Characterisation of Sand Accumulations in Wadi Fatmah and Wadi Ash Shumaysi, KSA, Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Method
3.1. Data Acquisition and Preparation
3.2. Determination of Dune Migration
4. Results
4.1. Climatic Parameters of the Study Area
4.2. Morphology of the Study Area
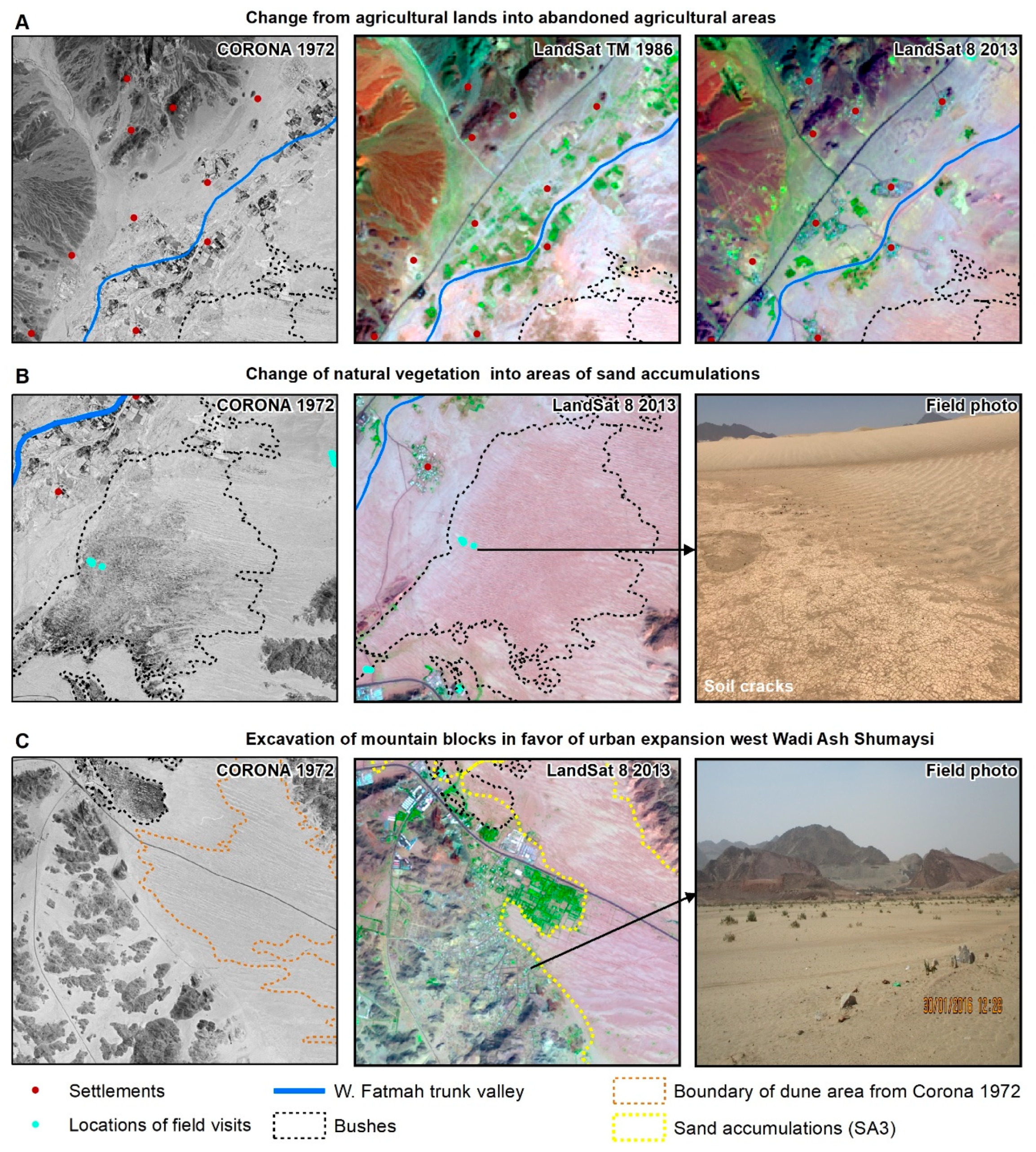
5. Discussion
5.1. Anthropogenic Activities in the Study Area
5.2. Dune Migration Rates of Sand Accumulations in the Study Area
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lancaster, N. Dune Morphology and Dynamics. In Geomorphology of Desert Environments; Parsons, A.J., Abrahams, A.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 557–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, K.F.; Psuty, N.; Carter, B. Coastal Dunes: Form and Process; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, I.G. Ergs. Sediment. Geol. 1973, 10, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryberger, S.G.; Ahlbrandt, T.S.; Andrews, S. Origin, sedimentary features, and significance of low-angle eolian “sand sheet” deposits, Great Sand Dunes National Monument and vicinity, Colorado. J. Sediment. Res. 1979, 49, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.W. Erosional History and Surficial Geology of Western Saudi Arabia. Technical Report USGS-TR-04-1; Ministry of Petroleum and Mineral Resources: Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 1983.
