Spatial Analysis of Land Subsidence in the San Luis Potosi Valley Induced by Aquifer Overexploitation Using the Coherent Pixels Technique (CPT) and Sentinel-1 InSAR Observation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of Study Area
2.1. Description of San Luis Potosi Valley
2.2. Geological Settings
2.3. Groundwater Pumping and Piezometric Evolution
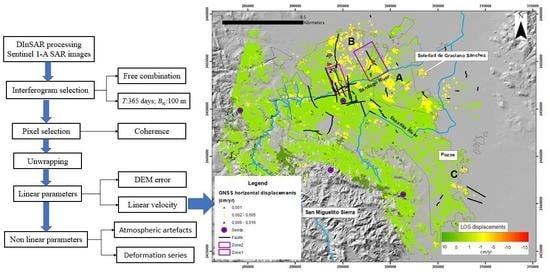
3. Methods and Data Processing
3.1. The Coherent Pixel Technique
3.2. Data Processing
3.3. GNSS Data Processing
4. CPT Results and Analysis
4.1. Deformation Rate Map
4.2. Validation of Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Relationship between Faults and Land Subsidence
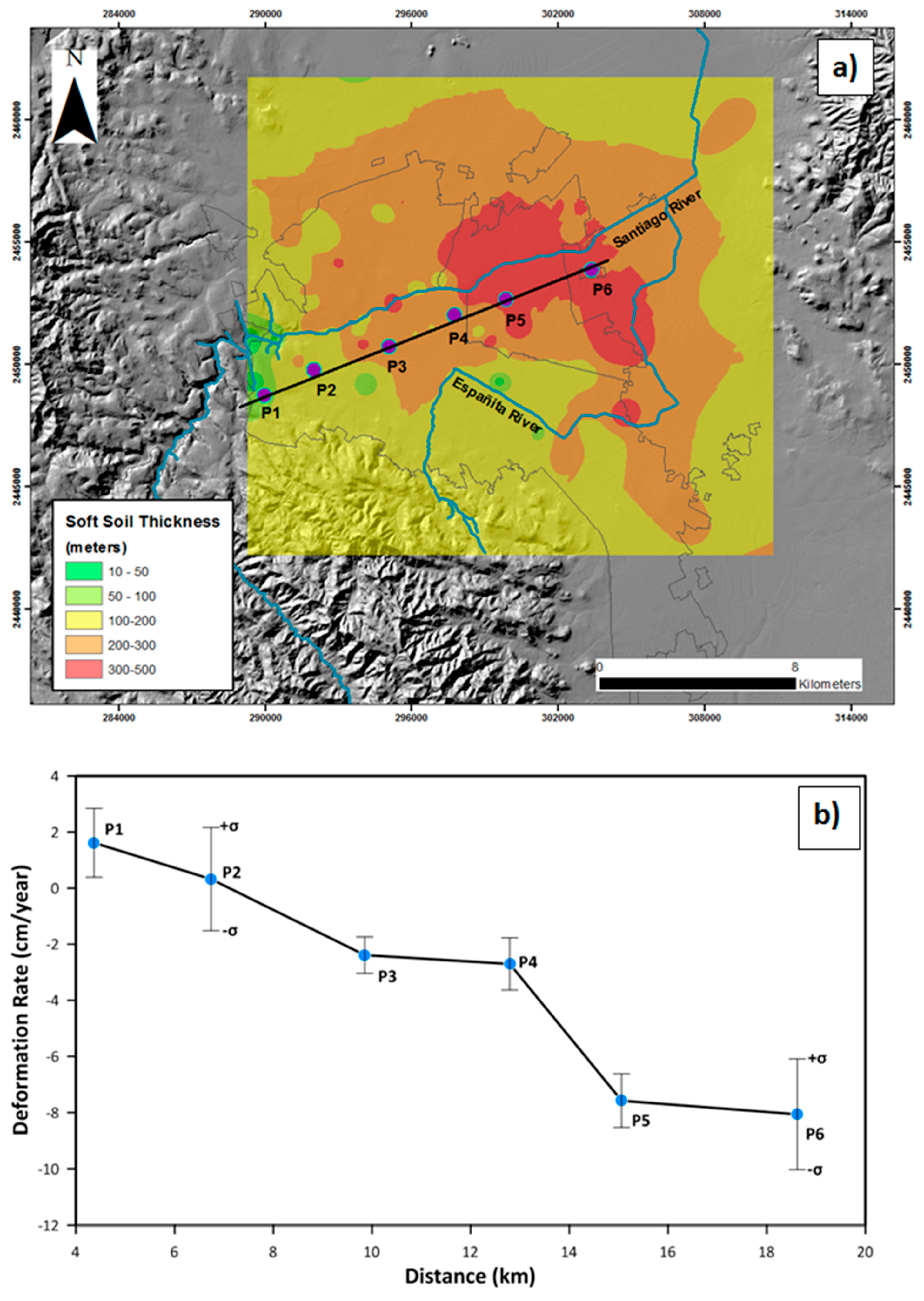
5.2. Relationship between Soft Soil Thickness and Land Subsidence
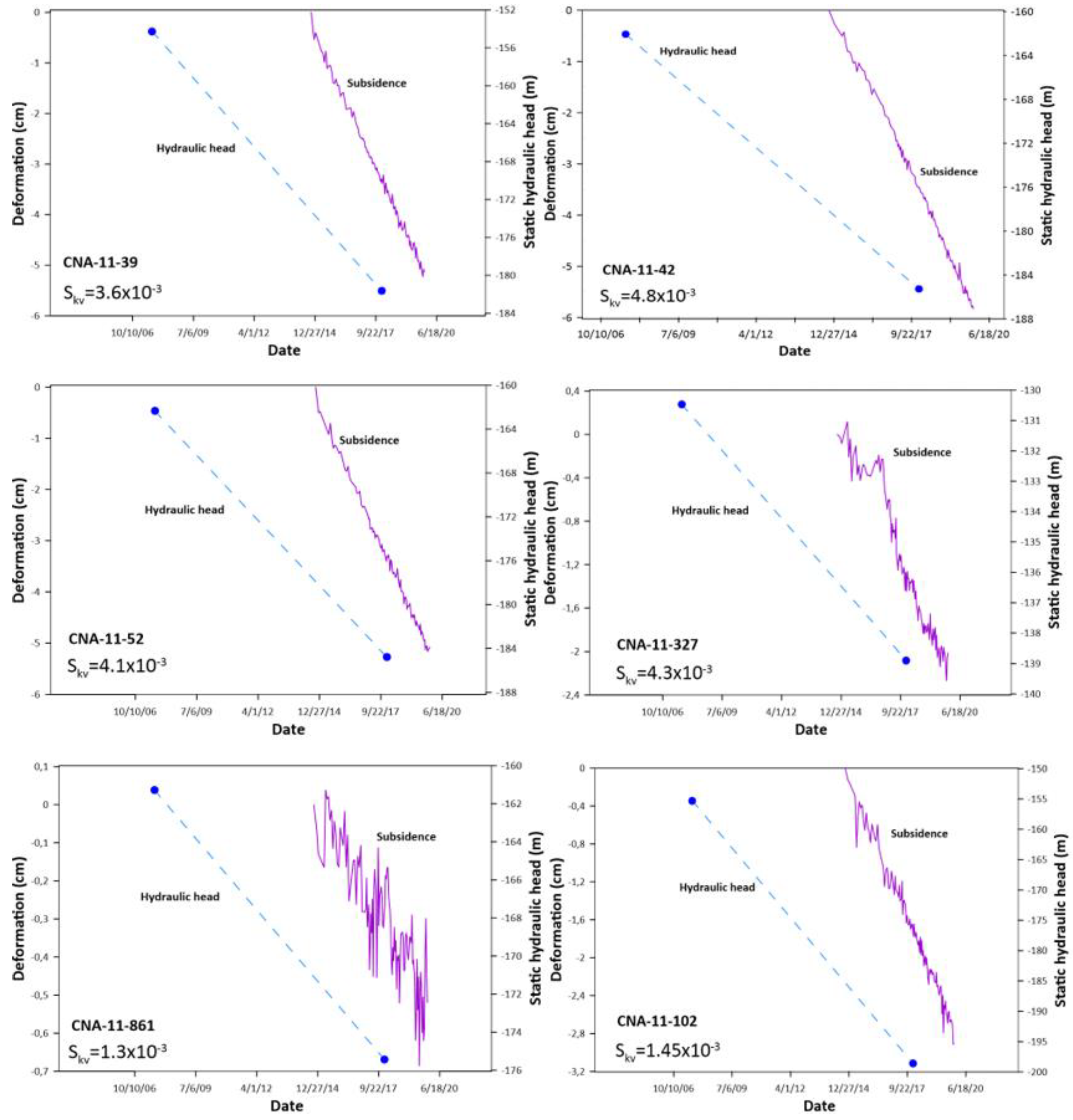
5.3. Relationship between Piezometric Level Evolution and Land Subsidence
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galloway, D.L.; Bawden, G.W.; Leake, S.A.; Honegger, D.G. Land Subsidence Hazards. In Landslide L. Subsid. Hazards to Pipelines; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Modoni, G.; Darini, G.; Spacagna, R.; Saroli, M.; Russo, G.; Croce, P. Spatial analysis of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawal. Eng. Geol. 2013, 167, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Miranda, S.; Tuxpan-Vargas, J.; Ramos-Leal, J.A.; Hernández-Madrigal, V.M.; Villaseñor-Reyes, C.I. Land subsidence by groundwater over-exploitation from aquifers in tectonic valleys of Central Mexico: A review. Eng. Geol. 2018, 246, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, B.L.; Park, Y.-J.; Unger, A.J.; Sudicky, E.A. Simulating the pre-development hydrologic conditions in the San Joaquin Valley, California. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, P.-Y.; Gerard, P.; Pirard, E.; Perissin, D.; Walstra, J.; Devleeschouwer, X. Subsidence related to groundwater pumping for breweries in Merchtem area (Belgium), highlighted by Persistent Scaterrer Interferometry. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 63, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Arroyo-Domínguez, N.; Martel, R.; Calderhead, A.I.; Normand, J.C.L.; Gárfias, J.; Rivera, A. Land subsidence in major cities of Central Mexico: Interpreting InSAR-derived land subsidence mapping with hydrogeological data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 47, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowter, A.; Bin, M.; Amat, C.; Cigna, F.; Marsh, S.; Athab, A. Mexico City land subsidence in 2014–2015 with Sentinel-1 IW TOPS : Results using the Intermittent SBAS ( ISBAS ) technique. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmano, B.; Dixon, T.H.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-cano, E.; Jiang, Y. Mexico City subsidence observed with persistent scatterer InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Dai, K.; Xing, C.; Li, Z.; Tomás, R.; Clark, B.; Shi, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Qiu, Q.; et al. Land subsidence in Beijing and its relationship with geological faults revealed by Sentinel-1 InSAR observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 82, 101886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.