Spatio-Temporal Variations of Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Relationship with Climatic Factors in the Songnen Plain, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
MODIS and Meteorological Data
2.3. Estimating NPP with the CASA Model
2.4. Calculation of CUE
2.5. Extraction of Land Surface Phenology Metrics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
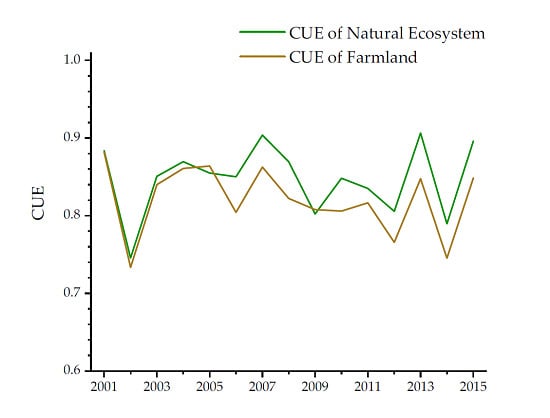
3.1. Monthly Change of CUE
3.2. Seasonal Changes in CUE
3.3. The Mean Spatial Distribution of LSP
3.4. Response of CUE to LSP Variation
3.5. Direct Effects of Local Climate Factors on CUE Change
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, H.; Adams, J. Global pattern of NPP to GPP ratio derived from MODIS data: Effects of ecosystem type, geographical location and climate. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wang, P.; Chang, S.; Li, B. Rain use efficiency changes and its effects on land surface phenology in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. In Proceedings of the SPIE Remote Sensing 2018, Berlin, Germany, 11–12 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Carvalhais, N.; Moura, C.; Ahrens, B.; Koirala, S.; Fan, S.; Guan, F.; Zhang, W.; Gao, S.; Magliulo, V.; et al. Global variability of carbon use efficiency in terrestrial ecosystems. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delucia, E.; Drake, J.; Thomas, R.; Gonzalez, M. Forest carbon use efficiency: Is respiration a constant fraction of gross primary production? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyssaert, S.; Inglima, I.; Jung, M.; Richardson, A.; Reichsteins, M.; Papale, D.; Piao, S.; Schulzes, E.; Wingate, L.; Matteucci, G. CO2 balance of boreal, temperate, and tropical forests derived from a global database. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 2509–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Jian, Y.; Wimberly, M.; Zhang, X.; Jian, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, J. Climate-driven global changes in carbon use efficiency. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campioli, M.; Gielen, B.; Gockede, M.; Papale, D.; Bouriaud, O.; Granier, A. Temporal variability of the NPP-GPP ratio at seasonal and interannual time scales in a temperate beech forest. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2481–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, J.; Tribuzy, E.; Toledo, L. Rrepiration from a tropical forest ecosystem: Partitioning of sources and low carbon use efficiency. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, S72–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amthor, J. The McCree–de Wit–Penning de Vries–Thornley Respiration Paradigms: 30 Years Later. Ann. Bot. 2000, 86, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Hu, Z.; Shao, Q.; Harris, W. Comparison of evapotranspiration components and water-use efficiency among different land use patterns of temperate steppe in the Northern China pastoral-farming ecotone. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 60, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, J. Modeling the water use efficiency of soybean and maize plants under environmental stresses: Application of a synthetic model of photosynthesis-transpiration based on stomatal behavior. J. Plant Physiology 2004, 161, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Wang, S. Forest annual carbon cost: A global-scale analysis of autotrophic respiration. Ecology 2010, 91, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Piao, S.; Li, X.; Chen, A.; Qin, D. Global patterns of vegetation carbon use efficiency and their climate drivers deduced from MODIS satellite data and process-based models. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noormets, A. (Ed.) Phenology of Ecosystem Processes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.; Keenan, T.; Migliavacca, M.; Ryu, Y.; Sonnentag, O.; Toomey, M. Climate change, phenology, and phenological control of vegetation feedbacks to the climate system. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ying, W.; Zhen, Z.; Magliulo, V.; Min, C. Phenology plays an important role in the regulation of terrestrial ecosystem water-use efficiency in the Northern Hemisphere. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J. Evaluation of vegetation phenology remote sensing identification method based on carbon exchange data of flux tower net ecosystem. