Fine-Resolution Mapping of Soil Total Nitrogen across China Based on Weighted Model Averaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
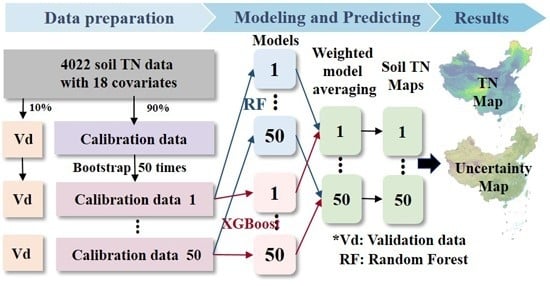
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Data
2.2. Environmental Covariates
2.3. Model Development
2.3.1. Machine-Learning Approaches
2.3.2. Weighted Model Averaging
2.3.3. Model Calibration and Validation
2.4. Uncertainty Assessment
2.5. One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Test
3. Results
3.1. Importance of Covariates
3.2. Evaluation of the Approaches
3.3. Mapping of Soil TN and Its Uncertainty
3.4. Soil TN of Different Soil Types and Land-Use Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Quality of the Prediction
4.2. Spatial Distribution of Soil TN
4.3. Uncertainty in Soil TN Prediction
4.4. Effect of Land Use on Soil TN Contents
4.5. Limitations and Perspectives
5. Conclusions
- Using the weighted average of these two models, a reasonable result was obtained, with the lowest RMSE (1.15 g·kg−1) and the highest R2 (0.41) compared with individual models, that explained 41% of the spatial discrepancy in the soil TN contents and reduced the prediction uncertainty as well.
- The TN map showed high spatial heterogeneity, with the spatial variation influenced by variables related to climate, relief and organisms. The spatial trends were similar to previous TN maps in coarser resolution, with high TN in the eastern Tibetan Plateau and north-eastern China, and low TN in the desert area.
- The uncertainty map can help policymakers and stakeholders to understand the reliability of the map produced in our study. It should be noted that the uncertainties can be reduced by using more covariates or supplementing the number of soil profiles in the future.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinfield, J.V.; Fagerman, D.; Colic, O. Evaluation of sensing technologies for on-the-go detection of macro-nutrients in cultivated soils. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 70, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, M.; Lal, R.; Logan, T.; Sigarán, J. Soil Nitrogen and Carbon Response to Maize Cropping System, Nitrogen Source, and Tillage. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Porder, S.; Houlton, B.Z.; Chadwick, O.A. Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: Mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen–phosphorus interactions. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledley, T.S.; Sundquist, E.T.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hall, D.K.; Fellows, J.D.; Killeen, T.L. Climate change and greenhouse gases. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. 2013, 80, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S. Quantifying greenhouse gas emissions from soils: Scientific basis and modeling approach. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2007, 53, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Corell, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrouays, D.; Deslais, W.; Badeau, V. The carbon content of topsoil and its geographical distribution in France. Soil Use Manag. 2001, 17, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.B.; Santos, M.L.M.; Minasny, B. On digital soil mapping. Geoderma 2003, 117, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, H. Factors of Soil Formation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, Z. Effects of land use, climate, topography and soil properties on regional soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in the Upstream Watershed of Miyun Reservoir, North China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, X.; Huang, L.; Shao, M. Vertical distribution of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus in the critical zone on the loess plateau, China. Catena 2018, 166, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selige, T.; Böhner, J.; Schmidhalter, U. High resolution topsoil mapping using hyperspectral image and field data in multivariate regression modeling procedures. Geoderma 2006, 136, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, W. Predictive mapping of soil total nitrogen at a regional scale: A comparison between geographically weighted regression and cokriging. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 42, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasiouny, H.; Abowaly, M.; Abu_Alkheir, A.; Gad, A. Spatial variation of soil carbon and nitrogen pools by using ordinary Kriging method in an area of north Nile Delta, Egypt. Catena 2014, 113, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, D.; Ding, J.Z.; Li, F.; Wei, N.; Fang, K.; Yang, G.; Zhang, B.; Liu, L.; Qin, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Spatially-explicit estimate of soil nitrogen stock and its implication for land model across Tibetan alpine permafrost region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, F.; Hughes, P.; McBratney, A.B.; Minasny, B.; Malone, B.P. Evaluating the spatial and vertical distribution of agriculturally important nutrients—Nitrogen, phosphorous and boron—In North West Iran. Catena 2019, 173, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. ECONOMETRICS; Department of Economics, University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 2019; p. 846. Available online: http://www.ssc.wisc.edu/~bhansen/econometrics/ (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Wang, S.; Zhuang, Q.L.; Wang, Q.B.; Jin, X.; Han, C. Mapping stocks of soil organic carbon and soil total nitrogen in Liaoning Province of China. Geoderma 2017, 305, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Adhikari, K.; Li, W.; Yu, M.