-F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, N.-S. Monitoring large-area mining subsidence by GNSS based on IGS stations. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, B.; Dai, Z.; Teatini, P. Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal in the northern Beijing plain, China. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Lei, K.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Gao, M.; Guan, H.; Lv, W. Land subsidence lagging quantification in the main exploration aquifer layers in Beijing plain. China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 75, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wu, J.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, J. Regional land subsidence simulation in Su-Xi-Chang area and Shanghai City, China. Eng. Geol. 2008, 100, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Guangtong, S. Monitoring of urban subsidence with SAR interferometric point target analysis: A case study in Suzhou, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.L.; Yue, Z.Q.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, S.J. Review on current status and challenging issues of land subsidence in China. Eng. Geol. 2004, 76, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Pei, S.; Jimmy, J. Land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in Suzhou City, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W. Remote Sensing of Environment Monitoring land subsidence in the southern part of the lower Liaohe plain, China with a multi-track PS-InSAR technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomás, R.; Herrera, G.; Cooksley, G.; Mulas, J. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry subsidence data exploitation using spatial tools: The Vega Media of the Segura River Basin case study. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Fernández, J.A.; Tomás, R.; Cooksley, G.; Mulas, J. Advanced interpretation of subsidence in Murcia (SE Spain) using A-DInSAR data–modelling and validation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foroughnia, F.; Nemati, S.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Perissin, D. An iterative PS-InSAR method for the analysis of large spatio-temporal baseline data stacks for land subsidence estimation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 74, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudpour, M.; Khamehchiyan, M.; Nikudel, M.R.; Ghassemi, M.R. Characterization of regional land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawals in Tehran, Iran. Geopersia 2013, 3, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Poluzzi, L.; Barbarella, M.; Tavasci, L.; Gandolfi, S.; Cenni, N. Monitoring of the Garisenda Tower through GNSS using advanced approaches toward the frame of reference stations. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 38, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Garfias, J.; Martel, R.; Brouard, C.; Rivera, A. InSAR to support sustainable urbanization over compacting aquifers: The case of Toluca Valley, Mexico. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 63, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-González, G.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Franceschini, A.; Cerca, M.; Teatini, P. Overexploitation of groundwater resources in the faulted basin of Querétaro, Mexico: A 3D deformation and stress analysis. Eng. Geol. 2018, 245, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Martínez, J.; Hernandez-Marín, M.; Burbey, T.J.; González-Cervantes, N.; Ortíz-Lozano, J. Ángel; Zermeño-De-Leon, M.E.; Solís-Pinto, A. Land subsidence and ground failure associated to groundwater exploitation in the Aguascalientes Valley, México. Eng. Geol. 2013, 164, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Olivera, J.A.; Garduño-Monroy, V.H. A GPR study of subsidence-creep-fault processes in Morelia, Michoacán, Mexico. Eng. Geol. 2008, 100, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Osmanoglu, B.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Dixon, T.; Ávila-Olivera, J.; Garduño-Monroy, V.; DeMets, C.; Mdowinski, S. Remote Sensing of Environment Monitoring land subsidence and its induced geological hazard with Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry: A case study in Morelia, Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Marín, M.; Pachecomartinez, J.; Ramirez-Cortes, A.; Burbey, T.J.; Ortiz-Lozano, J.A.; Zermeño-De-Leon, M.E.; Guinzberg-Velmont, J.; Pinto-Aceves, G. Evaluation and analysis of surface deformation in west Chapala basin, central Mexico. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Ochoa-González, G.; Ye, S.; Galloway, D.; Hernández-Marin, M. Ground ruptures attributed to groundwater overexploitation damaging Jocotepec city in Jalisco, Mexico: 2016 field excursion of IGCP-641. Episodes 2018, 41, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julio-Miranda, P.; Órtiz-Rodríguez, A.; Palacio-Aponte, A.; López-Doncel, R.; Baroboza-Gudiño, R. Damage assessment associated with land subsidence metropolitan area, Mexico, elements for risk. Natural Hazards 2012, 64, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Romero, R.; Mulas, J.; Marturià, J.J.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; González, P.J.; Fernandez, J.M.G.; et al. Radar interferometry techniques for the study of ground subsidence phenomena: A review of practical issues through cases in Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khorrami, M.; Alizadeh, B.; Tousi, E.G.; Shakerian, M.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Rahgozar, P. How Groundwater Level Fluctuations and Geotechnical Properties Lead to Asymmetric Subsidence: A PSInSAR Analysis of Land Deformation over a Transit Corridor in the Los Angeles Metropolitan Area. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shi, M. Wuhan Surface Subsidence Analysis in 2015–2016 Based on Sentinel-1A Data by SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, K.; Shi, X.; Gou, J.; Hu, L.; Chen, M.; Zhao, L.; Dong, X.; Li, Z. Diagnosing Subsidence Geohazard at Beijing Capital International Airport, from High-Resolution SAR Interferometry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Tomás, R.; Li, Z.; Motagh, M.; Li, T.; Hu, L.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Gong, X. Imaging Land Subsidence Induced by Groundwater Extraction in Beijing (China) Using Satellite Radar Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aobpaet, A.; Cuenca, M.C.; Hooper, A.; Trisirisatayawong, I. Land subsidence evaluation usin InSAR time series analysis in Bankok metropolitan area. In Proceedings of the Fringe 2009 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 30 November–4 December 2009. (ESA SP-677, March 2010). [Google Scholar]
- Duque, S.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Blanco-Sánchez, P.; Monells, D. Application of the Coherent Pixels Technique (CPT) to urban monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2007 Urban Remote Sensing Joint Event, Paris, France, 11–13 April 2007; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, A.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Martínez-Díaz, J.J. Monitoring of Guadalentín valley (southern Spain) through a fast SAR Interferometry method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 91, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Loupasakis, C.; Rozos, D.; Adam, N.; Moretti, S. Ground subsidence phenomena in the Delta municipality region (Northern Greece): Geotechnical modeling and validation with Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 28, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amighpey, M.; Arabi, S. Remote Sensing Applications : Society and Environment Studying land subsidence in Yazd province, Iran, by integration of InSAR and levelling measurements. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Horst, T.; Rutten, M.M.; Van De Giesen, N.; Hanssen, R.F. Monitoring land subsidence in Yangon, Myanmar using Sentinel-1 persistent scatterer interferometry and assessment of driving mechanisms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderhead, A.I.; Therrien, R.; Rivera, A.; Martel, R.; Garfias, J. Advances in Water Resources Simulating pumping-induced regional land subsidence with the use of InSAR and field data in the Toluca Valley, Mexico. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarychikhina, O.; Glowacka, E.; Suarez-Vidal, F.; Mellors, R.; Hernández, J.R. Aplicación de DInSAR a los estudios de subsidencia en el Valle de Mexicali. Boletín Soc. Geológica Mex. 2011, 63, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Sánchez, P.; Mallorquí, J.; Duque, S.; Monells, D. The Coherent Pixels Technique (CPT): An Advanced DInSAR Technique for Nonlinear Deformation Monitoring. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2008, 165, 1167–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-márquez, E.L.; Ledesma, I.K.; Arango-galván, C. Sustainable geohydrological model of San Luis Potosí aquifer, Mexico. Geofísica Int. 2011, 50, 425–438. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, S.; Escolero, O.; Kralisch, S. Water Management in San Luis Potosí Metropolitan Area, Mexico. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2010, 26, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-alvarez, B.; Ramos-leal, J.A.; Leon, G.S.; Morán-ramirez, J.; Carranco-lozada, S.E.; Noyola-medrano, C. Subsidence Associated with Land Use Changes in Urban Aquifers with Intensive Extraction. Nat. Sci. 2013, 5, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Hernández, J. Identificación de la Recarga Natural e Inducida en la Cuenca de San Luis Potosí. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí, San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tristán-gonzález, M.; Aguillón-Robles, A.; Barboza-Gudiño, J.; Torres-Hernández, J.; Bellon, H.; López-Doncel, R.; Rodríguez-Ríos, R.; Labarthe-Hernández, G. Geocronología y distribución espacial del vulcanismo en el Campo Volcánico de San Luis Potosí. Boletín Soc. Geológica Mex. 2009, 61, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Banda, L. Identificación de la Contaminación Difusa en el Acuífero Somero de la Ciudad de San Luis Potosí. Ph.D. Thesis, Univerisidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí, San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Aguillón-Robles, A. Cartografía Geológica de las Hojas Espíritu Santo, Pinos, El Obraje, Ojuelos, Edos. de San Luis Potosí, Jalisco, Guanajuato y Zacatecas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí, San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Heiming, A. Numerical modeling with vertical flow component of the deep aquifer in the graben of San Luis Potosí, Mexico. Master’s Thesis, RWTH AAchen University, Aachen, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Noyola-Medrano, M.C.; Ramos-Leal, J.A.; Domínguez-Mariani, E.; Pineda-Martínez, L.F.; López-Loera, H.; Carbajal, N. Factores que dan origen al minado de acuíferos en ambientes áridos: Caso Valle de San Luis Potosí. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2009, 26, 395–410. [Google Scholar]
- CONAGUA. Actualización de la Disponibilidad Media Anual de Agua en el Acuífero San Luis Potosí (2411) Estado de San Luis Potosí; Diario oficial de la federación: San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez, J.; Romero, R.; Carrasco, D.; Martínez, A.; Mallorquí, J.J. Advanced DInSAR based on Coherent Pixels: Development and results using CPT technique. In Proceedings of the Fringe 2005 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 28 November–2 December 2005; Volume 610, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Awange, J.L. GNSS Enviromental Sensing: Revolutionizing Enviromental Monitoring; No. 9783540882558; Springer: Perth, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, D.; Jones, D.R.; Ingebritsen, S.E. Land Subsidence in the United States; U.S.Geolog.: Reston, VI, USA, 1999.