- Al-Harthi, A. Geohazard assessment of sand dunes between Jeddah and Al-Lith, western Saudi Arabia. Environ. Geol. 2002, 42, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.R.; Tsoar, H. Slope effect on saltation over a climbing sand dune. Geomorphology 1998, 22, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.O.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D. A general framework for modeling sediment supply to coastal dunes including wind angle, beach geometry, and fetch effects. Geomorphology 2003, 49, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, J.D.; Rasmussen, K.R. The effect of wind speed and bed slope on sand transport. Sedimentology 1999, 46, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Dong, Z.; Luo, W.; Lu, J. Mean airflow patterns upwind of topographic obstacles and their implications for the formation of echo dunes: A wind tunnel simulation of the effects of windward slope. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, I.; Warren, A. Aeolian Geomorphology: An Introduction; Longman: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, S.; Meigs, A.J.; Yeats, R.S.; Ding, R.; Shen, X. Tectonic controls for transverse drainage and timing of the Xin-Ding paleolake breach in the upper reach of the Hutuo River, north China. Geomorphology 2014, 206, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.D.; Zimbelman, J.R. Dune Worlds: How Windblown Sand Shapes Planetary Landscapes; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Muhs, D.R. Evaluation of simple geochemical indicators of aeolian sand provenance: Late Quaternary dune fields of North America revisited. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 260–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naji, A.J.; Al-Shammery, T.A. Mineralogical study of Sand Dunes Fields in Najaf Governorate, Southern Iraq. Iraqi J. Sci. 2019, 60, 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, N.; Baas, A. Influence of vegetation cover on sand transport by wind: Field studies at Owens Lake, California. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, H. Sand dunes mobility and stability in relation to climate. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2005, 357, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, S.L.; Oglesby, R.; Webb, R.S. Temporal and spatial patterns of Holocene dune activity on the Great Plains of North America: Megadroughts and climate links. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2001, 29, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, R.; Kinast, S.; Tsoar, H.; Yizhaq, H.; Zaady, E.; Ashkenazy, Y. The effect of wind and precipitation on vegetation and biogenic crust covers in the Sde-Hallamish sand dunes. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Loucks, O.L. From Balance of Nature to Hierarchical Patch Dynamics: A Paradigm Shift in Ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 1995, 70, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifan, M. Long-term effects of anthropogenic activities on semi-arid sand dunes. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, H. The ecological background, deterioration and reclamation of desert dune sand. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1990, 33, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Reynolds, J.F.; Cunningham, G.L.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jarrell, W.M.; Virginia, R.A.; Whitford, W.G. Biological feedbacks in global desertification. Science 1990, 247, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briske, D.D.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Smeins, F.E. Vegetation dynamics on rangelands: A critique of the current paradigms. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, L.; Forman, S.L.; Valdez, A.; Bunch, F. Twentieth century dune migration at the Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Colorado, relation to drought variability. Geomorphology 2005, 70, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, R.; Castilho, A.M.; Dinis, P.A.; Almeida, A.C.; Callapez, P.M. Holocene interplay between a dune field and coastal lakes in the Quiaios—Tocha region, central littoral Portugal. Holocene 2012, 22, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hurban, A.E. Effects of recent anthropogenic activities on the surface deposits of Kuwait. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 665–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Vega, L.L.; Cruz-Avero, N.; Hernández-Calvento, L.; Hernández-Cordero, A.I.; Fernández-Cabrera, E. Morphological changes in dunes as an indicator of anthropogenic interferences in arid dune fields. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskin, J.; Sivan, D.; Shtienberg, G.; Roskin, E.; Porat, N.; Bookman, R. Natural and human controls of the Holocene evolution of the beach, aeolian sand and dunes of Caesarea (Israel). Aeolian Res. 2015, 19, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, E.D. Introduction to a study of global sand seas. In A Study of Global Sand Seas; U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper: Reston, VA, USA, 1979; Volume 1052, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Breed, C.S.; Fryberger, S.G.; Andrews, S.; McCauley, C.; Lennartz, F.; Gebel, D.; Horstman, K. Regional studies of sand seas using Landsat (ERTS) imagery. In A Study of Global Sand Seas; U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper: Reston, VA, USA, 1979; Volume 1052, pp. 305–397. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, R.C.; Kocurek, G.; Lake, L.W. Pattern analysis of dune-field parameters. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 1176–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.C.; Kocurek, G. Aeolian dune interactions and dune-field pattern formation: White Sands Dune Field, New Mexico. Sedimentology 2010, 57, 1199–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.C.; Kocurek, G. Aeolian dune-field pattern boundary conditions. Geomorphology 2010, 114, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, C.H.; Barchyn, T.E. Spatial analysis of sand dunes with a new global topographic dataset: New approaches and opportunities. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, C.H.; Levin, N.; Barchyn, T.E.; Baddock, M.C. Remote sensing and spatial analysis of aeolian sand dunes: A review and outlook. Earth Sci. Rev. 2012, 111, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, D.G. Remote Sensing of Desert Dune Forms by Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Ben-Dor, E.; Karnieli, A. Topographic information of sand dunes as extracted from shading effects using Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, J.; Vallejo, I.; Malvarez, G.C. Morphometric evolution of the active dunes system of the Doñana National Park, Southern Spain (1977–1999). J. Coast. Res. 2005, 49, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kocurek, G.A. Desert aeolian systems. In Sedimentary Environments: Processes, Facies and Stratigraphy, 3rd ed.; Reading, H.G., Ed.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz, C.H.; Wolfe, S.A. Biogeomorphic model of dunefield activation and stabilization on the northern Great Plains. Geomorphology 2005, 70, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, H.J. The Barchans of Southern Peru. J. Geol. 1959, 67, 614–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merk, G.P. Dune Form and Structure at Great Sand Dunes National Monument. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.T.; Sharp, R.P. Barchan-dune movement in imperial valley, California. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1964, 75, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkin, P.E.; Rutford, R.H. The sand dunes of Victoria Valley, Antarctica. Geogr. Rev. 1974, 64, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, J.P. Dune Morphology and Sedimentology at Great Sand Dunes National Monument. Doctoral Dissertation, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, T.A.; Haynes, C.V. Sand sheet dynamics and Quaternary landscape evolution of the Selima Sand Sheet, southern Egypt. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2001, 20, 1623–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aql, M.T. Movement of sands east Suez Canal and its impact on human activities: A study in applied geomorphology. Al Ensaniat 2002, 19, 1–75. (In Arabic) [Google Scholar]
- Mitasova, H.; Overton, M.; Harmon, R.S. Geospatial analysis of a coastal sand dune field evolution: Jockey’s Ridge, North Carolina. Geomorphology 2005, 72, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, M.C.; Ewing, R.C.; Finnegan, D.; McGowan, H.A. Sand dune movement in the Victoria Valley, Antarctica. Geomorphology 2009, 109, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, H. The Dynamics of Longitudinal Dunes: Final Technical Report; U.S. Army; European Research Office: London, UK, 1978; p. 171. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoar, H.; Blumberg, D.G.; Stoler, Y. Elongation and migration of sand dunes. Geomorphology 2004, 57, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Capes, R.; Haynes, M.; Moore, J.M. ERS SAR multi-temporal coherence image as a tool for sand desert study (sand movement, sand encroachment and erosion). In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference and Workshop on Applied Geologic Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 17–19 November 1997; pp. I-478–I-485. [Google Scholar]
