Abstract
Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) images containing cities may exhibit misclassified areas when using polarimetric decompositions. Several articles relate this problem to the effects of orientation between the facades of buildings and the acquisition trajectory. Materials also play a role in polarimetric behavior. This paper deals with this combined effect of material and orientation. It analyzes different sets of data, airborne or space-borne, at L-, C- and X-bands, and for different orientation angles. It shows that considering dielectric dihedral rather than metallic in the polarimetric mechanism of double-bounce has a very important impact on the differences of intensities between the channels HH and VV. This difference is very important for small angles of orientation, and then decreases for large angles. Furthermore, the curves of the ratios between polarimetric intensities as a function of the orientation angle vary little with the materials and the frequencies encountered in all the scenarios envisaged. The signal of the ratio VV/HH raises a plateau around −1 dB for orientations higher than 30°. We also observe a plateau for HV/HH, but with a value around −5 dB.
1. Introduction
In Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images, urban areas are often characterized by many high responses resulting from scattering by dihedral structures. This observation has been exploited in model-based decompositions to help for the classification. The rationale of these classification tools is to decompose any SAR observations using canonical scattering mechanisms, expressed mostly with different polarimetric coherency matrices. Each scattering matrix is analytically derived from a canonical scattering mechanism. The well known Pauli-basis can be regarded as a model-based decomposition. We can see an illustration in Figure 1. This polarimetric SAR image has been acquired by JPL using the UAVSAR sensor at L-band. The classical color code is applied: red refers to double-bounces, blue to single scattering, and green to cross-polarization contribution. For this basis, the double-bounce is an ideal scattering mechanism modeled by a perfectly aligned dihedral corner reflector made of Perfectly Electrically Conducting (PEC) material. With this pure double-bounce, VV and HH intensities are equal, and there is no cross-polarization.

Figure 1.
PolSAR image acquired by UAVSAR in the Pauli basis (double-bounce in red, single scattering in blue, cross-polarization in green) over New Orleans, Louisiana, U.S.
Other propositions exist, depending on either the number of mechanisms or the way each scattering mechanism is analytically derived. We can quote, for instance, [1,2,3], or [4]. As an example, Freeman and Durden consider the same three scattering mechanisms as for the Pauli basis [1]; however, the latter are not modeled in the same way. Thus, the double-bounce scattering mechanism is still ideally oriented but associated with a dielectric dihedral. The surface scattering is modeled as a Bragg scattering, initially intended to represent a rough surface with regular ripples. Finally, the volume scattering is rendered by a set of dipoles whose tilts follow a uniform distribution.
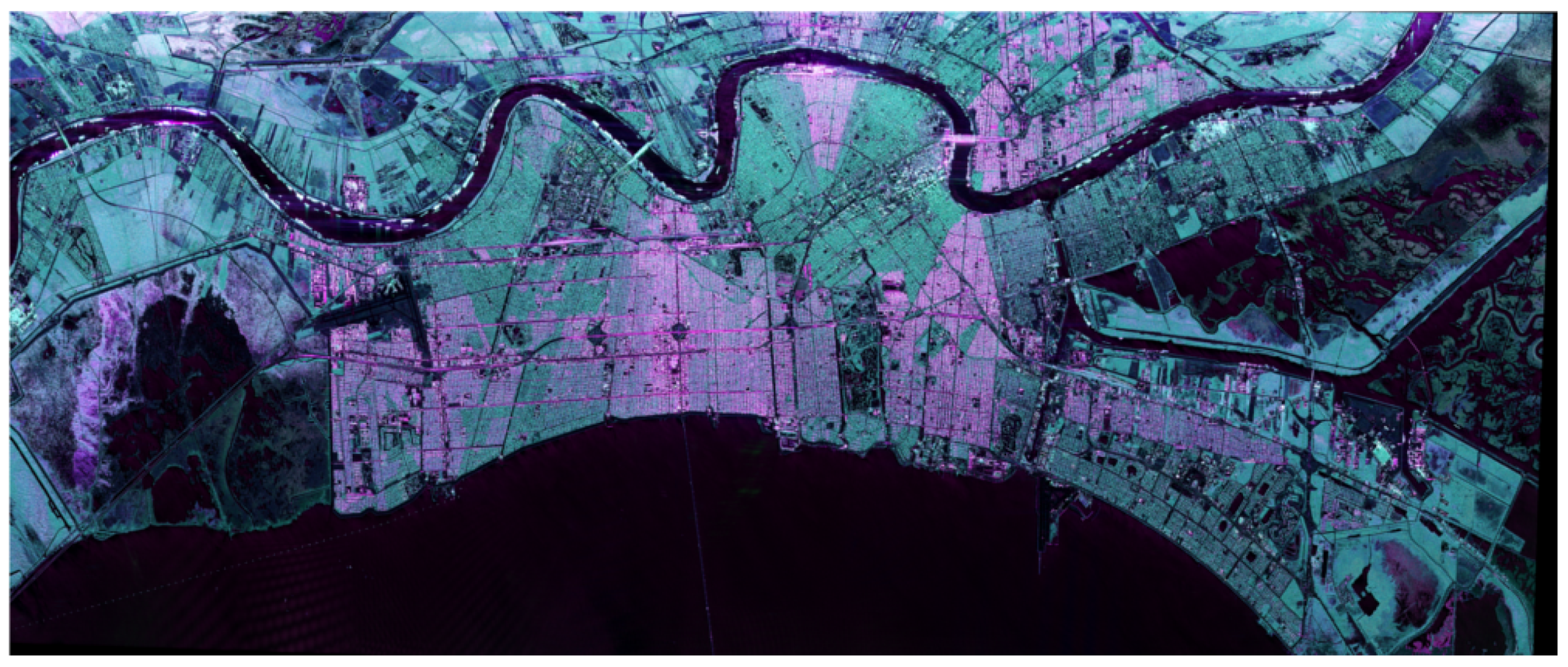
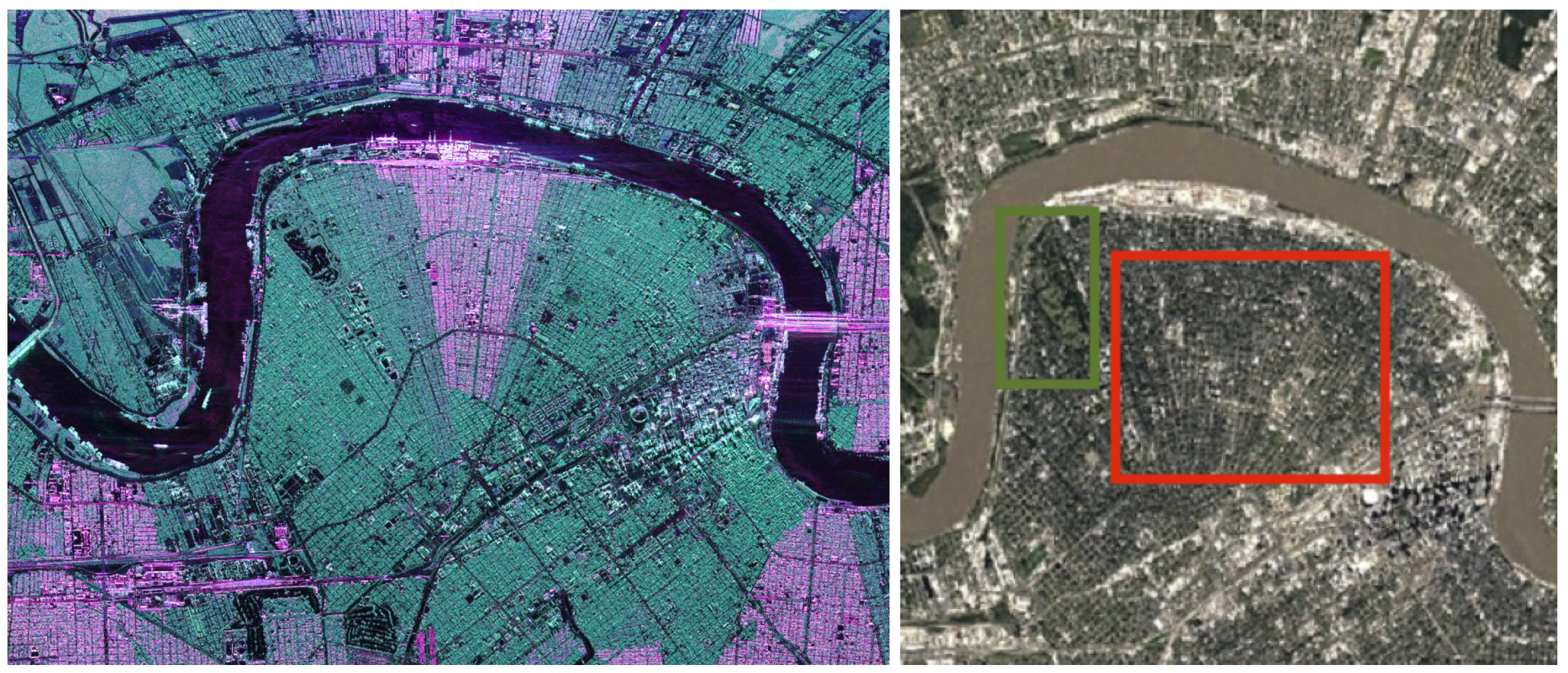
