Wetland Monitoring Using SAR Data: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Wetland Studies Using SAR Data
3.2. SAR Specifications and Wetland Monitoring
4. Discussion
4.1. SAR Incidence Angle and Wetland Monitoring
4.2. SAR Wavelength and Wetland Monitoring
4.3. SAR Polarization and Wetland Monitoring
4.4. SAR and Wetland Monitoring Applications
4.5. SAR Sensors and Wetland Monitoring
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (Program) (Ed.) Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Wetlands and Water Synthesis: A Report of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-1-56973-597-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Kasischke, E.S.; Brunzell, S.M.; Mudd, J.P.; Smith, K.B.; Frick, A.L. Analysis of space-borne SAR data for wetland mapping in Virginia riparian ecosystems. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3665–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, W.; Touzi, R. Optimum RADARSAT-1 configurations for wetlands discrimination: A case study of the Mer Bleue peat bog. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 33, S46–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, F.; Brown, I.; Castellazzi, P.; Espinosa, L.; Guittard, A.; Hong, S.-H.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H.; Wdowinski, S. Assessment of hydrologic connectivity in an ungauged wetland with InSAR observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, W.J.; Subin, Z.M.; Lawrence, D.M.; Swenson, S.C.; Torn, M.S.; Meng, L.; Mahowald, N.M.; Hess, P. Barriers to predicting changes in global terrestrial methane fluxes: Analyses using CLM4Me, a methane biogeochemistry model integrated in CESM. Biogeosciences 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrissey, L.A.; Livingston, G.P.; Durden, S.L. Use of SAR in regional methane exchange studies. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, A.; Brisco, B. Wetland Monitoring Using the Curvelet-Based Change Detection Method on Polarimetric SAR Imagery. Water 2013, 5, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowardin, L.M.; Carter, V.; Golet, F.C.; LaRoe, E.T. Classification of Wetlands and Deepwater Habitats of the United States; U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979.
- Dahl, T.E.; Johnson, C.E. Wetlands, Status and Trends in the Conterminous United States, Mid-1970′s to Mid-1980′s: First Update of the National Wetlands Status Report; U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; ISBN 978-0-16-035916-3.
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D.; Ismail, R. Field Spectrometry of Papyrus Vegetation (Cyperus papyrus L.) in Swamp Wetlands of St Lucia, South Africa; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 4, pp. 260–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, U. Monthly Analysis of Wetlands Dynamics Using Remote Sensing Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; Paradella, W.R.; Rodrigues, S.W.P.; Costa, F.R.; Mura, J.C.; Gonçalves, F.D. Discrimination of coastal wetland environments in the Amazon region based on multi-polarized L-band airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 95, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchard, E.T.A.; Saatchi, S.S.; White, L.J.T.; Abernethy, K.A.; Jeffery, K.J.; Lewis, S.L.; Collins, M.; Lefsky, M.A.; Leal, M.E.; Woodhouse, I.H.; et al. Mapping tropical forest biomass with radar and spaceborne LiDAR in Lope National Park, Gabon: Overcoming problems of high biomass and persistent cloud. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Niu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, P.; Liu, W. Applicability Assessment of Uavsar Data in Wetland Monitoring: A Case Study of Louisiana Wetland. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-3, 2375–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hensley, S.; Wheeler, K. The UAVSAR instrument: Description and first results. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 26–30 May 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlfart, C.; Winkler, K.; Wendleder, A.; Roth, A. TerraSAR-X and Wetlands: A Review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glenn, N.F.; Neuenschwander, A.; Vierling, L.A.; Spaete, L.; Li, A.; Shinneman, D.J.; Pilliod, D.S.; Arkle, R.S.; McIlroy, S.K. Landsat 8 and ICESat-2: Performance and potential synergies for quantifying dryland ecosystem vegetation cover and biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, W.; Gao, X. Mapping Wetlands of Dongting Lake in China Using Landsat and Sentinel-1 Time Series at 30M. ISPAr 2018, 42, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swatantran, A.; Tang, H.; Barrett, T.; DeCola, P.; Dubayah, R. Rapid, High-Resolution Forest Structure and Terrain Mapping over Large Areas using Single Photon Lidar. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Deventer, H.; Cho, M.A.; Mutanga, O. Multi-season RapidEye imagery improves the classification of wetland and dryland communities in a subtropical coastal region. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 157, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, D.M.; Barrera, V.C.S.; Lara, Z.M. Spatio-temporal modelling of wetland ecosystems using Landsat time series: Case of the Bajo Sinú Wetlands Complex (BSWC)– Córdoba– Colombia. Ann. GIS 2019, 25, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frohn, R.C.; Autrey, B.C.; Lane, C.R.; Reif, M. Segmentation and object-oriented classification of wetlands in a karst Florida landscape using multi-season Landsat-7 ETM+ imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 1471–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, U. Evaluating the utilization of the red edge and radar bands from sentinel sensors for wetland classification. CATENA 2019, 178, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, M.; Mariano, F.; Francisco, G.; Perna, P.; Martino, R.; Haydee, K.; Ferrazzoli, P. Estimating Flow Resistance of Wetlands Using SAR Images and Interaction Models. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 992–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touzi, R.; Omari, K.; Sleep, B.; Jiao, X. Scattered and Received Wave Polarization Optimization for Enhanced Peatland Classification and Fire Damage Assessment Using Polarimetric PALSAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4452–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, L.-M. Eco-Hydrological Characterization of Inland Wetlands in Africa Using L-Band SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti-Cardona, B.; Lopez-Martinez, C.; Dolz-Ripolles, J.; Bladè-Castellet, E. ASAR polarimetric, multi-incidence angle and multitemporal characterization of Doñana wetlands for flood extent monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2802–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engheta, N.; Elachi, C. Radar Scattering from a Diffuse Vegetation Layer over a Smooth Surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1982, GE-20, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwoun, O.-I.; Lu, Z. Multi-temporal RADARSAT-1 and ERS backscattering signatures of coastal wetlands in southeastern Louisiana. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, Y.; Yasuoka, Y. Classification of wetland vegetation by texture analysis methods using ERS-1 and JERS-1 images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS ’93—IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, 18–21 August 1993; Volume 4, pp. 1614–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Allen, T. Estuarine shoreline change detection using Japanese ALOS PALSAR HH and JERS-1 L-HH SAR data in the albemarle-pamlico sounds, north carolina, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4429–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.P.F.; Niemann, O.; Novo, E.; Ahern, F. Biophysical properties and mapping of aquatic vegetation during the hydrological cycle of the Amazon floodplain using JERS-1 and Radarsat. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1401–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, L.L.; Melack, J.M.; Affonso, A.G.; Barbosa, C.; Gastil-Buhl, M.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Wetlands of the Lowland Amazon Basin: Extent, Vegetative Cover, and Dual-season Inundated Area as Mapped with JERS-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar. Wetlands 2015, 35, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, L.L.; Melack, J.M.; Simonett, D.S. Radar detection of flooding beneath the forest canopy: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hess, L.L.; Filoso, S.; Melack, J.M. Understanding the radar backscattering from flooded and nonflooded Amazonian forests: Results from canopy backscatter modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lu, Z.; Lee, H.; Shum, C.K.; Swarzenski, C.M.; Doyle, T.W.; Baek, S.-H. Integrated analysis of PALSAR/Radarsat-1 InSAR and ENVISAT altimeter data for mapping of absolute water level changes in Louisiana wetlands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzandeh, S.; Wang, J. Texture evaluation of RADARSAT imagery for wetland mapping. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 28, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Murnaghan, K.; Wdowinski, S.; Hong, S.-H. Evaluation of RADARSAT-2 Acquisition Modes for Wetland Monitoring Applications. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandeira, N.S.; Grings, F.; Facchinetti, C.; Kandus, P. Mapping Plant Functional Types in Floodplain Wetlands: An Analysis of C-Band Polarimetric SAR Data from RADARSAT-2. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, M.W.; Kasischke, E.S. Using C-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Data to Monitor Forested Wetland Hydrology in Maryland’s Coastal Plain, USA. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widhalm, B.; Bartsch, A.; Heim, B. A novel approach for the characterization of tundra wetland regions with C-band SAR satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5537–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Chini, M.; Guerriero, L. Monitoring Flood Evolution in Vegetated Areas Using COSMO-SkyMed Data: The Tuscany 2009 Case Study. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betbeder, J.; Rapinel, S.; Corgne, S.; Pottier, E.; Hubert-Moy, L. TerraSAR-X dual-pol time-series for mapping of wetland vegetation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 107, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Brisco, B. An assessment of simulated compact polarimetric SAR data for wetland classification using random Forest algorithm. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 43, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; McNairn, H.; Davidson, A.; Rezaee, M.; Salehi, B.; Homayouni, S. Mid-season Crop Classification Using Dual-, Compact-, and Full-Polarization in Preparation for the Radarsat Constellation Mission (RCM). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadimanesh, F.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Brisco, B.; Gill, E. Full and simulated compact polarimetry sar responses to canadian wetlands: Separability analysis and classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartsch, A.; Kidd, R.A.; Pathe, C.; Scipal, K.; Wagner, W. Satellite radar imagery for monitoring inland wetlands in boreal and sub-arctic environments. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2007, 17, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, J.N.R.; Lozano-Garcia, D.F. Spatial filtering of radar data (RADARSAT) for wetlands (brackish marshes) classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, T.L.; Kelly, J.P.; Lee, J.