Downscaling TRMM Monthly Precipitation Using Google Earth Engine and Google Cloud Computing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Precipitation
2.2.2. Vegetation
2.2.3. Land Cover
2.2.4. Elevation
2.2.5. Rain Gauge
2.3. Machine Learning Algorithms
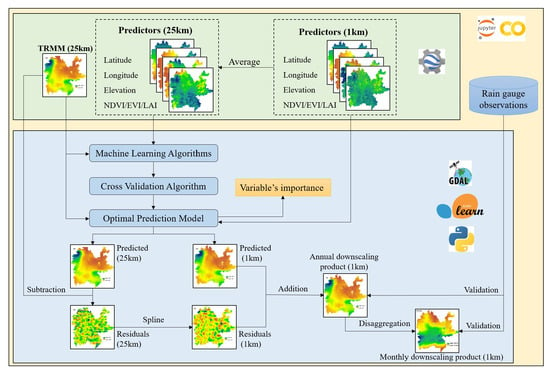
2.4. Downscaling Framework
2.4.1. Data Preparation and Pre-Processing
2.4.2. Hyper-Parameter Optimization
2.4.3. Generation of 1 km TRMM Product
2.4.4. Assessment Indices
3. Results
3.1. The Optimal Prediction Model
3.2. Variable Importance
3.3. Annual Downscaled Products
3.4. Monthly Downscaled Products
4. Discussion
4.1. Result Compared to Previous Studies
4.2. Importance of Each Predictor and the Role of Vegetation Indices in TRMM Downscaling
4.3. Advantage and Disadvantage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Source Code
Appendix A
| Reference | Predictors | Residual correction | Regression model | Performance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | MAE | ||||
| (mm month−1) | ||||||
| [34] * | DEM, aspect, roughness, humidity, temperature | Spline | MLR | 0.58 | 19.99 | -- |
| TRMM | 0.58 | 39.45 | -- | |||
| [24] | NDVI, DEM | Area-to-point Kriging | MLR | -- | 20.03 | 13.03 |
| Ordinary Kriging | -- | 24.81 | 17.73 | |||
| [57] | DEM, Long, Lat | Spline | ANN | 0.936 | 40.56 | -- |
| MF | 0.934 | 41.20 | -- | |||
| [74] | NDVI, LST, DEM, slope, Long, Lat | Ordinary Kriging | GWRK | 0.95 | 25 | 16 |
| TRMM | 0.95 | 30 | 19 | |||
| [75] | EVI, DEM, aspect, slope, Long, Lat | Bilinear | RF | 0.78 | 25 | 14 |
| TRMM | 0.73 | 31 | 16 | |||
| [54] | NDVI, VWSI, albedo, DEM, | Spline | MLR | 0.47 | 54 | -- |
| ANN | 0.60 | 59 | -- | |||
| TRMM | -- | 37 | -- | |||
| [76] | NDVI, DEM, LST | - | SVM | 0.75 | 29.90 | -- |
| RF | 0.82 | 26.10 | -- | |||
| [35] | NDVI, DEM, LST | Spline | MLR | 0.46 | 27 | 14 |
| kNN | 0.71 | 17 | 12 | |||
| CART | 0.70 | 18 | 12 | |||
| SVM | 0.73 | 16 | 11 | |||
| RF | 0.74 | 16 | 11 | |||
| [29] ** | NDVI, DEM, slope, Long, Lat | Kriging | GWRK | 0.91 | 22.2 | 13.5 |
| 0.84 | 7.50 | 4.8 | ||||
| 0.80 | 30.5 | 22.2 | ||||
| TRMM | 0.88 | 26.5 | 13.7 | |||
| -- | 5.10 | 3.8 | ||||
| 0.69 | 37.1 | 23.7 | ||||
| [25] *** | NDVI, DEM | Bilinear | Exponential | 0.74 | 24 | -- |
| 0. 60 | 25 | |||||
| GWR | 0.67 | 32 | -- | |||
| 0.42 | 20 | |||||
| MLR | 0.80 | 22 | -- | |||
| 0.26 | 15 | |||||
| QPP | 0.89 | 16 | -- | |||
| 0.45 | 11 | |||||
| TRMM | 0.94 | 11 | -- | |||
| 0.64 | 9 | -- | ||||
| [77] | DEM, Long, Lat, TRMM-1 km | - | GWR | 0.87 | 32.92 | 18.19 |
| Ordinary Kriging | GWRK | 0.89 | 31.11 | 17.05 | ||
| TRMM downscaled by ATPK to 1 km (TRMM-1 km) | 0.76 | 46.14 | 26.44 | |||
| TRMM | 0.72 | 49.63 | 28.66 | |||
| [30] | EVI, DEM | -- | GWR | -- | -- | -- |
| NDVI, DEM | 0.86 | 35 | 23 | |||
| TRMM | 0.85 | 38 | 26 | |||
Appendix B
| Metrics | Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p-Value | F crit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Between Groups | 0.0008 | 2 | 0.00038 | 20 | 0.002 | 5.14 |
| Within Groups | 0.0001 | 6 | 0.00002 | ||||
| Total | 0.0009 | 8 | |||||
| RMSE | Between Groups | 2069 | 2 | 1035 | 22 | 0.002 | 5.14 |
| Within Groups | 286 | 6 | 48 | ||||
| Total | 2355 | 8 | |||||
| MAE | Between Groups | 728 | 2 | 364 | 72 | 0.0001 | 5.14 |
| Within Groups | 30 | 6 | 5 | ||||
| Total | 758 | 8 |
Appendix C

Appendix D

References
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Duan, Z. Hydrologic evaluation of TRMM and GPM IMERG Satellite-Based precipitation in a Humid Basin of China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.; Wu, W.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Ji, X. Hydrological simulation using TRMM and CHIRPS precipitation estimates in the Lower Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Hirose, M.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Global Precipitation Map Using Satellite-Borne Microwave Radiometers by the GSMaP Project: Production and Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations-a new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily Precipitation Climate Data Record from Multisatellite Observations for Hydrological and Climate Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.K.; Shige, S. Implementation of an orographic/nonorographic rainfall classification scheme in the GSMaP algorithm for microwave radiometers. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wu, B.; Zhang, N.; Tian, F.; Phiri, E.; Musakwa, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, L.; Mashonjowa, E. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Precipitation in the Sparsely Gauged Zambezi River Basin Using Remote Sensing and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Guo, B.; Su, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J. Multidimensional evaluation of the TRMM 3B43V7 satellite-based precipitation product in mainland China from 1998–2016. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Song, L.; Xia, Z.; Lin, Y.; Myneni, R.B.; Choi, S.; Wang, L.; Ni, X.; Lao, C.; Yang, F. Mapping annual precipitation across Mainland China in the Period 2001–2010 from TRMM3B43 product using spatial downscaling approach. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikary, S.K.; Yilmaz, A.G.; Muttil, N. Optimal design of rain gauge network in the Middle Yarra River catchment, Australia. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2582–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, W.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhao, X. A Spatial Downscaling Algorithm for Satellite-Based Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau Based on NDVI, DEM, and Land Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulloa, J.; Ballari, D.; Campozano, L.; Samaniego, E. Two-Step Downscaling of TRMM 3B43 V7 Precipitation in Contrasting Climatic Regions with Sparse Monitoring: The Case of Ecuador in Tropical South America. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weltzin, J.F.; Loik, M.E.; Schwinning, S.; Williams, D.G.; Fay, P.A.; Haddad, B.M.; Harte, J.; Huxman, T.E.; Knapp, A.K.; Lin, G.; et al. Assessing the Response of Terrestrial Ecosystems to Potential Changes in Precipitation. BioScience 2003, 53, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, D.L.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Butterfield, B.J.; Fay, P.A.; Hultine, K.R. Bloom and Bust: Ecological consequences of precipitation variability in aridlands. Plant Ecol. 2019, 220, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Smith, L.; Qian, T.; Dai, A.; Fasullo, J. Estimates of the Global Water Budget and Its Annual Cycle Using Observational and Model Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Beaudoing, H.K.; L’Ecuyer, T.S.; Olson, W.S.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Houser, P.R.; Adler, R.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Clayson, C.A.; Chambers, D.; et al. The Observed State of the Water Cycle in the Early Twenty-First Century. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 8289–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, R.; Meadows, M.E.; Ji, G.; Xu, J. Modelling water yield with the InVEST model in a data scarce region of northwest China. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López López, P.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Rodríguez Sandoval, E.A.; Sterk, G.; Schellekens, J. Spatial Downscaling of Satellite-Based Precipitation and Its Impact on Discharge Simulations in the Magdalena River Basin in Colombia. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutta, D.; Das, S.; Kundu, A.; Taj, A. Soil erosion risk assessment in Sanjal watershed, Jharkhand (India) using geo-informatics, RUSLE model and TRMM data. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2015, 1, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Ma, Z.; Chappell, A.; Shi, Z.; Liang, Z.; Yu, W. Improving Rainfall Erosivity Estimates Using Merged TRMM and Gauge Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phinzi, K.; Ngetar, N.S. The assessment of water-borne erosion at catchment level using GIS-based RUSLE and remote sensing: A review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.-W. Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation using geostatistics and fine scale environmental variables. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 237126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, Q.; Xu, L.; Jiang, Y. Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation data considering the impacts of macro-geographical factors and local elevation in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, R.; Yarlequé, C.; Posadas, A.; Mares, V.; Immerzeel, W.W. Improving daily rainfall estimation from NDVI using a wavelet transform. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. First results from version 7 TRMM 3B43 precipitation product in combination with a new downscaling-calibration procedure. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Nie, N. Spatial Downscaling of TRMM precipitation data using an optimal subset regression model with NDVI and terrain factors in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 3491960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Luo, X.; Li, X. Fine-resolution precipitation mapping in a mountainous watershed: Geostatistical downscaling of TRMM products based on environmental variables. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; She, D.; Chen, J. Spatial downscaling of Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) annual and monthly precipitation data over the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin, China. Water 2019, 11, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maki, M.; Homma, K. Empirical Regression Models for Estimating Multiyear Leaf Area Index of Rice from Several Vegetation Indices at the Field Scale. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4764–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Din, M.; Zheng, W.; Rashid, M.; Wang, S.; Shi, Z. Evaluating hyperspectral vegetation indices for leaf area index estimation of Oryza sativa L. at diverse phenological stages. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Zhu, W.; Lű, A.; Yan, T. A statistical spatial downscaling algorithm of TRMM precipitation based on NDVI and DEM in the Qaidam Basin of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3069–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Du, J.; Xu, W.; Shi, P.; Li, M.; Ming, X. Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation data based on the orographical effect and meteorological conditions in a mountainous area. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 61, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhao, X. A Comparison of Different Regression Algorithms for Downscaling Monthly Satellite-Based Precipitation over North China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Mutanga, O. Google Earth Engine applications since inception: Usage, trends, and potential. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobell, D.B.; Thau, D.; Seifert, C.; Engle, E.; Little, B. A scalable satellite-based crop yield mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelestov, A.; Lavreniuk, M.; Kussul, N.; Novikov, A.; Skakun, S. Exploring Google Earth Engine platform for big data processing: Classification of multi-temporal satellite imagery for crop mapping. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, D.; Kumar, V.; Bhattacharya, A.; Rao, Y.S.; Siqueira, P.; Bera, S. Sen4Rice: A Processing Chain for Differentiating Early and Late Transplanted Rice Using Time-Series Sentinel-1 SAR Data with Google Earth Engine. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wu, B.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. Efficient identification of corn cultivation area with multitemporal synthetic aperture radar and optical images in the Google Earth Engine cloud platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, T.; Zhang, Z.; He, G.; Jiao, W.; Tang, C.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Yin, R. 30 m resolution global annual burned area mapping based on Landsat images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso, A.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Kennedy, R.E.; Murcia, C. Wetland landscape spatio-temporal degradation dynamics using the new Google Earth Engine cloud-based platform: Opportunities for non-specialists in remote sensing. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 59, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Stow, D.; Chen, H.L.; Lewison, R.; An, L.; Shi, L. Mapping Vegetation and Land Use Types in Fanjingshan National Nature Reserve Using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E. The first wetland inventory map of Newfoundland at a spatial resolution of 10 m using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data on the Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Gan, R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; McVicar, T.R.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. Coupled estimation of 500m and 8-day resolution global evapotranspiration and gross primary production in 2002–2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foolad, F.; Blankenau, P.; Kilic, A.; Allen, R.G.; Huntington, J.L.; Erickson, T.A.; Ozturk, D.; Morton, C.G.; Ortega, S.; Ratcliffe, I. Comparison of the automatically calibrated Google evapotranspiration application-EEFlux and the manually calibrated METRIC application. Preprints 2018, 2018070040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, T.; Da Nóbrega, R.V.M.; Nepomuceno, T.; Bian, G.-B.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Filho, P.P.R. Performance analysis of Google Colaboratory as a tool for accelerating deep learning applications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 61677–61685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmerdam, F. The Geospatial Data Abstraction Library. In Open Source Approaches in Spatial Data Handling; Hall, G.B., Leahy, M.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisong, E. Google Colaboratory. In Building Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models on Google Cloud Platform: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners; Bisong, E., Ed.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, C. Spatiotemporal analysis of precipitation trends under climate change in the upper reach of Mekong River basin. Quat. Int. 2016, 392, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Xin, H.; Zhang, W.; Cao, W. Spatial and temporal trends of temperature and precipitation during 1960–2008 at the Hengduan Mountains, China. Quat. Int. 2011, 236, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.M.; Xiao, H.F.; Tong, G.B. The variation of the southwest monsoon from the high resolution pollen record in Heqing Basin, Yunnan Province, China for the last 2.78Ma. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2010, 287, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.D.; Tsanis, I.K. Comparison of multiple linear regression and artificial neural network models for downscaling TRMM precipitation products using MODIS data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Wu, H.; Dong, G.; Jiang, X.; Xue, H. A Temporal Disaggregation Approach for TRMM Monthly Precipitation Products Using AMSR2 Soil Moisture Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunink, J.E.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P. A High-resolution Precipitation 2-step mapping Procedure (HiP2P): Development and application to a tropical mountainous area. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, A.Y.; Wang, K. Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation product using a combined multifractal and regression approach: Demonstration for South China. Water 2015, 7, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4, Available from the CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90 m. 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Thirion, B.; Michel, V.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.H. Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2002, 38, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smola, A.J.; Schölkopf, B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Specht, D.F. A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E. Connectionist learning procedures. Artif. Intell. 1989, 40, 185–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Das, I.; Gairola, R.; Sarkar, A.; Agarwal, V.K. Rainfall retrieval from TRMM radiometric channels using artificial neural networks. Indian J. Radio Space Phys. 2007, 36, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht-Nielsen, R. Kolmogorov’s mapping neural network existence theorem. In Proceedings of the IEEE First International Conference on Neural Networks, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–24 June 1987; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- LeNail, A. NN-SVG: Publication-Ready Neural Network Architecture Schematics. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.; Rutten, M.; Droogers, P. Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation using vegetative response on the Iberian Peninsula. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.F.; Golub, G.H.; Leveque, R.J. Algorithms for Computing the Sample Variance: Analysis and Recommendations. Am. Stat. 1983, 37, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, Y. A spatial data mining algorithm for downscaling TMPA 3B43 V7 data over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau with the effects of systematic anomalies removed. Remote Sens. 2017, 200, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jing, W.; Zhang, P. Mapping Fine Spatial Resolution Precipitation from TRMM Precipitation Datasets Using an Ensemble Learning Method and MODIS Optical Products in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keppel, G.; Zedeck, S. Data Analysis for Research Designs: Analysis of Variance and Multiple Regression/Correlation Approaches; Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, D.; Luo, X.; Ji, X. Spatial downscaling of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission precipitation using geographically weighted regression kriging over the Lancang River Basin, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Song, L. Spatial downscaling of monthly TRMM precipitation based on EVI and other geospatial variables over the Tibetan Plateau from 2001 to 2012. Mt. Res. Dev. 2015, 35, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, X. Reconstructing Satellite-Based Monthly Precipitation over Northeast China Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Sheng, S.; Mansaray, L.R.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, X. A new downscaling-integration framework for high-resolution monthly precipitation estimates: Combining rain gauge observations, satellite-derived precipitation data and geographical ancillary data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Predictors | R2 | RMSE | MAE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static | Dynamic | ANN | GBR | SVR | ANN | GBR | SVR | ANN | GBR | SVR |
| Elevation, Longitude, Latitude | NDVI | 0.983 | 0.971 | 0.953 | 73 | 95 | 121 | 54 | 69 | 77 |
| EVI | 0.984 | 0.975 | 0.959 | 71 | 89 | 114 | 51 | 66 | 76 | |
| LAI | 0.977 | 0.97 | 0.965 | 85 | 96 | 105 | 56 | 67 | 72 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elnashar, A.; Zeng, H.; Wu, B.; Zhang, N.; Tian, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, W.; Yan, N.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Z.; et al. Downscaling TRMM Monthly Precipitation Using Google Earth Engine and Google Cloud Computing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233860
Elnashar A, Zeng H, Wu B, Zhang N, Tian F, Zhang M, Zhu W, Yan N, Chen Z, Sun Z, et al. Downscaling TRMM Monthly Precipitation Using Google Earth Engine and Google Cloud Computing. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(23):3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233860
Chicago/Turabian StyleElnashar, Abdelrazek, Hongwei Zeng, Bingfang Wu, Ning Zhang, Fuyou Tian, Miao Zhang, Weiwei Zhu, Nana Yan, Zeqiang Chen, Zhiyu Sun, and et al. 2020. "Downscaling TRMM Monthly Precipitation Using Google Earth Engine and Google Cloud Computing" Remote Sensing 12, no. 23: 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233860
APA StyleElnashar, A., Zeng, H., Wu, B., Zhang, N., Tian, F., Zhang, M., Zhu, W., Yan, N., Chen, Z., Sun, Z., Wu, X., & Li, Y. (2020). Downscaling TRMM Monthly Precipitation Using Google Earth Engine and Google Cloud Computing. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233860