Flood Inundation Mapping of the Sparsely Gauged Large-Scale Brahmaputra Basin Using Remote Sensing Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
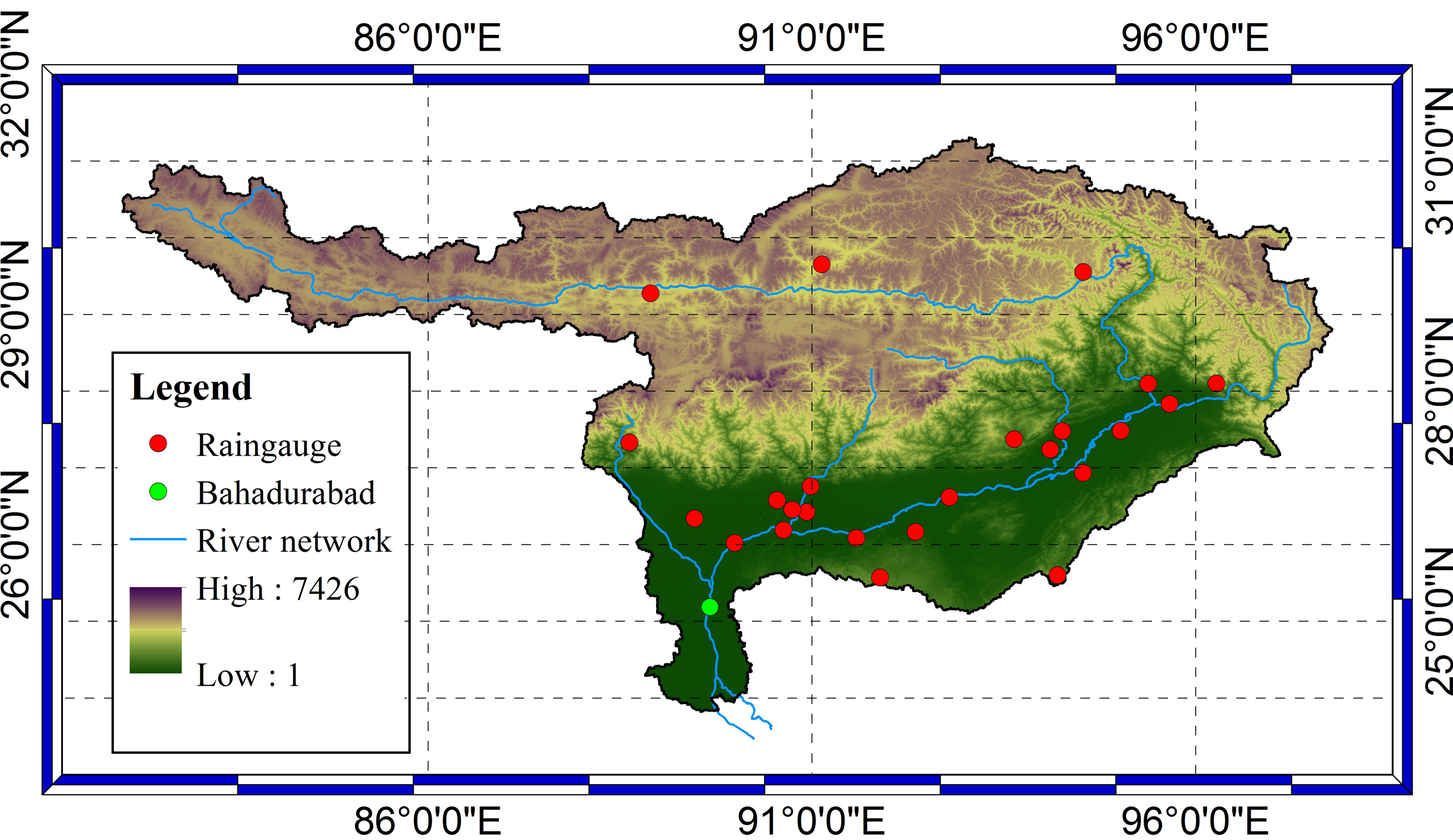
2. Study Area: The Brahmaputra Basin
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Collection and Processing
3.2. Bias Correction for Satellite Rainfall Estimates
3.3. Hydrological Modelling
3.4. Hydraulic Modelling
3.5. Performance Indices
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Bias Correction
4.2. Hydrological and Hydraulic Modelling
4.3. Flood Extent Results
5. Limitations and Recommendations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) sensor package. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Bolvin, D.; Nelkin, E.; Wolff, D.; Adler, R.; Gu, G. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multilayer, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrom. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetia, R.; As-syakur, A.R.; Osawa, T. Validation of TRMM precipitation radar satellite data over Indonesian region. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneis, D.; Chatterjee, C.; Singh, R. Evaluation of TRMM rainfall estimates over large Indian river basin (Mahanadi). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2502–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Shi, J.; Ni-Meister, W.; Zhao, T.; Ji, D. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) products and their potential hydrological application at an arid and semiarid basin in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3915–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Chen, B.; Gourley, J.J.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Gong, L. Intercomparison of the Version 6 and Version 7 TMPA precipitation products over high and low latitudes basins with independent gauge networks: Is the newer version better in both real-time and post-real-time analysis for water resources and hydrologic extremes? J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, A.; Guan, D.; Wu, J.; Yuan, F.; Xu, L. Spatial-temporal analysis of the accuracy of Tropical Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis 3B42 precipitation data in mid-high latitudes of China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120026. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Behrangi, A.; Hong, Y.; Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Cao, J.; Hu, B.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X. Hydrologic evaluation of the TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis over Ganjiang Basin in humid south-eastern China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 3, 4568–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, A.; Guan, D.; Wu, J.; Yuan, F.; Xu, L. Comprehensive precipitation evaluation of TRMM 3B42 with dense rain gauge networks in amid-latitude basin, northeast, China. Theo. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Gautam, A.K.; Palmate, S.S.; Pandey, A.; Suryavanshi, S.; Rathore, N. Evaluation of TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) against terrestrial measurement over humid sub-tropical basin, India. Theo. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 129, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, A.; Pineda, L.; Crespo, P.; Willems, P. Evaluation of TRMM 3B42 precipitation estimates and WRF retrospective precipitation simulation over the Pacific-Andean region of Ecuador and Peru. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3179–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Meneghini, R. Validation of TRMM precipitation radar through comparison of its multi-year measurements to ground-based radar. J. Appl. Meterol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozante, J.R.; Moreira, D.S.; De Goncalves, L.G.; Vila, D.A. Combining TRMM and surface observations of precipitation: Technique and validation over South America. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 25, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Hidalgo, M.; Bhattacharya, B.; Mynett, A.E.; Griensven, A.V. Experience in using the TMPA-3B42R satellite data to compliment rain gauge measurements in the Ecuadorian coastal foothills. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2905–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collischonn, B.; Collischonn, W.; Tucci, C.M. Daily hydrological modelling in the Amazon basin using TRMM rainfall estimates. J. Hydrol. 2008, 360, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Yu, Z.; Yang, C.; Ju, Q.; Lu, B.-J.; Liang, C. Hydrological assessment of TRMM rainfall data over Yangtze River Basin. Water Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 418–430. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, I.K.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Gao, B.; Jiao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xu, T. Multiscale hydrologic applications of the latest satellite precipitation products in the Yangtze River Basin using a distributed hydrologic model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, H.; Yang, D.; Sothea, K.; Jiao, Y.; Gao, B.; Peng, X.; Pang, Z. Modelling hydrologic processes in the Mekong River Basin using a distributed model driven by satellite precipitation and rain gauge observations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Hu, H.; Tian, F.; Ni, G.; Hu, Q. Correcting the TRMM rainfall product for hydrological modelling in sparsely-gauged mountainous basins. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, Q.; Lu, Y.; Hu, B. Hydrological evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis for Nanliu River in humid Southwestern China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2045–2322. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Hsu, K.; Liu, C.; Sorooshian, S. Evaluating the streamflow simulation capability of PERSIANN-CDR daily rainfall products in two river basins on the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, V.; Khoi, D.; Linh, D. Using gridded rainfall products in simulating streamflow in a tropical catchment—A case study of the Srepok River Catchment, Vietnam. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2016, 65, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazzy, A.A.; Lü, H.; Chen, R.; Ali, A.B.; Zhu, Y.; Su, L. Evaluation of satellite precipitation products and their potential influence on hydrological modeling over the Ganzi River Basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 3695285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, M.M.; Gebremichael, M. Evaluation of satellite rainfall products through hydrologic simulation in a fully distributed hydrologic model. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W06526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, M.M.; Gebremichael, M. Assessment of satellite rainfall products for streamflow simulation in medium watersheds of the Ethiopian highlands. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhani, H.; Hsu, K.; Hong, Y.; Sorooshian, S. Investigating the impact of remotely sensed precipitation and hydrologic model uncertainties on the ensemble streamflow forecasting. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L12401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, J.; Tolson, B.A. Progress in integrating remote sensing data and hydrologic modeling. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2014, 38, 464–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, V.; Massari, C. On the performance of satellite precipitation products in riverine flood modeling: A review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.J.-P.; Neal, J.C.; Voisin, N.; Andreadis, K.M.; Pappenberger, F.; Phanthuwongpakdee, N.; Hall, A.C.; Bates, P.D. A first large scale flood inundation forecasting model. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6248–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Thorstensen, A.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; AghaKouchak, A. Flood forecasting and inundation mapping using HiResFlood-UCI and near-real-time satellite precipitation data: The 2008 Iowa Flood. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, R.C.D.; Collischonn, W.; Tucci, C.E.M. Large scale hydrologic and hydrodynamic modeling using limited data and a GIS based approach. J. Hydrol. 2011, 406, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, J.M.; Haag, A.V.; van Dam, A.; Winsemius, H.C.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Assessing the impact of hydrodynamics on large-scale flood wave propagation—A case study for the Amazon Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Amarnath, G. Applications of Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimates in Flood Inundation Modeling—A Case Study in Mundeni Aru River Basin, Sri Lanka. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, C.; Zaman, A.M.; Shah Newaz, S.M.; Rahman, S.M.M.; Mazumdar, T.K.; Choudhury, R.; Borah, P.J.; Saikia, L. Physical Assessment of the Brahmaputra River; International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), 2014; Available online: https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2014-083.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Banerjee, P.; Salehin, M.; Ramesh, V. Water Management Practices and Policies along Brahmaputra River Basin: India and Bangladesh; SaciWaters, 2014; Available online: http://brahmaputrariversymposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/report_12-05-2014_v16.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Mirza, M. Three recent extreme floods in Bangladesh: A hydrological analysis. Nat. Hazards 2003, 28, 35–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parua, P.K. The Ganga: Water Use in the Indian Subcontinent; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Futter, M.N.; Whitehead, P. Rainfall runoff modelling of the Upper Ganga and Brahmaputra Basins using PERSiST. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, M. Water Wars: The Brahmaputra River and Sino-Indian Relations; US Naval War College: New Port, RI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mahanta, C. Water Resources on the Northeast: State of the Knowledge Base; Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, 2006; Available online: http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTSAREGTOPWATRES/Resources/Background_Paper_2.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Schneider, R.; Godiksen, P.N.; Villadsen, H.; Madsen, H.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Application of CrySat-2 altimetry data for river analysis and modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.; Morris, C.S.; Belz, J.E.; Chapin, E.C.; Martin, J.M.; Daffer, W.; Hensley, S. An Assessment of the SRTM Topographic Products; Jet Propulsion Laboratory D-31639 (Report); NASA. Available online: https://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/srtm/SRTM_D31639.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Hartmann, J.; Moosdorf, N. The new global lithological map database GLiM: A representation of rock properties at the Earth surface. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 13, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.G.; Cripps, J.C.; Culshaw, M.G. A review of the engineering behaviour of soils and rocks with respect to groundwater. Eng. Geol. Spec. Pubs. 1986, 3, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.L.; Kundu, P.K. Comparing satellite rainfall estimates with rain gauge data: Optimal strategies suggested by a spectral model. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.K.; Bell, T.L. A stochastic model of space-time variability of mesoscale rainfall: Statistics of spatial averages. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, SWC 1-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omranian, E.; Sharif, H.O. Evaluation of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Satellite Rainfall Products over the Lower Colorado River Basin, Texas. J Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018, 54, 882–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.A.; Gray, R. Correcting bias in rainfall inputs to a semidistributed hydrological model using downstream flow simulation errors. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 2427–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeneghetti, A. On the use of SRTM and altimetry data for flood modeling in data-sparse regions. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2901–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, C.A.; Bates, P.D.; Schumann, G.; Trigg, M.A. SRTM vegetation removal and hydrodynamic modeling accuracy. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5276–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Hamski, J.; Durand, M.; Alsdorf, D.; Hossain, F.; Lee, H.; Hossain, A.K.M.A.; Hasan, K.; Khan, A.S.; Hoque, A.K.M.Z. Characterization of complex fluvial systems using remote sensing of spatial and temporal water level variations in the Amazon, Congo, and Brahmaputra river. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2010, 35, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Pietroń, J.; Bring, A.; Thorslund, J.; Jarsjö, J. Present to future sediment transport of the Brahmaputra River: Reducing uncertainty in predictions and management. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, F.; Bala, S.K.; Pandey, R.K.; Durand, F.; Gopalkrishna, V.V.; Rahman, A.; Rossow, W.B. Ganga-Brahmaputra river discharge from Jason-2 radar altimetry: An update to the long term satellite-derived estimates of continental freshwater forcing flux into Bay of Bengal. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Baldassarre, G.D.; Solomatine, D.P.; Schumann, G.J. A review of low-cost space-borne data for flood modelling: Topography, flood extent and water level. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3368–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, J.T. The critical success index as an indicator of warning skill. Weather Forecast. 1990, 5, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horritt, M.S.; Bates, P.D. Evaluation of 1D and 2D numerical models for predicting river flood inundation. J. Hydrol. 2002, 268, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, C.M.; Rao, G.S.; Diwakar, P.G.; Dadhwal, V.K. Development of flood inundation extent libraries over a range of potential flood levels: A practical framework for quick flood response, Geomatics. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 384–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, O.E.J.; Bates, P.D.; Sampson, C.C.; Smith, A.M.; Johnson, K.A.; Erickson, T.A. Validation of a 30 m resolution floodhazard model of the conterminousUnited States. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 7968–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhofen, M.V.; Whyman, C.; Trigg, M.A.; Sleigh, P.A.; Smith, A.M.; Sampson, C.C.; Yamazaki, D.; Ward, P.J.; Rudari, R.; Pappenberger, F.; et al. A first collective validation of global fluvial flood models for major floods in Nigeria and Mozambique. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1748–9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfreda, S.; Nardi, F.; Samela, C.; Grimaldi, S.; Taramasso, A.C.; Roth, G.; Sole, A. Investigation on the Use of Geomorphic Approaches for the Delineation of Flood Prone Areas. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, S.R.; Palash, W.; Shrestha, M.S.; Khadgi, V.R.; Duo, C.; Das, P.J.; Dorji, C. Systematic Evaluation of Satellite-Based Rainfall Products over the Brahmaputra Basin for Hydrological Applications. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 398687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USACE. HEC GeoRAS GIS Tools for Support of HEC-RAS Using ArcGIS: User’s Manual; (version 4.3); US Army Corps of Engineers, 2011. Available online: http://www.hec.usace.army.mil/software/hec-georas/documentation/HEC-GeoRAS_43_Users_Manual.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Dartmouth Flood Observatory. Retrieved from Dartmouth Flood Observatory. 2010. Available online: http://floodobservatory.colorado.edu/index.html (accessed on 17 April 2018).
- Chini, M.; Hostache, R.; Giustarini, L.; Matgen, P. A Hierarchical Split-Based Approach for Parametric Thresholding of SAR Images: Flood Inundation as a Test Case. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6975–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroselli, A.; Grimaldi, S. Design hydrograph estimation in small and fully ungauged basins: A preliminary assessment of the EBA4SUB framework. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S197–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostache, R.; Chini, M.; Giustarini, L.; Neal, J.; Kavetski, D.; Wood, M.; Corato, G.; Pelich, R.M.; Matgen, P. Near-real-time assimilation of SAR derived flood maps for improving flood forecasts. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5516–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.; Hostache, R.; Neal, J.; Wagener, T.; Giustarini, L.; Chini, M.; Corato, G.; Matgen, P.; Bates, P. Calibration of channel depth and friction parameters in the LISFLOOD-FP hydraulic model using medium-resolution SAR data and identifiability techniques. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4983–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Data Type | Availability | Spatial Resolution | Source | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRMM rainfall (TMPA 3B42 V7) | 1998–2015, daily | 0.25° × 0.25° | NASA | Hydrological simulation |