-S. Classification comparisons between dual-pol, compact polarimetric and quad-pol SAR imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Du, L.J.; Schuler, D.L.; Cloude, S.R. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, F.; Tian, B.; Liang, D. Multi-temporal SAR image classification of coastal plain wetlands using a new feature selection method and random forests. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistolesi, L.I.; Ni-Meister, W.; McDonald, K.C. Mapping wetlands in the Hudson Highlands ecoregion with ALOS PALSAR: An effort to identify potential swamp forest habitat for golden-winged warblers. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnqvist, A.; Rauste, Y.; Molinier, M.; Häme, T. Polarimetric SAR Data in Land Cover Mapping in Boreal Zone. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3652–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Schmid, T.; Reyes, M.; Gumuzzio, J. Evaluating Full Polarimetric C- and L-Band Data for Mapping Wetland Conditions in a Semi-Arid Environment in Central Spain. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Pereira, F.R.; Kampel, M.; Cunha-Lignon, M. Mapping of mangrove forests on the southern coast of São Paulo, Brazil, using synthetic aperture radar data from ALOS/PALSAR. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xu, J.; Wan, Z.; Fang, L. Analysis of ALOS PALSAR InSAR data for mapping water level changes in Yellow River Delta wetlands. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clewley, D.; Whitcomb, J.; Moghaddam, M.; McDonald, K.; Chapman, B.; Bunting, P. Evaluation of ALOS PALSAR Data for High-Resolution Mapping of Vegetated Wetlands in Alaska. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7272–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliver-Cabrera, T.; Wdowinski, S. InSAR-Based Mapping of Tidal Inundation Extent and Amplitude in Louisiana Coastal Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlaffer, S.; Chini, M.; Dettmering, D.; Wagner, W. Mapping Wetlands in Zambia Using Seasonal Backscatter Signatures Derived from ENVISAT ASAR Time Series. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierdicca, N.; Pulvirenti, L.; Boni, G.; Squicciarino, G.; Chini, M. Mapping Flooded Vegetation Using COSMO-SkyMed: Comparison With Polarimetric and Optical Data Over Rice Fields. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2650–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.L.; Costa, M.; Tomas, W.M.; Camilo, A.R. Large-scale habitat mapping of the Brazilian Pantanal wetland: A synthetic aperture radar approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Rezaee, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Zhang, Y. Very deep convolutional neural networks for complex land cover mapping using multispectral remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadimanesh, F.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Gill, E.; Molinier, M. A new fully convolutional neural network for semantic segmentation of polarimetric SAR imagery in complex land cover ecosystem. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Zhang, Y.; Salehi, B. Deep convolutional neural network for complex wetland classification using optical remote sensing imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3030–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Wegmüller, U. Multi-temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar Metrics Applied to Map Open Water Bodies. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3225–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, E.A.; Kouraev, A.V.; Rémy, F.; Zemtsov, V.A.; Kirpotin, S.N. Seasonal variability of the Western Siberia wetlands from satellite radar altimetry. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Smith, L.C.; Melack, J.M. Amazon floodplain water level changes measured with interferometric SIR-C radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-H.; Wdowinski, S.; Kim, S.-W. Evaluation of TerraSAR-X Observations for Wetland InSAR Application. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, O.; Khali Aziz, H.; Mohd Hasmadi, I. L- band ALOS PALSAR for biomass estimation of Matang Mangroves, Malaysia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yeh, A.G.-O.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Liu, X.; Qian, J.; Chen, X. Regression and analytical models for estimating mangrove wetland biomass in South China using Radarsat images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5567–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Fatoyinbo, T.E. TanDEM-X Pol-InSAR Inversion for Mangrove Canopy Height Estimation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3608–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Shen, G.; Dong, L. Biomass estimation of wetland vegetation in Poyang Lake area using ENVISAT advanced synthetic aperture radar data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 073579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartsch, A.; Pathe, C.; Wagner, W.; Scipal, K. Detection of permanent open water surfaces in central Siberia with ENVISAT ASAR wide swath data with special emphasis on the estimation of methane fluxes from tundra wetlands. Hydrol. Res. 2008, 39, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, T.P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, J.-M.; Le Toan, T. Mapping of flood dynamics and spatial distribution of vegetation in the Amazon floodplain using multitemporal SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Resources Canada (NR). Sensitivity of Peatlands to Climate Change. Available online: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/environment/resources/maps/11019 (accessed on 20 November 2019).