In practice, the dihedral structures are not always well-aligned with the sensor trajectory. In this case, an angle of rotation is introduced to measure this misalignment. This Orientation Angle (OA) has been widely studied to understand and compensate for its impact on model-based decompositions. In particular, in [3], the authors present the negative scattering powers problem—a physical inconsistency that occurs in several model-based decompositions—that can be partly reduced by the compensation of this orientation angle. To illustrate another effect of this rotation angle, we propose to consider Figure 2 with a PolSAR and an optical image of New Orleans in Louisiana. On the optical image, below the Mississipi river, around the quarter called Milan, we can observe a residential area, highlighted by the red rectangle. On the left, inside the green rectangle, there is the Audubon park, including a golf course. In the PolSAR image, the residential area appears partly in reddish colors, partly in green. According to the Pauli basis, the green parts of this residential area are not characterized by the double-bounces. On the contrary, its radar signature is dominated by the high level of its cross-polarization terms. This difference in the polarimetric signature is related to the angle of rotation between the sensor trajectory and the main orientation of the buildings. Several publications have been dedicated to this specific classification issue, such as [5,6,7].
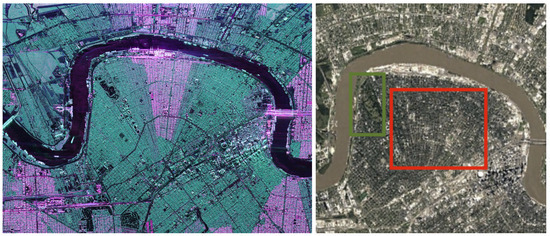
Figure 2.
New Orleans, Louisiana, U.S. (Left) PolSAR image acquired by UAVSAR in the Pauli basis (double-bounce in red, single scattering in blue, cross-polarization in green). The sensor trajectory is parallel to the top of the figure; (right) Google Earth image of the same region acquired by Landsat and Copernicus.
The solution proposed by these studies is to estimate the orientation angle to compensate for this rotation. This correction implies several issues. First, a strong assumption is generally made to apply the compensation for this OA: there is a dominant scattering mechanism—the double-bounce mechanism—so that the compensation technique only concerns this mechanism. For low OAs, this assumption is correct, and this technique improves the results of classification [6]. However, when OA is large, we have shown that there is no more dominant mechanism [8,9], and unsurprisingly, these decompositions failed to classify them correctly (see, for instance, [5]). Indeed, this orientation angle compensation is applied to a covariance matrix mixing several mechanisms of similar amplitudes. Besides, this mixing of mechanisms is amplified by the speckle filtering, which is applied before the orientation angle compensation, as highlighted by Shang et al. [10]. Finally, we can also question the way this orientation is compensated, as there is not a strict equivalence between the orientation of the target and the rotation angle estimated for this compensation [10]. In [11], Thirion-Lefevre and Guinvarc’h have investigated the phenomenology of the polarimetric backscattering by a dielectric dihedral structure with no orientation angle. In particular, they show the existence of a strong attenuation effect, called the DBE for Double Brewster’s angle Effect, that affects differently VV and HH intensities. The ratio of the backscattering coefficients can reach tens of dB depending on the effective permittivity of the dihedral components and providing that the double bounce scattering mechanism exists.
We propose in this paper to further investigate the phenomenology of dielectric dihedral structures and to study the impact of the orientation angle on the DBE. The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 recalls what the DBE is, and we present some simulation results. Section 3 explains the methodology of our study. Then the data sets and the results are presented in Section 4. Finally, we discuss the possible applications of this study before conclude in Section 5.
