Land Use Changes in the Zoige Plateau Based on the Object-Oriented Method and Their Effects on Landscape Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
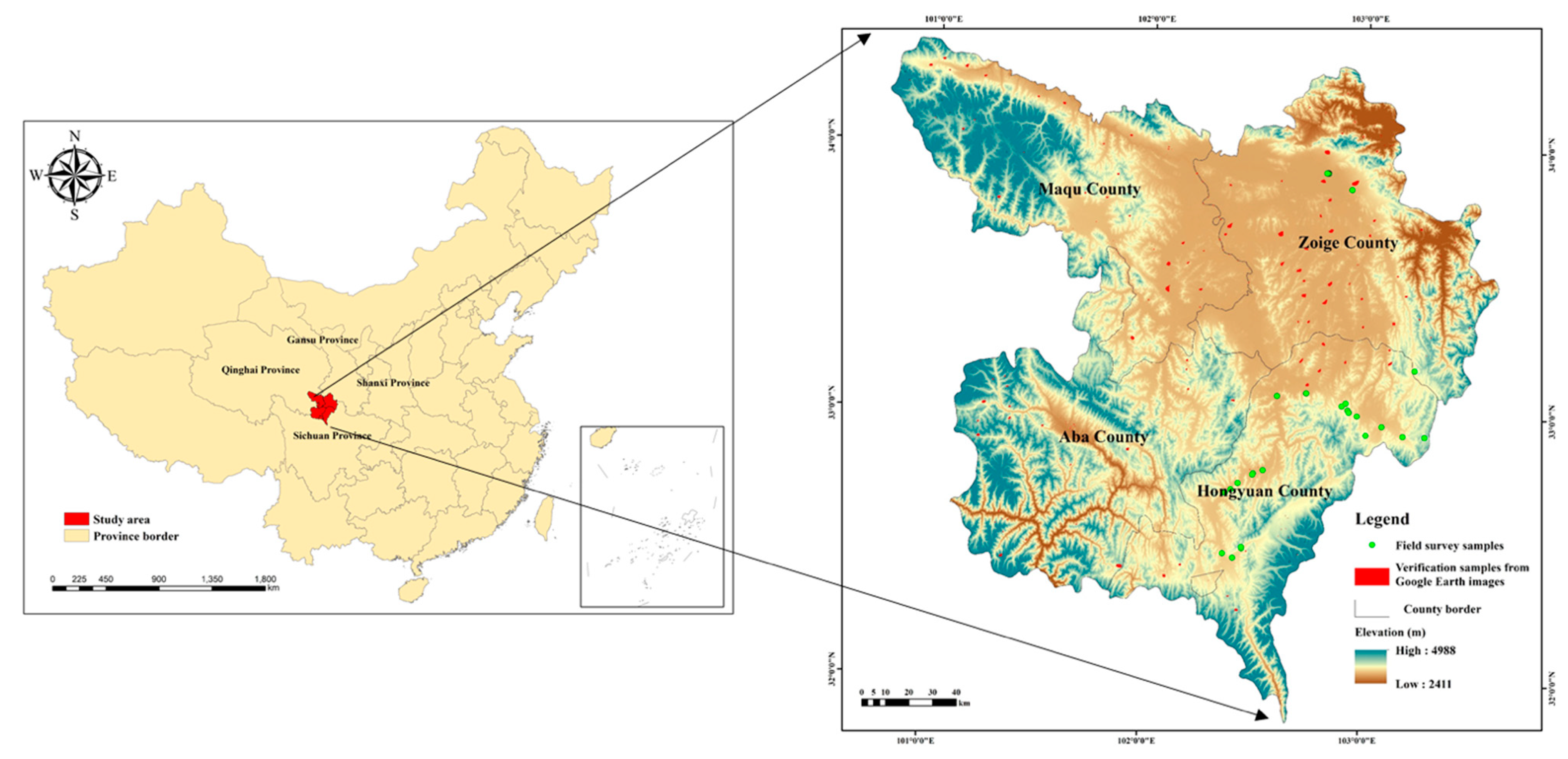
2. Profile of the Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Sources and Processing
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Land Use Information Extraction by the Object-oriented Method
3.2.2. Land Use Change Analysis
3.2.3. Analysis of the Effects of LUCC on Landscape Pattern
4. Results
4.1. Assessment of Classification Accuracy
4.2. Characteristics of the Distribution of Land Use Types
4.3. Characteristics of Land Use Change
4.3.1. Dynamic Degree of Land Use
4.3.2. Transfer Matrix of Land Use
4.4. Analysis of the Effects of LUCC on Landscape Pattern
4.4.1. Temporal Changes of the Overall Landscape Pattern
4.4.2. Effects of LUCC on the Landscape Pattern
4.4.3. Effects of LUCC on the Landscape Pattern at Different Time Periods
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, B.L.; Lambin, E.F.; Reenberg, A. The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20666–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, E.C.; Neerchal, N.; Peng, K.; Xiao, H.S.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, S.C.; Wu, J.X.; Jiao, J.G.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Estimating long–term changes in China’s village landscapes. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.E.; Granados, E.L.; Geneletti, D.; Pérez–Salicrup, D.R.; Salinas, V. Analysing land cover and land use change processes at watershed level: A multitemporal study in the Lake Cuitzeo Watershed, Mexico (1975–2003). Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsanjani, J.J. Dynamic Land Use/Cover Change Simulation: Geosimulation and Multi Agent–Based Modelling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Verburg, P.H.; Steeg, J.V.D.; Veldkamp, A.; Willemen, L. From land cover change to land function dynamics: A major challenge to improve land characterization. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.G.; Canadell, J.G.; Randerson, J.T.; Jackson, R.B.; Hungate, B.A.; Baldocchi, D.D. Biophysical considerations in forestry for climate protection. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, H.A.; Duraiappah, A.; Larigauderie, A. Evolution of natural and social science interactions in global change research programs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110 (Suppl. 1), 3665–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, S.M.; Ducharne, A.; Polcher, J. The impact of global land–cover change on the terrestrial water cycle. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Sun, G.; Chappelka, A. Century–scale responses of ecosystem carbon storage and flux to multiple environmental changes in the southern united states. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 674–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, F.; Taha, N.; Nyssen, J.; Girma, A.; Zenebe, A.; Behailu, M. The impacts of watershed management on land use and land cover dynamics in Eastern Tigray (Ethiopia). Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 53, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tashpolat, T.; Kung, H.T.; Ding, J. The change of land use/cover and characteristics of landscape pattern in arid areas oasis: An application in Jinghe, Xinjiang. Geospat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 13, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jin, S.M.; Yang, L.M.; Danielson, P.; Homer, C.; Fry, J.; Xian, G. A comprehensive change detection method for updating the national land cover database to circa 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Niu, T.L.; Kejia, D.; Zhou, Q.P.; Ma, T.X.; Gao, Y.Y. Ecological restorationand its effects on a regional climate: The source region of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5897–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.P.; Hansen, M.C.; Stehman, S.V.; Potapov, P.V.; Alexandra, T.; Vermote, E.F.; Townshend, J.R. Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 2018, 560, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, M.; Arini, N.; Schape, A.; Binnig, G.; Linssen, B. Object–oriented image analysis for high content screening: Detailed quantification of cells and sub cellular structures with the Cellenger software. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2006, 69, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wu, W.B.; Xia, T.; Yu, Q.Y.; Yang, P.; Li, Z.G.; Song, Q. Exploring the use of Google Earth imagery and object–based methods in land use/cover mapping. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6026–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyport, R.N.; Oommen, T.; Martha, T.R.; Sajinkumar, K.S.; Gierke, J.S. A comparative analysis of pixel– and object–based detection of landslides from very high–resolution images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, A.; Kerle, N. Object–oriented mapping of landslides using random forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2564–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Godron, M. Landscape Ecology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.G.; Hobbs, R. Key issues and research priorities in landscape ecology: An idiosyncratic synthesis. Landscape Ecol. 2002, 17, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, V.H.; Brown, S.; Haeuber, R.; Hobbs, N.T.; Huntly, N.; Naiman, R.J.; Riebsame, W.E.; Turner, M.G.; Valone, T. Ecological principles and guidelines for managing the use of land. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 639–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.X.; Wang, Y.B. Changes in alpine wetland ecosystems of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau from 1967 to 2004. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 180, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice: Pattern and Process, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.G. Landscape Ecology: Pattern, Process, Scale and Hierarchy; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H. Quantitative Methods in Landscape Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G.; O’Neill, R.V.; Gardner, R.H.; Milne, B.T. Effects of changing spatial scale on the analysis of landscape pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 1989, 3, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, S.T.A.; White, P.S. The ecology of natural disturbance and patch dynamics. Science 1985, 230, 434–435. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Wu, J.G. Use and misuse of landscape indices. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Du, Y.; Ling, F.; Wu, S.J.; Feng, Q. Using a sub–pixel mapping model to improve the accuracy of landscape pattern indices. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.H.; Ouyang, H.; Cui, B.S.; Wang, Q.G.; Chen, H. Changes in landscape pattern of alpine wetlands on the Zoige Plateau in the past four decades. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.H.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Hua, O.; Wei, D.; Li, A.N. Landscape pattern evolution processes of alpine wetlands and their driving factors in the Zoige Plateau of China. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubaida, M.; Xia, J.X.; Polat, M.; Zhang, R. Land use and landscape pattern changes in the middle reaches of the Keriya River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.C.; Wang, W.L.; Hu, G.Y.; Wei, Z.H. Changes in ecosystem service values in Zoige plateau, china. