Classification of Rainfall Types Using Parsivel Disdrometer and S-Band Polarimetric Radar in Central Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
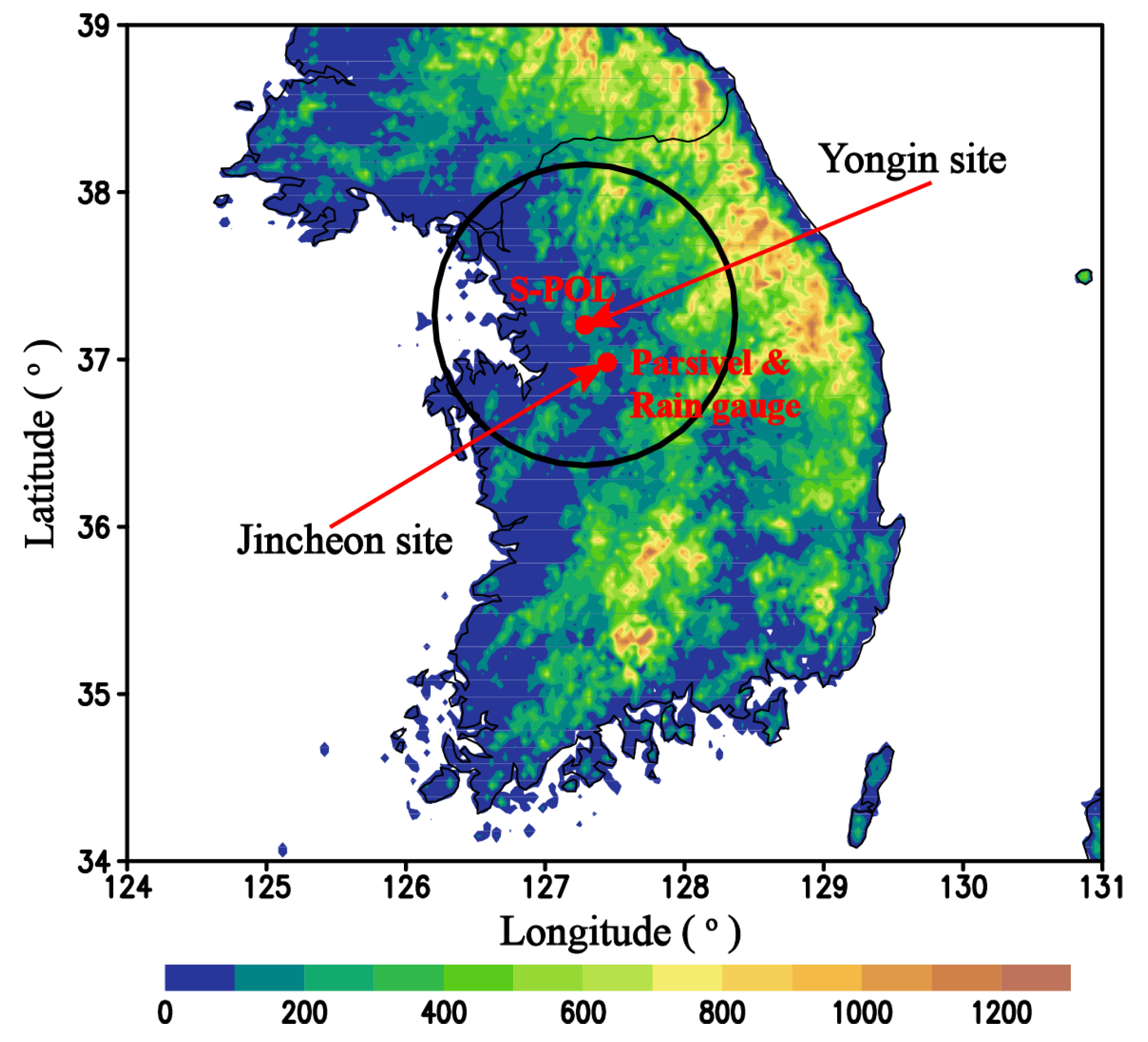
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Parsivel Disdrometer
2.2.1. Quality Control
2.2.2. DSD Parameters
2.3. S-POL Radar
2.3.1. Quality Control
2.3.2. DSD Parameters
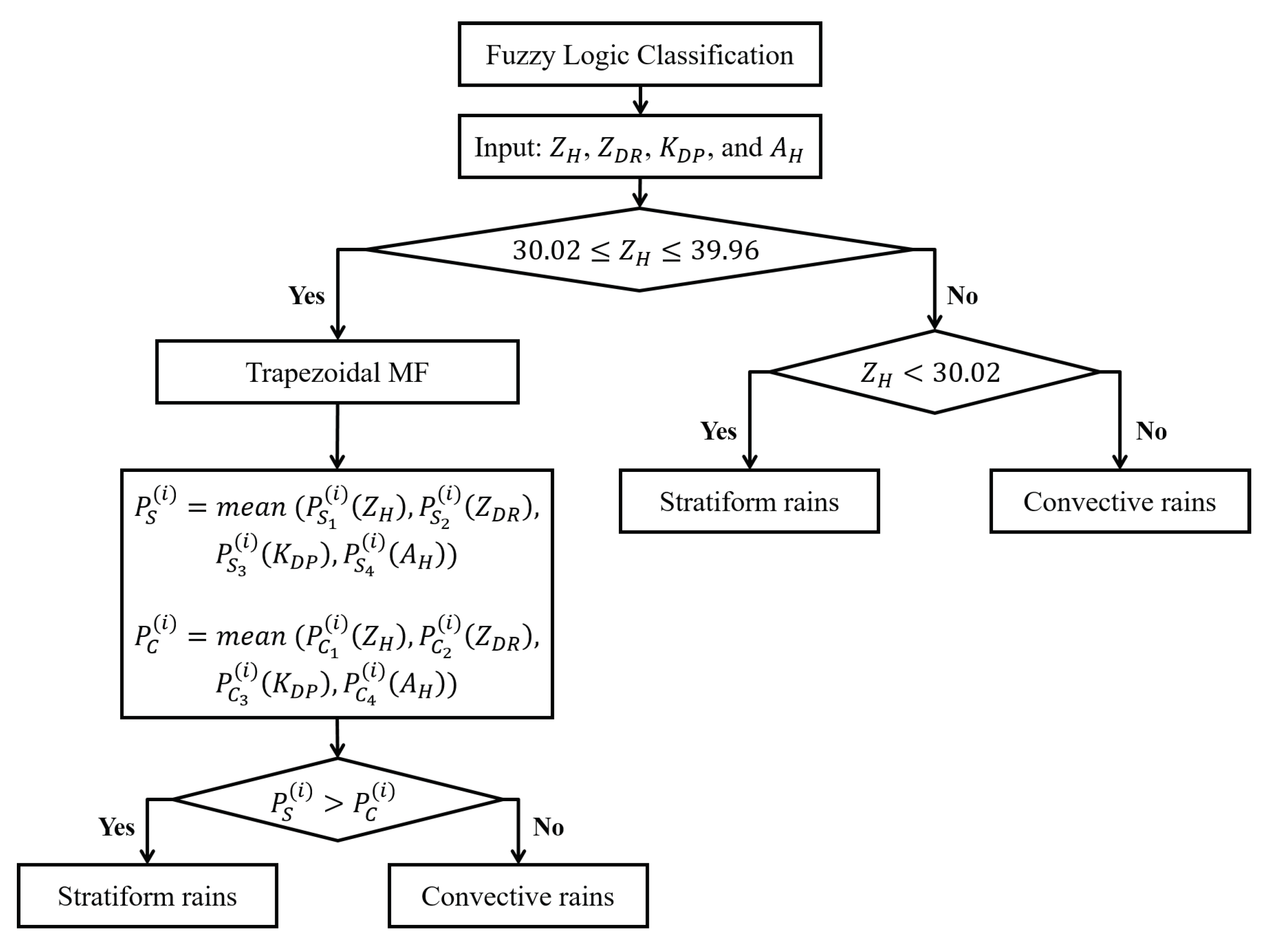
2.4. Methods for Rainfall Classification Using Disdrometer and S-POL Radar
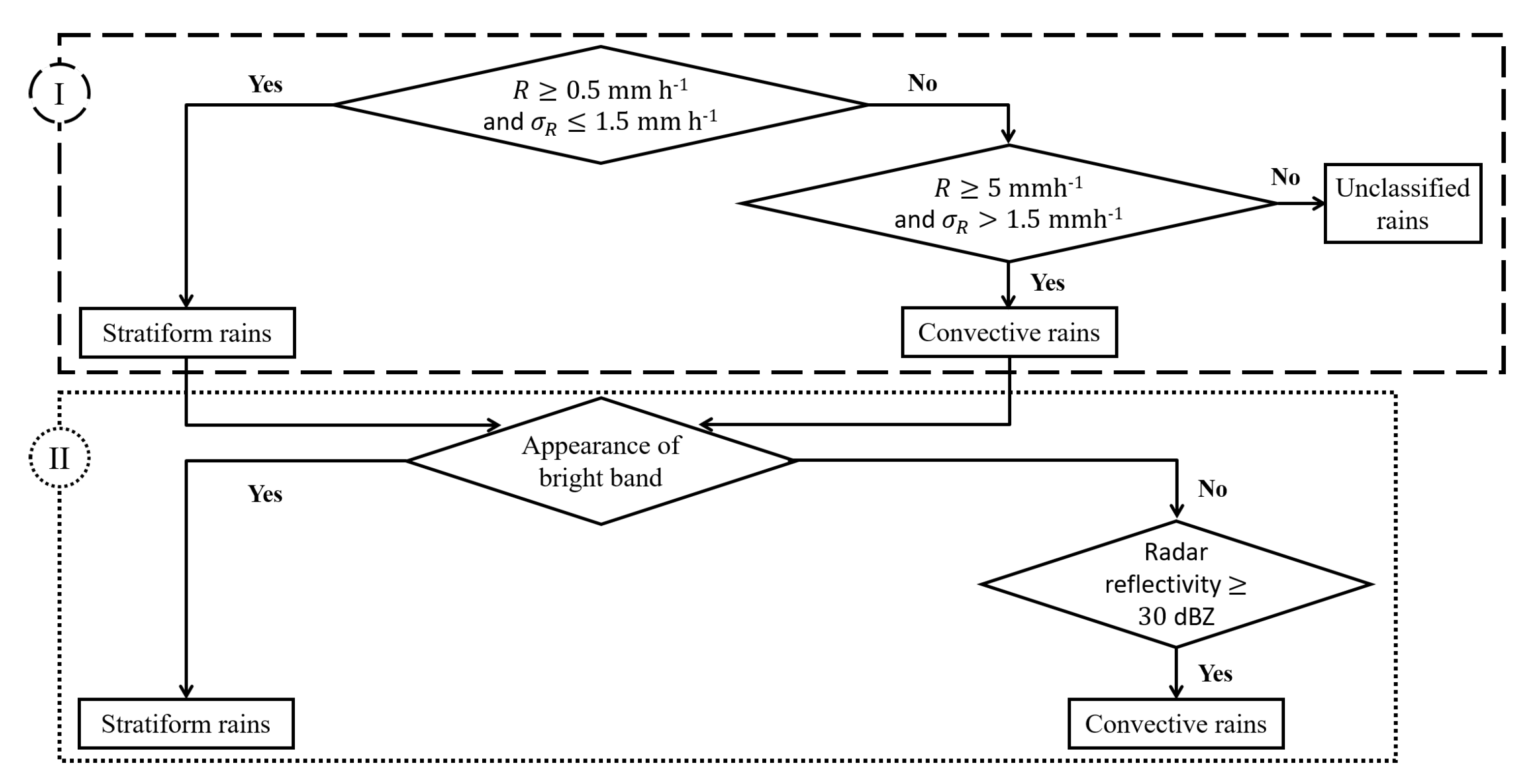
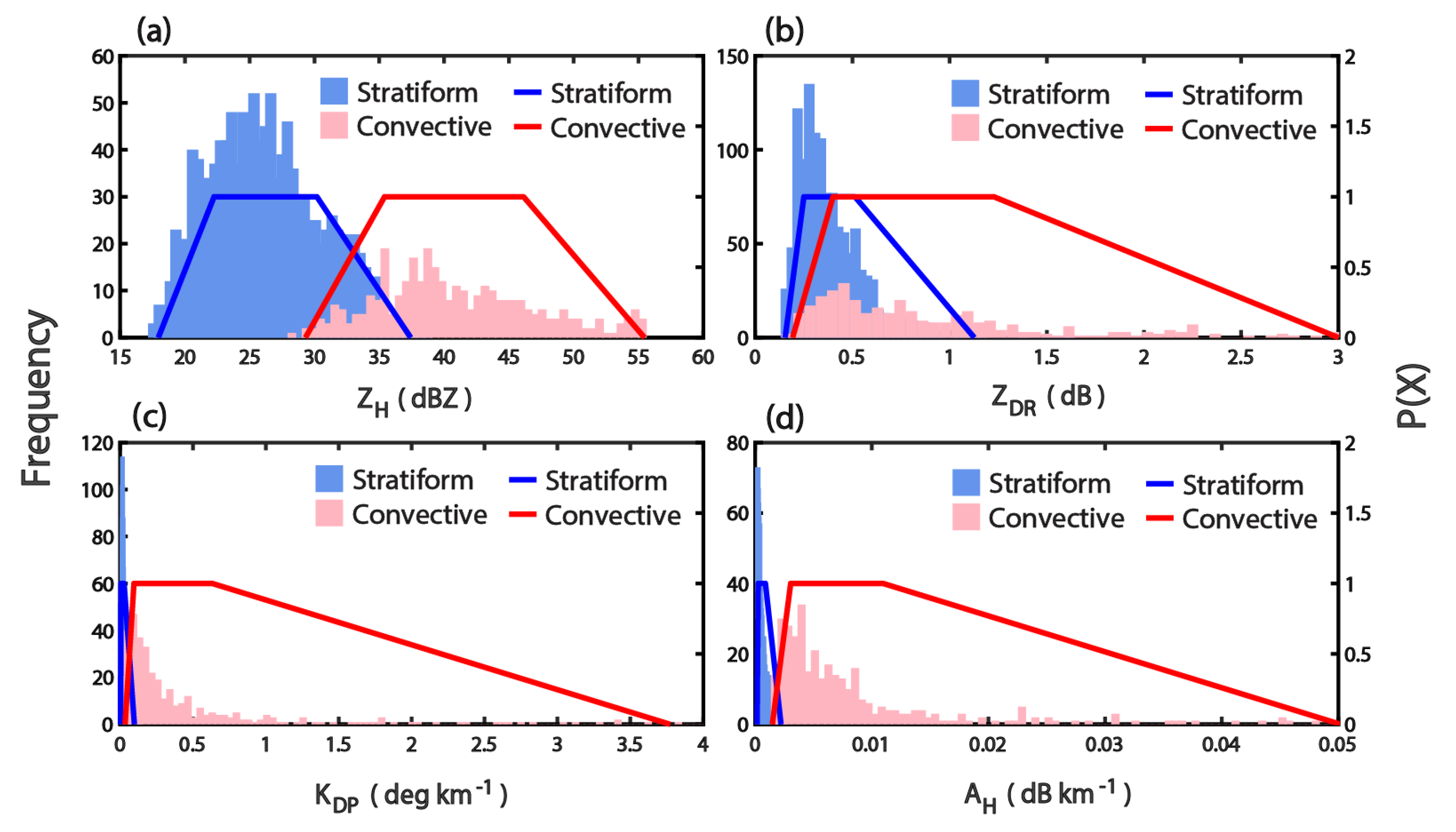
2.4.1. General Identification Methods
2.4.2. Classification with DSDs Variables Measured by Parsivel Disdrometer
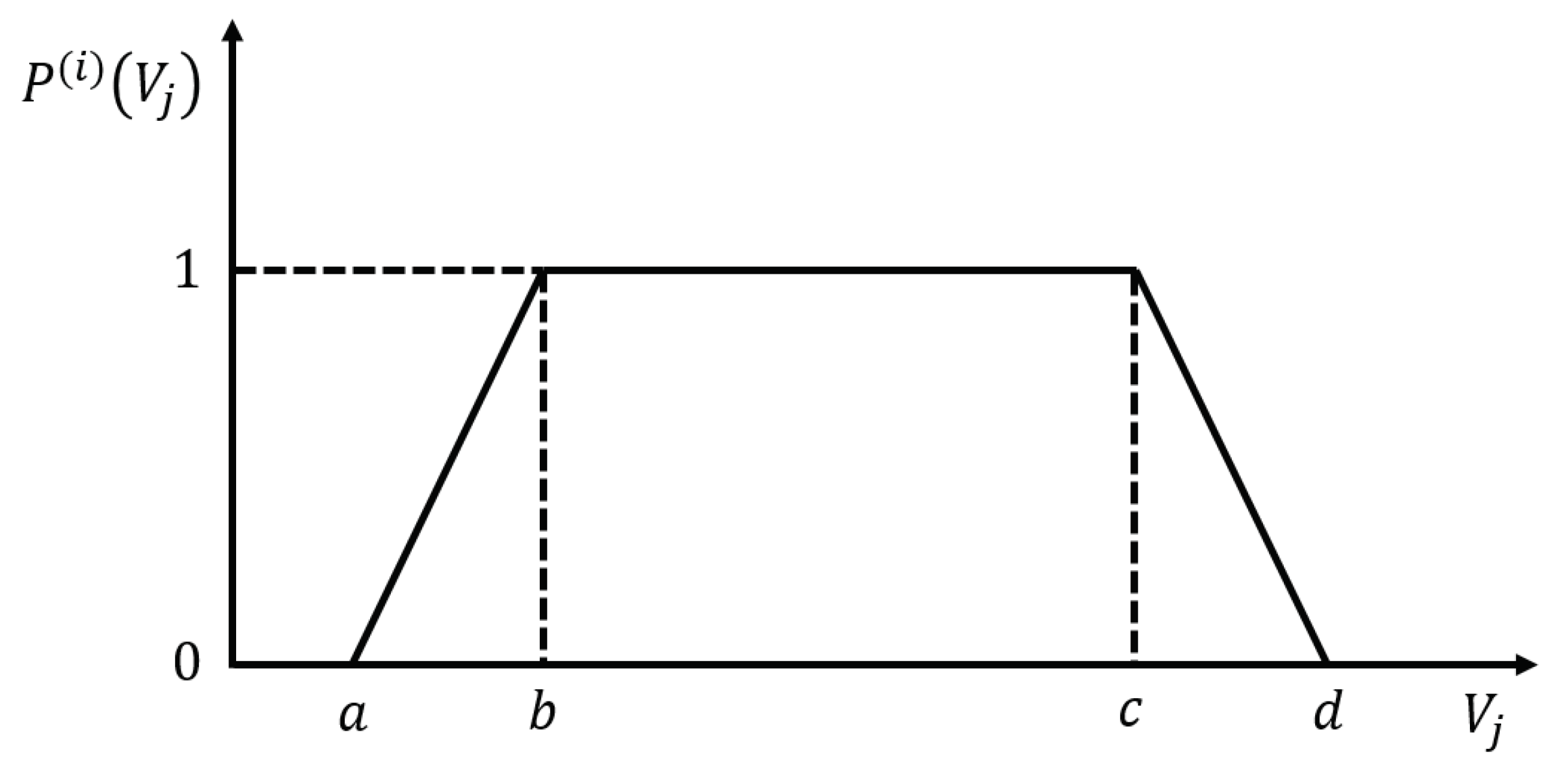
2.4.3. Classification by S-POL Radar
3. Results
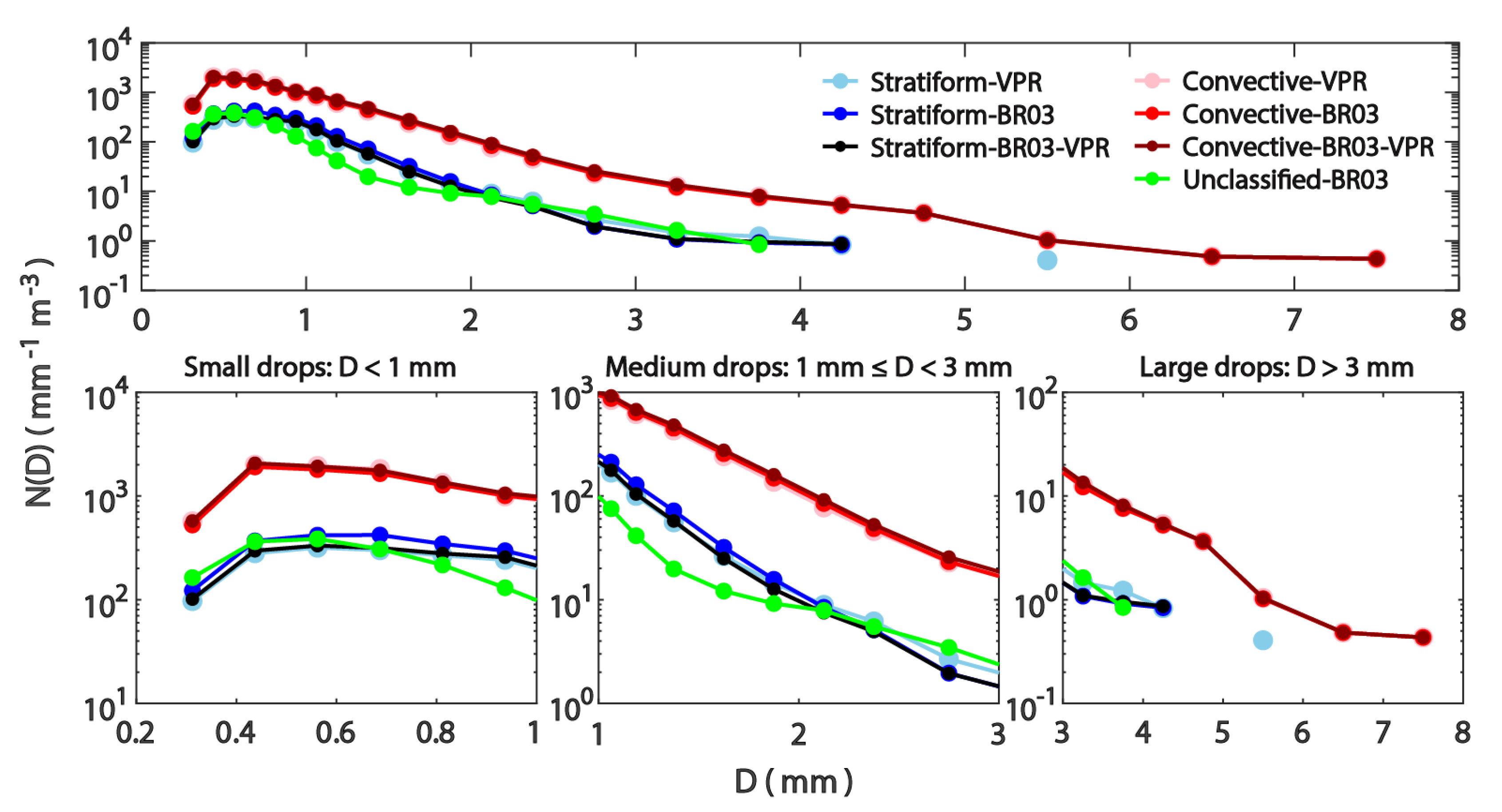
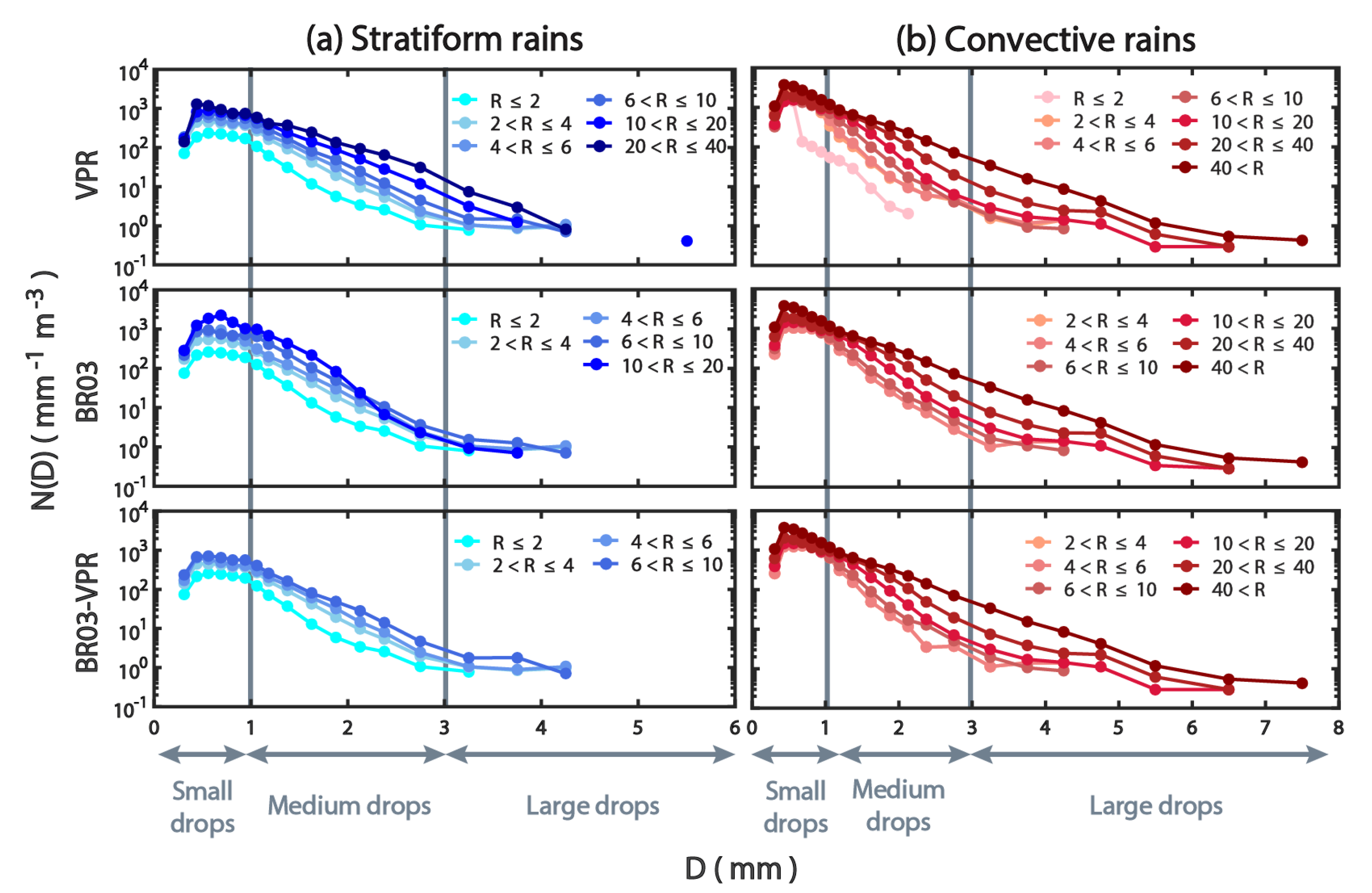
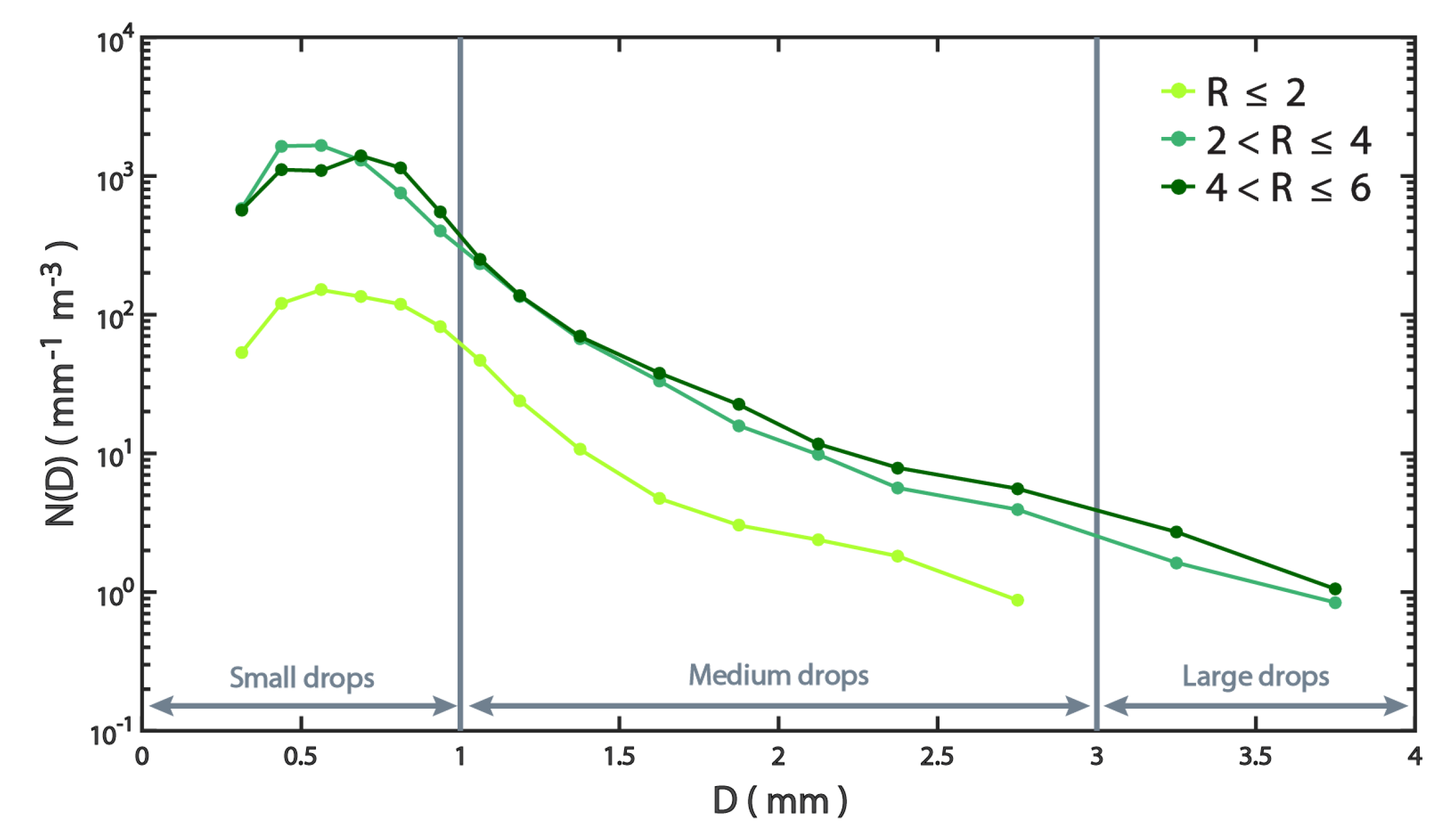
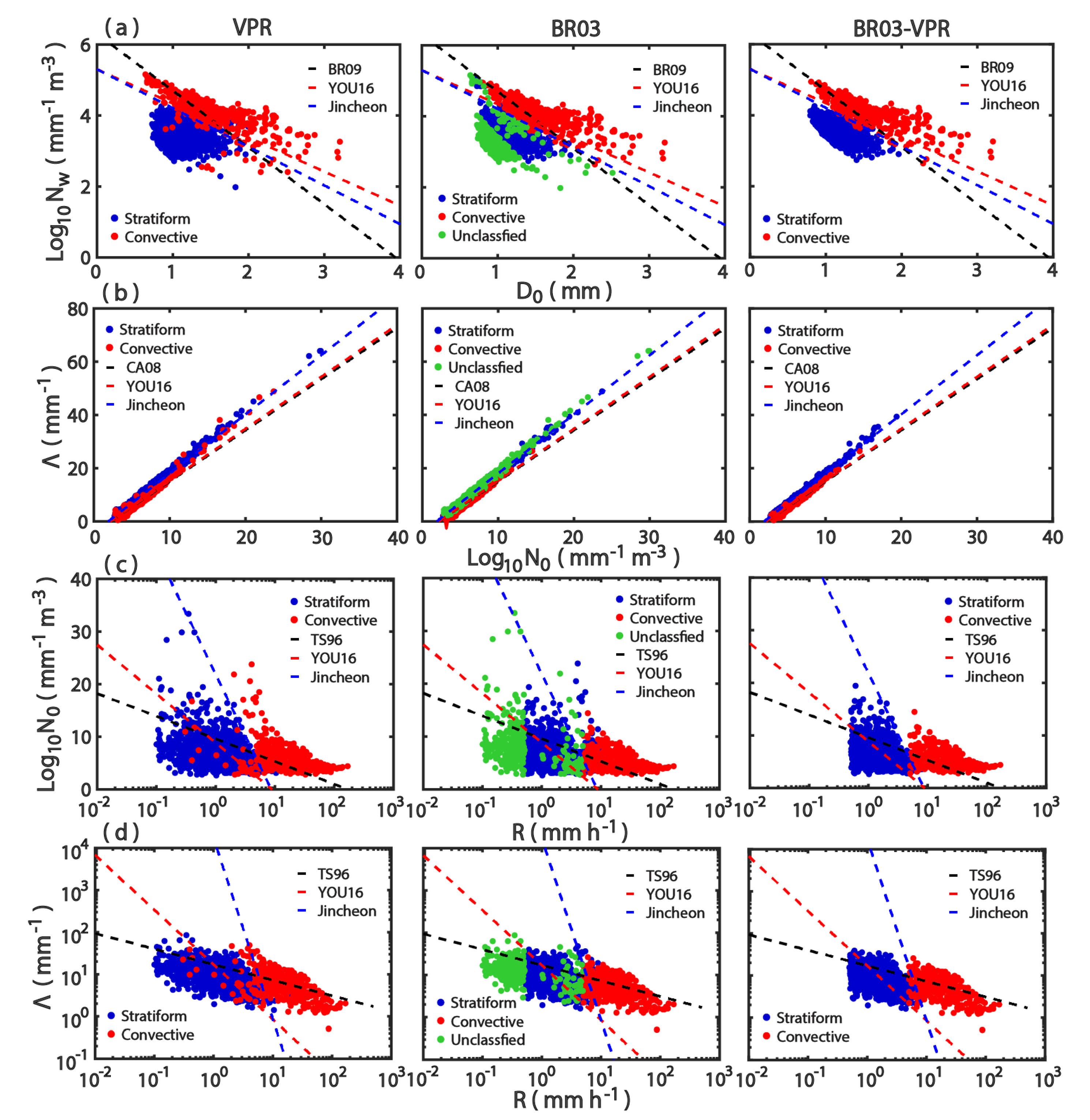
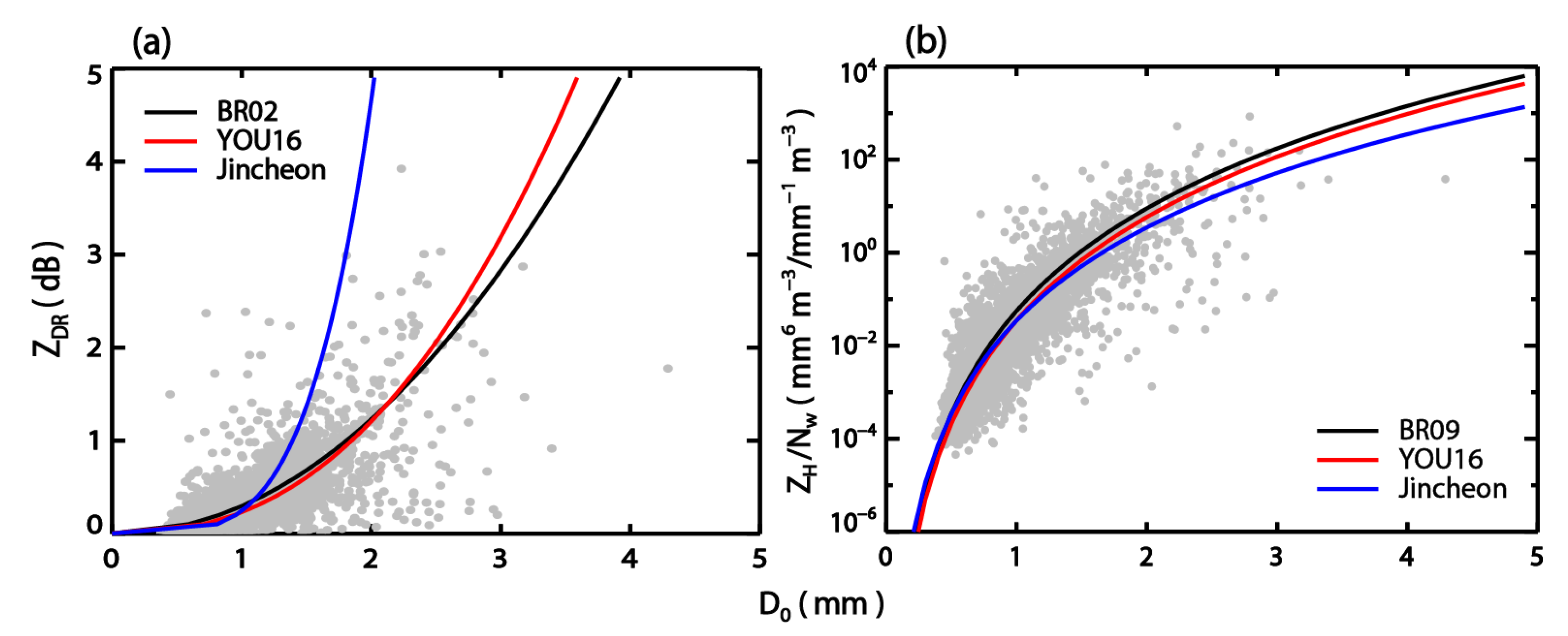
3.1. The Characteristics of DSDs
3.2. Relationship between DSD and R
3.3. Comparison of Rainfall Classification
3.3.1. Parsivel Disdrometer
3.3.2. S-POL Radar
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2DVD | 2-Dimensional Video Disdrometer |
| BR02 | Bringi et al. [66] |
| BR03 | Bringi et al. [15] |
| BR03-VPR | Bringi et al. [15]-vertical profile of reflectivity |
| BR09 | Bringi et al. [12] |
| BRA04 | Brandes et al. [23] |
| CA08 | Caracciolo et al. [16] |
| DSDs | Drop size distributions |
| JWD | Joss-Waldvogel disdrometer |
| KMA | Korea Meteorological Administration |
| LWC | Liquid water content |
| MF | Memebership Function |
| Parsivel | PARticle SIze and VELocity |
| PIA | Path Integrated Attenuation |
| Pludix | X-band pluvio-disdrometer |
| S-POL | S-band polarimetric |
| SHY95 | Steiner et al. [7] |
| STD | Standard deviation |
| T-matrix | Transition-matrix |
| TS96 | Tokay and Short [8] |
| VPR | Vertical profile of reflectivity |
| YOU16 | You et al. [4] |
Appendix A
| Stratiform Rains | Convective Rains | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dBZ) | (dB) | (deg km) | (dB km) | (dBZ) | (dB) | (deg km) | (dB km) | |
| a (0.5th) | 17.95 | 0.15 | 0.003 | 0.0002 | 29.30 | 0.19 | 0.034 | 0.0015 |
| b (20th) | 22.25 | 0.25 | 0.006 | 0.0003 | 35.41 | 0.40 | 0.095 | 0.0030 |
| c (80th) | 30.18 | 0.51 | 0.027 | 0.0009 | 46.13 | 1.23 | 0.632 | 0.0110 |
| d (99.5th) | 37.42 | 1.13 | 0.098 | 0.0022 | 55.47 | 3.00 | 3.773 | 0.0502 |
| Stratiform Rains | Convective Rains | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dBZ) | (dB) | (deg km) | (dB km) | (dBZ) | (dB) | (deg km) | (dB km) | |
| a (0.5th) | 30.02 | 0.35 | 0.022 | 0.0005 | 30.31 | 0.21 | 0.038 | 0.0014 |
| b (20th) | 30.94 | 0.48 | 0.030 | 0.0009 | 34.05 | 0.33 | 0.0077 | 0.0024 |
| c (80th) | 34.07 | 0.78 | 0.0055 | 0.0014 | 38.68 | 0.65 | 0.170 | 0.0051 |
| d (99.5th) | 38.03 | 1.44 | 0.111 | 0.0024 | 39.96 | 1.53 | 0.251 | 0.0083 |
References