2. The Dielectric Dihedral and the Double Brewster’s Angle Effect
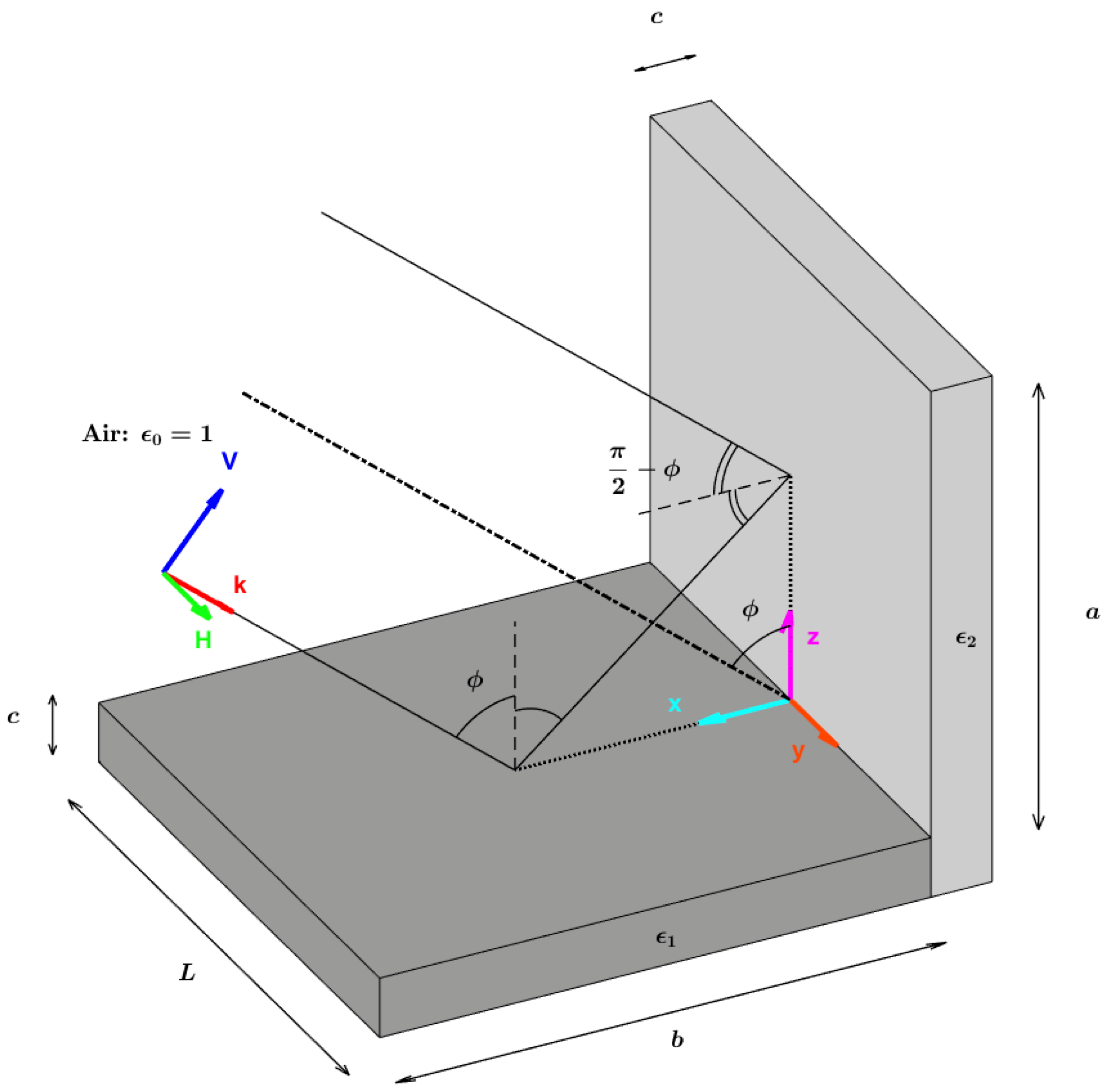
We propose to consider Figure 3 to set up the configuration of our problem. The dihedral structure is here made of two parts, with the same width c: the horizontal one is a homogeneous block of relative permittivity ; the vertical one is a homogeneous block of relative permittivity ; and are complex numbers. This dihedral structure is illuminated with a plane wave, impinging with an incidence angle ϕ. The plane of symmetry of the dihedral contains the wave vector k. The orientation angle ψ is the rotation angle around z-axis. In this configuration, there is no orientation angle: ψ = 0. When a dielectric dihedral is well aligned with the radar line of sight, its response is maximum. In this case, we have shown that the double-bounce scattering mechanism can be approximated using two successive specular reflections over the two parts of the dihedral [11], as illustrated in Figure 3. When there is a specular mechanism, a particular incidence angle ϕ exists—known as Brewster’s angle (BA) or Pseudo Brewster’s Angle (PBA)—for which the VV reflected field is either null or minimum whether the dielectric material has losses or not. When this dielectric is lossless, its permittivity ε is real, and can be analytically derived using the Snell–Descartes law. We obtain the well-known relation:
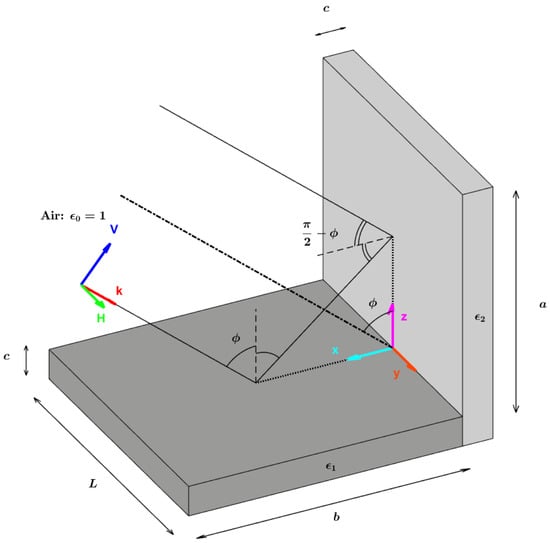
Figure 3.
Illustration of a dielectric dihedral illuminated by an incident angle ϕ and with no orientation angle (ψ = 0).
If there are losses, ε is complex, and then the PBA can be estimated as a solution of a polynomial equation, as shown in [12]. It could be more convenient to consider the following empirical equation as proposed in [11]:
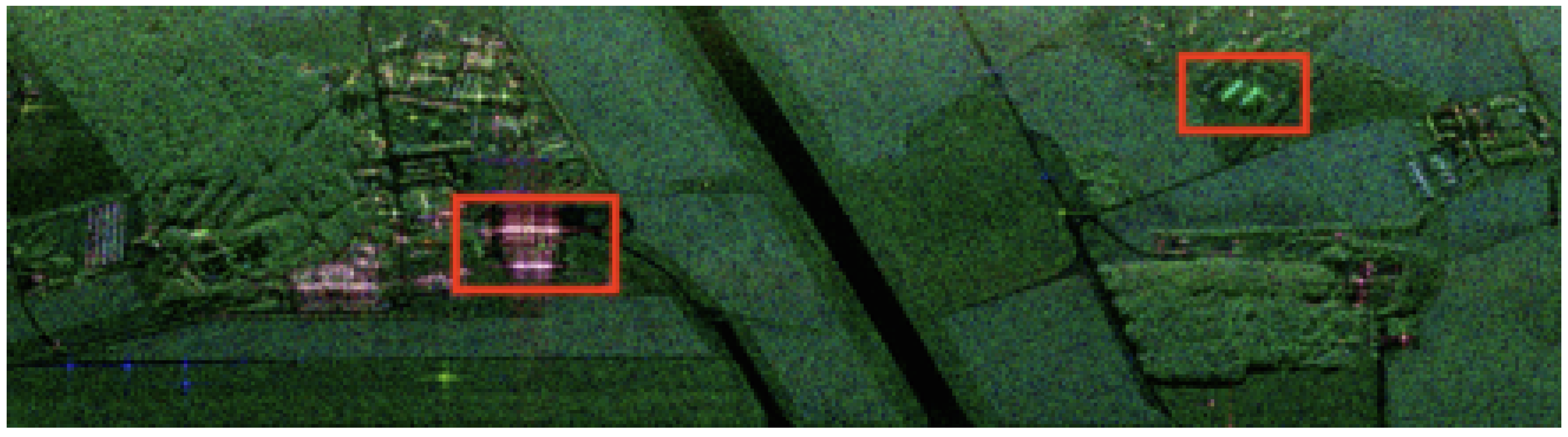
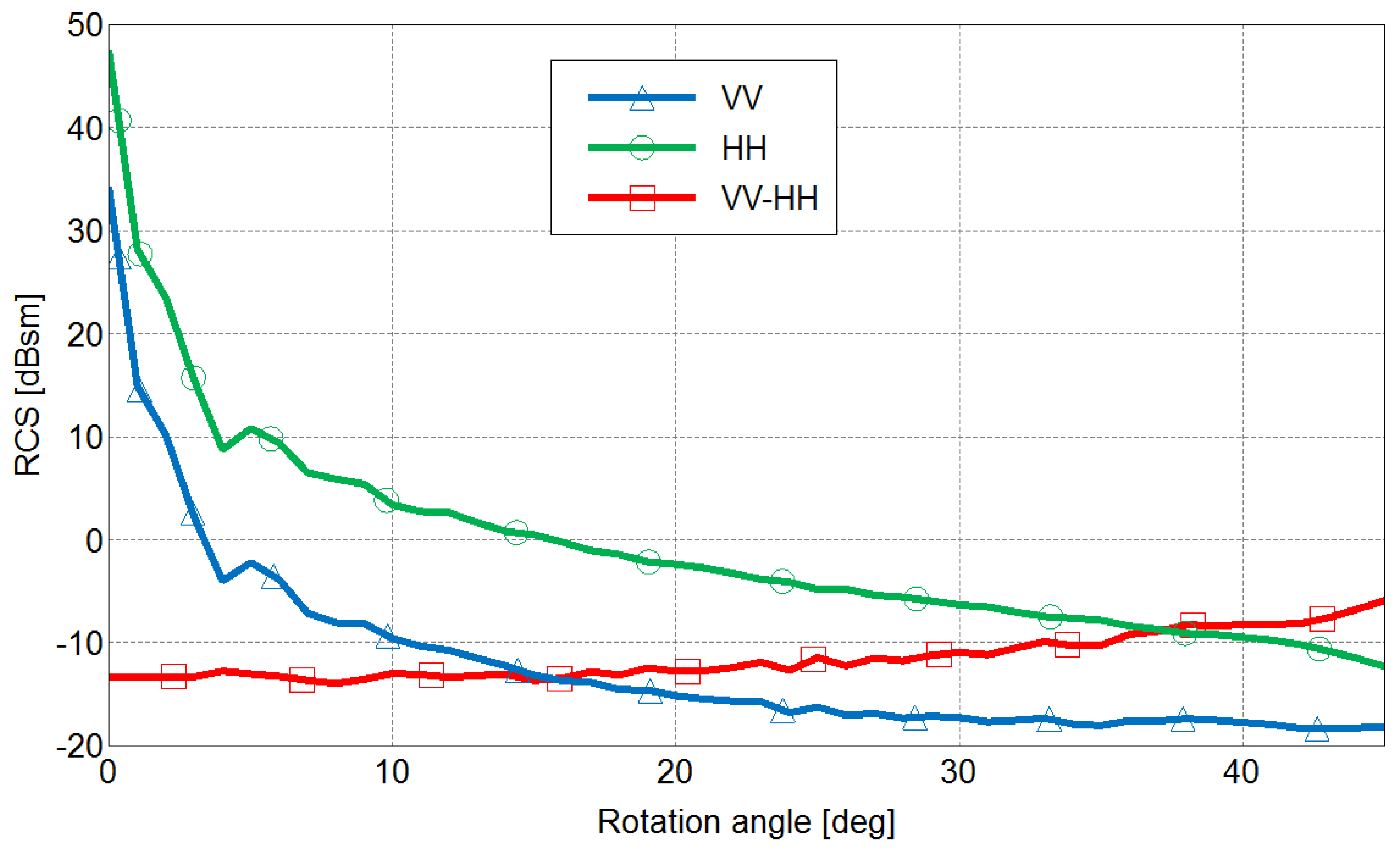
The angles and range in for a horizontal dielectric interface. As the two specular mechanisms composing the double-bounce occur on two orthogonal interfaces, the BA or PBA associated with the vertical interface belongs to the complementary angular domain . Thus, when we consider a dielectric dihedral structure on a SAR image, we may observe a significant difference between VV and HH backscattering coefficients, with , for a large range of incidence angles (see [11] for more details on this part). The DBE has been analytically and numerically established, as well as observed over SAR images when buildings exhibit no orientation angle. We illustrated this effect using Figure 4, a polarimetric SAR image, acquired by ONERA with RAMSES at X-band. We measured more than a 10 dB difference between VV and HH for the building located in the red rectangle. We used the values collected for the trihedral reflectors installed for radar calibration, in the left bottom corner (in blue in Pauli basis) to check the accuracy of the polarimetric intensities. This effect can also be noticed in the results presented in several publications related to forests with flat grounds (see, for instance, [1] or [13]). For human-made targets, this effect has also been retrieved. For instance, in [14], the authors report a very strong double-bounce, with HH polarization channel 30 dB higher than that for the VV polarization channel for a simulation of a dielectric target over a surface (both ). This angular behavior is radically different from the PEC case. Indeed, in this configuration, VV and HH are equal, at least for low orientation angles, as shown in [8]. A difference may appear for large orientation angles when these intensities drop but with HH