Radar-Based Non-Contact Continuous Identity Authentication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cardiopulmonary Diversity and Physiological Motion Measurement
3. Radar-based Continuous Identity Authentication Research
3.1. Radar-Based Identity Authentication through Respiration Related Features
3.2. Radar-Based Identity Authentication through Heart-Based Features
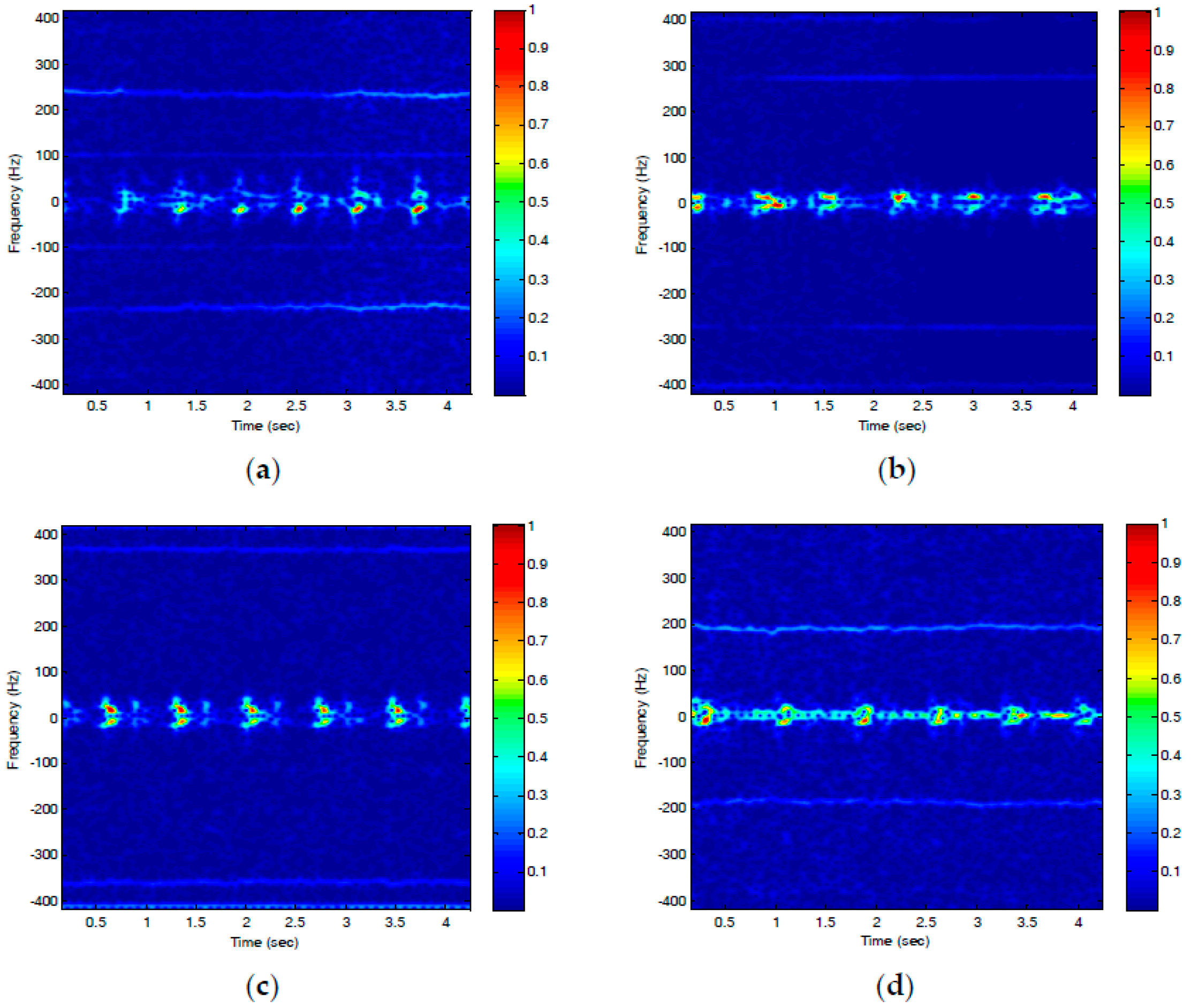
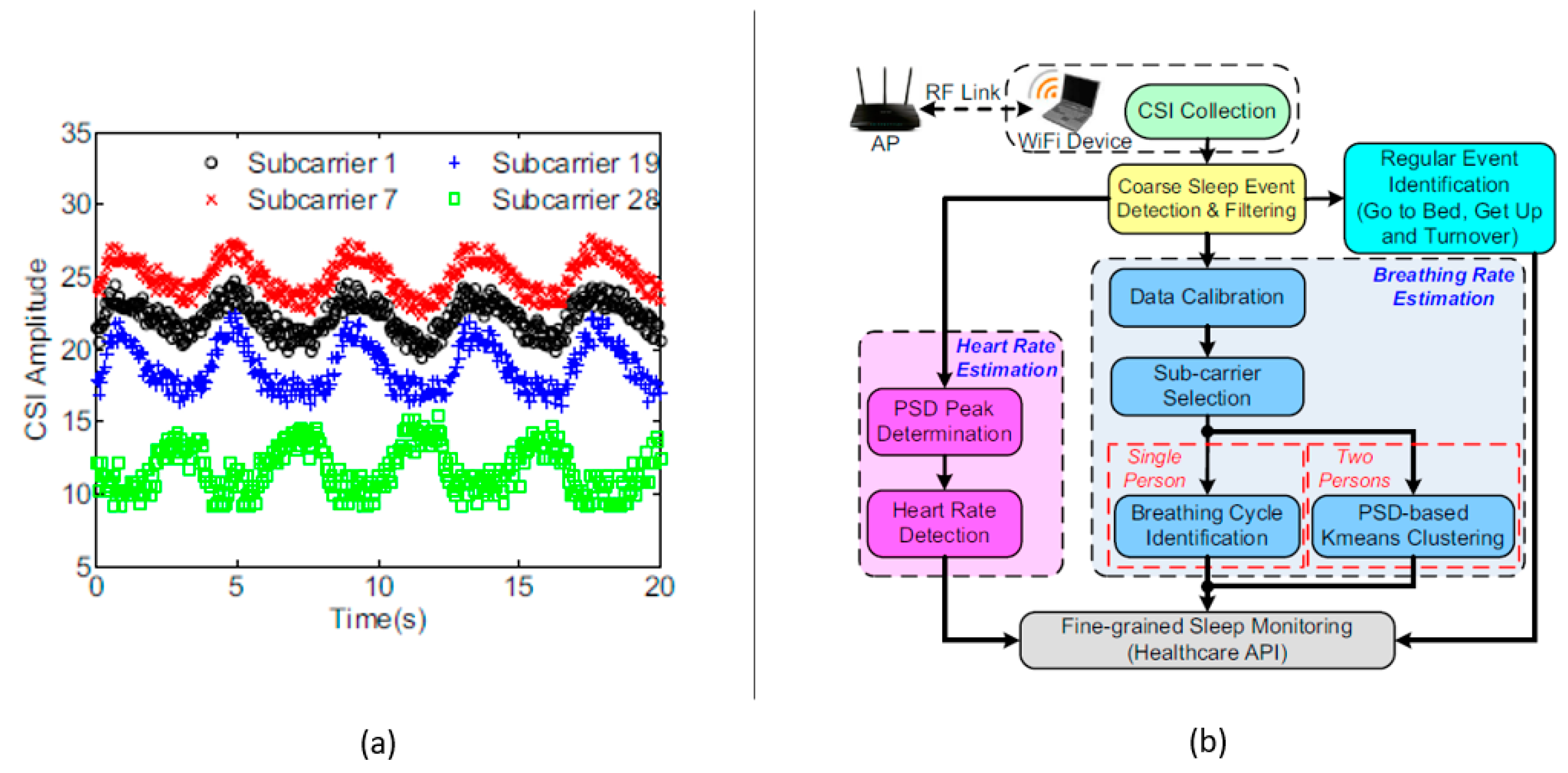
3.3. WiFi-ID: Non-Contact Human Identification Using WiFi Signals
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watson-Watt, R. Radar in war and in peace. Nature 1945, 156, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C. Microwave sensing of physiological movement and volume change: A review. Bioelectromagnetics 1992, 13, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-M.; Misra, D.; Wang, H.; Chuang, H.-R.; Postow, E. An X-band microwave life-detection system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1986, BME-33, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droitcour, A.; Lubecke, V.; Lin, J.; Boric-Lubecke, O. A microwave radio for Doppler radar sensing of vital signs. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (Cat. No.01CH37157), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 20–24 May 2001; Volume 1, pp. 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaev, A.S.; Vasil’ev, I.A.; Ivashov, S.V.; Chapurskii, V.V. Radar methods of detection of human breathing and heartbeat. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 2006, 51, 1154–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldovieri, F.; Catapano, I.; Crocco, L.; Anishchenko, L.N.; Ivashov, S.I. A feasibility study for life signs monitoring via a continuous-wave radar. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2012, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.-D.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, K.-M. Automatic clutter-canceler for microwave life-detection systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1991, 40, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J. Noncontact measurement of cardiopulmonary movements: A review of system architectures and the path to micro-radars. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on RF and Wireless Technologies for Biomedical and Healthcare Applications (IMWS-BIO), Singapore, 9–11 December 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, X.; Weiss, M.D.; Lin, J. Verification of a non-contact vital sign monitoring system using an infant simulator. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009; pp. 4836–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboli, M.; Singh, A.; Soll, B.