| Gauge rainfall | 2013–2014, daily | 24 stations- | Indian Met Dept. | Correcting TRMM |
| Temperature | Aug-2002–Dec-2015, daily | 0.25° × 0.25° | NASA | Hydrological simulation |
| Temperature | Jan-2000–Jul-2012, daily | 0.25° × 0.25° | Era-Interim | Hydrological simulation |
| Land use | 2009 | 300 m × 300 m | GlobCover of European Space Agency | Hydrological simulation |
| Soil | 2008 | 1 km × 1 km | Harmonised World Soil Database, V 1.2, GeoNetwork, FAO | Hydrological simulation |
| Lithology | 2012 | 0.5° × 0.5° | Global Lithological Map (GLIM), V 1.0 | Hydrological simulation |
| Evapotranspiration | 2000–2015, monthly | 5 km × 5 km | GeoNetwork, FAO | Hydrological simulation |
| SRTM DEM | 2000 | 90 m × 90 m | NASA | Digital elevation model of the catchment |
| Discharge data | 2000–26/12/2015 | Bahadurabad station | Bangladesh Water Development Board | Hydrological model calibration and validation |
| Water level | 2012–2015, every 10 days | Barpeta | Jason2 Altimetry data | Hydraulic model calibration and validation |
| Flood extent | 06/2012–09/2012 | Vector | Dartmouth Flood Observatory of the Colorado University | Flood extent validation |
| Total Period | Calibration | Validation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrological | 01/01/2000–26/12/2015 | 01/01/2005–29/04/2013 | 01/01/2000–31/12/2004 |
| Hydraulic | 03/01/2011–26/12/2015 | 01/01/2013–31/12/2013 | 03/01/2012–31/12/2012, 01/01/2015–26/12/2015 |
| Average Discharge [m3/s] | Uncorrected TRMM | Corrected TRMM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 [-] | NSC [-] | RMSE [m3/s] | R2 [-] | NSC [-] | RMSE [m3/s] | ||
| Calibration | 21,216 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 9625 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 7272 |
| Validation | 23,287 | 0.77 | 0.61 | 11643 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 9201 |
| Zones | Uncorrected TRMM | Corrected TRMM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pos. Rej. | False | Missed | Hit | Pos. Rej. | False | Missed | Hit | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Guwahati | 82 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 79 | 12 | 1 | 8 |
| Barpeta | 44 | 8 | 23 | 25 | 42 | 11 | 17 | 30 |
| Dhubri | 52 | 7 | 16 | 25 | 51 | 9 | 12 | 28 |
| Upper zone | 37 | 6 | 21 | 36 | 33 | 10 | 13 | 44 |
| Middle zone | 44 | 8 | 24 | 24 | 39 | 12 | 18 | 31 |
| Lower zone | 40 | 4 | 23 | 33 | 39 | 5 | 18 | 38 |
| Zones | Uncorrected TRMM | Corrected TRMM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pos. Rej. | False | Missed | Hit | Pos. Rej. | False | Missed | Hit | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Guwahati | 76 | 15 | 1 | 8 | 76 | 13 | 1 | 10 |
| Barpeta | 37 | 15 | 11 | 37 | 25 | 20 | 13 | 42 |
| Dhubri | 48 | 12 | 8 | 32 | 53 | 14 | 7 | 26 |
| Upper zone | 30 | 13 | 8 | 49 | 32 | 11 | 8 | 49 |
| Middle zone | 35 | 17 | 12 | 36 | 34 | 12 | 13 | 41 |
| Lower zone | 36 | 8 | 12 | 44 | 38 | 14 | 10 | 38 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhattacharya, B.; Mazzoleni, M.; Ugay, R. Flood Inundation Mapping of the Sparsely Gauged Large-Scale Brahmaputra Basin Using Remote Sensing Products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050501
Bhattacharya B, Mazzoleni M, Ugay R. Flood Inundation Mapping of the Sparsely Gauged Large-Scale Brahmaputra Basin Using Remote Sensing Products. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(5):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050501
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhattacharya, Biswa, Maurizio Mazzoleni, and Reyne Ugay. 2019. "Flood Inundation Mapping of the Sparsely Gauged Large-Scale Brahmaputra Basin Using Remote Sensing Products" Remote Sensing 11, no. 5: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050501
APA StyleBhattacharya, B., Mazzoleni, M., & Ugay, R. (2019). Flood Inundation Mapping of the Sparsely Gauged Large-Scale Brahmaputra Basin Using Remote Sensing Products. Remote Sensing, 11(5), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050501