superior to VV. As the DBE is intrinsically related to the double-bounce mechanism, we would like to study the joint effect of the material and the orientation angle on the polarimetric backscattering level of a dihedral structure. In other words, is this effect robust to the orientation angle ψ? To do so, we investigated this effect initially through numerical experiments using the electromagnetic software FEKO [15], using an approximate method based on the Ray Launching and Geometrical Optics. The result is shown in Figure 5 for a dihedral with at 9 GHz. When OA is equal to 0 degree, there is no orientation angle, and we observe a difference of 23.5 dB between HH and VV, HH being higher. This result is fully consistent with the DBE. When there is an orientation angle, this difference decreases and goes down to 3 dB at 45 degrees, always with HH larger than VV. Other dielectric materials gave other values, but always with HH larger than VV. This result seems quite logical; the strength of the double-bounce mechanism drops when the sensor or the target is tilted, and so does the DBE. We also plotted the variation of the difference between these intensities with the orientation angle (see the red dotted line in Figure 5). It appears that for this example, this difference monotonically varies and remains inferior to 0 dB. This simple monotonic variation is not systematically reproduced with different permittivities, but the values remain lower than or equal to 0 dB.

Figure 4.
PolSAR image of the former Air Force Base of Bretigny acquired by ONERA (RAMSES, X-band) in the Pauli basis. The sensor trajectory is parallel to the top of the figure. Red rectangles refer to selected areas.
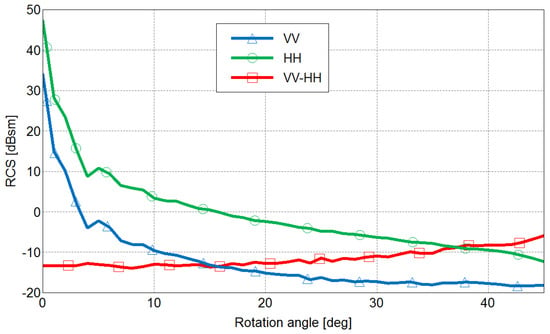
Figure 5.
Variation of the backscattering coefficients at VV (blue) and HH (green) for an orientation angle ψ ranging from 0 to 45 degrees. In red, the result of .
However, this configuration cannot correctly reflect a real configuration in an urban environment. First, these urban structures are often made of a mix of materials; then, the selected permittivity corresponds to measurements generally made in ideal conditions. For instance, the samples are often dried and infinitely thick compared to the radar wavelength. Second, a house or a block of flats resembles a cuboid standing on the ground, not a dihedral. A solution to partly remove these difficulties is to rely on real data, extracted from SAR images. We present our methodology in the next section.
3. Methodology and Data Sets
3.1. Methodology
We propose to select several cities in the world for which we have access to the full polarimetric radar data: San Francisco (U.S), New Orleans (U.S), and Amsterdam (Netherlands). We can reasonably assume that the building materials in the U.S are different than in the Netherlands. In particular, in San Francisco, many buildings are made of wood. Besides, for the two American cities, we have two different sensors: one operating at C-band (RADARSAT-2), and the other at L-band (UAVSAR). Even if we consider that the building materials are the same in these cities, the different central frequencies lead to different permittivities. We do not control the value of these permittivities, but we presume that they vary from one set to another. For each city, we select some Regions of Interest (ROI), so that we have various tilt angles ψ respecting to the sensor trajectory. We select these ROIs so that they exhibit a homogeneous signature in the Pauli basis. We have also included an area with isolated buildings, near Bretigny in France (observed by ONERA RAMSES).