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M. Wireless sleep apnea detection using continuous wave quadrature Doppler radar. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M.; Droitcour, A.D.; Park, B.K.; Singh, A. Doppler Radar Physiological Sensing; Willey-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Ertin, E.; Kumar, S.; Alabsi, M. Contactless sensing of physiological signals using wideband RF probes. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asilomar Conference on Signals, System and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1230–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubekce, V.M. Concurrent respiration monitoring of multiple subjects by phase-comparison monopulse radar using Independent Component Analysis (ICA) with JADE Algorithm and Direction of Arrival (DOA). IEEE Access 2020, 8, 73558–73569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, M.; Lorato, I.R.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wieringa, F.; Hoof, C.V.; Torfs, T. Vital-sign monitoring and spatial tracking of multiple people using a contactless radar-based sensor. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.-C.; Tang, M.-C.; Arif, R.E.; Horng, T.-S.; Wang, F.-K. Stepped-frequency continuous-wave radar with self-injection-locking technology for monitoring multiple human vital signs. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 5396–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, B.-H.; Park, J.-K.; Yook, J.-G. A novel vital-sign sensing algorithm for multiple subjects based on 24-GHz FMCW doppler radar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yavari, E.; Song, C.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Is there anybody in there? Intelligent radar occupancy sensors. IEEE Microw. 2014, 15, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C. Noninvasive microwave measurement of respiration. Proc. IEEE 1975, 63, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greneker, E.F. Radar sensing of heartbeat and respiration at a distance with applications of the technology. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference, Edinburg, UK, 14–16 October 1997; pp. 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, N.; Mostafanezhad, I.; Lubecke, V.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Host-Madsen, A. Non-contact cardiopulmonary sensing with a baby monitor. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 2300–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Li, C.; Lin, J.; Long, J.; Huangfu, J.; Ran, L. Instrument-based non-contact Doppler radar vital sign detection system using heterodyne digital quadrature demodulation architecture. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 59, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafanezhad, I.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M.; Mandic, D.P. Application of empirical mode decomposition in removing fidgeting interference in Doppler radar life signs monitoring devices. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009; pp. 340–343. [Google Scholar]
- Yunqiang, Y.; Fathy, A.E. Development and implementation of a real time see-through-wall radar system based on FPGA. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lv, H.; Lu, G.; Jing, X.; Wang, J. Human-target detection and surrounding structure estimation under a simulated rubble via UWB radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lubecke, V.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lin, J. A review on recent advances in doppler radar sensor for non-contact healthcare monitoring. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 2046–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capp, P.K.; Pearl, P.L.; Lewin, D. Pediatric sleep disorders. Prim. Care 2005, 32, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, H.; Ipsiroglu, O.; Kerbl, R.; Paditz, E. Sudden infant death and pediatric sleep disorders. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2003, 115, 847–849. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Lee, S.; Buttler, M.; Lubekce, V.M. Activity monitoring and motion classification of the lizard chamaeleon jacksonii using multiple doppler radars. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 4525–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Hafner, N.; Buttler, M.; Lubekce, V.M. A data efficient method for characterization of chameleon tongue motion using Doppler radar. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drazen, N.H.; Lubekce, V.M. Fish heart rate monitoring by body-contact Doppler radar. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Baboli, M.; Gao, X.; Yavari, E.; Padasdao, B.; Soll, B.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V. Considerations for integration of a physiological radar monitoring system with gold standard clinical sleep monitoring systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2120–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kai Sensors Receives FDA Clearance For Its Wireless, Non-Contact Respiratory Device. Available online: https://www.meddeviceonline.com/doc/kai-sensors-receives-fda-clearance-for-its-0001 (accessed on 17 June 2009).