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Q. Mapping total soil nitrogen from a site in northeastern China. Catena 2018, 166, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Webster, R.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S. Baseline map of soil organic carbon in Tibet and its uncertainty in the 1980s. Geoderma 2019, 334, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, M.; Spiess, K.; Baltensweiler, A.; Grob, U.; Keller, A.; Greiner, L.; Schaepan, M.E.; Papritz, A. Evaluation of digital soil mapping approaches with large sets of environmental covariates. Soil 2018, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Liang, Z.Z.; Webster, R.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhou, Y.; Teng, H.F.; Hu, B.F.; Arrouays, D.; Shi, Z. A high-resolution map of soil pH in China made by hybrid modeling of sparse soil data and environmental covariates and its implications for pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehmke, B.C.; Greenwell, B.M. Hands-On Machine Learning with R, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; in press; Available online: https://bradleyboehmke.github.io/HOML/ (accessed on 6 December 2019).
- Malone, B.P.; Minasny, B.; Odgers, N.P.; McBrantney, A. Using model averaging to combine soil property rasters from legacy soil maps and from point data. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Smith, S.E.; Grunwaldb, S.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Wani, S.P.; Nair, V.D. Estimating soil total nitrogen in smallholder farm settings using remote sensing spectral indices and regression kriging. Catena 2017, 163, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, H.; Yu, K.; Lu, K.; Shi, P.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, B. Soil total nitrogen sources on dammed farmland under the condition of ecological construction in a small watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 121, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Dong, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Su, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks in alpine ecosystems of Altun Mountain National Nature Reserve in dry China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 191, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Cao, L.; Zeng, J. Spatial distribution of soil nitrogen in gully hillsides of Sejila Mountain, Southeastern Tibet. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- National Soil Survey Office. Chinese Soil Genus Records; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1993; Volume 1, (In Chinese).
- National Soil Survey Office. Chinese Soil Genus Records; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1994; Volume 2, (In Chinese).
- National Soil Survey Office. Chinese Soil Genus Records; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1994; Volume 3, (In Chinese).
- National Soil Survey Office. Chinese Soil Genus Records; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1995; Volume 4, (In Chinese).
- National Soil Survey Office. Chinese Soil Genus Records; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1995; Volume 5, (In Chinese).
- National Soil Survey Office. Chinese Soil Genus Records; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1996; Volume 6, (In Chinese).
- Gregorich, E.G.; Carter, M.R.; Angers, D.A.; Monreal, C.M.; Ellert, B.H. Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic-matter quality in agricultural soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1994, 74, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, T.F.A.; McBratney, A.B.; Laslett, G.M. Modeling soil attribute depth functions with equal-area quadratic smoothing splines. Geoderma 1999, 91, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, B.P.; Mcbratney, A.B.; Minasny, B.; Laslett, G.M. Mapping continuous depth functions of soil carbon storage and available water capacity. Geoderma 2009, 154, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J.; Pinzon, J.E.; Brown, M.E. Global Inventory Modeling and Mapping Studies; NA94apr15b.n11-VIg, 2.0; Global Land Cover Facility, University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, S.D.; Small, J. AVHRR Global Production Efficiency Model, 1981–2000; The Global Land Cover Facility, University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Goovaerts, P. Using elevation to aid the geostatistical mapping of rainfall erosivity. Catena 1999, 34, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Z.; Yu, D.S.; Warner, E.D.; Pan, X.Z.; Petersen, G.W.; Gong, Z.G.; Weindorf, D.C. Soil database of 1: 1,000,000 digital soil survey and reference system of the chinese genetic soil classification system. Soil Horiz. 2004, 45, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.Z.; Yu, D.S.; Xu, S.X.; Warner, E.D.; Wang, H.J.; Sun, W.X.; Zhao, Y.C.; Gong, Z.T. Cross-reference for relating Genetic Soil Classification of China with WRB at different scales. Geoderma 2010, 155, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M. Caret: Classification and Regression Training. R Package Version 6.0-84. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=caret (accessed on 27 April 2019).