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Wu, W.Z.; Liu, X.H.; Fath, B.D.; Sun, H.L.; Liu, X.C.; Xiao, X.R.; Cao, J. Land use/cover change and regional climate change in an arid grassland ecosystem of Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Model. 2017, 353, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetland China. The Report on the Second National Wetland Resources Survey (2009–2013). 2014. Available online: http://www.shidi.org (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Huo, L.L.; Chen, Z.K.; Zou, Y.C.; Lu, X.G.; Guo, J.W.; Tang, X.G. Effect of Zoige alpine wetland degradation on the density and fractions of soil organic carbon. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.Y.; Dong, Z.B.; Lu, J.F.; Yan, C.Z. Driving forces of land use and land cover change (LUCC) in the Zoige Wetland, Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2012, 4, 422–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.J.; Lu, Q.F.; Song, K.C.; Qin, G.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H.X.; Li, J.; Liu, G.D.; Li, H. Remotely sensing the ecological influences of ditches in Zoige Peatland, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 5186–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Yi, Y.H.; Song, K.C.; Kimball, J.S.; Lu, Q.F. Hydrological response of alpine wetlands to climate warming in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.H.; Cheng, L.; Li, M.C.; Zhao, R.F.; Duan, Y.W. Impacts of LUCC on soil properties in the riparian zones of desert oasis with remote sensing data: A case study of the middle Heihe River basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, A.P.; Li, C.H.; Wang, X.; Hu, J. Land use/cover change in response to driving forces of Zoige County, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiang, S.; Guo, R.Q.; Ning, W.; Sun, S.C.; Qin, P.; Mitsch, W.J. Current status and future prospects of Zoige marsh in Eastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.B.; Hu, G.Y.; Yan, C.Z.; Wang, W.L.; Lu, J.F. Aeolian desertification and its causes in the Zoige Plateau of China’s Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.L.; Zhang, S.M.; Zhou, W.C. Muti–source data–based remote sensing auto–survey of land use in Ruoergai wetland. Soils 2008, 40, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, G.; Xu, B.; Jin, Y.X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.B.; Guo, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, X.C. Advances in studies of wetlands in Zoige Plateau. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 32, 76–82. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.G.; Xu, W.H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.M.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratama, B.Y.; Sarno, R. Personality classification based on Twitter text using Naive Bayes, KNN and SVM. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Data & Software Engineering, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 25–26 November 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Bao, Y.H. Study on the methods of land use dynamic change research. Prog. Geogr. 1999, 18, 81–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps. Computer Software Program Produced by the Authors at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst. 2012. Available online: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- McGarigal, K.; Marks, B.J. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; General Technical Report; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1995.
