Measurement of Cloud Top Height: Comparison of MODIS and Ground-Based Millimeter Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MODIS CTH Retrieval Algorithm
2.2. Ka Band Radar
2.3. Other Data
2.4. Data Collocation Method
3. Results Overview of CTHs Derived from MODIS and KPDR
4. Factors Affecting Retrieval Accuracy and Their Impacts
4.1. Influences from Cloud Properties
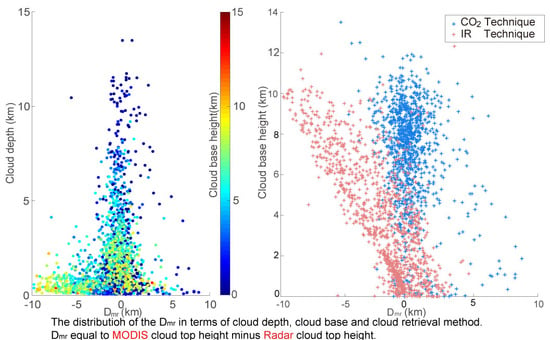
4.1.1. Dmr and Cloud Depth
4.1.2. Dmr and CBH
4.1.3. Dmr and Cloud Fraction
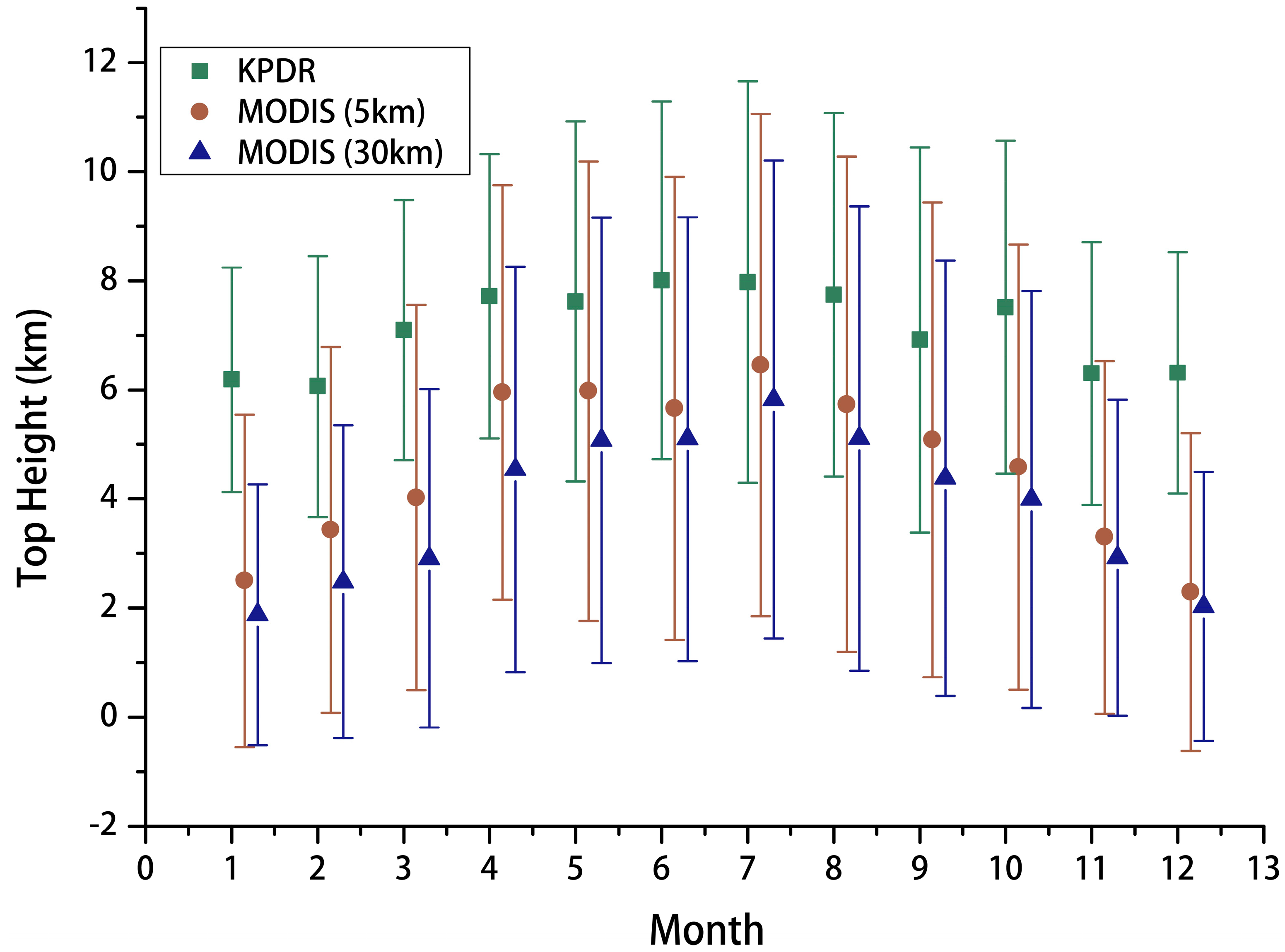
4.1.4. Dmr and Cloud Layer and Season
4.2. Influences from Atmospheric Parameters
4.2.1. Dmr, TWV and Ozone
4.2.2. Dmr and Temperature Inversion
4.2.3. Dmr and Surface Atmospheric Properties
4.3. Dmr, Retrieval Method and Viewing Angle
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Scheme | Mean | STD | Median | IQR | Peak | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dm0r5 | −1.018 | 2.782 | −0.670 | 2.195 | −0.501 | 1.836 |
| Dm5r5 | −1.076 | 2.484 | −0.645 | 2.510 | −0.384 | 2.051 |
| Dm5r30 | −1.305 | 2.506 | −0.760 | 2.419 | −0.537 | 1.945 |
| Dm30r30 | −1.343 | 2.293 | −0.958 | 2.436 | −0.683 | 1.897 |
| Average | −1.198 | 2.511 | −0.770 | 2.417 | −0.701 | 1.929 |
References
- Cess, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, X.; Dvortsov, V. Absorption of solar radiation by clouds: Interpretations of satellite, surface, and aircraft measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 23299–23309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, R.; Platnick, S.; Ackerman, S.A.; Hemler, R.S.; Hofmann, R.J.P. Reconciling simulated and observed views of clouds: MODIS, ISCCP, and the limits of instrument simulators. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 4699–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Cess, R.D.; Harrison, E.F.; Minnis, P.; Barkstrom, B.R.; Ahmad, E.; Hartman, D. Cloud-Radiative forcing and climate: Results from the earth radiation budget experiment. Science 1989, 243, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, K.S.; Pilewskie, P.; Mayer, B.; Wendisch, M.; Kindel, B. Apparent absorption of solar spectral irradiance in heterogeneous ice clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Clouds and aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G., Tignor, M., Allen, S., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P., Eds.; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 571–657. [Google Scholar]
- Riese, M.; Ploeger, F.; Rap, A.; Vogel, B.; Konopka, P.; Dameris, M.; Forster, P. Impact of uncertainties in atmospheric mixing on simulated UTLS composition and related radiative effects. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R. Updating a land surface model with MODIS-derived snow cover. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T.; et al. An introduction to Himawari-8/9—Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menzel, W.P.; Frey, R.A.; Zhang, H.; Wylie, D.P.; Moeller, C.C.; Holz, R.E.; Maddux, B.; Baum, B.; Strabala, K.; Gumley, L. Modis global cloud-top pressure and amount estimation: Algorithm description and results. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1175–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, Fengyun-4. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1637–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, R. Trends in ISCCP, MISR, and MODIS cloud-top-height and optical-depth histograms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, E.; Li, J.; Menzel, W.P.; Heidinger, A.K.; Kahn, B.H.; Liu, C.-Y. Comparison of AIRS, MODIS, CloudSat and CALIPSO cloud top height retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Luo, J.; Liang, J.; Wang, B.; Tian, W.; Chen, X. Comparisons of AGRI/FY-4A cloud fraction and cloud top pressure with MODIS/Terra measurements over East Asia. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, B.A.; Menzel, P.W.; Frey, R.A.; Tobin, D.C.; Holz, R.E.; Ackerman, S.A. MODIS cloud-top property refinements for collection 6. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 1145–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Minnis, P.; Ayers, J.K.; Mcgill, M.J.; Palikonda, R.; Spangenberg, D.A.; Smith, W.L.; Yost, C. Evaluation of satellite-based upper troposphere cloud top height retrievals in multilayer cloud conditions during TC4. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Minnis, P.; Xi, B.; Sun-Mack, S.; Chen, Y. Comparison of CERES-MODIS stratus cloud properties with ground-bases measurements at the DOE ARM southern great plains site. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genkova, I.; Seiz, G.; Zuidema, P.; Zhao, G.; Girolamo, L.D. Cloud top height comparisons from ASTER, MISR, and MODIS for trade wind cumuli. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, N.; Adok, C.; Anke, T.; Scheirer, R.; Hörnquist, S. Neural network cloud top pressure and height for MODIS. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3177–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, S.-H.; Sohn, B.-J.; Yang, P.; Baum, B.A. Assessment of the quality of MODIS cloud products from radiance simulation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2009, 48, 1591–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinonen, J.; Lebsock, M.; Oreopoulos, L.; Cho, N. Interregional differences in MODIS-derived cloud regimes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naud, C.; Muller, J.-P.; Clothiaux, E.E. Comparison of cloud top heights derived from MISR stereo and MODIS CO2-slicing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, B.; Dong, X.; Minnis, P.; Sun-Mack, S. Comparison of marine boundary layer cloud properties from CERES-MODIS Edition 4 and DOE ARM AMF measurements at the Azores. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purbantoro, B.; Aminuddin, J.; Manago, N.; Toyoshima, K.; Lagrosas, N.; Sumantyo, J.; Kuze, H. Comparison of Aqua/Terra MODIS and Himawari-8 satellite data on cloud mask and cloud type classification using split window algorithm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, R.; Teng, S.; Yi, B.; Letu, H.; Min, M.; Tang, S.; Liu, C. Comparison of cloud properties from Himawari-8 and FengYun-4A geostationary satellite radiometers