- Gennarelli, G.; Crocco, L.; Solodovieri, F. Doppler radar for real-time surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2018 18th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), Istanbul, Turkey, 31 October–2 November 2018; pp. 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Pathirana, P.N.; Evans, R.J.; Steinfort, C.L. Monitoring and analysis of respiratory patterns using microwave doppler radar. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2014, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaos Computer Club (CCC). Chaos Computer Club Breaks Apple Touch ID. September 2013. Available online: https://www.ccd.de/en/updates/2013/ccc-breaks-apple-touchid (accessed on 22 September 2013).
- Chaos Computer Club (CCC). Fingerprints Biometric Hacked Again. December 2014. Available online: https://www.ccd.de/en/updates/2014/ursel (accessed on 10 November 2016).
- Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Yang, G. Unmatched minutiae: Useful information to boost fingerprint recognition. Neurocomputing 2016, 171, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceo, A.; Crater, M.; Strommback, B. Palm prints. In Encyclopedia of Forensic Sciences; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, K.; Fookes, C.; Jillela, R.; Sridharan, S.; Ross, A. Long range iris recognition: A survey. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 72, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.P.; Vinod, A.P. Towards EEG based biometric systems: The great potential of Brain-wave based biometrics. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst 2017, 3, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, S.; Fang, Z.; Xiong, N.; Yoon, S.; Park, D.S. Exploring finger vein based personal authentication for secure IOT. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 77, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lach, J.; Lo, B.; Yang, G.Z. Towards pervasive gait analysis with wearable sensors: A systematic review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricanek, K.; Savvides, M.; Woodard, D.L.; Dozier, G. Unconstrained biometric identification: Emerging technologies. J. Comput. 2010, 43, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liang, Z.Q. Lightweight biometric sensing for walker classification using narrowband RF. Sensors 2010, 17, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derbel, A.; Vivet, D.; Emile, B. Access control based on gait analysis and face recognition. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazia, M.; Plataniotis, K.N. Human gait recognition from motion capture data in signature process. IET Biomed. 2017, 6, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Springer, S.; Seligmann, G.Y. Validity of the kinetic for Gait Assessment: A focused review. Sensors 2016, 16, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Luo, J.; Tjahjadi, T.; Gao, Y. 2.5D multi-view gait recognition based on point cloud registration. Sensors 2014, 14, 6124–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dorp, P.; Groen, F.C. Feature-based human motion parameter estimation with radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2008, 2, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.C. Doppler signatures of radar backscattering from objects with micro-motions. IET Signal Process. 2008, 2, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisheimer, J.L.; Marshall, W.S.; Greneker, E.A. Continuous-wave (CW) radar for gait analysis. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE Aslimar Conference on Signal, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 4–7 November 2001; Volume 1, pp. 834–838. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.; Yavari, E.; Lubecke, V.M.; Lubekce, O.-B. Noncontact Doppler radar unique identification system using neural network classifier on life signs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Topical Conference on Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems (BioWireless), Austin, TX, USA, 24 January 2016; pp. 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlo, O.M.; Jaakko, T.A.; Karen, O.E.; Alexander, V.T. Target Classification by using pattern features extracted from bispectrum-based radar doppler signatures. In Proceedings of the 2011 12th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Leipzig, Germany, 7–9 September 2011; pp. 791–796. [Google Scholar]
- Droitcour, A.D.; Kovacs, G.T.A.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Shenoy, K. Engineering, Measurement of Heart and Respiration Rates with a Single-Chip. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Benchetrit, G. Breathing pattern in humans: Diversity and individuality. Respir. Physiol. 2000, 122, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander, A.; Sherman, J.; Luciano, D. Human Physiology: The Mechanism of Body Function, 7th ed.; McGraw Hill: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Opie, L.H. Mechanisms of cardiac contraction and relaxation. In Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine; Braunwald, E., Zipes, D.P., Libby, P., Eds.; W.B. Saunders Company: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 443–478. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Song, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, C.; Ren, K. Cardiac scan: A non-contact and continuous heart-based user authentication system. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Mobile Computing and Communication (MobiCom), Snowbird, UT, USA, 16–20 October 2017; pp. 