On the Radiative Transfer Model for Soil Moisture across Space, Time and Hydro-Climates
Abstract
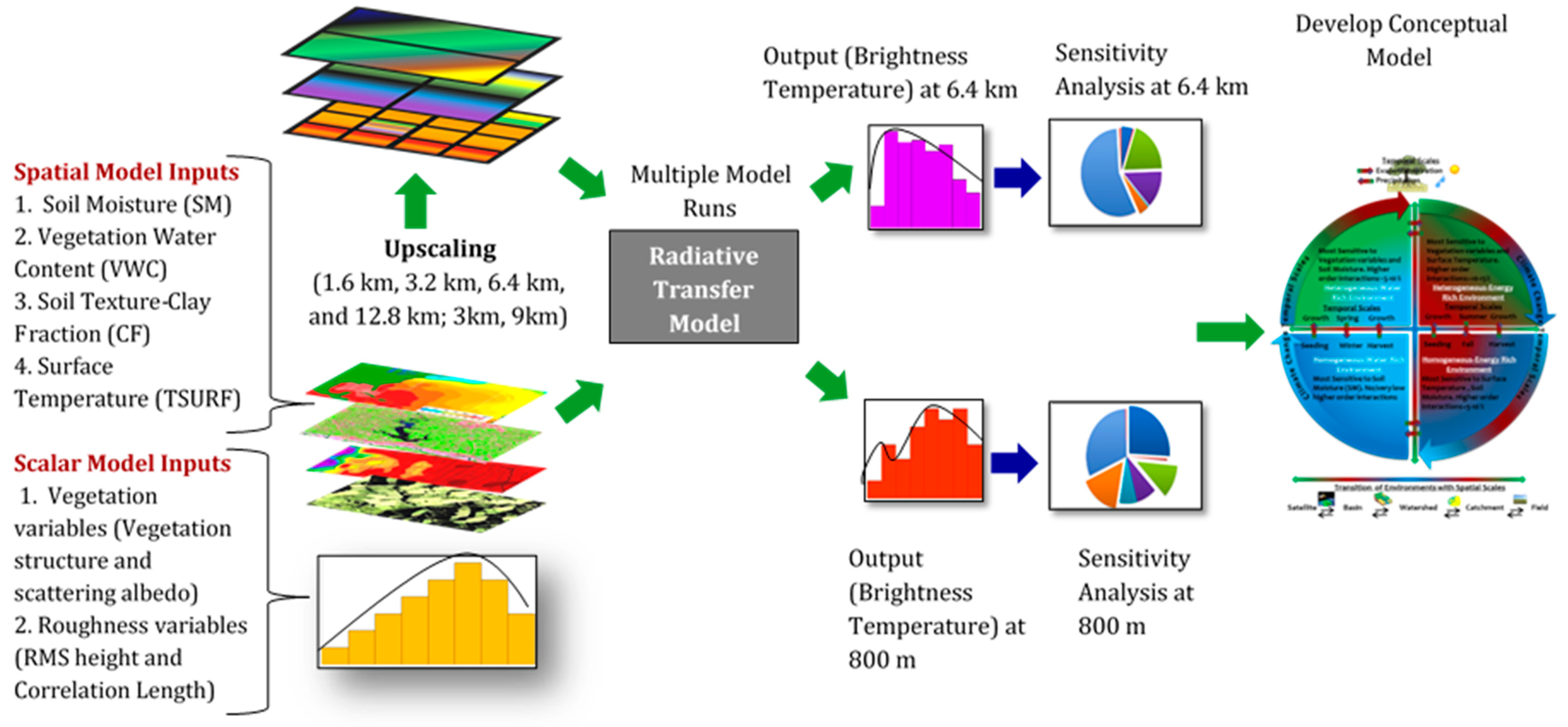
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Heterogeneity Observed in Various Hydroclimates
2.1.1. Southern Great Plains Experiment’1997 (SGP’97), Oklahoma
2.1.2. Soil Moisture Experiment’2002 (SMEX02), Iowa
2.1.3. Soil Moisture Experiment’2004 (SMEX04), Arizona
2.1.4. Soil Moisture Active Passive Validation Experiment’2012 (SMAPVEX12), Winnipeg
2.2. Soil Moisture Retrieval Algorithm
2.3. Global Spatial Sensitivity Analysis: Sobol Method
2.4. Upscaling Methods: Linear Upscaling vs. Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) Upscaling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Plant Structure
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Scales in Different Hydroclimates
3.2.1. Semi-Arid (SMEX04) Hydroclimate
3.2.2. Sub-Humid (SGP97) Hydroclimate
3.2.3. Humid-Dfa (SMEX02) Hydroclimate
3.2.4. Humid-Dfb (SMAPVEX12) Hydroclimate
3.3. Upscaling and Environmental Heterogeneity
3.3.1. Homogeneous Environment (Sub-Humid and Semi-Arid)
3.3.2. Heterogeneous Environment (Humid Dfa and Humid Dfb)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Moran, M.S.; Doorn, B.; Escobar, V.; Brown, M.E. Connecting NASA science and engineering with earth science applications. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mecklenburg, S.; Drusch, M.; Kaleschke, L.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; Reul, N.; Kerr, Y.; Font, J.; Martin-Neira, M.; Oliva, R.; Daganzo-Eusebio, E. ESA’s Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity mission: From science to operational applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.; Wheeler, K.; White, C.; West, R.; Piepmeier, J.; Hudson, D.; Medeiros, J. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission L-band radar/radiometer instrument. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3240–3243. [Google Scholar]
- Merlin, O.; Rudiger, C.; Al Bitar, A.; Richaume, P.; Walker, J.P.; Kerr, Y.H. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture in Southeastern Australia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; Shi, J.J.; Johnson, J.T.; Colliander, A. Tests of the SMAP combined radar and radiometer algorithm using airborne field campaign observations and simulated data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Walker, J.P.; Das, N.N.; Panciera, R.; Rüdiger, C. Evaluation of the SMAP brightness temperature downscaling algorithm using active–passive microwave observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero, B.; Merlin, O.; Malbéteau, Y.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Stefan, V.; Kerr, Y.; Bacon, S.; Cosh, M.H.; Bindlish, R. SMOS disaggregated soil moisture product at 1 km resolution: Processor overview and first validation results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piles, M.; Entekhabi, D.; Camps, A. A change detection algorithm for retrieving high-resolution soil moisture from SMAP radar and radiometer observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 4125–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piles, M.; Camps, A.; Vall-Llossera, M.; Corbella, I.; Panciera, R.; Rudiger, C.; Kerr, Y.H.; Walker, J. Downscaling SMOS-derived soil moisture using MODIS visible/infrared data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3156–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Mohanty, B.P. Development of a deterministic downscaling algorithm for remote sensing soil moisture footprint using soil and vegetation classifications. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6208–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M. Retrieving high-resolution surface soil moisture by downscaling AMSR-E brightness temperature using MODIS LST and NDVI data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamai, N.; Magagi, R.; Goita, K.; Merlin, O.; Kerr, Y.; Walker, A. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture over the Canadian Prairies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Western, A.W.; Blöschl, G. On the spatial scaling of soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 1999, 217, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Griend, A.A.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Waldteufel, P. Consequences of surface heterogeneity for parameter retrieval from 1.4-GHz multiangle SMOS observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.A.; Scipal, K.; Parinussa, R.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wagner, W.; De Jeu, R.A.; Naeimi, V. Error characterisation of global active and passive microwave soil moisture datasets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlin, O.; Malbéteau, Y.; Notfi, Y.; Bacon, S.; Khabba, S.E.-R.S.; Jarlan, L. Performance metrics for soil moisture downscaling methods: Application to DISPATCH data in central Morocco. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3783–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Njoku, E.G.; Entekhabi, D. Passive microwave remote sensing of soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 1996, 184, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, A.W.; Grayson, R.B.; Blöschl, G. Scaling of soil moisture: A hydrologic perspective. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2002, 30, 149–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.; Famiglietti, J.S. Multi-scale spatial correlation and scaling behavior of surface soil moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaur, N.; Mohanty, B.P. Evolution of physical controls for soil moisture in humid and subhumid watersheds. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1244–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, N.; Mohanty, B.P. Land-surface controls on near-surface soil moisture dynamics: Traversing remote sensing footprints. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 6365–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakhankar, T.; Ghedira, H.; Temimi, M.; Azar, A.E.; Khanbilvardi, R. Effect of land cover heterogeneity on soil moisture retrieval using active microwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.K.; Rowlandson, T.L.; Berg, A.A.; Champagne, C.; Adams, J.R. Impact of sub-pixel heterogeneity on modelled brightness temperature for an agricultural region. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, E.J.; Simmonds, L.P. Effects of sub-pixel heterogeneity on the retrieval of soil moisture from passive microwave radiometry. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2085–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam, M.; Mohanty, B.P. Global sensitivity analysis of the radiative transfer model. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 2428–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Geours, N.; Lavergne, C.; Bailly, J.-S.; Grelot, F. Sensitivity analysis of spatial models using geostatistical simulation. In Proceedings of the Mathematical Geosciences at the Crossroads of Theory and Practice—IAMG 2011 Conference, Salzburg, Austria, 5–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrazin, F.; Pianosi, F.; Wagener, T. Global Sensitivity Analysis of environmental models: Convergence and validation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 79, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pianosi, F.; Beven, K.; Freer, J.; Hall, J.W.; Rougier, J.; Stephenson, D.B.; Wagener, T. Sensitivity analysis of environmental models: A systematic review with practical workflow. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 79, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Tarantola, S.; Saltelli, A. Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis in spatial modelling based on GIS. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 81, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosh, M.H.; Jackson, T.J.; Moran, S.; Bindlish, R. Temporal persistence and stability of surface soil moisture in a semi-arid watershed. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Cosh, M.H.; Bindlish, R.; Starks, P.