Coastal Wetland Mapping Using Ensemble Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study of Bagging, Boosting and Stacking Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
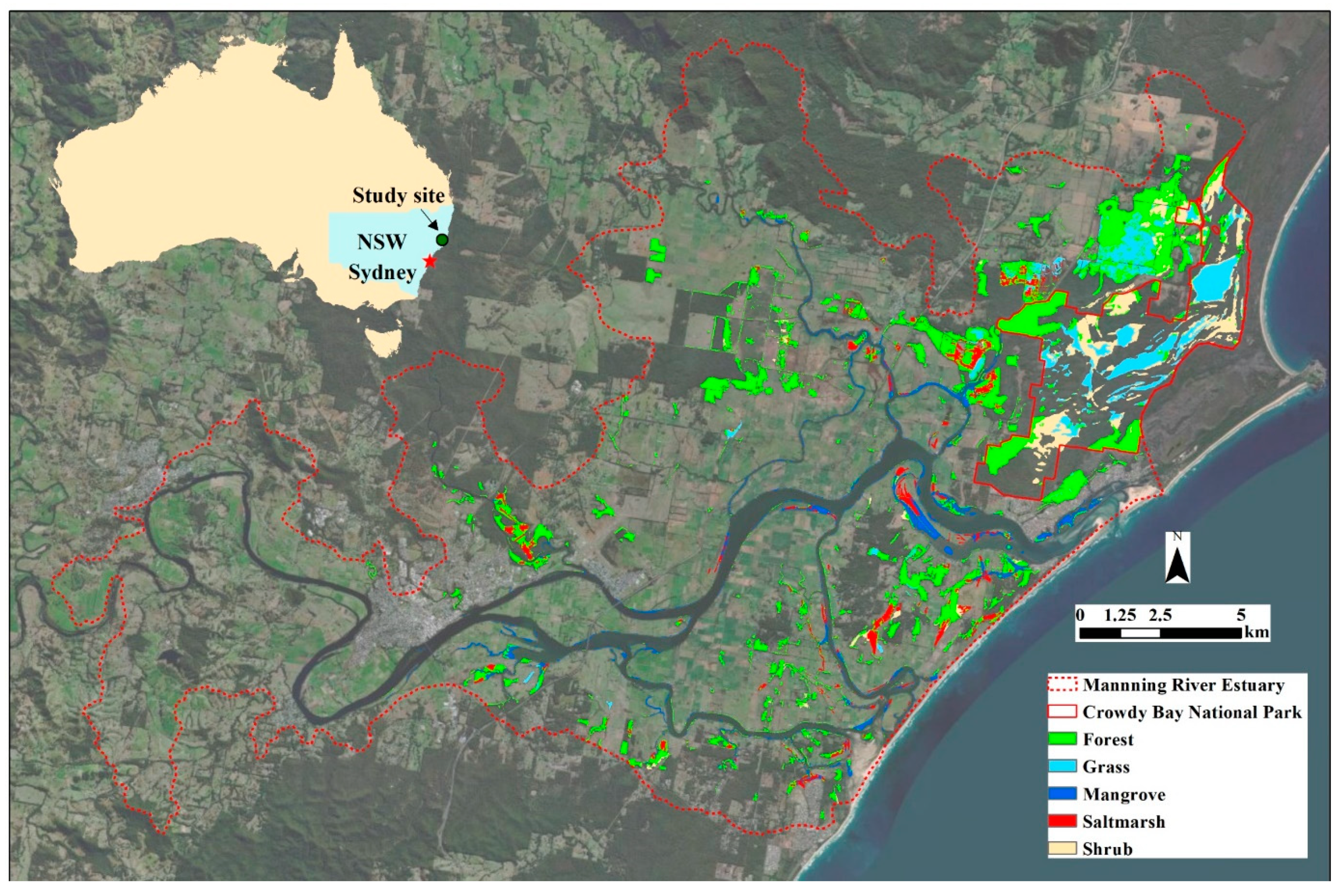
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data Source and Preparation
2.2.1. Wetland Map
2.2.2. Sentinel-2 Fractional Cover
2.2.3. Hydro-geomorphological Variables
3. Modelling
3.1. Bagging
3.2. Boosting
3.3. Stacking
3.4. Performance Metrics for Classification Assessment
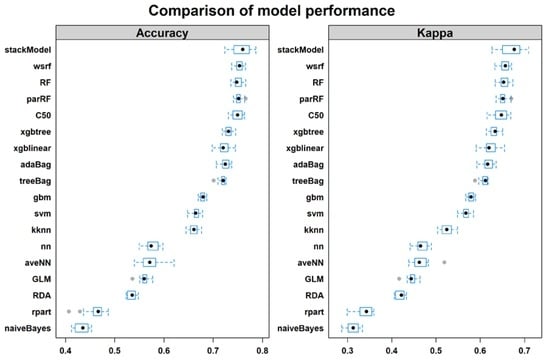
4. Results
4.1. Training Performance
4.2. Testing Performance
4.3. Predicted Wetland Type Maps
4.4. Variable Importance
5. Discussion
5.1. Overall Performance of Boosting, Bagging and Stacking Classifiers
5.2. Individual Class Performance
5.3. Variable Importance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sievers, M.; Brown, C.J.; Tulloch, V.J.; Pearson, R.M.; Haig, J.A.; Turschwell, M.P.; Connolly, R.M. The role of vegetated coastal wetlands for marine megafauna conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, R.; Rogers, D.I.; Hansen, B.D.; Gosbell, K.; Minton, C.D.; Straw, P.; Bamford, M.; Woehler, E.J.; Milton, D.A.; Weston, M.A.; et al. Continental-scale decreases in shorebird populations in Australia. Emu-Austral Ornithol. 2016, 116, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, J.M.; Attuquayefio, D. Mammal fauna of the Muni-Pomadze Ramsar site, Ghana. Biodivers. Conserv. 2000, 9, 541–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedan, K.B.; Kirwan, M.L.; Wolanski, E.; Barbier, E.B.; Silliman, B.R. The present and future role of coastal wetland vegetation in protecting shorelines: Answering recent challenges to the paradigm. Clim. Chang. 2011, 106, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleway, J.J.; Saintilan, N.; Macreadie, P.I.; Skilbeck, C.G.; Zawadzki, A.; Ralph, P.J. Seventy years of continuous encroachment substantially increases ‘blue carbon’capacity as mangroves replace intertidal salt marshes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bellerby, R.; Craft, C.; Widney, S.E. Coastal wetland loss, consequences, and challenges for restoration. Anthr. Coasts 2018, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkinson, C.S.; Wolanski, E.; Brinson, M.M.; Cahoon, D.R.; Perillo, G.M. Coastal wetlands: A synthesis. In Coastal Wetlands an Integrated Ecosystem Approach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, N.; Nagelkerken, I.; Agardy, T.; Wells, S.; Van Lavieren, H. The Importance of Mangroves to People: A Call to Action; United Nations Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC): Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Enwright, N.M.; Griffith, K.T.; Osland, M.J. Barriers to and opportunities for landward migration of coastal wetlands with sea-level rise. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, K.; MacDonald, G.; Guntenspergen, G.; Ambrose, R.; Buffington, K.; Dugger, B.; Freeman, C.; Janousek, C.; Brown, L.; Rosencranz, J.; et al. US Pacific coastal wetland resilience and vulnerability to sea-level rise. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weston, N.B. Declining sediments and rising seas: An unfortunate convergence for tidal wetlands. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing of wetlands: Case studies comparing practical techniques. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 418–427. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, N.J.; Keith, D.A.; Bland, L.M.; Ferrari, R.; Lyons, M.B.; Lucas, R.; Pettorelli, N.; Nicholson, E. The role of satellite remote sensing in structured ecosystem risk assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yapp, G.; Walker, J.; Thackway, R. Linking vegetation type and condition to ecosystem goods and services. Ecol. Complex. 