Where Does Nighttime Light Come From? Insights from Source Detection and Error Attribution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. NPP-VIIRS NTL Remote Sensing Dataset
2.2. EULUC-China 2018
3. Methods
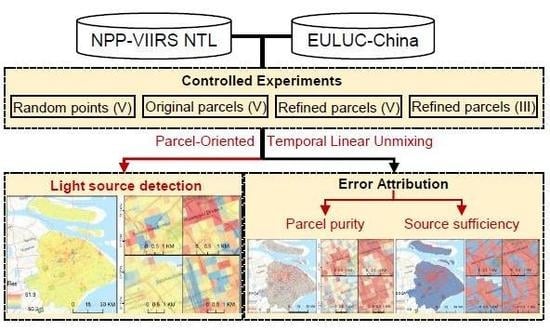
3.1. Parcel-Oriented Temporal Linear Unmixing Method (POTLUM)
3.2. Parcel Purity Index
3.3. Source Sufficiency Index
4. Results
4.1. Practicability of POTLUM, PPI, and SSI
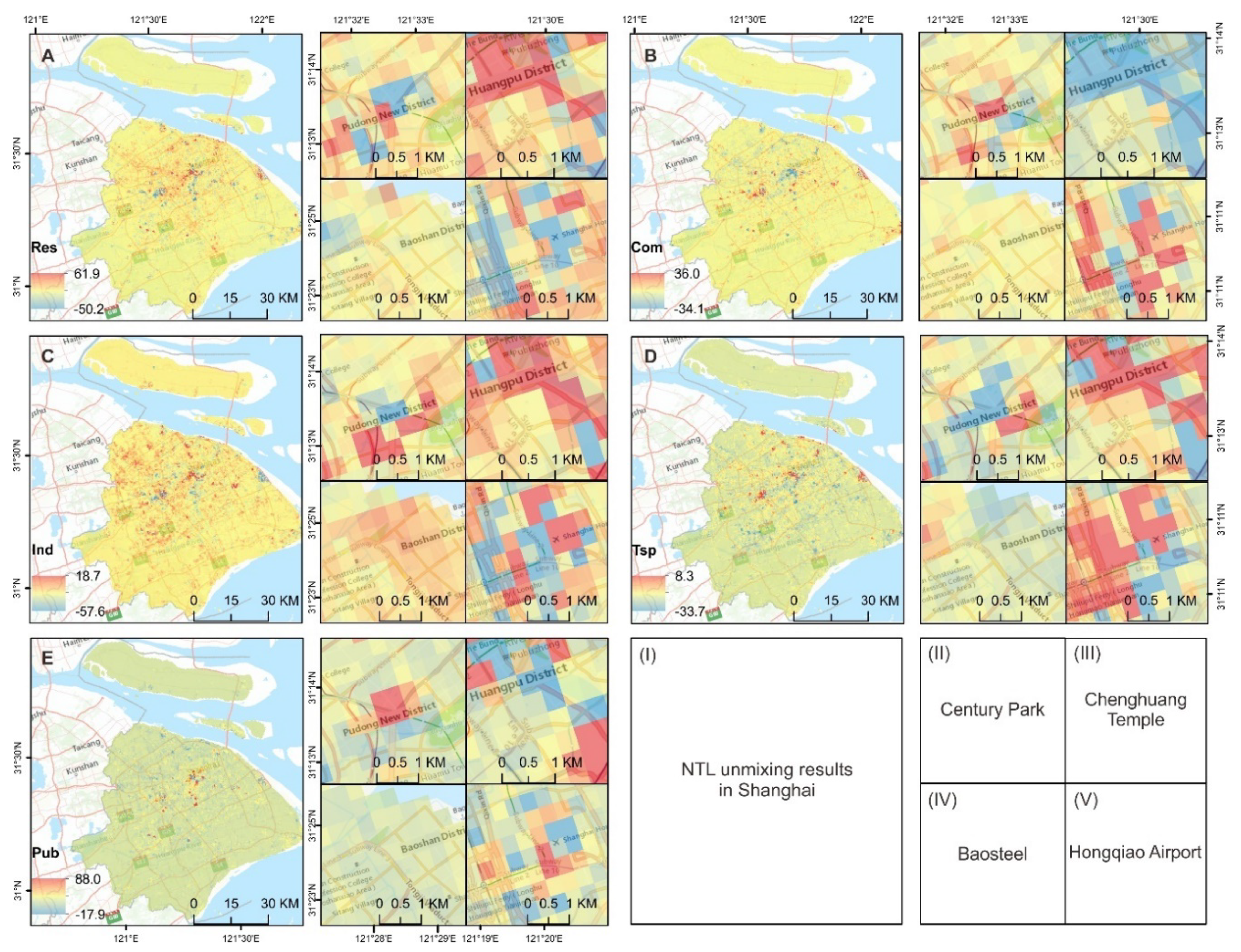
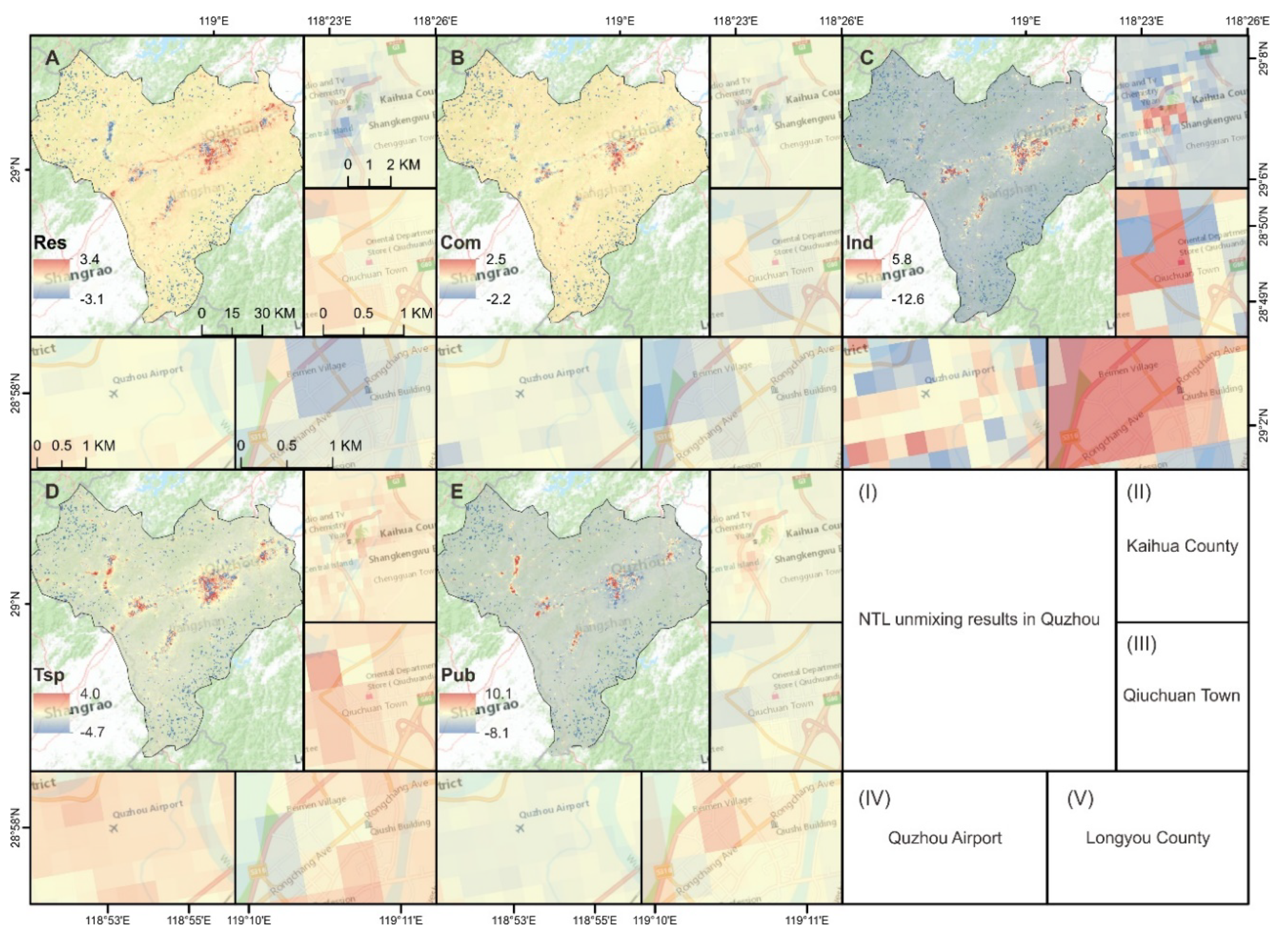
4.2. Nighttime Light Sources
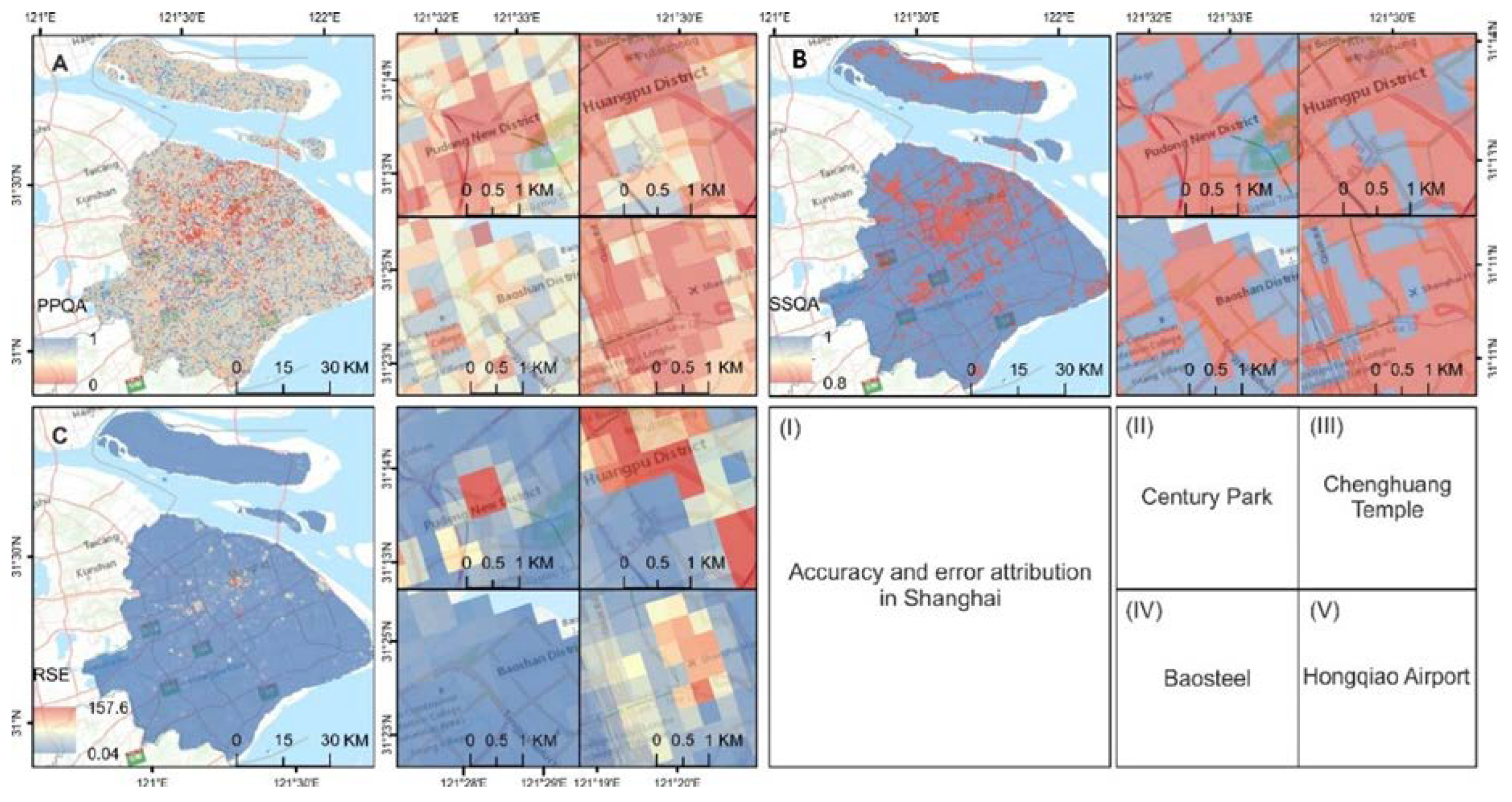
4.3. Unmixing Accuracy
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison with Previous Works
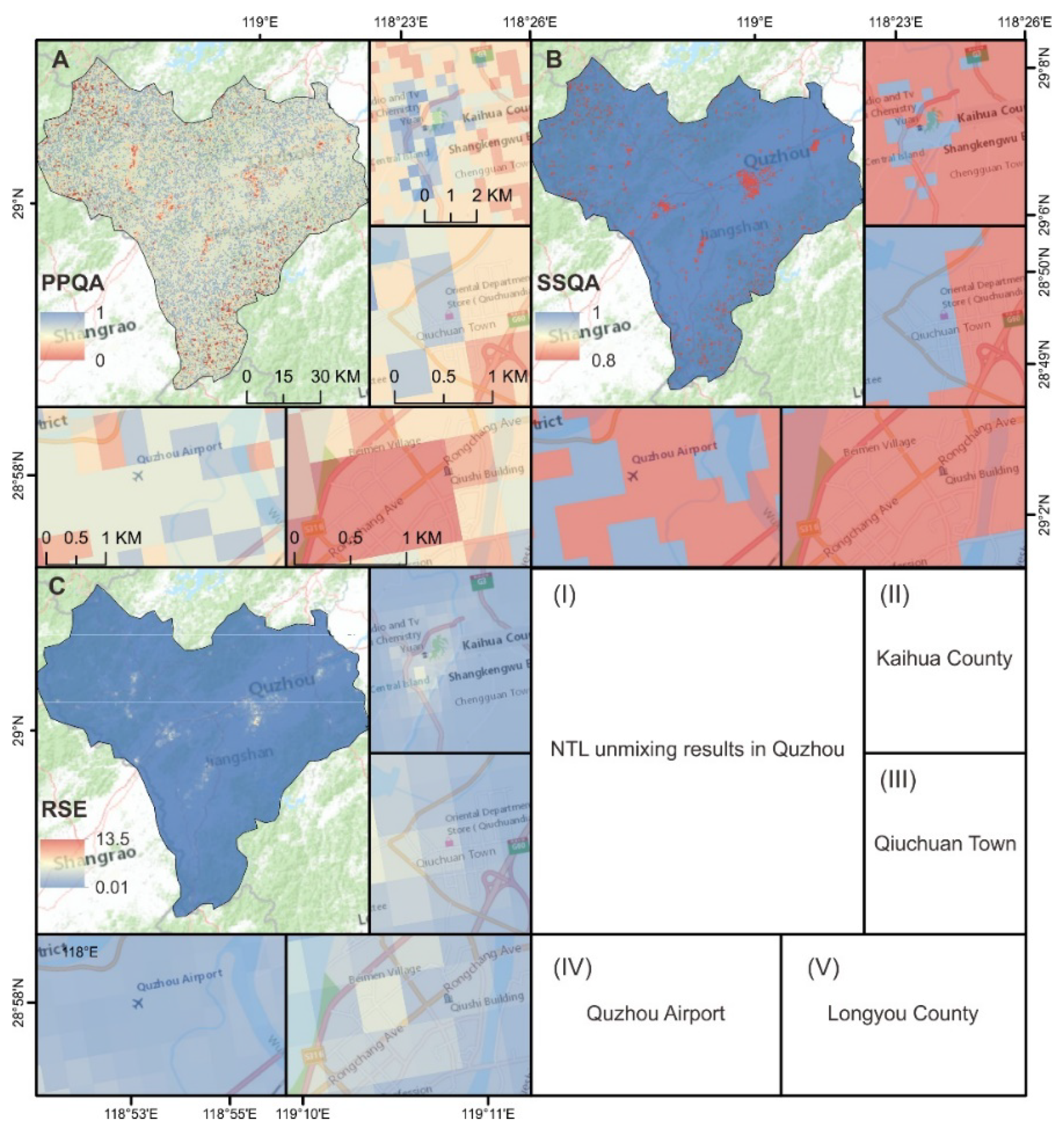
5.2. Visual Validation, RMSE-Related Indices and Error Attributing Indices
5.3. Uncertainty and Implications
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Zhao, X.; Li, X. Remote sensing of human beings—A perspective from nighttime light. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 19, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. Mapping Global Urban Areas From 2000 to 2012 Using Time-Series Nighttime Light Data and MODIS Products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T. Estimation of gross domestic product at sub-national scales using nighttime satellite imagery. Int. J. Ecol. Econ. Stat. 2007, 8, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty evaluation using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data at the county level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.; Roberts, D.