Quantification and Analysis of Impervious Surface Area in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo, Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
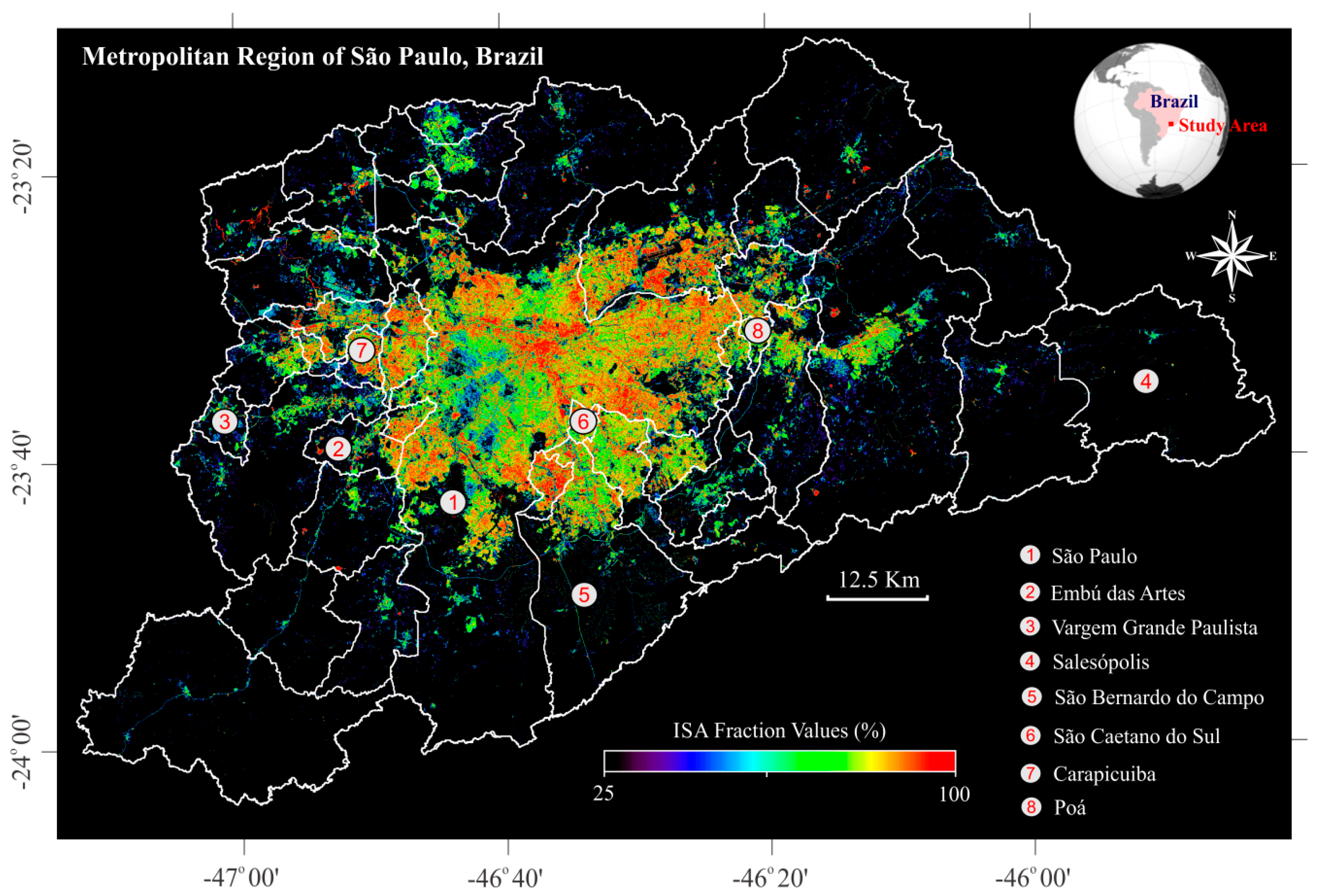
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data and Calibration
2.3. Spectral Unmixing
2.3.1. Linear Spectral-Mixture Model
2.3.2. Spectral Normalization
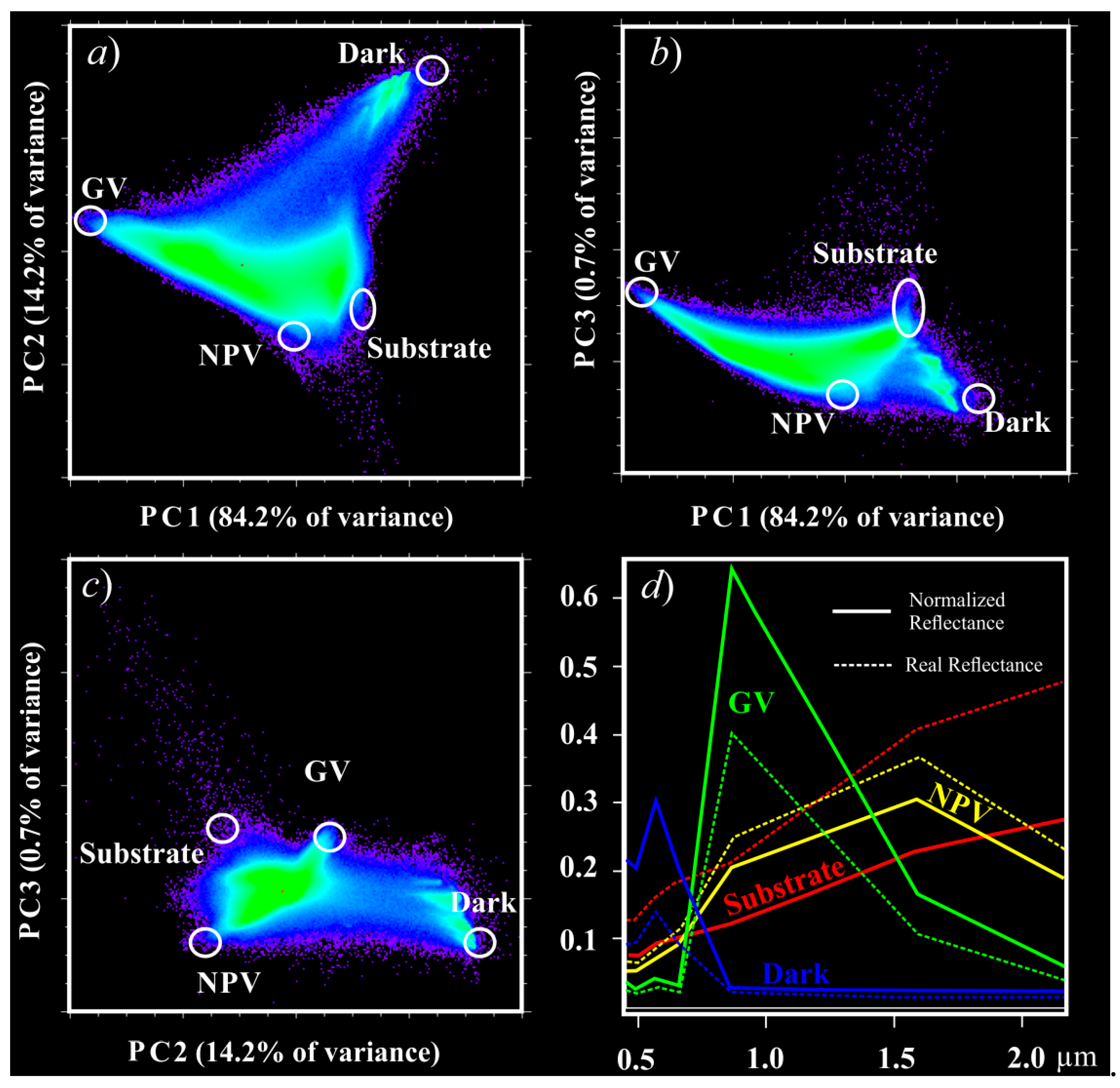
2.3.3. Selection of Endmembers
2.3.4. Modeling and Validation of Impervious Surface Fraction (ISF)
2.4. ISF Model Integration
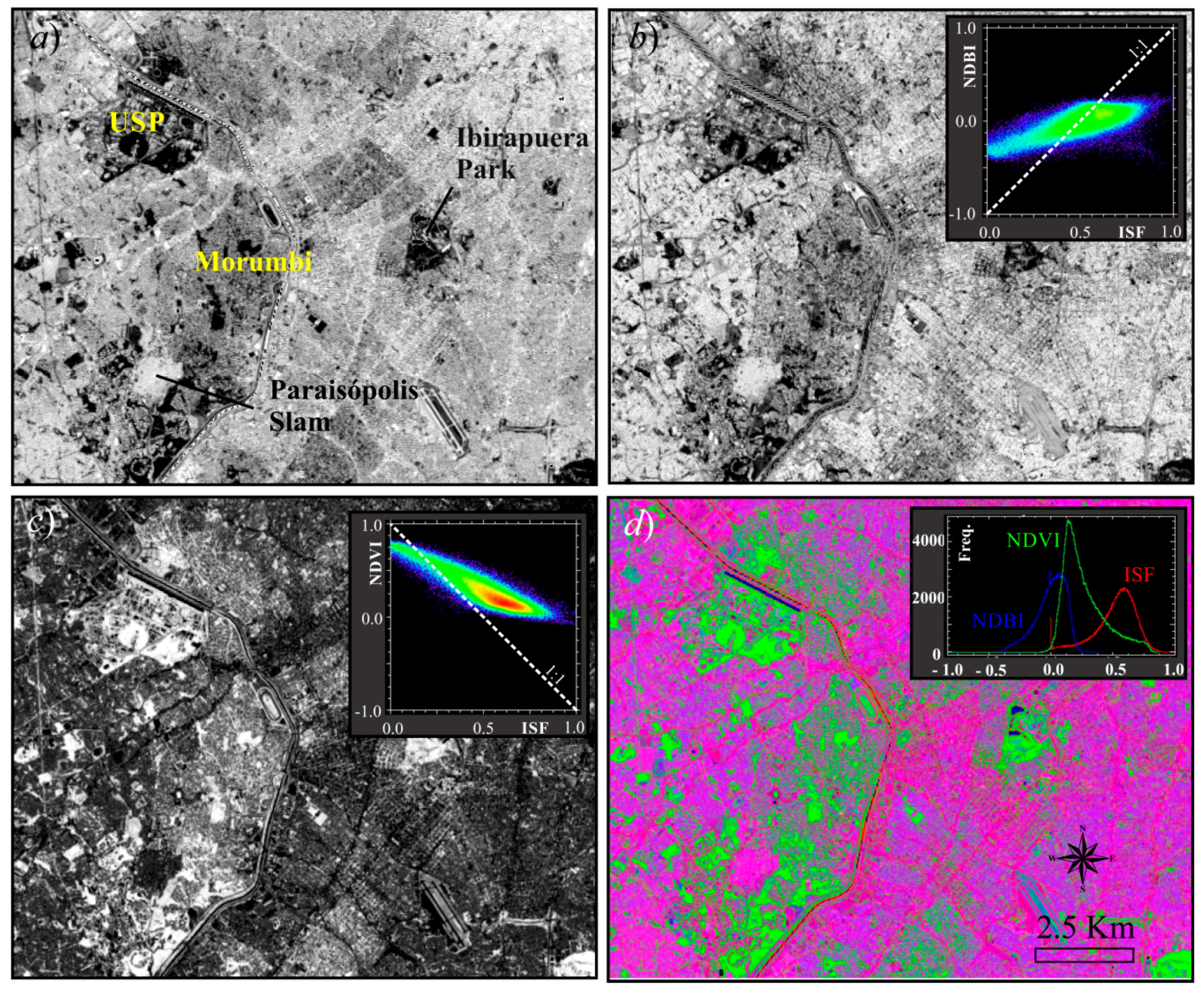
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tocci, C.E.M. Água no meio urbano. In Águas Doces No Brasil: Capital Ecológico, Uso e Conservação; Rebouças, A.C., Braga, B., Tundisi, J.G., Eds.; Escrituras: São Paulo, Brasil, 2002; pp. 473–502. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, E.A.; Smith, D.R.; Huang, C.; Shuster, W.D.; Bonta, J.V. Impervious surface impacts to runoff and sediment discharge under laboratory rainfall simulation. Catena 2008, 72, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormanski, J.; Van de Voorde, T.; De Roeck, T.; Batelaan, O.; Canters, F. Improving distributed runoff prediction in urbanized catchments with remote sensing based estimates of impervious surface cover. Sensors 2008, 8, 910–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changnon, S.A. Inadvertent weather modification in urban areas: Lessons for global climate change. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 73, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of impervious surface area and normalized difference vegetation index as indicators of surface urban heat island effects in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lin, D.; Tang, F. The impact of impervious surface development on land surface temperature in a subtropical city: Xiamen, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 33, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Fang, J.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X. An assessment of urban surface energy fluxes using a sub-pixel remote sensing analysis: A case study in Suzhou, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, T.R. The Importance of imperviousness. Waters Prot. Tech. 1994, 1, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious surface coverage: The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.D.; Greer, K.A. The effects of watershed urbanization on the stream hydrology and riparian vegetation of Los Pe˜nasquitos Creek, California. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 74, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Tuttle, B.T.; Sutton, P.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Howard, A.T.; Milesi, C.; Bhaduri, B.L.; Nemani, R. Global distribution and density of constructed impervious surfaces. Sensors 2007, 7, 1962–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Mapping impervious surface distribution with integration of SNNP VIIRS-DNB and MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12459–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonecker, E.T.; Jennings, D.B.; Garofalo, D. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces: A review. Remote Sens. Rev. 2001, 20, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Li, G.; Kuang, W.; Moran, E. Methods to extract impervious surface areas from satellite images. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 93–112. [Google Scholar]
- Small, C. A global analysis of urban reflectance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Roberts, D.A. The spectral dimension in urban remote sensing. In Remote Sensing of Urban and Suburban Areas; Rashed, T., Jürgens, C., Eds.; Springer: Austin, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 47–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Hetrick, S.; Moran, E. Impervious surface mapping with Quickbird imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 2519–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Homer, C.G.; Wylie, B.K.; Coan, M.J. An approach for mapping large-area impervious surfaces: Synergistic use Landsat-7 ETM+ and high spatial resolution imagery. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 29, 230–240. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Li, G.; Moran, E.; Batistella, M.; Freita, C.C. Mapping impervious surfaces with the integrated use of Landsat Thematic Mapper and radar data: A case study in an urban–rural landscape in the Brazilian Amazon. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parece, T.E.; Campbell, J.B. Comparing urban impervious surface identification using landsat and high resolution aerial photography. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4942–4960. [Google Scholar]
