Regional Atmospheric Aerosol Pollution Detection Based on LiDAR Remote Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
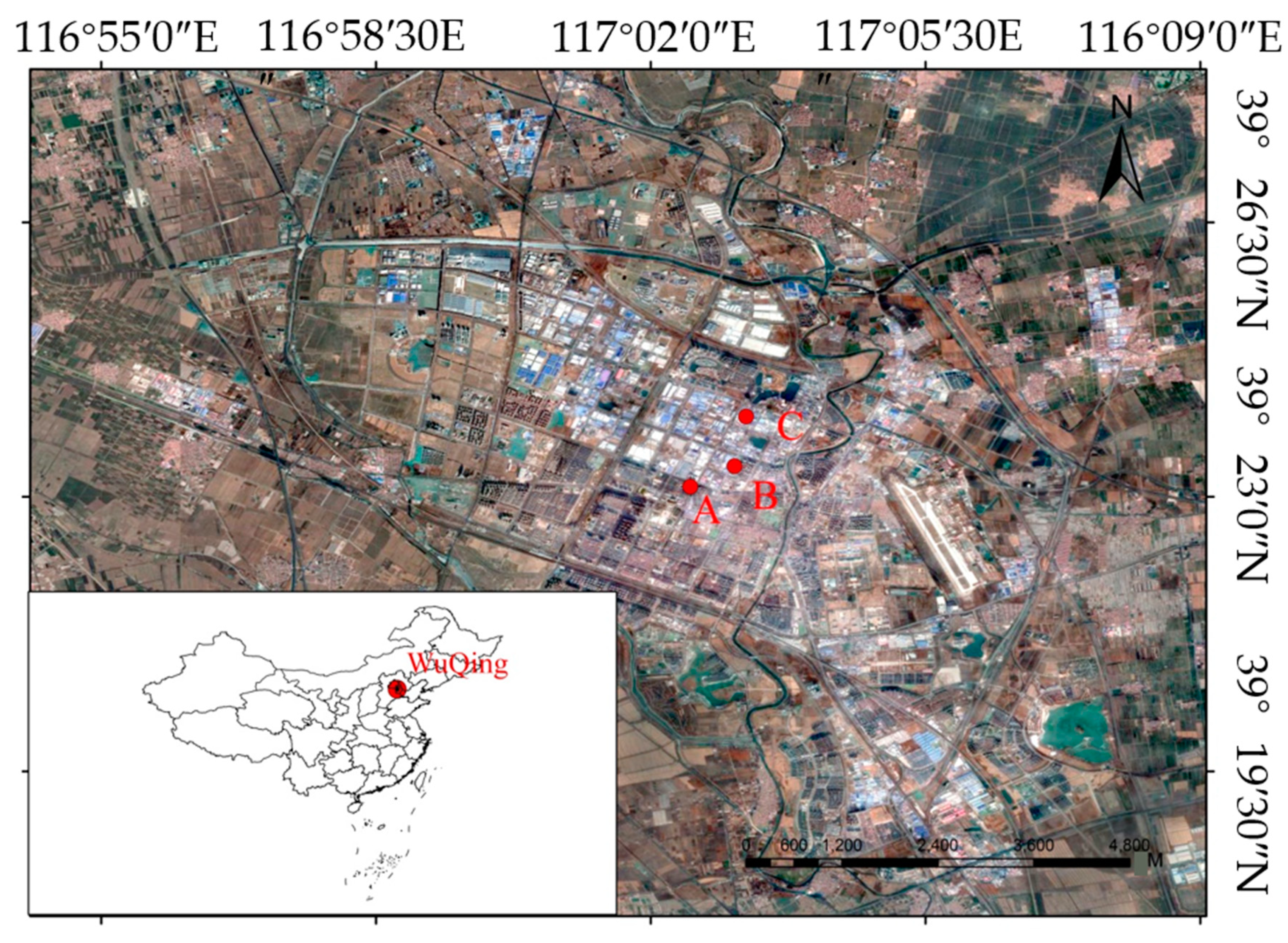
2. LiDARs and Study Area
3. Methods
3.1. Vertical Retrieval Method
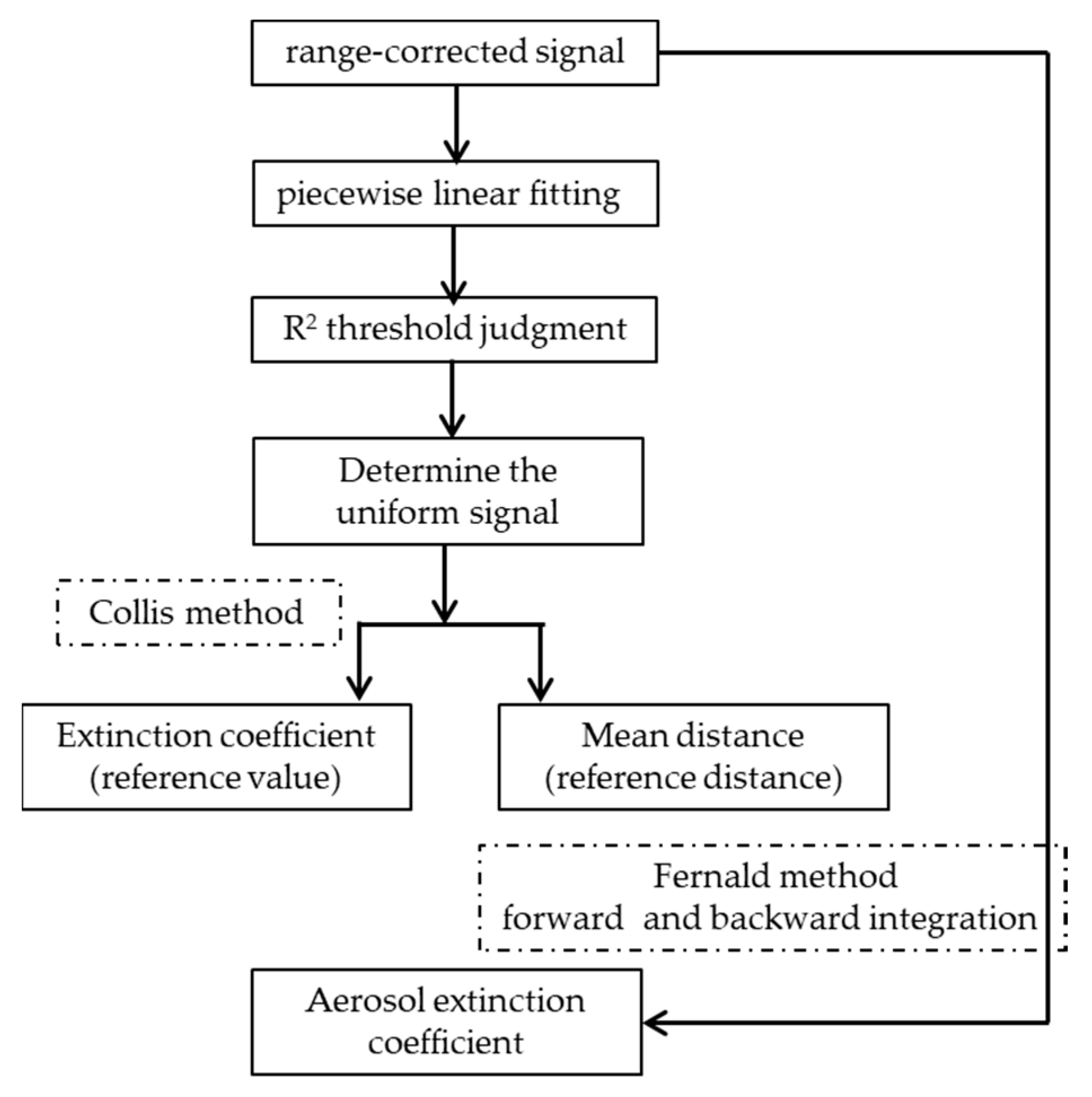
3.2. Horizontal Retrieval Method
- Determined the signal with uniform distribution in each LiDAR signal. The judging criteria indicated that, within a certain distance (taking 19 detection points as an example), the range-corrected signal was approximately linear with the distance change, and the goodness of fit (R2) was larger than 0.9.
- Calculated the mean extinction coefficient of the segmented LiDAR signal by using the Collis slope method.
- The extinction coefficient calculated in (B) was used as the initial value , and the midpoint of the distance in (A) was used as the reference point The two values were then incorporated into the Fernald formula to retrieve the atmospheric aerosol extinction coefficient.
- The aerosol extinction coefficients at the distance exceeding and those at the distance shorter than were obtained by Equations (1) and (2), respectively.
