A Cost-Effective Method to Reproduce the Morphology of the Nearshore and Intertidal Zone in Microtidal Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Description of the Study Area
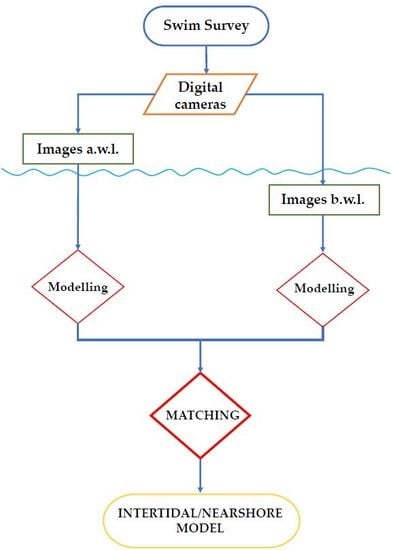
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Support Console and Cameras
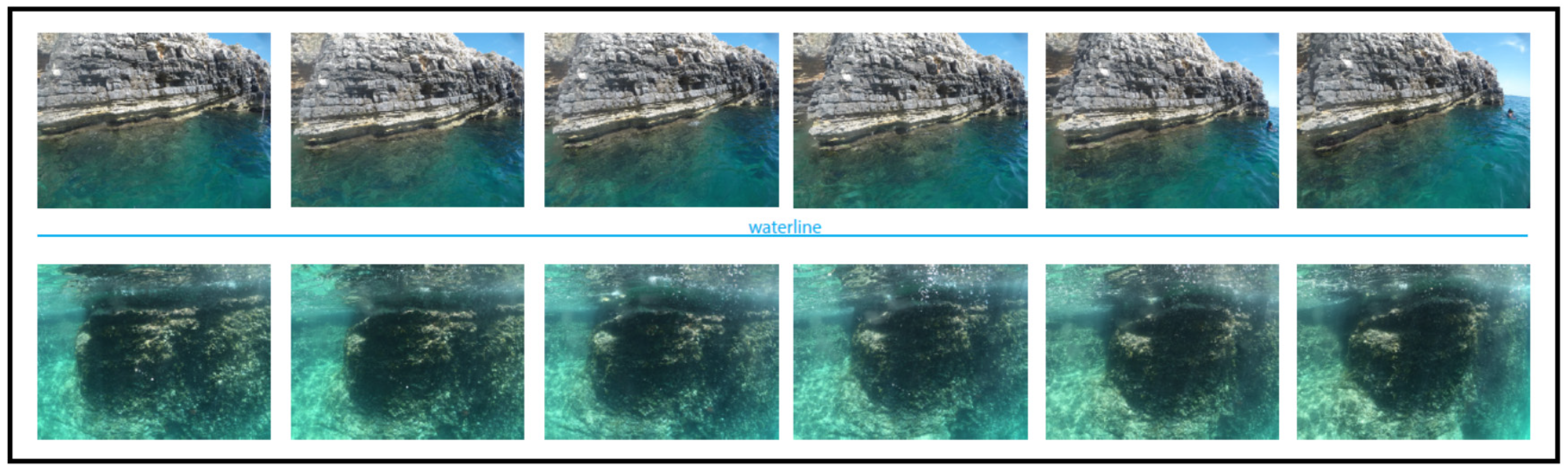
3.2. Acquisition Setting and Data Collection
3.3. Post-Processing of Time-Lapse Images
3.4. UAV Comparison
3.5. Weather Data during the Surveying Days
4. Case Studies
4.1. Site 1
4.2. Site 2
4.3. UAV Imagery at Site 2
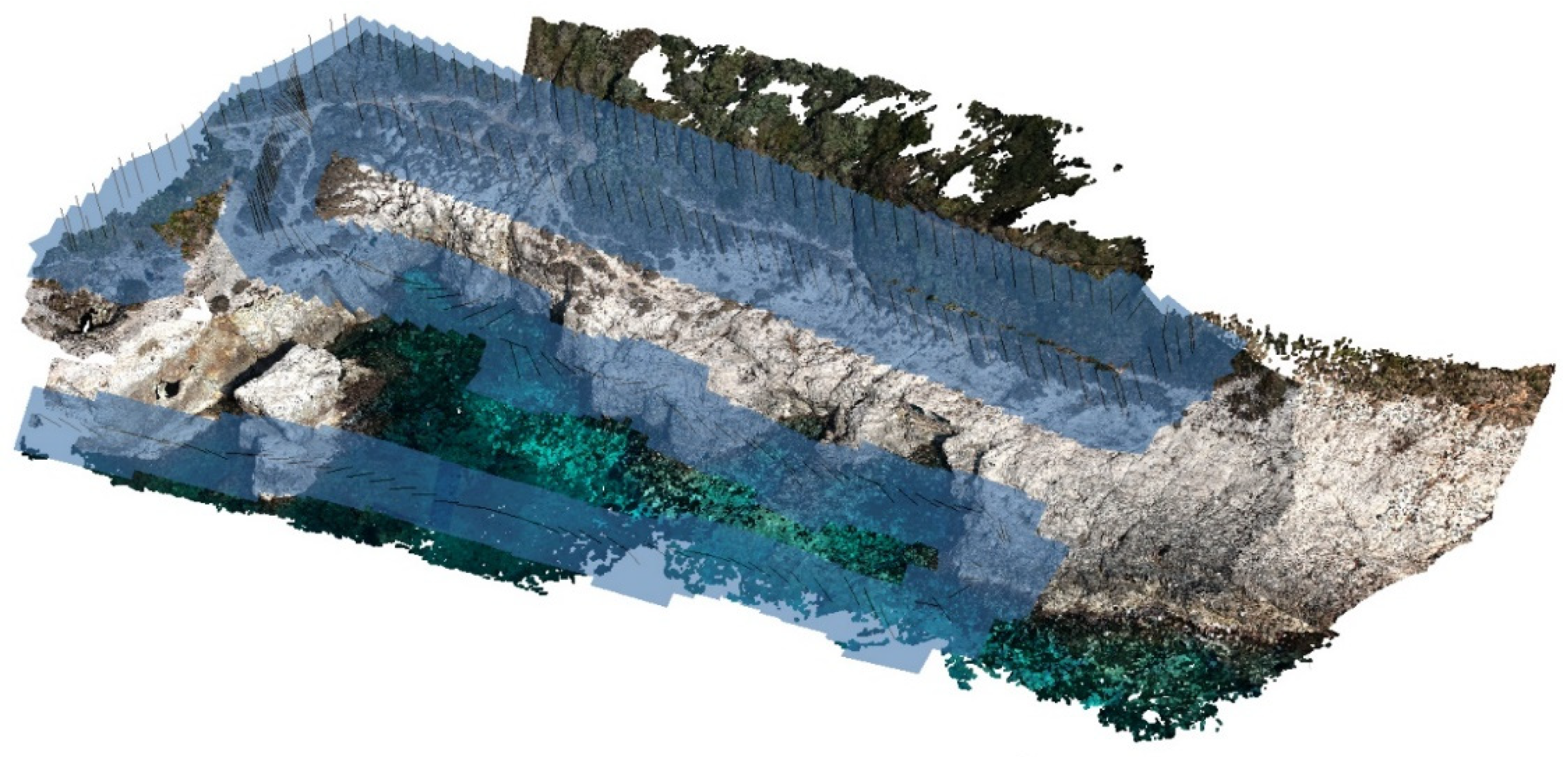
5. Data Post-Processing and Production of 3D Models
5.1. 3D Model at Site 1
5.2. 3D Model at Site 2 with Horizontal and Drone Images
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UAVs | Unmanned Aerial Vehicles |
| SfM | Structure-from-Motion |
| awl | above water level |
| blw | below water level |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| FOV | Field of View |
| GDS | Ground Sampling Distance |
| TPs | Tie Points |
| ODs | Orientation Devices |
| DP | Digital Photography |
| MBES | Multibeam Echosounder |
| ROV | Remotely Operated Vehicle |
| GCP | Ground Control Point |
References
- Kennedy, D.M.; Stephenson, W.J.; Naylor, L.A. Introduction to the rock coasts of the world. Geol. Soc. Lond. Mem. 2014, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.R. The Littoral Zone on Rocky Shores: A Biological or Physical Entity? Oikos 1961, 12, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolchi, S.; Furlani, S.; Devoto, S.; Gauci, R.; Castaldini, D.; Soldati, M. Geomorphological