- Small, C. High spatial resolution spectral mixture analysis of urban reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 170–186. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. Quantifying high-resolution impervious surfaces using spectral mixture analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2915–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Gillespie, A.R. Remote Sensing of Landscape with Spectral Images: A Physical Modelling Approach; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakubo, F.S.; Morato, R.G.; Luchiari, A. Use of fraction imagery, segmentation and masking techniques to classify land-use and land-cover types in the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5452–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O.; Johnson, P.E. Spectral mixture modeling: A new analysis of rock and soil types at the Viking Lander 1 site. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 8098–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, N.A.; Mackin, S.; Settle, J.J. Mapping vegetation, soils, and geology in semiarid shrublands using spectral matching and mixture modeling of SWIR AVIRIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Batista, G.T.; Mello, E.M.K.; Moreira, J.C.; Duarte, V. Using shade fraction image segmentation to evaluate deforestation in Landsat Thematic Mapper images of the Amazon region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C., Jr.; Firestone, L.; Silva, L.M.; Roberts, D.A. Mapping forest degradation in the Eastern Amazon from Spot 4 through spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.O.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Defries, R.S.; Morton, D. Assessment of deforestation in near real time over the Brazilian Amazon using multitemporal fraction images derived from Terra MODIS. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, M.A.; Souza, C.M., Jr. Linear mixture model classification of burned forests in the Eastern Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 3433–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintano, C.