Generation of a Large-Scale Surface Sediment Classification Map Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Data: A Case Study at the Hwang-do Tidal Flat, Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
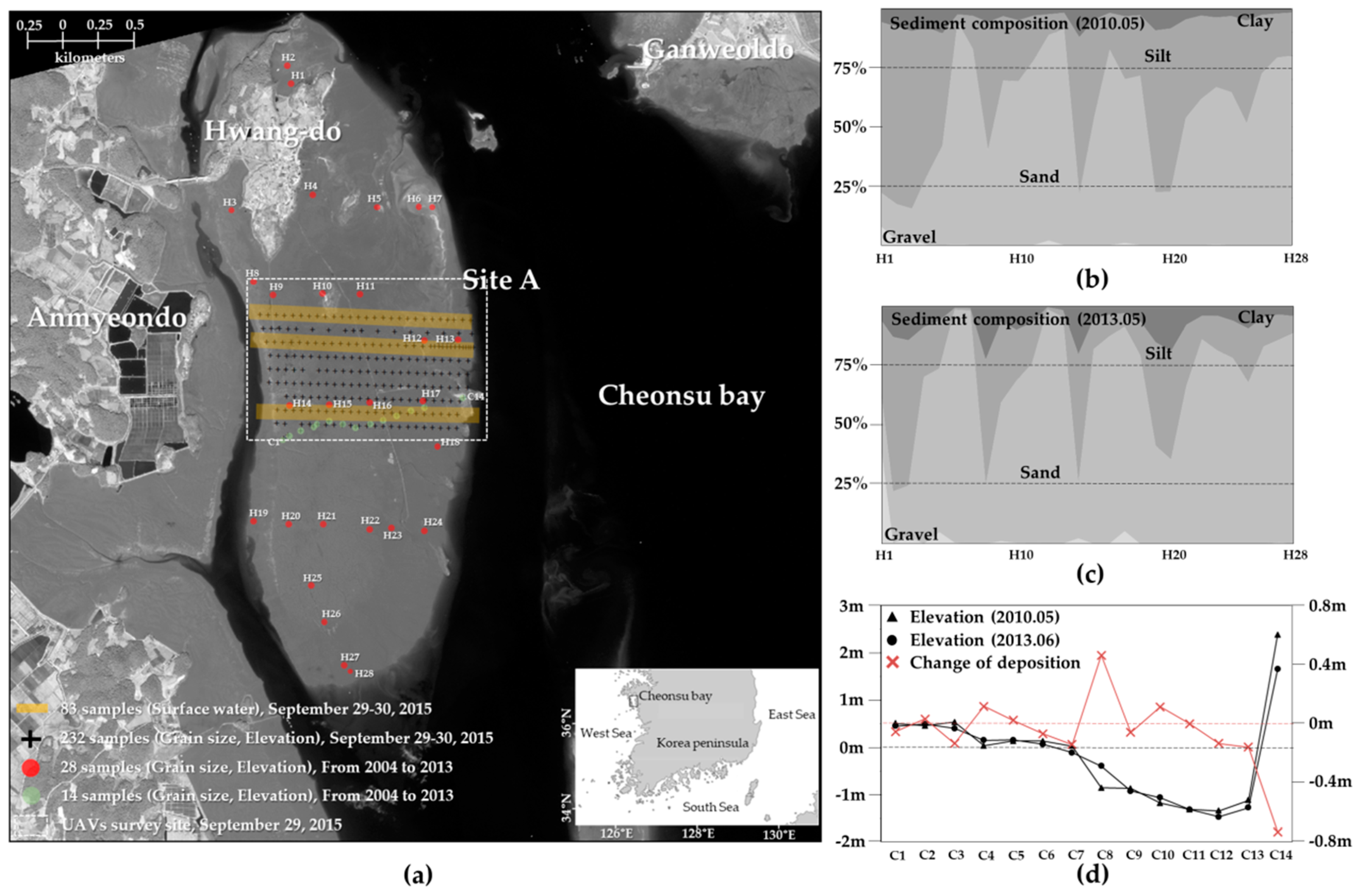
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets
3.2. UAVs for Data Acquisition and Processing
3.3. Surface Sediment Classification Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Grain Size Distribution
4.2. Surface Sediment Classification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marani, M.; D’Alpaos, A.; Lanzoni, S.; Carniello, L.; Rinaldo, A. Biologically-controlled multiple equilibria of tidal landforms and the fate of the Venice lagoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Na, Y.H.; Won, J.S.; Doerffer, R. A critical grain size for Landsat ETM+ investigations into intertidal sediments: A case study of the Gomso tidal flats, Korea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, M.P.; Tyler, A.N.; Bryant, R.G.; Gilvear, D.J.; McDonald, P. The influence of surface and interstitial moisture on the spectral characteristics of intertidal sediment: Implications for airborne image acquisition and processing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 3025–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.K.; Eom, J.; Ryu, J.H. Spatial relationship between surface sedimentary facies distribution and topography using remotely sensed data: Example from the Ganghwa tidal flat, Korea. Mar. Geol. 2011, 280, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerffer, R.; Murphy, D. Factor analysis and classification of remotely sensed data for monitoring tidal flats. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1989, 43, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, M.P.; Tyler, A.N.; Givear, D.J.; Bryant, R.G.; McDonald, P. Mapping intertidal estuarine sediment grain size distributions through airborne remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Remote Sensing of the Environment, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0131889507. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.H.; Choi, J.K.; Na, Y.H.; Won, J.S. Characteristics of Landsat ETM+ image for Gomso Bay tidal flat sediments Korean. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 19, 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholdy, J.; Folving, S. Sediment classification and surface type mapping in the Danish Wadden sea by remote-sensing. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1986, 20, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.G.; Jones, A.R.; McGrorty, S.; Goss-Custard, J.D. The use of satellite imagery to determine the distribution of intertidal surface sediments of the Wash, England. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1993, 36, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Yoo, H.R.; Woo, H.J.; Kim, C.H. Quantitative estimation of intertidal sediment characteristics using remote sensing and GIS. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, J.; Choi, J.K.; Lee, Y.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Won, J.S. Standardization of sedimentary facies and topography based on the tidal channel type in Western coastal area, Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.; Adolph, W.; Ehlers, M.; Farke, H. A multi-sensor approach for detecting the different land covers of tidal flats in the German Wadden Sea-a case study at Norderney. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolph, W.; Farke, H.; Lehner, S.; Ehlers, M. Remote Sensing Intertidal Flats with TerraSAR-X. A SAR Perspective of the Structural Elements of a Tidal Basin for Monitoring the Wadden Sea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.G.; Jeong, G.T.; Chae, J.W. Numerical Modeling of Changes in Tides and Tidal Currents Caused by Embankment at Chonsu Bay. JKSCOE 1998, 10, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.N. Biogenic sedimentary structures of crustaceans at the intertidal flat of Whang Island, Cheonsu Bay (Korean edn.). JKESS 1996, 17, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, H.S. Community structures of macrobenthos in Chonsu bay, Korea. J. Korea Soc. Oceanogr. 1998, 33, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Folk, R.L. A review of grain size parameters. Sedimentology 1968, 6, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J. Fractal Analysis of Inter-Tidal Channels and Creeks Using High Resolution Satellite Images Korea; Yonsei University: Seoul, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, T.; Strobl, J. What’s wrong with pixels? Some recent development interfacing remote sensing and GIS. Interfac. Remote Sens. GIS 2001, 6, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, S.J.; McCleary, A.L.; Mena, C.F.; Shao, Y.; Tuttle, J.P.; Gonzalez, A.; Atkinson, R. QuickBird and Hyperion data analysis of an invasive plant species in the Galapagos Islands of Ecuador: Implications for control and land use management. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1927–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desclee, B.; Bogaert, P.; Defourny, P. Forest change detection by statistical object-based method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conchedda, G.; Durieux, L.; Mayaux, P. An object-based method for mapping and change analysis in mangrove ecosystems. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble. eCognition® Developer 9.0 Reference Book; Trimble Germany GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, J.; Choi, J.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Woo, H.J.; Won, J.S.; Jang, S. Tidal channel distribution in relation to surface sedimentary facies based on remotely sensed data. Geosci. J. 2012, 16, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Han, H.; Lee, H. Observation of ridge-runnel and ripples in Mongsanpo intertidal flat by satellite SAR imagery. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2010, 26, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Wal, D.; Herman, P.M.J.; Wielemaker-van den Dool, A. Characteristics of surface roughness and sediment texture of intertidal flats using ERS SAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Baret, F.; Gu, X.; Tong, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, B. Relating soil surface moisture to reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 238–246. [Google Scholar]
- Neema, D.L.; Shah, A.; Patel, N. A statistical optical model for light reflection and penetration through sand. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Remotely Sensed Data | In-Situ Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data |
| |||
| Method |
|
|
|
|
| Extracted factors |
|
|
|
|
| Class | Sediment Type by Folk (1986) | Composition (%) | Statistical Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravel | Sand | Silt | Clay | Mean (ø) | Sorting (ø) | Skewness | Kurtosis | |||
| 1 | gS | Average | 17.6 | 76.9 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 2.0 | −0.1 | 1.2 |
| Range | 8.7~27.0 | 67.8~84.1 | 1.9~4.9 | 1.9~2.3 | 0.4~1.6 | 1.8~2.2 | −0.3~0.1 | 1.0~1.4 | ||
| (g)S | Average | 0.9 | 93.9 | 3.2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 1.6 | |
| Range | 0.1~3.3 | 89.6~98.0 | 3.3~7.1 | 1.6~3.6 | 0.8~2.6 | 0.4~1.7 | −0.2~0.3 | 1.0~2.9 | ||