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Census from Heaven: An estimate of the global human population using night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3061–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Hara, M.; Yagi, H.; Naoki, K.; Tana, G.; Nishio, F.; Shuhei, O. Estimating energy consumption from night-time DMPS/OLS imagery after correcting for saturation effects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.E.; Wagner, S.E.; Burch, J.; Bayakly, R.; Vena, J.E. A case-referent study: Light at night and breast cancer risk in Georgia. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2013, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonken, L.K.; Workman, J.L.; Walton, J.C.; Weil, Z.M.; Morris, J.S.; Haim, A.; Nelson, R.J. Light at night increases body mass by shifting the time of food intake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18664–18669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharti, N.; Tatem, A.J.; Ferrari, M.J.; Grais, R.F.; Djibo, A.; Grenfell, B.T. Explaining seasonal fluctuations of measles in Niger using nighttime lights imagery. Science 2011, 334, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longcore, T.; Rich, C. Ecological light pollution. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Ryu, S.-H.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, E.; Choi, J. Effects of artificial light at night on human health: A literature review of observational and experimental studies applied to exposure assessment. Chronobiol. Int. 2015, 32, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, N.; Burke, M.; Xie, M.; Davis, W.M.; Lobell, D.B.; Ermon, S. Combining satellite imagery and machine learning to predict poverty. Science 2016, 353, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Gou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L. Detecting global urban expansion over the last three decades using a fully convolutional network. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.; Howden-Chapman, P.; Capon, A. Understanding the systemic nature of cities to improve health and climate change mitigation. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, E.C.; Seto, K.C. Characterizing urban infrastructural transitions for the Sustainable Development Goals using multi-temporal land, population, and nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Siri, J.G.; Remais, J.V.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chan, K.K.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cong, N.; Li, X.; et al. The Tsinghua-Lancet Commission on Healthy Cities in China: Unlocking the power of cities for a healthy China. Lancet 2018, 391, 2140–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Ge, L.; Chen, X. Quantifying Contribution of Land Use Types to Nighttime Light Using an Unmixing Model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1667–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.; Zhang, Q.; de Miguel, A.S.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Ta, N.; Shi, K.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Deng, S.; Wu, J. Delineating Seasonal Relationships Between Suomi NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light and Human Activity Across Shanghai, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4275–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T. An Estimate of the Pixel-Level Connection between Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band (VIIRS DNB) Nighttime Lights and Land Features across China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bierwirth, P. Mineral mapping and vegetation removal via data-calibrated pixel unmixing, using multispectral images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 1999–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Asner, G.P. Cropland distributions from temporal unmixing of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, P.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Fang, L.; Feng, S.; et al. Mapping essential urban land use categories in China (EULUC-China): Preliminary results for 2018. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maselli, F. Multiclass spectral decomposition of remotely sensed scenes by selective pixel unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, J.; Brown, M.; Burian, S.; Chen, F.; Cionco, R.; Hanna, A.; Hultgren, T.; McPherson, T.; Sailor, D.; Taha, H.; et al. National urban database and access portal tool. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, S. High-resolution dataset of urban canopy parameters for Beijing and its application to the integrated WRF/Urban modelling system. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; González, J.; Miao, S.; Ramamurthy, P. On the Assessment of a Cooling Tower Scheme for High-Resolution Numerical Weather Modeling for Urban Areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 1399–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Passing Time | Band Range | Coverage | Spectral Resolution | Spatial Resolution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPP-VIIRS | 1:30 am | 0.5~0.9 μm | 65°S~70°N | 14-bit | 15 arc-sec |
| Level 1 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Categories | Residential | Commercial | Industrial | Transportation | Public management and service |
| Sample (Categories) | PPCA (%) | Overall Accuracy (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Res | Tsp | Com | Ind | Pub | PPOA | SSOA | rRMSE | |