identification, classification and spatial distribution of coastal landforms of Malta (Mediterranean Sea). J. Maps 2016, 12, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolchi, S.; Furlani, S.; Covelli, S.; Busetti, M.; Cucchi, F. Morphoneotectonic map of the coastal sector of the Gulf of Trieste (NE Italy). J. Maps 2016, 12, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, S. Integrated observational targets and instrumental data on rock coasts through snorkel surveys. Mar. Geol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, S.; Ninfo, A.; Zavagno, E.; Paganini, P.; Zini, L.; Biolchi, S.; Antonioli, F.; Coren, F.; Cucchi, F. Submerged notches in Istria and the Gulf of Trieste: Results from the Geoswim Project. Quat. Int. 2014, 332, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, S.; Antonioli, F.; Cavallaro, D.; Chirco, P.; Caldareri, F.; Martin, F.F.; Morticelli, M.G.; Monaco, C.; Sulli, A.; Quarta, G.; et al. Intertidal notches, coastal landforms and relative sea-level changes during the Late Quaternary at Ustica Island (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Geomorphology 2017, 299, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, S.; Antonioli, F.; Gambin, T.; Gauci, R.; Ninfo, A.; Zavagno, E.; Micallef, A.; Cucchi, F. Marine notches on the Maltese Islands (Central Mediterranean Sea). Quat. Int. 2017, 439, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, S.; Piacentini, D.; Troiani, F.; Biolchi, S.; Rocchegiani, M.; Tamburini, A.; Vaccher, V.; Antonioli, F.; Devoto, S.; Nesci, O.; et al. Tn (tidal notches) at the Conero area (W Adriatic coast): Implications for coastal instability. Geogr. Fis. e Din. Quat. 2018, 41, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Westoby, M.J.; Brasington, J.; Glasser, N.F.; Hambrey, M.J.; Reynolds, J.M. ‘Structure-from-Motion’photogrammetry: A low-cost, effective tool for geoscience applications. Geomorphology 2012, 179, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, F.; Nocerino, E.; Troisi, S.; Remondino, F. Joint alignment of underwater and above-the-water photogrammetric 3d models by independent models adjustment. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-5-W5, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrivick, J.L.; Smith, M.W.; Quincey, D.J. Structure from Motion in the Geosciences; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ružić, I.; Marović, I.; Benac, Č.; Ilić, S. Coastal cliff geometry derived from structure-from-motion photogrammetry at Stara Baška, Krk Island, Croatia. Geo Mar. Lett. 2014, 34, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, E.; Menna, F.; Farella, E.; Remondino, F. 3D virtualization of an underground semi-submerged cave system. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; El-Hakim, S. Image-based 3D modelling: A review. Photogramm. Rec. 2006, 21, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, N.A. Aerial and Close-Range Photogrammetric Technology: Providing Resource Documentation, Interpretation, and Preservation; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management, National Operations Center: Denver, CO, USA, 2008.