2010, 7, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, C.; Abdank, A.; Isermann, M.; Jansen, F.; Timmermann, T.; Dengler, J. Red Lists and conservation prioritization of plant communities – a methodological framework. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2014, 17, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; Sheng, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, L. A review of wetland remote sensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, M.J.; Colna, K.E.; El-Mezayen, M.M.; Laureano-Rosario, A.E.; Méndez-Lázaro, P.; Otis, D.B.; Toro-Farmer, G.; Vega-Rodriguez, M.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Satellite remote sensing for coastal management: A review of successful applications. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.S.; Skidmore, A.K. Spectral discrimination of vegetation types in a coastal wetland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, Z. Combining object-based texture measures with a neural network for vegetation mapping in the Everglades from hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szantoi, Z.; Escobedo, F.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Smith, S.; Pearlstine, L. Analyzing fine-scale wetland composition using high resolution imagery and texture features. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halls, J.; Costin, K. Submerged and emergent land cover and bathymetric mapping of estuarine habitats using worldView-2 and LiDAR imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, P.C.; Ridge, J.T.; Poulin, S.K.; Seymour, A.C.; Schwantes, A.M.; Swenson, J.J.; Johnston, D.W. Integrating drone imagery into high resolution satellite remote sensing assessments of estuarine environments. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartalev, S.A.; Egorov, V.A.; Loupian, E.A.; Khvostikov, S.A. A new locally-adaptive classification method LAGMA for large-scale land cover mapping using remote-sensing data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, J.; Franklin, J.; Stow, D.; Miller, J.; Woodcock, C.; Roberts, D. Mapping land-cover modifications over large areas: A comparison of machine learning algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2272–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Elith, J.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; Guillera-Arroita, G. Testing whether ensemble modelling is advantageous for maximising predictive performance of species distribution models. Ecography 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: An applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohavi, R.; Provost, F. Glossary of terms: Machine learning. Spec. Issue Appl. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Discov. Process 1998, 30, 271. [Google Scholar]
- Berhane, T.M.; Lane, C.R.; Wu, Q.; Autrey, B.C.; Anenkhonov, O.A.; Chepinoga, V.V.; Liu, H. Decision-tree, rule-based, and random forest classification of high-resolution multispectral imagery for wetland mapping and inventory. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crabbe, R.A.; Lamb, D.; Edwards, C. Discrimination of species composition types of a grazed pasture landscape using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 84, 101978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R.; Stone, C. Classification and Regression Trees; Belmont: Wadsworth, IL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Opitz, D.; Maclin, R. Popular ensemble methods: An empirical study. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1999, 11, 169–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikar, R. Ensemble based systems in decision making. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2006, 6, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Galiano, V.R.; Panday, P.; Neeti, N. An evaluation of bagging, boosting, and random forests for land-cover classification in Cape Cod, Massachusetts, USA. GIScience Remote Sens. 2012, 49, 623–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietterich, T.G. An experimental comparison of three methods for constructing ensembles of decision trees: Bagging, boosting, and randomization. Mach. Learn. 