- Ding, X.; Li, X. Shoreline movement monitoring based on SAR images in Shanghai, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3994–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; He, M.; Hu, B.; Mo, X.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z. Status of wetlands in China: A review of extent, degradation, issues and recommendations for improvement. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 146, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Zhai, L. Multi-Polarization ASAR Backscattering from Herbaceous Wetlands in Poyang Lake Region, China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4621–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, X.; Cao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, L.; Choi, S.; Shi, Y.; Park, T.; Fu, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, X. Estimation of Forest Biomass Patterns across Northeast China Based on Allometric Scale Relationship. Forests 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Melack, J.M.; Dunne, T.; Mertes, L.A.K.; Hess, L.L.; Smith, L.C. Interferometric radar measurements of water level changes on the Amazon flood plain. Nature 2000, 404, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canisius, F.; Brisco, B.; Murnaghan, K.; Van Der Kooij, M.; Keizer, E. SAR Backscatter and InSAR Coherence for Monitoring Wetland Extent, Flood Pulse and Vegetation: A Study of the Amazon Lowland. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, N.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.C.; Yu, H. Estimation of Water Level Changes of Large-Scale Amazon Wetlands Using ALOS2 ScanSAR Differential Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Almeida Furtado, L.F.; Silva, T.S.F.; de Moraes Novo, E.M.L. Dual-season and full-polarimetric C band SAR assessment for vegetation mapping in the Amazon várzea wetlands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sartori, L.R.; Imai, N.N.; Mura, J.C.; de Moraes Novo, E.M.L.; Silva, T.S.F. Mapping Macrophyte Species in the Amazon Floodplain Wetlands Using Fully Polarimetric ALOS/PALSAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4717–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.S.D.; Seyler, F.; Calmant, S.; Filho, O.C.R.; Roux, E.; Araújo, A.A.M.; Guyot, J.L. Water level dynamics of Amazon wetlands at the watershed scale by satellite altimetry. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3323–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grings, F.M.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Karszenbaum, H.; Salvia, M.; Kandus, P.; Jacobo-Berlles, J.C.; Perna, P. Model investigation about the potential of C band SAR in herbaceous wetlands flood monitoring. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5361–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, M.A.; Adams, J.R.; Berg, A.A.; Baltzer, J.L.; Quinton, W.L.; Chasmer, L.E. Contributions of C-Band SAR Data and Polarimetric Decompositions to Subarctic Boreal Peatland Mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1467–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Brisco, B.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E.; DeLancey, E.R.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L. Big Data for a Big Country: The First Generation of Canadian Wetland Inventory Map at a Spatial Resolution of 10-m Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data on the Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform: Mégadonnées pour un grand pays: La première carte d’inventaire des zones humides du Canada à une résolution de 10 m à l’aide des données Sentinel-1 et Sentinel-2 sur la plate-forme informatique en nuage de Google Earth EngineTM. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, T.L.; Costa, M. Landcover classification of the Lower Nhecolândia subregion of the Brazilian Pantanal Wetlands using ALOS/PALSAR, RADARSAT-2 and ENVISAT/ASAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmawan, S.; Takeuchi, W.; Vetrita, Y.; Wikantika, K.; Sari, D. Impact of Topography and Tidal Height on ALOS PALSAR Polarimetric Measurements to Estimate Aboveground Biomass of Mangrove Forest in Indonesia. J. Sens. 2015, 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-H.; Wdowinski, S. Multitemporal Multitrack Monitoring of Wetland Water Levels in the Florida Everglades Using ALOS PALSAR Data With Interferometric Processing. Ieee Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Tian, B.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, J. A method for monitoring hydrological conditions beneath herbaceous wetlands using multi-temporal ALOS PALSAR coherence data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, S.; Jüssi, M.; Martinis, S.; Twele, A. Mapping of flooded vegetation by means of polarimetric Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2/PALSAR-2 imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 3831–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Motagh, M. Random forest wetland classification using ALOS-2 L-band, RADARSAT-2 C-band, and TerraSAR-X imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, J.M.; Lu, X.X.; Flores-Verdugo, F.; Zhang, C.; Flores de Santiago, F.; Jiao, X. Applications of ALOS PALSAR for monitoring biophysical parameters of a degraded black mangrove (Avicennia germinans) forest. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 82, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Tien Bui, D.; Yoshino, K.; Le, N. Optimized Rule-Based Logistic Model Tree Algorithm for Mapping Mangrove Species Using ALOS PALSAR Imagery and GIS in the Tropical Region. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melrose, R.T.; Kingsford, R.T.; Milne, A.K. Using radar to detect flooding in arid wetlands and rivers. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 5242–5245. [Google Scholar]
