Extended Geometry and Probability Model for GNSS+ Constellation Performance Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. MEO and LEO Satellite Observing Probability
2.2. GEO and IGSO Satellite Observing Probability
2.3. HEO and QZO Satellite Observing Probability
2.4. Calculation of DOPs and Satellite Visibility
3. Method Validation
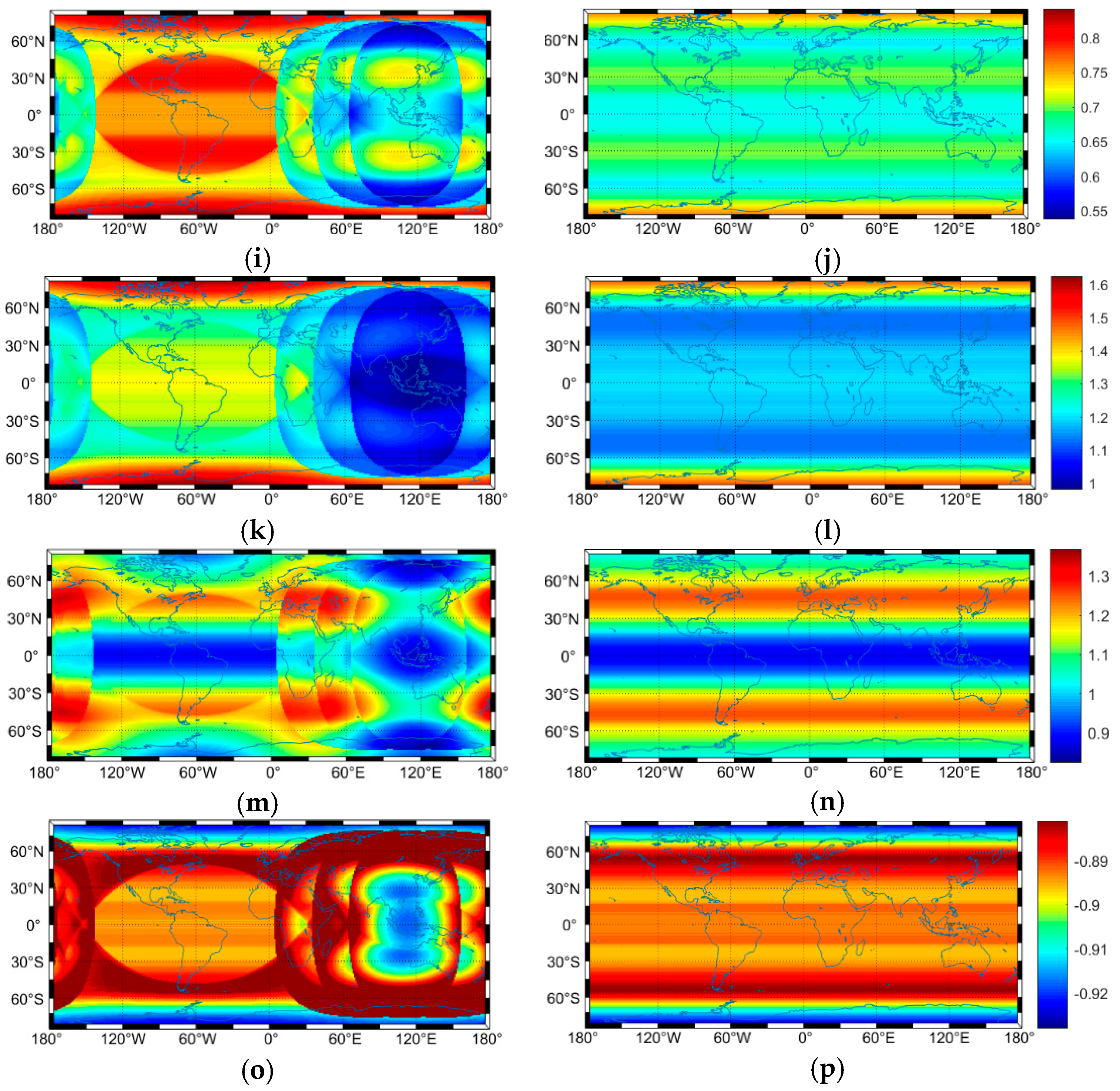
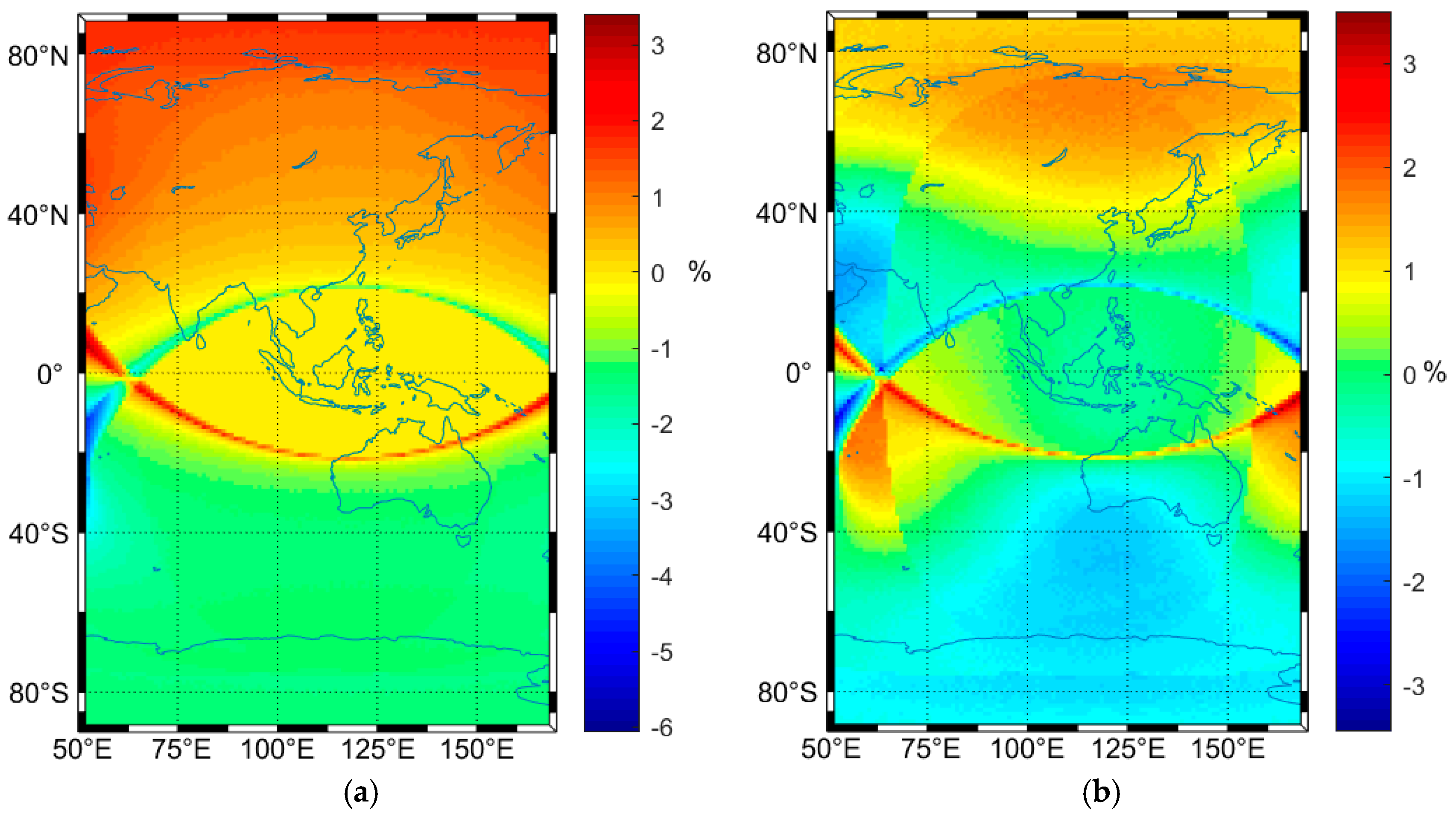
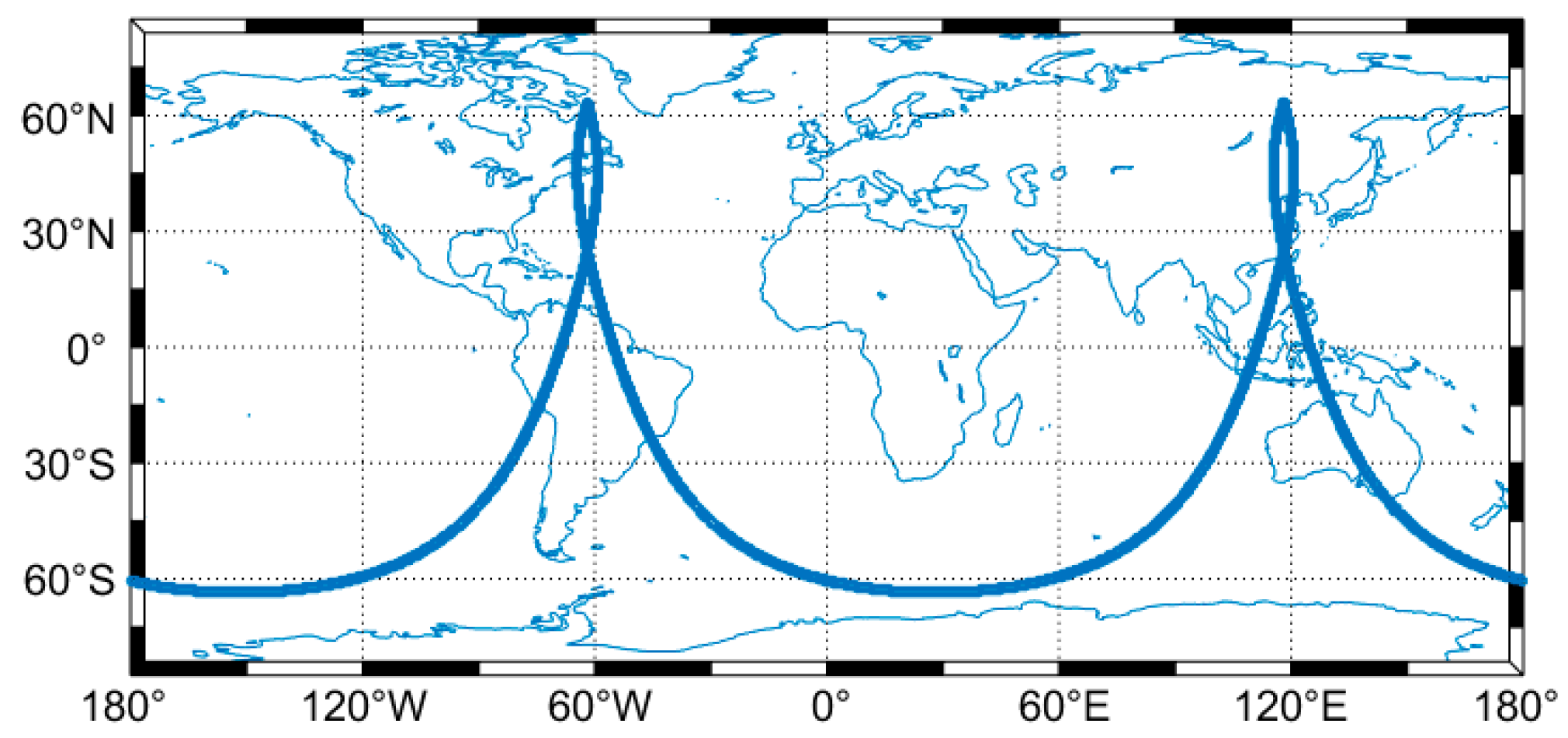
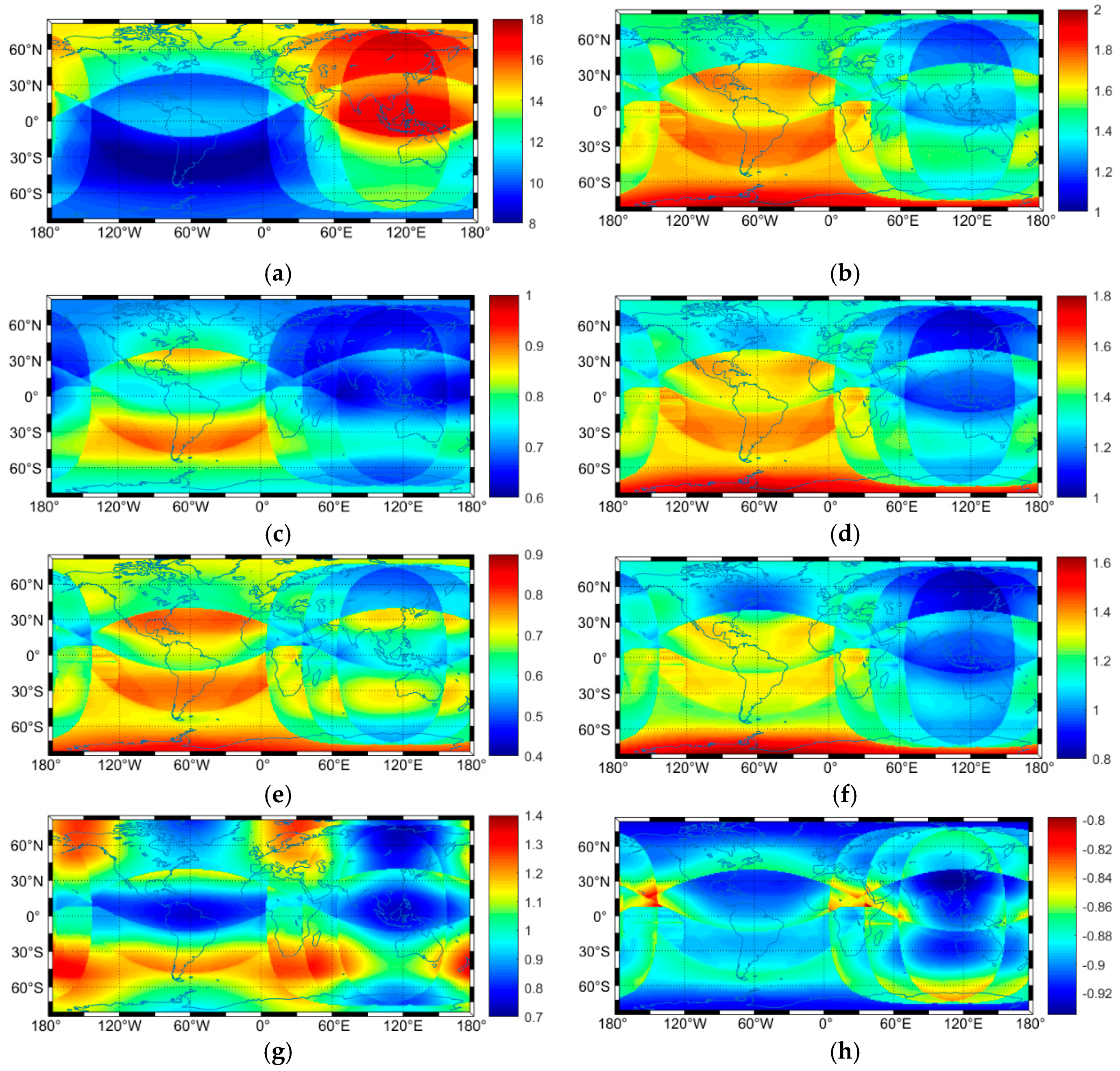
4. Experimental Results and Analyses
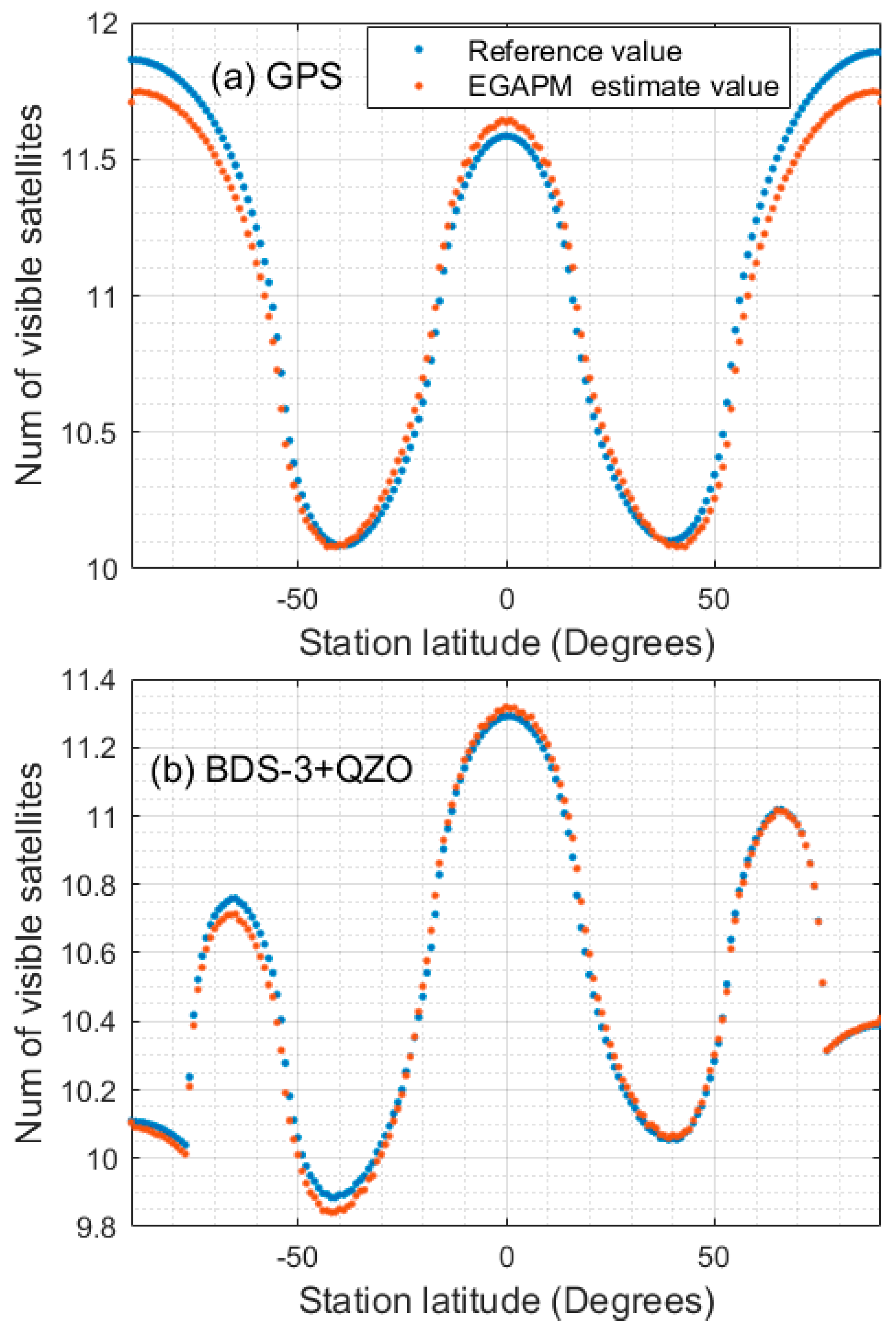
4.1. BDS-3 VS GPS
4.2. BDS-3+QZO Constellation
4.3. BDS-3+HEO Constellation
4.4. BDS-3+LEO+HEO Constellation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| ADOP | Ambiguity Dilution of Precision |
| BDS-3 | third-generation BeiDou navigation satellite system |
| GDOP | geometric DOP |
| CEA | cutoff elevation angle |
| DOP | dilution of precision |
| DOPs | GDOP (geometric DOP), HDOP (horizontal DOP), PDOP (position DOP), TDOP (time DOP), and VDOP (vertical DOP) |
| ECEF | earth centered earth fixed |
| EDOP | east DOP |
| EGAPM | extended geometry and probability model |
| GAPM | geometry and probability model |
| GEO | geostationary earth orbit |
| GFZ | GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global PositioningSystem |
| HDOP | horizontal DOP |
| HEO | highly eccentric orbits |
| IGSO | inclined geosynchronous orbit |
| LEO | low earth orbit |
| MEO | medium earth orbit |
| MGAPM | modified GAPM |
| NDOP | north DOP |
