Filling the Gaps of Missing Data in the Merged VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Ocean Color Product Using the DINEOF Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. VIIRS SNPP and NOAA-20 Ocean Color Level-2 and Global Level-3 Data
2.2. Merging VIIRS SNPP and NOAA-20 Global Level-3 Ocean Color Data
2.3. Gap-Filling of the Merged VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Data
3. Results
3.1. Merged VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Products
3.2. Gap-Filled VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Products
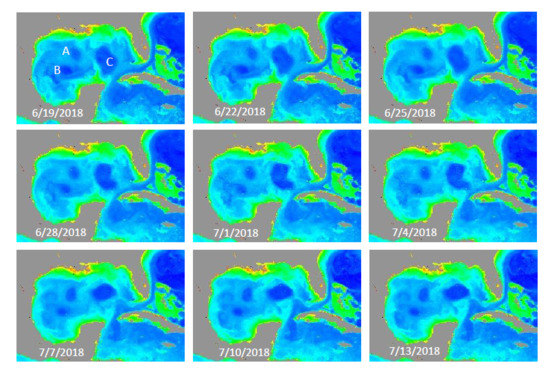
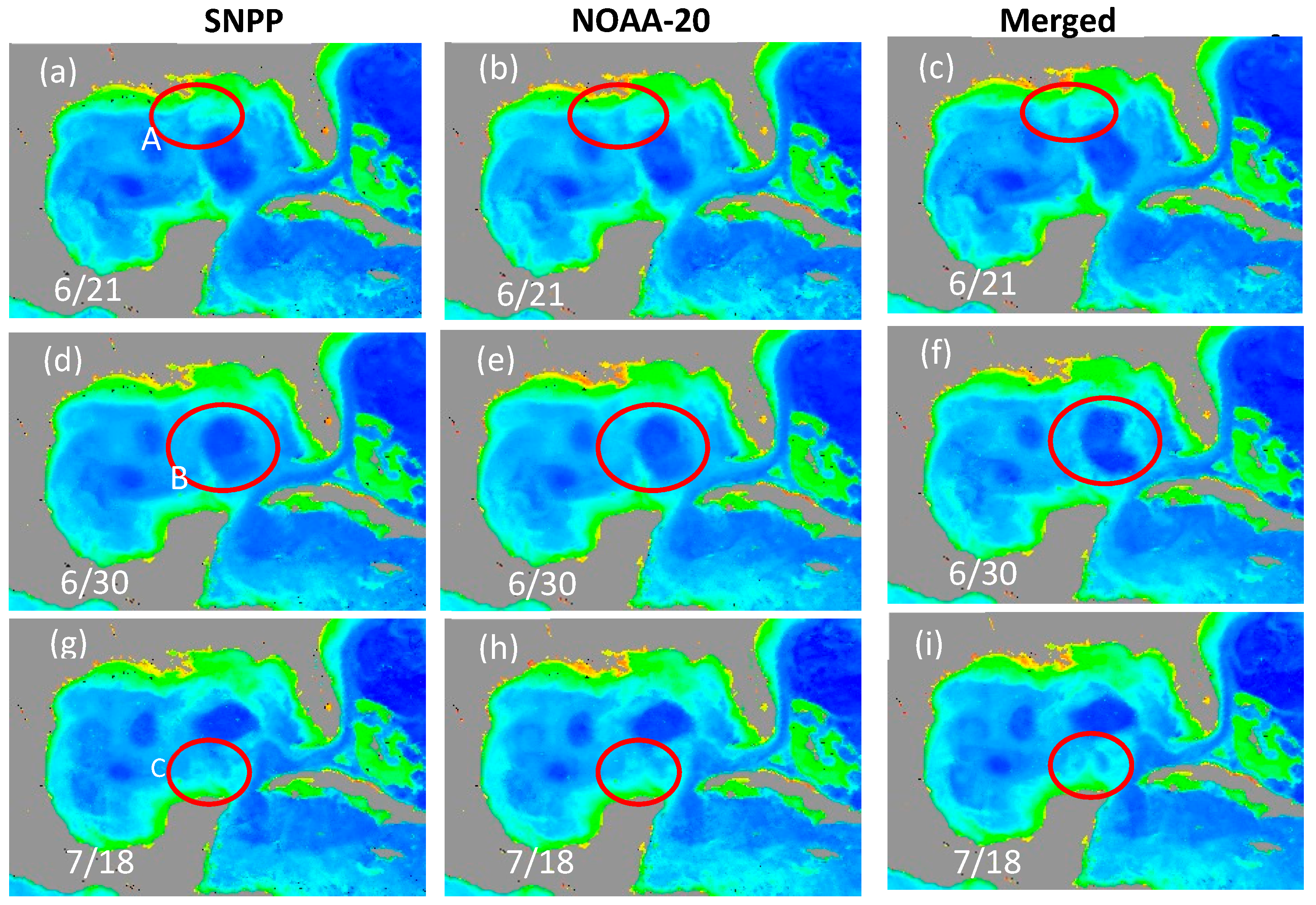
3.3. Ocean Features Revealed in the Gap-Filled VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Chl-a Data
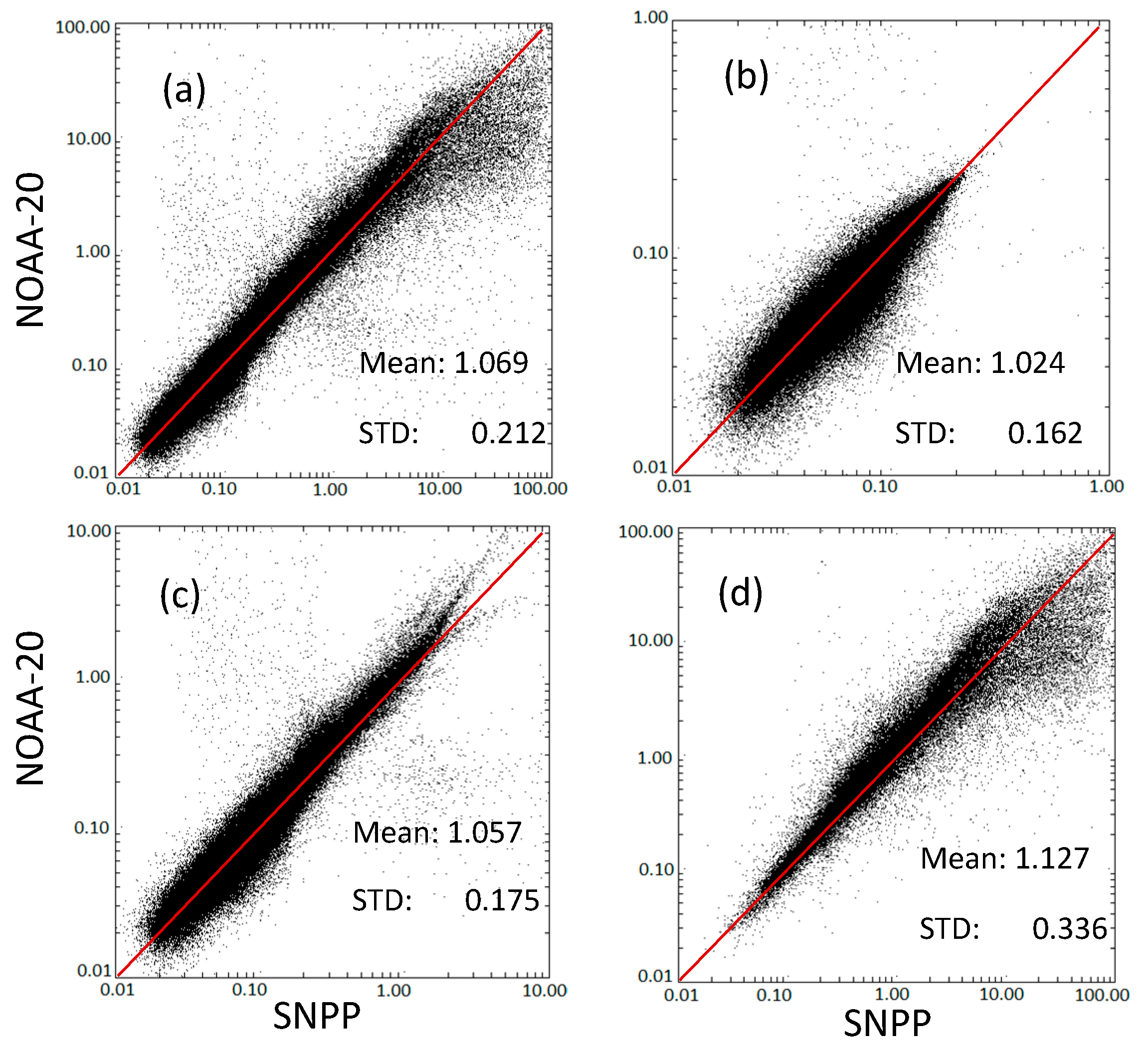
3.4. Comparison with Gap-Filled Data Based on VIIRS SNPP or NOAA-20
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoder, J.A.; Doney, S.C.; Siegel, D.A.; Wilson, C. Study of marine ecosystem and biogeochemistry now and in the future: Example of the unique contributions from the space. Oceanography 2010, 23, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.D.; Kilcoyne, H.; Cikanek, H.; Mehta, A. Joint Polar Satellite System: The United States next generation civilian polar-orbiting environmental satellite system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13463–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Jiang, L.; Son, S.; Shi, W.; Rausch, K.; Voss, K. Impact of VIIRS SDR performance on ocean color products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10347–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L.; Voss, K. NIR- and SWIR-based on-orbit vicarious calibrations for satellite ocean color sensors. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 20437–20453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Mitchell, B.G.; Siegel, D.A.; Carder, K.L.; Garver, S.A.; Kahru, M.; McClain, C.R. Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 24937–24953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Franz, B.A. Chlorophyll a algorithms for oligotrophic oceans: A novel approach based on three-band reflectance difference. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C01011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S. VIIRS-derived chlorophyll-a using the ocean color index method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. (Ed.) Atmospheric Correction for Remotely-Sensed Ocean-Colour Products; Reports of International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, L. VIIRS-derived ocean color product using the imaging bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Harding, J.L.W. Retrieval of diffuse attenuation coefficient in the Chesapeake Bay and turbid ocean regions for satellite ocean color applications. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, C10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Wang, M. Diffuse attenuation coefficient of the photosynthetically available radiation Kd(PAR) for global open ocean and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.P.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiple quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Characterization of particle backscattering of global highly turbid waters from VIIRS ocean color observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 9255–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lee, Z.; Shang, S. A system to measure the data quality of spectral remote-sensing reflectance of aquatic environments. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 8189–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. Estimation of ocean contribution at the MODIS near-infrared wavelengths along the east coast of the U.S.: Two case studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L13606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Tang, J. Water property monitoring and assessment for China’s inland Lake Taihu from MODIS-Aqua measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Evaluation of MODIS SWIR and NIR-SWIR atmospheric correction algorithm using SeaBASS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR combined atmospheric correction approach for MODIS ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, M. Radiometric calibration of the VIIRS reflective solar bands with robust characterizations and hybrid calibration coefficients. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 9331–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chu, M.; Wang, M. On-orbit characterization of the VIIRS solar diffuser and attenuation screens for NOAA-20 using yaw measurements. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 6605–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvera-Azcarate, A.; Barth, A.; Rixen, M.; Beckers, J. Reconstruction of incomplete oceanographic data sets using Empirical Orthogonal Functions. Application to the Adriatic Sea. Ocean Model. 2005, 9, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, J.; Rixen, M. EOF calculations and data filling from incomplete oceanographic data sets. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2003, 20, 1839–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzedo, U.; Alvera-Azcarate, A.; Esnaola, G.; Ezcurra, A.; Saenz, J. Reconstruction of sea surface temperature by means of DINEOF. A case study during the fishing season in the Bay of Biscay. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, E.; Poulain, P.M.; Juznic-Zontac, Z. MODIS chlorophyll variability in the northern Adriatic Sea and relationship with forcing parameters. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, C03S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, E.; Poulain, P.M.; Notarstefano, G. Spatial and temporal variability of the sea surface temperature in the Gulf of Trieste between January 2000 and December 2006. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Alvera-Azcarate, A.; Ruddick, K.; Greenwood, N. Reconstruction of MODIS total suspended matter time series maps by DINEOF and validation with autonomous platform data. Ocean Dyn. 2011, 61, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirjacobs, D.; Alvera-Azcarate, A.; Barth, A.; Lacroix, G.; Park, Y.; Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.; Beckers, J. Cloud filling of ocean color and sea surface temperature remote sensing products over the Southern North Sea by the data interpolating empirical orthogonal functions methodology. J. Sea Res. 2011, 65, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.; Nardelli, B.B.; Cipollini, P.; Santoleri, R.; Robinson, I.S. Seasonal to interannual phytoplankton response to physical processes in the Mediterranean Sea from satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, R. Spatial and temporal variability of SST and ocean color in the Gulf of Maine based on cloud-free SST and chlorophyll reconstructions in 2003–2012. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Kabiri, K. Spatio-temporal variability of SST and chlorophyll-a from MODIS data in the Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilborn, A.; Costa, M. Applications of DINEOF to Satellite-Derived Chlorophyll-a from a Productive Coastal Region. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvera-Azcarate, A.; Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K.G.; Barth, A.; Beckers, J.-M. Analysis of high frequency geostationary ocean colour data using DINEOF. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 159, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M. Analysis of diurnal variations from the Korean Geostationary Ocean Color Imager measurements using the DINEOF method. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 180, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M. Gap filling of missing data for VIIRS global ocean color product using the DINEOF method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4464–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. A sensitivity study of SeaWiFS atmospheric correction algorithm: Effects of spectral band variations. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 67, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Franz, B.A. Comparing the ocean color measurements between MOS and SeaWiFS: A vicarious intercalibration approach for MOS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Isaacman, A.; Franz, B.A.; McClain, C.R. Ocean color optical property data derived from the Japanese Ocean Color and Temperature Scanner and the French Polarization and Directionality of the Earth’s Reflectances: A comparison study. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 974–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, L. Atmospheric correction using the information from the short blue band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6224–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Satellite views of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 104, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L. Spring-neap tidal effects on satellite ocean color observations in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Ocean reflectance spectra at the red, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared from highly turbid waters: A study in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.W.; Blaisdell, J.M.; Darzi, M. Level-3 SeaWiFS Data Products: Spatial and Temporal Binning Algorithms. Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1996, 9, 952. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. Cloud masking for ocean color data processing in the coastal regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Rem. Sens. 2006, 44, 3196–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, M. Identification of pixels with stray light and cloud shadow contaminations in the satellite ocean color data processing. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 6757–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Bailey, S.W. Correction of the sun glint contamination on the SeaWiFS ocean and atmosphere products. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 4790–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikelsons, M.; Wang, M. Interactive online maps make satellite ocean data accessible. EOS 2018, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sensor | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | M9 | M10 | M11 | I1 | I2 | I3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIIRS-SNPP | 410 | 443 | 486 | 551 | 671 | 745 | 862 | 1238 | 1378 | 1610 | 2250 | 638 | 862 | 1610 |
| VIIRS-NOAA-20 | 411 | 445 | 489 | 555 | 667 | 746 | 868 | 1238 | 1376 | 1604 | 2258 | 642 | 867 | 1603 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, M. Filling the Gaps of Missing Data in the Merged VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Ocean Color Product Using the DINEOF Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020178
Liu X, Wang M. Filling the Gaps of Missing Data in the Merged VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Ocean Color Product Using the DINEOF Method. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020178
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoming, and Menghua Wang. 2019. "Filling the Gaps of Missing Data in the Merged VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Ocean Color Product Using the DINEOF Method" Remote Sensing 11, no. 2: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020178
APA StyleLiu, X., & Wang, M. (2019). Filling the Gaps of Missing Data in the Merged VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 Ocean Color Product Using the DINEOF Method. Remote Sensing, 11(2), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020178