3.2. The Data Sets
We have summarized the radar characteristics of these data in Table 1.

Table 1.
Radar characteristics of the sensors for the images considered for this study.
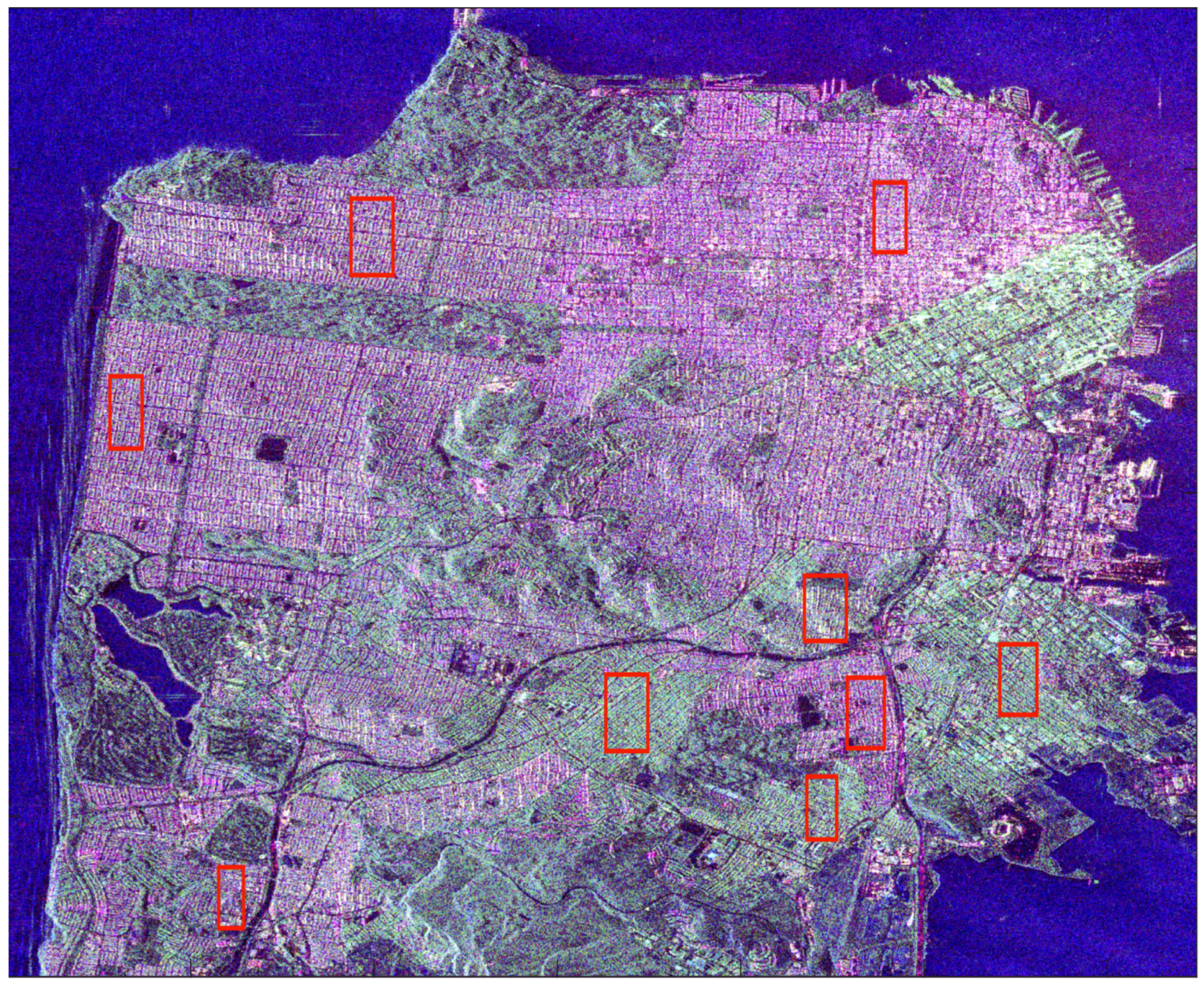
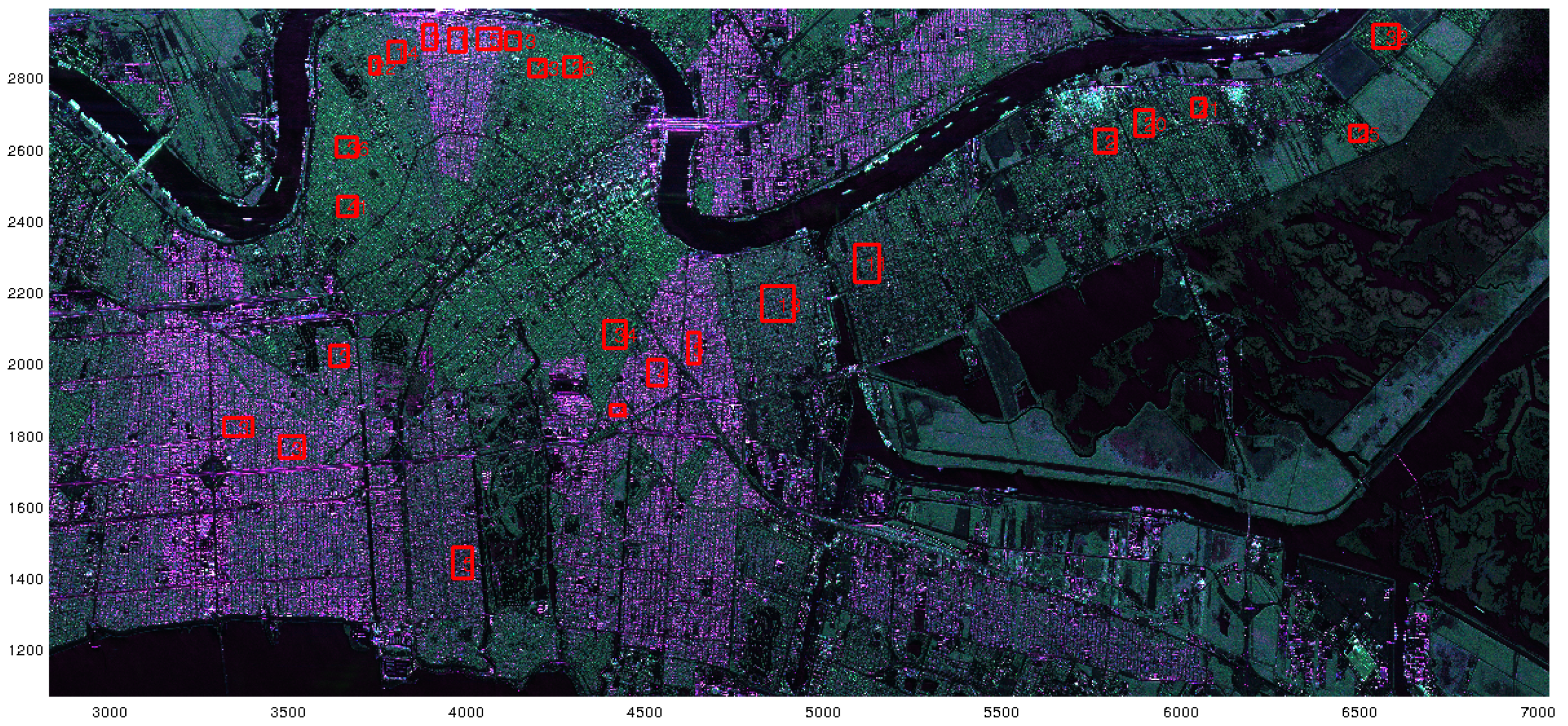
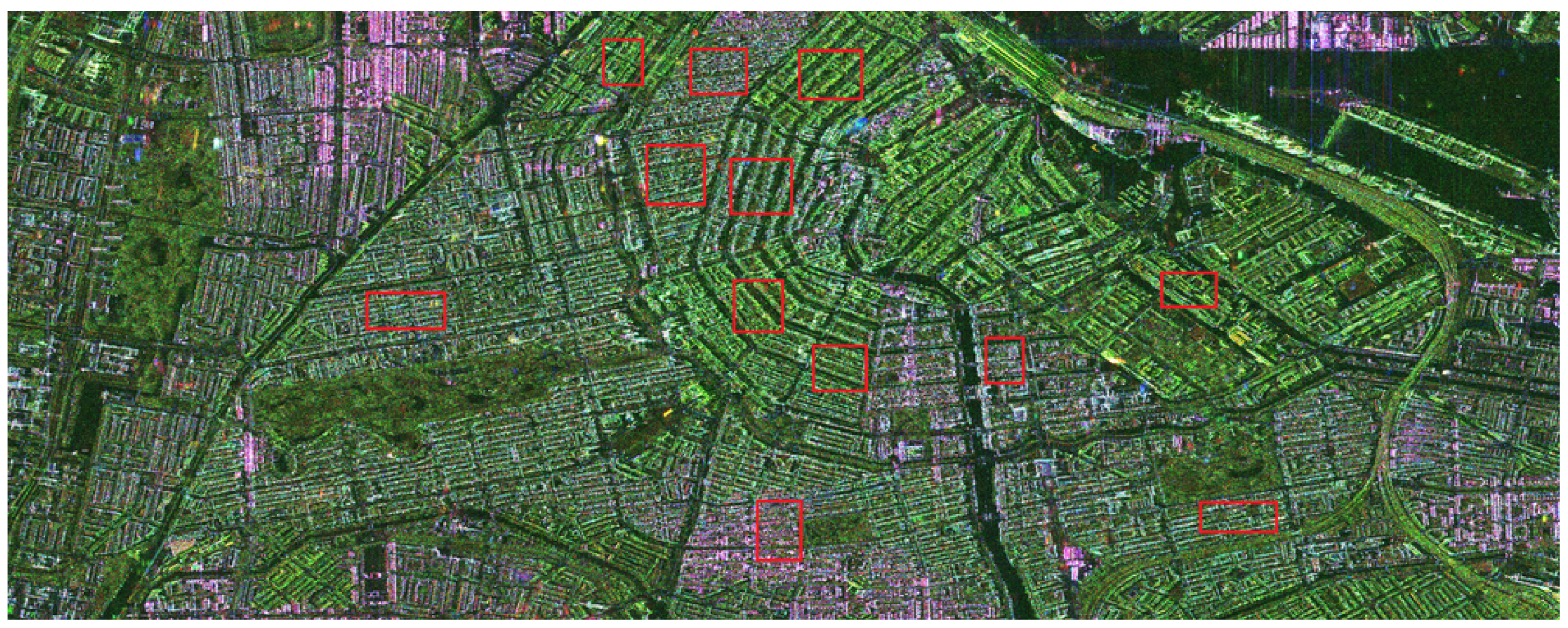
In Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8, SAR images are represented, with the zones we selected for the analysis. The images were calibrated using the calibration keys in metadata supplied with the images, and the calibration procedures given for each type of sensor in order to convert pixel values into the backscattering coefficient . The average has been computed for all the pixels belonging to the whole region. For the three first SAR images, the intensities of the ROIs have been averaged over each red box. The selection of these zones ensures that we can swipe a large variety of azimuth orientation angles. They only concern residential areas. In particular, we tried to avoid financial/commercial zones to preserve as far as possible a homogeneity in the buildings. The case of the SAR image of Bretigny is specific as it corresponds to the former Air Force base located