Normal Faulting in the 2020 Mw 6.2 Yutian Event: Implications for Ongoing E–W Thinning in Northern Tibet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
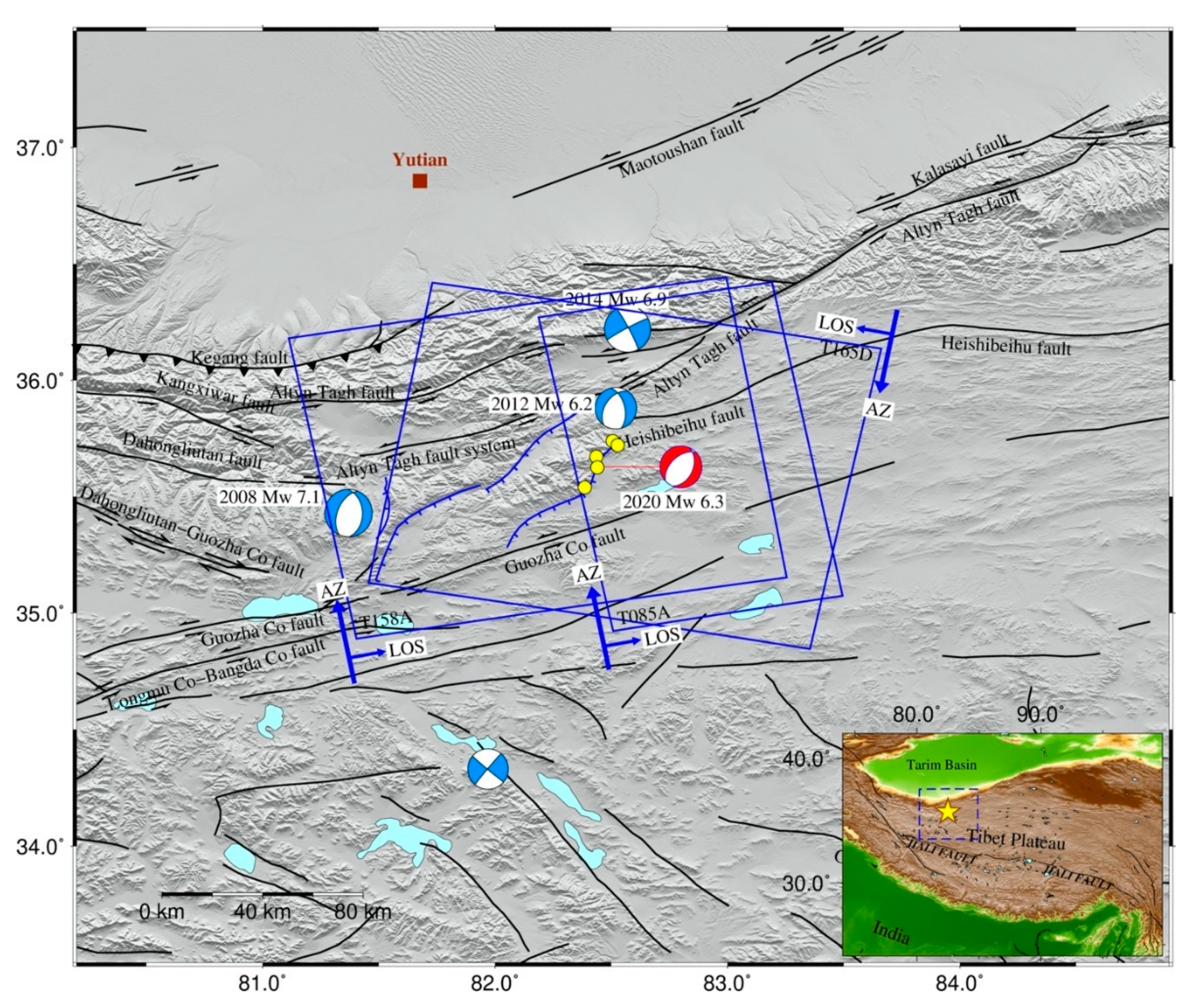
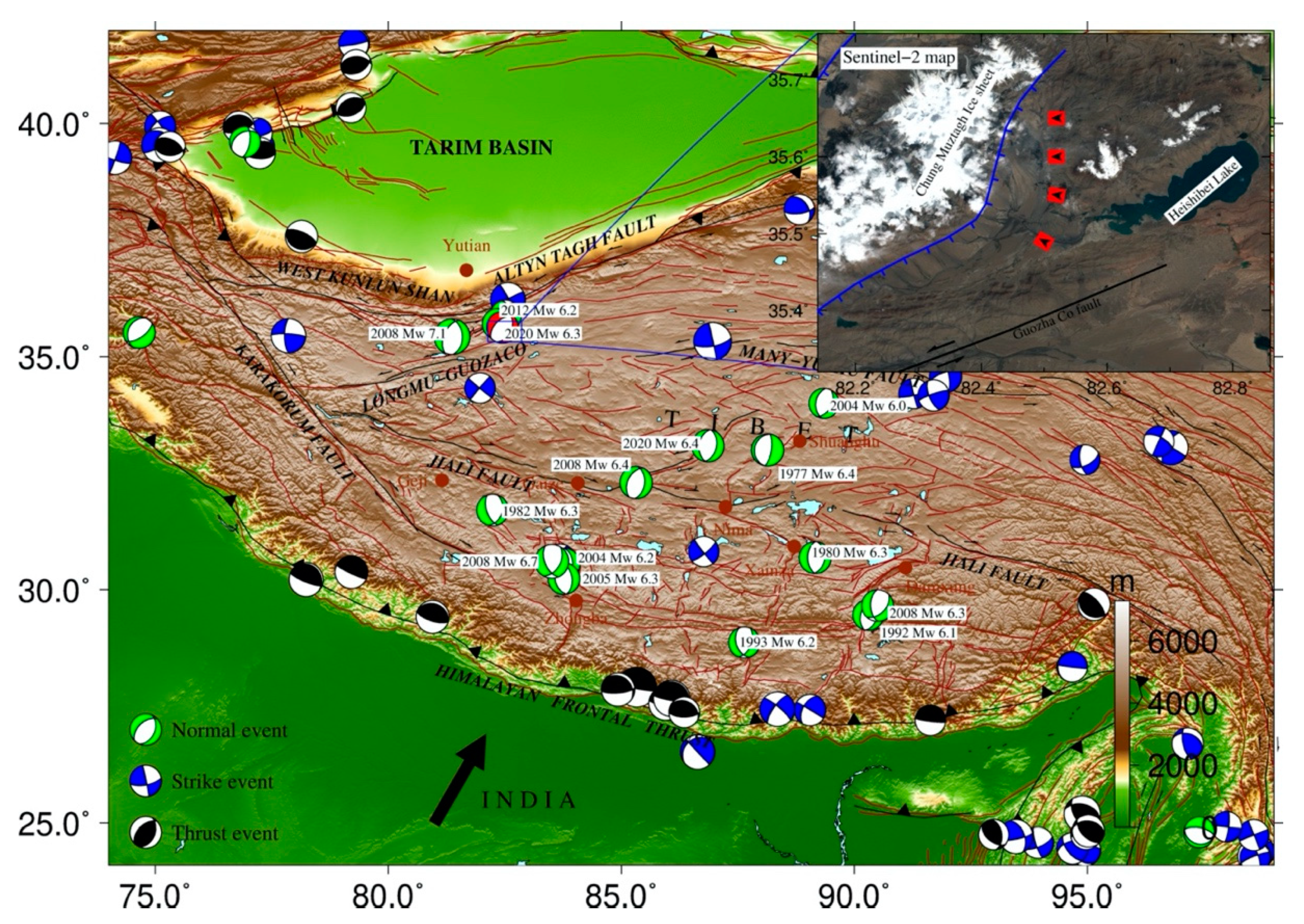
2. Tectonic Setting
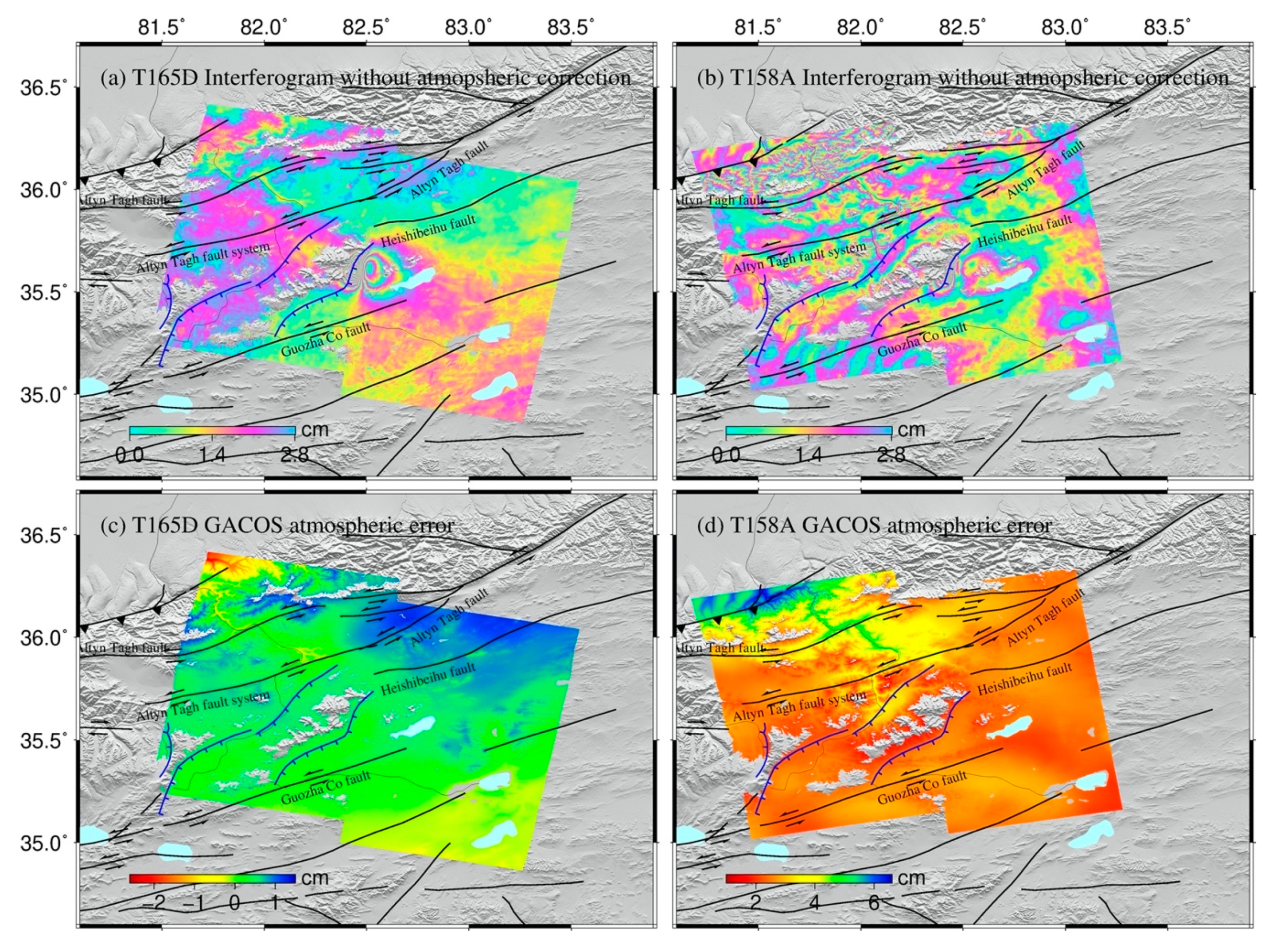
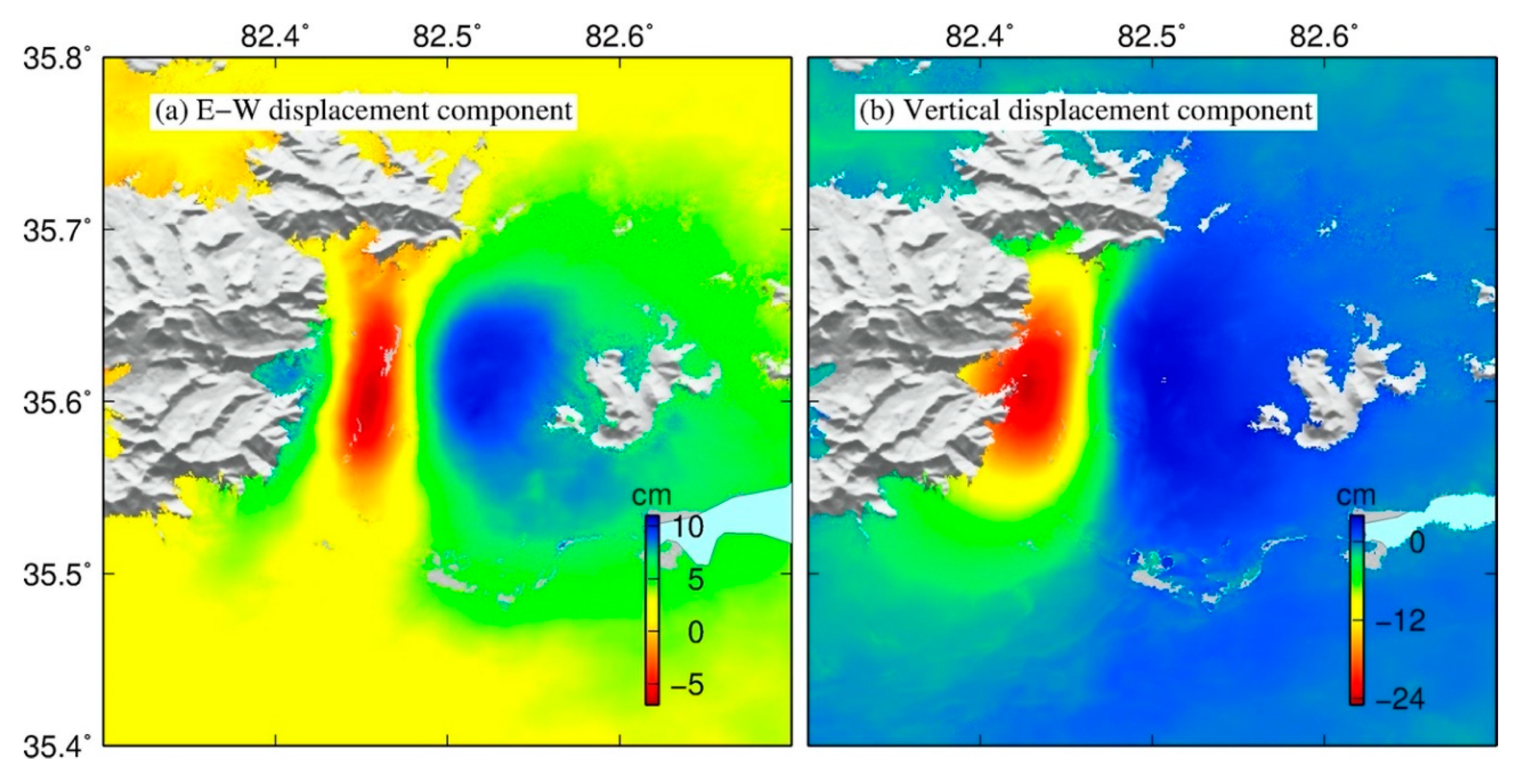
3. Coseismic Displacement Analyzed by InSAR Data
4. Source Modeling
5. Local Extension Determined by Interseismic GPS
6. Coulomb Stress Change Modeling
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tapponnier, P.; Xu, Z.Q.; Roger, F.; Meyer, B.; Arnaud, N.; Wittlinger, G.; Yang, J. Oblique Stepwise Rise and Growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science 2001, 294, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Shen, Z.; Wang, M.; Gan, W.; Molnar, P.; Bürgmann, R.; Wang, Q.; Niu, Z.; Sun, J.; Wu, J.; et al. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan plateau from global positioning system data. Geology 2004, 32, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Yin, A. Active structures of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen and their relationships to earthquake distribution, contemporary strain field, and cenozoic volcanism. Geosphere 2009, 5, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bischoff, S.H.; Flesch, L.M. Normal faulting and viscous buckling in the Tibetan plateau induced by a weak lower crust. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellart, W.P.; Chen, Z.; Strak, V.; Duarte, J.C.; Rosas, F.M. Pacific subduction control on Asian continental deformation including Tibetan extension and eastward extrusion tectonics. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Yang, Y. Extensional collapse of the Tibetan plateau: Results of three-dimensional finite element modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molnar, P.; Lyon-Caen, H. Some simple physical aspects of the support, structure, and evolution of mountain belts. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 1988, 218, 179–208. [Google Scholar]
