Impact of Stereo Camera Calibration to Object Accuracy in Multimedia Photogrammetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Calibration Techniques in Multimedia Photogrammetry
2.1. Planar Interfaces
2.2. Hemispherical Interfaces
2.3. System Configurations and Calibration Strategies
2.4. Calibration Fixtures
3. Synthetic Datasets
3.1. Notation and Assumptions
- Isotropic glass interface of 10 mm thickness
- Refractive index of air = 1.000
- Refractive index of water = 1.3318
- Refractive index of glass = 1.490
- Perpendicular arrangement of the interface with respect to the optical axis
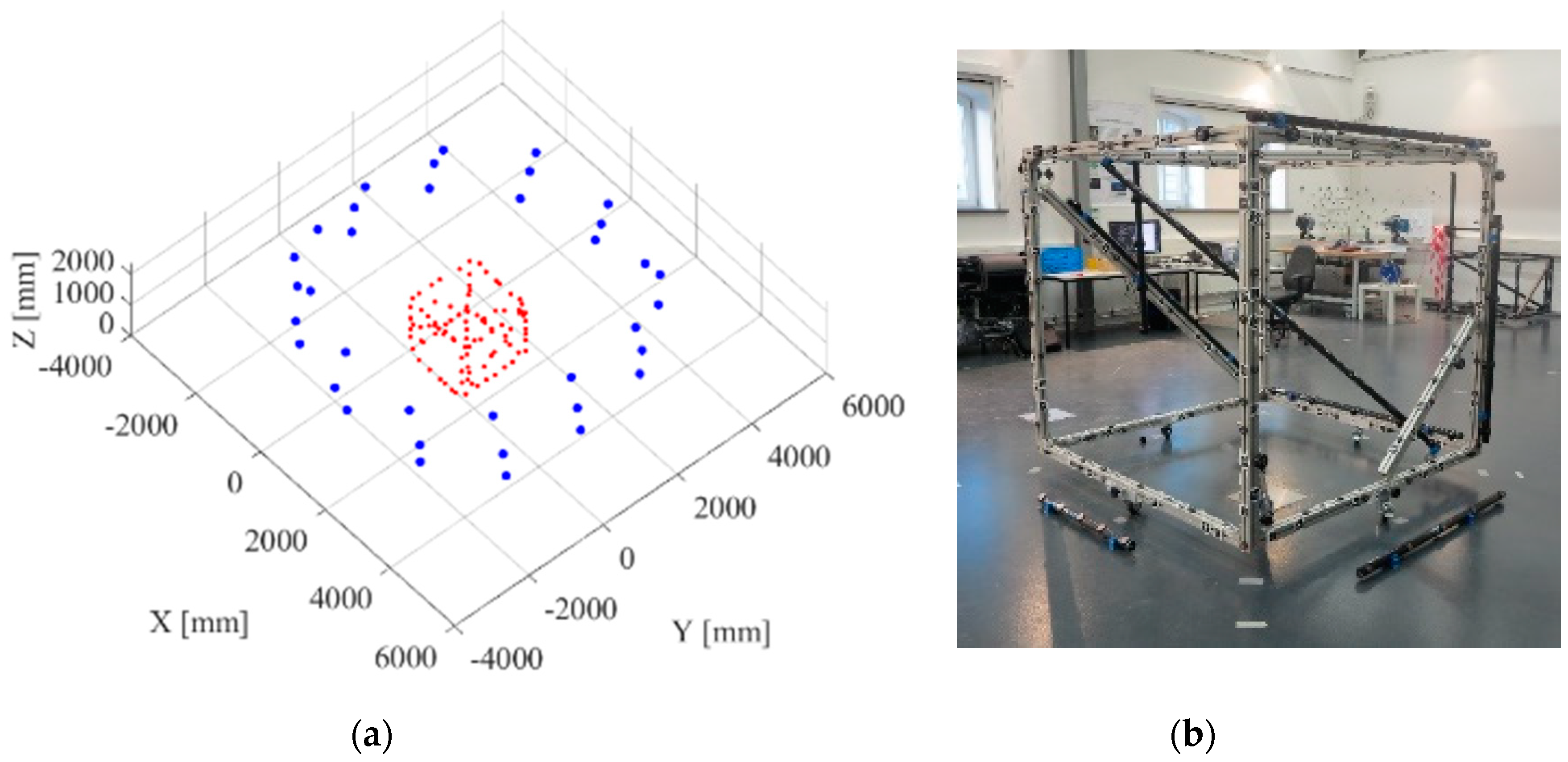
3.2. Dataset Cube
3.3. Dataset HS
3.4. Variation of Convergence
3.5. Variation of Air/Water Ratio
3.6. Quality Evaluation in Object Space via Forward Intersection
4. Analysis of Calibration and Orientation for Planar Interfaces in Implicit Form
4.1. Single-Camera Bundle Adjustment
4.2. Stereo Camera Bundle Adjustment
- 2SM-0°-1/99
- 2MM-0°-1/99
4.2.1. Variation of Convergence
4.2.2. Variation of Air/Water Ratio
4.3. Assessment of Simulated Data
5. Analysis of Calibration and Orientation for Planar Interfaces in Explicit Form
5.1. Explicit Modelling
| nair | = refractive index of air |
| nglass | = refractive index of glass |
| nwater | = refractive index of water |
| N1x, N1y, N1z, d | = plane parameters of interface 1 |
| N2x, N2y, N2z, d2 | = plane parameters of interface 2 |
| X0, Y0, Z0 | = translation of the relative orientation |
| ω, φ, κ | = rotation of relative orientation |
5.2. Synthetic Data
| nwater | ± 0.01 |
| Image coordinates | ± 1 pixel |
| Translation of exterior orientations | ± 200 mm |
| Rotation of exterior orientations | ± 1° |
6. Experiments
6.1. Description of the Experiments
6.2. Calibration Parameters
6.3. Deviations in Object Space
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- kbvresearch.com. Underwater Camera Market Size. Available online: https://www.kbvresearch.com/underwater-camera-market-size/ (accessed on 28 November 2019).
- Datainsightspartner.com. Underwater Drones Market Size Estimation, in-Depth Insights, Historical Data, Price Trend, Competitive Market Share & Forecast 2019–2027. Available online: https://datainsightspartner.com/report/underwater-drones-market/61 (accessed on 28 November 2019).
- Shortis, M.; Ravanbakskh, M.; Shaifat, F.; Harvey, E.S.; Mian, A.; Seager, J.W.; Culverhouse, P.F.; Cline, D.E.; Edgington, D.R. A review of techniques for the identification and measurement of fish in underwater stereo-video image sequences. In SPIE Optical Metrology; Remondino, F., Shortis, M.R., Beyerer, J., Puente León, F., Eds.; SPIE: Munich, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Torisawa, S.; Kadota, M.; Komeyama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Takagi, T. A digital stereo-video camera system for three-dimensional monitoring of free-swimming Pacific bluefin tuna, Thunnus orientalis, cultured in a net cage. Aquat. Living Resour. 2011, 24, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, F.; Nocerino, E.; Nawaf, M.M.; Seinturier, J.; Torresani, A.; Drap, P.; Remondino, F.; Chemisky, B. Towards real-time underwater photogrammetry for subsea metrology applications. In OCEANS 2019; IEEE: Marseille, France, 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, F.; Lagudi, A.; Collina, M.; Medaglia, S.; Davidde Petriaggi, B.; Petriaggi, R.; Ricci, S.; Sacco Perasso, C. Documentation and monitoring of underwater archaeological sites using 3d imaging techniques: The case study of the “nymphaeum of punta epitaffio” (baiae, naples). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W10, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E. The progress of survey techniques in underwater sites: The case study of cape stoba shipwreck. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W10, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahmen, O.; Rofallski, R.; Conen, N.; Luhmann, T. On scale definition within calibration of multi-camera systems in multimedia photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W10, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortis, M. Calibration Techniques for Accurate Measurements by Underwater Camera Systems. Sensors (Basel) 2015, 15, 30810–30826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, N.; Shortis, M.R.; Harvey, E.S. A comparison of calibration methods and system configurations of underwater stereo-video systems for applications in marine ecology. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2015, 13, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massot-Campos, M.; Oliver-Codina, G. Optical Sensors and Methods for Underwater 3D Reconstruction. Sensors (Basel) 2015, 15, 31525–31557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höhle, J. Zur Theorie und Praxis der Unterwasser-Photogrammetrie; Deutsche Geodätische Kommission: München, Germany, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, H.-G. Digitale Photogrammetrie in der Dreidimensionalen Strömungsmesstechnik. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich—Dissertation Nr. 9665, Zürich, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mandlburger, G. A case study on through-water dense image matching. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-2, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.C. Close-Range Camera Calibration. Photogramm. Eng. 1971, 37, 855–866. [Google Scholar]
- Kotowski, R. Zur Berücksichtigung Lichtbrechender Flächen im Strahlenbündel; Zugl.: Bonn, Univ., Diss., 1986; Beck: München, Germany, 1987; ISBN 3769693795. [Google Scholar]
- Bräuer-Burchardt, C.; Heinze, M.; Schmidt, I.; Kühmstedt, P.; Notni, G. Compact handheld fringe projection based underwater 3d-scanner. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-5/W5, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, H.-G. A modular geometric model for underwater photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-5/W5, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulsow, C. A flexible multi-media bundle approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, XXXVIII/5, 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Menna, F.; Nocerino, E.; Remondino, F. Flat versus hemispherical dome ports in underwater photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W3, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, E.; Menna, F.; Fassi, F.; Remondino, F. Underwater calibration of dome port pressure housings. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, XL-3/W4, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, F.; Nocerino, E.; Fassi, F.; Remondino, F. Geometric and Optic Characterization of a Hemispherical Dome Port for Underwater Photogrammetry. Sensors (Basel) 2016, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, F.; Nocerino, E.; Remondino, F. Optical aberrations in underwater photogrammetry with flat and hemispherical dome ports. In Videometrics, Range Imaging, and Applications XIV; SPIE: Munich, Germany, 2017; pp. 