in this town, not to its city center. The two ROIs contain military buildings: two sheds and two barracks. In this particular case, the backscattering coefficients have been averaged over the signal associated with buildings. The same color code is applied for all these SAR images, and they are represented in the Pauli basis: blue refers to single scattering, red to double-bounce and green to cross-polarization contribution. These three images illustrate the effect of the orientation angle on the signature of dihedral structures: if there is no rotation, the districts appear in reddish color, if the OA is large, they appear in green.
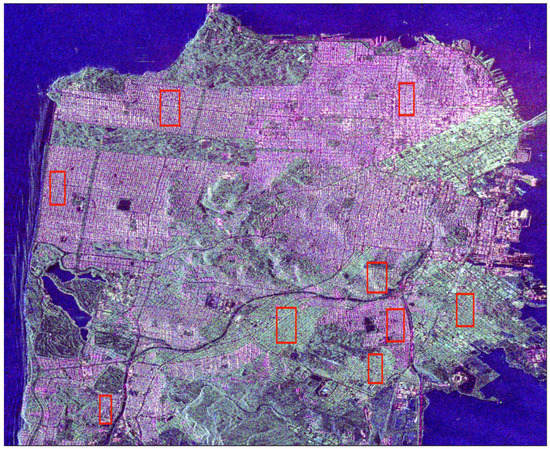
Figure 6.
PolSAR image of San Francisco acquired by RADARSAT-2 (C-band) in the Pauli basis (double-bounce in red, single scattering in blue, cross-polarization in green). The sensor trajectory is parallel to the left side of the figure. Red rectangles refer to selected areas.

Figure 7.
PolSAR image of New Orleans acquired by UAVSAR (L-band) in the Pauli basis. The sensor trajectory is parallel to the top of the figure. Red rectangles refer to selected areas.
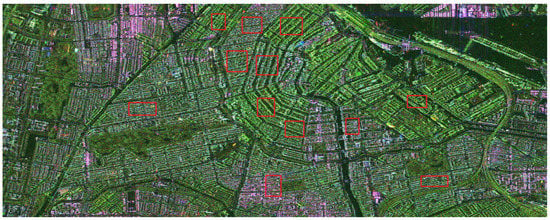
Figure 8.
