Spaceborne Multifrequency PolInSAR-Based Inversion Modelling for Forest Height Retrieval
Abstract
1. Introduction
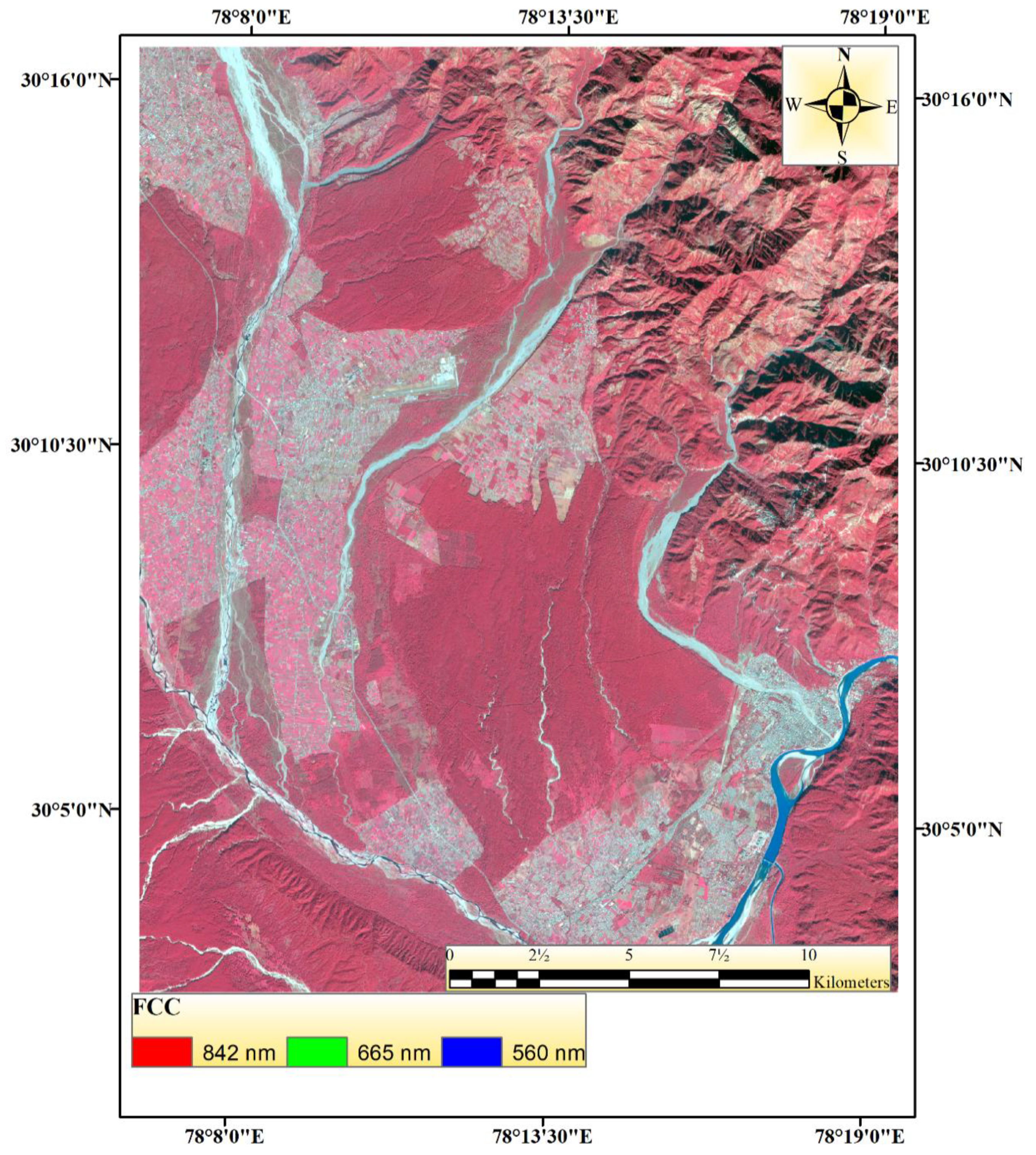
2. Study Area and Dataset
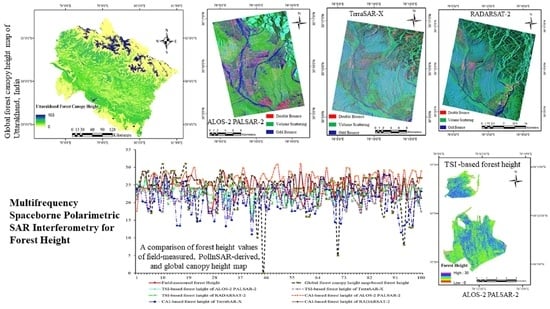
2.1. Global Forest Canopy Height Map
2.2. Polarimetric SAR Interferometry (PolInSAR) Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Three-Stage Inversion (TSI) Modelling
3.2. Coherence Amplitude Inversion (CAI) Modelling
4. Results
Multifrequency PolInSAR Data for Forest Height Estimation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chirici, G.; Chiesi, M.; Corona, P.; Salvati, R.; Papale, D.; Fibbi, L.; Sirca, C.; Spano, D.; Duce, P.; Marras, S.; et al. Estimating daily forest carbon fluxes using a combination of ground and remotely sensed data. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adloff, M.; Reick, C.H.; Claussen, M. Earth system model simulations show different feedback strengths of the terrestrial carbon cycle under glacial and interglacial conditions. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2018, 9, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pang, B.; Zhang, Z. Carbon footprint analysis of two different types of hydropower schemes: Comparing earth-rockfill dams and concrete gravity dams using hybrid life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Zeng, X.; Sakaguchi, K.; Monson, R.K.; Zeng, X. Terrestrial carbon cycle: Climate relations in eight CMIP5 earth system models. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8744–8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.; Scholes, R.J.; Boyle, E.; Canadell, J.; Canfield, D.; Elser, J.; Gruber, N.; Hibbard, K.; Hogberg, P.; Linder, S.; et al. The global carbon cycle: A test of our knowledge of earth as a system. Science 2000, 290, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.D.; Calvin, K.V.; Shi, X.; Di Vittorio, A.V.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Thornton, P.E.; Collins, W.D. Quantifying Human-Mediated Carbon Cycle Feedbacks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 11370–11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, C.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yang, G.; Tian, J.; et al. The impacts of climate change and human activities on biogeochemical cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2940–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.R. Ecosystem Services and the Global Carbon Cycle. In Ecosystem Services and Carbon Sequestration in the Biosphere; Lal, R., Lorenz, K., Hüttl, R.F., Schneider, B.U., von Braun, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 155–181. ISBN 978-94-007-6455-2. [Google Scholar]
- Van Leeuwen, M.; Nieuwenhuis, M. Retrieval of forest structural parameters using LiDAR remote sensing. Eur. J. For. Res. 2010, 129, 749–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, A.; Astrup, R.; Breidenbach, J.; Fridman, J.; Gobakken, T.; Korhonen, K.T.; Maltamo, M.; Nilsson, M.; Nord-Larsen, T.; Næsset, E.; et al. Remote sensing and forest inventories in Nordic countries–roadmap for the future. Scand. J. For. Res. 2018, 33, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, C.; Im, J. A review of remote sensing of forest biomass and biofuel: Options for small-area applications. GIScience Remote Sens. 2011, 48, 141–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; An, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, H. A review on forest ecosystem biophysical parameter retrieval from remotely sensed data. Chin. J. Ecol. 2005, 24, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. Review of forest vertical structure parameter inversion based on remote sensing technology. Yaogan Xuebao/J. Remote Sens. 2013, 17, 697–716. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, D.A.; Washington-Allen, R.A.; Shugart, H.H. Remote sensing of boreal forest biophysical and inventory parameters: A review. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 34, S286–S313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, M.; Polcyn, F.; Imhoff, M.; Vermillion, C.; Khan, F. Forest Canopy Characterization and Vegetation Penetration Assessment with Space-Borne Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, GE-24, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Beaudoin, A.; Le Toan, T.; Goze, S.; Nezry, E.; Lopes, A.; Mougin, E.; Hsu, C.C.; Han, H.C.; Kong, J.A.; Shin, R.T. Retrieval of forest biomass from SAR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 2777–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckman, A.; Baker, J.; Kuplich, T.M.; Corina da Costa, F.Y.; Alejandro, C.F. A study of the relationship between radar backscatter and regenerating tropical forest biomass for spaceborne SAR instruments. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckman, A.J. Correction of SAR imagery for variation in pixel scattering area caused by topography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, U.; Kushwaha, S.P.; Chatterjee, R.S.; Bijker, W. Aboveground biomass estimation of tropical forest from Envisat advanced synthetic aperture radar data using modeling approach. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, R.; Mathieu, R.; Kleynhans, W.; Wessels, K.; Naidoo, L.; Asner, G.P. Hyper-temporal C-band SAR for baseline woody structural assessments in deciduous savannas. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaglio, G.L.; Pirotti, F.; Callegari, M.; Chen, Q.; Cuozzo, G.; Lingua, E.; Notarnicola, C.; Papale, D. Potential of ALOS2 and NDVI to estimate forest above-ground biomass, and comparison with lidar-derived estimates. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningthoujam, R.K.; Balzter, H.; Tansey, K.; Morrison, K.; Johnson, S.C.M.; Gerard, F.; George, C.; Malhi, Y.; Burbidge, G.; Doody, S.; et al. Airborne S-band SAR for forest biophysical retrieval in temperate mixed forests of the UK. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, P.S.; Kumar, S.; Kushwaha, S.P.S.; Bijker, W. Polarimetric scattering model for estimation of above ground biomass of multilayer vegetation using ALOS-PALSAR quad-pol data. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 83–84, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, S.; Næsset, E.; Gobakken, T.; Bollandsås, O.-M. Forest biomass change estimated from height change in interferometric SAR height models. Carbon Balance Manag. 2014, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefsky, M.A.; Harding, D.J.; Keller, M.; Cohen, W.B.; Carabajal, C.C.; Bom Espirio-Santo, F.; Hunter, M.O.; Oliveira, R. Estimates of forest canopy height and aboveground biomass using ICESat. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, R.; Xiao, Z. Estimation of forest canopy height and aboveground biomass from spaceborne LiDAR and Landsat imageries in Maryland. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ouyang, S.; Sun, O.J.; Fang, J. Forest biomass patterns across northeast China are strongly shaped by forest height. For. Ecol. Manage. 2013, 293, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Madsen, S.N.; Moghaddam, M.; van Zyl, J.J. Vegetation characteristics and underlying topography from interferometric radar. Radio Sci. 1996, 31, 1449–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzter, H.; Rowland, C.S.; Saich, P. Forest canopy height and carbon estimation at Monks Wood National Nature Reserve, UK, using dual-wavelength {SAR} interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askne, J.I.H.; Dammert, P.B.G.; Ulander, L.M.H.; Smith, G.S. C-Band Repeat-Pass Interferometric SAR Observations of the Forest. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldini, S. Single and multipolarimetric SAR tomography of forested areas: A parametric approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2375–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, E.; Nannini, M.; Reigber, A. Wavelet-based compressed sensing for SAR tomography of forested areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 5283–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannini, M.; Scheiber, R.; Horn, R.; Moreira, A. First 3-D reconstructions of targets hidden beneath foliage by means of polarimetric SAR tomography. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Joshi, S.K. SAR Tomography for forest structure investigation. In Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Microwave Conference 2016, New Delhi, India, 5–9 December 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y. Polarimetric SAR Interferometry: A Tutorial for Analyzing System Parameters. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. PolInSAR and PolTomSAR based Modelling for Characterization of Forest Parameters; Indian Institute of Technology: Roorkee, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.; Champion, I.; Toan, T. Le Pine forest investigation using high resolution P-band Pol-InSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2897–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Toan, T.; Quegan, S.; Davidson, M.W.J.; Balzter, H.; Paillou, P.; Papathanassiou, K.; Plummer, S.; Rocca, F.; Saatchi, S.; Shugart, H.; et al. The BIOMASS mission: Mapping global forest biomass to better understand the terrestrial carbon cycle. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oveisgharan, S.; Saatchi, S.S.; Hensley, S. Sensitivity of Pol-InSAR Measurements to Vegetation Parameters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6561–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Three-stage inversion process for polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2003, 150, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A. Estimation of forest structure, ground, and canopy layer characteristics from multibaseline polarimetric interferometric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1086–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asopa, U.; Kumar, S. UAVSAR Tomography for Vertical Profile Generation of Tropical Forest of Mondah National Park, Gabon. Earth Sp. Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, K.P.; Cloude, S.R. Single-baseline polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Pine forest height inversion using single-pass X-band PolInSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Saatchi, S.S.; Ulander, L.M.H.; Fransson, J.E.S. Assessing Performance of L- and P-Band Polarimetric Interferometric SAR Data in Estimating Boreal Forest Above-Ground Biomass. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroma, G.H.X.; de Macedo, K.A.C.; Wimmer, C.; Moreira, J.R.; Fernandes, D. The Dual-Band PolInSAR Method for Forest Parametrization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3189–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Khati, U.G.; Chandola, S.; Agrawal, S.; Kushwaha, S.P.S. Polarimetric SAR Interferometry based modeling for tree height and aboveground biomass retrieval in a tropical deciduous forest. Adv. Sp. Res. 2017, 60, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; He, B.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Bai, X.; Quan, X. The impacts of spatial baseline on forest canopy height model and digital terrain model retrieval using P-band PolInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, F.; Lee, S.-K.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Forest Height Estimation by Means of Pol-InSAR Data Inversion: The Role of the Vertical Wavenumber. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5294–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erten, E.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Yuzugullu, O.; Hajnsek, I. Retrieval of agricultural crop height from space: A comparison of SAR techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, C.; Fàbregas, X.; Pipia, L. Forest parameter estimation in the Pol-InSAR context employing the multiplicative–additive speckle noise model. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Vicente-Guijalba, F.; Erten, E.; Campos-Taberner, M.; Garcia-Haro, F.J. Retrieval of vegetation height in rice fields using polarimetric SAR interferometry with TanDEM-X data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebler, O.; Meier, E.; Nüesch, D. Multi-baseline polarimetric {SAR} interferometry—First experimental spaceborne and airborne results. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2002, 56, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, C.; Xu, X.; Chen, D. Forest vertical parameter estimation using PolInSAR imagery based on radiometric correction. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Guo, R.; Suo, Z.; Lu, H. S-RVoG model for forest parameters inversion over underlying topography. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 618–620. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Fu, H.