4. Results
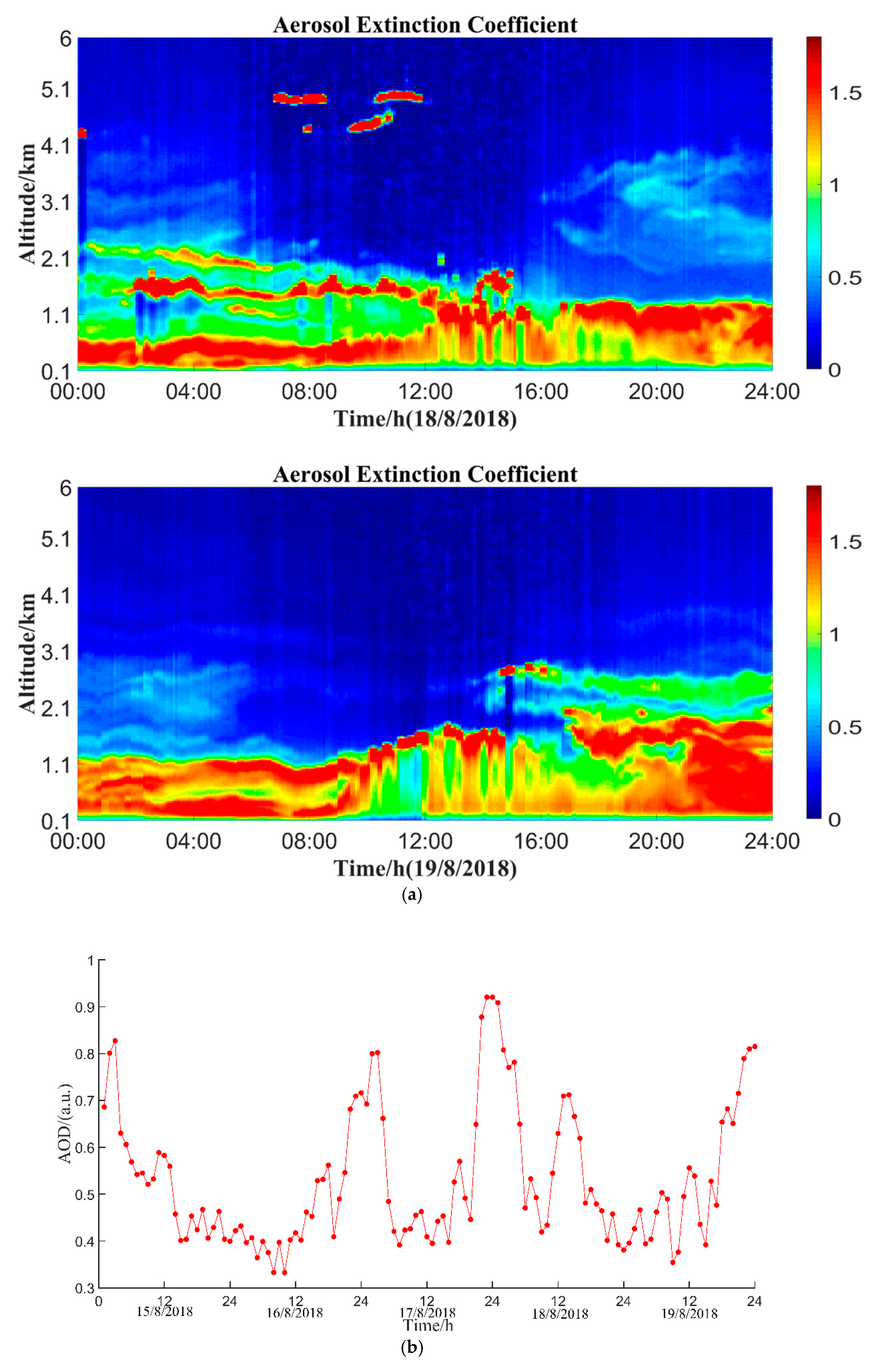
4.1. Analysis of Aerosol Vertical Distribution
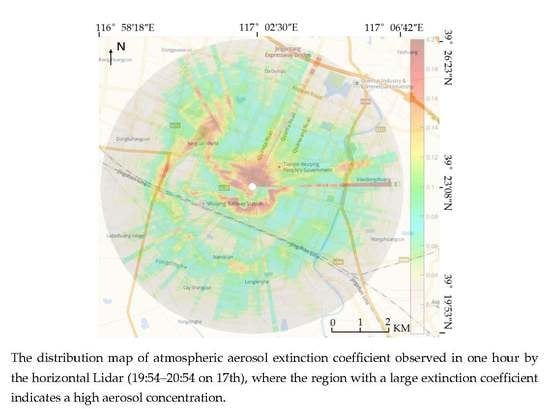
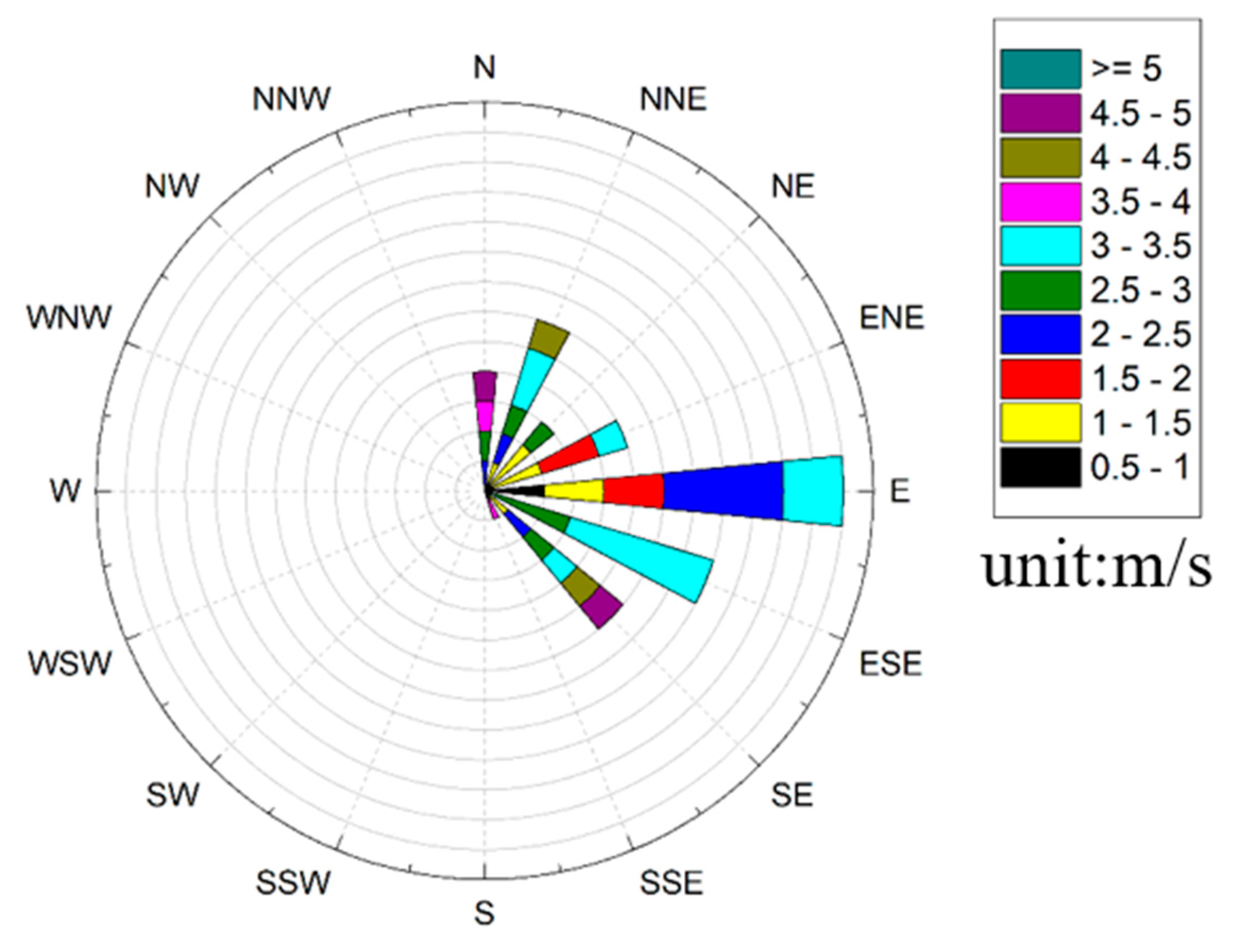
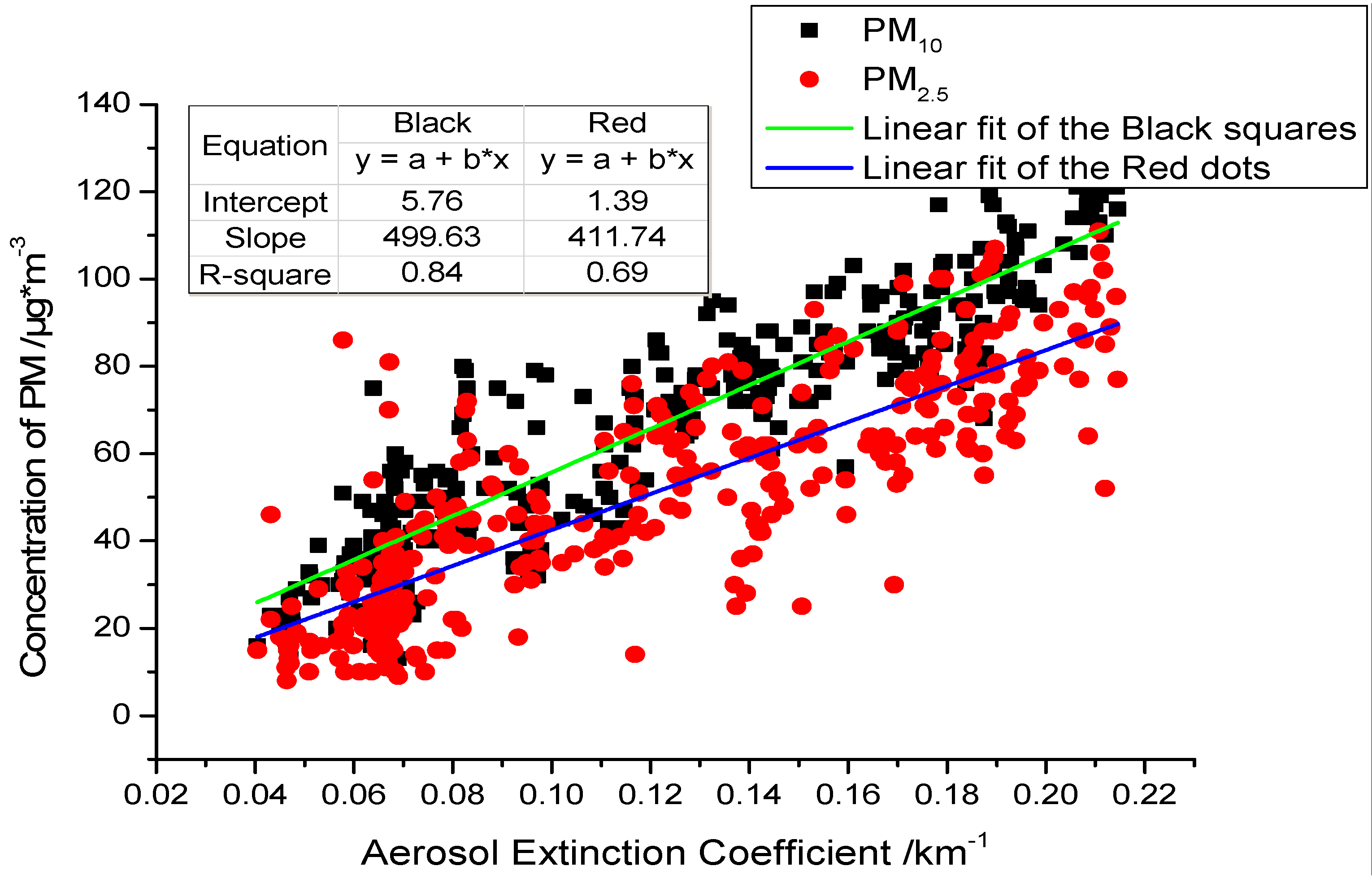
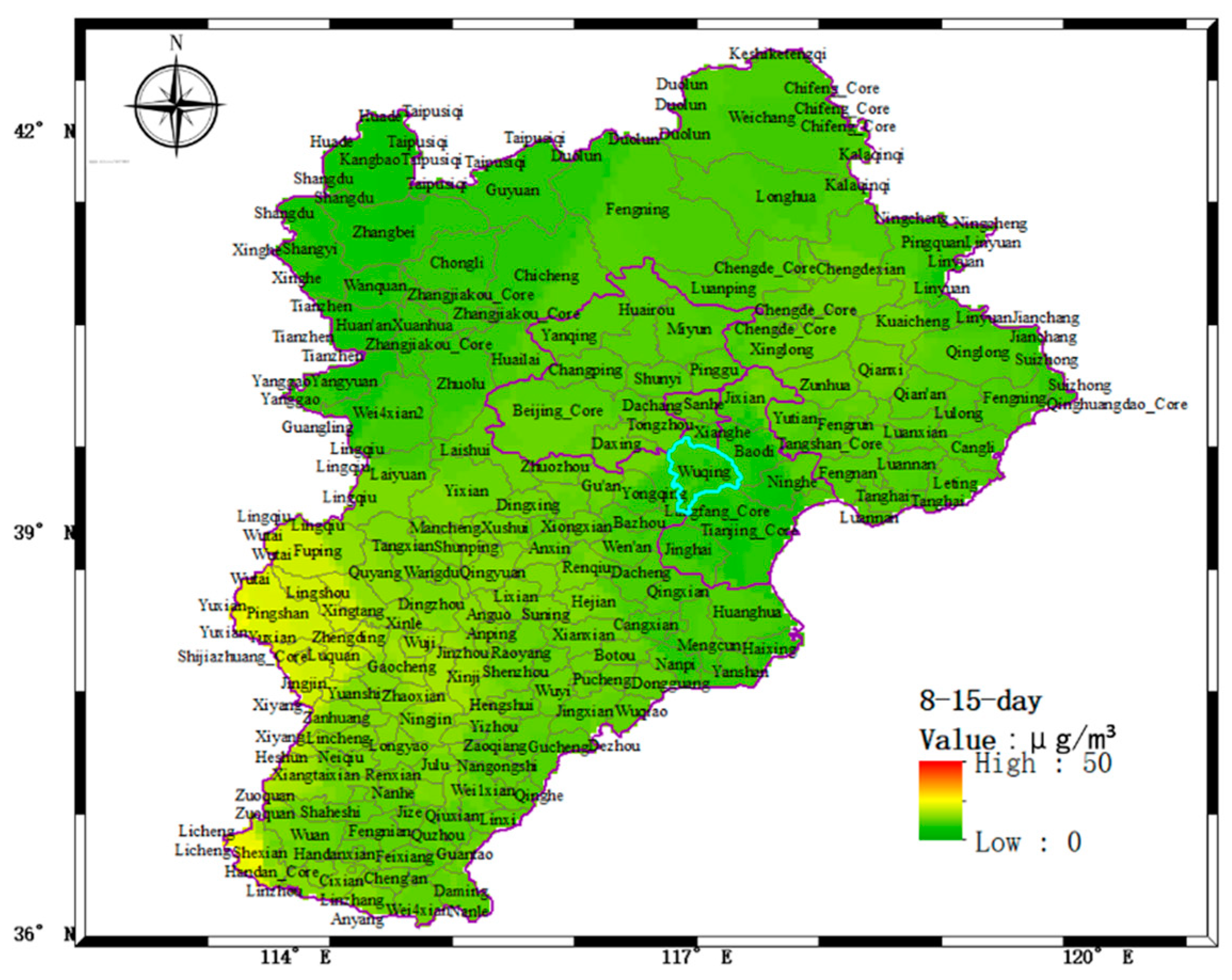
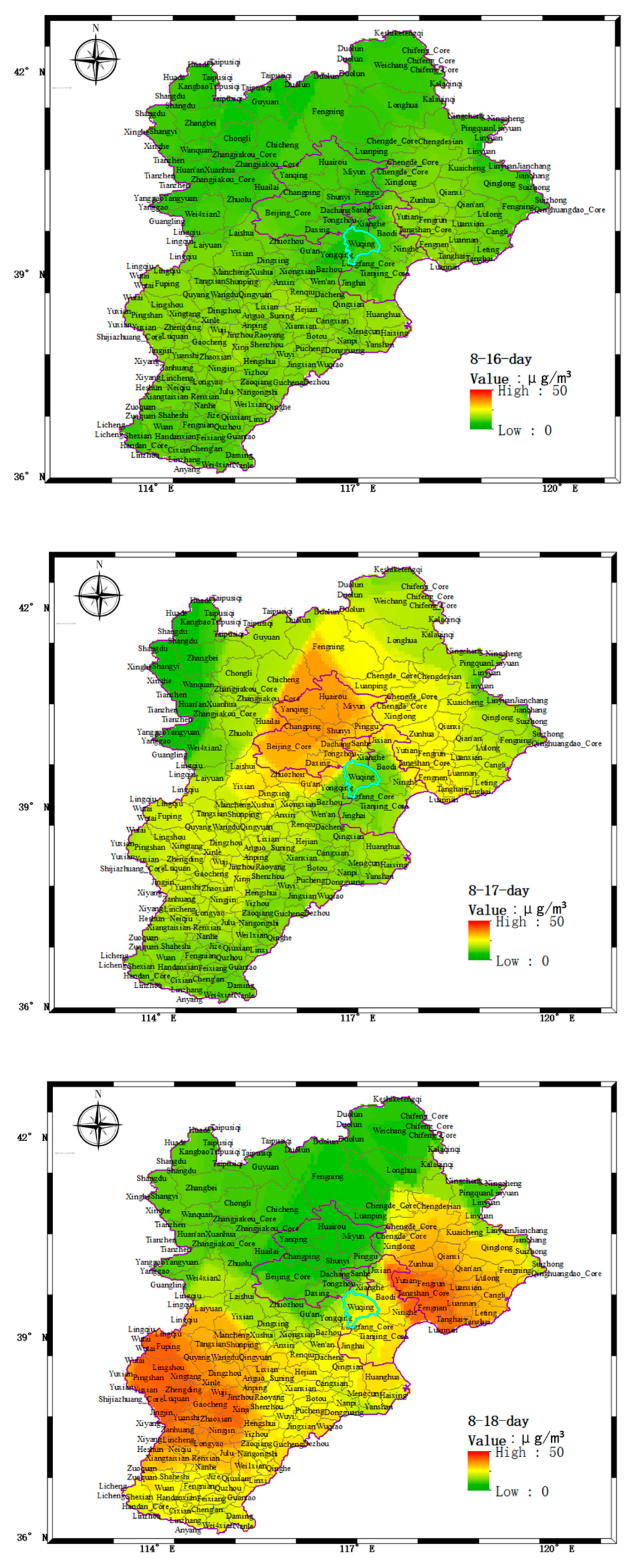
4.2. Horizontal Scanning to Monitor the Distribution of Aerosol Pollution Sources
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
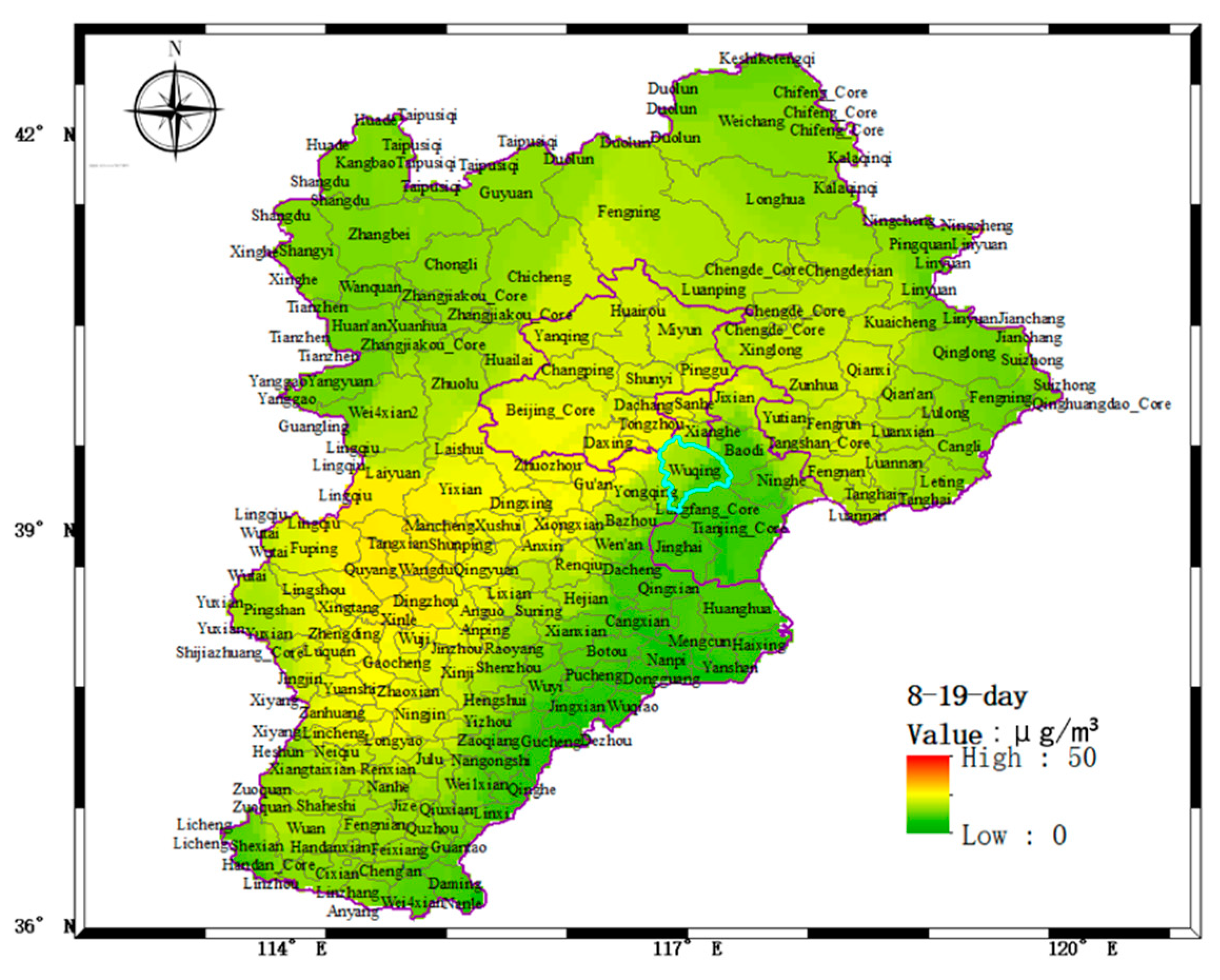
- On 17–19 August 2018, the particulate matter pollutants in Wuqing District were mainly from the local area. The particulate matter mainly accumulated at 2.0 km and the boundary layer height also changed around 1 to 2 km.
- The distribution of aerosol pollution in the scanning area was obtained by using the horizontal scanning LiDAR positioned on the top of a building to obtain the horizontal distribution result of aerosol.
- Using the LiDAR network observation and combining the satellite and ground-integrated observation mode in a certain area was conducive to the study of the regional distribution characteristics of pollutants and the cross-boundary transport of pollutant air masses. Providing reliable data support for regional atmospheric defense joint control policies and means was also beneficial to this study.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pöschl, U. Atmospheric aerosols: Composition, transformation, climate and health effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heal, M.R.; Kumar, P.; Harrison, R.M. Particles, air quality, policy and health. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6606–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandyck, T.; Keramidas, K.; Kitous, A.; Spadaro, J.V.; Van Dingenen, R.; Holland, M.; Saveyn, B. Air quality co-benefits for human health and agriculture counterbalance costs to meet Paris Agreement pledges. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Tong, D.; Davis, S.J.; Zhao, H.; Geng, G.; Feng, T.