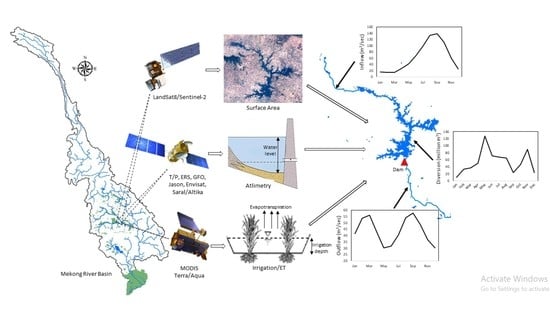
Deriving the Reservoir Conditions for Better Water Resource Management Using Satellite-Based Earth Observations in the Lower Mekong River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Storage Estimation Based on Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Reservoir Flow Estimation Based on Hydrological Modeling
2.3. Approach
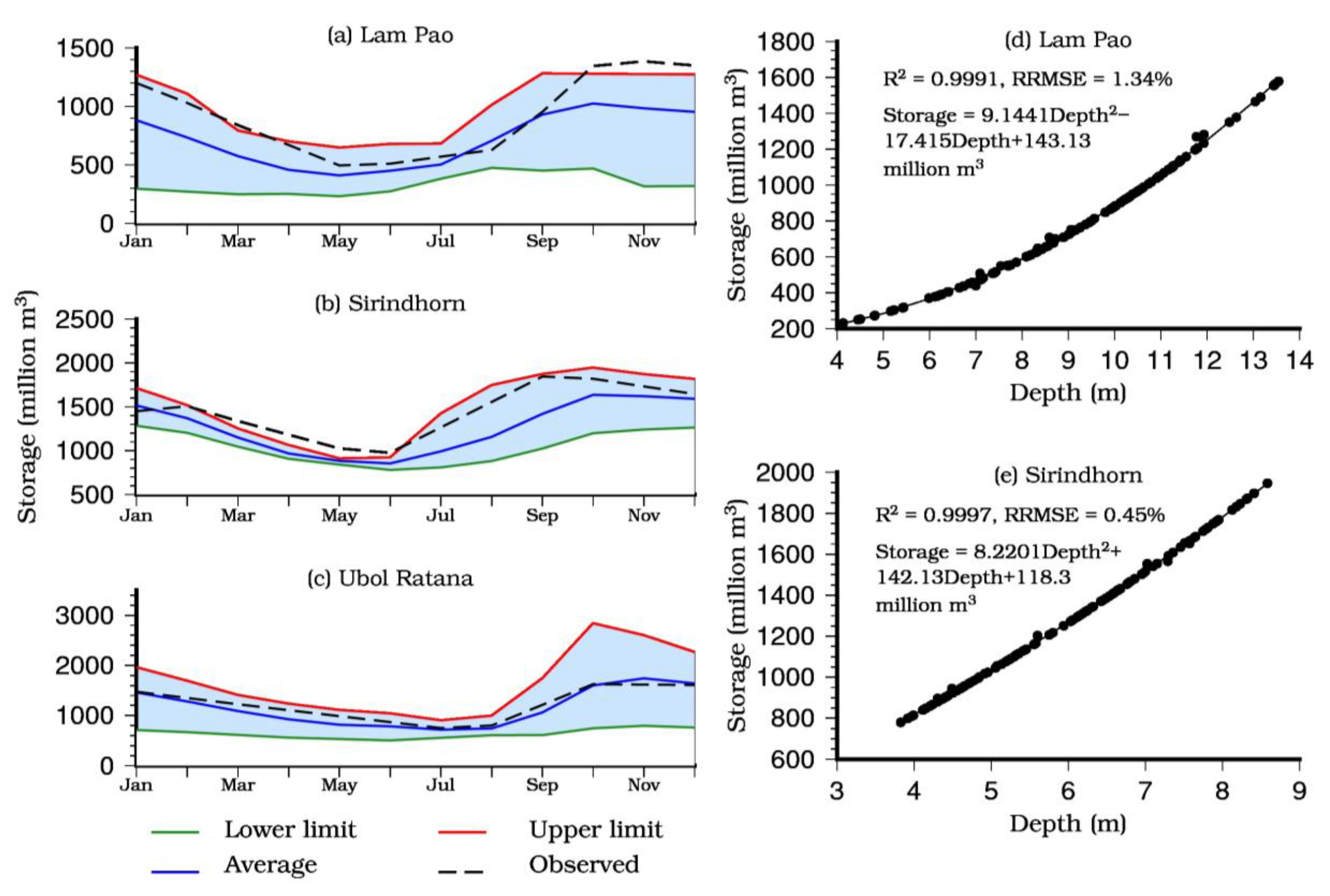
2.3.1. Storage Estimation Based on Remote Sensing Data
2.3.2. Reservoir Flow Estimation Based on Hydrological Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Storage Estimation Based on Remote Sensing Data
3.2. Reservoir Flow Estimation Based on Hydrological Modeling
3.2.1. Simulated Streamflow
3.2.2. Effect of Dams on Outflows
3.3. Rule Curve
3.4. Water Diversion from the Reservoirs and ET Analogy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

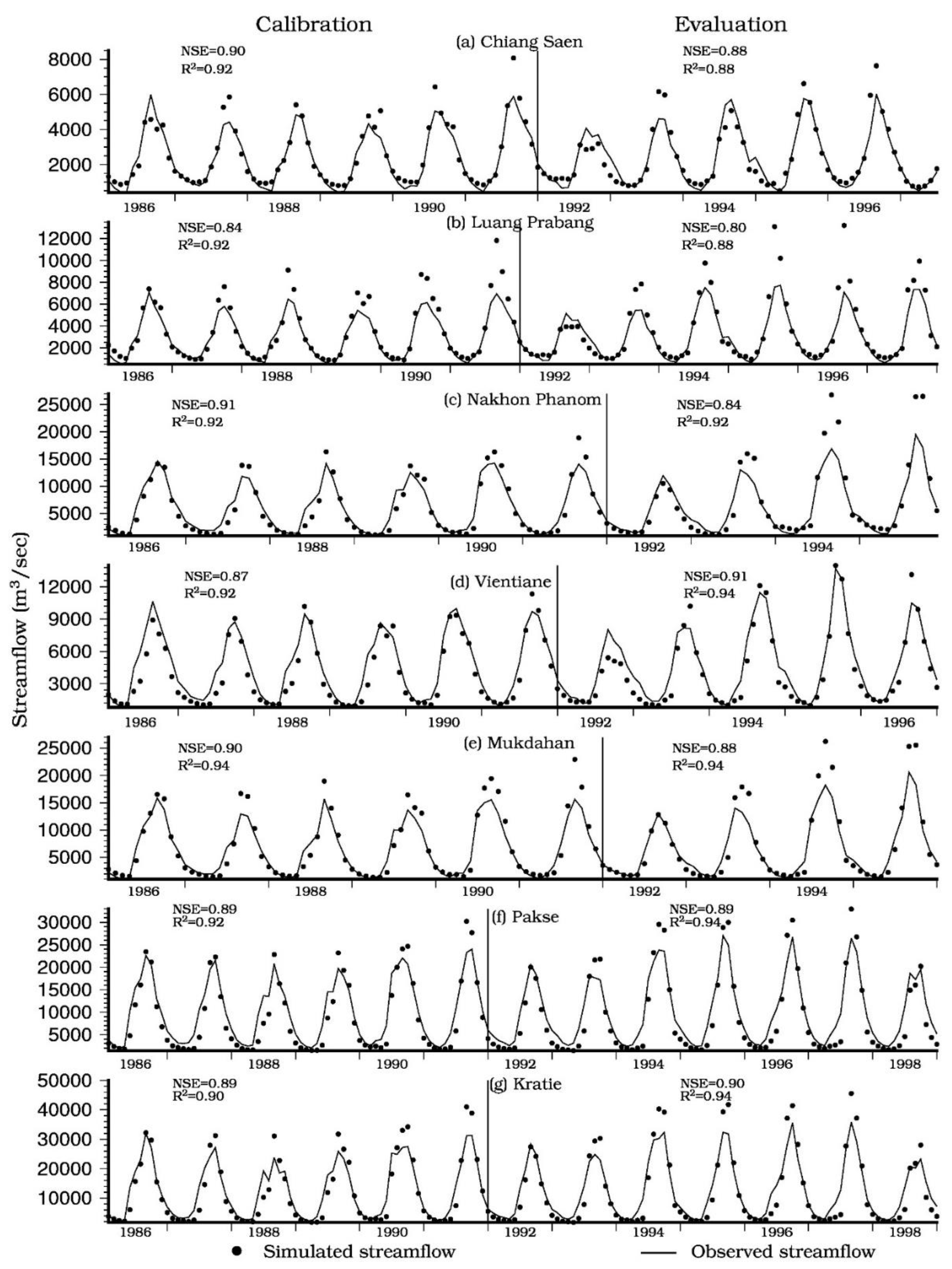
| Station | Calibration | Evaluation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | NSE | R2 | Period | NSE | R2 | |
| Chiang Saen | 1986–1991 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 1992–1997 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| Luang Prabang | 1986–1991 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 1992–1997 | 0.80 | 0.88 |
| Nakhon Phanom | 1986–1991 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 1992–1995 | 0.84 | 0.92 |
| Vientiane | 1986–1991 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 1992–1996 | 0.91 | 0.94 |
| Mukdahan | 1986–1991 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 1992–1995 | 0.88 | 0.94 |
| Pakse | 1986–1991 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 1992–1998 | 0.89 | 0.94 |
| Kratie | 1986–1991 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 1992–1998 | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| Dams | Storage | Inflow | Outflow | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE | R2 | NSE | R2 | NSE | R2 | |
| Lam Pao | 0.903 | 0.95 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.85 |
| Sirindhorn | 0.979 | 0.99 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.71 |
| Ubol Ratana | NA | NA | 0.65 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.53 |
References