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Roberts, D.A. Multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (MESMA) to map burn severity levels from Landsat images in Mediterranean countries. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Smith, M.O.; Adams, J.B. Green vegetation, non-photosynthetic vegetation and soils in AVIRIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 44, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Gardner, M.; Church, R.; Ustin, S.; Scheer, G.; Green, R.O. Mapping chaparral in the Santa Monica Mountains using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, F.S.; Pérez Machado, R.P. Mapping coffee crops in southeastern Brazil using spectral mixture analysis and data mining classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3414–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, T.; Weeks, J.R.; Roberts, D.; Rogan, J.; Powell, R. Measuring the physical composition of urban morphology using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. The Landsat ETM+ spectral mixing space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Lu, J.W.T. Estimation and vicarious validation of urban vegetation abundance by spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Machado, R.P.; Small, C. Identifying multi-decadal changes of the Sao Paulo urban agglomeration with mixed remote sensing techniques: Spectral mixture analysis and night-lights. Earsel Eproc. 2013, 12, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Murray, A.T. Estimating impervious surface distribution by spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Matsushita, B.; Fukushima, T. A pre-screened and normalized multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis for mapping impervious surface area in Lake Kasumigaura Basin, Japan. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2010, 65, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, C.R. The effects of endmember selection on modelling impervious surfaces using spectral mixture analysis: A case study in Sydney, Australia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, D.; Kuang, W. Examining urban impervious surface distribution and its dynamic change in Hangzhou metropolis. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emplasa. Available online: https://www.emplasa.sp.gov.br/ (accessed on 10 May 2018).