- England, P.; Houseman, G. Extension during continental convergence, with application to the Tibetan plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 17561–17579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houseman, G.; England, P. A lithospheric-thickening model for the Indo-Asian collision. World Reg. Geol. 1996, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, A. Mode of Cenozoic east-west extension in Tibet suggesting a common origin of rifts in Asia during the Indo-Asian collision. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 21745–21759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.R.; Walters, R.J.; England, P.C.; Jackson, J.A.; Li, Z.; Parsons, B. Extension on the Tibetan Plateau: Recent normal faulting measured by InSAR and body wave seismology. Geophy. J. Int. 2010, 183, 503–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Tan, X.; Yu, G.; Wu, G.; Fang, W.; Chen, J.; Song, H.; Shen, J. Normal- and oblique-slip of the 2008 Yutian earthquake: Evidence for eastward block motion, northern Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics 2013, 584, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Han, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, G.; Zhou, B.; Li, F.; Ma, B.; Chen, G.; Ran, Y. Seismic Tectonic Map of China and Adjacent Areas; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Freymueller, J.; Bliham, R.; Larson, K.; Lai, X.; You, X.; Niu, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Present-day crustal deformation in china constrained by global positioning system measurements. Science 2001, 294, 574–577. [Google Scholar]
- Kapp, P.; Taylor, M.; Stockli, D.; Ding, L. Development of active low-angle normal fault systems during orogenic collapse: Insight from Tibet. Geology 2008, 36, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, T.J.; Copley, A.; Jackson, J. Thermal and tectonic consequences of India underthrusting Tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 353–354, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copley, A.; Avouac, J.P.; Wernicke, B.P. Evidence for mechanical coupling and strong Indian lower crust beneath southern Tibet. Nature 2011, 472, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, G.; Nettles, M.; Dziewoński, A.M. The global CMT project 2004–2010: Centroid-moment tensors for 13,017 earth-quakes. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2012, 200, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, M.; Yasuda, T. The 2008 Yutian normal faulting earthquake (Mw 7.1), NW Tibet: Non-planar fault modeling and implications for the Karakax fault. Tectonophysics 2011, 511, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Qu, C.; Song, X.; Zhang, G.; Guo, L. Source characteristics of the Yutian earthquake in 2008 from inversion of the co-seismic deformation field mapped by InSAR. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G. Coseismic Coulomb stress changes caused by the Mw6.9 Yutian earthquake in 2014 and its correlation to the 2008 Mw 7.2 Yutian earthquake. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Han, N.; Shan, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, G.; Xiu, W. Three-dimensional fault geometry and kinematics of the 2008 Mw 7.1 Yutian earthquake revealed by very-high resolution satellite stereo imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, R.D.; Cowgill, E.; Arrowsmith, J.R.; Friedrich, A.M. Pulsed strain release on the Altyn Tagh fault, northwest China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 459, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Masek, J.G.; Isacks, B.L.; Fielding, E.J.; Browaeys, J. Rift flank uplift in Tibet: Evidence for a viscous lower crust. Tectonics 1994, 13, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Elliott, J.R.; Craig, T.J.; Wright, T.J.; Liu, Z.; Hooper, A. Normal faulting sequence in the Pumqu-Xainza Rift constrained by InSAR and teleseismic body-wave seismology. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 2947–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryder, I.; Bürgmann, R.; Fielding, E. Static stress interactions in extensional earthquake sequences: An example from the South Lunggar Rift, Tibet. J. Geophy. Res. 2012, 117, B09405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Xu, X.; Bürgmann, R. Synthetic normal faulting of the 9 January 2008 Nima (Tibet) earthquake from conventional and along-track SAR interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Peltzer, G. Poroelastic triggering in the 9–22 January 2008 Nima-Gaize (Tibet) earthquake sequence. Geology 2010, 38, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, L.; Ryder, I.; Nippress, S.E.J.; Bürgmann, R. Coseismic and post-seismic activity associated with the 2008 Mw 6.3 Damxung earthquake, Tibet, constrained by InSAR. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 788–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Peng, Z.; Meng, X. Remotely triggered earthquakes in South-Central Tibet following the 2004 Mw 9.1 Sumatra and 2005 Mw 8.6 Nias earthquakes. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 201, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, P.; Wang, Q.; Ding, K.; Wang, M.; Qiao, X.; Li, J.; Wen, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, S.; Zou, R. Source model of the 2015 Mw 6.4 Pishan earthquake constrained by interferometric synthetic aperture radar and GPS: Insight into blind rupture in the western Kunlun Shan. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Pan, J.; Lin, A.; Sun, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, K.; Chevalier, M.L.; Yun, K.; et al. Coseismic Surface Ruptures Associated with the 2014 Mw 6.9 Yutian Earthquake on the Altyn Tagh Fault, Tibetan Plateau. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2016, 106, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A.; Frey, O.; Santoro, M. Sentinel-1 Support in the GAMMA Software. Procedia Comp. Sci. 2016, 100, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth Seal, D.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.C. Small Magnitude Co-Seismic Deformation of the 2017 Mw 6.4 Nyingchi Earthquake Revealed by InSAR Measurements with Atmospheric Correction. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalié, O.; Doin, M.P.; Lasserre, C.; Briole, P. Ground motion measurement in the Lake Mead area, Nevada, by differential synthetic aperture radar interferometry time series analysis: Probing the lithosphere rheological structure. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fielding, E.J.; Sangha, S.S.; Bekaert, D.P.S.; Samsonov, S.V.; Chang, J.C. Surface Deformation of North-Central Oklahoma Related to the 2016 Mw 5.8 Pawnee Earthquake from SAR Interferometry Time Series. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2017, 88, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S. Atmospheric effects in interferometric synthetic aperture radar surface deformation and topographic maps. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 7547–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.R.; Biggs, J.; Parsons, B.; Wright, T.J. InSAR slip rate determination on the Altyn Tagh Fault, northern Tibet, in the presence of topographically corre-lated atmospheric delays. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolivet, R.; Agram, P.S.; Lin, N.Y.; Simons, M.; Doin, M.P.; Peltzer, G.; Li, Z. Improving InSAR geodesy using Global Atmospheric Models. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 2324–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar atmospheric correction using a GPS-based iterative tropospheric decomposition model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y. Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1985, 75, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Jónsson, S.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Amelung, F.C. Fault Slip Distribution of the 1999 Mw 7.1 Hector Mine, California, Earthquake, Estimated from Satellite Radar and GPS Measurements. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, R.B.; Barnhart, W.D. Evaluation of earthquake triggering during the 2005–2008 earthquake sequence on Qeshm Island, Iran. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnardi, M.; Hooper, A. Inversion of Surface Deformation Data for Rapid Estimates of Source Parameters and Uncertainties: A Bayesian Approach. Geochem. Geophy. Geosyst. 2018, 19, 2194–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Roth, F.; Enescu, B.; Hainzl, S.; Ergintav, S. Afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation following the 1999 M 7.4 Izmit earthquake from GPS measurements. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 178, 1220–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Gan, W.; Shen, C.; Xiao, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Ding, X.; Zhou, D. Three-dimensional velocity field of present-day crustal motion of the Tibetan Plateau derived from GPS measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 