SAR Target Recognition via Joint Sparse and Dense Representation of Monogenic Signal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
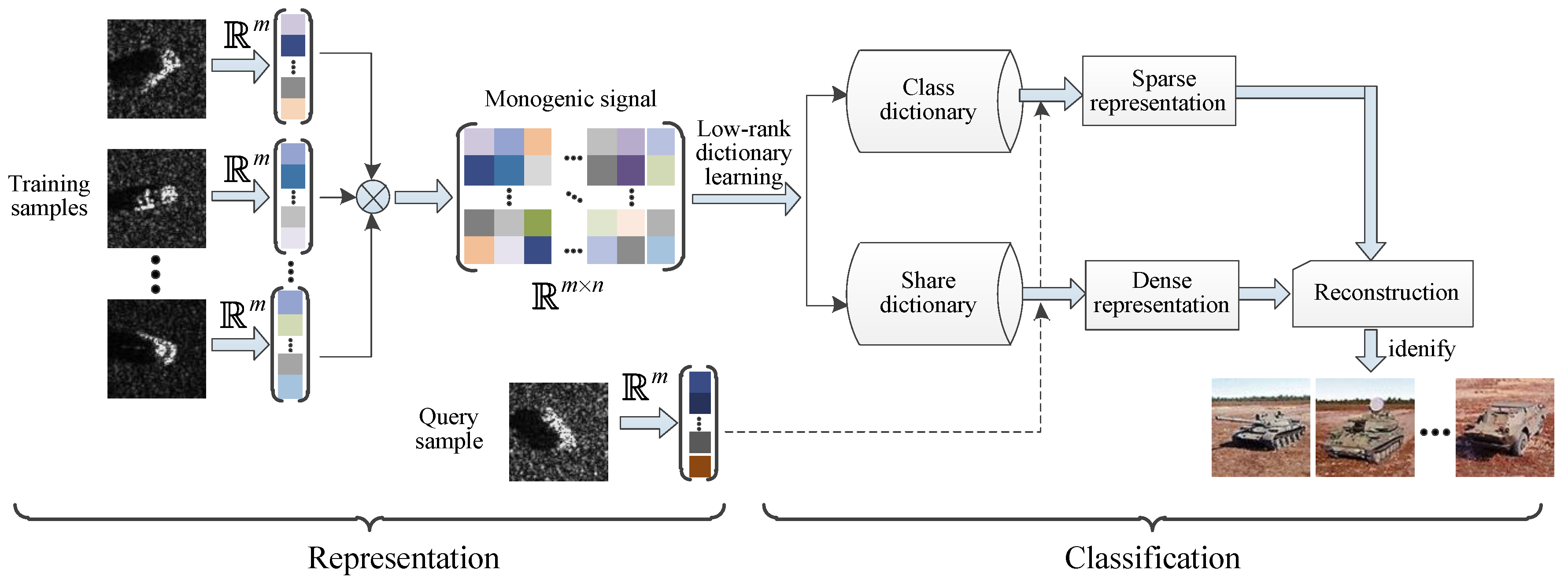
2. The Proposed Strategy
2.1. The Monogenic Signal
2.2. Low-Rank Dictionary Learning
| Algorithm 1 The procedure of solving the optimization problem in Equation (17). |
| Input: the monogenic features of training sample matrix class dictionary , shared dictionary parameters and , and threshold . Output: dense coefficient matrix . Initialization: . While not converged do Update by fixing Update by fixing Update Lagrange multiplier Update through Check convergence: if , then stop. End |
2.3. Implementation of Target Recognition
| Algorithm 2 Target recognition via joint sparse and dense representation of monogenic signal (JMSDR). |
| Input: training sample and query sample . Output: class label of . Step 1: Compute multi-scale monogenic features of training samples . Step 2: Compute multi-scale monogenic features of query sample . Step 3: Learn a shared dictionary and a class dictionary with Equation (9). Step 4: Compute the sparse representation and the dense representation of query sample over the learned dictionary, as shown in Equation (23). Step 5: Predict the identity by seeking the minimal reconstruction error, as defined in Equation (25). |
3. Experiments and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Verification
3.2. Results on 10-Class
3.3. Results on Configuration Variance
3.4. Results on Version Variance
3.5. Results on Noise Corruption
3.6. Results on Partial Occlusion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quan, S.; Xiang, D.X.B.K.G. Derivation of the Orientation Parameters in Built-up Areas: With Application to Model-based Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 56, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, S.; Yu, M.; Kuang, G. Adaptive and fast prescreening for SAR ATR via change detection technique. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 12, 4714–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Kuang, G.; Wang, N.; Wang, W. Classification via sparse representation of steerable wavelet frames on grassmann manifold: Application to target recognition in SAR image. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 2017, 26, 2892–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Xu, B.; Yang, J. SAR Target Recognition via Supervised Discriminative Dictionary Learning and Sparse Representation of the SAR-HOG Feature. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osullivan, J.A.; Devore, M.D.; Kedia, V.S.; Miller, M.I. SAR ATR performance using a conditionally Gaussian model. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2001, 37, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossing, J.C.; Ross, T.D. An Evaluation of SAR ATR Algorithm Performance Sensitivity to MSTAR Extended Operating Conditions. Proc. SPIE 1998, 3370, 554–565. [Google Scholar]
- Umamahesh, S.; Vishal, M. SAR automatic target recognition using discriminative graphical modals. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 591–606. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, L.M.; Owirka, G.J.; Netishen, C.M. Performance of a high-resolution Polarimetric SAR Automatic Target Recognition System. Linc. Lab. J. 1993, 6, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Y.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, B. SAR target configuration recognition using tensor global and local discriminant embedding. IEEE Geosc. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.T.; Zhao, L.J.; Zhao, S.Q.; Xiong, B.L.; Kuang, G.Y. SAR target reconition using parametric supervised t-stochastic neighbor embedding. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Dong, G.; Fan, H.; Kuang, G. SAR Target Recognition via Local Sparse Representation of Multi-Manifold Regularized Low-Rank Approximation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 211. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.Y.; Wen, G.J.; Huang, X.H.; Ma, C.H.; Yang, X.L. Data augmentation by multilevel reconstruction using attributed scattering center for SAR target recognition. IEEE Geosc. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Shi, Z.G.; Cheng, X.; Fu, Q. Automatic target recognition of SAR images based on global scattering center model. IEEE Trans. Geosc. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3713–3729. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Wang, N.; Kuang, G. Sparse representation of monogenic signal: With application to target recognition in SAR images. IEEE Signal Proc. Lett. 2014, 21, 952–956. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Kuang, G.; Wang, N.; Zhao, L.; Lu, J. SAR target recognition via joint sparse representation of monogenic signal. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3316–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, M.; Cao, Z.; Pi, Y. SAR Image Recognition with Monogenic Scale Selection-Based Weighted Multi-task Joint Sparse Representation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cao, R.; Feng, J. SAR Target Recognition via Joint Sparse Representation of Monogenic Components with 2D Cannonical Correlation Analysis. IEEE ACCESS 2019, 7, 25815–25826. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, I.; Sprechmann, P.; Sapiro, G. Classification and clustering via dictionary learning with structured incoherence and shared features. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3501–3508. [Google Scholar]
- Mairal, J.; Bach, F.; Ponce, J.; Sapiro, G. Online Learning for Matrix Factorization and Sparse Coding. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 19–60. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Davis, L.S. Label Consistent K-SVD: Learning a Discriminative Dictionary for Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 2651–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Wang, N.; Kuang, G.; Qiu, H. Sparsity and Low-Rank Dictionary Learning for Sparse Representation of Monogenic Signal. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Hu, J.; Guo, J. Extended SRC: Undersampled Face Recognition via Intraclass Variant Dictionary. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Hu, J.; Guo, J. In Defense of Sparsity Based Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Lai, J. Sparse and Dense Hybrid Representation via Dictionary Decomposition for Face Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, M.; Luo, G.; Kong, X. Coupled Dictionary Learning for Target Recognition in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otazo, R.; Candes, E.J.; Sodickson, D.K. Low rank plus sparse matrix decomposition for accelerated dynamic MRI with separation of background and dynamic components. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Wei, C.P.; Wang, Y.C.F. Low-rank matrix recovery with structural incoherence for robust face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Biondi, F. Low rank plus sparse decomposition of synthetic aperture radar data for maritime surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Workshop on Compressed Sensing Theory and its Applications to Radar, Sonar and Remote Sensing (CoSeRa), Aachen, Germany, 19–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich, M.; Papanicolaou, G.; Tsogka, C. Low rank plus sparse decomposition of synthetic aperture radar data for target imaging and tracking. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.02311. [Google Scholar]
- Felsberg, M.; Duits, R.; Florack, L. The Monogenic Scale Space on a Rectangular Domain and its Features. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2005, 64, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, L. Infrared Small Target Detection via Modified Random Walks. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.; Kwan, C.; Bernabe, S.J.; Plaza, A.; Koperski, K. A Joint Sparsity Approach to Soil Detection Using Expanded Bands of WV-2 Images. IEEE Geosc. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roweis, S.T.; Saul, L.K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 2000, 290, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.J.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Wright, J. Robust principal component analysis. J. ACM 2011, 58, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, M. The Concentration of Measure Phenomenon. Mathematical Surveys and Monographs. 2001, Volume 89. Available online: http://www.ams.org/books/surv/089/ (accessed on 14 November 2019).