- Leprince, S.; Barbot, S.; Ayoub, F.; Avouac, J. Automatic and precise orthorectification, coregistration, and subpixel correlation of satellite images, application to ground deformation measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1529–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermas, E.A. Monitoring the spatial occurrences and migration rates of sand dunes around Makkah city using remote sensing technology. Remote Sens. GIS 2015, 3, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeesch, P.; Drake, N. Remotely sensed dune celerity and sand flux measurements of the world’s fastest barchans (Bodélé, Chad). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necsoiu, M.; Leprince, S.; Hooper, D.M.; Dinwiddie, C.L.; McGinnis, R.N.; Walter, G.R. Monitoring migration rates of an active subarctic dune field using optical imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermas, E.A.; Leprince, S.; El-Magd, I.A. Retrieving sand dune movements using sub-pixel correlation of multi-temporal optical remote sensing imagery, northwest Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, K.A.; Hermas, E.A. Assessment of dune migration hazards against landuse northwest Al-lith City, Saudi Arabia, using multi-temporal satellite imagery. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 11007–11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutiry, M.; Hermas, E.A.; Al-Ghamdi, K.A.; Al-Awaji, H. Estimation of dune migration rates north Riyadh City, KSA, using SPOT 4 panchromatic images. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 124, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamandawana, H.; Eckardt, F.; Ringrose, S. The use of step-wise density slicing in classifying high-resolution panchromatic photographs. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4923–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.M.; Wickhorst, A.J.; Marsh, S.E. Estimation of Tree Cover in an Agricultural Parkland of Senegal Using Rule-Based Regression Tree Modeling. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4900–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, F.; Leprince, S.; Keene, L. User’s Guide to COSI-CORR Co-Registration of Optically Sensed Images and Correlation; California Institude of Tecnology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2009; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J. Nonlocal Image and Movie Denoising. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 76, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M. The Changing World Deserts: The Problem of Water in Arid Lands; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Harbi, N.M. Geomorphic Units and Their Relationships with Land Use and Land Cover in the Drainage Basin of Wadi. Ph.D. Thesis, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia, 2017. (In Arabic). [Google Scholar]
- Sadhan, A.S. Water Plan for Wadi Fatimah Basin, Saudi Arabia. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Wyoming, Laramie, WY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Alrhiliy, A.A. Climate Characteristics in Makkah Administrative Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia, 2010. (In Arabic). [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mealem, A.A. Geomorphology of Hassan Basin in Yemen. Ph.D. Thesis, Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq, 2004. (In Arabic). [Google Scholar]
- Hamimi, Z.; Matsah, M.; El-Shafei, M.; El-Fakharani, A.; Shujoon, A.; Al-Gabali, M. Wadi Fatima thin-skinned foreland FAT belt: A post amalgamation marine basin in the Arabian Shield. Open J. Geol. 2012, 2, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K.; Tsoar, H. Aeolian Bed Forms. In Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 175–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlJumaie, Z.M. Possibilities of Agricultural Development in Wadi Fatmah of Makkah Al-Mukarramah: An Applied Study on Agricultural Capabilities. Master’s Thesis, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia, 1990. (In Arabic). [Google Scholar]
- El-Barodi, M.S. Water Balance Estimates of Wadi Fatmah Basin. J. Kuwait Geogr. Soc. 1986, 88, 5–60. (In Arabic) [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Fonteyn, P.J.; Reiners, W.A. Effects of Overland Flow on Plant Water Relations, Erosion, and Soil Water Percolation on a Mojave Desert Landscape. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhs, D.R.; Been, J.; Mahan, S.A.; Burdett, J.; Skipp, G.; Rowland, Z.M.; Stafford, T.W., Jr. Holocene eolian activity in the Minot dune field, North Dakota. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1997, 34, 1442–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huenneke, L.F.; Anderson, J.P.; Remmenga, M.; Schlesinger, W.H. Desertification alters patterns of aboveground net primary production in Chihuahuan ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, A.; Tsoar, H. International borders and range ecology: The case of Bedouin transborder grazing. Hum. Ecol. 1996, 24, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, H. Critical Environments: Sand Dunes and Climate Change. In Treatise on Geomorphology, Aeolian Geomorphology; Shroder, J.F., Lancaster, N., Sherman, D.J., Baas, A.C.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 11, pp. 414–427. [Google Scholar]