| PDOP | position DOP |
| PNT | positioning, navigation and timing |
| PPP | Precise Point Positioning |
| QZO | Quasi-Zenith orbit |
| QZSS | Quasi-Zenith Satellite System |
| RMS | root mean squares |
| SBAS | satellites-based augment system |
| SPP | Standard Point Positioning |
| TDOP | time DOP |
| VDOP | vertical DOP |
| WAAS | Wide Area Augmentation System |
References
- Xiao, W.; Liu, W.; Sun, G. Modernization milestone: BeiDou M2-S initial signal analysis. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kubo, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Initial positioning assessment of BDS new satellites and new signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Multi-GNSS signal-in-space range error assessment—Methodology and results. Adv. Sp. Res. 2018, 61, 3020–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, B. Performance evaluation of the CNAV broadcast ephemeris. J. Navig. 2019, 72, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhou, R. Initial Assessment of BDS-3 preliminary system signal-in-space range error. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; de Jong, K.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Guo, J. Multipath analysis of code measurements for BeiDou geostationary satellites. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, D.; Li, H.; Han, L.; Chen, W. Comparison of three methods for estimating GPS multipath repeat time. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadas, T.; Kazmierski, K.; Sośnica, K. Performance of Galileo-only dual-frequency absolute positioning using the fully serviceable Galileo constellation. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Nie, L.; Wei, C.; Jia, S.; Jiang, S. Initial assessment of BeiDou-3 Global navigation satellite system: Signal quality, RTK and PPP. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozo-García, Á.; Herráiz-Monseco, E.; Martín-Peiró, A.B.; Romay-Merino, M.M. Galileo constellation design. GPS Solut. 2001, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santerre, R. Impact of GPS satellite sky distribution. Manuscr. Geod. 1991, 16, 28–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kihara, M.; Okada, T. A satellite selection method and accuracy for the global positioning system. Navigation 1984, 31, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Dong, D.; Ge, M.; Li, P.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Simultaneous estimation of GLONASS pseudorange inter-frequency biases in precise point positioning using undifferenced and uncombined observations. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Shen, J.; Dai, X. Preliminary assessment of the navigation and positioning performance of BeiDou regional navigation satellite system. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, D.; Meng, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Cui, H. Performance of BDS-3: Satellite visibility and dilution of precision. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Iz, B.; Lu, C. Dependency of GPS positioning precision on station location. GPS Solut. 2002, 6, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, C. BDS satellite-based augmentation service correction parameters and performance assessment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khon, V.C.; Mokhov, I.I.; Latif, M.; Semenov, V.A.; Park, W. Perspectives of northern sea route and northwest passage in the twenty-first century. Clim. Chang. 2010, 100, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Gill, E. Satellite Orbits; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 15–32. ISBN 78-3-540-67280-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.H.; Kamarudin, M.N. Analysis of GPS visibility and satellite-receiver geometry over different latitudinal regions. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Geoinformation (ISG 2008), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–15 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, K.-W.; Huang, Y.-S.; Tsai, M.-L.; Chen, K.-H. The perspective from Asia concerning the impact of Compass/Beidou-2 on future GNSS. Surv. Rev. 2010, 42, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Roberts, G.W.; Dodson, A.H.; Cosser, E.; Barnes, J.; Rizos, C. Impact of GPS satellite and pseudolite geometry on structural deformation monitoring: Analytical and empirical studies. J. Geod. 2004, 77, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. On Precise Orbit Determination of Low Earth Orbiters. Ph.D. Thesis, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Ge, H.; Ge, M.; Nie, L.; Shen, Y.; Schuh, H. LEO enhanced global navigation satellite system (LeGNSS) for real-time precise positioning services. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, F.; Li, X.; Lv, H.; Bian, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X. LEO Constellation-augmented multi-GNSS for rapid PPP convergence. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, H.; Ma, F.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z. GNSS RTK positioning augmented with large LEO constellation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CSNO. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Inter-Face Control Document—Open Service Signal B1I (Version 3.0); China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- CSNO. Report on the Development of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (Version 2.1); China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- QZSS. Quasi-Zenith Satellite System Performance Standard (PS-QZSS-001). Cabinet Office, National Space Policy Secretariat. 2018. Available online: https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/download/pdf/ps-is-qzss-001.pdf?t=1577867270694 (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Wasle, E. GNSS—Global Naviagtion Satellite System; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 322–341. ISBN 978-3-211-73012-62007. [Google Scholar]
- Zaminpardaz, S.; Wang, K.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Australia-first high-precision positioning results with new Japanese QZSS regional satellite system. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Kubo, N.; Chen, J.; Chu, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Contribution of QZSS with four satellites to multi-GNSS long baseline RTK. J. Spat. Sci. 2020, 65, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; El-Mowafy, A. The ADOP and PDOP: Two complementary diagnostics for GNSS positioning. J. Surv. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part IV: Precision versus reliability. J. Geod. 1997, 71, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G. ADOP in Closed form for a hierarchy of multi-frequency single-baseline GNSS models. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
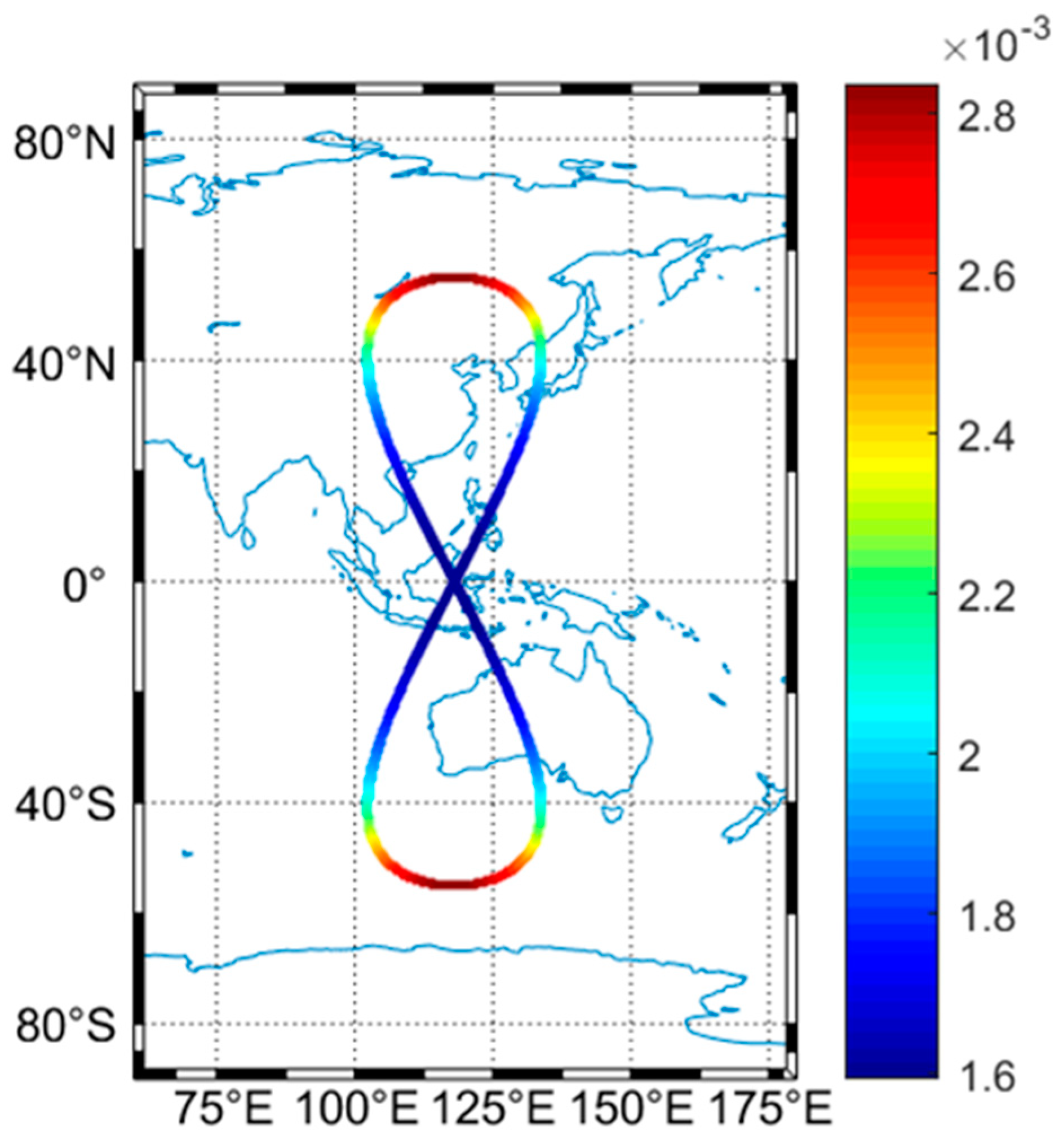
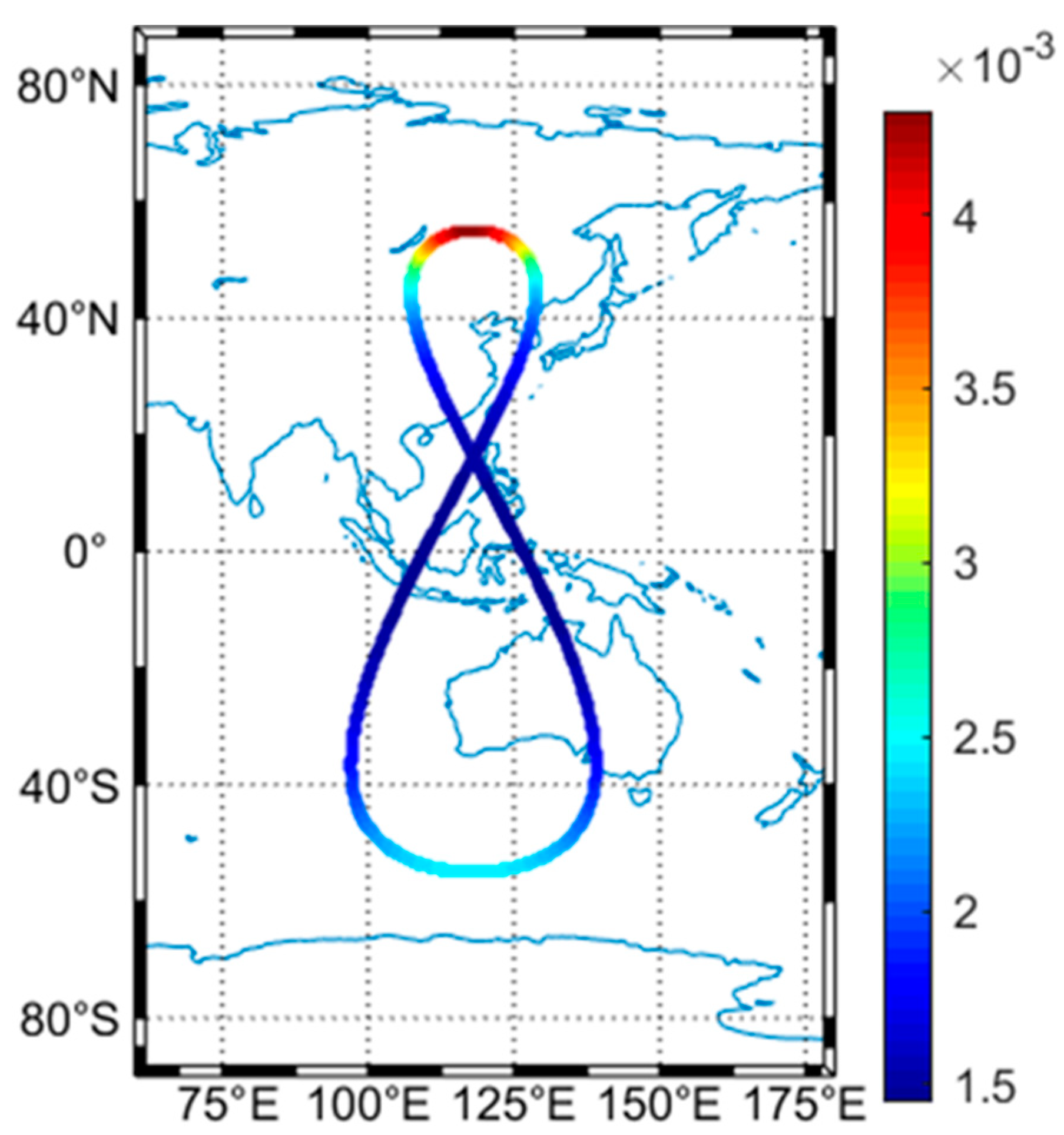


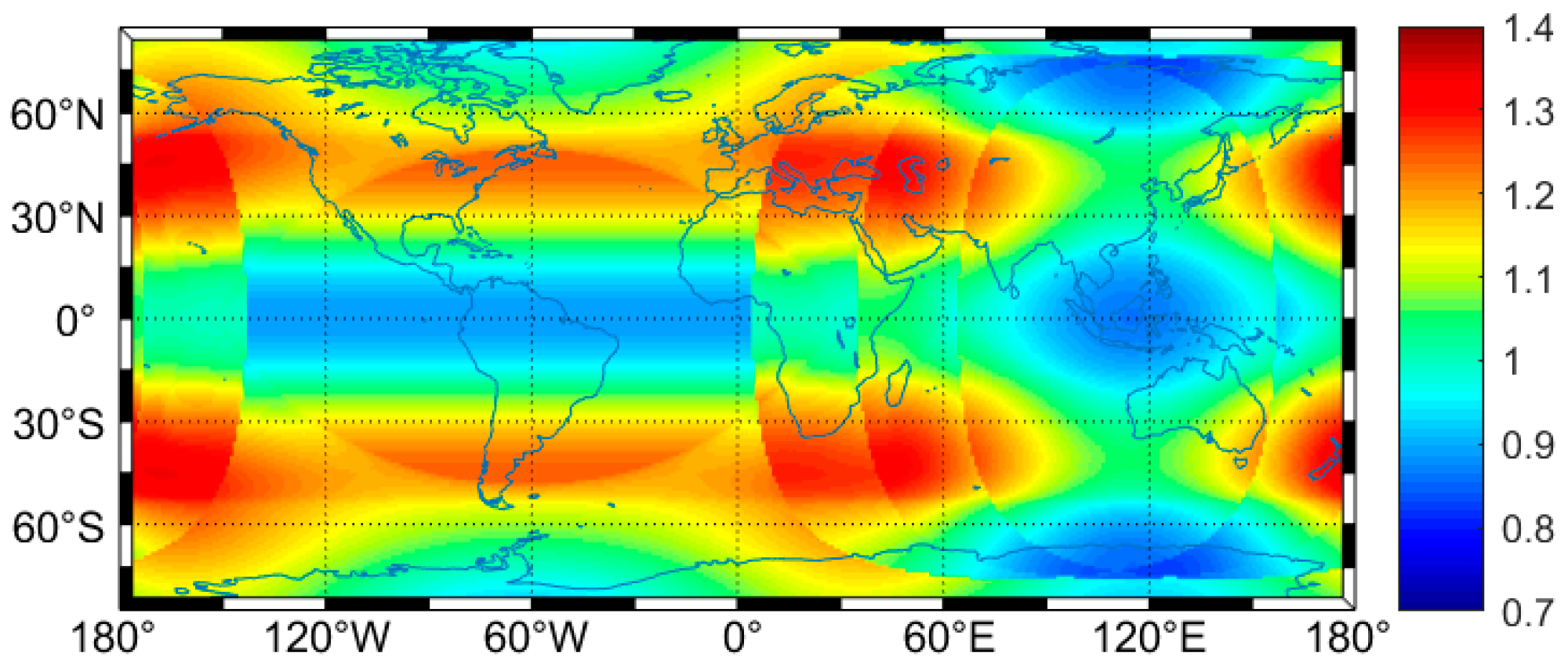
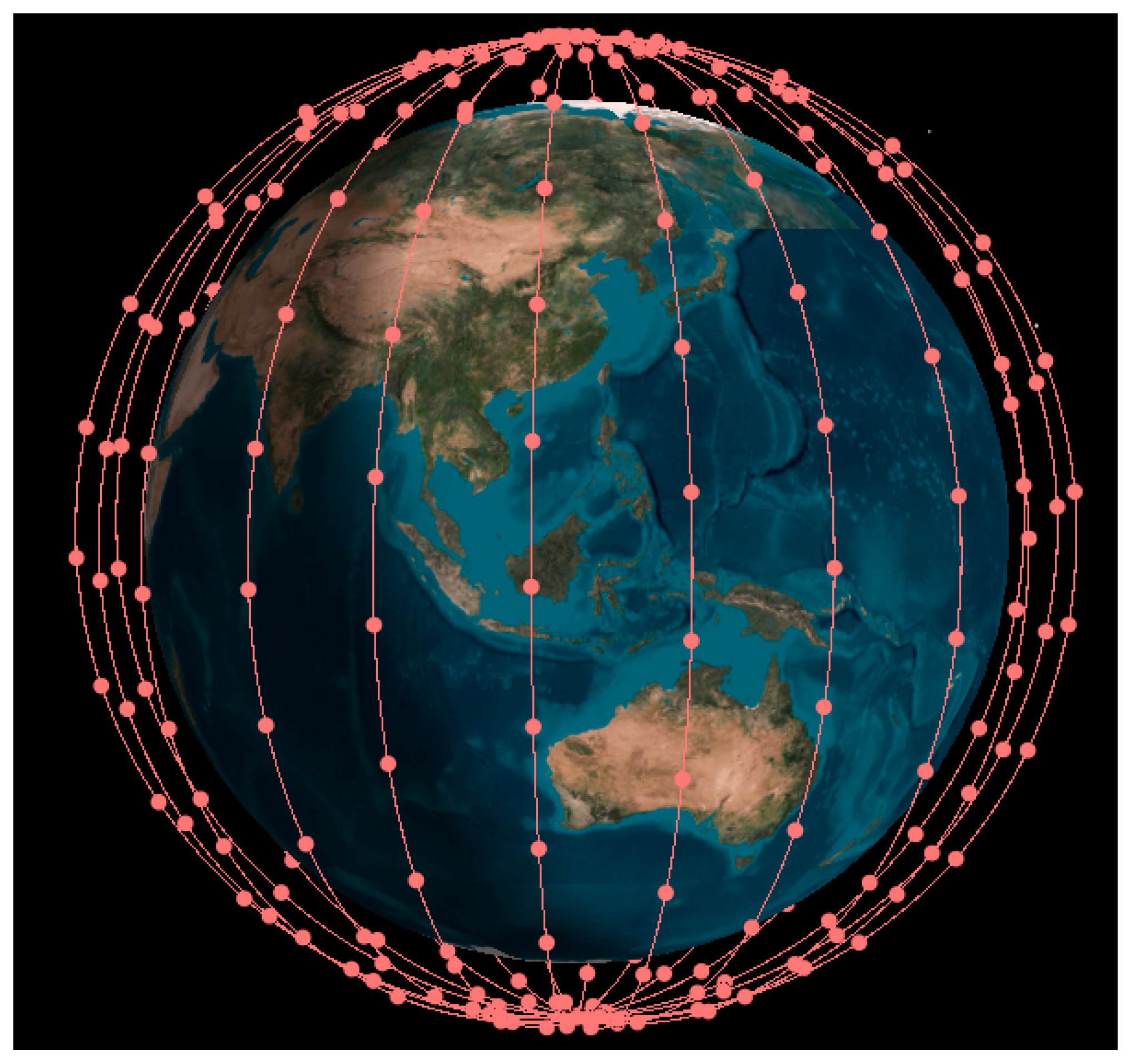
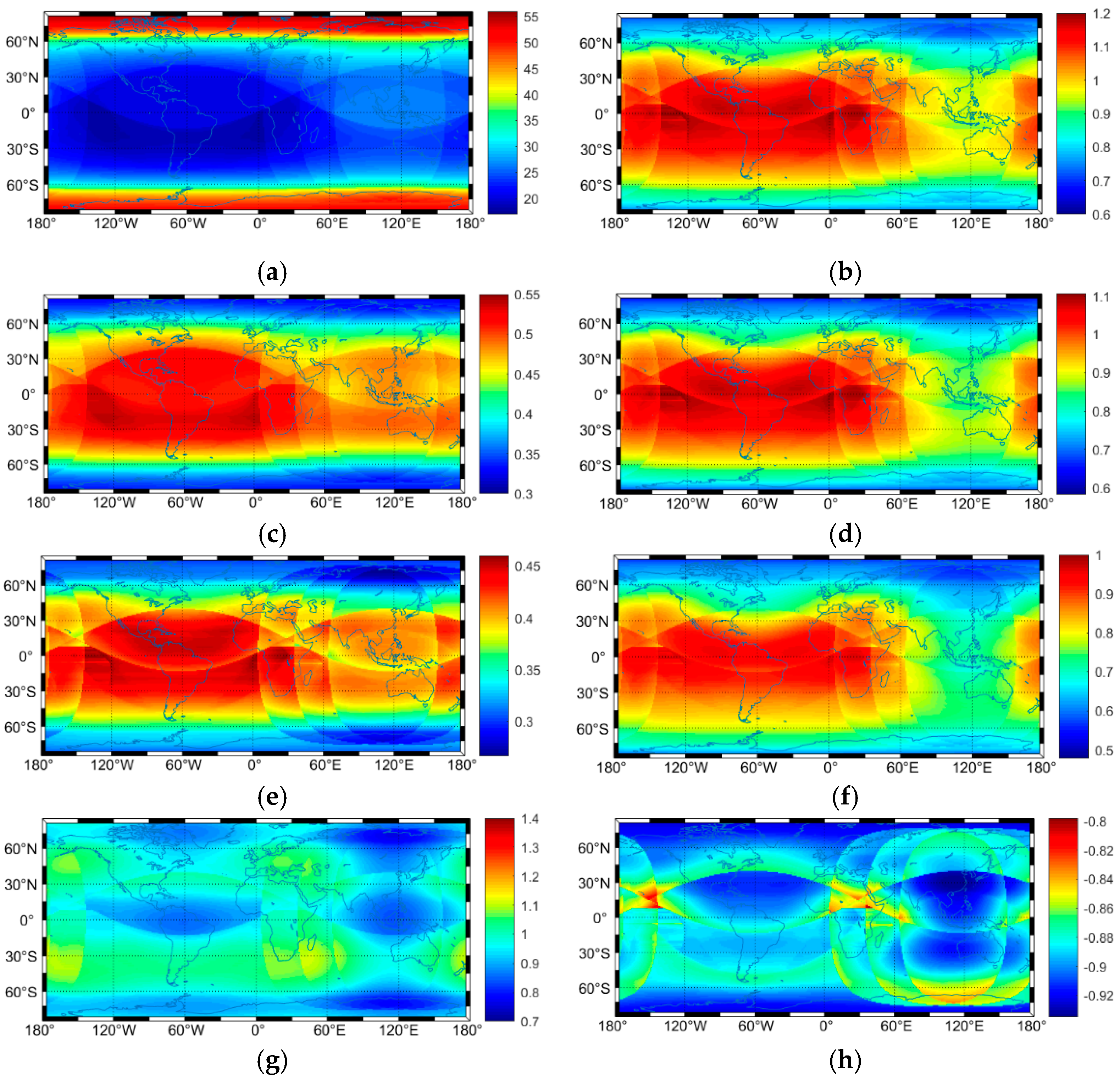
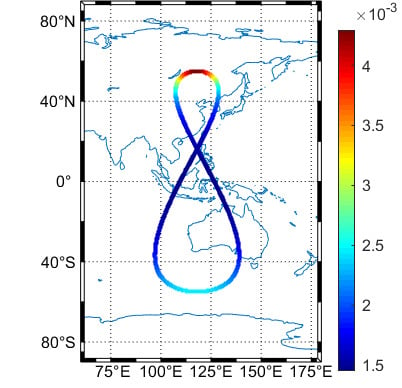
| Parameter | BDS-3+QZO | GPS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orbit Type | MEO | QZO | GEO | MEO |
| Nominal Number | 24 | 3 | 3 | 32 |
| Inclination | 55° | 55° | 0° | 55° |
| Altitude (KM) | 21,528 | 38,950.6 (Apogee) | 35,786 | 20,200 |
| Period(s) | 46,404 | 86,170.5 | 86,170.5 | 43,080 |
| Constellation | Underestimating Rates of DOPs (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (Min–Max) | ||||
| GDOP | PDOP | HDOP | VDOP | |
| GPS | 10.41 (5.06–13.10) | 9.85 (4.58–12.40) | 7.98 (3.96–10.63) | 10.33 (4.64–13.03) |
| BDS-3+QZO | 10.94 (6.93–16.12) | 10.39 (6.46–15.09) | 7.95 (4.44–10.55) | 11.07 (6.79–16.91) |