2000, 40, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H. Ensemble Methods: Foundations and Algorithms; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.C.W.; Huang, C.; DeFries, R. Enhanced algorithm performance for land cover classification from remotely sensed data using bagging and boosting. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 693–695. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Stacked regressions. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Laan, M.J.; Polley, E.C.; Hubbard, A.E. Super learner. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2007, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Abarca-Hernandez, F.; Atkinson, P.M.; Jeganathan, C. Random Forest classification of Mediterranean land cover using multi-seasonal imagery and multi-seasonal texture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.; Hodgins, G.; Danaher, T.; Ling, J.; Hughes, M.; Wen, L. Mapping Wetland Types in Semiarid Floodplains: A Statistical Learning Approach. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 22–27 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro, E.; García, N.; Gámez, M.; Elizondo, D. Bankruptcy forecasting: An empirical comparison of AdaBoost and neural networks. Decis. Support Syst. 2008, 45, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.J.; Kuncheva, L.I.; Alonso, C.J. Rotation forest: A new classifier ensemble method. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Wadsworth: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rish, I. An empirical study of the naive Bayes classifier. In Proceedings of the IJCAI 2001 Workshop on Empirical Methods in Artificial Intelligence, Seattle, WA, USA, 4–6 August 2001; Volume 3, pp. 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- BoM. Bureau of Meteorology, Australia. Online Data. 2020. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/data-services/ (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- Ozcoasts. Australian Online Coastal Information. Available online: http://www.ozcoasts.gov.au/ (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Greater Taree City Council. Manning River Estuary Management Plan. 2009. Available online: https://www.midcoast.nsw.gov.au/ (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Eco Logical Australia. Manning River Wetlands Mapping. Prepared for MidCoast Council. 2019. Available online: https://www.midcoast.nsw.gov.au/files/assets/public/document-resources/environment-docs/manning-river-catchment-wetland-mapping.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Neyman, J. On the two different aspects of the representative method: The method of stratified sampling and the method of purposive selection. In Breakthroughs in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Scarth, P.; Röder, A.; Schmidt, M.; Denham, R. Tracking grazing pressure and climate interaction-the role of Landsat fractional cover in time series analysis. In Proceedings of the 15th Australasian Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry Conference, Alice Springs, Australia, 13–17 September 2010; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Van Etten, J.; Cheng, J.; Mattiuzzi, M.; Sumner, M.; Greenberg, J.A.; Lamigueiro, O.P.; Bevan, A.; Racine, E.B.; Shortridge, A.; et al. Package ‘raster’. In R Package; 2015; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- R core team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, version 3.6.1.; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.S.; Ram, K. Package ‘spatialEco’. In R Package; 2019; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- Baddeley, A.; Turner, R. Package ‘spatstat’. In R Package; 2014; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- Hanslow, D.J.; Morris, B.D.; Foulsham, E.; Kinsela, M.A. A regional scale approach to assessing current and potential future exposure to tidal inundation in different types of estuaries. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M. Building predictive models in R using the caret package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.C.W.; Paelinckx, D. Evaluation of Random Forest and Adaboost tree-based ensemble classification and spectral band selection for ecotope mapping using airborne hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2999–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfield, R.E. Learning on complex simulations. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA, 2007. Available online: https://scholarcommons.usf.edu/etd/615 (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. Experiments with a new boosting algorithm. In icml; 1996; Volume 96, pp. 148–156. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.51.6252&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Peters, A.; Hothorn, T.; Ripley, B.D.; Therneau, T.; Atkinson, B. Package ‘ipred’. In R Package; p. 2009. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ipred/index.html (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Friedman, J.H. Regularized discriminant analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1989, 84, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechenbichler, K.; Schliep, K.P. Weighted k-Nearest-Neighbor Techniques and Ordinal Classification. Ph.D. Thesis, Discussion Paper 399, SFB 386. Ludwig-Maximilians University Munich, Munich, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ripley, B.D. Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Weihs, C.; Ligges, U.; Luebke, K.; Raabe, N. klaR analyzing German business cycles. In Data Analysis and Decision Support; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zeileis, A.; Hornik, K.; Smola, A.; Karatzoglou, A. Kernlab-an S4 package for kernel methods in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2004, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.H.; Hastie, T.J.; Tibshirani, R.J. Glmnet: Lasso and Elastic-Net Regularized Generalized Linear Models. R Package Version. 2010. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=glmnet (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- Ridgeway, G.; Southworth, M.H.; RUnit, S. Package ‘gbm’. Viitattu 2013, 10, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, R. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers: 1993. Available online: http://www.rulequest.com/see5-unix.html (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- Alfaro, E.; Gámez, M.; Garcia, N. Adabag: An R package for classification with boosting and bagging. J. Stat. Softw. 2013, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Williams, G.J.; Huang, J.Z. Wsrf: An R package for classification with scalable weighted subspace random forests. J. Stat Softw. 2017, 77, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, D.; Dimitriadou, E.; Hornik, K.; Weingessel, A.; Leisch, F. Misc Functions of the Department of Statistics. e1071, in R package version 1.7-2. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=e1071 (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- Healey, S.P.; Cohen, W.B.; Yang, Z.; Brewer, C.K.; Brooks, E.B.; Gorelick, N.; Hernandez, A.J.; Huang, C.; Hughes, M.J.; Kennedy, R.E.; et al. Mapping forest change using stacked generalization: An ensemble approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H. Stacked generalization. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, K.M.; Witten, I.H. Issues in stacked generalization. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1999, 10, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferri, C.; Hernández-Orallo, J.; Modroiu, R. An experimental comparison of performance measures for classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2009, 30, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.B.; Keith, D.A.; Phinn, S.R.; Mason, T.J.; Elith, J. A comparison of resampling methods for remote sensing classification and accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, C.X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H. AUC: A statistically consistent and more discriminating measure than accuracy. In Ijcai; 2003; Volume 3, pp. 519–524. Available online: https://cling.csd.uwo.ca/papers/ijcai03.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagenauer, J.; Omrani, H.; Helbich, M. Assessing the performance of 38 machine learning models: The case of land consumption rates in Bavaria, Germany. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 1399–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spencer, T.; Schuerch, M.; Nicholls, R.J.; Hinkel, J.; Lincke, D.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Reef, R.; McFadden, L.; Brown, S. Global coastal wetland change under sea-level rise and related stresses: The DIVA Wetland Change Model. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 139, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mellor, A.; Boukir, S. Exploring diversity in ensemble classification: Applications in large area land cover mapping. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 129, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, N.C.; Tumer, K. Classifier ensembles: Select real-world applications. Inf. Fusion 2008, 9, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džeroski, S.; Ženko, B. Is combining classifiers with stacking better than selecting the best one? Mach. Learn. 2004, 54, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jia, X. Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral data based on deep belief network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Lopez, V.; Galar, M.; Del Jesus, M.J.; Herrera, F. Analysing the classification of imbalanced datasets with multiple classes: Binarization techniques and ad-hoc approaches. Knowl. Based Syst. 2013, 42, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Garcia, E.A. Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 21, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, A.; Boukir, S.; Haywood, A.; Jones, S. Exploring issues of training data imbalance and mislabelling on random forest performance for large area land cover classification using the ensemble margin. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, C.E.; Strahler, A.H. The factor of scale in remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 21, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dronova, I.; Gong, P.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. A new time series vegetation–water index of phenological–hydrological trait across species and functional types for Poyang Lake wetland ecosystem. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 125, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, R.; Waser, L.T.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Schaub, M.; Berdos, S.; Ginzler, C.; Psomas, A. Combining ensemble modeling and remote sensing for mapping individual tree species at high spatial resolution. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 310, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing for identification and mapping of wetland vegetation: A review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sha, Z.; Yu, M. Remote sensing imagery in vegetation mapping: A review. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, K.L.; Mendelssohn, I.A.; Materne, M. Acute salt marsh dieback in the Mississippi River deltaic plain: A drought-induced phenomenon. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2004, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Family/Classifier | R Package | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Single | ||
