Mapping Maize Evapotranspiration at Field Scale Using SEBAL: A Comparison with the FAO Method and Soil-Plant Model Simulations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Acquisition of Satellite Imagery
2.2.2. Hydrological Monitoring
2.2.3. Meteorological Data and Estimation of Evapotranspiration by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Method (ETc)
2.2.4. Yield Data
2.3. Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) Method
2.4. Biomass Production and Maize Yield
2.5. 3D Soil-Plant Model
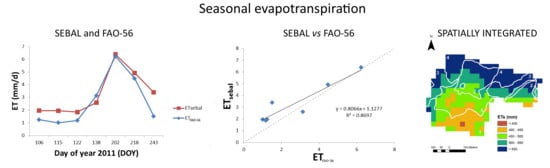
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serageldin, I. Looking ahead: Water, life and the environment in the twenty-first century. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1999, 15, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. SEBAL (Surface Energy Balance Algorithms for Land)—Idaho Implementation—Advanced Training and Users Manual. Available online: http://www.posmet.ufv.br/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/MET-479-Waters-et-al-SEBAL.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2018).
- Yang, J.; Mei, X.; Huo, Z.; Yan, C.; Ju, H.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Q. Water consumption in summer maize and winter wheat cropping system based on SEBAL model in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C. Accounting for water use: Terminology and implications for saving water and increasing production. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.; Lobell, D.B. Satellite-based assessment of yield variation and its determinants in smallholder African systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Ali, S. A new crop yield forecasting model based on satellite measurements applied across the Indus Basin, Pakistan. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 94, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, W.; Melesse, A. Crop Yield Estimation Using Remote Sensing and Surface Energy Flux Model. In Evaporation and Evapotranspiration: Measurements and Estimations, 1st ed.; Abtew, W., Melesse, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Molden, D.; Sakthivadivel, R. Water accounting to assess use and productivity of water. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1999, 15, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, B. A Procedure for Estimating Total Evapotranspiration Using Satellite-Based Vegetation Indices with Separate Estimates from Bare Soil. Master’s Thesis, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rwasoka, D.T.; Gumindoga, W.; Gwenzi, J. Estimation of actual evapotranspiration using the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) algorithm in the Upper Manyame catchment in Zimbabwe. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansouleh, B.; Karimi, A.; Hesadi, H. Evaluation of SEBAL and SEBS algorithms in the estimation of maize evapotranspiration. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2015, 6, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, C.; Wang, J. Assimilating remote sensing information into a coupled hydrology-crop growth model to estimate regional maize yield in arid regions. Ecol. Model. 2014, 291, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration. Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, C.G.; Huntington, J.L.; Pohll, G.M.; Allen, R.G.; Mcgwire, K.C.; Bassett, S.D. Assessing calibration uncertainty and automation for estimating evapotranspiration from agricultural areas using METRIC. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Gao, F.; Knipper, K.; Hain, C.; Dulaney, W.; Baldocchi, D.; Eichelmann, E.; Hemes, K.; Yang, Y.; Medellin-Azuara, J.; et al. Field-scale assessment of land and water use change over the California Delta using remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Ssegane, H.; Negri, M.C. Mapping intra-field yield variation using high resolution satellite imagery to integrate bioenergy and environmental stewardship in an agricultural watershed. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9753–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hank, T.B.; Bach, V.; Mauser, W. Using a remote sensing-supported hydro-agroecological model for field-scale simulation of heterogeneous crop growth and yield: Application for wheat in Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3934–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazifedoust, M.; van Dam, J.C.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Feddes, R.A. Assimilation of satellite data into agrohydrological models to improve crop yield forecasts. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2523–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, A.; Duveiller, G.; Defourny, P. Estimating regional winter wheat yield with WOFOST through the assimilation of green area index retrieved from MODIS observations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 164, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dente, L.; Satalino, G.; Mattia, F.; Rinaldi, M. Assimilation of leaf area index derived from ASAR and MERIS data into CERES-Wheat model to map wheat yield. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaddad, A.; Garcia, L. Surface Energy Balance-Based Model for Estimating Evapotranspiration Taking into Account Spatial Variability in Weather. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, A.A.; Bali, K.M.; Kleissl, J. Comparison of ALARM and SEBAL evapotranspiration of irrigated alfalfa. In Proceedings of the 2009 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Grand Sierra Resort and Casino, Reno, NV, USA, 21–24 June 2009; pp. 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez, J.; Neale, C.M.U.; Hipps, L.E.; Prueger, J.H.; Kustas, W.P. Comparing aircraft-based remotely sensed energy balance fluxes with eddy covariance tower data using heat flux source area functions. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, P.H.; Howell, T.A.; Paul, G.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Marek, T.H. Sebal for Estimating Hourly ET Fluxes over Irrigated and Dryland Cotton during BEAREX08; World Environmental and Water Resources Congress: Reston, VA, USA, 2011; pp. 2787–2795. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Noordman, E.M.; Davids, G.; Thoreson, B.P.; Allen, R.G. SEBAL model with remotely sensed data to improve water-resources management under actual field conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Irmak, A.; Irmak, S.; Martin, D.L. Application of SEBAL model for mapping evapotranspiration and estimating surface energy fluxes in South-Central Nebraska. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Teixeira, A.H.C.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Ahmad, M.D.; Bos, M.G. Reviewing SEBAL input parameters for assessing evapotranspiration and water productivity for the Low-Middle Sao Francisco River basin, Brazil. Part A: Calibration and validation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, R.; Li, Z.L.; Chen, K.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, X. Spatial-scale effect on the SEBAL model for evapotranspiration estimation using remote sensing data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 174–175, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Ahmad, M.D. Mapping root zone soil moisture using remotely sensed optical imagery. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, S.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. SEBAL for detecting spatial variation of water productivity and scope for improvement in eight irrigated wheat systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.; Thoreson, B.; Byron, C.; Davids, G. Discussion of “Application of SEBAL Model for Mapping Evapotranspiration and Estimating Surface Energy Fluxes in South-Central Nebraska” by Ramesh K. Singh, Ayse Irmak, Suat Irmak, and Derrel L. Martin. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2010, 136, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Deiana, R.; Teatini, P.; Cassiani, G.; Morari, F. Constrained optimization of spatial sampling in salt contaminated coastal farmland using EMI and continuous simulated annealing. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Teatini, P.; Corwin, D.L.; Deiana, R.; Berti, A.; Morari, F. Delineation of site-specific management units in a saline region at the Venice Lagoon margin, Italy, using soil reflectance and apparent electrical conductivity. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 99, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Teatini, P.; Corwin, D.L.; Dal Ferro, N.; Simonetti, G.; Morari, F. Spatio-temporal response of maize yield to edaphic and meteorological conditions in a saline farmland. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoli, G.; Bonetti, S.; Domec, J.C.; Putti, M.; Katul, G.; Marani, M. Tree root systems competing for soil moisture in a 3D soil-plant model. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 66, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Berti, A.; Teatini, P.; Morari, F. Simultaneous monitoring of soil water content and salinity with a low-cost capacitance-resistance probe. Sensors 2012, 12, 17588–17607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasumi, M.; Allen, R.G.; Trezza, R. At-surface albedo from Landsat and MODIS satellites for use in energy balance studies of evapotrans-piration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R.; Allen, R.G.; Wright, J.L. US Validation tests on the SEBAL model for evapotranspiration via satellite. In Proceedings of the 54th IEC Meeting of the International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID), Workshop Remote Sensing of ET for Large Regions, Montpellier, France, 14–19 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, B.L.; Barker, J.L. Landsat MSS and TM Post-Calibration Dynamic Ranges, Exoatmospheric Reflectances and At-Satellite Temperatures; EOSAT Landsat Technical Notes 1:3-8; Earth Observation Satellite Company: Lanham, MD, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandridis, T.K.; Cherif, I.; Chemin, Y.; Silleos, G.N.; Stavrinos, E.; Zalidis, G.C. Integrated methodology for estimating water use in mediterranean agricultural areas. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 445–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, M.G.; Leij, F.J.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Rosetta: A computer program for estimating soil hydraulic parameters with hierarchical pedotransfer functions. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRASS Development Team. GRASS GIS v7 Download. Available online: http://grass.itc.it/download/index.php (accessed on 9 July 2009).