- Heine, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Itzerott, S. Classification and Monitoring of Reed Belts Using Dual-Polarimetric TerraSAR-X Time Series. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martí-Cardona, B.; López-Martínez, C.; Dolz-Ripollés, J. Local Isotropy Indicator for SAR Image Filtering: Application to Envisat/ASAR Images of the Doñana Wetland (November 2014). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabboor, M.; Brisco, B. Wetland Monitoring and Mapping Using Synthetic Aperture Radar. In Wetlands Management-Assessing Risk and Sustainable Solutions; ResearchGate GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padalia, H.; Musthafa, M. Characterization and classification of freshwater marshy wetland using synthetic aperture radar polarimetry: A case study from Loktak wetland, Northeast India. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 016029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grings, F.; Salvia, M.; Karszenbaum, H.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Kandus, P.; Perna, P. Exploring the capacity of radar remote sensing to estimate wetland marshes water storage. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacome, A.; Bernier, M.; Chokmani, K.; Gauthier, Y.; Poulin, J.; De Sève, D. Monitoring Volumetric Surface Soil Moisture Content at the La Grande Basin Boreal Wetland by Radar Multi Polarization Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4919–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinis, S.; Kersten, J.; Twele, A. A fully automated TerraSAR-X based flood service. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Riordan, K.; Powell, R.B.; Miller, N.; Nowels, M. Improving Wetland Characterization with Multi-Sensor, Multi-Temporal SAR and Optical/Infrared Data Fusion. Adv. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Townsend, P.A. Mapping Seasonal Flooding in Forested Wetlands Using Multi-Temporal Radarsat SAR. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 857–864. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-W.; Wdowinski, S.; Amelung, F.; Dixon, T.H.; Won, J.-S. Interferometric Coherence Analysis of the Everglades Wetlands, South Florida. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 5210–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betbeder, J.; Rapinel, S.; Corpetti, T.; Pottier, E.; Corgne, S.; Hubert-Moy, L. Multitemporal classification of TerraSAR-X data for wetland vegetation mapping. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Schmitt, A.; Murnaghan, K.; Kaya, S.; Roth, A. SAR polarimetric change detection for flooded vegetation. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, J.S.; Kasischke, E.S.; French, N.H.; Gross, M.F.; Klemas, V. Preliminary Evaluation of A Multi-channel Sar Data Set For A Mid-atlantic Coastal Marsh. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, College Park, MD, USA, 20–24 May 1990; pp. 453–456. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.; Patnaik, C. Discrimination of mangrove forests and characterization of adjoining land cover classes using temporal C-band Synthetic Aperture Radar data: A case study of Sundarbans. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.M.; Mitchell, A.L.; Rosenqvist, A.; Proisy, C.; Melius, A.; Ticehurst, C. The potential of L-band SAR for quantifying mangrove characteristics and change: Case studies from the tropics. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2007, 17, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovey, T. Identification of the Rozwarowo marshes using radar remote sensing. Geogr. Pol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brisco, B.; Short, N.; van der Sanden, J.; Landry, R.; Raymond, D. A semi-automated tool for surface water mapping with RADARSAT-1. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 35, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, E.M.L.M.; Costa, M.P.F.; Mantovani, J.E.; Lima, I.B.T. Relationship between macrophyte stand variables and radar backscatter at L and C band, Tucuruí reservoir, Brazil. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1241–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Liao, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, J. Poyang Lake wetland vegetation biomass inversion using polarimetric RADARSAT-2 synthetic aperture radar data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 096077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Tian, B.; Zhou, J.; Tang, P. The backscattering characteristics of wetland vegetation and water-level changes detection using multi-mode SAR: A case study. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Park, J.-W.; Choi, J.-K.; Oh, Y.; Won, J.