Monitoring the Variation of Vegetation Water Content with Machine Learning Methods: Point–Surface Fusion of MODIS Products and GNSS-IR Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Resources
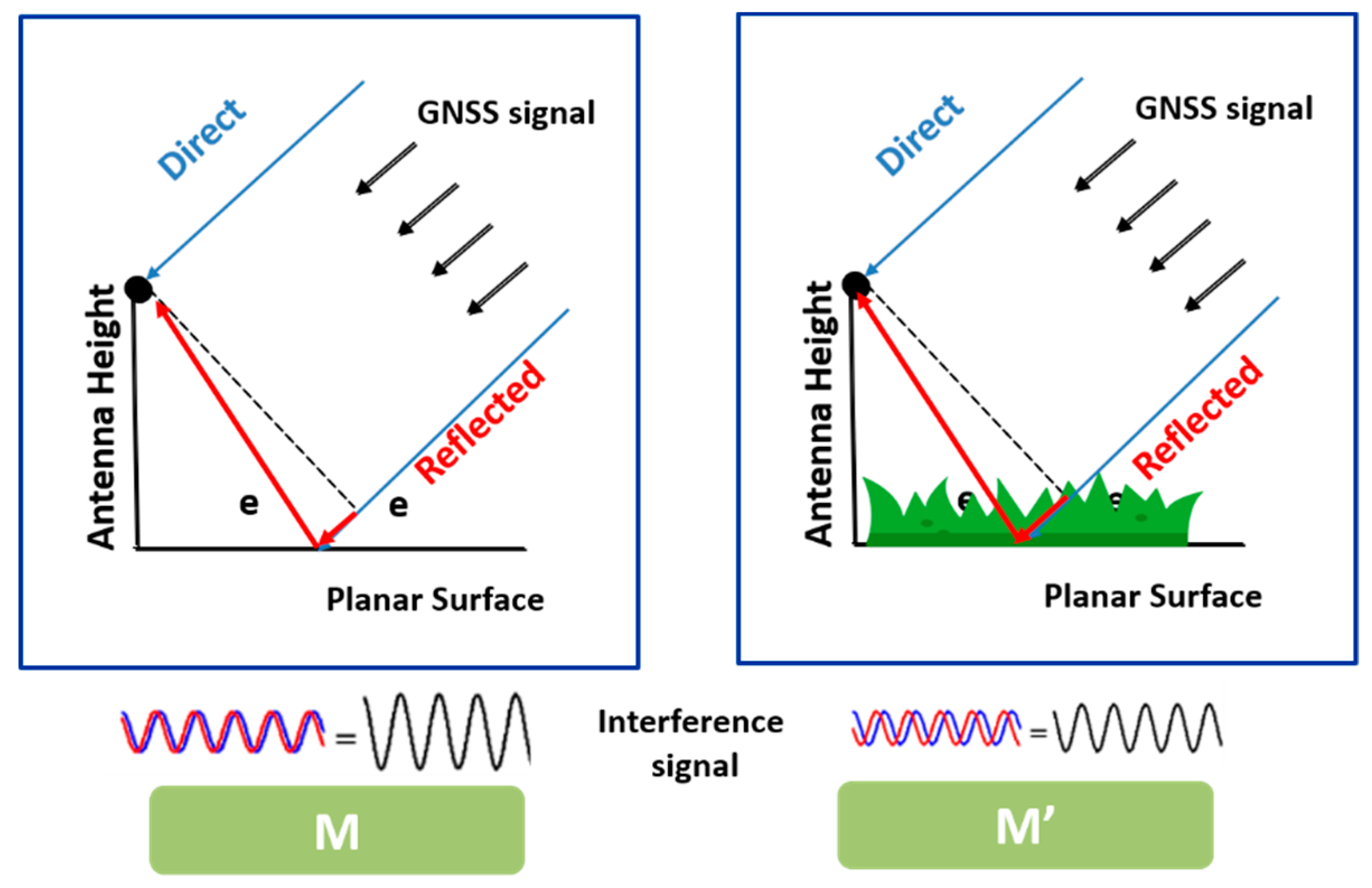
2.2.1. The Normalized Microwave Reflection Index (NMRI)
2.2.2. Indices Related to the VWC
3. Methodology
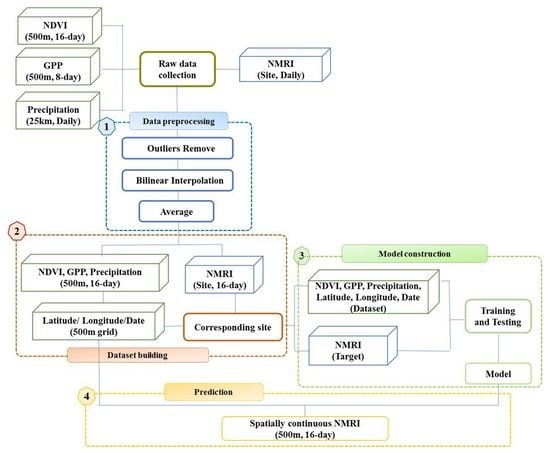
3.1. Data Processing and Dataset Selection
3.2. Machine Learning Methods
3.2.1. Back-Propagation Neural Network (BPNN)
3.2.2. Generalized Regression Neural Network (GRNN)
3.2.3. Random Forest (RF)
3.3. Traditional Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) Method for Comparison
3.4. Validation Methods and Evaluation Indicators
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Dataset Selection
4.2. Performance of the Models
4.2.1. Overall Performance of the Models
4.2.2. Model Performance for Each Site
4.3. Point–Surface Fusion Results of NMRI
4.4. Long Time-Series Variation of NMRI and Drought Events
5. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Procedure to Calculate GNSS-IR Index NMRI.
References
- Zhang, C.; Pattey, E.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Shang, J.; Dong, T. Retrieving Leaf and Canopy Water Content of Winter Wheat using Vegetation Water Indices. IEEE J. Stars 2017, 99, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Xu, Y.; Yao, F.M.; Wang, P.J.; Guo, W.J.; Li, L. Advances in estimation methods of vegetation water content based on optical remote sensing techniques. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzman, M.E.; Carmona, F.; Rivas, R.; Niclòs, R. Early assessment of crop yield from remotely sensed water stress and solar radiation data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 45, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rud, R.; Cohen, Y.; Alchanatis, V.; Levi, A.; Brikman, R.; Shenderey, C. Crop water stress index derived from multi-year ground and aerial thermal images as an indicator of potato water status. Precis. Agric. 2014, 15, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, L. Evaluation and comparison of MODIS Collection 6.1 aerosol optical depth against AERONET over regions in China with multifarious underlying surfaces. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvieco, E.; Riaño, D.; Aguado, I.; Cocero, D. Estimation of fuel moisture content from multitemporal analysis of Landsat Thematic Mapper reflectance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2145–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.D. Remote sensing of biotic and abiotic plant stress. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2003, 24, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, W. Quantitative retrieval of crop water content under different soil moistures levels. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6411, 64110D. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardisky, M.A.; Lemas, V.; Smart, R.M. The influence of soil salinity, growth form, and leaf moisture on the spectral radiance of spartina alterniflora canopies. Photogramm. Eng. Rem. Sens. 1983, 49, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Rueda, C.A.; Ustin, S.L. Water content estimation in vegetation with MODIS reflectance data and model inversion methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccato, P.; Gobron, N.; Flasse, S.; Pinty, B.; Tarantola, S. Designing a spectral index to estimate vegetation water content from remote sensing data: Part 1: Theoretical approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakke, T.W.; Kanemasu, E.T.; Steiner, J.L.; Ulaby, F.T.; Wilson, E. Microwave radar response to canopy moisture, leaf-area index, and dry weight of wheat, corn, and sorghum. Remote Sens. Environ. 1981, 11, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R.; Lee, H.; Hong, S. Radar Vegetation Index for Estimating the Vegetation Water Content of Rice and Soybean. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens Lett. 2012, 9, 564–568. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.K.; O’Neill, P.; Cosh, M.; Lang, R.; Joseph, A. Evaluation of radar vegetation indices for vegetation water content estimation using data from a ground-based SMAP simulator. In Proceedings of the IEEE. Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 1296–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Calvet, J.C.; Wigneron, J.P.; Walker, J.; Karbou, F.; Chanzy, A.; Albergel, C. Sensitivity of Passive Microwave Observations to Soil Moisture and Vegetation Water Content: L-Band to W-Band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J.P.; van Dijk, A. Global long-term passive microwave satellite-based retrievals of vegetation optical depth. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.; O‘Neill P., O.; Michael, S.; Jackson, T.; Entin, J.; Im, E.; Kellogg, K. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission. Proc. IEEE 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Qu, J.J. Combining MODIS and AMSR-E-based vegetation moisture retrievals for improved fire risk monitoring. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chai, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z. Gravimetric Vegetation Water Content Estimation for Corn Using L-Band Bi-Angular, Dual-Polarized Brightness Temperatures and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10543–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E. Normalized Microwave Reflection Index, I: A Vegetation Measurement Derived from GPS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Neira, M. A Passive reflectometry and interferometry system (PARIS) application to ocean altimetry. ESA J. 1993, 17, 331–355. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, D.; Axelrad, P.; Katzberg, S. Initial results of land-reflected GPS bistatic radar measurements in SMEX02. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, J.L.; Komjathy, A.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Katzberg, S.J. Wind speed measurement using forward scattered GPS signals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komjathy, A.; Maslanik, J.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Axelrad, P. Sea ice remote sensing using surface reflected GPS signals. Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proc. IGARSS 2000, 7, 2855–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Semmling, A.M.; Beyerle, G.; Stosius, R.; Dick, G.; Wickert, J.; Fabra, F.; Cardellach, E.; Ribó, S.; Rius, A.; Helm, A.; et al. Detection of arctic ocean tides using interferometric GNSS-R signals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Ray, R.D.; Nievinski, F.G.; Freymueller, J.T. The Accidental Tide Gauge: A Case Study of GPS Reflections from Kachemak Bay, Alaska. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellach, E.; Fabra, F.; Rius, A.; Pettinato, S.; D’Addio, S. Characterization of Dry-snow Sub-structure using GNSS Reflected Signals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Bosch-Lluis, X.; Camps, A.; Aguasca, A.; Vall-Llossera, M.; Valencia, E.; Ramos-Perez, I. Review of crop growth and soil moisture monitoring from a ground-based instrument implementing the Interference Pattern GNSS-R technique. Radio Sci. 2011, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Camps, A.; Vall-Llossera, M.; Bosch-Lluis, X.; Monerris, A.; Ramos-Perez, I.; Valencia, E.; Marchan-Hernandez, J.F.; Martinez-Fernandez, J.; Baroncini-Turricchia, G.; et al. Land Geophysical Parameters Retrieval Using the Interference Pattern GNSS-R Technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Rem. Sens. 2011, 49, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egido, A.; Caparrini, M.; Ruffini, G.; Paloscia, S.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Floury, N. Global Navigation Satellite System Reflectometry as a Remote Sensing Tool for Agriculture. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2356–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Chew, C.C.; Braun, J.J. Using geodetic GPS receivers to measure vegetation water content. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.E.; Larson, K.M.; Smith, W. Normalized Microwave Reflection Index, II: Validation of Vegetation Water Content Estimates at Montana Grasslands. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Representations by Back Propagating Errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, D.F. A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Space Agency (ESA). CCI Land Cover Product User Guide Version 2.4. ESA CCI LC Project, 2014. Available online: http://maps.elie.ucl.ac.be/CCI/viewer/index.php (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Bontemps, S.; Herold, M.; Kooistra, L.; van Groenestijn, A.; Hartley, A.; Arino, O.; Moreau, I.; Defourny, P. Revisiting land cover observation to address the needs of the climate modeling community. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H. Quality Improvement of Satellite Soil Moisture Products by Fusing with In-Situ Measurements and GNSS-R Estimates in the Western Continental U.S. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.E.; Roesler, C.J.; Larson, K.M. Vegetation Response to the 2012–2014 California Drought from GPS and Optical Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The NASA Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC). Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Melillo, J.M.; Mcguire, A.D.; Kicklighter, D.W.; Moore, B.; Vorosmarty, C.J.; Schloss, A.L. Global Climate-Change and Terrestrial Net Primary Production. Nature 1993, 363, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.J. Comparative Physiological Studies on the Growth of Field Crops: I. Variation in Net Assimilation Rate and Leaf Area between Species and Varieties, and within and between Years. Ann. Bot. 1947, 11, 41–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishi, L.; Chadwick, O.A.; Roberts, D.A.; Still, C.J. Relationships between GPP, Satellite Measures of Greenness and Canopy Water Content with Soil Moisture in Mediterranean-Climate Grassland and Oak Savanna. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2011, 2011, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, E.R., Jr.; Qu, J.; Hao, X.; Wang, L. Remote sensing of canopy water content: Scaling from leaf data to MODIS. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7454, 745409. [Google Scholar]
- Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center. TRMM (TMPA-RT) Near Real-Time Precipitation L3 1 day 0.25 degree × 0.25 degree V7. Savtchenko, A., Greenbelt, M.D., Eds.; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC). Available online: https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/TRMM_3B42RT_Daily_V7/summary?keywords=TRMM_3B42RT_Daily (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Ding, S.; Su, C.; Yu, J. An optimizing BP neural network algorithm based on genetic algorithm. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2011, 36, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zeng, C.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. Point-surface fusion of station measurements and satellite observations for mapping PM 2.5, distribution in China: Methods and Assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C.; Vohland, M. Downscaling land surface temperatures at regional scales with random forest regression. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, G.; Liu, F.; Lu, Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, F.