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Shortis, M.; Harvey, E.; Seager, J. A Review of the Status and Trends in Underwater Videometric Measurement. In Proceedings of the SPIE Conference 6491, Videometrics IX, IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging, San Jose, CA, USA, 28 January–1 February 2007. Invited paper. [Google Scholar]
- Menna, F.; Nocerino, E.; Troisi, S.; Remondino, F. A photogrammetric approach to survey floating and semi-submerged objects. In SPIE Optical Metrology; Remondino, F., Shortis, M.R., Beyerer, J., Puente León, F., Eds.; SPIE: Munich, Germany, 2013; 87910H. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Roberson, M.; Pizarro, O.; Williams, S.B.; Mahon, I. Generation and visualization of large-scale three-dimensional reconstructions from underwater robotic surveys. J. Field Robotics 2010, 27, 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofallski, R.; Luhmann, T. Fusion von Sensoren mit optischer 3D-Messtechnik zur Positionierung von Unterwasserfahrzeugen. In Hydrographie 2018, Trend zu Unbemannten Messsystemen; Wißner-Verlag: Augsburg, Germany, 2018; pp. 223–234. ISBN 978-3-95786-165-8. [Google Scholar]
- Luhmann, T.; Fraser, C.; Maas, H.-G. Sensor modelling and camera calibration for close-range photogrammetry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester-Ebbinghaus, W. Verfahren zur Feldkalibrierung von photogrammetrischen Aufnahmekammern im Nahbereich. In Kammerkalibrierung in der Photogrammetrischen Praxis; Reihe, B., Kupfer, G., Wester-Ebbinghaus, W., Eds.; Heft Nr. 275; Deutsche Geodätische Kommission: München, Germany, 1985; pp. 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Luhmann, T. Erweiterte Verfahren zur Geometrischen Kamerakalibrierung in der Nahbereichsphotogrammetrie; Beck: München, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-7696-5057-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, F.; Bianco, G.; Muzzupappa, M.; Barone, S.; Razionale, A.V. Experimentation of structured light and stereo vision for underwater 3D reconstruction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drap, P.; Seinturier, J.; Hijazi, B.; Merad, D.; Boi, J.-M.; Chemisky, B.; Seguin, E.; Long, L. The ROV 3D Project. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2015, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhmann, T.; Robson, S.; Kyle, S.; Boehm, J. Close-Range Photogrammetry and 3D Imaging, 3rd ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9783110607246. [Google Scholar]
- Wester-Ebbinghaus, W. Einzelstandpunkt-Selbstkalibrierung. Ein Beitrag zur Feldkalibrierung von Aufnahmekammern; Zugl.: Bonn, Univ., Habil.-Schr., 1982; Beck: München, Germany, 1983; ISBN 3769693396. [Google Scholar]