- Conway, B.D. Land subsidence and earth fissures in south-central and southern Arizona, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 24, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, R.; Herrera, G.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Vicente, F.; Cuenca, A.; Mallorquí, J.J. Study of the land subsidence in Orihuela City (SE Spain) using PSI data: Distribution, evolution and correlation with conditioning and triggering factors. Eng. Geol. 2010, 115, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Ezquerro, P.; Herrera, G.; Tomás, R.; Guardiola-Albert, C.; Ruiz, J.; Fernández, J.; Marchamalo, M.; Martínez, R. Mapping groundwater level and aquifer storage variations from InSAR measurements in the Madrid aquifer, Central Spain. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hudnut, K.W.; Ingebritsen, S.E.; Phillips, S.P.; Peltzer, G.; Rogez, F.; Rosen, P.A. Detection of aquifer system compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, F.S. Analysis of borehole extensometer data from central California, in Land Subsidence, vol. 2, edited by L. K. Tison. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. 1969, 89, 423–431. [Google Scholar]
- Tomás, R.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Delgado, J.; Mallorquí, J.J. Hydrological parameters of the vega media of the segura river aquifer (SE Spain) obtained by means of advanced DInSAR. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hoffmann, J. The application of satellite differential SAR interferometry-derived ground displacements in hydrogeology. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomás, R.; Herrera, G.; Delgado, J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Mulas, J. A ground subsidence study based on DInSAR data: Calibration of soil parameters and subsidence prediction in Murcia City (Spain). Eng. Geol. 2010, 111, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Zebker, H.A.; Galloway, D.L.; Amelung, F. Seasonal subsidence and rebound in Las Vegas Valley, Nevada, observed by synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro-Hernández, M.I.; Tomás, R.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Cárdenas-Tristán, A.; Mallorquí, J.J. Spatial Analysis of Land Subsidence in the San Luis Potosi Valley Induced by Aquifer Overexploitation Using the Coherent Pixels Technique (CPT) and Sentinel-1 InSAR Observation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223822
Navarro-Hernández MI, Tomás R, Lopez-Sanchez JM, Cárdenas-Tristán A, Mallorquí JJ. Spatial Analysis of Land Subsidence in the San Luis Potosi Valley Induced by Aquifer Overexploitation Using the Coherent Pixels Technique (CPT) and Sentinel-1 InSAR Observation. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(22):3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223822
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro-Hernández, María Inés, Roberto Tomás, Juan M. Lopez-Sanchez, Abraham Cárdenas-Tristán, and Jordi J. Mallorquí. 2020. "Spatial Analysis of Land Subsidence in the San Luis Potosi Valley Induced by Aquifer Overexploitation Using the Coherent Pixels Technique (CPT) and Sentinel-1 InSAR Observation" Remote Sensing 12, no. 22: 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223822
APA StyleNavarro-Hernández, M. I., Tomás, R., Lopez-Sanchez, J. M., Cárdenas-Tristán, A., & Mallorquí, J. J. (2020). Spatial Analysis of Land Subsidence in the San Luis Potosi Valley Induced by Aquifer Overexploitation Using the Coherent Pixels Technique (CPT) and Sentinel-1 InSAR Observation. Remote Sensing, 12(22), 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223822