PolSAR image of Amsterdam acquired by TerraSAR-X (X-band)in the Pauli basis. The sensor trajectory is parallel to the left side of the figure. Red rectangles refer to selected areas.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Co-Pol Response
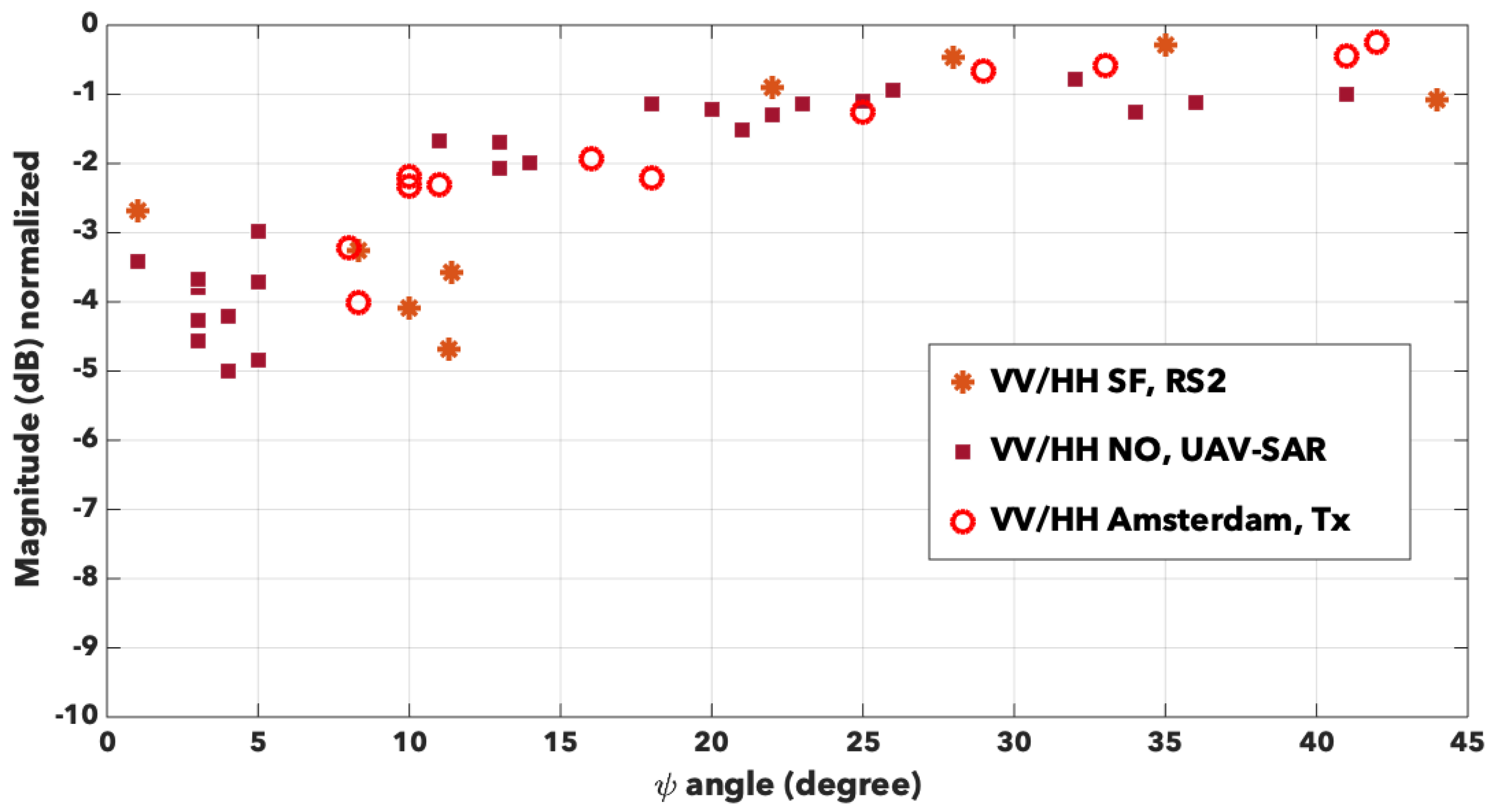
To plot the angular variation of the DBE, we note the co-pol ratio defined as , where denotes the backscattering coefficient at polarisation XX. If the DBE occurs, then . In Figure 9, we plot the ratios that we collected for all the red rectangles. We can immediately notice that this quantity is always inferior to 0 dB. Two domains can be then empirically defined, before and after around 20°. Before 20°, we can observe a significant difference between VV and HH, ranging from −5 dB to −1.5 dB with a noticeable dispersion. For Bretigny, for the two sheds well aligned with the sensor trajectory, we obtain −8.5 dB and −12 dB. After 20°, the variation of is clearly smaller and almost all data are contained in dB for the remaining angles. Surprisingly, we notice no difference associated with the radar characteristics or to the specificity of the cities, as if we reached a limit value for this DBE. If we consider additional results issued from Bretigny or the financial district of San Francisco, we have equal respectively to 0 dB and +0.4 dB at maximum. Regarding the accuracy of the sensor, we could confidently assess that even for other buildings than residential ones, this observation is still true.
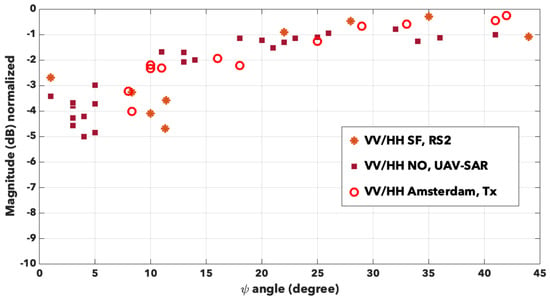
Figure 9.
Variation of the co-pol ratio with the orientation angle for San Francisco (stars), New Orleans (full squares) and Amsterdam (empty circles).
4.2. Cross-Pol Response
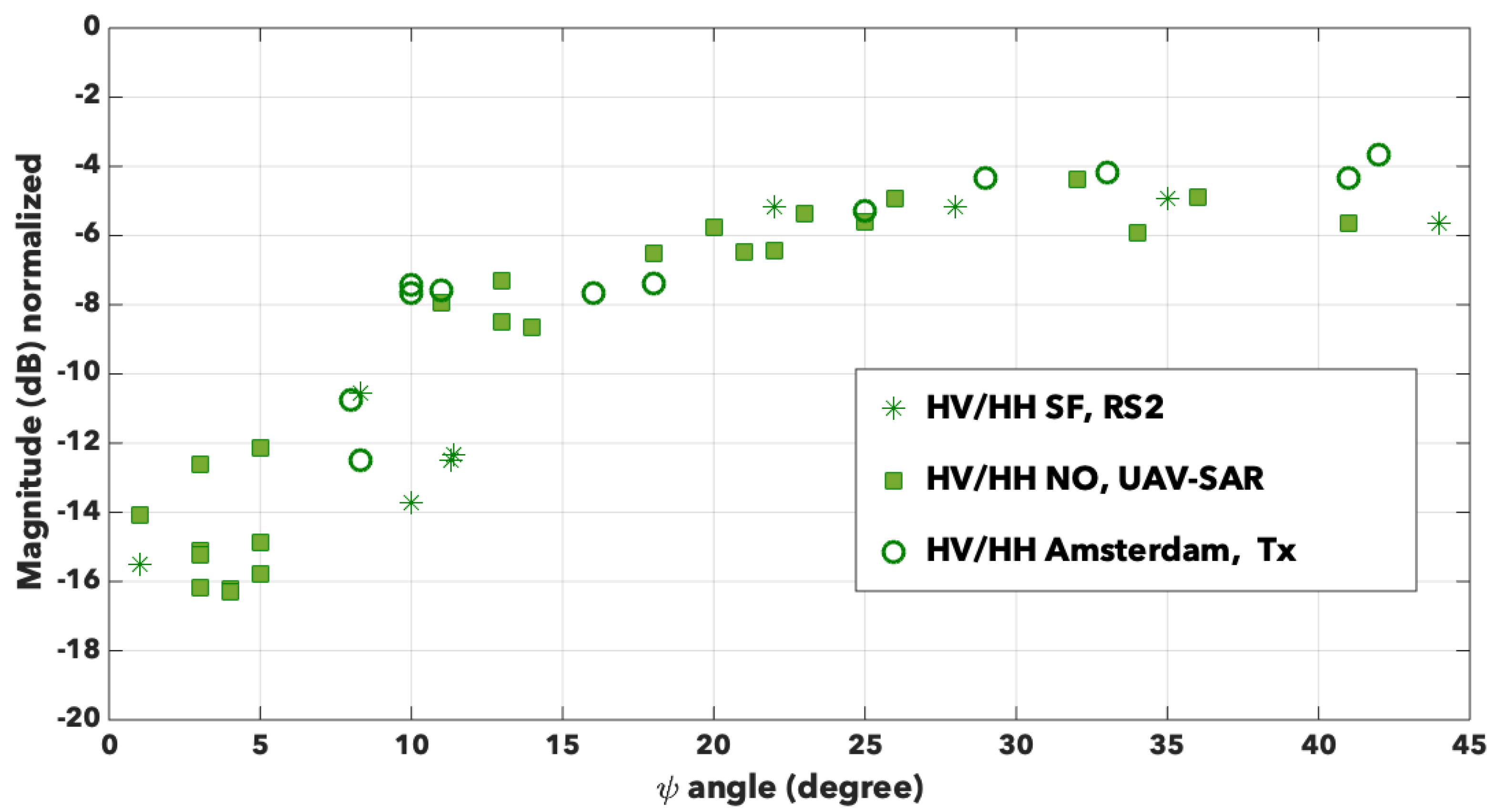
We know that the cross-polarization backscattering signals are supposed to be null when there is no orientation angle of the dihedral structures, and we expect to observe an increase of their values with increasing orientation angle. To plot a quantity similar to the one in the previous section, we propose to consider the ratio , defined in the same way as . The result is available in Figure 10. First of all, we notice that again, the data seem to follow the same trends, whatever the sensor, whatever the radar frequency, the resolution, and the urban areas under observation. We can still define two angular domains before and after around 20°. Before 20°, this ratio varies approximately within dB. Afterwards, the variations are contained within 2 dB around −5 dB. It seems there again that the curve reaches a plateau as if increasing the orientation angle produces no more effect on this cross-polarization ratio. For comparison, we measure −5.11 dB for the barracks in Bretigny with an orientation angle of 45°, and −1.8 dB for the financial district SOMA in San Francisco with an orientation angle of 30°.