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade. Nature 2017, 543, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.L.; Wiegner, M.; Flentje, H.; Mattis, I.; Wagner, F.; Gasteiger, J.; Geiß, A. Evaluation of ECMWF-IFS (version 41R1) operational model forecasts of aerosol transport by using ceilometer network measurements. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 3807–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Hu, M.; Zamora, M.L.; Peng, J.; Shang, D.; Zheng, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, Z.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L. Elucidating severe urban haze formation in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17373–17378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Ji, D.; Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Hu, B.; Xin, J. Mechanism for the formation of the January 2013 heavy haze pollution episode over central and eastern China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K. Biomass burning sources and their contributions to the local air quality in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K. Aerosol optical depths and their contributing sources in Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Chan, K.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Y.; Fan, G. Observations of the summertime atmospheric pollutants vertical distributions and the corresponding ozone production in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 2017, 14275–14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Retalis, A.; Flocas, H.A. Particulate matter estimation from photochemistry: A modelling approach using neural networks and synoptic clustering. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2067–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Xu, H.; Gong, W.; Liu, J.; Du, J.; Ma, X.; Liang, A. Feasibility Study on Measuring Atmospheric CO2 in Urban Areas by Using Spaceborne CO2-IPDA LIDAR. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Ma, X.; Liang, A.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gong, W. Performance Evaluation for China’s Planned CO2-IPDA. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X. Hyperspectral Target Detection via Adaptive Information-Theoretic Metric Learning with Local Constraints. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Dimensionality Reduction and Classification of Hyperspectral Images Using Ensemble Discriminative Local Metric Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2509–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shi, T.; Xu, H.; He, B.; Qiu, R.; Han, G.; Gong, W. On-line wavenumber optimization for a ground-based CH4-DIAL. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 229, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wu, S.; Song, X. Depolarization ratio profiles calibration and observations of aerosol and cloud in the Tibetan Plateau based on polarization Raman lidar. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, C. Denoising and retrieval algorithm based on a dual ensemble Kalman filter for elastic lidar data. Opt. Commun. 2019, 433, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Che, H.; Qi, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, H. Characterization of vertical distribution and radiative forcing of ambient aerosol over the Yangtze River Delta during 2013–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1846–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, V.; Balis, D.; Bösenberg, J.; Eixmann, R.; Iarlori, M.; Komguem, L.; Mattis, I.; Papayannis, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Perrone, M. Vertical aerosol distribution over Europe: Statistical analysis of Raman lidar data from 10 European Aerosol Research Lidar Network (EARLINET) stations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, K.; Sreekanth, V.; Madhavan, B.; Krishna Moorthy, K. Wintertime aerosol characteristics at a north Indian site Kharagpur in the Indo-Gangetic plains located at the outflow region into Bay of Bengal. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, H.; Shentu, G.; Shangguan, M.; Xia, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Pelc, J.S.; Fejer, M.; Zhang, Q. Long-range micro-pulse aerosol lidar at 1.5 μm with an upconversion single-photon detector. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Li, X.; Qin, W.; Cui, S.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Q. Retrieval of horizontal distribution of aerosol mass concentration by micro pulse lidar. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2017, 25, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Li, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, X. Monitoring the distributed point pollution sources based on a scanning Lidar. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 4078–4084. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, J.; Han, Y.; Huang, S.; Sun, D.; Zheng, J.; Han, F.; Zhou, A.; Yang, S.; Xu, W.; Song, Q. Novel Lidar algorithm for horizontal visibility measurement and sea fog monitoring. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 34853–34863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Xia, M.; Ge, Y.; Guo, W.; Yang, K. On-site ocean horizontal aerosol extinction coefficient inversion under different weather conditions on the Bo-hai and Huang-hai Seas. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 177, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, G.; Xu, C.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y. Optical and hygroscopic properties of Asian dust particles based on a horizontal Mie lidar: Case study at Hefei, China. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2017, 15, 020102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Bilal, M.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, G. The Characteristics of the Aerosol Optical Depth within the Lowest Aerosol Layer over the Tibetan Plateau from 2007 to 2014. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Wong, M.S. Vertical Profiling of Aerosol Optical Properties From LIDAR Remote Sensing, Surface Visibility, and Columnar Extinction Measurements. Remote Sensing of Aerosols, Clouds, and Precipitation; Academic Press, Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, T.; Boiyo, R.; Chen, S.; Lu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Vertical Structures of Dust Aerosols over East Asia Based on CALIPSO Retrievals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaestner, M. Lidar inversion with variable backscatter/extinction ratios: Comment. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, 833–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klett, J.D. Lidar inversion with variable backscatter/extinction ratios. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klett, J.D. Stable analytical inversion solution for processing lidar returns. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, G.J.; de Leeuw, G. Inversion of lidar signals with the slope method. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasano, Y.; Nakane, H. Significance of the extinction/backscatter ratio and the boundary value term in the solution for the two-component lidar equation. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorg, A. The extinction-to-backscatter ratio of tropospheric aerosol: A numerical study. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Lu, D.; Pan, W. A New Method for Aerosol Retrieval Based on Lidar Observations in Beijing. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2014, 7, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Miffre, A.; Chacra, M.; Geffroy, S. Aerosol load study in urban area by Lidar and numerical model. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Mao, F.; Du, L.; Pan, Z.; Gong, W.; Fang, S. Deriving hourly PM2.5 concentrations from himawari-8 aods over beijing–tianjin–hebei in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. Validation of OMI HCHO Products Using MAX-DOAS observations from 2010 to 2016 in Xianghe, Beijing: Investigation of the Effects of Aerosols on Satellite Products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Mao, F.; Wang, W.; Logan, T.; Hong, J. Examining Intrinsic Aerosol-Cloud Interactions in South Asia Through Multiple Satellite Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 11–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Mao, F.; Guo, J.; Wang, W.; Pan, Z.; Shen, H.