- Necsoiu, M.; Hooper, D.; Roseberry, J. Physical properties of volcanic material (tephra) using visible near-infrared spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A. The Geomorphology of Sand Dunes of South and Southeast Qattara Depression. Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoar, H. Dynamic processes acting on a longitudinal (seif) sand dune. Sedimentology 1983, 30, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misak, R.F.; El Ghazawy, M.M. Desertification Processes in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. In Proceedings of the International Meeting on Environmental Disasters and Desertification, Palermo, Italy, 16 June 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Scheidt, S.P.; Lancaster, N. The application of COSI-Corr to determine dune system dynamics in the southern Namib Desert using ASTER data. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, H. Desert dunes morphology and dynamics, El Arish, northern Sinai. Z. Geomorphol. 1974, 20, 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Assal, E.M. Sedimentological Studies on the Quaternary Sand Dunes and Sabkhas. Master’s Thesis, Damiatta Faculty of Science, University of Mansura, Northern Sinai, Egypt, 1999; p. 268. [Google Scholar]
- Embabi, N.S. Landscapes and Landforms of Egypt; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]











| Acquisition Dates | Pointing Angle | Orientation Angle | Sun Azimuth Angle | Sun elevation Angle | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| November 09, 2011 | −8.58 | 8.80 | 155.79 | 48.64 | 15 |
| November 27, 2012 | −8.59 | 8.80 | 157.48 | 43.94 | 15 |
| November 14, 2013 | −8.59 | 8.80 | 156.87 | 47.20 | 15 |
| September 30, 2014 | −8.58 | 8.80 | 142.38 | 60.15 | 15 |
| September 24, 2015 | 2.87 | 8.80 | 141.049 | 62.855 | 15 |
| Statistics | Correlation Pairs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011–2012 | 2012–2013 | 2013–2014 | 2014–2015 | |||||
| E-W | N-S | E-W | N-S | E-W | N-S | E-W | N-S | |
| Min. | −13.47 | −24.48 | −19.22 | −16.27 | −30.44 | −27.5 | −24.16 | −24.61 |
| Max. | 24.94 | 19.75 | 18.48 | 15.18 | 29.54 | 28.46 | 25.61 | 23.95 |
| Mean | 1.22 | −0.38 | 0.76 | −0.38 | 0.79 | −1.03 | 1.82 | −0.83 |
| SD | 4.22 | 2.52 | 2.97 | 2.29 | 3.63 | 2.91 | 3.79 | 3.01 |
| Correlation Pairs of Annual Rates | Statistics of Annual Rates | Dune Areas | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA1 | SA2 | SA3 | Temporal Ranges and Means | ||
| 2011–2012 | Min | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Max | 17.0 | 26.5 | 24.3 | 22.6 | |
| Average | 8.1 | 9.8 | 5.0 | 7.6 | |
| 2012–2013 | Min | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Max | 14.8 | 23.0 | 24.4 | 20.7 | |
| Average | 6.1 | 7.2 | 4.6 | 6.0 | |
| 2013–2014 | Min | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Max | 22.0 | 37.8 | 38.8 | 32.9 | |
| Average | 8.2 | 10.1 | 6.2 | 8.2 | |
| 2014–2015 | Min | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Max | 28.6 | 30.9 | 34.1 | 31.2 | |
| Average | 6.5 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 6.6 | |
| Accumulative mean (in 4 years) | 28.9 | 34.4 | 21.6 | ||
| Spatial ranges and means | Min | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Max | 20.6 | 29.6 | 30.4 | ||
| Means | 7.2 | 8.6 | 5.5 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hermas, E.; Alharbi, O.; Alqurashi, A.; Niang, A.J.; Al-Ghamdi, K.; Al-Mutiry, M.; Farghaly, A. Characterisation of Sand Accumulations in Wadi Fatmah and Wadi Ash Shumaysi, KSA, Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232824
Hermas E, Alharbi O, Alqurashi A, Niang AJ, Al-Ghamdi K, Al-Mutiry M, Farghaly A. Characterisation of Sand Accumulations in Wadi Fatmah and Wadi Ash Shumaysi, KSA, Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(23):2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232824
Chicago/Turabian StyleHermas, ElSayed, Omar Alharbi, Abdullah Alqurashi, Abdoul Jelil Niang, Khalid Al-Ghamdi, Motirh Al-Mutiry, and Abudeif Farghaly. 2019. "Characterisation of Sand Accumulations in Wadi Fatmah and Wadi Ash Shumaysi, KSA, Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Imagery" Remote Sensing 11, no. 23: 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232824
APA StyleHermas, E., Alharbi, O., Alqurashi, A., Niang, A. J., Al-Ghamdi, K., Al-Mutiry, M., & Farghaly, A. (2019). Characterisation of Sand Accumulations in Wadi Fatmah and Wadi Ash Shumaysi, KSA, Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing, 11(23), 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232824