- Anagnostou, E.N. A convective/stratiform precipitation classification algorithm for volume scanning weather radar observations. Meteorol. Appl. 2004, 11, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penide, G.; Kumar, V.V.; Protat, A.; May, P.T. Statistics of drop size distribution parameters and rain rates for stratiform and convective precipitation during the North Australian wet season. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 3222–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penide, G.; Protat, A.; Kumar, V.V.; May, P.T. Comparison of two convective/stratiform precipitation classification techniques: Radar reflectivity texture versus drop size distribution–based approach. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 2788–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.H.; Lee, D.I.; Kang, M.Y.; Kim, H.J. Classification of rain types using drop size distributions and polarimetric radar: Case study of a 2014 flooding event in Korea. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, E.N.; Kummerow, C. Stratiform and convective classification of rainfall using SSM/I 85-GHz brightness temperature observations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1997, 14, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Qi, Y. Classification of convective/stratiform echoes in radar reflectivity observations using a fuzzy logic algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.; Houze, R.A., Jr.; Yuter, S.E. Climatological characterization of three-dimensional storm structure from operational radar and rain gauge data. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1995, 34, 1978–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Short, D.A. Evidence from tropical raindrop spectra of the origin of rain from stratiform versus convective clouds. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitchen, M.; Brown, R.; Davies, A. Real-time correction of weather radar data for the effects of bright band, range and orographic growth in widespread precipitation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 120, 1231–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaka, J.; Iguchi, T.; Okamoto, K. TRMM PR standard algorithm 2A23 and its performance on bright band detection. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2009, 87, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biggerstaff, M.I.; Listemaa, S.A. An improved scheme for convective/stratiform echo classification using radar reflectivity. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 2129–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.; Williams, C.; Thurai, M.; May, P. Using dual-polarized radar and dual-frequency profiler for DSD characterization: A case study from Darwin, Australia. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.; May, P. CPOL radar-derived drop size distribution statistics of stratiform and convective rain for two regimes in Darwin, Australia. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.J.; Rutledge, S.A.; Dolan, B.; Thurai, M. Drop size distributions and radar observations of convective and stratiform rain over the equatorial Indian and West Pacific Oceans. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 4091–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, C.; Porcu, F.; Prodi, F. Precipitation classification at mid-latitudes in terms of drop size distribution parameters. Adv. Geosci. 2008, 16, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Guo, C.; Feng, L. Characteristics of the raindrop size distributions and their retrieved polarimetric radar parameters in northern and southern China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijlenhoet, R.; Steiner, M.; Smith, J.A. Variability of raindrop size distributions in a squall line and implications for radar rainfall estimation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.W. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1983, 22, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Ulbrich, C.W. Cloud microphysical properties, processes, and rainfall estimation opportunities. Radar Atmos. Sci. Collect. Essays Honor. David Atlas 2003, 52, 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Pu, J. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Meiyu season observed in eastern China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Meneghini, R.; Zawadzki, I. Global and local precipitation measurements by radar. In Radar and Atmospheric Science: A Collection of Essays in Honor of David Atlas; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 215–236. [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Comparison of polarimetric radar drop size distribution retrieval algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Drop size distribution retrieval with polarimetric radar: Model and application. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vivekanandan, J.; Zhang, G.; Brandes, E. Polarimetric radar estimators based on a constrained gamma drop size distribution model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesnard, F.; Pujol, O.; Sauvageot, H.; Costes, C.; Bon, N.; Artis, J.P. Discrimination between convective and stratiform precipitation in radar-observed rainfield using fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology (ERAD 2008), Helsinki, Finland, 30 June–4 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, M.; Houze, R. Three-dimensional validation at TRMM ground truth sites: Some early results from Darwin, Australia. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Radar Meteorology, Norman, OK, USA, 24–28 May 1993; pp. 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Xiao, R. Raindrop axis ratios and size distributions in Florida rainshafts: An assessment of multiparameter radar algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anagnostou, M.N.; Anagnostou, E.N. Performance of algorithms for rainfall retrieval from dual-polarization X-band radar measurements. In Precipitation: Advances in Measurement, Estimation and Prediction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 313–340. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, B.; Fuchs, B.; Rutledge, S.; Barnes, E.; Thompson, E. Primary modes of global drop size distributions. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 1453–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zrnić, D.; Kim, K.E. The hydrometeor classification algorithm for the polarimetric WSR-88D: Description and application to an MCS. Weather Forecast. 2009, 24, 730–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, J.; Zrnić, D. An algorithm to deduce hydrometeor types and contents from multi-parameter radar data. In Proceedings of the 26th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Norman, OK, USA, 24–28 May 1993; pp. 513–515. [Google Scholar]
- Straka, J. Hydrometeor fields in a supercell storm as deduced from dual-polarization radar. In Proceedings of the 18th Conference on Severe Local Storms, San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 February 1996; Volume 55, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vivekanandan, J.; Zrnić, D.; Ellis, S.; Oye, R.; Ryzhkov, A.; Straka, J. Cloud microphysics retrieval using S-band dual-polarization radar measurements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrnić, D.S.; Ryzhkov, A.V. Polarimetry for weather surveillance radars. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chandrasekar, V. Classification of hydrometeors based on polarimetric radar measurements: Development of fuzzy logic and neuro-fuzzy systems, and in situ verification. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 140–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T. Hydrometeor classification with a C-band polarimetric radar. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 2003, 52, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V.N. Hydrometeor classification system using dual-polarization radar measurements: Model improvements and in situ verification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, F.S.; Cimini, D.; Montopoli, M. Investigating precipitation microphysics using ground-based microwave remote sensors and disdrometer data. Atmos. Res. 2010, 97, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sakka, H.; Boumahmoud, A.A.; Fradon, B.; Frasier, S.J.; Tabary, P. A new fuzzy logic hydrometeor classification scheme applied to the French X-, C-, and S-band polarimetric radars. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 2328–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, V.N.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M. Fuzzy logic classification of S-band polarimetric radar echoes to identify three-body scattering and improve data quality. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 2017–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.H.; Lee, D.I.; Jang, M.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.E. Variation of rainrate and radar reflectivity in Busan area and its measurement by clouds type. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 41, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- You, C.H.; Lee, D.I.; Jang, S.M.; Jang, M.; Uyeda, H.; Shinoda, T.; Kobayashi, F. Characteristics of rainfall systems accompanied with Changma front at Chujado in Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 46, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.H.; You, C.H.; Lee, D.I. Climatological characteristics of raindrop size distributions in Busan, Republic of Korea. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sc. 2016, 20, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh, J.L.; Lee, D.I.; You, C.H. Inter-comparison of DSDs between Jincheon and Miryang at South Korea. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Joss, J. An optical disdrometer for measuring size and velocity of hydrometeors. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Srivastava, R.; Sekhon, R.S. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev. Geophys. 1973, 11, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.; Krajewski, W.F. Two-dimensional video disdrometer: A description. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.Y.; Wang, T.C.C.; Lin, P.L. Characteristics of the raindrop size distribution and drop shape relation in typhoon systems in the western Pacific from the 2D video disdrometer and NCU C-band polarimetric radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1973–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.W.; Atlas, D. Rainfall microphysics and radar properties: Analysis methods for drop size spectra. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1998, 37, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.H.; Lee, D.I.; Kang, M.Y. Rainfall estimation using specific differential phase for the first operational polarimetric radar in Korea. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryzhkov, A.; Diederich, M.; Zhang, P.; Simmer, C. Potential utilization of specific attenuation for rainfall estimation, mitigation of partial beam blockage, and radar networking. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 599–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.H.; Lee, D.I. Algorithm development for the optimum rainfall estimation using polarimetric variables in Korea. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Keenan, T.; Chandrasekar, V. Correcting C-band radar reflectivity and differential reflectivity data for rain attenuation: A self-consistent method with constraints. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, K.V.; Chuang, C. A new model for the equilibrium shape of raindrops. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andsager, K.; Beard, K.V.; Laird, N.F. Laboratory measurements of axis ratios for large raindrops. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 2673–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.J.; Bringi, V.; Thurai, M. Orientation angle distributions of drops after an 80-m fall using a 2D video disdrometer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterman, P.C. Symmetry, unitarity, and geometry in electromagnetic scattering. Phys. Rev. D. 1971, 3, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I.; Travis, L.D.; Mackowski, D.W. T-matrix computations of light scattering by nonspherical particles: A review. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1996, 55, 535–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Jia, X.; Sang, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Distributions of raindrop sizes and fall velocities in a semiarid plateau climate: Convective versus stratiform rains. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Du, B.; Dai, T. Radar Meteorology; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2001.