with MODIS cloud retrievals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holz, R.E.; Ackerman, S.A.; Nagle, F.W.; Frey, R.; Dutcher, S.; Kuehn, R.E.; Vaughan, M.A.; Baum, B. Global Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) cloud detection and height evaluation using CALIOP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garay, M.; Szoeke, S.; Moroney, C. Comparison of marine stratocumulus cloud top heights in the southeastern Pacific retrieved from satellites with coincident ship-based observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frisch, A.S.; Feingold, G.; Fairall, C.W.; Uttal, T.; Snider, J.B. On cloud radar and microwave radiometer measurements of stratus cloud liquid water profiles. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 23195–23197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görsdorf, U.; Lehmann, V.; Bauer-Pfundstein, M.; Peters, G.; Vavriv, D.; Vinogradov, V.; Volkov, V. A 35-GHz polarimetric Doppler radar for long-term observation of cloud parameters-description of system and data processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.; Bansemer, A.; Wood, N.B.; Liu, G.; Tanelli, S.; Sy, O.O.; Poellot, M.; Liu, C. Toward improving ice water content and snow-rate retrievals from radars. Part II: Results from three wavelength radar–collocated in situ measurements and CloudSat-GPM-TRMM radar data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2018, 57, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Clothiaux, E.E.; Miller, M.A.; Albrecht, B.A.; Stephens, G.L.; Ackerman, T.P. Millimeter-Wavelength radars: New frontier in atmospheric cloud and precipitation research. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1608–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, G.L.; Vane, D.G.; Boain, R.J.; Mace, G.G.; Sassen, K.; Wang, Z.; Illingworth, A.J.; O’Connor, E.J.; Rossow, W.B.; Durden, S.L.; et al. The CloudSat mission and the A-Train. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1771–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieman, S.; Schmetz, J.; Menzel, W. A comparison of several techniques to assign heights to cloud tracers. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1993, 32, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Platt, C. Comparison of satellite deduced cloud heights with indications from radiosonde and ground-based laser measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1978, 17, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derber, J.; Parrish, D.; Lord, S. The new global operational analysis system at the National Meteorological Center. Weather Forecast. 1991, 6, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menzel, W.; Schmit, T.; Wylie, P. Cloud characteristics over central amazonia during GTE/ABLE 2B derived from multispectral visible and infrared spin scan radiometer atmospheric sounder observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1990, 95, 17039–17042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W. An improved method for calculating tropospheric temperature and moisture from satellite radiometer measurements. Mon. Weather Rev. 1968, 96, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Frey, R. On cloud altitude determinations from high resolution interferometer sounder (HIS) observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1990, 29, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ackerman, S.; Menzel, P.; Frey, R. MODIS Atmosphere L2 Cloud Product (06_L2). 