5722–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Shi, C.; Huang, J.; Wei, N. Crustal Deformation in the India-Eurasia Collision Zone From 25 Years of GPS Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 9290–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, e2019JB018774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansari, S. Co-seismic Stress Transfer and Magnitude-Frequency Distribution due to the 2012 Varzaqan-Ahar Earthquake Doublets (M w 6.5 and 6.4), NW of Iran. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 132, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, S.; Stein, R.S.; Richards-Dinger, K.; Bozkurt, S.B. Forecasting the evolution of seismicity in southern California: Animations built on earthquake stress transfer. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.B.S.; Gahalaut, V.K.; Chopra, S.; Shan, B. Tectonic implications and seismicity triggering during the 2008 Baluchistan, Pakistan earthquake sequence. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 45, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, L.D.; Ryder, I. Recent seismic and aseismic activity in the Ashikule stepover zone, NS Tibet. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 198, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.B.; Zhao, L.F.; Xie, X.B.; Cao, J.X.; Yao, Z.X. Static Coulomb stress changes and seismicity rate in the source region of the 12 February, 2014 Mw 7.0 Yutian earthquake in Xinjiang, China. Chin. J. Geophy. 2016, 59, 3732–3743. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, J.; Wright, T.J. How satellite InSAR has grown from opportunistic science to routine monitoring over the last decade. Nat. Commun. 2002, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.P.; Arrowsmith, J.R.; Nissen, E.; Lajoie, L.; Maruyama, T.; Chiba, T. The M7 2016 Kumamoto, Japan, earthquake: 3-D deformation along the fault and within the damage zone constrained from differential Lidar topography. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 6138–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, E.; Tizzani, P.; Carminati, E.; Doglioni, C.; Pepe, S.; Petricca, P.; De Luca, C.; Bignami, C.; Solaro, G.; Castaldo, R.; et al. Ground deformation and source geometry of the 30 October 2016 Mw 6.5 Norcia earthquake (central Italy) investigated through seismological data, DInSAR measurements, and numerical modelling. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J. Satellite geodetic imaging reveals internal deformation of western Tibet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daout, S.; Doin, M.; Peltzer, G.; Lasserre, C.; Socquet, A.; Volat, M.; Sudhaus, H. Strain Partitioning and Present-Day Fault Kinematics in NW Tibet From Envisat SAR Interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 2462–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yuan, X.; Liu, H.; Kumar, P.; Pei, S.; Kind, R.; Zhang, Z.; Teng, J.; Ding, L.; Gao, X.; et al. The boundary between the Indian and Asian tectonic plates below Tibet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11229–11233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

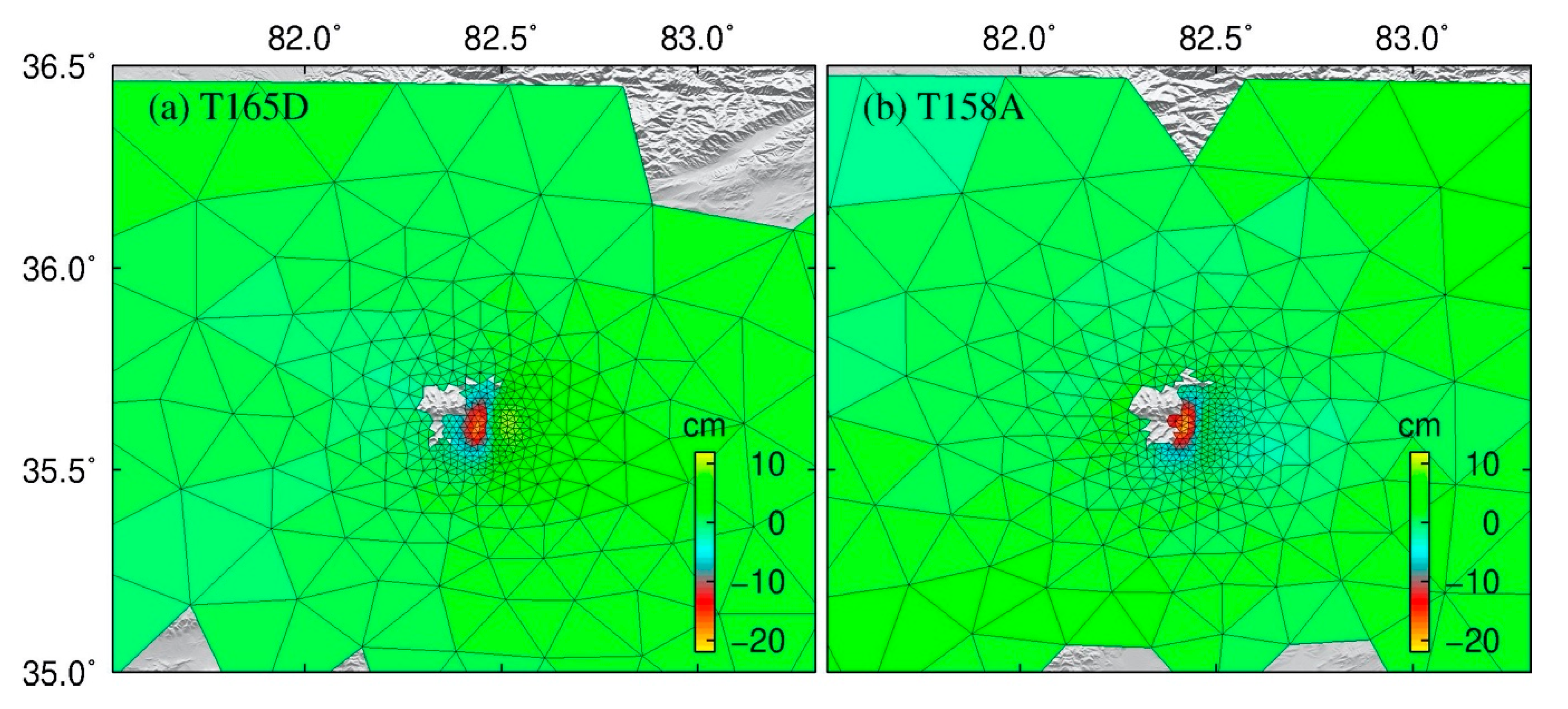
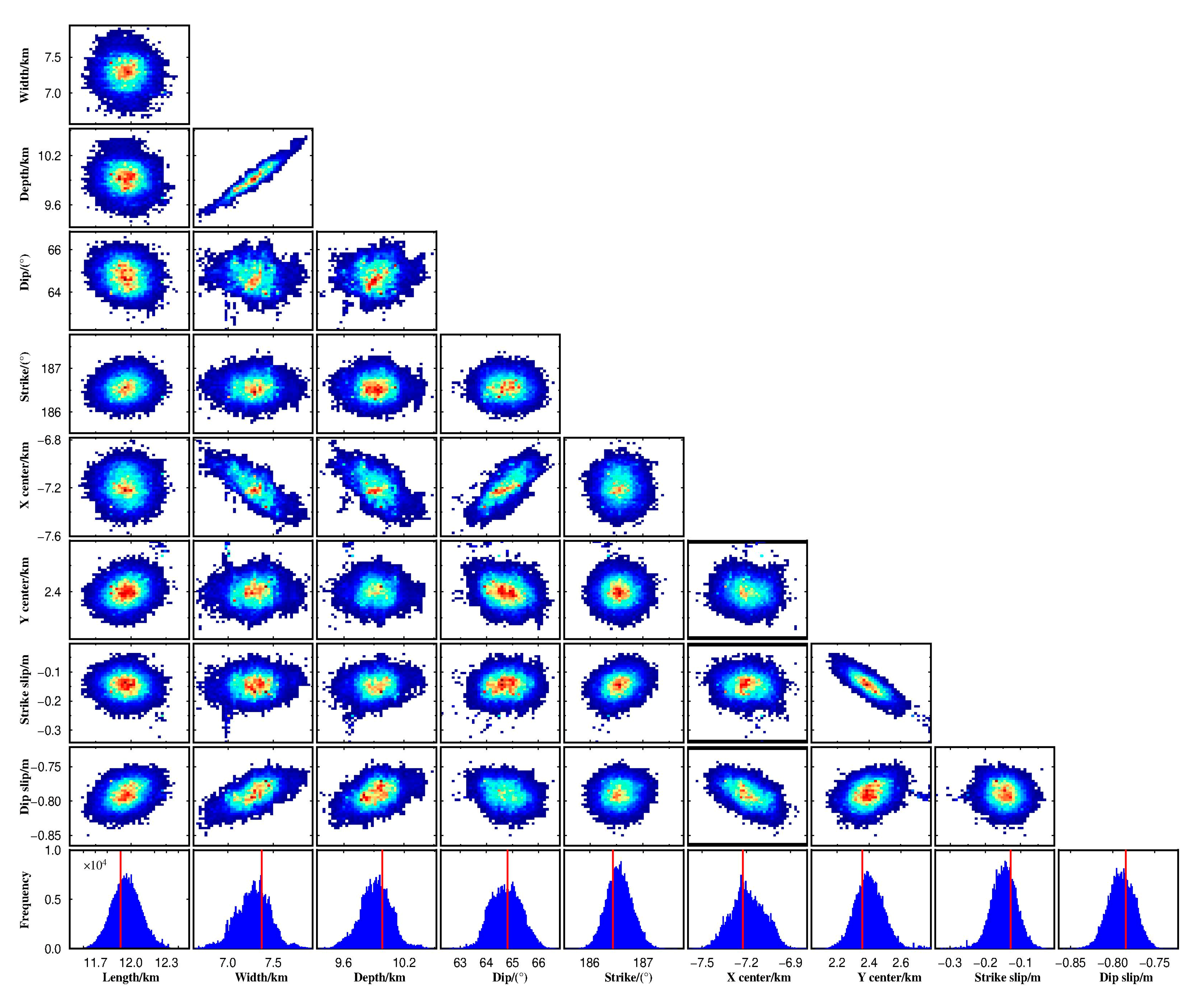



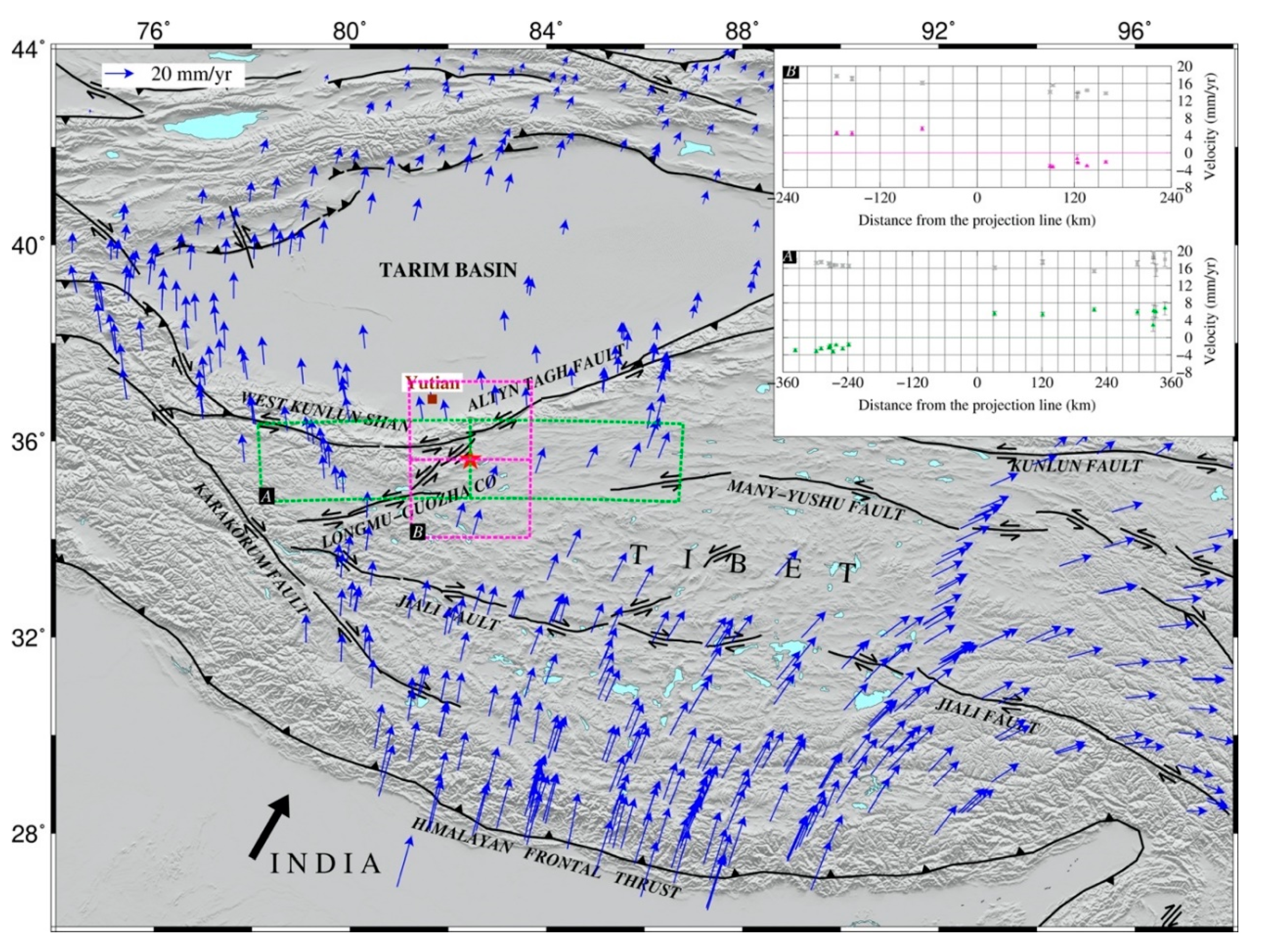

| Track | Master | Slave | Perp. B | Inc. Angle | Azi. Angle | Original | Corrected | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ | α | σ | α | ||||||
| (YYYYMMDD) | (YYYYMMDD) | (m) | (°) | (°) | (mm) | (km) | (mm) | (km) | |
| T165 (D) | 20200617 | 20200629 | −86.3 | 29–44 | 190.3 | 0.75 | 30.0 | 0.45 | 12.4 |
| T158 (A) | 20200622 | 20200704 | 84.6 | 35–48 | −9.8 | 3.52 | 57.4 | 0.8 | 24.7 |
| Rectangular Dislocation with Uniform Slip [42] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | Width | Depth a | Dip | Strike | X Center | Y Center | Strike Slip b | Dip Slip c | |
| (m) | (m) | (m) | (°) | (°) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | |
| Lower | 1000 | 4000 | 2000 | −90 | 0 | −20,000 | −20,000 | −1.0 | −2.0 |
| Upper | 30,000 | 10,000 | 20,000 | 90 | 360 | 20,000 | 20,000 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Optimal | 11,914 | 7372 | 9985 | 64.8 | 186.4 | −7225 | 2357 | −0.13 | −0.78 |
| 2.5% | 11,720 | 6785 | 9593 | 63.7 | 186.1 | −7413 | 2230 | −0.22 | −0.82 |
| 97.5% | 12,223 | 7658 | 10229 | 65.9 | 187.0 | −6975 | 2596 | −0.08 | −0.76 |
