaceous particulate species from in situ burning of wheat straw in agricultural fields in India. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9173–9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Bhatia, A.; Pathak, H. Emission of air pollutants from crop residue burning in India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyendra, T.; Singh, R.N.; Shaishav, S. Emissions from crop/biomass residue burning risk to atmospheric quality. Int. Res. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 1, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Granier, C.; Bessagnet, B.; Bond, T.; D’Angiola, A.; van Der Gon, H.D.; Frost, G.J.; Heil, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Kinne, S.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Evolution of anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of air pollutants at global and regional scales during the 1980–2010 period. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J.W.; Heil, A.; Andreae, M.O.; Benedetti, A.; Chubarova, N.; Jones, L.; Morcrette, J.J.; Razinger, M.; Schultz, M.G.; Suttie, M.; et al. Biomass burning emissions estimated with a global fire assimilation system based on observed fire radiative power. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 527–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Zhang, Y.H. Boreal forest fires burn less intensely in Russia than in North America. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Giglio, L.; Wooster, M.J.; Remer, L.A. Global characterization of biomass-burning patterns using satellite measurements of fire radiative energy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2950–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Kaufman, Y.J. A method to derive smoke emission rates from MODIS fire radiative energy measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2636–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, B.; Wooster, M.J. A new top-down approach for directly estimating biomass burning emissions and fuel consumption rates and totals from geostationary satellite fire radiative power (FRP). Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Csiszar, I.; Ellicott, E.; Giglio, L.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Vermote, E.; Justice, C. Hotspot analysis of vegetation fires and intensity in the Indian region. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Zhukov, B.; Oertel, D. Fire radiative energy for quantitative study of biomass burning: Derivation from the BIRD experimental satellite and comparison to MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Descloitres, J.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y. An enhanced contextual fire detection algorithm for MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Roberts, G.; Perry, G.L.W.; Kaufman, Y.J. Retrieval of biomass combustion rates and totals from fire radiative power observations: FRP derivation and calibration relationships between biomass consumption and fire radiative energy release. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Collatz, G.J.; Kasibhatla, P. Global estimation of burned area using MODIS active fire observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 957–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.; Oliva, P.; Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.A. The new VIIRS 375 m active fire detection data product: Algorithm description and initial assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; Collatz, G.J.; Mu, M.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Morton, D.C.; DeFries, R.S.; Jin, Y.V.; van Leeuwen, T.T. Global fire emissions and the contribution of deforestation, savanna, forest, agricultural, and peat fires (1997–2009). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11707–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Boschetti, L.; Justice, C.O.; Ju, J. The collection 5 MODIS burned area product—Global evaluation by comparison with the MODIS active fire product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3690–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Loboda, T.; Roy, D.P.; Quayle, B.; Justice, C.O. An active-fire based burned area mapping algorithm for the MODIS sensor. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Chen, X. Long-term trends and spatial patterns of satellite-retrieved PM 2.5 concentrations in South and Southeast Asia from 1999 to 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polivka, T.; Wang, J.; Ellison, L.; Hyer, E.; Ichoku, C. Improving nocturnal fire detection with the VIIRS day-night band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5503–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ichoku, C.; Ellison, L.; Zeng, J. Mitigating satellite-based fire sampling limitations in deriving biomass burning emission rates: Application to WRF-Chem model over the Northern Sub-saharan African Region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 507–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Parmita, P.; Srivastava, M.K.; Attri, S.D. Diurnal and seasonal variations of black carbon and PM2. 5 over New Delhi, India: Influence of meteorology. Atmos. Res. 2013, 125, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A. Potential of crop residue in India as a source of energy. Int. J. Glob. Energy Issues 2007, 28, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Revised 1996 Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, National Greenhouse Gas Inventory Program (NGGIP). 1997. Available online: www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/gl/invs1.html (accessed on 10 June 2018).
- Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Justice, C.O. The collection 6 MODIS active fire detection algorithm and fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeborn, P.H.; Wooster, M.J.; Hao, W.M.; Ryan, C.A.; Nordgren, B.L.; Baker, S.P.; Ichoku, C. Relationships between energy release, fuel mass loss, and trace gas and aerosol emissions during laboratory biomass fires. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Roberts, G.; Freeborn, P.H.; Govaerts, Y.; Beeby, R.; He, J.; Lattanzia, A.; Mullen, R. Meteosat SEVIRI Fire Radiative Power (FRP) products from the Land Surface Analysis Satellite Applications Facility (LSA SAF): Part 1-algorithms, product contents & analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13217–13239. [Google Scholar]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Ellicott, E.; Giglio, L.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Lau, W.K. Vegetation fires in the himalayan region–Aerosol load, black carbon emissions and smoke plume heights. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.; Freitas, S.R.; Moraes, E.C.; Ferreira, N.J.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Rao, V.B.; Longo, K.M. Estimating trace gas and aerosol emissions over South America: Relationship between fire radiative energy released and aerosol optical depth observations. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6388–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Ellicott, E.; Dubovik, O.; Lapyonok, T.; Chin, M.; Giglio, L.; Roberts, G.J. An approach to estimate global biomass burning emissions of organic and black carbon from MODIS fire radiative power. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Ellison, L. Global top-down smoke-aerosol emissions estimation using satellite fire radiative power measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6643–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Randerson, J.T.; Werf, G.R. Analysis of daily, monthly, and annual burned area using the fourth-generation global fire emissions database (GFED4). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Alvarado, M.J.; Reid, J.S.; Karl, T.; Crounse, J.D.; Wennberg, P.O. Emission factors for open and domestic biomass burning for use in atmospheric models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4039–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasko, K.; Vadrevu, K.P.; Tran, V.T.; Ellicott, E.; Nguyen, T.T.N.; Bui, H.Q.; Justice, C. Satellites may underestimate rice residue and associated burning emissions in Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Agarwal, R.; Mittal, S.K.; Singh, N.; Singh, K.; Gupta, P.K. Study of size and mass distribution of particulate matter due to crop residue burning with seasonal variation in rural area of Punjab, India. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.K.; Singh, N.; Agarwal, R.; Awasthi, A.; Gupta, P.K. Ambient air quality during wheat and rice crop stubble burning episodes in Patiala. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vadrevu, K.; Lasko, K. Intercomparison of MODIS AQUA and VIIRS I-Band Fires and Emissions in an Agricultural Landscape—Implications for Air Pollution Research. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10070978
Vadrevu K, Lasko K. Intercomparison of MODIS AQUA and VIIRS I-Band Fires and Emissions in an Agricultural Landscape—Implications for Air Pollution Research. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(7):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10070978
Chicago/Turabian StyleVadrevu, Krishna, and Kristofer Lasko. 2018. "Intercomparison of MODIS AQUA and VIIRS I-Band Fires and Emissions in an Agricultural Landscape—Implications for Air Pollution Research" Remote Sensing 10, no. 7: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10070978
APA StyleVadrevu, K., & Lasko, K. (2018). Intercomparison of MODIS AQUA and VIIRS I-Band Fires and Emissions in an Agricultural Landscape—Implications for Air Pollution Research. Remote Sensing, 10(7), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10070978