| Constellation | Average (Min–Max) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VisiNum | HDOP | PDOP | TDOP | VDOP | |
| BDS-3 in augmentation area | 13.20 (11.27–14.86) | 0.73 (0.66–0.80) | 1.46 (1.31–1.61) | 0.67 (0.56–0.74) | 1.08 (0.98–1.21) |
| BDS-3 on global scale | 10.48 (7.69–14.86) | 0.78 (0.66–0.93) | 1.68 (1.31–1.98) | 0.73 (0.54–0.84) | 1.29 (0.98–1.63) |
| GPS on global scale | 10.99 (10.8–11.75) | 0.75 (0.68–0.81) | 1.61 (1.51–1.86) | 0.69 (0.64–0.78) | 1.24 (1.12–1.54) |
| Orbit Parameter | Nominal Value |
|---|---|
| Semi-major axis | 42,165 km |
| Eccentricity | 0.075 |
| Inclination | 41° |
| Argument of perigee | 270° |
| Center of longitude | 139° East |
| Orbit Parameter | Nominal Value |
|---|---|
| Semi-major axis | 42,165 km |
| Eccentricity | 0.740969 |
| Inclination | 63.4° |
| Argument of perigee | 270° |
| Center of longitude | 118° E |
| Parameter | BDS-3+HEO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orbit Type | MEO | IGSO | GEO | HEO |
| Nominal Number | 24 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| Inclination | 55° | 55° | 0° | 63.4° |
| Altitude (km) | 21,528 | 35,786 | 35,786 | 500–40,000 |
| Period(s) | 46,404 | 86,170.5 | 86,170.5 | 43,061 |
| Average (Min–Max) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VisiNum | GDOP | PDOP | HDOP | VDOP | TDOP |
| 38.76 (17.31–50.88) | 15.70 (2.30–23.25) | 16.65 (2.65–24.96) | 10.35 (4.04–18.68) | 16.65 (2.65–24.96) | 11.52 (0–22.73) |