-S. Potential uses of TerraSAR-X for mapping herbaceous halophytes over salt marsh and tidal flats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.A. Estimating forest structure in wetlands using multitemporal SAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadimanesh, F.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Brisco, B.; Motagh, M. Multi-temporal, multi-frequency, and multi-polarization coherence and SAR backscatter analysis of wetlands. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Sato, R.; Yamada, H.; Boerner, W.-M. POLSAR Image Analysis of Wetlands Using a Modified Four-Component Scattering Power Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clint Slatton, K.; Crawford, M.M.; Chang, L.-D. Modeling temporal variations in multipolarized radar scattering from intertidal coastal wetlands. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, K.; Richardson, M. Quantifying the relative contributions of vegetation and soil moisture conditions to polarimetric C-Band SAR response in a temperate peatland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, C.; Pottier, E.; Hubert-Moy, L.; Rapinel, S. One year wetland survey investigations from quad-pol RADARSAT-2 time-series SAR images. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touzi, R. Target Scattering Decomposition in Terms of Roll-Invariant Target Parameters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, G.; Touzi, R.; Cavayas, F. Polarimetric Radarsat-2 wetland classification using the Touzi decomposition: Case of the Lac Saint-Pierre Ramsar wetland. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 39, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, A.; Wagner, W.; Scipal, K.; Pathe, C.; Sabel, D.; Wolski, P. Global monitoring of wetlands – the value of ENVISAT ASAR Global mode. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2226–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melendez-Pastor, I.; Navarro-Pedreno, J.; Koch, M.; Gomez, I. Multi-resolution and temporal characterization of land-use classes in a Mediterranean wetland with land-cover fractions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5365–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Lee, Y.M.; Battaglia, M.; Endres, S.L.; Laubach, Z.M.; Scarbrough, K. Identification of Woodland Vernal Pools with Seasonal Change PALSAR Data for Habitat Conservation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thanh Noi, P.; Kappas, M. Comparison of Random Forest, k-Nearest Neighbor, and Support Vector Machine Classifiers for Land Cover Classification Using Sentinel-2 Imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banks, S.; White, L.; Behnamian, A.; Chen, Z.; Montpetit, B.; Brisco, B.; Pasher, J.; Duffe, J. Wetland Classification with Multi-Angle/Temporal SAR Using Random Forests. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, J.M.; Knight, J.F.; Gallant, A.L. Influence of Multi-Source and Multi-Temporal Remotely Sensed and Ancillary Data on the Accuracy of Random Forest Classification of Wetlands in Northern Minnesota. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3212–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Ding, X.; Zhang, C.; Cropp, R. A novel unsupervised bee colony optimization (UBCO) method for remote-sensing image classification: A case study in a heterogeneous marsh area. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 5726–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jimenez, M.; Castanedo, S.; Medina, R.; Camus, P. A methodology for the classification of estuary restoration areas: A management tool. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2012, 69, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiminia, H.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.; Adeli, S.; Brisco, B. Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E. The first wetland inventory map of newfoundland at a spatial resolution of 10 m using sentinel-1 and sentinel-2 data on the google earth engine cloud computing platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Davis, L.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. An assessment of support vector machines for land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, S.S.; Mountrakis, G. Meta-analysis of deep neural networks in remote sensing: A comparative study of mono-temporal classification to support vector machines. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, S.; Zang, S. Lake Wetland Classification Based on an SVM-CNN Composite Classifier and High-resolution Images Using Wudalianchi as an Example. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 93, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yamada, H.; Boerner, W.-M. Seasonal Change Monitoring of Wetlands by Using Airborne and Satellite Polsar Sensing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008-2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; Volume 2, pp. 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Gallant, A.L.; Kaya, S.G.; White, L.; Brisco, B.; Roth, M.F.; Sadinski, W.J.; Rover, J. Detecting emergence, growth, and senescence of wetland vegetation with polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data. Water 2014, 6, 694–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasischke, E.; Morrissey, L.; Way, J.; French, N.