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Seyfried, M.; Goodrich, D.C.; Moran, M.S.; Du, J. Validation of Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer Soil Moisture Products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4256–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNairn, H.; Jackson, T.J.; Wiseman, G.; Belair, S.; Berg, A.; Bullock, P.; Colliander, A.; Cosh, M.H.; Kim, S.-B.; Magagi, R. The soil moisture active passive validation experiment 2012 (SMAPVEX12): Prelaunch calibration and validation of the SMAP soil moisture algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 2784–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2007, 4, 439–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, T.J.; Le Vine, D.M.; Hsu, A.Y.; Oldak, A.; Starks, P.J.; Swift, C.T.; Isham, J.D.; Haken, M. Soil moisture mapping at regional scales using microwave radiometry: The Southern Great Plains Hydrology Experiment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2136–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Mohanty, B.P.; Hsu, E.-C.; Miller, D. SMEX02: Field scale variability, time stability and similarity of soil moisture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J.; Gasiewski, A.J.; Klein, M.; Njoku, E.G. Soil moisture mapping and AMSR-E validation using the PSR in SMEX02. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.T.; Hunt, E.R.; Jackson, T.J. Remote sensing of vegetation water content from equivalent water thickness using satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.J.; Chazanoff, S.; McNairn, H.; Powers, J.; Cosh, M.H. Retrieving soil moisture for non-forested areas using PALS radiometer measurements in SMAPVEX12 field campaign. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, T.; Choudhury, B.J.; Schmugge, T.J.; Wang, J.R.; Jackson, T.J. A model for microwave emission from vegetation-covered fields. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1982, 87, 11229–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Chen, D.; Cosh, M.; Li, F.; Anderson, M.; Walthall, C.; Doriaswamy, P.; Hunt, E.R. Vegetation water content mapping using Landsat data derived normalized difference water index for corn and soybeans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Schmugge, T.J. Vegetation effects on the microwave emission of soils. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 36, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Razani, M.; Dobson, M.C. Effects of Vegetation Cover on the Microwave Radiometric Sensitivity to Soil Moisture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1983, GE-21, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.; Kothyari, U.C.; Arora, M.K. Vegetation effects on soil moisture estimation from ERS-2 SAR images. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunfeldt, D.R.; Ulaby, F.T. Microwave emission from row crops. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, GE-24, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam, M.; Colliander, A.; Mohanty, B.P.; Cosh, M.H.; Misra, S.; Jackson, T.J. Multiscale Surface Roughness for Improved Soil Moisture Estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.; Chan, S.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R. Algorithm theoretical basis document (ATBD): L2 & L3 radiometer soil moisture (Passive) data products. Smap Proj. Rev. A 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sobol, I.M. Sensitivity estimates for nonlinear mathematical models. Math. Model. Comput. Exp. 1993, 1, 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Saltelli, A. Making best use of model evaluations to compute sensitivity indices. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2002, 145, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Ratto, M.; Andres, T.; Campolongo, F.; Cariboni, J.; Gatelli, D.; Saisana, M.; Tarantola, S. Global sensitivity analysis: The primer; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 0-470-72517-6. [Google Scholar]