- Fraser, C.S.; Cronk, S. A hybrid measurement approach for close-range photogrammetry. ISPRS J. Photogram Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadie, A.; Boissery, P.; Viala, C. Georeferenced underwater photogrammetry to map marine habitats and submerged artificial structures. Photogramm. Rec. 2018, 33, 448–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drap, P.; Merad, D.; Hijazi, B.; Gaoua, L.; Nawaf, M.; Saccone, M.; Chemisky, B.; Seinturier, J.; Sourisseau, J.C.; Gambin, T.; et al. Underwater photogrammetry and object modeling: A case study of Xlendi Wreck in Malta. Sensors 2015, 15, 30351–30384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, N.; Chandler, J.H.; Lane, S.N. Structure from motion (SFM) photogrammetry. Br. Soc. Geomorphol. Geomorphol. Tech. 2015, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Teague, J.; Scott, T. Underwater photogrammetry and 3D reconstruction of submerged objects in shallow environments by ROV and underwater GPS. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. Japan 2017, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Remondino, F.; Barazzetti, L.; Nex, F.; Scaioni, M.; Sarazzi, D. UAV photogrammetry for mapping and 3d modelling–current status and future perspectives. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2011, 38, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Drap, P.; Merad, D.; Boi, J.-M.; Mahiddine, A.; Peloso, D.; Chemisky, B.; Seguin, E.; Alcala, F.; Bianchimani, O. Underwater multimodal survey: Merging optical and acoustic data. In Underwater Sascapes; Musard, O., Le Du-Blayo, L., Francour, P., Beurier, J.P., Feunteun, E., Talassinos, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 221–238. [Google Scholar]
- Vlahović, I.; Tišljar, J.; Velić, I.; Matičec, D. Evolution of the adriatic carbonate platform: Palaeogeography, main events and depositional dynamics. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 220, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolchi, S.; Demaniel, C.; Devoto, S.; Korbar, T.; Macovaz, V.; Sciccchitano, G.; Vilibic, I.; Furlani, S. Impact of the October 2018 Storm Vaia on Coastal Boulders in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Water 2019, 11, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, F.; Cerasuolo, M.; Tomasin, A.; Canestrelli, P. La nebbia a Venezia nel quarantennio 1951–1990. Analisi comparata degli andamenti di visibilità, pressione, temperatura e vento. Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti, Commissione di studio dei provvedimenti per la conservazione e difesa della laguna e della città di Venezia. Rapporti e Studi 1995, 12, 235–271. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, L. Ufficio idrografico. La laguna di Grado e le sue foci: Ricerche e rilievi idrografici. Magistrato alle Acque 1965, 155, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Polli, S. Tabelle di Previsione delle Maree per Trieste e L’Adriatico Settentrionale per L’anno 1971; Istituto Sperimentale Talassografico “Francesco Vercelli”: Trieste, Italy, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Cin, R.; Simeoni, U. A model for determining the classification, vulnerability and risk in the southern coastal zone of the Marche (Italy). J. Coast Res. 1994, 8, 18–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cavaleri, L.; Bergamasco, L.; Bertotti, L.; Bianco, L.; Drago, M.; Iovenitti, L.; Lavagnini, A.; Liberatore, G.; Martorelli, S.; Mattioli, F.; et al. Wind and waves in the northern Adriatic Sea. Il Nuovo Cimento C 1996, 19, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raicich, F.; Colucci, R.R. A near-surface temperature time series from Trieste, northern Adriatic Sea (1899–2015). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, F.; Nocerino, E.; Fassi, F.; Remondino, F. Geometric and optic characterization of a hemispherical dome port for underwater photogrammetry. Sensors 2016, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbrucker, A.R.; Major, J.J.; Spicer, K.R.; Pitlick, J. Camera system considerations for geomorphic applications of SfM photogrammetry. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltner, A.; Kaiser, A.M.; Castillo, C.; Rock, G.; Neugirg, F.; Abellán, A. Image-based surface reconstruction in geomorphometry–merits, limits and developments. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2016, 4, 359–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agisoft. Agisoft Metashape User Manual, Professional Edition, Version 1.5; Agisoft: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brooke-Holland, L. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (Drones): An Introduction; House of Commons Library: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giordan, D.; Hayakawa, Y.; Nex, F.; Remondino, F.; Tarolli, P. Review article: The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASSs) for natural hazards monitoring and management. Nat-Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 1079–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Qin, R.; Chen, X. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Remote Sensing Applications-A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirilli, S. Marea Astronomica 2019; Technical Report; Ente Tutela Patrimonio Ittico, Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia: Udine, Italy, 2019; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Cirilli, S. Marea Astronomica 2020; Technical Report; Ente Tutela Patrimonio Ittico, Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia: Udine, Italy, 2020; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, J. Biological and inorganic factors in the destruction of limestone coasts. Contrib. Sedimentol. 1976, 6, 1–112. [Google Scholar]
- Antonioli, F.; Lo Presti, V.; Anzidei, M.; Deiana, G.; De Sabata, E.; Ferranti, L.; Furlani, S.; Mastronuzzi, G.; Orrù, P.; Pagliarulo, R.; et al. Tidal notches in the Mediterranean Sea. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 119, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenhaile, A.S. Coastal notches: Their morphology, formation, and function. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, K.; Huvenne, V.A.; Georgiopoulou, A.; Jones, D.O.; Marsh, L.; Carter, G.D.; Chaumillon, L. New approaches to high-resolution mapping of marine vertical structures. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Survey Sites | Date | Time [UTC] | Rain [mm] | Temp [°C] | Relative Humidity [%] | Wind Speed [km/h] | Wind Direction | Sea Temperature [°C] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lazzaretto | 16/08/2019 | 07:00 | 0.0 | 22.9 | 53 | 27 | ESE | 27.5 |
| 16/08/2019 | 14:00 | 0.0 | 27.2 | 40 | 15 | E | 27.2 | |
| 16/08/2019 | 21:00 | 0.0 | 22.7 | 59 | 11 | SSE | 27.0 | |
| Premantura | 21/06/2019 | 07:00 | 0.0 | 25.7 | 71 | 11 | E | 25.8 |
| 21/06/2019 | 14:00 | 0.0 | 31.0 | 50 | 10 | SE | 26.2 | |
| Premantura (UAV survey) | 21/06/2019 20/02/2020 20/02/2020 20/02/2020 | 21:00 07:00 14:00 21:00 | 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 | 25.4 9.9 12.5 5.3 | 70 45 31 57 | 6 19 15 10 | ESE NE ENE NE | 26.2 11.3 11.6 10.9 |
| Number of Images | Frequency [n/s] | Starting Point | Ending Point | Camera | Elevation [m] | Dome [Y/N] | Markers [Y/N] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| awl | 298 | 1 | 45°35′50.33″N 13°43′18.33″E | 45°35′50.09″N 13°43′17.29″E | GoPro 5 | 1 | N | Y |
| bwl | 213 | 1 | GoPro 6 | 0.5 | Y | N |
| Number of Images | Frequency [n/s] | Starting Point | Ending Point | Camera | Elevation [m] | Dome [Y/N] | Markers [Y/N] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| awl | 715 | 1 | 44°46′4.34″N 13°55′0.48″E | 44°46′5.14″N 13°54′57.90″E | GoPro 5 | 1 | N | Y |
| bwl | 1453 | 0.5 | GoPro 6 | 0.5 | N | N |
| Number of Images | Frequency [n/s] | Elevation [m] | Markers [Y/N] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 247 | 2 | 25 | N |
| awl | bwl | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of images | 298 | 213 | |
| Markers (Y/N) | 7 | 7 | |
| TPs | n° | 413,025 | 190,293 |
| Quality | High | High | |
| Dense cloud | n° | 3,847,764 | 8,336,219 |
| Quality | Medium | High | |
| awl | bwl | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of images | 715 | 1453 | |
| Markers (Y/N) | 2 | / | |
| TPs | n° | 1,577,941 | 400,478 |
| Quality | High | High | |
| Dense cloud | n° | 18,383,030 | 37,567,000 |
| Quality | Medium | Medium | |
| Source | Resolution (mm/Pixel) | Mean Reprojection Error (pixel) | Error (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time-lapse awl | 1.990 | 1.080 | 2.149 |
| Time-lapse bwl | 0.846 | 1.110 | 0.939 |
| Time-lapse drone | 7.000 | 0.876 | 6.132 |
| SWOT Analysis | INTERNAL | EXTERNAL |
|---|---|---|
| HELPFUL | Strengths: | Opportunities: |
|
| |
| HARMFUL | Weakness: | Threats: |
|
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furlani, S.; Vaccher, V.; Macovaz, V.; Devoto, S. A Cost-Effective Method to Reproduce the Morphology of the Nearshore and Intertidal Zone in Microtidal Environments. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111880
Furlani S, Vaccher V, Macovaz V, Devoto S. A Cost-Effective Method to Reproduce the Morphology of the Nearshore and Intertidal Zone in Microtidal Environments. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(11):1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111880
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurlani, Stefano, Valeria Vaccher, Vanja Macovaz, and Stefano Devoto. 2020. "A Cost-Effective Method to Reproduce the Morphology of the Nearshore and Intertidal Zone in Microtidal Environments" Remote Sensing 12, no. 11: 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111880
APA StyleFurlani, S., Vaccher, V., Macovaz, V., & Devoto, S. (2020). A Cost-Effective Method to Reproduce the Morphology of the Nearshore and Intertidal Zone in Microtidal Environments. Remote Sensing, 12(11), 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111880