- Ekkel, T.; Schmik, J.; Luhmann, T.; Hastedt, H. Precise laser-based optical 3d measurement of welding seams under water. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-5/W5, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VDI. VDI/VDE. 2634.1: Optical 3-D Measuring Systems—Imaging Systems with Point-by-Point Probing; VDI: Düsseldorf, Geramny, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.; Loy, A.; Cataudella, S.; Davis, D.; Scardi, M. Extracting fish size using dual underwater cameras. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 35, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschinelli, P.D.V.; Matos, G.; Pinto, T.; Albertazzi, A. Underwater 3D shape measurement using inverse triangulation through two flat refractive surfaces. In OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE, Monterey, CA, USA, 19–23 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–7. ISBN 978-1-5090-1537-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lavest, J.M.; Rives, G.; Laprest, J.T. Dry camera calibration for underwater applications. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2003, 13, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Anderson, J.; Winger, P.; Krouglicof, N. Calibration of an Underwater Stereoscopic Vision System. In 2013 OCEANS—San Diego; IEEE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrafiotis, P.; Georgopoulos, A. Camera constant in the case of two media photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-5/W5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlazeck, A.; Koch, R. Calibration of Housing Parameters for Underwater Stereo-Camera Rigs. In British Machine Vision Conference 2011; Hoey, J., McKenna, S., Trucco, E., Zhang, J., Eds.; BMVA Press: Dundee, UK, 2011; pp. 118.1–118.11. [Google Scholar]
- Sedlazeck, A.; Koch, R. Perspective and Non-perspective Camera Models in Underwater Imaging—Overview and Error Analysis. In Outdoor and Large-Scale Real-World Scene Analysis; Hutchison, D., Kanade, T., Kittler, J., Kleinberg, J.M., Mattern, F., Mitchell, J.C., Naor, M., Nierstrasz, O., Pandu Rangan, C., Steffen, B., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 212–242. ISBN 978-3-642-34090-1. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, H.-G. On the Accuracy Potential in Underwater/Multimedia Photogrammetry. Sensors (Basel) 2015, 15, 18140–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






















| Cube | HS |
|---|---|
| 2SM-0-Cube | 2SM-0-HS |
| 2MM-0-XX-Cube | 2MM-0-XX-HS |
| 2MM-5-XX-Cube | 2MM-5-XX-HS |
| 2MM-10-XX-Cube | 2MM-10-XX-HS |
| 2MM-15-XX-Cube | 2MM-15-XX-HS |
| 2MM-20-XX-Cube | 2MM-20-XX-HS |
| 2MM-25-XX-Cube | 2MM-25-XX-HS |
| Cube | HS |
|---|---|
| 2SM-XX-Cube | 2SM-XX-HS |
| 2MM-XX-1/99-Cube | 2MM-XX-1/99-HS |
| 2MM-XX-10/90-Cube | 2MM-XX-10/90-HS |
| 2MM-XX-20/80-Cube | 2MM-XX-20/80-HS |
| 2MM-XX-30/70-Cube | 2MM-XX-30/70-HS |
| 2MM-XX-40/60-Cube | 2MM-XX-40/60-HS |
| 2MM-XX-50/50-Cube | 2MM-XX-50/50-HS |
| No. | Experiment | Principal Distance c [mm] | A1 | A2 | A3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nominal | −23.908 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 1SM-1/99-Cube | −23.908 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 3 | 1SM-1/99-HS | −23.908 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 4 | 1MM-1/99-Cube | −33.980 | 3.1e-4 | 1.4e-7 | 1.3e-10 |
| 5 | 1MM-1/99-HS | −33.979 | 3.1e-4 | 1.5e-7 | 1.1e-10 |
| No. | Dataset | Relative Orientation | c [mm] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X0 [mm] | Y0 [mm] | Z0 [mm] | ω [°] | φ [°] | κ [°] | |||
| 0 | nominal | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0–25 | 0.000 | −23.908 |
| 1 | 2SM-0°-1/99-Cube | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −23.908 |
| 2 | 2MM-0°-1/99-Cube | 199.994 | 0.000 | 0.019 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −33.979 |
