Ground Deformation and Its Causes in Abbottabad City, Pakistan from Sentinel-1A Data and MT-InSAR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
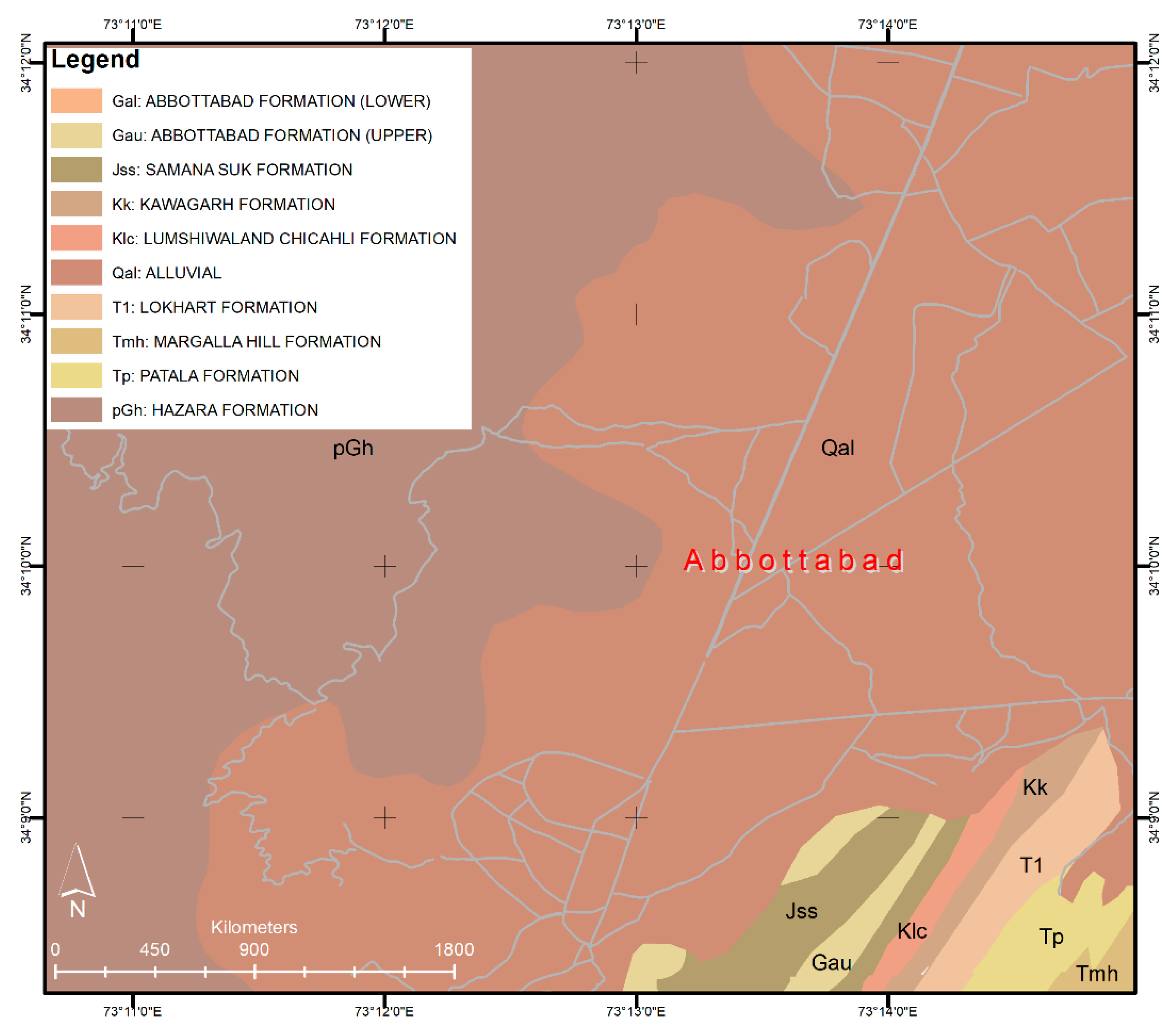
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Area
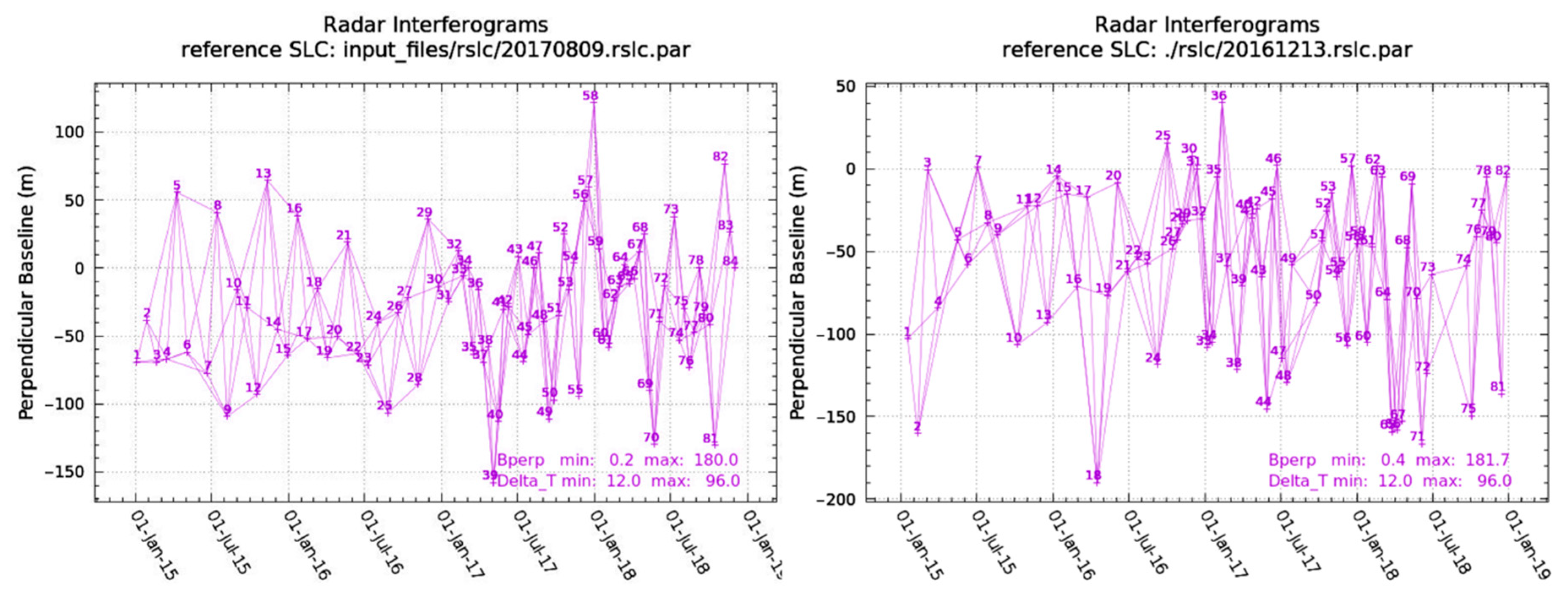
2.2. Datasets
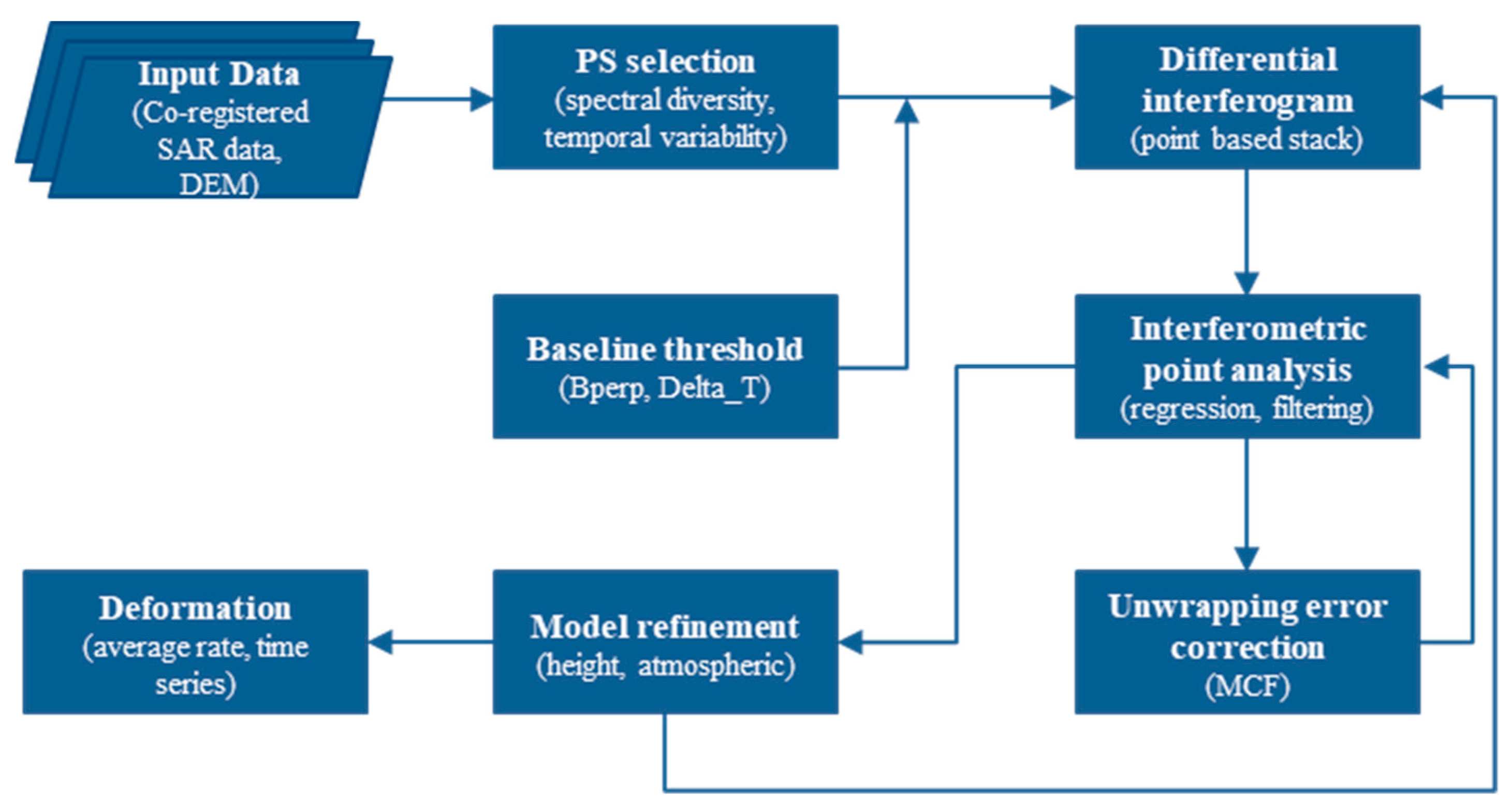
3. Methodology
3.1. Generation of Point List and Differential Interferograms
3.2. Interferometric Point Target Processing
3.3. Deformation Rate and Time Series Retrieval
3.4. Decomposition of LOS Displacements into 2D Displacement Fields
3.5. Causal Factors of Deformation
4. Results
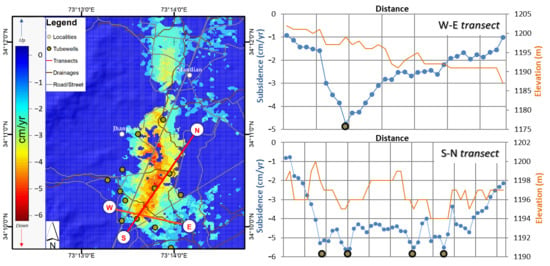
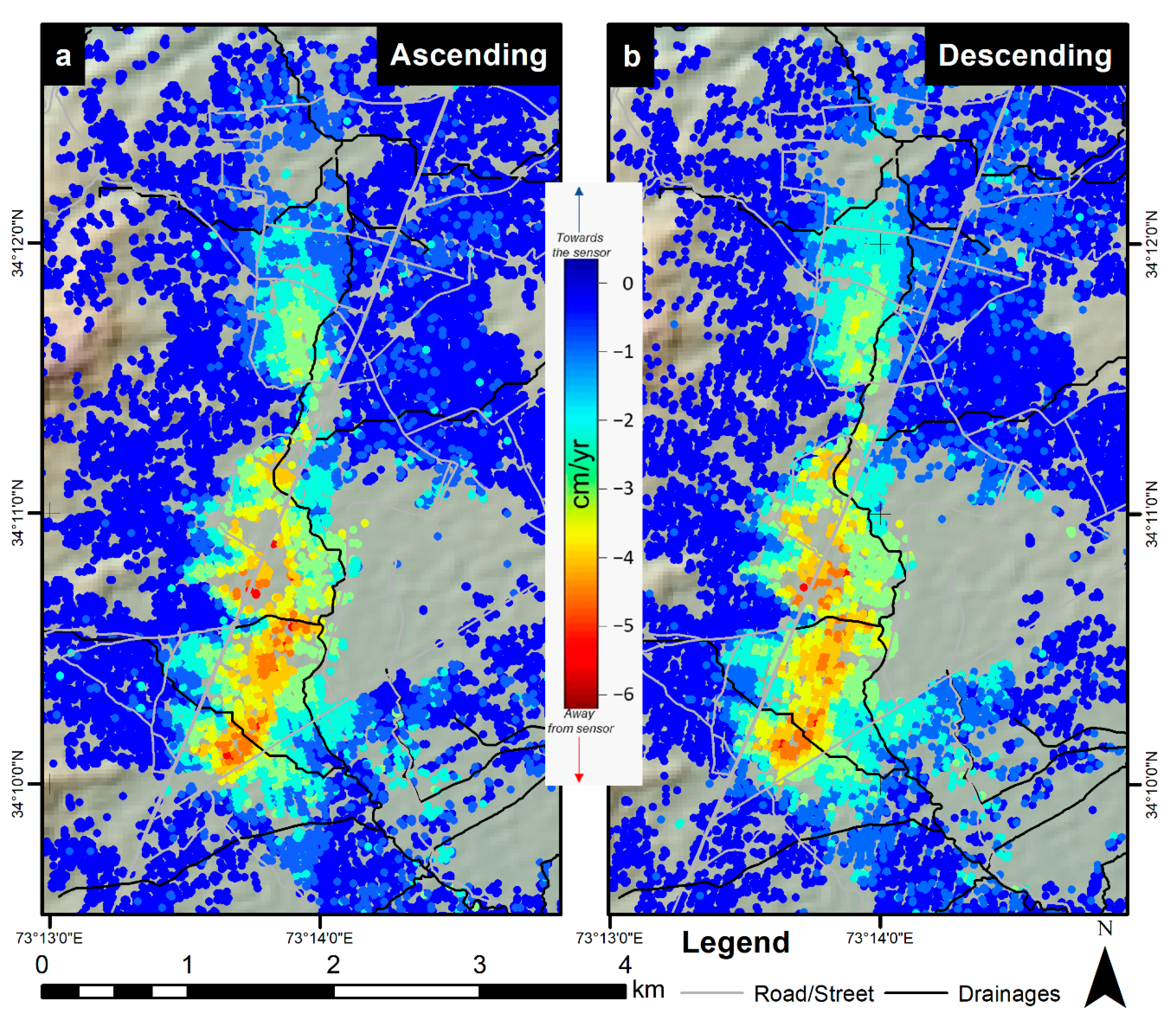
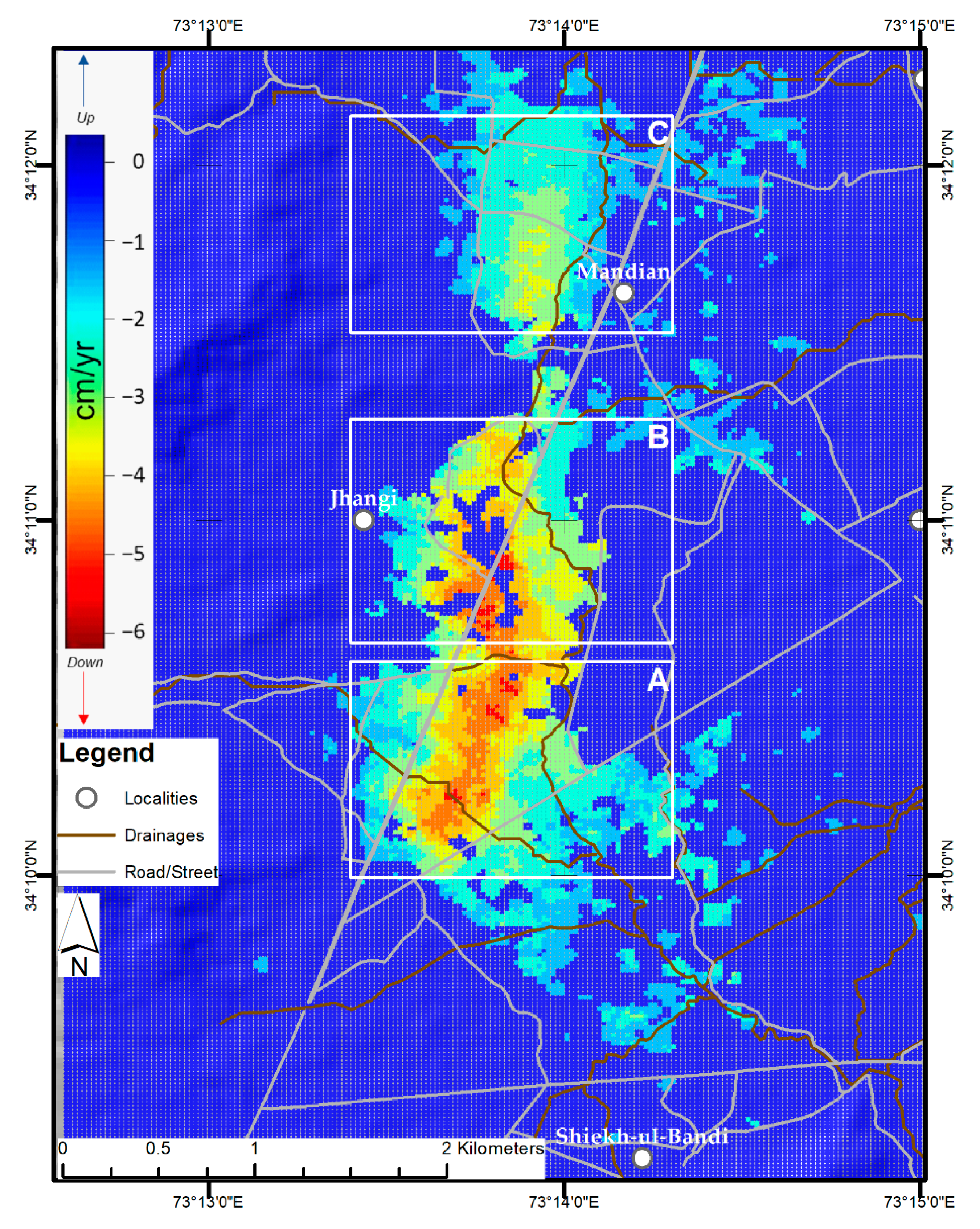
4.1. Average Subsidence Rate Map
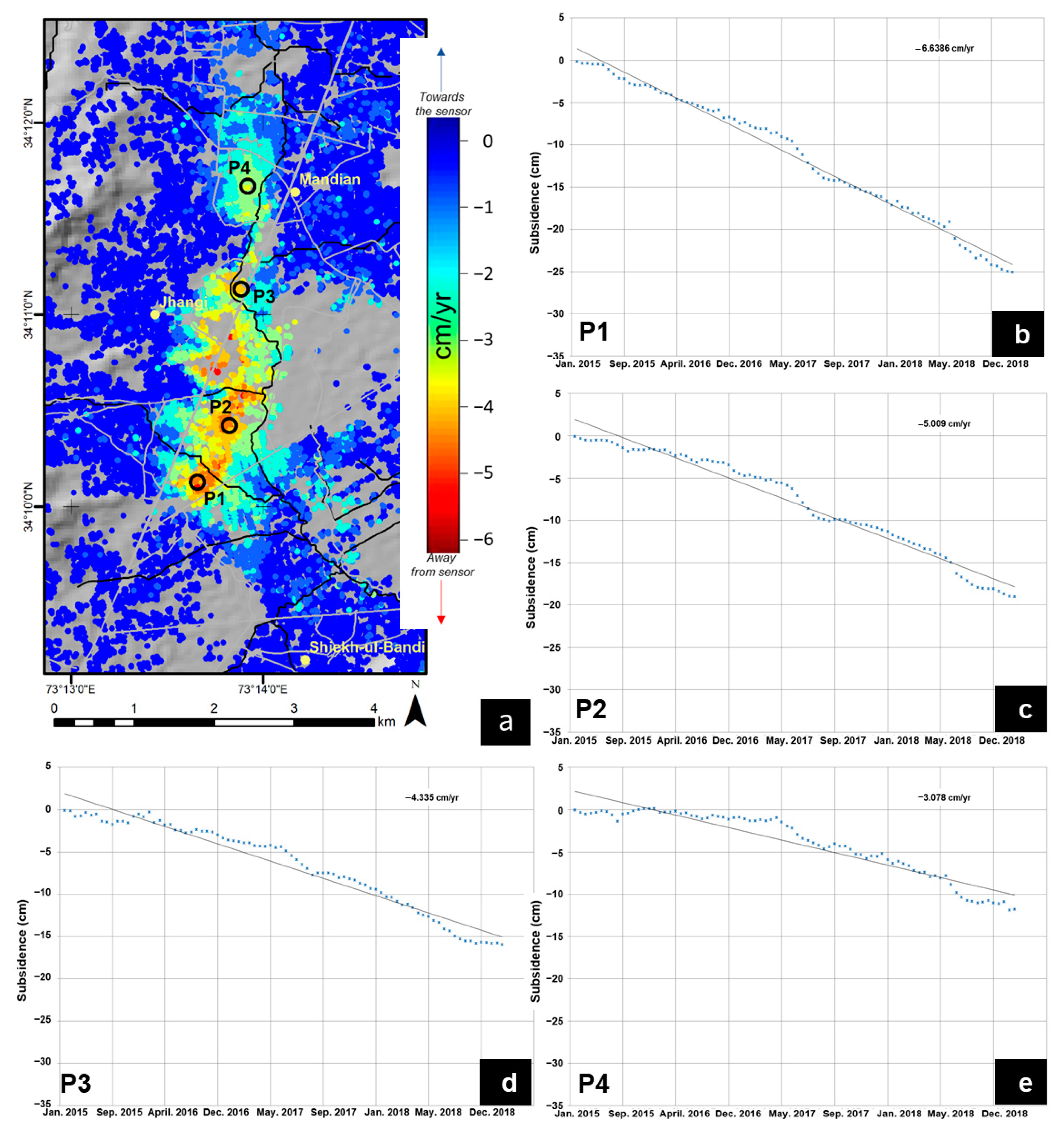
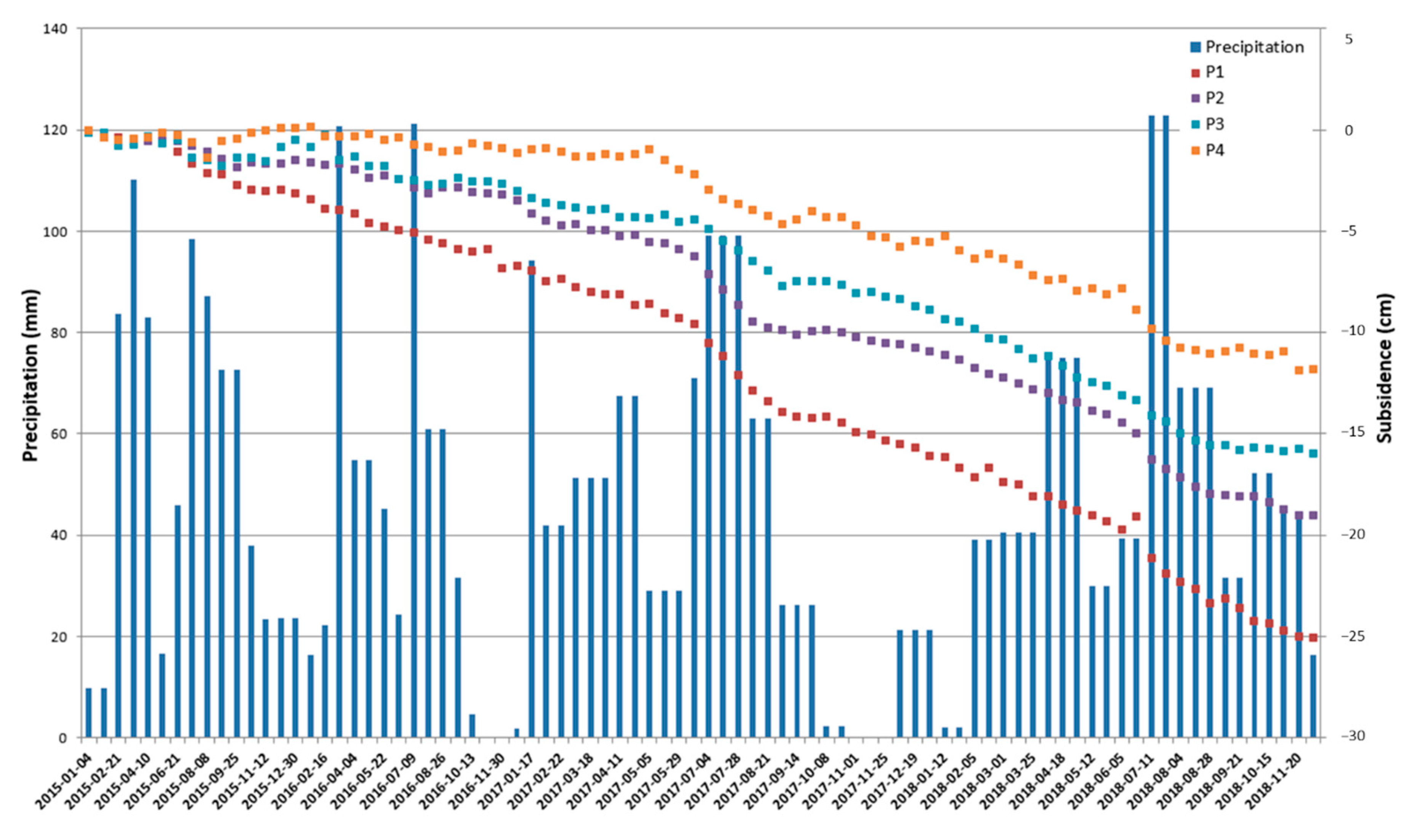
4.2. Subsidence Time Series
5. Discussion and Analysis
5.1. Soil Consolidation
5.2. Effect of Ground Water Withdrawal
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shi, M. Wuhan surface subsidence analysis in 2015–2016 based on Sentinel-1A data by SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deltares. Sinking Cities: An Integrated Approach Towards Solutions; Deltares—Taskforce Subsidence: Delft/Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Xu, B.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhu, J. Deriving spatio-temporal development of ground subsidence due to subway construction and operation in delta regions with PS-InSAR data: A case study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.L.; Liu, G.X.; Li, Z.W.; Li, Z.L.; Chen, Y.Q. Ground subsidence monitoring in Hong Kong with satellite SAR interferometry. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.A.; Overeem, I.; Steckler, M.S.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Seeber, L.; Akhter, S.H. InSAR measurements of compaction and subsidence in the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, Bangladesh. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, T.L.; Johnson, A.I. Land subsidence caused by ground water withdrawal in urban areas. GeoJournal 1985, 11, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, W.; Hanson, R.T.; Leake, S.A.; Hughes, J.D.; Niswonger, R.G. Feedback of land subsidence on the movement and conjunctive use of water resources. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radutu, A.; Nedelcu, I.; Gogu, C.R. An overview of ground surface displacements generated by groundwater dynamics, revealed by InSAR techniques. Procedia Eng. 2017, 209, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.L.; Huang, D.F.; Yin, J.H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Lau, C.K.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.R.; Chen, W. A new generation of multi-antenna GPS system for landslide and structural deformation monitoring. In Advances in Building Technology; Anson, M., Ko, J.M., Lam, E.S.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 1611–1618. ISBN 978-0-08-044100-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lingyun, J.; Qingliang, W.; Shuangxu, W. Present-day 3D deformation field of Northeast China, observed by GPS and leveling. Geod. Geodyn. 2014, 5, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aimaiti, Y.; Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W. Multi-Sensor InSAR Analysis of progressive land subsidence over the coastal city of Urayasu, Japan. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikuemonisan, F.E.; Ozebo, V.C.; Olatinsu, O.B. Geostatistical evaluation of spatial variability of land subsidence rates in Lagos, Nigeria. Geod. Geodyn. 2020, 11, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Feng, G.; Long, J. Atmospheric effects on InSAR measurements and their mitigation. Sensors 2008, 8, 5426–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis (Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing); van der Meer, F., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Norwell, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780792369455. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z. Mitigating ionospheric artifacts in coseismic interferogram based on offset field derived from ALOS-PALSAR data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoah-Afari, P.; Ding, X.L.; Zhong Lu, Z.L.; Omura, M. Magnitude and extent of six years of land subsidence in shanghai revealed by JERS-1 SAR data. In Geoscience and Remote Sensing New Achievements; Imperatore, P., Riccio, D., Eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, A.; Calò, F. A review of interferometric synthetic aperture RADAR (InSAR) multi-track approaches for the retrieval of Earth’s surface displacements. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.L.; Lu, Z. Ground deformation mapping by fusion of multi-temporal interferometric synthetic aperture radar images: A review. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2015, 6, 289–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. 3D coseismic displacement of 2010 Darfield, New Zealand earthquake estimated from multi-aperture InSAR and D-InSAR measurements. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.V.; Feng, W.; Peltier, A.; Geirsson, H.; d’Oreye, N.; Tiampo, K.F. Multidimensional small baseline subset (MSBAS) for volcano monitoring in two dimensions: Opportunities and challenges. Case study Piton de la Fournaise volcano. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2017, 344, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ding, X.L.; Li, Q.; Shan, X.; Liu, P. Using an integer least squares estimator to connect isolated InSAR fringes in earthquake slip inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangcai, F.; Zhiwei, L.; Xinjian, S.; Bing, X.; Yanan, D. Source parameters of the 2014 Mw 6.1 South Napa earthquake estimated from the Sentinel 1A, COSMO-SkyMed and GPS data. Tectonophysics 2015, 655, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Ming, L.U.O.; Xin-Jian, S.; Wen-Wu, Z.H.U.; Kai-Fu, D.U.; Wen-Ni, W.A.N.; Hong-Bao, L.; Zhi-Guang, L.I.U. Monitoring vertical ground deformation in the North China Plain using the multitrack PSInSAR technique. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 2139–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, J. Subsidence prediction and susceptibility zonation for collapse above goaf with thick alluvial cover: A case study of the Yongcheng coalfield, Henan Province, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2016, 75, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmuller, U.; Walter, D.; Spreckels, V.; Werner, C.L.; Wegmüller, U.; Walter, D.; Spreckels, V.; Werner, C.L. Nonuniform ground motion monitoring with TerraSAR-X persistent scatterer interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, U.; Haq, M.; Ahmad, I. Environmental Fiscal Reform in Abbottabad: Drinking Water; Pastakia, F., Ed.; International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Islamabad, Pakistan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, Z.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Waseem, M.; Ahmed, W. Mapping sediment thickness of the Abbottabad basin, Pakistan. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 128, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakistan Bureau of Statistics. Available online: http://www.pbs.gov.pk/ (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Big Earth data for cultural heritage in the Copernicus era. In Remote Sensing for Archaeology and Cultural Landscapes: Best Practices and Perspectives Across Europe and the Middle East; Hadjimitsis, D.G., Themistocleous, K., Cuca, B., Agapiou, A., Lysandrou, V., Lasaponara, R., Masini, N., Schreier, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 31–46. ISBN 978-3-030-10979-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Ding, X.L.; Liu, G.X. Method for optimum selection of common master acquisition for PS-InSAR. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2007, 36, 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and nonlinear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmuller, U.; Wiesmann, A.; Strozzi, T. Interferometric Point Target Analysis with JERS-1 L-band SAR data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 7, pp. 4359–4361. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, M. A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabus, B.; Werner, C.; Wegmueller, U.; McCardle, A. Interferometric point target analysis of RADARSAT-1 data for deformation monitoring at the Belridge/Lost Hills oil fields. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, C.L.; Wegmüller, U.; Strozzi, T. Deformation time-series of the lost-hills oil field using a multi-baseline interferometric SAR inversion algorithm with finite difference smoothing constraints. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Lu, Z. Toward mapping surface deformation in three dimensions using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samiei-Esfahany, S.; Hanssen, R.F.; Van Thienen-visser, K.; Muntendam-bos, A. On the effect of horizontal deformation on InSAR subsidence estimates. In Proceedings of the Fringe 2009, Frascati, Italy, 30 November–4 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, G.; Cakir, Z.; Lasserre, C.; Renard, F. Investigating subsidence in the Bursa Plain, Turkey, using ascending and descending Sentinel-1 Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Z.D.; Yang, J.Q.; Yuan, L. Land subsidence caused by the interaction of high-rise buildings in soft soil areas. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSP. Geological Map of Abbottabad area NWFP, Pakistan. Map series Vol. III at 1:50,000 scale, Issued by Director General. Geological Survey of Pakistan (GSP). 2002. Available online: https://www.gsp.gov.pk/ (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). Basic Design Study Report on the Project for Improvement of the Water Supply in Abbottabad, Pakistan; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). Preparatory Survey Report on the Project for the Improvement of Water Supply System in Abbottabad, Pakistan; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). Ex-Post Project Evaluation 2017: Package IV—5 (Pakistan, Bangladesh); Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Recorder, B. Rain Continues to Paralysis Life in Hazara. Available online: https://fp.brecorder.com/2018/08/20180809397986/ (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Ahmed, T.; Pervez, A.; Mehtab, M.; Sherwani, S.K. Assessment of drinking water quality and its potential health impacts in academic institutions of Abbottabad (Pakistan). Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Gifts Water Supply System to Abbottabad. Available online: https://www.jica.go.jp/pakistan/english/office/topics/press151015.html (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Jing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Wei, J.; Chen, Y. Monitoring land subsidence in Wuhan city (China) using the SBAS-INSAR method with radarsat-2 imagery data. Sensors (Switzerland) 2019, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galloway, D.L.; Coplin, L.S.; Ingebritsen, S.E. Effects of land subsidence in the Greater Houston Area. In Managing Urban Water Supply; Agthe, D.E., Billings, R.B., Buras, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 187–203. ISBN 978-94-017-0237-9. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahzad, N.; Ding, X.; Wu, S.; Liang, H. Ground Deformation and Its Causes in Abbottabad City, Pakistan from Sentinel-1A Data and MT-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203442
Shahzad N, Ding X, Wu S, Liang H. Ground Deformation and Its Causes in Abbottabad City, Pakistan from Sentinel-1A Data and MT-InSAR. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(20):3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203442
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahzad, Naeem, Xiaoli Ding, Songbo Wu, and Hongyu Liang. 2020. "Ground Deformation and Its Causes in Abbottabad City, Pakistan from Sentinel-1A Data and MT-InSAR" Remote Sensing 12, no. 20: 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203442
APA StyleShahzad, N., Ding, X., Wu, S., & Liang, H. (2020). Ground Deformation and Its Causes in Abbottabad City, Pakistan from Sentinel-1A Data and MT-InSAR. Remote Sensing, 12(20), 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203442