- Sridhar, V.; Jaksa, W.T.A.; Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Hubbard, K.G.; Jin, X. Evaluating Bias-Corrected AMSR-E Soil Moisture using in situ Observations and Model Estimates. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillard, U.; Sridhar, V.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; McDonald, K.C. Assessing snowmelt dynamics with NASA scatterometer (NSCAT) data and a hydrologic process model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Reshmidevi, T. Remote sensing applications in water resources. J. Indian Inst. 2013, 93, 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Kansal, M.L.; Sridhar, V.; Mwanga, E.E. Transboundary Issues of Water Governance in Mekong River Basin. In The World Environmental and Water Resources Congress; American Society of Civil Engineers: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 130–143. [Google Scholar]
- Gander, M.J. International water law and supporting water management principles in the development of a model transboundary agreement between riparians in international river basins. Water Int. 2014, 39, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, G.; Baran, E.; Nam, S.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, I.; Levin, S.A. Trading-off fish biodiversity, food security, and hydropower in the Mekong River Basin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5609–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kummu, M.; Lu, X.X.; Wang, J.J.; Varis, O. Basin-wide sediment trapping efficiency of emerging reservoirs along the Mekong. Geomorphology 2010, 119, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Babel, M.S.; Maskey, S.; van Griensven, A.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Green, A.; Akkharath, I. Impact of climate change on sediment yield in the Mekong River basin: A case study of the Nam Ou basin, Lao PDR. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M.; Zebker, H.A. Groundwater extraction, land subsidence, and sea-level rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, H.; Ruby Leung, L.; Li, H.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, K.; Sothea, K. Dam Construction in Lancang-Mekong River Basin Could Mitigate Future Flood Risk from Warming-Induced Intensified Rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 10,378–10,386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.S.; Kanashiro, E.A.; Valverde, R.; Sridhar, V. Dynamic Framework for Intelligent Control of River Flooding: Case Study. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2014, 140, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, K.R.; Morton, L.W. Tonle Sap Lake and River and confluence with the Mekong River in Cambodia Soil management View project. Artic. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 60A–66A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, S.M.; Lorenzen, K. Livelihood Diversification in Rural Laos. World Dev. 2016, 83, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, P.T.; Rutherfurd, I.D.; Peel, M.C.; Conlan, I.A. The Hydrology of the Mekong River. In The Mekong; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, R. Mayhem on the Mekong. Science 2011, 333, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekong River Commission. Assessment of Basin-Wide Development Scenarios—Main Report; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Winemiller, K.O.; McIntyre, P.B.; Castello, L.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Giarrizzo, T.; Nam, S.; Baird, I.G.; Darwall, W.; Lujan, N.K.; Harrison, I.; et al. Balancing hydropower and biodiversity in the Amazon, Congo, and Mekong. Science 2016, 351, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauri, H.; de Moel, H.; Ward, P.J.; Räsänen, T.A.; Keskinen, M.; Kummu, M. Future changes in Mekong River hydrology: Impact of climate change and reservoir operation on discharge. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4603–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Sarkkula, J. Impact of the Mekong River Flow Alteration on the Tonle Sap Flood Pulse. AMBIO 2008, 37, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlak, A.K.; Lautze, J.; Giordano, M. Water resources data and information exchange in transboundary water treaties. Int. Environ. Agreem. Polit. Law Econ. 2011, 11, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliagha, C. Environmental Clearinghouse as an Institutional Incentive for Data and Information Sharing and Conflict Reuction in the Mekong River Basin. In Proceedings of the OpenSIUC, Carbondale, IL, USA, 20 July 2004; pp. 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Affeltranger, B. Mekong Studies at Crossed Glances. In Proceedings of the 4th French-MFU Seminar, Chiang Rai, Thailand, 25–26 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Affeltranger, B. Sustainability of Environmental Regimes: The Mekong River Commission; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 593–601. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi, K.; Yamashiki, Y. Effect of irrigation water withdrawals on water and energy balance in the Mekong River Basin using an improved VIC land surface model with fewer calibration parameters. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Ali, S.A.; Lakshmi, V. Assessment and validation of total water storage in the Chesapeake Bay watershed using GRACE. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 24, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipitone, C.I.; Maltese, A.; Dardanelli, G.I.; Lo Brutto, M.I.; La Loggia, G.I. Monitoring Water Surface and Level of a Reservoir Using Different Remote Sensing Approaches and Comparison with Dam Displacements Evaluated via GNSS. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Qin, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Ling, F.; Tian, L.; Ding, Y. Estimating the relationship between dam water level and surface water area for the Danjiangkou Reservoir using Landsat remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Birkett, C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Global monitoring of large reservoir storage from satellite remote sensing. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abileah, R.; Vignudelli, S.; Scozzari, A. A Completely Remote Sensing Approach to Monitoring Reservoirs Water Volume. Int. Water Technol. J. 2011, 1, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, L.N.; Sano, E.E.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Passo, D.P. Estimation of small reservoir storage capacities with remote sensing in the Brazilian Savannah region. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.P.; Banerji, S. Monitoring of reservoir volume using LANDSAT data. J. Hydrol. 1985, 77, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Guo, S.; Liu, P.; Liu, T. Reservoir Storage Curve Estimation Based on Remote Sensing Data. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muala, E.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Duan, Z.; Van der Zaag, P. Estimation of Reservoir Discharges from Lake Nasser and Roseires Reservoir in the Nile Basin Using Satellite Altimetry and Imagery Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7522–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Estimating water volume variations in lakes and reservoirs from four operational satellite altimetry databases and satellite imagery data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Papa, F.; Frappart, F.; Alsdorf, D.; Calmant, S.; da Silva, J.S.; Prigent, C.; Seyler, F. Satellite-based estimates of surface water dynamics in the Congo River Basin. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 66, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonnema, M.; Hossain, F. Inferring reservoir operating patterns across the Mekong Basin using only space observations. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 3791–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastham, J.; Mpelasoka, F.; Mainuddin, M.; Ticehurst, C.; Dyce, P.; Hodgson, G.; Ali, R.; Kirby, M. Mekong River Basin Water Resources Assessment: Impacts of Climate Change; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2008.