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L.; Rignot, E.; Stearn, J.; Livingston, G. Monitoring Seasonal Variations in Boreal Ecosystems Using Multi-Temporal Spaceborne SAR Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 21, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.C. Toward Estimating Wetland Water Level Changes Based on Hydrological Sensitivity Analysis of PALSAR Backscattering Coefficients over Different Vegetation Fields. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3153–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouvet, A.; Le Toan, T. Use of ENVISAT/ASAR wide-swath data for timely rice fields mapping in the Mekong River Delta. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasischke, E.S.; Smith, K.B.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Romanowicz, E.A.; Brunzell, S.; Richardson, C.J. Effects of seasonal hydrologic patterns in south Florida wetlands on radar backscatter measured from ERS-2 SAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Kwoun, O. Radarsat-1 and ERS InSAR Analysis Over Southeastern Coastal Louisiana: Implications for Mapping Water-Level Changes Beneath Swamp Forests. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2167–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimitdorzhiev, T.N.; Dagurov, P.N.; Bykov, M.E.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Kirbizhekova, I.I. Comparison of ALOS PALSAR interferometry and field geodetic leveling for marshy soil thaw/freeze monitoring, case study from the Baikal lake region, Russia. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 016006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowinski, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Amelung, F.; Dixon, T.H.; Miralles-Wilhelm, F.; Sonenshein, R. Space-based detection of wetlands’ surface water level changes from L-band SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Fuertes, A.; Marti-Cardona, B.; Bladé, E.; Dolz, J. Envisat/ASAR Images for the Calibration of Wind Drag Action in the Doñana Wetlands 2D Hydrodynamic Model. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilusz, D.C.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C.R.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Mladenova, I.E. Monthly flooded area classification using low resolution SAR imagery in the Sudd wetland from 2007 to 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, C.M. Contribution of the TOPEX NASA Radar Altimeter to the global monitoring of large rivers and wetlands. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 1223–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmering, D.; Schwatke, C.; Boergens, E.; Seitz, F. Potential of ENVISAT Radar Altimetry for Water Level Monitoring in the Pantanal Wetland. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasischke, E.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L. Monitoring South Florida wetlands using ERS-1 SAR imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, M.; Mishima, Y.; Natsume, S. Estimation of surface soil properties in peatland using ALOS/PALSAR. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 5, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.; Rebelo, L.-M.; Fatoyinbo, L.; Rosenqvist, A.; Itoh, T.; Shimada, M.; Simard, M.; Souza-Filho, P.W.; Thomas, N.; Trettin, C.; et al. Contribution of L-band SAR to systematic global mangrove monitoring. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagi, R.; Bernier, M.; Ung, C.H. Quantitative analysis of RADARSAT SAR data over a sparse forest canopy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.C.; Ulaby, F.T.; Pierce, L.E.; Sharik, T.L.; Bergen, K.M.; Kellndorfer, J.; Kendra, J.R.; Li, E.; Lin, Y.C.; Nashashibi, A.; et al. Estimation of forest biophysical characteristics in Northern Michigan with SIR-C/X-SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 877–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasischke, E.S.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Rober, A.R.; Wyatt, K.H.; Waddington, J.M.; Turetsky, M.R. Effects of soil moisture and water depth on ERS SAR backscatter measurements from an Alaskan wetland complex. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Bernier, M.; Gauthier, R.; Neeson, I. Evaluation of C-band SAR data for wetlands mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 22, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Cresson, R.; Hajj, M.E.; Ludwig, R.; Jeunesse, I.L. Estimation of soil parameters over bare agriculture areas from C-band polarimetric SAR data using neural networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Budzynska, M.; Tomaszewska, M.; Malinska, A.; Gatkowska, M.; Bartold, M.; Malek, I. Assessment of Carbon Flux and Soil Moisture in Wetlands Applying Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, K.; McDonald, K.; Podest, E.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Horna, V.; Steiner, N. Assessing L-Band GNSS-Reflectometry and Imaging Radar for Detecting Sub-Canopy Inundation Dynamics in a Tropical Wetlands Complex. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Townsend, P.A. Relationships between forest structure and the detection of flood inundation in forested wetlands using C-band SAR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Smith, K.B.; Brunzell, S.M.; Kasischke, E.S.; Romanowicz, E.A.; Richardson, C.J. Remote monitoring of regional inundation patterns and hydroperiod in the Greater Everglades using Synthetic Aperture Radar. Wetlands 2005, 25, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Yan, T.