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, J. The Impact of Forest Density on Forest Height Inversion Modeling from Polarimetric InSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Garg, R.D.; Kushwaha, S.P.S.; Jayawardhana, W.G.N.N.; Agarwal, S. Bistatic PolInSAR Inversion Modelling for Plant Height Retrieval in a Tropical Forest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. A Phys. Sci. 2017, 87, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sara, R.; Singh, J.; Agrawal, S.; Kushwaha, S.P.S. Spaceborne PolInSAR and ground-based TLS data modeling for characterization of forest structural and biophysical parameters. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 11, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Kommareddy, I. Global Forest Canopy Height. 2019. Available online: https://glad.umd.edu/dataset/gedi (accessed on 22 November 2020).
- Potapov, P.; Li, X.; Hernandez-Serna, A.; Tyukavina, A.; Hansen, M.C.; Kommareddy, A.; Pickens, A.; Turubanova, S.; Tang, H.; Silva, C.E.; et al. Mapping global forest canopy height through integration of GEDI and Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 112165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Prats-iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Sato, A.; Boerner, W.M.; Sato, R.; Yamada, H. Four-Component Scattering Power Decomposition With Rotation of Coherency Matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency Sentinel Application Platform (SNAP) V 6.0. Available online: https://step.esa.int/main/toolboxes/snap/ (accessed on 14 September 2018).
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A Review of Target Decomposition Theorems in Radar Polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Siqueira, P.R. Vertical structure of vegetated land surfaces from interferometric and polarimetric radar. Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 141–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Fu, H.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Ballester-Berman, J.D. A modified dual-baseline PolInSAR method for forest height estimation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; He, B.; Bai, X.; Quan, X. Improving Forest Height Retrieval by Reducing the Ambiguity of Volume-Only Coherence Using Multi-Baseline PolInSAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8856–8866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenxue, F.; Huadong, G.; Xinwu, L.; Bangsen, T.; Zhongchang, S. Extended Three-Stage Polarimetric SAR Interferometry Algorithm by Dual-Polarization Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2792–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khati, U.; Singh, G.; Kumar, S. Potential of Space-Borne PolInSAR for Forest Canopy Height Estimation Over India-A Case Study Using Fully Polarimetric L-, C-, and X-Band SAR Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2406–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Pol-InSAR Training Course. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/documents/653194/656796/Pol-InSAR_Training_Course.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Cloude, S.R. Polarization coherence tomography. Radio Sci. 2006, 41, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekanov, S.V. Probability and Statistics. In Numeric Computation and Statistical Data Analysis on the Java Platform; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 351–397. ISBN 978-3-319-28531-3. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; He, B.; Quan, X.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Qiu, S.; Yin, C. Biomass estimation in dense tropical forest using multiple information from single-baseline P-band PolInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denbina, M.; Simard, M.; Hawkins, B. Forest Height Estimation Using Multibaseline PolInSAR and Sparse Lidar Data Fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3415–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghabalaei, A.; Ebadi, H.; Maghsoudi, Y. Forest height estimation based on the RVoG inversion model and the PolInSAR decomposition technique. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 2684–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Hajnsek, I. Quantification of temporal decorrelation effects at L-band for polarimetric SAR interferometry applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, M.; Denbina, M. An assessment of temporal decorrelation compensation methods for forest canopy height estimation using airborne L-band same-day repeat-pass polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Treuhaft, R.; Gonçalves, F. Automated estimation of forest height and underlying topography over a Brazilian tropical forest with single-baseline single-polarization TanDEM-X SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Fatoyinbo, T.E. TanDEM-X Pol-InSAR Inversion for Mangrove Canopy Height Estimation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3608–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, F.; Schulze, D.; Hajnsek, I.; Pretzsch, H.; Papathanassiou, K.P. TanDEM-X Pol-InSAR performance for forest height estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6404–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, F. A PolinSAR Inversion Error Model on Polarimetric System Parameters for Forest Height Mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5669–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, B.; Xiang, M.; Jiang, S.; Fu, X. Forest height estimation based on constrained Gaussian Vertical Backscatter model using multi-baseline P-band Pol-InSAR data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigot, G.; Simard, M.; Colin-Koeniguer, E.; Boulch, A. Retrieval of forest vertical structure from PolInSAR Data by machine learning using LIDAR-Derived features. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, A.; Lohberger, S.; Zhang, D.; Siegert, F. Canopy height and above-ground biomass retrieval in tropical forests using multi-pass X-and C-band Pol-InSAR data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Forest Vegetation Type | No. of Plots |
|---|---|
| Khair-Sisham Forest | 5 |
| Mixed Miscellaneous Forest | 18 |
| Sal Forest | 77 |
| PolInSAR Data | TerraSAR-X | RADARSAT-2 | ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition | Reference | Secondary | Reference | Secondary | Reference | Secondary |
| Date of acquisition | 21 January 2015 | 12 February 2015 | 27 January 2014 | 20 February 2014 | 9 August 2015 | 23 August 2015 |
| Polarisation | Quad-pol (HH+HV+VH+VV) | |||||
| Wavelength (cm)/frequency (GHz) | 3.10/9.64 | 5.55/5.4 | 24.25/1.236 | |||
| Resolution (m), range & azimuth | 1.36 & 2.86 | 4.7 & 9.5 | 2.86 & 3.236 | |||
| Absolute orbit | 42159 | 42493 | 32291 | 31948 | 6545 | 6752 |
| Near range incidence angle | 24.59 | 24.54 | 33.45 | 33.45 | 21.56 | 21.55 |
| Far range incidence angle | 26.73 | 26.79 | 35.07 | 35.07 | 25.93 | 25.93 |
| Perpendicular baseline (m) | 105 | 67.92 | 84.37 | |||
| Temporal baseline (days) | 22 | 24 | 14 | |||
| Altitude of ambiguity (m) | 35.85 | 215.05 | 455.16 | |||
| Mission | Approach | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | Standard Error (SE) | p-Value with 95% Confidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 | TSI | 0.53 | 2.87 m | 1.56 m | 1.73 × 10−17 |
| CAI | 0.04 | 4.48 m | 2.53 m | 0.040 | |
| RADARSAT-2 | TSI | 0.32 | 3.74 m | 1.73 m | 1.22 × 10−9 |
| CAI | 0.00 | 3.88 m | 2.09 m | 0.906 | |
| TerraSAR-X | TSI | 0.43 | 4.53 m | 2.17 m | 2.08 × 10−13 |
| CAI | 0.05 | 4.90 m | 3.91 m | 0.019 | |
| GEDI | Integration of GEDI-derived canopy height with Landsat timeseries data | 0.0022 | 5.82 m | 5.33 m | 0.644 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.; Govil, H.; Srivastava, P.K.; Thakur, P.K.; Kushwaha, S.P.S. Spaceborne Multifrequency PolInSAR-Based Inversion Modelling for Forest Height Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244042
Kumar S, Govil H, Srivastava PK, Thakur PK, Kushwaha SPS. Spaceborne Multifrequency PolInSAR-Based Inversion Modelling for Forest Height Retrieval. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(24):4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244042
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Shashi, Himanshu Govil, Prashant K. Srivastava, Praveen K. Thakur, and Satya P. S. Kushwaha. 2020. "Spaceborne Multifrequency PolInSAR-Based Inversion Modelling for Forest Height Retrieval" Remote Sensing 12, no. 24: 4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244042
APA StyleKumar, S., Govil, H., Srivastava, P. K., Thakur, P. K., & Kushwaha, S. P. S. (2020). Spaceborne Multifrequency PolInSAR-Based Inversion Modelling for Forest Height Retrieval. Remote Sensing, 12(24), 4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244042