2015. Available online: https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/mod06.php (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Huo, J.; BI, Y.; Lu, D.; Duan, S. Cloud classification and distribution of cloud types in Beijing using Ka Band radar data. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Huo, J.; Bi, Y.H. Ground-Based Ka-band cloud radar data quality control. J. Chengdu Univ. Inf. Technol. 2018, 33, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | Technical Specification |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 35.075 GHz |
| Peak power | 29 kW |
| Pulse length | 0.2 μs |
| Type | Magnetron |
| Diameter | 1.5 m |
| Gain | 54 dB |
| Scanning mode | Vertically pointing, plan position indicator, range–height indicator |
| Beam width | 0.4° |
| Vertical resolution | 30 m |
| Dmr | Mean | STD | Median | IQR | Peak | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | −1.08 | 2.48 | −0.65 | 2.19 | −0.38 | 1.84 |
| Hm < 4 km | −2.73 | 2.83 | −2.00 | 4.25 | −1.18 | 2.46 |
| Hm > 6 km | 0.03 | 1.58 | −0.17 | 1.39 | −0.25 | 1.06 |
| Dmr | CD ∈(0,1) | CD ∈(1,2) | CD ∈(2,3) | CD ∈(3,4) | CD ∈(4,5) | CD > 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | −1.62 | −0.73 | −0.50 | −0.30 | −0.16 | −0.07 |
| STD | 2.92 | 2.00 | 1.45 | 1.30 | 1.53 | 1.29 |
| Median | −1.10 | −0.49 | −0.34 | −0.20 | −0.15 | −0.28 |
| IQR | 3.39 | 1.80 | 1.30 | 1.21 | 1.23 | 1.26 |
| Peak | −0.81 | −0.39 | −0.10 | −0.10 | −0.02 | −0.41 |
| Model | 2.45 | 1.44 | 1.01 | 0.86 | 0.98 | 0.92 |
| Dmr | Mean | STD | Median | IQR | Peak | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2-slicing | 0.09 | 1.58 | −0.13 | 1.40 | −0.25 | 1.19 |
| IRW | −2.20 | 2.73 | −1.58 | 3.62 | −0.95 | 2.33 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, J.; Li, J.; Duan, M.; Lv, D.; Han, C.; Bi, Y. Measurement of Cloud Top Height: Comparison of MODIS and Ground-Based Millimeter Radar. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101616
Huo J, Li J, Duan M, Lv D, Han C, Bi Y. Measurement of Cloud Top Height: Comparison of MODIS and Ground-Based Millimeter Radar. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(10):1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101616
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Juan, Jie Li, Minzheng Duan, Daren Lv, Congzheng Han, and Yongheng Bi. 2020. "Measurement of Cloud Top Height: Comparison of MODIS and Ground-Based Millimeter Radar" Remote Sensing 12, no. 10: 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101616
APA StyleHuo, J., Li, J., Duan, M., Lv, D., Han, C., & Bi, Y. (2020). Measurement of Cloud Top Height: Comparison of MODIS and Ground-Based Millimeter Radar. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101616