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, A.E.; Welkenhuysen, L.; Montald, J.; de Wolf, L.; Geivers, H.; Minten, J.; Kesteloot, H.; Geest, H. Laser method for recording displacement of the heart and chest wall. J. Biomed. Eng. 1984, 6, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinvuo, T.; Hannula, M.; Sorvoja, H. Measurement of respiratory rate with high resolution accelerometer and EMFit pressure sensor. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 7–9 February 2006; pp. 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.; Bonnet, S.; Guillemaud, R.; Castelli, E.; Yen, P. Estimation of respiratory waveform using an accelerometer. In Proceedings of the 2008 5th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Paris, France, 14–17 May 2008; pp. 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E. Gayton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, K.E.; Barman, S.M.; Boitano, S. Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology; McGraw Hill: New Delhi, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, X. Verification based ECG biometrics with cardiac irregular conditions using heartbeat level and segment level information fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Conference on Acoustic Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 3769–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, S. Continuous authentication by analysis of keyboard typing characteristics in security and detection. In Proceedings of the European Convention on Security and Detection, Brighton, UK, 16–18 May 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, M.K. The Future X Network: A Bell Lab Perspective; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafanezhad, I.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V. A coherent low IF receiver architecture for Doppler radar motion detectors used in life signs monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–14 January 2010; pp. 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, A.; Lubecke, V.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Prins, J.H.; Sakamoto, T. Doppler radar techniques for accurate respiration characterization and subject identification. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2018, 8, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facts+Statistics: Identity Theft and Cybercrime. Available online: https://www.iii.org/fact-statistic/facts-statistics-identity-theft-and-cybercrime (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Islam, S.M.M.; Rahman, A.; Prasad, N.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M. Identity authentication system using support vector machine on radar respiration measurement. In Proceedings of the 93rd ARFTG Microwave Measurement Conference (ARFTG’19), Boston, MA, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Sylvester, A.; Orpilla, G.; Lubecke, V.M. Respiratory feature extraction for radar-based continuous identity authentication. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), San Antonio, TX, USA, 26–29 January 2020; pp. 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Rahman, A.; Yavari, E.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M. Identity authentication of OSA patients using microwave doppler radar and machine learning classifiers. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), San Antonio, TX, USA, 26–29 January 2020; pp. 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissacher, D.; Galy, D. Cardiac radar for biometric identification using nearest neighbor for continuous wavelet transform peaks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Identity, Security and Behavior Analysis (ISBA 2015), Hong Kong, China, 23–25 March 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Will, C.; Weigel, R.; Koelpin, A. Contactless person identification using cardiac radar signals. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, T.; Izumi, S.; Kawaguchi, H.; Yoshimoto, M. Non-contact biometric identification and authentication using microwave Doppler sensor. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Torino, Italy, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Xia, W.; Li, Y. Heart id: Human identification based on radar micro-doppler signatures of the heart using deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, B.; Hu, W.; Kanhere, S.S. WiFi-ID: Human identification using WiFi signal. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (DCOSS), Washington, DC, USA, 26–28 May 2016; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Yao, Y.D. Continuous user verification via respiratory biometrics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM’20), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–9 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelnasser, H.; Harras, K.A.; Yousef, M. Ubibreathe: A ubiquitous non-invasive Wi-Fi based breathing estimators. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing (ACM MobiHoc), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 June 2015; pp. 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J. Tracking Vital Signs during sleep leveraging off-the-shelf Wi-Fi. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing (ACM MobiHoc), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 June 2015; pp. 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum from nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keysight. Concepts of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) and 802.11 WLAN. Available online: https://tinyurl.com/y9h36ryy (accessed on 20 August 2016).