| 2 | S | Average | 0.0 | 92.1 | 5.5 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 1.8 |
| Range | 0.0~0.0 | 90.8~95.1 | 3.3~7.1 | 1.6~3.6 | 2.4~3.4 | 0.6~1.2 | 0.1~0.4 | 1.2~2.8 | ||
| 3 | gmS | Average | 9.2 | 71.4 | 13.1 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| Range | 5.2~15.8 | 61.7~79.8 | 8.3~23.2 | 3.8~11.0 | 2.0~3.8 | 2.2~3.0 | −0.2~0.4 | 1.3~2.7 | ||
| (g)mS | Average | 0.8 | 77.0 | 16.3 | 5.9 | 3.4 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 1.9 | |
| Range | 0.0~4.9 | 52.6~89.1 | 6.1~33.3 | 1.8~19.0 | 1.9~5.0 | 0.8~3.0 | 0.0~0.7 | 0.9~3.2 | ||
| 4 | zS | Average | 0.0 | 72.3 | 21.6 | 6.1 | 3.8 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 1.8 |
| Range | 0.0~0.0 | 50.9~89.1 | 7.8~39.9 | 2.3~14.4 | 2.9~5.5 | 0.9~2.5 | 0.2~0.7 | 1.2~3.2 | ||
| mS | Average | 0.0 | 70.9 | 16.5 | 12.6 | 4.0 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 1.8 | |
| Range | 0.0~0.0 | 56.7~89.2 | 6.5~23.9 | 4.3~24.0 | 2.4~5.5 | 1.4~2.9 | 0.3~0.8 | 0.8~2.8 | ||
| 5 | sZ | Average | 0.0 | 34.7 | 48.9 | 16.4 | 5.4 | 2.3 | 0.5 | 1.2 |
| Range | 0.0~0.0 | 13.2~49.3 | 38.3~63.9 | 9.7~28.4 | 4.6~6.8 | 1.9~2.8 | 0.3~0.7 | 0.9~1.6 | ||
| 6 | (g)sM | Average | 0.4 | 28.3 | 48.6 | 22.7 | 6.0 | 2.7 | 0.3 | 1.0 |
| Range | 0.1~1.3 | 12.6~46.4 | 34.5~62.4 | 12.2~31.4 | 4.8~6.8 | 2.2~3.3 | 0.2~0.5 | 0.8~1.4 | ||
| sM | Average | 0.0 | 16.8 | 53.6 | 29.7 | 6.7 | 2.8 | 0.3 | 0.9 | |
| Range | 0.0~0.0 | 10.7~21.8 | 49.4~58.1 | 28.0~31.8 | 6.4~7.0 | 2.6~2.9 | 0.2~0.4 | 0.8~1.0 | ||
| Class | Classification of UAV Orthoimagery | Total Points | User Accuracy | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||||
| Reference data (in situ measurement) | 1 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 0.71 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.33 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 23 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 31 | 0.74 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 29 | 1 | 0 | 34 | 0.85 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 9 | 0.56 | |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 0.50 | |
| Total points | 6 | 2 | 30 | 37 | 9 | 8 | 92 | - | |
| Producer Accuracy | 0.83 | 0.50 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.56 | 0.50 | - | - | |
| Overall accuracy | 72.38 | ||||||||
| Kappa coefficient | 0.62 | ||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.-L.; Kim, B.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Ryu, J.-H. Generation of a Large-Scale Surface Sediment Classification Map Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Data: A Case Study at the Hwang-do Tidal Flat, Korea. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030229
Kim K-L, Kim B-J, Lee Y-K, Ryu J-H. Generation of a Large-Scale Surface Sediment Classification Map Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Data: A Case Study at the Hwang-do Tidal Flat, Korea. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(3):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030229
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kye-Lim, Bum-Jun Kim, Yoon-Kyung Lee, and Joo-Hyung Ryu. 2019. "Generation of a Large-Scale Surface Sediment Classification Map Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Data: A Case Study at the Hwang-do Tidal Flat, Korea" Remote Sensing 11, no. 3: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030229
APA StyleKim, K.-L., Kim, B.-J., Lee, Y.-K., & Ryu, J.-H. (2019). Generation of a Large-Scale Surface Sediment Classification Map Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Data: A Case Study at the Hwang-do Tidal Flat, Korea. Remote Sensing, 11(3), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030229