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Huang, F.; Zhai, H. Monitoring spatio-temporal changes of terrestrial ecosystem soil water use efficiency in Northeast China using time series remote sensing data. Sensors 2019, 19, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, F.; Chang, S.; Sun, N. The variations of satellite-based ecosystem water use and carbon use efficiency and their linkages with climate and human drivers in the Songnen Plain, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 8659138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. Land use/cover change and its driving forces of west of Songnen Plain. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 17, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Guo, Q. Application of CASA model to the estimation of Chinese terrestrial net primary productivity. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 2001, 25, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; He, H.; Yu, D.; Hu, H. Simulation of maximum light utilization rate of typical vegetation in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Han, J.; Ren, C. Temporal and spatial patterns and driving factors of vegetation NPP in Northeast China from 1982 to 2010. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, M. Estimation of vegetation net primary productivity and carbon sink in western jilin province based on CASA model. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Li, H.; Desai, A.; Nagy, Z.; Luo, J.; Kolb, T.; Olioso, A.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Kutsch, W. How is water-use efficiency of terrestrial ecosystems distributed and changing on Earth? Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Duan, H.; Feng, J. Drought events and its influence in spring of 2012 in China. J. Arid Meteorol. 2012, 30, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, L. Carbon-use efficiency of terrestrial ecosystems under stress conditions in Southeast Europe (MODIS, NASA). Proceedings 2018, 2, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, S. A general model of forest ecosystem processes for regional applications I. Hydrologic balance, canopy gas exchange and primary production processes. Ecol. Model. 1988, 42, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, R. The global carbon cycle: A viewpoint on the missing sink. Funct. Plant Biol. 1994, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, R.; Medlyn, B.; Mcmurtrie, R. Acclimation of the respiration/photosynthesis ratio to temperature: Insights from a model. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 5, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Yuste, J.; Janssens, I.; Roskams, P.; Nachtergale, L.; Carrara, A.; Sanchez, B.Y.; Ceulemans, R. Above- and belowground biomass and net primary production in a 73-year-old scots pine forest. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.; Elagib, N.; Ribbe, L.; Schneider, K. Spatio-temporal variations in climate, primary productivity and efficiency of water and carbon use of the land cover types in Sudan and Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 790–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, A.; Kelliher, F.; McSeveny, T.; Byers, J. Net ecosystem productivity, net primary productivity and ecosystem carbon sequestration in a pinus radiata plantation subject to soil water deficit. Tree Physiol. 1998, 18, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotelli, D.; Montagnani, L.; Manca, G.; Tagliavini, M. Net primary productivity, allocation pattern and carbon use efficiency in an apple orchard assessed by integrating eddy-covariance, biometric and continuous soil chamber measurements. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3089–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, L.E.; Subke, J.A.; Sommerkorn, M.; Sloan, V.; Ducrotoy, H.; Phoenix, G.K.; Williams, M. The role of mosses in carbon uptake and partitioning in arctic vegetation. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, B.; Falge, E.; Gu, L.; Baldocchi, D.; Bakwin, P.; Berbigier, P.; Davis, K.; Dolman, A.; Falk, M.; Fuentes, J. Environmental controls over carbon dioxide and water vapor exchange of terrestrial vegetation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 113, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Duan, H.; Feng, J. Drought events and its influence in autumn of 2014 in China. J. Arid Meteorol. 2014, 32, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.; Gray, J.; Friedl, M.; Toomey, M.; Bohrer, G. Net carbon uptake has increased through warming-induced changes in temperate forest phenology. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.; Linder, S.; Vose, J.; Hubbard, R. Dark respiration of pines. Ecol. Bull 1994, 43, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.; Crowther, T. Carbon use efficiency and storage in terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P. Description of the “Triffid” Dynamic Global Vegetation Model. Hadley Centre Technical Note. 2001. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/245877262_Description_of_the_TRIFFID_dynamic_global_vegetation_model/related (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- Giardina, C.P.; Ryan, M.G.; Binkley, D.; Fownes, J.H. Giardina, Primary production and carbon allocation in relation to nutrient supply in a tropical experimental forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Han, Z.; Huang, C.; Tan, Z. Remote sensing monitoring on dynamic of sandy desertification degree in Horqin sandy land at the beginning of 21st century. J. Desert Res. 2007, 27, 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, C.; Song, G. The dynamic monitoring of desertification in Horqin sandy land on the basis of MODIS NDVI. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2009, 21, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Dataset | Source | Temporal Resolution | Time Range | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPP | MOD17 | 8-day composite | 2001–2015 | 1 km |
| Land cover | MCD12Q1 | annual | 2001–2015 | 1 km |
| NDVI | MOD13 | 16-day composite | 2001–2015 | 0.25 km |
| Temperature | http://data.cma.cn/ | monthly | 2001–2015 | / |
| Precipitation | http://data.cma.cn/ | monthly | 2001–2015 | / |
| Solar radiation | http://data.cma.cn/ | monthly | 2001–2015 | / |
| Month | Positive Pixels (%) | Negative Pixels (%) |
|---|---|---|
| May | 67,293 (91.60%) | 6170 (8.40%) |
| June | 58,717 (79.93%) | 14,746 (20.07%) |
| July | 49,180 (66.95%) | 24,283 (33.05%) |
| August | 61,691 (83.98%) | 11,772 (16.02%) |
| September | 69,366 (94.42%) | 4097 (5.58%) |
| October | 44,115 (60.05%) | 29,348 (39.95%) |
| November | 20,398 (27.77%) | 53,065 (72.23%) |
| Month | Positive Pixels (%) | Negative Pixels (%) |
|---|---|---|
| May | 25,181 (34.28%) | 48,282 (65.72%) |
| June | 48,525 (66.05%) | 24,938 (33.95%) |
| July | 43,585 (59.33%) | 29,878 (40.67%) |
| August | 39,588 (53.89%) | 33,875 (46.11%) |
| September | 7667 (10.44%) | 65,796 (89.56%) |
| October | 38,603 (52.55%) | 34,860 (47.45%) |
| November | 72,078 (98.11%) | 1385 (1.89%) |
| Ecosystem | Time Scale | CUE | Scale | Type of Data | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WET | Annual | 0.607 ± 0.133 | Global | Site data | Tang [3] |
| Annual | 0.550–0.60 | Sudan and Ethiopia | Remote sensing data | Khalifa [32] | |
| Annual | 0.542 | SNP | Remote sensing data | Li [19] | |
| Growing season | 0.488 | SNP | Remote sensing data | Our article | |
| GRA | Annual | 0.457 ± 0.109 | Global | Site data | Tang |
| Annual | 0.220–0.560 | Sudan and Ethiopia | Remote sensing data | Khalifa | |
| Annual | 0.567 | SNP | Remote sensing data | Li | |
| Growing season | 0.482 | SNP | Remote sensing data | Our article | |
| MF | Annual | 0.464 ± 0.127 | Global | Site data | Tang |
| Annual | 0.350–0.480 | Sudan and Ethiopia | Remote sensing data | Khalifa | |
| Annual | 0.480 | SNP | Remote sensing data | Li | |
| Growing season | 0.530 | SNP | Remote sensing data | Our article | |
| DBF | Annual | 0.464 ± 0.127 | Global | Site data | Tang |
| Annual | 0.340–0.420 | Sudan and Ethiopia | Remote sensing data | Khalifa | |
| Annual | 0.479 | SNP | Remote sensing data | Li | |
| Growing season | 0.477 | SNP | Remote sensing data | Our article |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Huang, F.; Qin, L.; Qi, H.; Sun, N. Spatio-Temporal Variations of Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Relationship with Climatic Factors in the Songnen Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2513. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212513
Li B, Huang F, Qin L, Qi H, Sun N. Spatio-Temporal Variations of Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Relationship with Climatic Factors in the Songnen Plain, China. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(21):2513. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212513
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bo, Fang Huang, Lijie Qin, Hang Qi, and Ning Sun. 2019. "Spatio-Temporal Variations of Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Relationship with Climatic Factors in the Songnen Plain, China" Remote Sensing 11, no. 21: 2513. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212513
APA StyleLi, B., Huang, F., Qin, L., Qi, H., & Sun, N. (2019). Spatio-Temporal Variations of Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Relationship with Climatic Factors in the Songnen Plain, China. Remote Sensing, 11(21), 2513. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212513