- Plexida, S.G.; Sfougaris, A.I.; Ispikoudis, I.P.; Papanastasis, V.P. Selecting landscape metrics as indicators of spatial heterogeneity—A comparison among Greek landscapes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.M.; Niu, Z.G.; Gong, P.; Li, M.N.; Hu, L.L.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.X.; Gu, H.J.; Mu, J.R.; Dou, G.J.; et al. A method for alpine wetland delineation and features of border: Zoigê Plateau, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Gao, P.; Hu, X.Y.; Yi, Y.J.; Pan, B.Z.; You, Y.C. Coupled impact of decadal precipitation and evapotranspiration on peatland degradation in the Zoige basin, china. Phys. Geogr. 2019, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Bo, Y.C.; Zhu, Y.X.; Ji, X.L. A novel method for assessing the segmentation quality of high–spatial resolution remote–sensing images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3816–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.J.; Niu, Z.G.; Chen, Y.F.; Li, L.F.; Zhang, H.Y. Global wetlands: Potential distribution, wetland loss, and status. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.Y.; Dong, Z.B.; Lu, J.F.; Yan, C.Z. The developmental trend and influencing factors of aeolian desertification in the Zoige Basin, eastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Aeolian Res. 2015, 19, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.F.; Lehmkuhl, F.; Folk, D. Quantifying land degradation in the Zoige Basin, NE Tibetan Plateau using satellite remote sensing data. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.C.; Li, Z.W.; Li, X.L. Land cover change in Zoige Plateau during 1990–2011. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2018, 38, 62–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Baker, C.; Graham, S. Restoration approaches used for degraded peatlands in Ruoergai (Zoige), Tibetan Plateau, China, for sustainable land management. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 38, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Fan, X.Y.; Ma, J.K.; Pimm, S.L.; Kong, L.Q.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.S.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.G.; et al. Hidden loss of wetlands in China. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3065–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.H.; Pimm, S.L.; Du, A.; Su, Y.; Fan, X.Y.; An, L.; Liu, J.G.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Transforming protected area management in China. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Band 1-Coastal | 0.433–0.453 | 30 |
| Band 2-Blue | 0.450–0.515 | 30 |
| Band 3-Green | 0.525–0.600 | 30 |
| Band 4-Red | 0.630–0.680 | 30 |
| Band 5-NIR (Near Infrared) | 0.845–0.885 | 30 |
| Band 6-SWIR (Short-wave infrared) 1 | 1.560–1.651 | 30 |
| Band 7-SWIR2 | 2.100–2.300 | 30 |
| Band 8-Pan | 0.500–0.680 | 15 |
| Band 9-Cirrus | 1.360–1.390 | 30 |
| Type | Path Row | Time | Cloud Cover (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OLI | 130037 | 20150706 | 8.12 |
| OLI | 131036 | 20150729 | 1.9 |
| OLI | 131037 | 20150729 | 6.97 |
| OLI | 131038 | 20151102 | 0.74 |
| OLI | 132036 | 20150922 | 0.85 |
| OLI | 132037 | 20150922 | 2 |
| Category | Index Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Area | Number of patches (NP) | Total number of patch. |
| Landscape fragmentation index (LFI) | The ratio of number of patches and the area of corresponding the landscape. | |
| Patch density (PD) | Number of patches per unit area. | |
| Shape | Landscape shape index (LSI) | A standardized measure of patch compactness that adjusts for the size of the patch. |
| Perimeter area fractal dimension (PAFRAC) | Non-randomness or degree of aggregation for different patches. | |
| Mean fractal dimension (FRAC_MN) | The shape complexity of patches, which approaches 1 for shapes with simple perimeters and 2 for complex shapes. | |
| Accumulation and dispersion | Mean patch contiguity index (CONTIG_MN) | It equals the average contiguity value for the cells in a patch. |
