Assimilation of GPSRO Bending Angle Profiles into the Brazilian Global Atmospheric Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Brazilian Global Atmospheric Model (BAM)
2.2. Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation (GSI) Setup
2.3. Experimental Design
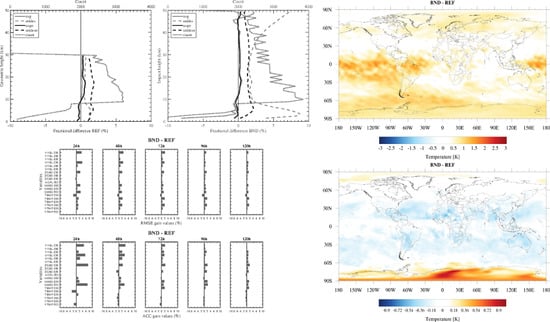
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assimilated GPSRO Data
3.2. Observation-Minus-First Guess (OmF)
3.3. Cost Function Minimization
3.4. Analyses Differences
3.5. Balance in the First Guess
3.6. Forecasts Skill
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauer, P.; Thorpe, A.; Brunet, G. The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, T.; Hagedorn, R. Predictability of Weather and Climate; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; p. 702. [Google Scholar]
- Kalnay, E. Atmospheric Modeling, Data Assimilation, and Predictability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 54, p. 341. [Google Scholar]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Hajj, G.A.; Bertiger, W.I.; Leroy, S.S.; Meehan, T.K.; Romans, L.J.; Schofield, J.T.; McCleese, D.J.; Melbourne, W.G.; Thornton, C.L.; et al. Initial results of radio occultation observations of Earth’s atmosphere using the Global Positioning System. Science 1996, 271, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, J. Assimilation of Radio Occultation measurements into a numerical weather prediction system. In ECMWF Technical Memoranda; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 1994; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali, C.; Healy, S. Impact of GPS radio occultation measurements in the ECMWF system using adjoint-based diagnostics. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 2315–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fussen, D.; Tétard, C.; Dekemper, E.; Pieroux, D.; Mateshvili, N.; Vanhellemont, F.; Franssens, G.; Demoulin, P. Retrieval of vertical profiles of atmospheric refraction angles by inversion of optical dilution measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 3135–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, E.; Hajj, G.; Schofield, J.T.; Linfield, R.P.; Hardy, K.R. Observing Earth’s atmosphere with radio occultation measurements using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 23429–23465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, C.; Healy, S. GPS-RO at ECMWF. In Proceedings of the ECMWF Seminar on Data Assimilation for Atmosphere and Ocean, Reading, UK, 6–9 September 2011; pp. 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Cucurull, L.; Anthes, R.A. Impact of Infrared, Microwave, and Radio Occultation Satellite Observations on Operational Numerical Weather Prediction. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 4164–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Anthes, R.A. Impact of Loss of U.S. Microwave and Radio Occultation Observations in Operational Numerical Weather Prediction in Support of the U.S. Data Gap Mitigation Activities. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Derber, J.C. Operational Implementation of COSMIC Observations into NCEP’s Global Data Assimilation System. Weather Forecast. 2008, 23, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Derber, J.C.; Treadon, R.; Purser, R.J. Assimilation of Global Positioning System Radio Occultation Observations into NCEP’s Global Data Assimilation System. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 3174–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, M.P. The impact of GPS radio occultation assimilation at the Met Office. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 136, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, S.B.; Thepaut, J.N. Assimilation experiments with CHAMP GPS radio occultation measurements. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavita, M. On some aspects of the impact of GPSRO observations in global numerical weather prediction. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 2546–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Kuo, Y.H.; Barker, D.; Rizvi, S.R.H. Assessing the Impact of Simulated COSMIC GPS Radio Occultation Data on Weather Analysis over the Antarctic: A Case Study. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 3283–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Derber, J.C.; Treadon, R.; Purser, R.J. Preliminary Impact Studies Using Global Positioning System Radio Occultation Profiles at NCEP. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L. Improvement in the Use of an Operational Constellation of GPS Radio Occultation Receivers in Weather Forecasting. Weather Forecast. 2010, 25, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Derber, J.C.; Purser, R.J. A bending angle forward operator for global positioning system radio occultation measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, S.N.; Bonatti, J.P.; Kubota, P.Y.; Grell, G.A.; Morrison, H.; Barros, S.R.M.; Fernandez, J.P.R.; Ramirez, E.; Siqueira, L.; Luzia, G.; et al. The Brazilian Global Atmospheric Model (BAM): Performance for Tropical Rainfall Forecasting and Sensitivity to Convective Scheme and Horizontal Resolution. Weather Forecast. 2016, 31, 1547–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapucci, L.F.; Diniz, F.L.R.; Bastarz, C.F.; Avanço, L.A. Inclusion of Global Navigation Satellite System radio occultation data into Center for Weather Forecast and Climate Studies Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter (LETKF) using the Radio Occultation Processing Package as an observation operator. Meteorol. Appl. 2016, 23, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, H.B.D.; Gonçalves, L.G.G.D.; Bastarz, C.F.; Silveira, B.B. Observing System Experiments in a 3DVAR Data Assimilation System at CPTEC/INPE. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, I.F.; Marengo, J.A.; Satyamurty, P.; Nobre, C.A.; Trosnikov, I.; Bonatti, J.P.; Manzi, A.O.; Tarasova, T.; Pezzi, L.P.; D’Almeida, C.; et al. Global climatological features in a simulation using the CPTEC-COLA AGCM. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2965–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.; Randall, D.A.; Corsetti, T.G. A fast radiation parameterization for atmospheric circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, M.D.; Suarez, M.J. A Solar Radiation Parameterization Atmospheric Studies. In Technical Report Series on Global Modeling and Data Assimilation; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Grell, G.A.; Dévényi, D. A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 38-1–38-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedtke, M. The sensitivity of the time-mean large-scale flow to cumulus convection in the ECMWF model. In Proceedings of the ECMWF Workshop on Convection in Large-Scale Models, Shinfield Park, Reading, 28 November–1 December 1983; European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 1983; pp. 297–316. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Sellers, P.; Kinter, J.; Shukla, J. A Simplified Biosphere Model for Global Climate Studies. J. Clim. 1991, 4, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtslag, A.A.M.; Boville, B.A. Local versus nonlocal boundary-layer diffusion in a global climate model. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1825–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, G.; Yamada, T. Development of a turbulence closure for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1982, 20, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Developmental Testbed Center. Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation (GSI) User’s Guide for Version 3.3. In Community Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation System; Developmental Testbed Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014; p. 108. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, T.B.; Sapucci, L.F.; Lima, W.; Ferreira, D.S. Sensitivity of Numerical Weather Prediction to the Choice of Variable for Atmospheric Moisture Analysis into the Brazilian Global Model Data Assimilation System. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Chiswell, S.; Herring, T.A.; Anthes, R.A.; Rocken, C.; Ware, R.H. GPS Meteorology: Mapping Zenith Wet Delays onto Precipitable Water. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüeger, J.M. Refractive Index Formulae for Radio Waves. In Proceedings of the JS28 Integration of Techniques and Corrections to Achieve Accurate Engineering, FIG Proceedings XXII International Congress, Washington, DC, USA, 19–26 April 2002; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Cardellach, E.; Xie, F. GNSS Remote Sensing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 19, pp. 215–239. [Google Scholar]
- Desroziers, G.; Berre, L.; Chapnik, B.; Poli, P. Diagnosis of observation, background and analysis-error statistics in observation space. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 3385–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Barker, D.; Huang, W.; Kuo, Y.H. First Guess at Appropriate Time (FGAT) with WRF 3DVAR. J. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 41, 495–505. [Google Scholar]
- Syndergaard, S. On the ionosphere calibration in GPS radio occultation measurements. Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 865–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpechko, A.; Tummon, F.; Secretariat WMO. Climate Predictability in the Stratosphere. Bull. World Meteorol. Organ. 2016, 65, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, P.; Huang, X.Y. Initialization of the HIRLAM Model Using a Digital Filter. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.G.; Wu, Z.S.; Kang, S.F.; Zhao, Z.W. Monitoring the marine atmospheric refractivity profiles by ground-based GPS occultation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, R.A.; Ector, D.; Hunt, D.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Rocken, C.; Schreiner, W.S.; Sokolovskiy, S.V.; Syndergaard, S.; Wee, T.K.; Zeng, Z.; et al. The COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 Mission: Early Results. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Long-wave radiation | Harshvardhan et al. [25] |
| Short-wave radiation | CliRAD (Chou and Suarez [26]) |
| Deep convection | Grell and Dévényi [27] |
| Shallow convection | Tiedtke [28] |
| Surface scheme | SSIB (Xue et al. [29]) |
| Boundary layer top | Holtslag and Boville [30] |
| Boundary layer bottom | Mellor and Yamada [31] |
| Rüeger [35] | Bevis et al. [34] | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 77.6890 | 77.60 | K mb | |
| 3.75463 | 3.739 | K mb | |
| 71.2952 | 70.4 | K mb |
| CNT | REF | BND |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional data | Conventional data | Conventional data |
| Unconventional data | Unconventional data | Unconventional data |
| (Radiances) | (Radiances) | (Radiances) |
| (No GPSRO data) | (GPSRO refractivity profiles) | (GPSRO bending angles) |
| BND | % | REF | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of available observations | 21,385.736 | 100 | 20,935.518 | 97.9 |
| Assimilated observations | 15,688.745 | 73.4 | 9002.718 | 42.1 |
| 0–30 km | 9736.151 | 45.5 | 9002.718 | 42.1 |
| 30–50 km | 5952.594 | 27.8 | - | - |
| Not Assimilated observations | 5696.991 | 26.6 | 11,932.800 | 55.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banos, I.H.; Sapucci, L.F.; Cucurull, L.; Bastarz, C.F.; Silveira, B.B. Assimilation of GPSRO Bending Angle Profiles into the Brazilian Global Atmospheric Model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030256
Banos IH, Sapucci LF, Cucurull L, Bastarz CF, Silveira BB. Assimilation of GPSRO Bending Angle Profiles into the Brazilian Global Atmospheric Model. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(3):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030256
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanos, Ivette H., Luiz F. Sapucci, Lidia Cucurull, Carlos F. Bastarz, and Bruna B. Silveira. 2019. "Assimilation of GPSRO Bending Angle Profiles into the Brazilian Global Atmospheric Model" Remote Sensing 11, no. 3: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030256
APA StyleBanos, I. H., Sapucci, L. F., Cucurull, L., Bastarz, C. F., & Silveira, B. B. (2019). Assimilation of GPSRO Bending Angle Profiles into the Brazilian Global Atmospheric Model. Remote Sensing, 11(3), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030256