- Friedman, J. Glmnet: Lasso and Elastic-Net Regularized Generalized Linear Models. R Package Version 3.0-2. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/glmnet/index.html (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- National Soil Survey Office. Chinese Soil; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1998; (In Chinese).
- Fernandez-Delgado, M.; Cernadas, E.; Barro, S.; Amorim, D. Do we need hundreds of classifiers to solve real world classification problems? J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 3133–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, W.; Dai, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhu, A.X.; Duan, Q.Y.; Wu, L.Z.; Ji, D.Y.; Ye, A.Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A China data set of soil properties for land surface modeling. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2013, 5, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Q.; Yue, T.X.; Fan, Z.M.; Du, Z.P.; Chen, C.F.; Lu, Y.M. Spatial simulation of topsoil TN at the national scale in China. Geogr. Res. 2010, 29, 1981–1992. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Arrouays, D.; Grundy, M.G.; Hartemink, A.E.; Hempel, J.W.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Hong, S.Y.; Lagacherie, P.; Lelyk, G.; McBratney, A.B.; McKenzie, N.J.; et al. Globalsoilmap: Toward a fine-resolution global grid of soil properties. Adv. Agron. 2014, 125, 93–134. [Google Scholar]
- Follett, R.F.; Stewart, C.E.; Pruessner, E.G.; Kimble, J.M. Effects of climate change on soil carbon and nitrogen storage in the US Great Plains. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 67, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, C.C.; Chen, Z.S.; Hsieh, C.F. Relationships between soil properties and slope position in a lowland rain forest of southern Taiwan. Geoderma 2004, 123, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmillan, R.A.; Moon, D.E.; Coupé, R.A.; Phillips, N. Predictive Ecosystem Mapping (PEM) for 8.2 Million ha of Forestland. In Digital Soil Mapping: Bridging Research, Environmental Application, and Operation; Boettinger, J.L., Howell, D.W., Moore, A.C., Hartemink, A.E., Kienast-Brown, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 337–356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Hartemink, A.E.; Shi, Z.; Liang, Z.Z.; Lu, Y.L. Land use and climate change effects on soil organic carbon in North and Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.Z.; Chen, S.C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhao, R.Y.; Shi, Z.; Rossel, R.A.V. National digital soil map of organic matter in topsoil and its associated uncertainty in 1980’s China. Geoderma 2019, 335, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Q.; Mao, F.; Sun, H.; Hou, Y.Y. Study of normalized difference vegetation index variation and its correlation with climate factors in the three-river-source region. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.Q.; Shi, Z. Modeling and mapping soil erosion potential in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.T.; Li, G.S.; Fu, W.L.; Yi, X.S.; Lan, J.C.; Yuang, B. Temporal-spatial variations of total nitrogen in the degraded grassland of Three-River Headwaters region in Qinghai Province. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.C.; Martin, M.P.; Saby, N.P.; Walter, C.; Angers, D.A.; Arrouays, D. Fine resolution map of top-and subsoil carbon sequestration potential in France. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, A.; Barringer, J.; Forrester, G.; McNeill, S.J. Soilscapes Basis for Digital Soil Mapping in New Zealand. In Digital Soil Mapping: Bridging Research, Environmental Application, and Operation; Boettinger, J.L., Howell, D.W., Moore, A.C., Hartemink, A.E., Kienast-Brown, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.Z.; Chen, S.C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z. High-resolution three-dimensional mapping of soil organic carbon in China: Effects of SoilGrids products on national modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, D.; Kirschbaum, M.U.F.; Mcmurtrie, R.E.; McGilvray, A. Does conversion of forest to agricultural land change soil carbon and nitrogen? A review of the literature. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Gong, Z.T. Assessment and analysis of soil quality changes after eleven years of reclamation in subtropical China. Geoderma 1998, 81, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Adhikari, K.; Wang, Q.B.; Sui, Y.Y.; Xin, G. Effect of cultivation history on soil organic carbon status of arable land in northeastern China. Geoderma 2019, 342, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Xiao, H.L.; Liu, Z.M.; Li, J. Soil degradation and restoration as affected by land use change in the semiarid Bashang area, northern China. Catena 2005, 59, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.B.; Gifford, R.M. Soil carbon stocks and land use change: A meta analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahani, U.; Behera, N. Impact of deforestation on soil physicochemical characteristics, microbial biomass and microbial activity of tropical soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 12, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berihu, T.; Girmay, G.; Sebhatleab, M.; Berhane, E.; Zenebe, A.; Sigua, G.C. Soil carbon and nitrogen losses following deforestation in Ethiopia. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Mao, R.; Gong, D.Y.; Liu, H.B.; Yang, J. Modeled responses of summer climate to realistic land use/cover changes from the 1980s to the 2000s over eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinda, J.A.; Trac, C.J.; Zhai, D.; Harrell, S. Dual-function forests in the returning farmland to forest program and the flexibility of environmental policy in china. Geoforum 2016, 78, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yao, Y.F.; Qin, X.; Wei, X.R.; Jia, X.X.; Shao, M.G. Response of carbon and nitrogen to afforestation from 0 to 5 m depth on two semiarid cropland soils with contrasting inorganic carbon concentrations. Geoderma 2020, 357, 113940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Rao, L.; Sun, K.; Han, Y.; Guo, X. Spatio-temporal distribution of soil nitrogen in Poyang lake ecological economic zone (South-China). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Statistic Almanac of 1999. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/yearbook/indexC.htm (accessed on 20 September 1999).
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.X.; Zhu, Z.L. Regional Nitrogen Budgets for China and Its Major Watersheds. Biogeochemistry 2002, 57, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Set | Covariate | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terrain | Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | 90 m | https://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/srtm/ |
| Slope | |||
| Aspect | |||
| Curvature | |||
| Terrain ruggedness index (TRI) | |||
| Topographic wetness index (TWI) | |||
| Multi-resolution Valley-bottom flatness (MrVBF) | |||
| Organism | Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | 8000 m | [40] |
| Net primary productivity (NPP) | 8000 m | [41] | |
| Vegetation types | 1000 m | http://www.resdc.cn/ | |
| Land use types | 1000 m | http://www.resdc.cn/ | |
| Climate | Land surface temperature, day time (LSTD) | 1000 m | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/ |
| Land surface temperature, night time (LSTN) | 1000 m | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/ | |
| Mean annual solar radiation (MASR) | 1000 m | http://www.geodata.cn | |
| Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 1000 m | http://www.resdc.cn/ | |
| Mean annual precipitation (MAP) | 1000 m | http://www.resdc.cn/ | |
| Evapotranspiration (ET) | 1000 m | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/ | |
| Soil | Soil types (1:1,000,000 map) | [43] |
| R2 | RMSE 1 (g·kg−1) | ME 2 (g·kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| XGBoost | 0.34 | 1.20 | −0.26 |
| RF | 0.38 | 1.18 | −0.27 |
| WMA | 0.41 | 1.15 | −0.29 |
| Grade | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN content (g·kg−1) | >2 | 1.5–2 | 1.0–1.5 | 0.75–1 | 0.5–0.75 | <0.5 | |
| Arable land | area | 1.57 | 2.09 | 4.43 | 3.39 | 2.09 | 0.17 |
| proportion | 11.4% | 15.2% | 32.3% | 24.7% | 15.2% | 1.2% | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Xue, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, N.; Shi, Z. Fine-Resolution Mapping of Soil Total Nitrogen across China Based on Weighted Model Averaging. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010085
Zhou Y, Xue J, Chen S, Zhou Y, Liang Z, Wang N, Shi Z. Fine-Resolution Mapping of Soil Total Nitrogen across China Based on Weighted Model Averaging. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yue, Jie Xue, Songchao Chen, Yin Zhou, Zongzheng Liang, Nan Wang, and Zhou Shi. 2020. "Fine-Resolution Mapping of Soil Total Nitrogen across China Based on Weighted Model Averaging" Remote Sensing 12, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010085
APA StyleZhou, Y., Xue, J., Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Liang, Z., Wang, N., & Shi, Z. (2020). Fine-Resolution Mapping of Soil Total Nitrogen across China Based on Weighted Model Averaging. Remote Sensing, 12(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010085