- Harrison, D.; Norman, K.; Darlington, T.; Adams, D.; Husnoo, N.; Sandford, C. The evolution of the Met Office radar data quality control and product generation system: Radarnet. In Proceedings of the 37th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Norman, OK, USA, 14–18 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, M.; Sánchez-Diezma, R.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Zawadzki, I. An improved methodology for classifying convective and stratiform rain. In Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Radar Meteorology, Alvarado, Mexico, 22–29 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gorgucci, E.; Scarchilli, G.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V. Rainfall estimation from polarimetric radar measurements: Composite algorithms immune to variability in raindrop shape–size relation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 1773–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V.; Scarchilli, G. Estimation of raindrop size distribution parameters from polarimetric radar measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bringi, V.; Huang, G.J.; Chandrasekar, V.; Gorgucci, E. A methodology for estimating the parameters of a gamma raindrop size distribution model from polarimetric radar data: Application to a squall-line event from the TRMM/Brazil campaign. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Maki, M.; Lee, D. Retrieval of three-dimensional raindrop size distribution using X-band polarimetric radar data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 1265–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Blackman, T.M. The need to represent raindrop size spectra as normalized gamma distributions for the interpretation of polarization radar observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E. A method for estimating rain rate and drop size distribution from polarimetric radar measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. An evaluation of a drop distribution–based polarimetric radar rainfall estimator. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Brandes, E.; Schuur, T.; Ryzhkov, A.; Ikeda, K. Analysis of video disdrometer and polarimetric radar data to characterize rain microphysics in Oklahoma. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 2238–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. In Fuzzy Sets, Fuzzy Logic, and Fuzzy Systems: Selected Papers by Lotfi a Zadeh; World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 1996; pp. 394–432. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, A.; Termini, S. A definition of a nonprobabilistic entropy in the setting of fuzzy sets theory. Inf. Control 1972, 20, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, Y.; Yu, T.Y.; Lakshmanan, V.; Kingfield, D.M.; Lee, D.I.; You, C.H. Neuro-fuzzy gust front detection algorithm with S-band polarimetric radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schuur, T.; Ryzhkov, A.; Heinselman, P.; Zrnić, D.; Burgess, D.; Scharfenberg, K. Observations and classification of echoes with the polarimetric WSR-88D radar. Rep. Natl. Sev. Storms Lab. 2003, 73069, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Zrnić, D.; Bringi, V.; Balakrishnan, N.; Aydin, K.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J. Polarimetric measurements in a severe hailstorm. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 2223–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zrnić, D.; Ryzhkov, A. Advantages of rain measurements using specific differential phase. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straka, J.M.; Zrnić, D.S.; Ryzhkov, A.V. Bulk hydrometeor classification and quantification using polarimetric radar data: Synthesis of relations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1341–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, F.S.; Scaranari, D.; Vulpiani, G. Supervised fuzzy-logic classification of hydrometeors using C-band weather radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3784–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y. Application of Artificial Intelligence to Gust Front Detection with S-band Polarimetric WSR-88D. Master’s Thesis, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, X. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distributions observed in East China during the Asian summer monsoon season using 2-D video disdrometer and Micro Rain Radar data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2265–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
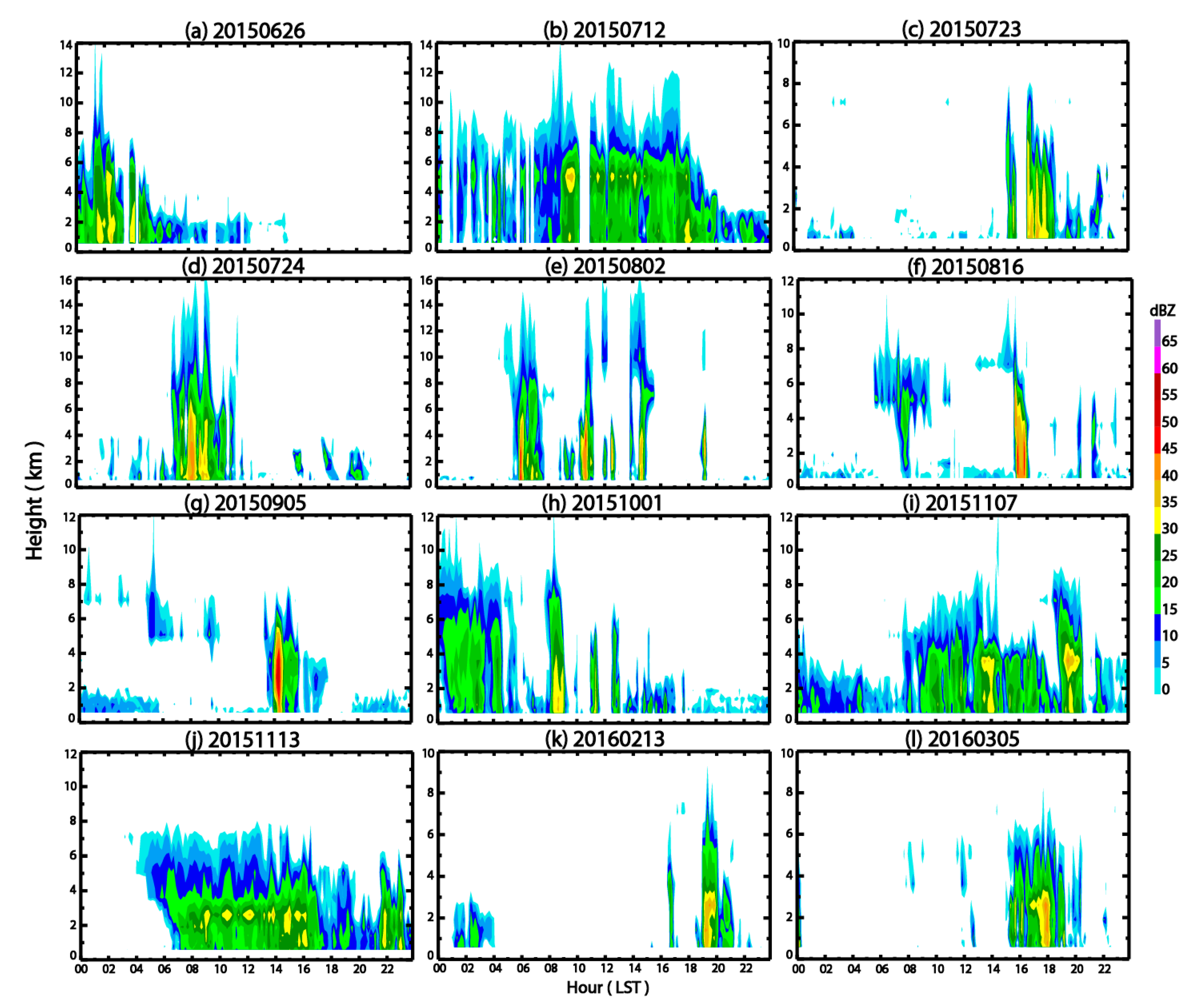
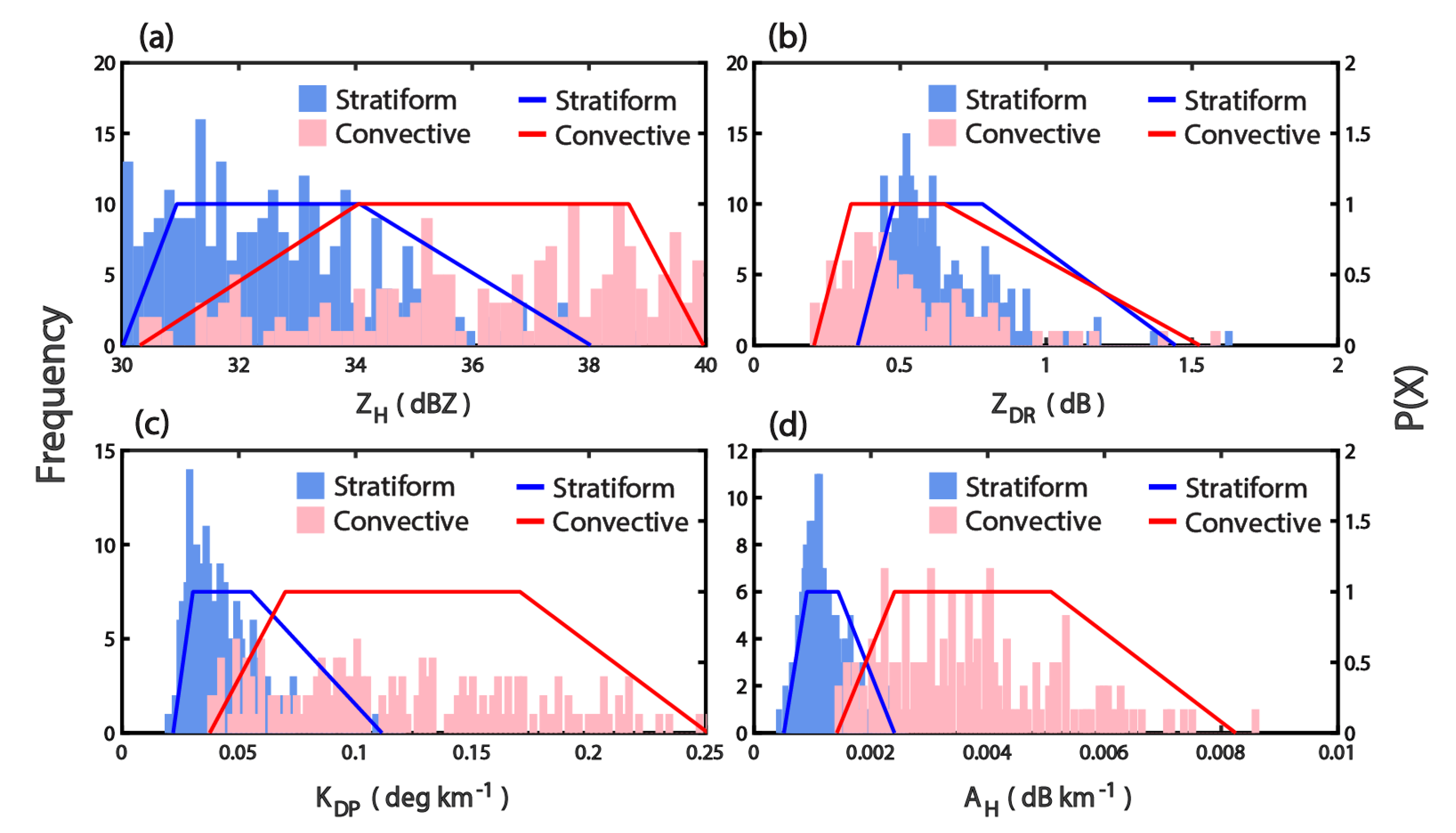
| No. | Dates | Stratiform Rains | Convective Rains |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 26 June 2015 | 01:30–02:00 | |
| 02:30–03:00 | |||
| 04:00–04:30 | |||
| 2. | 12 July 2015 | 09:00–18:00 | |
| 3. | 23 July 2015 | 16:30–18:00 | |
| 4. | 24 July 2015 | 07:30–09:30 | |
| 5. | 2 August 2015 | 06:00–06:10 | |
| 10:30–10:50 | |||
| 14:30–14:40 | |||
| 6. | 16 August 2015 | 05:20–09:20 | 15:30–16:20 |
| 7. | 5 September 2015 | 14:10–14:30 | |
| 8. | 1 October 2015 | 01:00–05:00 | |
| 9. | 7 November 2015 | 13:10–14:30 | |
| 19:10–20:20 | |||
| 10. | 13 November 2015 | 08:00–16:20 | |
| 11. | 13 February 2016 | 19:00–20:00 | |
| 12. | 5 March 2016 | 16:30–17:30 | 17:40–18:10 |
| DSD Parameters | Statistics | All | Stratiform Rains | Convective Rains | Unclassified Rains | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPR | BR03 | BR03-VPR | VPR | BR03 | BR03-VPR | BR03 | |||
| Mean | 0.97 | 1.16 | 1.19 | 1.19 | 1.52 | 1.61 | 1.62 | 1.01 | |
| (mm) | Max. | 4.29 | 1.99 | 1.96 | 1.96 | 3.20 | 3.20 | 3.20 | 2.52 |
| STD | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.24 | |
| Mean | 3.97 | 3.51 | 3.59 | 3.54 | 4.07 | 4.01 | 4.04 | 3.36 | |