- Lin, Z.; Chen, M.; Yi, M. The Augmented Lagrange Multiplier Method for Exact Recovery of Corrupted Low-Rank Matrices. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1009.5055. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Lei, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, D. Fisher Discrimination Dictionary Learning for sparse representation. Proceedings 2011, 24, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.H.; Monga, V. Learning a low-rank shared dictionary for object classification. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.00310. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Feng, X.; Jin, Y.Q. Target Classification Using the Deep Convolutional Networks for SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.D.; Worrell, S.W.; Velten, V.J.; Mossing, J.C.; Bryant, M.L. Standard SAR ATR evaluation experiments using the MSTAR public release data set. Proc. SPIE 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Bhanu, B. Recognition of articulated and occluded objects. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1999, 21, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
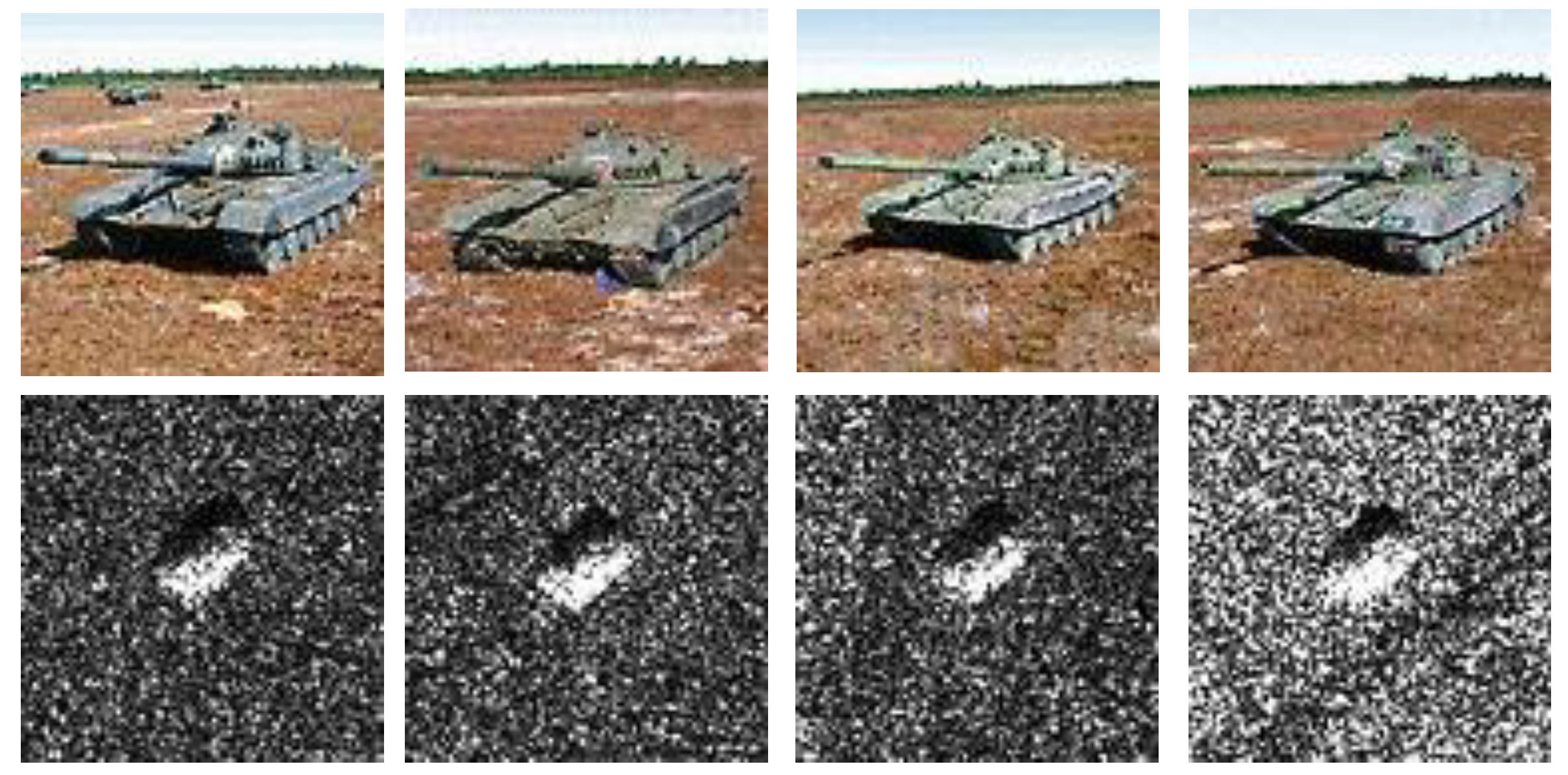











| Type | Depr. | BMP2 | BTR60 | T72 | T62 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 17° | 233(SN_9563) | 256 | 233(SN_132) | 299 | 1020 |
| Testing | 15° | 195(SN_9563) 196(SN_9566) 196(SN_C21) | 195 | 196(SN_132) 195(SN_812) 195(SN_S7) | 273 | 1637 |
| Method | MSRC | FDDL | ESRC | LRSDL | SSRC | JMSDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.9096 | 0.8931 | 0.9198 | 0.9023 | 0.9267 | 0.9318 |
| Depr. | BMP2 | BTR70 | T72 | 2S1 | BRDM | BTR60 | D7 | T62 | ZIL | ZSU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17° | 233(SN_9563) | 233 | 233(SN_132) | 299 | 298 | 256 | 299 | 299 | 299 | 299 |
| 15° | 196(SN_9566) 196(SN_c21) | 196 | 195(SN_812) 191(SN_s7) | 274 | 274 | 195 | 273 | 273 | 274 | 274 |
| Method | MSRC | FDDL | ESRC | LRSDL | SSRC | A-ConvNets | JMSDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.9279 | 0.8868 | 0.9317 | 0.9168 | 0.9420 | 0.9552 | 0.9356 |