- Brutsaert, W.; Sugita, M. Application of self-preservation in the diurnal evolution of the surface energy budget to determine daily evaporation. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemin, Y.; Alexandridis, T. Improving spatial resolution of et seasonal for irrigated rice in Zhanghe, China. In Proceedings of the 22nd Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Singapore, 5–9 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chemin, Y.; Platonov, A.; Abdullaev, I.; Ul-Hassan, M. Supplementing farm-level water productivity assessment by remote sensing in transition economies. Water Int. 2005, 30, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardini, L.; Berti, A.; Morari, F. Simulation of two cropping systems with EPIC and CropSyst models. Ital. J. Agron. 1998, 1–2, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Manoli, G.; Bonetti, S.; Scudiero, E.; Morari, F.; Putti, M.; Teatini, P. Modeling soil—Plant dynamics: Assessing simulation accuracy by comparison with spatially distributed crop yield measurements. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katul, G.; Manzoni, S.; Palmroth, S.; Oren, R. A stomatal optimization theory to describe the effects of atmospheric CO2 on leaf photosynthesis and transpiration. Ann Bot. 2010, 105, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, J.G.; Cratchley, C.R.; Kay, J.A.; Casterad, M.A.; Martínez-Cob, A.; Domínguez, R. Evaluation of satellite evapotranspiration estimates using ground-meteorological data available for the Flumen District into the Ebro Valley of N.E. Spain. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kite, G.W.; Droogers, P. Comparing evapotranspiration estimates from satellites, hydrological models and field data. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G. Using the FAO-56 dual crop coefficient method over an irrigated region as part of an evapotranspiration intercomparison study. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerji, N.; Rana, G. Modelling evapotranspiration of six irrigated crops under Mediterranean climate conditions. Agric. Meteorol. 2006, 138, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchi, A.; Gharsallah, O.; Gandolfi, C. Evapotranspiration models for a maize agro-ecosystem in irrigated and rainfed conditions. J. Agric. Eng. 2013, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abedinpour, M.; Sarangi, A.; Rajput, T.B.S.; Singh, M.; Pathak, H.; Ahmad, T. Performance evaluation of AquaCrop model for maize crop in a semi-arid environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 110, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.B.; Minasny, B.; Whelan, B.M. Obtaining ‘useful’ high-resolution soil data from proximally sensed electrical conductivity/resistivity (PSEC/R) surveys. Precis. Agric. 2005, 5, 503–510. [Google Scholar]
- Cannavo, P.; Recous, S.; Parnaudeau, V.; Reau, R. Modeling N dynamics to assess environmental impacts of cropped soils. Adv. Agron. 2008, 97, 131–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Steduto, P. The water productivity score (WPS) at global and regional level: Methodology and first results from remote sensing measurements of wheat, rice and maize. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grosso, C.; Manoli, G.; Martello, M.; Chemin, Y.H.; Pons, D.H.; Teatini, P.; Piccoli, I.; Morari, F. Mapping Maize Evapotranspiration at Field Scale Using SEBAL: A Comparison with the FAO Method and Soil-Plant Model Simulations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091452
Grosso C, Manoli G, Martello M, Chemin YH, Pons DH, Teatini P, Piccoli I, Morari F. Mapping Maize Evapotranspiration at Field Scale Using SEBAL: A Comparison with the FAO Method and Soil-Plant Model Simulations. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(9):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091452
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrosso, Carla, Gabriele Manoli, Marco Martello, Yann H. Chemin, Diego H. Pons, Pietro Teatini, Ilaria Piccoli, and Francesco Morari. 2018. "Mapping Maize Evapotranspiration at Field Scale Using SEBAL: A Comparison with the FAO Method and Soil-Plant Model Simulations" Remote Sensing 10, no. 9: 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091452
APA StyleGrosso, C., Manoli, G., Martello, M., Chemin, Y. H., Pons, D. H., Teatini, P., Piccoli, I., & Morari, F. (2018). Mapping Maize Evapotranspiration at Field Scale Using SEBAL: A Comparison with the FAO Method and Soil-Plant Model Simulations. Remote Sensing, 10(9), 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091452