| Proportion of like adjacency (PLADJ) | It equals the number of like adjacencies involving the focal class, divided by the total number of cell adjacencies involving the focal class; multiplied by 100 (to convert to a percentage). It measures the degree of aggregation of the focal patch type. | |
| Interspersion and juxtaposition index (IJI) | The measurement of evenness of patch adjacencies and the degree of intermixing of patch types. | |
| Patch cohesion index (COHESION) | It is proportional to the area-weighted mean perimeter-area ratio divided by the area-weighted mean patch shape index. | |
| Effective mesh size (MESH) | The ratio of square of summed patch areas and the total area. It expresses the fragmentation independent of the extent of the studied landscape. | |
| Splitting index (SPILIT) | The number of patches obtained with subdividing the landscape into equal-sized patches based on the effective mesh size. | |
| Aggregation index (AI) | The ratio of the observed number of like adjacencies and the maximum possible number of like adjacencies given the proportion of the landscape comprised of each patch type. | |
| Diversity | Shannon’s diversity index (SHDI) | Uncertainties and landscape heterogeneity of patches. |
| Simpson’s diversity index (SIDI) | It equals 1 minus the sum, across all patch types, of the proportional abundance of each patch type squared |
| SVM | KNN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User’s Accuracy (%) | Producer’s Accuracy (%) | User’s Accuracy (%) | Producer’s Accuracy (%) | |
| Grassland | 99.54 | 98.64 | 96.94 | 34.75 |
| Farmland | 91.62 | 99.52 | 57.53 | 79.64 |
| Forest land | 42.19 | 100 | 33.72 | 49.45 |
| Unused land | 99.77 | 100 | 78.16 | 85.82 |
| Construction land | 100 | 100 | 69.78 | 56.14 |
| Wetland | 100 | 86.52 | 95.27 | 88.35 |
| Water body | 70.95 | 100 | 98.34 | 70.87 |
| Overall accuracy (%): SVM = 93.2, KNN = 57.7 | ||||
| Kappa: SVM = 0.889, KNN = 0.456 | ||||
| Category | Grassland | Farmland | Forest Land | Unused Land | Construction Land | Wetland | Water Body |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | 0.706 * | 0.820 *** | 0.873 ** | 0.962 *** | 0.621 * | 0.766 ** | 0.768 ** |
| Shape | 0.993 *** | 0.608 * | 0.966 *** | 0.919 *** | 0.386 | 0.863 *** | 0.816 ** |
| Accumulation and dispersion | 0.153 | −0.274 | −0.360 # | −0.285 | 0.023 | −0.190 | −0.230 |
| Grassland | Farmland | Forest Land | Unused Land | Construction Land | Wetland | Water Body | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2005 | 0.998 *** | 0.953 *** | 0.561 * | 0.727 ** | 0.940 *** | 0.788 ** | 0.268 |
| 2005–2010 | 0.842 *** | −0.613 * | −0.587 * | 0.030 | −0.570 * | 0.428 | 0.288 |
| 2010–2015 | 0.328 | −0.011 | −0.325 | −0.286 | 0.164 | 0.086 | −0.222 |
| 2000–2015 | 0.363 | 0.959 *** | 0.158 | 0.833 *** | 0.752 ** | 0.681 ** | 0.154 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, G.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Luo, S.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Q. Land Use Changes in the Zoige Plateau Based on the Object-Oriented Method and Their Effects on Landscape Patterns. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010014
Shen G, Yang X, Jin Y, Luo S, Xu B, Zhou Q. Land Use Changes in the Zoige Plateau Based on the Object-Oriented Method and Their Effects on Landscape Patterns. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Ge, Xiuchun Yang, Yunxiang Jin, Sha Luo, Bin Xu, and Qingbo Zhou. 2020. "Land Use Changes in the Zoige Plateau Based on the Object-Oriented Method and Their Effects on Landscape Patterns" Remote Sensing 12, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010014
APA StyleShen, G., Yang, X., Jin, Y., Luo, S., Xu, B., & Zhou, Q. (2020). Land Use Changes in the Zoige Plateau Based on the Object-Oriented Method and Their Effects on Landscape Patterns. Remote Sensing, 12(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010014