- Harris. Available online: https://www.harrisgeospatial.com/ (accessed on 10 February 2018).
- Wu, C. Normalized spectral mixture analysis for monitoring urban composition using ETM+ imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Benoit, R.; Arturo, S. Spectral unmixing of normalized reflectance data for the deconvolution of lichen and rock mixtures. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Voorde, T.; De Roeck, T.; Canters, F. A comparison of two spectral mixture modelling approaches for impervious surface mapping in urban areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4785–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J. Introductory. In Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, Y.; Rebello, N.S. Supervised and unsupervised spectral angle classifiers. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr. Quantification error versus location error in comparison of categorical maps. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Plane, D.A.; Rogerson, P.A. The Geographical Analysis of Population with Applications to Planning and Business; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Asner, G.P.; Lobell, D.B. A biogeophysical approach for automated SWIR unmixing of soils and vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. Comparative analysis of urban reflectance and surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinn, S.; Stanford, M.; Scarth, P.; Murray, A.T.; Shyy, P.T. Monitoring the composition of urban environments based on the Vegetation-Impervious Surface-Soil (VIS) model by subpixel analysis techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 4131–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridd, M.K. Exploring a V-I-S (Vegetation-Impervious Surface-Soil) model for urban ecosystem analysis through remote sensing: Comparative anatomy for cities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2165–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. Use of impervious surface in urban land use classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.R.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ETRS. In Third Earth Resources Technology Satellite-1 Symposium-Volume I: Technical Presentations; NASA SP-351; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, M.H.; Morato, R.G.; Kawakubo, F.S. Mapping impervious surface areas using orthophotos, satellite imagery and linear regression. RDG 2018, 35, 91–101. [Google Scholar]






| Date | Path/Row | Solar Elevation Angle (°) | Solar Azimuth Angle (°) | Wavelength (μm) | Band |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 August 2015 | 219/76 | 53.9 | 54.2 | 0.435–0.451 | B1 – Ultra Blue |
| 219/77 | 52.9 | 52.9 | 0.452–0.512 | B2 – Blue | |
| 0.533–0.590 | B3 – Green | ||||
| 0.636–0.673 | B4 – Red | ||||
| 0.851–0.879 | B5 – Near infrared (NIR) | ||||
| 1.566–1.651 | B6 – Short-wave infrared (SWIR) 1 | ||||
| 2.107–2.294 | B7–Short-wave infrared (SWIR) 2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawakubo, F.; Morato, R.; Martins, M.; Mataveli, G.; Nepomuceno, P.; Martines, M. Quantification and Analysis of Impervious Surface Area in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo, Brazil. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080944
Kawakubo F, Morato R, Martins M, Mataveli G, Nepomuceno P, Martines M. Quantification and Analysis of Impervious Surface Area in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo, Brazil. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(8):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080944
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawakubo, Fernando, Rúbia Morato, Marcos Martins, Guilherme Mataveli, Pablo Nepomuceno, and Marcos Martines. 2019. "Quantification and Analysis of Impervious Surface Area in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo, Brazil" Remote Sensing 11, no. 8: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080944
APA StyleKawakubo, F., Morato, R., Martins, M., Mataveli, G., Nepomuceno, P., & Martines, M. (2019). Quantification and Analysis of Impervious Surface Area in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo, Brazil. Remote Sensing, 11(8), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080944