- Saltelli, A.; Ratto, M.; Tarantola, S.; Campolongo, F. Sensitivity analysis for chemical models. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2811–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Annoni, P.; Azzini, I.; Campolongo, F.; Ratto, M.; Tarantola, S. Variance based sensitivity analysis of model output. Design and estimator for the total sensitivity index. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2010, 181, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.J.; Ahmed, N.U.; Idso, S.B.; Reginato, R.J.; Daughtry, C.S.T. Relations between evaporation coefficients and vegetation indices studied by model simulations. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Blöschl, G. Scaling issues in snow hydrology. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 2149–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Sivapalan, M. Scale issues in hydrological modelling: A review. Hydrol. Process. 1995, 9, 251–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.R.; Finnigan, J.J. Scale issues in boundary-layer meteorology: Surface energy balances in heterogeneous terrain. Hydrol. Process. 1995, 9, 589–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, T.; Wei, P.; Jia, Y.; Luo, C. Ecological application of wavelet analysis in the scaling of spatial distribution patterns of Ceratoides ewersmanniana. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 2704–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenovský, Z.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Acerbi-Junior, F.W.; Schopfer, J.T.; Painter, T.H.; Epema, G.F.; Bregt, A.K. Scaling dimensions in spectroscopy of soil and vegetation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Berg, A.A.; Cosh, M.H.; Loew, A.; Mohanty, B.P.; Panciera, R.; de Rosnay, P.; Ryu, D.; Walker, J.P. Upscaling sparse ground-based soil moisture observations for the validation of coarse-resolution satellite soil moisture products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lu, H. Inter-comparison of spatial upscaling methods for evaluation of satellite-based soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wen, J.; Tian, H. Representativeness of the ground observational sites and up-scaling of the point soil moisture measurements. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Cosh, M.H.; Misra, S.; Jackson, T.J.; Crow, W.T.; Chan, S.; Bindlish, R.; Chae, C.; Collins, C.H.; Yueh, S.H. Validation and scaling of soil moisture in a semi-arid environment: SMAP validation experiment 2015 (SMAPVEX15). Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Chan, S.; Kim, S.; Das, N.; Yueh, S.; Cosh, M.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.; Njoku, E. Long term analysis of PALS soil moisture campaign measurements for global soil moisture algorithm development. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Das, N.; Kim, S.B.; Cosh, M.H.; Dunbar, R.S.; Dang, L.; Pashaian, L.; et al. Validation of SMAP surface soil moisture products with core validation sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Islam, S. A framework for analyzing and designing scale invariant remote sensing algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 747–755. [Google Scholar]
- Garrigues, S.; Allard, D.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. Influence of landscape spatial heterogeneity on the non-linear estimation of leaf area index from moderate spatial resolution remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Wood, E.F.; Simmer, C. Up-scaling effects in passive microwave remote sensing: ESTAR 1.4 GHz measurements during SGP’97. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Radcliffe, D.E.; Selim, H.M. Scaling Methods in Soil Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-203-01106-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, X.; Crow, W.T.; Jackson, T.J.; O’Neill, P.E. Improving Spaceborne Radiometer Soil Moisture Retrievals With Alternative Aggregation Rules for Ancillary Parameters in Highly Heterogeneous Vegetated Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Spatial-temporal variability of soil moisture and its estimation across scales. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z.