| 3 | 2MM-5°-1/99-Cube | 200.572 | 0.000 | −0.062 | 0.000 | 5.001 | 0.000 | −33.978 |
| 4 | 2MM-10°-1/99-Cube | 201.143 | −0.002 | −0.116 | 0.000 | 10.000 | 0.000 | −33.978 |
| 5 | 2MM-15°-1/99-Cube | 201.715 | −0.007 | −0.192 | 0.000 | 15.003 | 0.000 | −33.979 |
| 6 | 2MM-20°-1/99-Cube | 202.266 | −0.010 | −0.339 | −0.001 | 20.003 | 0.000 | −33.979 |
| 7 | 2MM-25°-1/99-Cube | 202.884 | −0.011 | −0.378 | 0.001 | 25.004 | 0.000 | −33.981 |
| No. | Dataset | Relative Orientation | c [mm] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X0 [mm] | Y0 [mm] | Z0 [mm] | ω [°] | φ [°] | κ [°] | |||
| 0 | nominal | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0–25 | 0.000 | −23.908 |
| 1 | 2SM-0°-1/99-HS | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −23.908 |
| 2 | 2MM-0°-1/99-HS | 199.987 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −33.978 |
| 3 | 2MM-5°-1/99-HS | 200.573 | 0.000 | −0.047 | 0.000 | 5.000 | 0.000 | −33.977 |
| 4 | 2MM-10°-1/99-HS | 201.164 | −0.001 | −0.037 | 0.000 | 10.000 | 0.000 | −33.978 |
| 5 | 2MM-15°-1/99-HS | 201.736 | −0.004 | −0.082 | 0.000 | 15.000 | 0.000 | −33.979 |
| 6 | 2MM-20°-1/99-HS | 202.314 | −0.008 | −0.113 | 0.002 | 20.001 | 0.000 | −33.980 |
| 7 | 2MM-25°-1/99-HS | 202.845 | −0.005 | −0.290 | 0.001 | 25.000 | 0.000 | −33.981 |
| Parameter | Dataset | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cube | HS | Cube | HS | Cube | HS | Cube | HS | Cube | HS | |
| X | −0.58 | −0.65 | ||||||||
| Y | ||||||||||
| Z | −0.69 | −0.78 | ||||||||
| ω | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.80 | ||||||
| φ | −0.82 | −0.82 | −0.79 | −0.74 | ||||||
| κ | −0.88 | −0.90 | −0.85 | −0.87 | ||||||
| c | Xh | Yh | B1 | B2 | ||||||
| No. | Dataset | Relative Orientation | c [mm] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X0 [mm] | Y0 [mm] | Z0 [mm] | ω [°] | Φ [°] | κ [°] | |||
| 0 | nominal | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0–25 | 0.000 | −23.908 |
| 1 | 2SM-0°-1/99-Cube | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −23.908 |
| 2 | 2MM-0°-1/99-Cube | 199.994 | 0.000 | 0.019 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −33.979 |
| 3 | 2MM-0°-10/90-Cube | 199.912 | −0.018 | 0.012 | −0.001 | −0.008 | 0.001 | −33.891 |
| 4 | 2MM-0°-20/80-Cube | 199.780 | 0.021 | 1.491 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.001 | −33.806 |
| 5 | 2MM-0°-30/70-Cube | 199.732 | 0.142 | 1.501 | 0.019 | 0.002 | −0.002 | −33.744 |
| 6 | 2MM-0°-40/60-Cube | 199.664 | 0.219 | 1.594 | 0.018 | 0.015 | −0.001 | −33.654 |
| 7 | 2MM-0°-50/50-Cube | 199.702 | 0.234 | 2.345 | 0.021 | 0.033 | 0.000 | −33.549 |
| No. | Dataset | Relative Orientation | c [mm] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X0 [mm] | Y0 [mm] | Z0 [mm] | ω [°] | Φ [°] | κ [°] | |||
| 0 | nominal | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0–25 | 0.000 | −23.908 |
| 1 | 2SM-0°-1/99-HS | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −23.908 |
| 2 | 2MM-0°-1/99-HS | 199.987 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −33.978 |
| 3 | 2MM-0°-10/90-HS | 199.782 | −0.019 | 0.616 | −0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −33.878 |
| 4 | 2MM-0°-20/80-HS | 199.586 | −0.039 | 1.288 | −0.004 | 0.004 | 0.000 | −33.758 |
| 5 | 2MM-0°-30/70-HS | 199.441 | −0.056 | 2.092 | −0.006 | 0.007 | 0.000 | −33.630 |
| 6 | 2MM-0°-40/60-HS | 199.345 | −0.028 | 2.187 | −0.003 | 0.011 | 0.000 | −33.496 |