| Point (V) | 42.01 | 50.14 | 57.79 | 52.83 | 38.04 | 48.16 | 93.19 | 5.32 |
| Original (V) | 67.27 | 71.12 | 35.76 | 34.37 | 46.92 | 51.09 | 96.70 | 3.44 |
| Refined (V) | 65.50 | 59.34 | 57.88 | 37.36 | 52.32 | 54.48 | 96.53 | 3.38 |
| Refined (III) | 66.08 | 68.76 | 43.87 | 59.57 | 93.32 | 3.57 | ||
| Sample (Categories) | PPCA (%) | Overall Accuracy (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Res | Tsp | Com | Ind | Pub | PPOA | SSOA | rRMSE | |
| Point (V) | 67.35 | 71.52 | 27.20 | 65.48 | 22.30 | 50.77 | 96.53 | 0.71 |
| Original (V) | 59.53 | 21.04 | 7.05 | 95.41 | 82.18 | 53.04 | 99.50 | 0.87 |
| Refined (V) | 78.89 | 94.03 | 30.04 | 78.66 | 38.82 | 64.09 | 99.55 | 1.04 |
| Refined (III) | 74.70 | 95.97 | 57.39 | 76.02 | 99.36 | 1.33 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Xu, B. Where Does Nighttime Light Come From? Insights from Source Detection and Error Attribution. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121922
Ren Z, Liu Y, Chen B, Xu B. Where Does Nighttime Light Come From? Insights from Source Detection and Error Attribution. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(12):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121922
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Zhehao, Yufu Liu, Bin Chen, and Bing Xu. 2020. "Where Does Nighttime Light Come From? Insights from Source Detection and Error Attribution" Remote Sensing 12, no. 12: 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121922
APA StyleRen, Z., Liu, Y., Chen, B., & Xu, B. (2020). Where Does Nighttime Light Come From? Insights from Source Detection and Error Attribution. Remote Sensing, 12(12), 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121922