| Method | MSRC | FDDL | ESRC | LRSDL | SSRC | A-ConvNets | JMSDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.8852 | 0.8812 | 0.8967 | 0.8949 | 0.9109 | 0.9436 | 0.9213 |
| Type | BMP2 | BTR60 | T72 | T62 | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMP2 | 358 | 4 | 28 | 2 | 0.9132 |
| BTR60 | 2 | 180 | 2 | 11 | 0.9230 |
| T72 | 0 | 1 | 339 | 46 | 0.8782 |
| T62 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 271 | 0.9926 |
| Average | 0.9213 |
| Type | Depr. | BMP2 | BRDM | BTR70 | T72 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 17° | 233(SN_C21) | 298(SN_E71) | 233(SN_C71) | 232(SN_132) | 996 |
| Testing | 15° | 428(SN_9563) | 0 | 0 | 426(SN_812) | 3568 |
| 573(SN_A04) | ||||||
| 428(SN_9566) | 573(SN_A05) | |||||
| 573(SN_A07) | ||||||
| 573(SN_A10) |
| Method | MSRC | FDDL | ESRC | LRSDL | SSRC | A-ConvNets | JMSDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.9148 | 0.9176 | 0.9403 | 0.9190 | 0.9279 | 0.9770 | 0.9543 |
| Type | Depr. | BMP2 | BRDM | BTR70 | T72 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 17° | 233(SN_C21) | 298(SN_E71) | 233(SN_C71) | 232(SN_132) | 996 |
| Testing | 15° and 17° | 0 | 0 | 0 | 419(SN_S7) 572(SN_A32) 573(SN_A62) 573(SN_A63) 573(SN_A64) | 2710 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, M.; Quan, S.; Kuang, G.; Ni, S. SAR Target Recognition via Joint Sparse and Dense Representation of Monogenic Signal. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222676
Yu M, Quan S, Kuang G, Ni S. SAR Target Recognition via Joint Sparse and Dense Representation of Monogenic Signal. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(22):2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222676
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Meiting, Sinong Quan, Gangyao Kuang, and Shaojie Ni. 2019. "SAR Target Recognition via Joint Sparse and Dense Representation of Monogenic Signal" Remote Sensing 11, no. 22: 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222676
APA StyleYu, M., Quan, S., Kuang, G., & Ni, S. (2019). SAR Target Recognition via Joint Sparse and Dense Representation of Monogenic Signal. Remote Sensing, 11(22), 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222676