-L. Scale issues in remote sensing: A review on analysis, processing and modeling. Sensors 2009, 9, 1768–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.; Englund, E. Evaluation and comparison of spatial interpolators. Math. Geol. 1992, 24, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyeed, R.A.; Papritz, A. An empirical comparison of kriging methods for nonlinear spatial point prediction. Math. Geol. 2002, 34, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, O.; Deutsch, C.V. Statistical approach to inverse distance interpolation. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2009, 23, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.; Njoku, E.G.; Colliander, A. Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP), Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, Level 1C Radiometer Data Product, Revision A. Jet Propuls. Lab. Calif. Inst. Technol. PasadenaCa. Retrieved 2017, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive. Volume 1-Microwave Remote Sensing Fundamentals and Radiometry; 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Chanzy, A.; Calvet, J.-C.; Bruguier, N. A simple algorithm to retrieve soil moisture and vegetation biomass using passive microwave measurements over crop fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Wood, E.F.; Dubayah, R. Potential for downscaling soil moisture maps derived from spaceborne imaging radar data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mood, A.M. Introduction to the Theory of Statistics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]






| Southern Great Plains 1997 (SGP97) | Soil Moisture Experiments 2002 (SMEX02) | Soil Moisture Experiments 2004 (SMEX04) | Soil Moisture Active Passive Validation Experiments 2012 (SMAPVEX12) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oklahoma (Sub-Humid) | Iowa (Dfa-Humid | Arizona (Semi-Arid) | Winnipeg (Dfb-Humid) |
| Mean Soil Moisture: 0.14 v/v | Mean Soil Moisture: 0.19 v/v | Mean Soil Moisture: 0.07 v/v | Mean Soil Moisture: 0.25 v/v |
| Mean Soil Temperature: 298 K | Mean Soil Temperature: 315 K | Mean Soil Temperature: 319 K | Mean Soil Temperature: 290 K |
| Mean Vegetation Water Content: 0.32 kg/m2 | Mean Vegetation Water Content: 1.9 kg/m2 | Mean Vegetation Water Content: 0.09 kg/m2 | Mean Vegetation Water Content: 1.4 kg/m2 |
| Root Mean Square (RMS) height (cm): 0.27–1.73 | Root Mean Square (RMS) height (cm): 0.19–3.05 | Root Mean Square (RMS) height (cm): 0.71–23.28 | Root Mean Square (RMS) height (cm): 0.23–3.21 |
| Correlation length (L) (cm): 3.4–32.18 | Correlation length (L) (cm): 0.43–26.95 | Correlation length (L) (cm): 8.7–119.5 | Correlation length (L) (cm): 2.5–24.5 |
| Vegetation structure (B): 0–0.15 | Vegetation structure (B): 0–0.15 | Vegetation structure (B): 0–0.15 | Vegetation structure (B): 0–0.15 |
| Scattering albedo (ω): 0–0.05 | Scattering albedo (ω): 0–0.05 | Scattering albedo (ω): 0–0.05 | Scattering albedo (ω): 0–0.05 |
| ESTAR support scales: 0.8 km,1.6 km, 3.2 km, 6.4 km, 12.8 km | PSR/C support scales: 0.8 km,1.6 km, 3.2 km, 6.4 km, and 12.8 km | PALS support scales: 0.8 km,1.6 km, 3.2 km, 6.4 km, and 12.8 km | PALS support scales: 1.5 km,3 km, and 9 km |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neelam, M.; Mohanty, B.P. On the Radiative Transfer Model for Soil Moisture across Space, Time and Hydro-Climates. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162645
Neelam M, Mohanty BP. On the Radiative Transfer Model for Soil Moisture across Space, Time and Hydro-Climates. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(16):2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162645
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeelam, Maheshwari, and Binayak P. Mohanty. 2020. "On the Radiative Transfer Model for Soil Moisture across Space, Time and Hydro-Climates" Remote Sensing 12, no. 16: 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162645
APA StyleNeelam, M., & Mohanty, B. P. (2020). On the Radiative Transfer Model for Soil Moisture across Space, Time and Hydro-Climates. Remote Sensing, 12(16), 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162645