- Sridhar, V.; Kang, H.; Ali, S.A. Human-Induced Alterations to Land Use and Climate and Their Responses for Hydrology and Water Management in the Mekong River Basin. Water 2019, 11, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remote Pixel|Home. Available online: https://remotepixel.ca/ (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Crétaux, J.-F.; Jelinski, W.; Calmant, S.; Kouraev, A.; Vuglinski, V.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Gennero, M.-C.; Nino, F.; Abarca Del Rio, R.; Cazenave, A.; et al. SOLS: A lake database to monitor in the Near Real Time water level and storage variations from remote sensing data. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Birkett, C.; Reynolds, C.; Beckley, B.; Doorn, B. From Research to Operations: The USDA Global Reservoir and Lake Monitor. In Coastal Altimetry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 19–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield, J.; Goteti, G.; Wood, E.F. Development of a 50-Year High-Resolution Global Dataset of Meteorological Forcings for Land Surface Modeling. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3088–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thilakarathne, M.; Sridhar, V. Characterization of future drought conditions in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2017, 17, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-L.; Cazenave, A. Satellite Altimetry and Earth Sciences: A Handbook of Techniques and Applications; Academic: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780080516585. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.T.; Marshall, L.; Johnson, F.; Sharma, A. Deriving daily water levels from satellite altimetry and land surface temperature for sparsely gauged catchments: A case study for the Mekong River. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 212, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 14415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosby, B.J.; Hornberger, G.M.; Clapp, R.B.; Ginn, T.R. A Statistical Exploration of the Relationships of Soil Moisture Characteristics to the Physical Properties of Soils. Water Resour. Res. 1984, 20, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franchini, M.; Pacciani, M. Comparative analysis of several conceptual rainfall-runoff models. J. Hydrol. 1991, 122, 161–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.J. Evaporation. In Handbook of Hydrology; Maidment, D.R., Ed.; McGRaw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 4.1–4.53. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, E.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Zartarian, V.G. A land-surface hydrology parameterization with subgrid variability for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, D.; Nolte-Holube, R.; Raschke, E. A large-scale horizontal routing model to be coupled to land surface parametrization schemes. Tellus Ser. Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1996, 48, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, D.; Raschke, E.; Nijssen, B.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Regional scale hydrology: II. Application of the VIC-2L model to the Weser River, Germany. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1998, 43, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haddeland, I.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Skaugen, T. Effects of irrigation on the water and energy balances of the Colorado and Mekong river basins. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Sridhar, V. Assessment of Future Drought Conditions in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018, 54, 160–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Billah, M.M.; Hildreth, J.W. Coupled Surface and Groundwater Hydrological Modeling in a Changing Climate. Groundwater 2018, 56, 618–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekema, D.J.; Sridhar, V. A System Dynamics Model for Conjunctive Management of Water Resources in the Snake River Basin. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 1327–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Jin, X.; Jaksa, W.T.A. Explaining the hydroclimatic variability and change in the Salmon River basin. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 1921–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.A.; Aadhar, S.; Shah, H.L.; Mishra, V. Projected Increase in Hydropower Production in India under Climate Change. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Saint, V.; Saint-Venant, A.J.C. Théorie du mouvement non-permanent des eaux, avec application aux crues des rivieres eta l’introduction des marées dans leur lit. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. 1871, 73, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, H.; Huang, M.; Leung, L.R. Representing Natural and Manmade Drainage Systems in an Earth System Modeling Framework. Irrig. Drain. Syst. Eng. 2012, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kangrang, A.; Prasanchum, H.; Hormwichian, R. Development of Future Rule Curves for Multipurpose Reservoir Operation Using Conditional Genetic and Tabu Search Algorithms. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. Mekong River Commission: Hydrometeorological database of the Mekong River Commission; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Chen, X. Remote Sensing of the Water Storage Dynamics of Large Lakes and Reservoirs in the Yangtze River Basin from 2000 to 2014. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumphon, B. Genetic Algorithms for Multi-objective Optimization: Application to a Multi-reservoir System in the Chi River Basin, Thailand. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4369–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, R.; Masumoto, T.; Horikawa, N. Modeling of paddy water management with large reservoirs in Northeast Thailand and its application to climate change assessment. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2015, 49, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Dam | Lam Pao | Sirindhorn | Ubol Ratana | Mekong River Basin | ||||||
| Commercial Operation Date (COD) | 1968 | 1971 | 1966 | |||||||
| Height (m) | 33.0 | 42.0 | 35.1 | |||||||
| Total storage (million m3) | 1940 | 1967 | 2859 | |||||||
| Max reservoir area (km2) | 240 | 288 | 410 | |||||||
| Installed capacity (Mega Watt) | NA | 36.0 | 25.5 | |||||||
| Year | Wet (%) | Dry (%) | Pcp (mm) | Wet (%) | Dry (%) | Pcp (mm) | Wet (%) | Dry (%) | Pcp (mm) | Pcp (mm) |
| 2008 | −83.9 | 59.0 | 1798.4 | NA | NA | 1555.8 | −39.1 | 31.0 | 1388.5 | 1554.2 |
| 2009 | −47.5 | 247.0 | 1368.6 | −57.5 | 78.0 | 2045.4 | −64.2 | 52.1 | 1229.3 | 1482.5 |
| 2010 | −40.9 | 108.8 | 1382.6 | −82.3 | −21.5 | 1265.4 | −77.3 | 57.0 | 1220.9 | 1393.4 |
| 2011 | −49.9 | 120.1 | 1725.1 | −68.4 | 133.5 | 2179.7 | −23.5 | 75.2 | 1572.7 | 1735.8 |
| 2012 | 28.8 | 1.4 | 989.9 | −76.8 | −8.0 | 1764.3 | −32.5 | −51.9 | 912.6 | 1551.0 |
| 2013 | −90.1 | 118.7 | 1285.3 | −56.9 | 68.0 | 1702.1 | −67.4 | 39.9 | 1237.4 | 1652.5 |
| 2014 | −71.4 | 101.6 | 1184.4 | −54.2 | 180.5 | 2120.7 | −78.4 | −53.2 | 1135.5 | 1363.0 |
| 2015 | −60.8 | 161.1 | 1096.2 | −95.5 | −49.5 | 1459.7 | −63.5 | −78.6 | 1052.3 | 1304.6 |
| 2016 | −76.1 | −70.4 | 1432.9 | −69.7 | −89.9 | 1875.9 | −93.0 | −76.4 | 1321.1 | 1499.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.A.; Sridhar, V. Deriving the Reservoir Conditions for Better Water Resource Management Using Satellite-Based Earth Observations in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232872
Ali SA, Sridhar V. Deriving the Reservoir Conditions for Better Water Resource Management Using Satellite-Based Earth Observations in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(23):2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232872
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Syed A., and Venkataramana Sridhar. 2019. "Deriving the Reservoir Conditions for Better Water Resource Management Using Satellite-Based Earth Observations in the Lower Mekong River Basin" Remote Sensing 11, no. 23: 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232872
APA StyleAli, S. A., & Sridhar, V. (2019). Deriving the Reservoir Conditions for Better Water Resource Management Using Satellite-Based Earth Observations in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Remote Sensing, 11(23), 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232872