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Z. Estimation of spatiotemporal PM1.0 distributions in China by combining PM2.5 observations with satellite aerosol optical depth. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Mao, F.; Pan, Z.; Gong, W.; Wang, W.; Tian, L.; Fang, S. Three-dimensional physical and optical characteristics of aerosols over central China from long-term CALIPSO and HYSPLIT Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Vertical LiDAR | Horizontal LiDAR |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 1064 nm | 1064 nm |
| Pulse energy | >100 μJ | >20 μJ |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 2.5 kHz | 10 kHz |
| Telescope diameter | 100 mm | 100 mm |
| FOV | <1 mrad | <0.2 mrad |
| Range resolution | 30 m | 15 m |
| Detection blind zone | 100 m | 150 m |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Han, G.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, J. Regional Atmospheric Aerosol Pollution Detection Based on LiDAR Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202339
Ma X, Wang C, Han G, Ma Y, Li S, Gong W, Chen J. Regional Atmospheric Aerosol Pollution Detection Based on LiDAR Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(20):2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202339
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xin, Chengyi Wang, Ge Han, Yue Ma, Song Li, Wei Gong, and Jialin Chen. 2019. "Regional Atmospheric Aerosol Pollution Detection Based on LiDAR Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 11, no. 20: 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202339
APA StyleMa, X., Wang, C., Han, G., Ma, Y., Li, S., Gong, W., & Chen, J. (2019). Regional Atmospheric Aerosol Pollution Detection Based on LiDAR Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 11(20), 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202339