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Sheng, L. Mapping deciduous broad-leaved forested swamps using ALOS/Palsar data. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cazals, C.; Rapinel, S.; Frison, P.-L.; Bonis, A.; Mercier, G.; Mallet, C.; Corgne, S.; Rudant, J.-P. Mapping and Characterization of Hydrological Dynamics in a Coastal Marsh Using High Temporal Resolution Sentinel-1A Images. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLancey, E.R.; Kariyeva, J.; Cranston, J.; Brisco, B. Monitoring Hydro Temporal Variability in Alberta, Canada with Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, J.; Canty, M.; Conradsen, K.; Hüttich, C.; Nielsen, A.A.; Skriver, H.; Remy, F.; Strauch, A.; Thonfeld, F.; Menz, G. Short-Term Change Detection in Wetlands Using Sentinel-1 Time Series. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mleczko, M.; Mróz, M. Wetland Mapping Using SAR Data from the Sentinel-1A and TanDEM-X Missions: A Comparative Study in the Biebrza Floodplain (Poland). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, A.L.; Filmer, M.S.; Featherstone, W.E. First Results from Sentinel-1A InSAR over Australia: Application to the Perth Basin. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Musial, J.; Malinska, A.; Budzynska, M.; Gurdak, R.; Kiryla, W.; Bartold, M.; Grzybowski, P. Soil Moisture in the Biebrza Wetlands Retrieved from Sentinel-1 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabboor, M.; White, L.; Brisco, B.; Charbonneau, F. Change Detection with Compact Polarimetric SAR for Monitoring Wetlands. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-L.; Shaffer, S.; Niamsuwan, N.; Li, S.; Vines, K.; Yang, M.-W. NISAR L-band digital electronics subsystem: A multichannel system with distributed processors for digital beam forming and mode dependent filtering. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2–6 May 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Duncanson, L.; Neuenschwander, A.; Hancock, S.; Thomas, N.; Fatoyinbo, T.; Simard, M.; Silva, C.A.; Armston, J.; Luthcke, S.B.; Hofton, M.; et al. Biomass estimation from simulated GEDI, ICESat-2 and NISAR across environmental gradients in Sonoma County, California. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.P.; Horst, S.; Ghaemi, H. Digital calibration system for the proposed NISAR (NASA/ISRO) mission. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 7–14 March 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, P.; Hensley, S.; Shaffer, S.; Edelstein, W.; Kim, Y.; Kumar, R. The NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) mission dual-band radar instrument preliminary design. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3832–3835. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, P.; Hensley, S.; Shaffer, S.; Edelstein, W. An update on the NASA-ISRO dual-frequency DBF SAR (NISAR) mission. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 2106–2108. [Google Scholar]

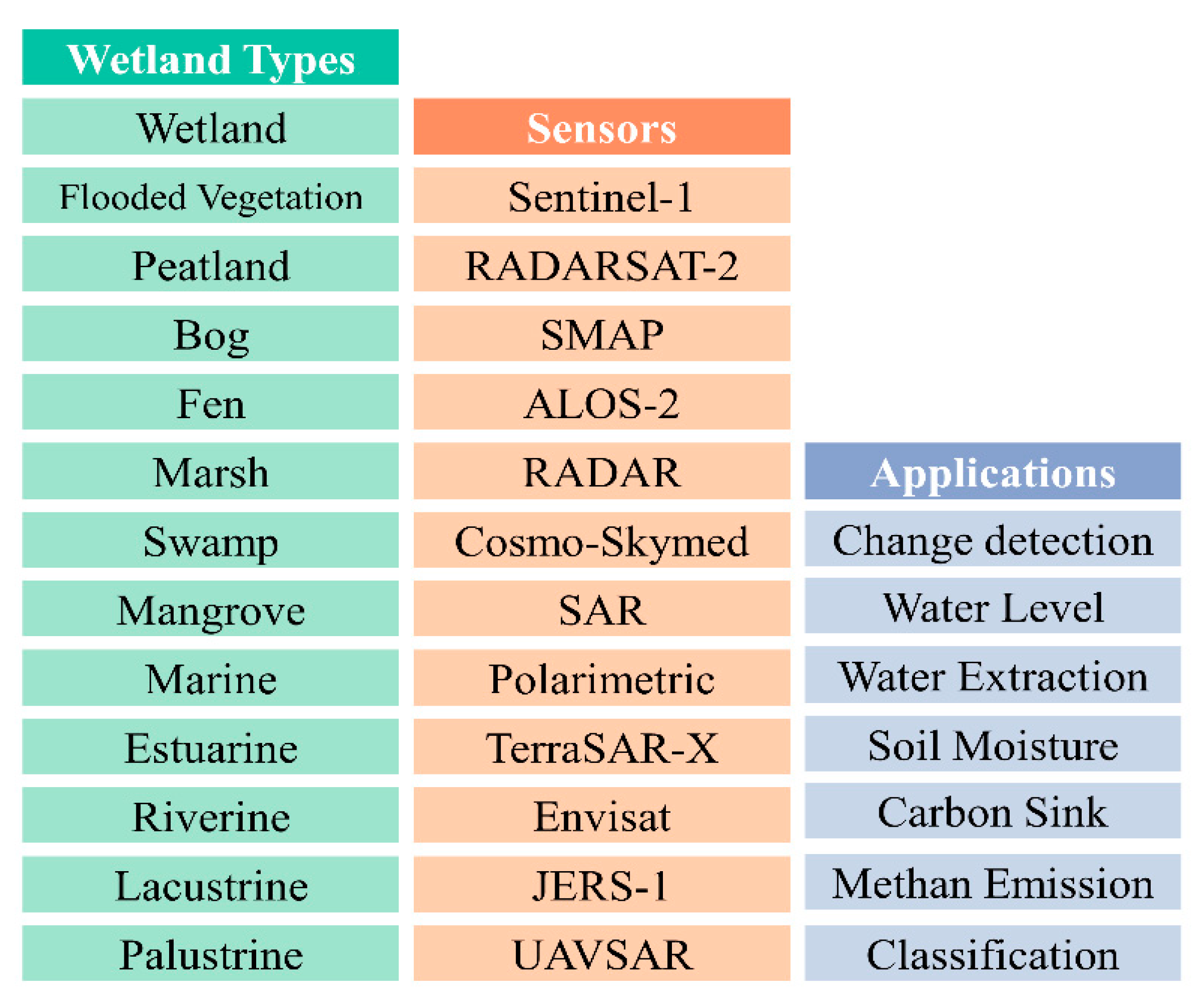















| # | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Title | – |
| 2 | Year | – |
| 3 | Citation | – |
| 4 | Publisher | Journal name |
| 5 | Author(s) | – |
| 6 | Affiliation | – |
| 7 | Geographic location | Countries |
| 8 | Study site size | Km2 |
| 9 | Wetland type | Marine, estuarine, lacustrine, riverine, palustrine |
| 10 | Sensor | Available SAR sensors |
| 11 | Platform | Spaceborne or airborne |
| 12 | Single or multi frequency | – |
| 13 | Used frequency | P, C, L, X bands |
| 14 | Polarization | Single, dual or quad polarization |
| 15 | Incident angle | Range of incidence angles |
| 16 | Usage | Intensity, PolSAR, InSAR |
| 17 | Spatial resolution | Meters |
| 18 | Research objective | Wetland mapping, classification, change detection, water level monitoring, biomass estimation, soil moisture |
| 19 | Single or multidate | Multitemporal or single date |
| 20 | Accuracy Assessment | In percent |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adeli, S.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Brisco, B.; Tamiminia, H.; Shaw, S. Wetland Monitoring Using SAR Data: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142190
Adeli S, Salehi B, Mahdianpari M, Quackenbush LJ, Brisco B, Tamiminia H, Shaw S. Wetland Monitoring Using SAR Data: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(14):2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142190
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdeli, Sarina, Bahram Salehi, Masoud Mahdianpari, Lindi J. Quackenbush, Brian Brisco, Haifa Tamiminia, and Stephen Shaw. 2020. "Wetland Monitoring Using SAR Data: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review" Remote Sensing 12, no. 14: 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142190
APA StyleAdeli, S., Salehi, B., Mahdianpari, M., Quackenbush, L. J., Brisco, B., Tamiminia, H., & Shaw, S. (2020). Wetland Monitoring Using SAR Data: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review. Remote Sensing, 12(14), 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142190