| (mm m) | Max. | 5.41 | 4.25 | 5.10 | 4.25 | 5.16 | 4.93 | 4.93 | 5.16 |
| STD | 0.57 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.46 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.44 | |
| Mean | 1.32 | 1.64 | 2.35 | 1.94 | 21.76 | 24.77 | 26.76 | 0.41 | |
| (mm h) | Max. | 169.79 | 27.45 | 14.59 | 9.66 | 169.79 | 169.79 | 169.79 | 4.95 |
| STD | 5.50 | 2.06 | 2.29 | 1.39 | 23.14 | 23.91 | 24.67 | 0.91 | |
| Relations | Separation | Convective Rains (%) | Stratiform Rains (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | VPR | BR03 | BR03-VPR | VPR | BR03 | BR03-VPR | |
| BR09 | 36.14 | 29.84 | 23.67 | 0.56 | 1.61 | 0.00 | |
| YOU16 | 16.19 | 18.32 | 10.36 | 0.50 | 4.46 | 0.00 | |
| Jincheon | 5.32 | 5.76 | 1.78 | 2.39 | 6.99 | 1.23 | |
| CA08 | 57.87 | 49.21 | 50.00 | 10.79 | 12.76 | 13.15 | |
| YOU16 | 58.54 | 50.26 | 50.89 | 9.96 | 11.68 | 12.01 | |
| Jincheon | 67.85 | 60.99 | 61.54 | 5.90 | 6.69 | 6.94 | |
| TS96 | 22.62 | 27.23 | 20.12 | 10.12 | 15.07 | 11.03 | |
| YOU16 | 3.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 31.92 | 43.50 | 40.03 | |
| Jincheon | 6.43 | 1.83 | 1.18 | 4.62 | 8.76 | 3.35 | |
| TS96 | 57.65 | 66.75 | 63.02 | 9.07 | 14.07 | 11.03 | |
| YOU16 | 3.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 31.81 | 44.89 | 41.50 | |
| Jincheon | 12.42 | 8.90 | 5.03 | 2.11 | 5.92 | 0.90 | |
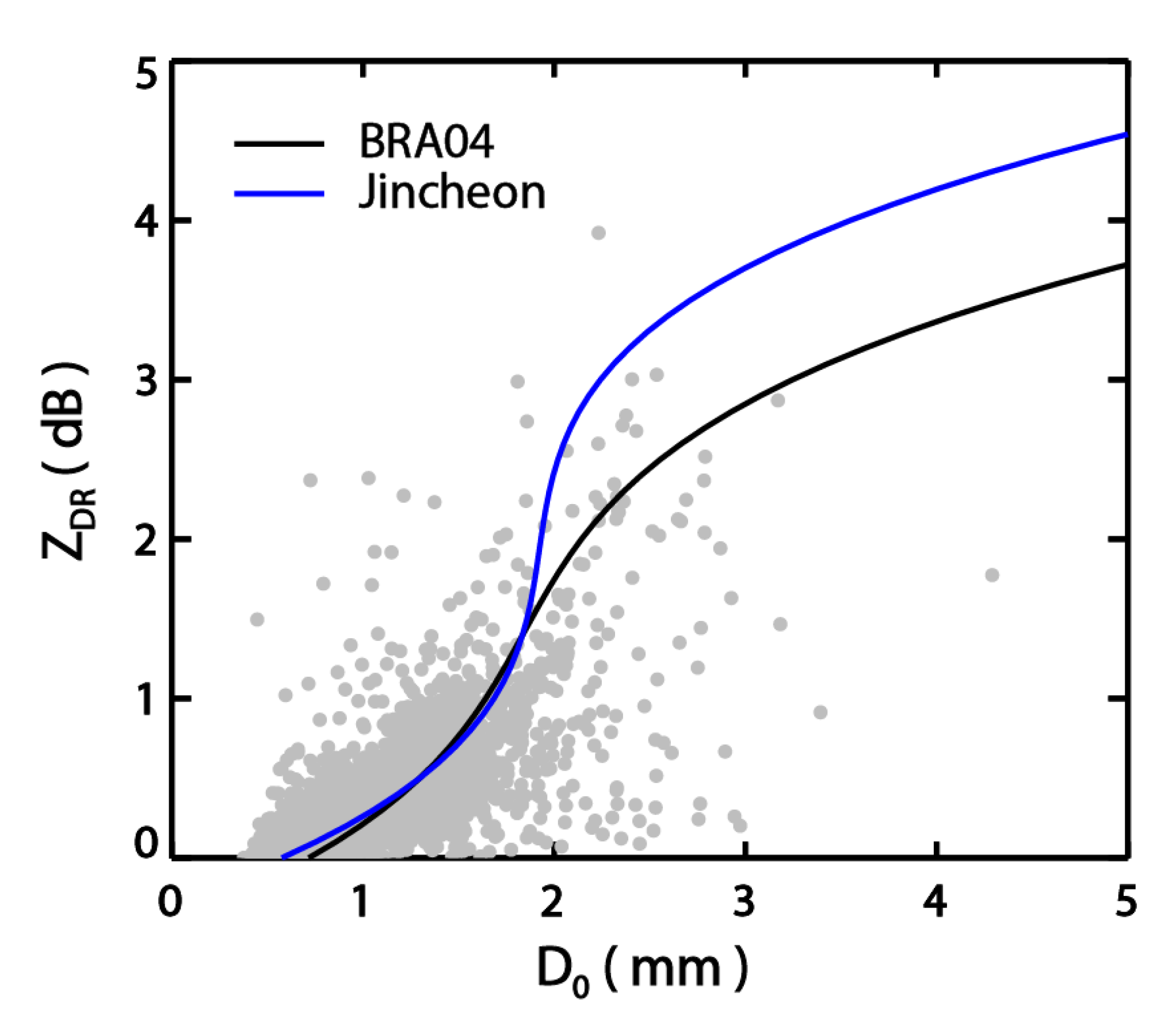
| Equations | Power-Law Relations | Polynomial Function | |
|---|---|---|---|
| References | BR02: 0.8123 | BR09: 0.1796 | BRA04: 0.5033 |
| YOU16 | 0.8094 | 0.1782 | |
| Jincheon: BR03-VPR | 0.7815 | 0.1998 | 0.8116 |
| Methods | Rainfall Types (unit: %) | |
|---|---|---|
| Stratiform Rains | Convective Rains | |
| SHY95 | 85.47 | 22.55 |
| [Misc: 0.00; Error: 14.53] | [Misc: 76.47; Error: 0.98] | |
| DSD retrieval | 61.45 | 68.83 |
| [Misc: 24.02; Error: 14.53] | [Misc: 30.39; Error: 0.78] | |
| Fuzzy | 79.61 | 64.71 |
| [Misc: 5.87; Error: 14.52] | [Misc: 34.31; Error: 0.98] | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loh, J.L.; Lee, D.-I.; Kang, M.-Y.; You, C.-H. Classification of Rainfall Types Using Parsivel Disdrometer and S-Band Polarimetric Radar in Central Korea. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040642
Loh JL, Lee D-I, Kang M-Y, You C-H. Classification of Rainfall Types Using Parsivel Disdrometer and S-Band Polarimetric Radar in Central Korea. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(4):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040642
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoh, Jui Le, Dong-In Lee, Mi-Young Kang, and Cheol-Hwan You. 2020. "Classification of Rainfall Types Using Parsivel Disdrometer and S-Band Polarimetric Radar in Central Korea" Remote Sensing 12, no. 4: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040642
APA StyleLoh, J. L., Lee, D.-I., Kang, M.-Y., & You, C.-H. (2020). Classification of Rainfall Types Using Parsivel Disdrometer and S-Band Polarimetric Radar in Central Korea. Remote Sensing, 12(4), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040642