| rpart: regression and classification tree | rpart | [67] |
| RDA: regularised discriminant analysis | MASS | [68] |
| kknn: weighted k-Nearest Neighbours | kknn | [69] |
| nn: feed-forward neural network | nnet | [70] |
| naiveBayes: the Bayes rule | klaR | [71] |
| svm: Support Vector Machines with Radial Basis Function Kernel | kernlab | [72] |
| GLM: elastic net regression | glmnet | [73] |
| Boosting | ||
| gbm: Stochastic Gradient Boosting | gbm | [74] |
| C50: rule-based models | C5.0 | [75] |
| adaBag: Boosted CART | adabag | [76] |
| extreme gradient boosting: regression (xgbLinear) | xgboost | [46] |
| extreme gradient boosting tree (xgbtree) | xgboost | [46] |
| Bagging | ||
| RF: Random Forests * | randomForest | [39] |
| wsrf: weighted subspace random forest * | wsrf | [77] |
| parRF: Parallel Random Forest * | e1071 | [78] |
| treeBag: Bagged CART | Ipred | [66] |
| avNNet: averaged neural networks | NNet | [69] |
| stackModel: stacking of top four classifiers with GBM | Various | [79] |
| Classifier | Accuracy | Kappa | MBA | Balanced accuracy (BA) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG | Forest | Grass | Shrub | Saltmarsh | Mangrove | ||||
| stackModel | 0.7655 | 0.6817 | 0.8439 | 0.8817 | 0.8315 | 0.8699 | 0.8174 | 0.7701 | 0.8928 |
| RF | 0.7734 | 0.6865 | 0.8321 | 0.8826 | 0.8386 | 0.8606 | 0.8145 | 0.7198 | 0.8765 |
| wsrf | 0.7722 | 0.6833 | 0.8293 | 0.8846 | 0.8336 | 0.8490 | 0.8046 | 0.7299 | 0.8743 |
| parRF | 0.7684 | 0.6765 | 0.8220 | 0.8778 | 0.8343 | 0.8556 | 0.7893 | 0.7167 | 0.8583 |
| C50 | 0.7639 | 0.6693 | 0.8173 | 0.8734 | 0.8285 | 0.8578 | 0.7905 | 0.7015 | 0.8521 |
| xgbtree | 0.7426 | 0.6511 | 0.8286 | 0.8668 | 0.8154 | 0.8704 | 0.8049 | 0.7502 | 0.8640 |
| adabag | 0.7410 | 0.6408 | 0.8099 | 0.8598 | 0.8130 | 0.8493 | 0.7914 | 0.7121 | 0.8339 |
| xgblinear | 0.7350 | 0.6437 | 0.8326 | 0.8668 | 0.8052 | 0.8591 | 0.8234 | 0.7741 | 0.8671 |
| treeBag | 0.7363 | 0.6347 | 0.8098 | 0.8562 | 0.8077 | 0.8446 | 0.7888 | 0.7305 | 0.8307 |
| gbm | 0.6969 | 0.6035 | 0.8286 | 0.8434 | 0.7800 | 0.8577 | 0.8315 | 0.7839 | 0.8751 |
| svm | 0.6740 | 0.5797 | 0.8229 | 0.8485 | 0.7632 | 0.8429 | 0.8147 | 0.8114 | 0.8564 |
| kknn | 0.6657 | 0.5346 | 0.7523 | 0.8196 | 0.7618 | 0.8092 | 0.7288 | 0.6626 | 0.7317 |
| rda avNNet | 0.6060 | 0.5002 | 0.7869 | 0.7949 | 0.7236 | 0.7947 | 0.7825 | 0.7684 | 0.8575 |
| nn | 0.5875 | 0.4814 | 0.7828 | 0.8088 | 0.6913 | 0.8280 | 0.7816 | 0.7552 | 0.8320 |
| GLM | 0.5647 | 0.4500 | 0.7625 | 0.7431 | 0.7057 | 0.7799 | 0.7705 | 0.7393 | 0.8367 |
| rda | 0.5405 | 0.4272 | 0.7620 | 0.6870 | 0.7085 | 0.7921 | 0.8090 | 0.7683 | 0.8073 |
| naiveBayes | 0.5297 | 0.4201 | 0.7611 | 0.7001 | 0.6912 | 0.7901 | 0.8147 | 0.7340 | 0.8364 |
| rpart | 0.4474 | 0.3301 | 0.7080 | 0.7090 | 0.6203 | 0.7449 | 0.7006 | 0.6878 | 0.7851 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, L.; Hughes, M. Coastal Wetland Mapping Using Ensemble Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study of Bagging, Boosting and Stacking Techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101683
Wen L, Hughes M. Coastal Wetland Mapping Using Ensemble Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study of Bagging, Boosting and Stacking Techniques. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(10):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101683
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Li, and Michael Hughes. 2020. "Coastal Wetland Mapping Using Ensemble Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study of Bagging, Boosting and Stacking Techniques" Remote Sensing 12, no. 10: 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101683
APA StyleWen, L., & Hughes, M. (2020). Coastal Wetland Mapping Using Ensemble Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study of Bagging, Boosting and Stacking Techniques. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101683