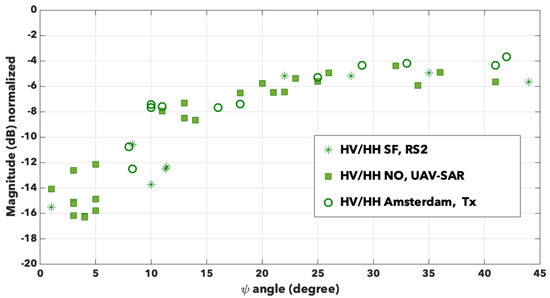
Figure 10.
Variation of the ratio with the orientation angle for San Francisco (stars), New Orleans (full squares) and Amsterdam (empty circles).
5. Discussion and Conclusions
When Freeman and Durden introduced the so-called Freeman–Durden Decomposition [1], their goal was to interpret radar backscattering from forests. By fitting their three-component scattering model to their polarimetric data, these authors first aimed at retrieving the main scattering mechanisms occurring in the scene. Besides, each mechanism can be associated with a type and a state of land cover: dense vegetation, sparse forest, or clearings, for instance. In this case, the use of the Fresnel reflection coefficients to model the double-bounce scattering was relevant and particularly adapted to trees over flat surfaces, as they exhibit an azimuthal symmetry. In forests, the impact of a possible orientation angle is not crucial. When Yamaguchi and his co-authors introduced the fourth-component scattering model [2], their goal was to apply the tool of Freeman and Durden to SAR images containing urban areas. However, adaptations were required, as the assumption of reflection symmetry was no more true in these conditions. Besides another scattering component and the modification of the volume scattering component, they also modified the double-bounce scattering. The dihedral is no more dielectric, but metallic, as in the Pauli basis. For these model-based decompositions, the choice of a dielectric or a metallic dihedral structure to mimic the double-bounce scattering mechanism is impactful. As seen in Section 3 with simulated data, the co-pol ratio does not vary in the same way with the orientation angle. For low orientation angles, the intensities backscattered at HH and VV are equal for PEC dihedral corner reflector, while there may be a significant difference in the dielectric case. Besides, we have shown that this property can be exploited to retrieve the complex permittivities of dielectric dihedral structures [16]. When an orientation angle is applied, this choice is still crucial. Thus, a difference may appear for the PEC case with , which increases with ψ. On the contrary, for the diectrice case, tends to but still being inferior. The variation of the co-pol ratio with ψ derived using the real data confirms the choice of a dielectric dihedral in these model-based decompositions. In this article, we first confirmed that for double-bounce whatever the orientation angle. Simulations and real data both confirm the DBE at low orientation angles. This effect diminishes with increasing ψ until a plateau, that we cannot explain for the moment. In subsequent studies, we will have to investigate the effect on the co-pol ratio of a group of dielectric dihedrals, as in [17]. Futhermore, we have to evaluate the relevancy of a dihedral structure to study the double-bounce by a tilted building, compared with a dielectric cuboid standing on a ground, as in [14].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, L.T.-L. and R.G. Validation, software and formal analysis, L.T.-L., R.G. and E.C.-K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ishido, M.; Yamada, H. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Wang, Y. Generalized polarimetric model-based decompositions using incoherent scattering models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2474–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Malik, R.; Mohanti, S.; Rathore, V.S.; Yamada, K.; Umemura, M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Seven-component scattering power decomposition of POLSAR Coherency matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8371–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Wdowinski, S. Double-Bounce Component in Cross-Polarimetric SAR From a New Scattering Target Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3039–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ohki, M.; Shimada, M.; Sato, M. Deorientation Effect Investigation for Model-Based Decomposition Over Oriented Built-Up Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Sato, A.; Boerner, W.M.; Sato, R.; Yamada, H. Four-Component Scattering Power Decomposition With Rotation of Coherency Matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinvarc’h, R.; Thirion-Lefevre, L. Cross-Polarization Amplitudes of Obliquely Orientated Buildings With Application to Urban Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeniguer, E.C.; Weissgerber, F.; Trouve, N.; Nicolas, J.; Onera, F. A new light on origins of polarimetric misclassification of the SoMa district due to the difficulty to predict entropy. In Proceedings of the POLINSAR, Frascati, Italy, 26–30 January 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, F.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Hirose, A. Data Arrangement With Rotation Transformation for Fully Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirion-Lefevre, L.; Guinvarc’h, R. The Double Brewster Angle Effect. C.-R. Phys. 2018, 19, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, R.M.A.; Ugbo, E.E. Contours of constant pseudo-Brewster angle in the complex ϵ plane and an analytical method for the determination of optical constants. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 5222–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Toan, T.; Beaudoin, A.; Riom, J.; Guyon, D. Relating forest biomass to SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Simone, A.; Fuscaldo, W.; Millefiori, L.M.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G.; Braca, P.; Willett, P. Analytical Models for the Electromagnetic Scattering From Isolated Targets in Bistatic Configuration: Geometrical Optics Solution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altair. FEKO™: A Comprehensive Computational Electromagnetics Code. Introduction. Available online: https://altairhyperworks.com/product/FEKO (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Couderc, O.; Thirion-Lefevre, L.; Guinvarc’h, R. Analytical Solution for Permittivities of a Dihedral Configuration. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, D.K.; Thirion-Lefevre, L. Polarimetric Phase and Implications for Urban Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).