| 7 | 2MM-0°-50/50-HS | 199.287 | −0.028 | 2.254 | −0.001 | 0.013 | 0.000 | −33.362 |
| Parameter | Dataset | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cube | HS | Cube | HS | Cube | HS | Cube | HS | Cube | HS | |
| X | ||||||||||
| Y | ||||||||||
| Z | −0.54 | −0.58 | ||||||||
| ω | 0.55 | 0.63 | 0.54 | 0.63 | ||||||
| φ | −0.64 | −0.64 | −0.64 | −0.62 | ||||||
| κ | ||||||||||
| c | Xh | Yh | B1 | B2 | ||||||
| No. | Dataset | Relative Orientation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X0 [mm] | Y0 mm] | Z0 [mm] | ω [°] | φ [°] | κ [°] | ||
| 0 | nominal | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0–25 | 0.000 |
| 1 | 2MM-25°-1/99-Cube | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 25.000 | 0.000 |
| 2 | 2MM-0°-50/50-Cube | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 3 | 2MM-25°-50/50-Cube | 200.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Data | c | xh | yh | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | C1 | C2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | ||||||||
| σc | σxh | σyh | σA1 | σA2 | σA3 | σB1 | σB2 | σC1 | σC2 | |
| IO AIR | −10.52 | −6.84E-02 | −4.24E-02 | −1.13E-03 | 1.04E-05 | −4.45E-08 | −4.08E-05 | −3.79E-05 | −1.83E-04 | −6.51E-05 |
| 1.08E-03 | 7.43E-04 | 7.96E-04 | 4.88E-06 | 2.25E-07 | 3.18E-09 | 2.50E-06 | 2.02E-06 | 1.16E-05 | 1.15E-05 | |
| IO Water | −14.49 | −4.41E-02 | −3.01E-02 | 6.35E-04 | 2.64E-06 | 6.87E-08 | 4.62E-05 | −1.34E-05 | −1.30E-04 | −2.02E-04 |
| 3.07E-03 | 2.73E-03 | 2.85E-03 | 9.32E-06 | 4.41E-07 | 6.31E-09 | 8.22E-06 | 8.39E-06 | 2.53E-05 | 3.09E-05 |
| No. | Dataset | Relative Orientation | c [mm] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X0 [mm] | Y0 [mm] | Z0 [mm] | ω [°] | Φ [°] | κ [°] | |||
| 0 | air, parallel | −37.914 | 0.886 | 0.214 | 0.120 | −0.022 | −0.180 | −10.520 |
| 1 | parallel-2D | −37.817 | 0.916 | 0.251 | 0.197 | 0.040 | −0.194 | −14.547 |
| 2 | parallel-3D | −37.814 | 0.939 | 0.510 | 0.139 | 0.022 | −0.180 | −14.492 |
| 3 | parallel-2Dex | −37.544 | 0.838 | 0.940 | 0.079 | −0.053 | −0.197 | −10.520 |
| 4 | parallel-3Dex | −37.744 | 0.935 | 0.450 | 0.080 | 0.069 | −0.193 | −10.520 |
| 5 | convergent-2D | −75.961 | −2.683 | −17.026 | 2.461 | −27.792 | −2.859 | −14.555 |
| 6 | convergent-3D | −75.611 | −2.735 | −16.769 | 2.452 | −27.556 | −2.862 | −14.501 |
| 7 | convergent-2Dex | −72.735 | −2.602 | −15.273 | 2.446 | −27.334 | −2.846 | −10.520 |
| 8 | convergent-3Dex | −74.194 | −4.169 | 5.248 | 3.285 | −28.640 | −2.828 | −10.520 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kahmen, O.; Rofallski, R.; Luhmann, T. Impact of Stereo Camera Calibration to Object Accuracy in Multimedia Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122057
Kahmen O, Rofallski R, Luhmann T. Impact of Stereo Camera Calibration to Object Accuracy in Multimedia Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(12):2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKahmen, Oliver, Robin Rofallski, and Thomas Luhmann. 2020. "Impact of Stereo Camera Calibration to Object Accuracy in Multimedia Photogrammetry" Remote Sensing 12, no. 12: 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122057
APA StyleKahmen, O., Rofallski, R., & Luhmann, T. (2020). Impact of Stereo Camera Calibration to Object Accuracy in Multimedia Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing, 12(12), 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122057