Evaluating k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) Imputation Models for Species-Level Aboveground Forest Biomass Mapping in Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
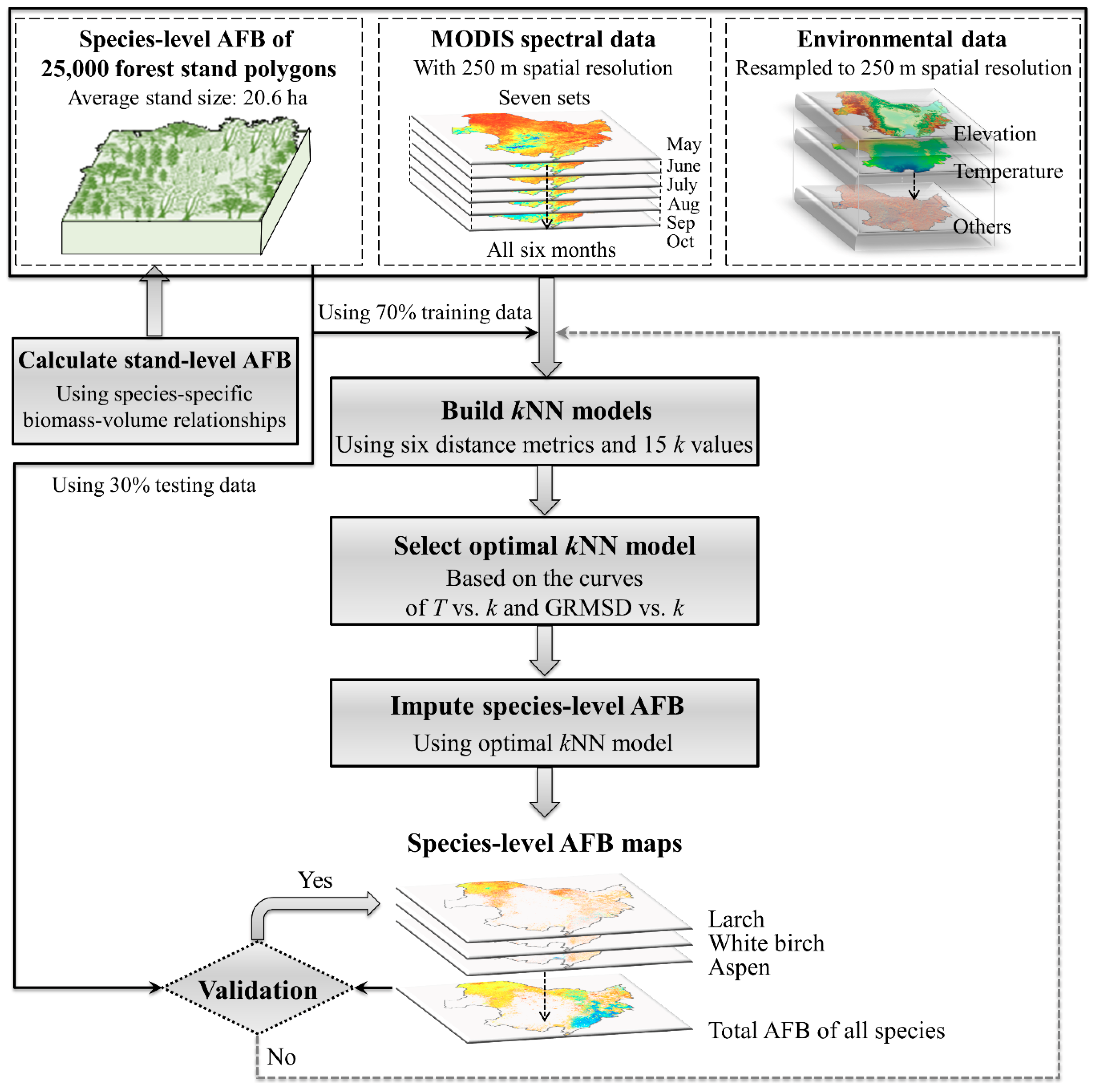
2.2. Forest Inventory Data
2.3. MODIS Data
2.4. Environmental Data
2.5. Optimizing kNN Models and Species-Level Biomass Imputation
2.6. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Performance of Different kNN Models
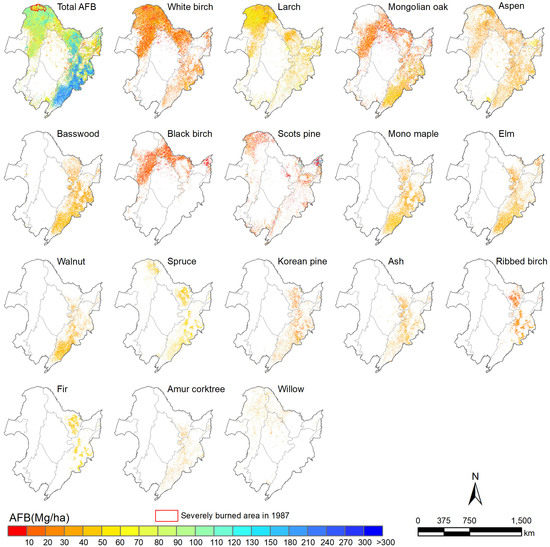
3.2. Species-Level AFB Estimation in Northeast China
3.3. Relationship between Environmental Variables and Species-Level AFB
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Optimal Distance Metric, k value and MODIS Imagery
4.2. Environmental Factors and Species Distribution
4.3. Imputation Accuracy and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Guo, Q.; Tao, S.; Kelly, M.; Xu, G. Lidar with multi-temporal MODIS provide a means to upscale predictions of forest biomass. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xue, B.; Hu, T.; Alvarez, O.; Tao, S.; Fang, J. Spatial distribution of forest aboveground biomass in China: Estimation through combination of spaceborne lidar, optical imagery, and forest inventory data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolkos, S.; Goetz, S.; Dubayah, R. A meta-analysis of terrestrial aboveground biomass estimation using lidar remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.S. Forest landscape models: Definitions, characterization, and classification. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 254, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duveneck, M.J.; Thompson, J.R.; Wilson, B.T. An imputed forest composition map for New England screened by species range boundaries. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 347, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zald, H.S.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Hilker, T.; Hermosilla, T.; Hobart, G.W.; Coops, N.C. Integrating Landsat pixel composites and change metrics with lidar plots to predictively map forest structure and aboveground biomass in Saskatchewan, Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.T.; Lister, A.J.; Riemann, R.I. A nearest-neighbor imputation approach to mapping tree species over large areas using forest inventory plots and moderate resolution raster data. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 271, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ganguly, S.; Nemani, R.R.; White, M.A.; Milesi, C.; Hashimoto, H.; Wang, W.; Saatchi, S.; Yu, Y.; Myneni, R.B. Estimation of forest aboveground biomass in California using canopy height and leaf area index estimated from satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 151, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, T.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Hobart, G.W. An integrated Landsat time series protocol for change detection and generation of annual gap-free surface reflectance composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmann, J.L.; Gregory, M.J. Predictive mapping of forest composition and structure with direct gradient analysis and nearest-neighbor imputation in coastal Oregon, USA. Can. J. For. Res. 2002, 32, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomppo, E.; Olsson, H.; Ståhl, G.; Nilsson, M.; Hagner, O.; Katila, M. Combining national forest inventory field plots and remote sensing data for forest databases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1982–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRoberts, R.E. Estimating forest attribute parameters for small areas using nearest neighbors techniques. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 272, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelson, B.N.; Temesgen, H.; Lemay, V.; Barrett, T.M.; Crookston, N.L.; Hudak, A.T. The roles of nearest neighbor methods in imputing missing data in forest inventory and monitoring databases. Scand. J. For. Res. 2009, 24, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauhkonen, J.; Korpela, I.; Maltamo, M.; Tokola, T. Imputation of single-tree attributes using airborne laser scanning-based height, intensity, and alpha shape metrics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosofske, K.D.; Froese, R.E.; Falkowski, M.J.; Banskota, A. A review of methods for mapping and prediction of inventory attributes for operational forest management. For. Sci. 2013, 60, 733–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, A.; Bernier, P.; Guindon, L.; Villemaire, P.; Guo, X.; Stinson, G.; Bergeron, T.; Magnussen, S.; Hall, R. Mapping attributes of Canada’s forests at moderate resolution through kNN and MODIS imagery. Can. J. For. Res. 2014, 44, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, A.T.; Crookston, N.L.; Evans, J.S.; Hall, D.E.; Falkowski, M.J. Nearest neighbor imputation of species-level, plot-scale forest structure attributes from lidar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2232–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeur, M.; Stage, A.R. Most similar neighbor: An improved sampling inference procedure for natural resource planning. For. Sci. 1995, 41, 337–359. [Google Scholar]
- Crookston, N.L.; Finley, A.O. Yaimpute: An R package for kNN imputation. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, M.J.; Hudak, A.T.; Crookston, N.L.; Gessler, P.E.; Uebler, E.H.; Smith, A.M. Landscape-scale parameterization of a tree-level forest growth model: A k-nearest neighbor imputation approach incorporating lidar data. Can. J. For. Res. 2010, 40, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmann, J.L.; Gregory, M.J.; Henderson, E.B.; Roberts, H.M. Mapping gradients of community composition with nearest-neighbour imputation: Extending plot data for landscape analysis. J. Veg. Sci. 2011, 22, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, H.S.; Liang, Y.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Henne, P.D.; Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, Z.; Huang, C. Integrating forest inventory data and MODIS data to map species-level biomass in Chinese boreal forests. Can. J. For. Res. 2018, 48, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, S.; Sun, G. Forest biomass mapping of northeastern China using GLAS and MODIS data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Yang, Q.; Wu, S.; Li, B. Study on Eco-geographic System of China; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinses) [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H.; Sun, G.; Huang, J.; Guo, Z.; Ni, W.; Fu, A. National forest aboveground biomass mapping from ICESat/GLAS data and MODIS imagery in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5534–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Wang, G.G.; Liu, G.-H.; Xu, S.-L. Forest biomass of China: An estimate based on the biomass–volume relationship. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Fang, J.; Zhu, B. Forest biomass and root–shoot allocation in Northeast China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 4007–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhang, X.-s.; Scurlock, J.M. Synthesis and analysis of biomass and net primary productivity in Chinese forests. Ann. For. Sci. 2001, 58, 351–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.B.; Burgess, N.D.; Coad, L.; Belokurov, A.; Besançon, C.; Boisrobert, L.; Campbell, A.; Fish, L.; Gliddon, D.; Humphries, K. Global analysis of the protection status of the world’s forests. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.F. Derivation of leaf-area index from quality of light on the forest floor. Ecology 1969, 50, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Huete, A.; Kerr, Y.; Sorooshian, S. A modified soil adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Stark, R.; Rundquist, D. Novel algorithms for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt Jr, E.R.; Rock, B.N. Detection of changes in leaf water content using near-and middle-infrared reflectances. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 30, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M. Gemi: A non-linear index to monitor global vegetation from satellites. Vegetatio 1992, 101, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A. Wide dynamic range vegetation index for remote quantification of biophysical characteristics of vegetation. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 161, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Hong, Y.; Qin, Q.; Zhu, L. Evaluation of the visible and shortwave infrared drought index in China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2013, 4, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; He, H.S.; Zhao, J.; Larsen, D.R.; Zhang, H.; Sunde, M.G.; Duan, S. Climate and spring phenology effects on autumn phenology in the Greater Khingan Mountains, northeastern China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; IIASA; ISRIC; ISSCAS; JRC. Harmonized World Soil Database (Version 1.2); FAO: Rome, Italy; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Crookston, N.L.; Finley, A.O. Yaimpute: Nearest Neighbor Observation Imputation and Evaluation Tools. R Package Version 1.0-30. 2018. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=yaImpute (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Zhang, Y.; He, H.S.; Dijak, W.D.; Yang, J.; Shifley, S.R.; Palik, B.J. Integration of satellite imagery and forest inventory in mapping dominant and associated species at a regional scale. Environ. Manage. 2009, 44, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemann, R.; Wilson, B.T.; Lister, A.; Parks, S. An effective assessment protocol for continuous geospatial datasets of forest characteristics using USFS forest inventory and analysis (FIA) data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2337–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.H.; Reid, I.; Hobson, P.R. The two-dimensional Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. In Proceedings of the XI International Workshop on Advanced Computing and Analysis Techniques in Physics Research, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 23–27 April 2007; pp. 196–206. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; He, H.S.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Henne, P.D.; Zhu, Z.; Larsen, D.R. Data Release For: Evaluating k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) Imputation Models for Species-Level Aboveground Forest Biomass Mapping in Northeast China. U.S. Geological Survey Data Release. 2019. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5066/P9MOB5E3 (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Yu, X.-f.; Zhuang, D.-f. Monitoring forest phenophases of Northeast China based on MODIS NDVI data. Resour. Sci. 2006, 28, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Q.; Watanabe, M.; Koike, T. Growth characteristics of two promising tree species for afforestation, birch and larch in the northeastern part of Asia. Eurasian J. For. Res. 2010, 13, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Forest in Great Xing’an Mountains of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Kang, H.; Tan, H.; Xu, M. Effects of drought stresses induced by polyethylene glycol on germination of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seeds from natural and plantation forests on sandy land. J. For. Res. 2006, 11, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Ding, H.; Fang, X.; Jiang, S.; Dai, L. Climatic effects on radial growth of major tree species on Changbai Mountain. Ann. For. Sci. 2011, 68, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Ying, W.; Chun-Yu, Z.; Qing-Yu, J. Impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems in Northeast China. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2013, 4, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Bu, R.; Chang, Y.; Deng, H.; Qin, Q. Predicting impacts of climate change on the aboveground carbon sequestration rate of a temperate forest in northeastern China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, S. Changes in forest biomass and linkage to climate and forest disturbances over northeastern China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatchi, S.S.; Harris, N.L.; Brown, S.; Lefsky, M.; Mitchard, E.T.; Salas, W.; Zutta, B.R.; Buermann, W.; Lewis, S.L.; Hagen, S. Benchmark map of forest carbon stocks in tropical regions across three continents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2011, 108, 9899–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Cao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, L.; Choi, S.; Shi, Y.; Park, T.; Fu, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, X. Estimation of forest biomass patterns across Northeast China based on allometric scale relationship. Forests 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.S.; Mladenoff, D.J.; Radeloff, V.C.; Crow, T.R. Integration of GIS data and classified satellite imagery for regional forest assessment. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, S.; Tomppo, E.; McRoberts, R.E. A model-assisted k-nearest neighbour approach to remove extrapolation bias. Scand. J. For. Res. 2010, 25, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matasci, G.; Hermosilla, T.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Hobart, G.W.; Zald, H.S. Large-area mapping of Canadian boreal forest cover, height, biomass and other structural attributes using Landsat composites and lidar plots. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Category and Subcategory | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Spectral | ||
| Spectral bands | b1 | Red, 620–670 nm |
| b2 | Short wave near-infrared, 841–876 nm | |
| b3 | Blue, 459–479 nm | |
| b4 | Green, 545–565 nm | |
| b5 | Long wave near-infrared, 1230–1250 nm | |
| b6 | Long wave near-infrared, 1628–1652 nm | |
| b7 | Long wave near-infrared, 2105–2155 nm | |
| Spectral indices | NDVI | ) [30] |
| RVI | [31] | |
| EVI | [32] | |
| MSAVI | [33] | |
| VARI | [34] | |
| NDWI | [35] | |
| NDIIb6 | [36] | |
| NDIIb7 | [36] | |
| SAVI | [37] | |
| GEMI | [38] | |
| WDVI | [39] | |
| MSI | [36] | |
| SWCI | [40] | |
| Topographic | ELEV | Elevation (m) |
| SLOPE | Slope (°) | |
| COSASP | Cosine transformation of aspect | |
| Climatic | ||
| Temperature | TEM | Mean annual temperature (°C) |
| GTEM | Mean temperature during the growing season (°C) | |
| Precipitation | PRE | Mean annual precipitation (mm) |
| GPRE | Mean precipitation during the growing season (mm) | |
| Moisture | ACMI | Mean annual climate moisture index (annual precipitation minus annual potential evapotranspiration) (mm) [16] |
| GCMI | Mean climate moisture index during the growing season (mm) | |
| Radiation | RAD | Mean annual radiation (W/m2) |
| GRAD | Mean radiation during the growing season (W/m2) | |
| Soil | SBULK | Bulk of soil (kg/dm3) |
| SPH | PH of soil | |
| GRAVEL | Content (%) of gravel | |
| SAND | Content (%) of sand | |
| SILT | Content (%) of silt | |
| CLAY | Content (%) of clay | |
| SOC | Content (%) of soil organic carbon | |
| Location | X | Coordinate x of each raster cell center (m) |
| Y | Coordinate y of each raster cell center (m) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; He, H.S.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Henne, P.D.; Zhu, Z.; Larsen, D.R. Evaluating k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) Imputation Models for Species-Level Aboveground Forest Biomass Mapping in Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172005
Fu Y, He HS, Hawbaker TJ, Henne PD, Zhu Z, Larsen DR. Evaluating k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) Imputation Models for Species-Level Aboveground Forest Biomass Mapping in Northeast China. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(17):2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172005
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yuanyuan, Hong S. He, Todd J. Hawbaker, Paul D. Henne, Zhiliang Zhu, and David R. Larsen. 2019. "Evaluating k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) Imputation Models for Species-Level Aboveground Forest Biomass Mapping in Northeast China" Remote Sensing 11, no. 17: 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172005
APA StyleFu, Y., He, H. S., Hawbaker, T. J., Henne, P. D., Zhu, Z., & Larsen, D. R. (2019). Evaluating k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) Imputation Models for Species-Level Aboveground Forest Biomass Mapping in Northeast China. Remote Sensing, 11(17), 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172005