| Parameter | BDS-3+LEO+HEO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orbit Type | MEO | IGSO | GEO | LEO | HEO |
| Nominal Number | 24 | 3 | 3 | 288 | 5 |
| Inclination | 55° | 55° | 0° | 90° | 63.4° |
| Altitude (km) | 21,528 | 35,786 | 35,786 | 1000 | 500–40,000 |
| Period(s) | 46,404 | 86,170.5 | 86,170.5 | 6307 | 43,061 |
| Constellation | VisiNum | GDOP | HDOP | PDOP | TDOP | VDOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDS-3 | 197.81% | 42.86% | 43.59% | 47.62% | 49.32% | 41.09% |
| GPS | 183.99% | 40.00% | 41.33% | 45.34% | 46.38% | 38.71% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y. Extended Geometry and Probability Model for GNSS+ Constellation Performance Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162560
Meng L, Wang J, Chen J, Wang B, Zhang Y. Extended Geometry and Probability Model for GNSS+ Constellation Performance Evaluation. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(16):2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162560
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Lingdong, Jiexian Wang, Junping Chen, Bin Wang, and Yize Zhang. 2020. "Extended Geometry and Probability Model for GNSS+ Constellation Performance Evaluation" Remote Sensing 12, no. 16: 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162560
APA StyleMeng, L., Wang, J., Chen, J., Wang, B., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Extended Geometry and Probability Model for GNSS+ Constellation Performance Evaluation. Remote Sensing, 12(16), 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162560