| Model | Long. | Lat. | Strike | Dip | Rake | Depth | Length | Width | Slip a | Moment | Mw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (km) | (km) | (km) | (m) | (1018 N·m) | ||
| USGS | 82.379 | 35.596 | 24 | 42 | −108 | 10.0 | – | – | – | 3.22 | 6.27 |
| 227 | 50 | −74 | |||||||||
| GCMT | 82.36 | 35.70 | 357 | 44 | −11 | 13.3 | – | – | – | 3.29 | 6.28 |
| 213 | 52 | −66 | |||||||||
| CENC | 82.33 | 35.73 | – | – | – | 10 | – | – | – | – | Ms 6.4 |
| Uniform | 82.420 | 35.621 | 186.4 | 64.8 | −99 b | 9.985 | 11.9 | 7.4 | 0.79 | 2.30 d | 6.18 |
| −0.3 +0.3 km | −0.2 +0.2 km | −0.4 +0.6 | −1.8 +1.2 | – | −0.2 +0.4 | −0.3 +0.3 | −0.4 +0.1 | −0.17 +0.04 | |||
| Distributed | 82.487 c | 35.724 c | 186.4 | 64.8 | – | 0c | 24 | 20 | – | 2.69 d | 6.23 |
| Event | Long. | Lat. | Depth | Strike | Dip | Rake | Length | Width | Slip | Mw | Refer to |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ° | ° | km | ° | ° | ° | km | km | m | |||
| 2008 | 81.39 | 35.42 | 10.0 | 354 | 47 | -113 | 66 | 34 | 1.26 | 7.1 | [55] |
| 2012 | 82.435 | 35.59 | 7.8 | 14.7 | 50 | -90 | 16.0 | 10 | 0.49 | 6.2 | [54] |
| 2014 | 82.50 | 36.10 | 10.1 | 240 | 71.9 | -2.2 | 85 | 21 | 2.79 | 7.0 | [55] |
| 2020 | 82.50 | 35.60 | 6.7 | 186.4 | 64.8 | -99.5 | 11.9 | 7.4 | 0.79 | 6.2 | This study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, P.; Wen, Y.; Ding, K.; Xu, C. Normal Faulting in the 2020 Mw 6.2 Yutian Event: Implications for Ongoing E–W Thinning in Northern Tibet. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183012
He P, Wen Y, Ding K, Xu C. Normal Faulting in the 2020 Mw 6.2 Yutian Event: Implications for Ongoing E–W Thinning in Northern Tibet. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(18):3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183012
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Ping, Yangmao Wen, Kaihua Ding, and Caijun Xu. 2020. "Normal Faulting in the 2020 Mw 6.2 Yutian Event: Implications for Ongoing E–W Thinning in Northern Tibet" Remote Sensing 12, no. 18: 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183012
APA StyleHe, P., Wen, Y., Ding, K., & Xu, C. (2020). Normal Faulting in the 2020 Mw 6.2 Yutian Event: Implications for Ongoing E–W Thinning in Northern Tibet. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183012