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, D. Comparison of boosted regression tree and random forest models for mapping topsoil organic carbon concentration in an alpine ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Were, K.; Bui, D.T.; Dick Øystein, B.; Singh, B.R. A comparative assessment of support vector regression, artificial neural networks, and random forests for predicting and mapping soil organic carbon stocks across an afromontane landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.D.; Pérez, A.; Lozano, J.A. S Sensitivity analysis of k-Fold Cross validation in prediction error estimation. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jing, W.; Zhang, P. Mapping Fine Spatial Resolution Precipitation from TRMM Precipitation Datasets Using an Ensemble Learning Method and MODIS Optical Products in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Song, L. Spatial Downscaling of Monthly TRMM Precipitation Based on EVI and Other Geospatial Variables Over the Tibetan Plateau From 2001 to 2012. Mt. Res. Dev. 2015, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Liu, Y. Unsupervised Segmentation Evaluation Using Area-Weighted Variance and Jeffries-Matusita Distance for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Lin, H.; Yan, E.; Jiang, Q.; Lu, H.; Wu, S. Optimal selection of remote sensing feature variables for land cover classification. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Xi’an, China, 18–20 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Novelli, A.; Tarantino, E.; Caradonna, G.; Apollonio, C.; Balacco, G.; Piccinni, F. Improving the ANN classification accuracy of landsat data through spectral indices and linear transformations (PCA and TCT) aimed at LU/LC monitoring of a river basin. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 24–27 June 2017; pp. 420–432. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Ge, Y.; Ling, F.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Urban Land Use Mapping by Combining Remote Sensing Imagery and Mobile Phone Positioning Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, M.S. Multipath Effects. In Global Positioning System: Theory and Applications; Parkinson, B.W., Spilker, J.J., Jr., Axelrad, P., Enge, P., Eds.; the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 547–568. [Google Scholar]















| Index | Resolution | Product | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMRI [37] | Daily/site-based | PBO H2O | 2007.01.01–2016.12.31 |
| NDVI [6] | 16 day/500 m | MOD13A1 | 2007.01.01–2013.12.31 |
| NDWI [9] | 8 day/500 m | MOD09A1 (bands 2,5) | 2007.01.01–2013.12.31 |
| NDII [10] | 8 day/500 m | MOD09A1 (bands 2,6) | 2007.01.01–2013.12.31 |
| GPP [42] | 8 day/500 m | MOD17A2H | 2007.01.01–2013.12.31 |
| LAI [43] | 8 day/500 m | MCD15A2H | 2007.01.01–2013.12.31 |
| Precipitation [46] | Daily/25 km | TRMM_3B42RT_Daily | 2007.01.01–2013.12.31 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Q.; Li, S.; Yue, L.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Monitoring the Variation of Vegetation Water Content with Machine Learning Methods: Point–Surface Fusion of MODIS Products and GNSS-IR Observations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121440
Yuan Q, Li S, Yue L, Li T, Shen H, Zhang L. Monitoring the Variation of Vegetation Water Content with Machine Learning Methods: Point–Surface Fusion of MODIS Products and GNSS-IR Observations. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121440
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Qiangqiang, Shuwen Li, Linwei Yue, Tongwen Li, Huanfeng Shen, and Liangpei Zhang. 2019. "Monitoring the Variation of Vegetation Water Content with Machine Learning Methods: Point–Surface Fusion of MODIS Products and GNSS-IR Observations" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121440
APA StyleYuan, Q., Li, S., Yue, L., Li, T., Shen, H., & Zhang, L. (2019). Monitoring the Variation of Vegetation Water Content with Machine Learning Methods: Point–Surface Fusion of MODIS Products and GNSS-IR Observations. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121440