A Double Epipolar Resampling Approach to Reliable Conjugate Point Extraction for Accurate Kompsat-3/3A Stereo Data Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Epipolar Resampling
2.2. Conjugate Point Extraction
2.2.1. Feature-Based Matching Using Local Templates
2.2.2. Area-Based Matching Using Feature-Centered Local Templates
2.3. Relative Orientation Based on Bias Compensation of RPCs with Outlier Removal
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Experimental Dataset
3.2. Coarse Epipolar Image Resampling Using Raw RPCs
3.3. Conjugate Point Extraction
3.4. RPC Bias Compensation with Quasi-GCPs
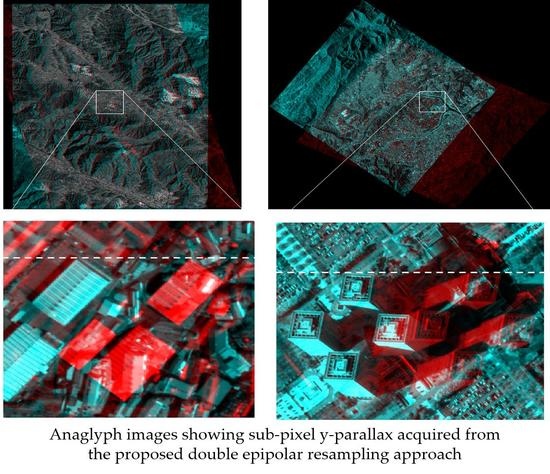
3.5. Fine Epipolar Image Resampling and Y-Parallax Analysis
4. Conclusions
- Coarse epipolar images from Kompsat-3/3A data show a large y-parallax of up to 17–25 pixels; this parallax should be minimized for precise 3D mapping.
- Coarse epipolar images allow the extraction of a larger number of conjugate points compared to the original images regardless of the matching methods. Moreover, the transformation models constructed from the conjugate points extracted from coarse epipolar images showed better reliability and accuracy than the ones from the original images.
- Area-based local-template-matching methods, i.e., PC and MI, tended to extract more conjugate points than the feature-based local-template-matching methods such as SURF and Harris. The distribution of the conjugate points was better in the case of the former methods because of the large number of points.
- Given coarse epipolar images, MI and PC with larger patch sizes (>400 pixels) show stable sub-pixel accuracy and y-parallax for along-track and across-track Kompsat-3/3A data.
- Between PC and MI, MI provides more stable results, while PC provides faster results.
- Harris provided quite unstable results in all cases, but SURF provided mixed results of approximately 1–2 pixels in many cases.
- The coarse epipolar image is very helpful for realizing accurate conjugate point extraction. The double epipolar approach showed high effectiveness especially for across-track stereo data for which realizing high stereo consistency is a challenge because of low similarity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granshaw, S. Photogrammetric terminology: Third edition. Photogramm. Rec. 2016, 31, 210–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yang, C.; Soergel, U.; Lanaras, C.; Baltsavias, E.; Rupnik, E.; Nex, F.; Remondino, F. Rapidmap project for disaster monitoring. In Proceedings of the 35th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing (ACRS), Nay Pyi Taw, Myanmar, 27–31 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tsanis, I.K.; Seiradakis, K.D.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Grillakis, M.; Koutroulis, A. Assessment of GeoEye-1 stereo-pair-generated DEM in flood mapping of an ungauged basin. J. Hydroinformatics 2013, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosu, A.-M.; Pierrot-Deseilligny, M.; Delorme, A.; Binet, R.; Klinger, Y. Measurement of ground displacement from optical satellite image correlation using the free open-source software MicMac. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2015, 100, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ren, Z.; Wu, C.; Lei, Q.; Gong, W.; Ou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ren, G.; Li, C. DEM generation from Worldview-2 stereo imagery and vertical accuracy assessment for its application in active tectonics. Geomorphology 2019, 336, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, C.; Binet, R.; Pierrot-Deseilligny, M. Automatic detection of elevation changes by differential DSM analysis: Application to urban areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2014, 7, 4020–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, G.; Dowman, I. Data fusion of high-resolution satellite imagery and LiDAR data for automatic building extraction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2007, 62, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Qin, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, K. A multi-scale filtering building index for building extraction in very high-resolution satellite imagery. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heipke, C.; Oberst, J.; Albertz, J.; Attwenger, M.; Dorninger, P.; Dorrer, E.; Ewe, M.; Gehrke, S.; Gwinner, K.; Hirschmüller, H.; et al. Evaluating planetary digital terrain models—The HRSC DTM test. Planet. Space Sci. 2007, 55, 2173–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Wu, B. An integrated photogrammetric and photoclinometric approach for illumination-invariant pixel-resolution 3D mapping of the lunar surface. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2020, 159, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Lee, W.H.; Toth, C.; Grejner-Brzezinska, D.A.; Lee, C. A piecewise approach to epipolar resampling of pushbroom satellite images based on RPC. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 2010, 76, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, F.; Li, J. Epipolar resampling of linear pushbroom satellite imagery by a new epipolarity model. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2011, 66, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.-W.; Yang, H.-S. Unified piecewise epipolar resampling method for pushbroom satellite images. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2016, 2016, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.S.; Hanley, H.B. Bias-compensated RPCs for sensor orientation of high-resolution satellite imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 2005, 71, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.S.; Ravanbakhsh, M. Georeferencing accuracy of GeoEye-1 imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 634–638. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.H.; Lee, C.N. Relative RPCs bias-compensation for satellite stereo images processing. J. Korean Soc. Surv. Geod. Photogramm. Cart. 2018, 36, 287–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zitová, B.; Flusser, J. Image registration methods: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Byun, Y. Automatic and accurate registration of VHR optical and SAR images using a quadtree structure. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2015, 36, 2277–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Chatterji, B. An FFT-based technique for translation, rotation, and scale-invariant image registration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1996, 5, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, C.V. A robust method for semi-automatic extraction of road centerlines using a piecewise parabolic model and least square template matching. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 2004, 70, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Pan, C.; Huo, L.; Zhou, Z. Multilevel SIFT matching for large-size VHR image registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Holden, E.-J. A fast and fully automatic registration approach based on point features for multi-source remote-sensing images. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutenegger, S.; Chli, M.; Siegwart, R. BRISK: Binary Robust invariant scalable keypoints. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Shanghai, China, 10–12 June 2011; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 2548–2555. [Google Scholar]
- Hasheminasab, S.M.; Zhou, T.; Habib, A. GNSS/INS-assisted structure from motion strategies for uav-based imagery over mechanized agricultural fields. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Han, Y.; Xiong, W.; He, F.; Zhang, Z.; Crawford, M. Automated ortho-rectification of UAV-based hyperspectral data over an agricultural field using frame RGB imagery. Remote. Sens. 2016, 8, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Zhao, S.; Jiao, L.; Tian, D.; Wang, S. A novel coarse-to-fine scheme for automatic image registration based on SIFT and mutual information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2014, 52, 4328–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R. A coarse-to-fine approach for remote-sensing image registration based on a local method. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2010, 3, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.; Mokhtarzade, M.; Ebadi, H. Uniform robust scale-invariant feature matching for optical remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2011, 49, 4516–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franchis, C.; Meinhardt-Llopis, E.; Michel, J.; Morel, J.-M.; Facciolo, G. An automatic and modular stereo pipeline for pushbroom images. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuffar, S. Satellite stereo based digital surface model generation using semi global matching in object and image space. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XXIII ISPRS Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–19 July 2016; pp. 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, K.; Fritsch, D. Relative orientation and modified piecewise epipolar resampling for high resolution satellite images. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mashad, S.Y.; Shoukry, A. Evaluating the robustness of feature correspondence using different feature extractors. In Proceedings of the 2014 19th International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR), Międzyzdroje, Poland, 2–5 September 2014; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Verma, G.K. A computer vision based framework for visual gun detection using Harris interest point detector. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 54, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Stephens, M. A combined corner and edge detector. In Proceedings of the Alvey Vision Conference 1988, Manchester, UK, 31 August–2 September 1988; British Machine Vision Association and Society for Pattern Recognition, 1988; pp. 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Alahi, A.; Ortiz, R.; VanderGheynst, P. FREAK: Fast Retina Keypoint. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RH, USA, 16–21 June 2012; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Choi, J.; Jung, J.; Chang, A.; Oh, S.; Yeom, J. Automated co-registration of multi-sensor orthophotos generated from unmanned aerial vehicle platforms. J. Sens. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarda, W. A Testing Procedure for Use in Geodetic Networks; Netherlands Geodetic Commission, Publications on Geodesy; New Series; Rijkscommissie voor Geodesie: Delft, The Netherlands, 1968; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Wu, B.; Xu, Z.-X.; Qing, Z. Seed point selection method for triangle constrained image matching propagation. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Kim, T.; Yeom, J.; Han, Y.; Kim, Y. Improved piecewise linear transformation for precise warping of very-high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
























| Sensor | Kompsat-3 | Kompsat-3A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Along-Track) | (Across-Track) | |||
| Scene ID | K3-944 | K3-102 | K3A-4099 | K3A-4205 |
| Spatial resolution | 0.75 m | 0.75 m | 0.68 m | 0.76 m |
| Processing level | 1R | 1R | 1R | 1R |
| Acquisition date | 25 January 2013 | 25 January 2013 | 22 December 2015 | 29 December 2015 |
| Roll/Pitch | 18.64°/19.85° | 16.51°/−20.16° | −26.45°/−1.00° | 20.81°/−27.06° |
| Size | 24,060 × 18,304 pixels | 24,060 × 18,304 pixels | 24,060 × 21,720 pixels | 24,060 × 17,080 pixels |
| (line × sample) | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, J.; Han, Y. A Double Epipolar Resampling Approach to Reliable Conjugate Point Extraction for Accurate Kompsat-3/3A Stereo Data Processing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182940
Oh J, Han Y. A Double Epipolar Resampling Approach to Reliable Conjugate Point Extraction for Accurate Kompsat-3/3A Stereo Data Processing. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(18):2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182940
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Jaehong, and Youkyung Han. 2020. "A Double Epipolar Resampling Approach to Reliable Conjugate Point Extraction for Accurate Kompsat-3/3A Stereo Data Processing" Remote Sensing 12, no. 18: 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182940
APA StyleOh, J., & Han, Y. (2020). A Double Epipolar Resampling Approach to Reliable Conjugate Point Extraction for Accurate Kompsat-3/3A Stereo Data Processing. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182940