- Tan, B.; Chen, Q.; Chetty, K.; Woodbridge, K. Monitoring health using WiFi sensing and machine learning. In EngineerIT; Coventry University: Coventry, UK, 2018; pp. 1–5. Available online: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10058873 (accessed on 17 October 2018).
- Massagram, W.; Lubecke, V.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Feasibility assessment of Doppler radar long-term physiological measurement. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 1544–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massagram, W.; Lubecke, V.M.; Host-Madsen, A.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Assessment of heart rate variability and respiratory sinus arrhythmia via doppler radar. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 57, 2542–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lin, J. Random body movement cancellation in doppler radar vital sign detection. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2008, 56, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, G.; Inoue, T.; Li, C. Doppler radar vital sign detection with random body movement cancellation based on adaptive phase compensation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (MTT), Seattle, WA, USA, 2–7 June 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Inoue, T.; Li, C. A hybrid radar-camera sensing system with phase compensation for random body movement cancellation in doppler vital sign detection. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 4678–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, C.; Vieira, J.; Pinho, P. A review on methods for random motion detection and compensation in bio-radar systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Yavari, E.; Rahman, A.; Lubecke, V.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Separation of respiratory signature for multiple subjects using independent component analysis with the JADE Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; pp. 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegara, A.; Petrochilos, N.; Madsen, A.H.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Blind source separation of human body motion using direct conversion doppler radar. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–20 June 2008; pp. 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Yavari, E.; Rahman, A.; Lubecke, V.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Multiple subject respiratory pattern recognition and estimation of direction of arrival using phase-comparison monopulse radar. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), Orlando, FL, USA, 20–23 January 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafanezhad, I.; Yavari, E.; Boric-Lubecke, O. A low-cost simple RF front end using time-domain multiplexing for direction of arrival estimation of physiological signals. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (MTT), Seattle, WA, USA, 2–7 June 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Motoyama, N.; Pacheco, S.; Lubecke, V.M. Non-contact vital signs monitoring of multiple subjects using a millimeter wave FMCW automotive radar. In Proceedings of the International Microwave Symposium (IMS’20), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 21–26 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafanezhad, I.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.; Host-Madsen, A. Cancellation of unwanted motion in a handheld Doppler radar used for non-contact life sign monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–20 June 2008; pp. 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafanezhad, I.; Yavari, E.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M.; Mandic, D.P. Cancellation of unwanted doppler radar sensor motion using empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Reference Year of Publication | Hardware (RF Frequency) | Identification Features | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| [52] A. Rahman et al., 2016 | 2.4 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [58] F. Lin et al., 2017 | 2.4 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [68] A. Rahman et al., 2018 | 2.4 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [70] S. M. M. Islam et al., 2019 | 2.4 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [71] S. M. M. Islam et al., 2020 | 2.4 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [72] S. M. M. Islam et al., 2020 | 2.4 GHz and 24-GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [73] D. Rissacher et al., 2015 | 2.4 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [74] K. Shi et al., 2018 | 24 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [75] T. Okano et al., 2017 | 24 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [76] P. Cao et al., 2020 | 24 GHz Doppler Radar |
|
|
| [77] J. Zhang et al., 2016 | WiFi router & Laptop |
|
|
| [78] J. Liu et al., 2020 | WiFi router & Laptop |
|
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, S.M.M.; Borić-Lubecke, O.; Zheng, Y.; Lubecke, V.M. Radar-Based Non-Contact Continuous Identity Authentication. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142279
Islam SMM, Borić-Lubecke O, Zheng Y, Lubecke VM. Radar-Based Non-Contact Continuous Identity Authentication. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(14):2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142279
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Shekh Md Mahmudul, Olga Borić-Lubecke, Yao Zheng, and Victor M. Lubecke. 2020. "Radar-Based Non-Contact Continuous Identity Authentication" Remote Sensing 12, no. 14: 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142279
APA StyleIslam, S. M. M., Borić-Lubecke, O., Zheng, Y., & Lubecke, V. M. (2020). Radar-Based Non-Contact Continuous Identity Authentication. Remote Sensing, 12(14), 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12142279