An Efficient Method for Infrared and Visual Images Fusion Based on Visual Attention Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Visual Attention Technique for Image Fusion
2.1. Feasibility
2.2. Superiority
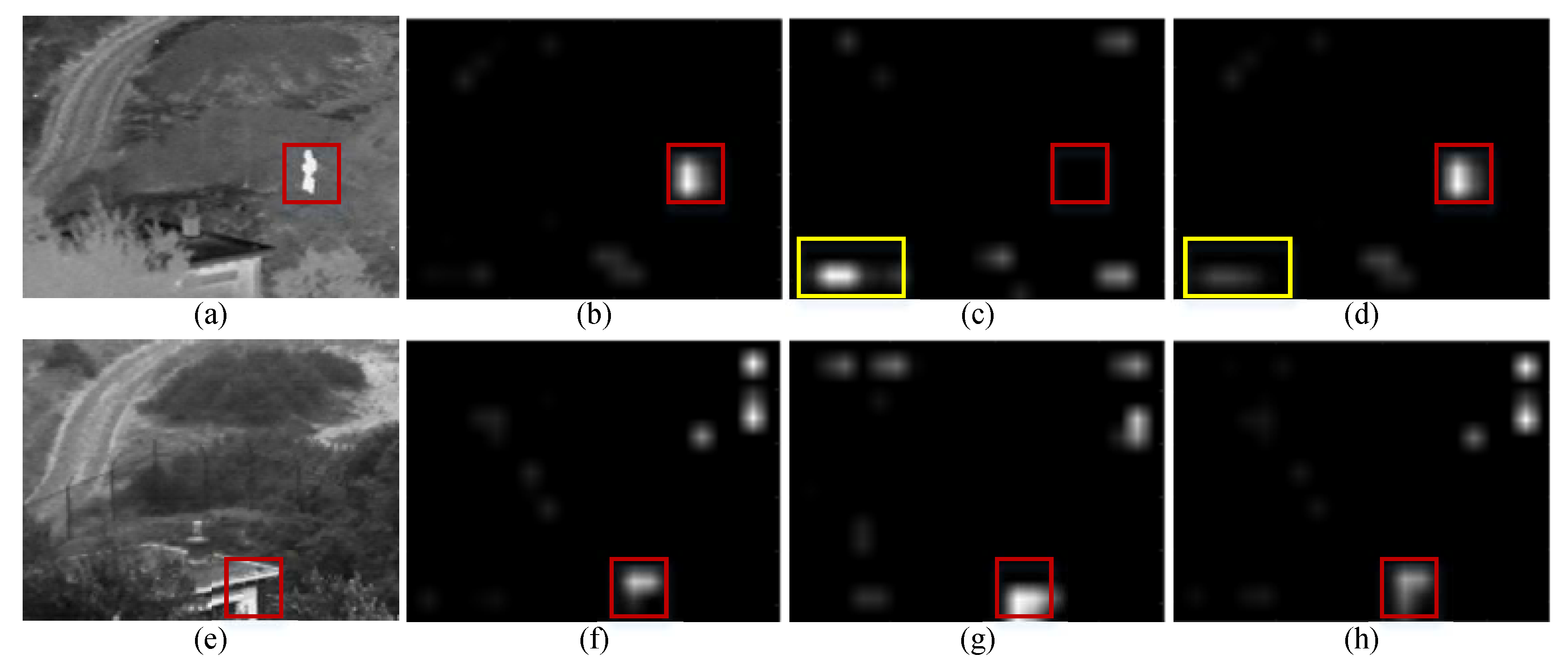
2.3. The Original VAM for Image Fusion
3. Image Fusion Algorithm Based on Visual Attention Technique
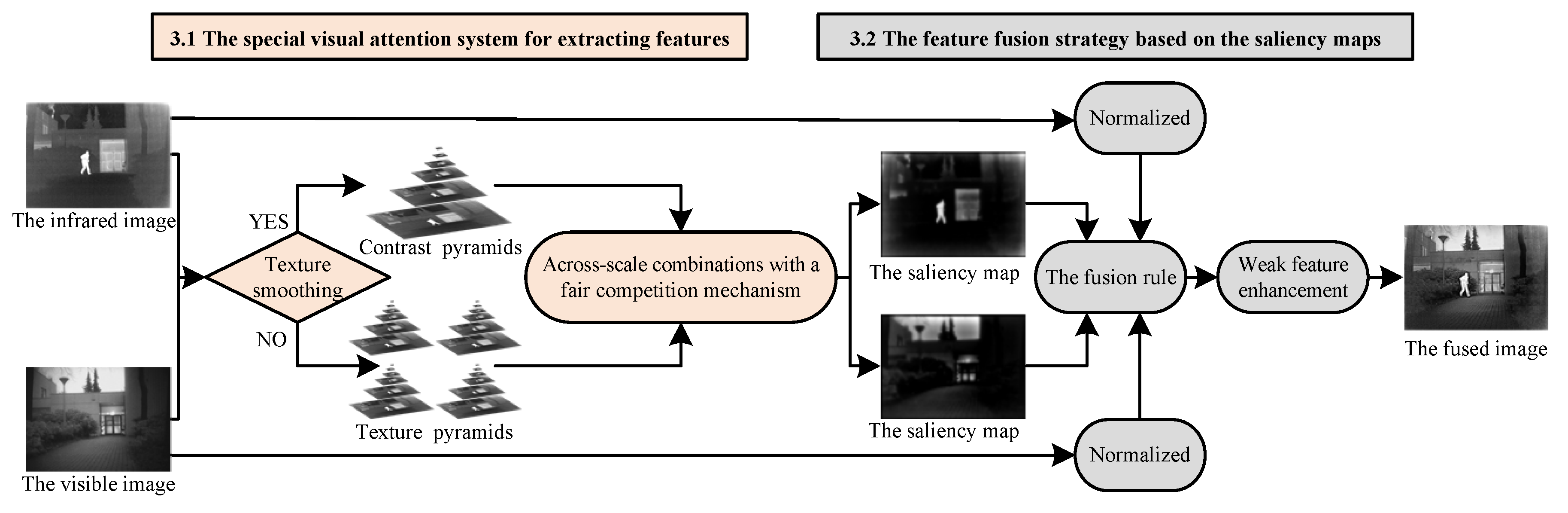
3.1. The Special Visual Attention System for Extracting Features
3.1.1. Modality Selection Based on Texture Complication Evaluation
- Collecting saliency information from intensity modality is an effective method when image texture smoothing. Since it is very sensitive to the image contrast, the intensity modality can use local contrast to measure the image activity level in the absence of direction information.
- When the texture details are rich, only the orientation modality can be used to achieve the best effect. In texture-rich image, gradient information in different directions is strong. Therefore, when synthesizing the four directions features maps into a single saliency map, the saliency information is much stronger than the signal intensity modality.
3.1.2. Across-Scale Combinations with a Fair Competition Mechanism
3.2. Feature Fusion Strategy Based on the Saliency Maps
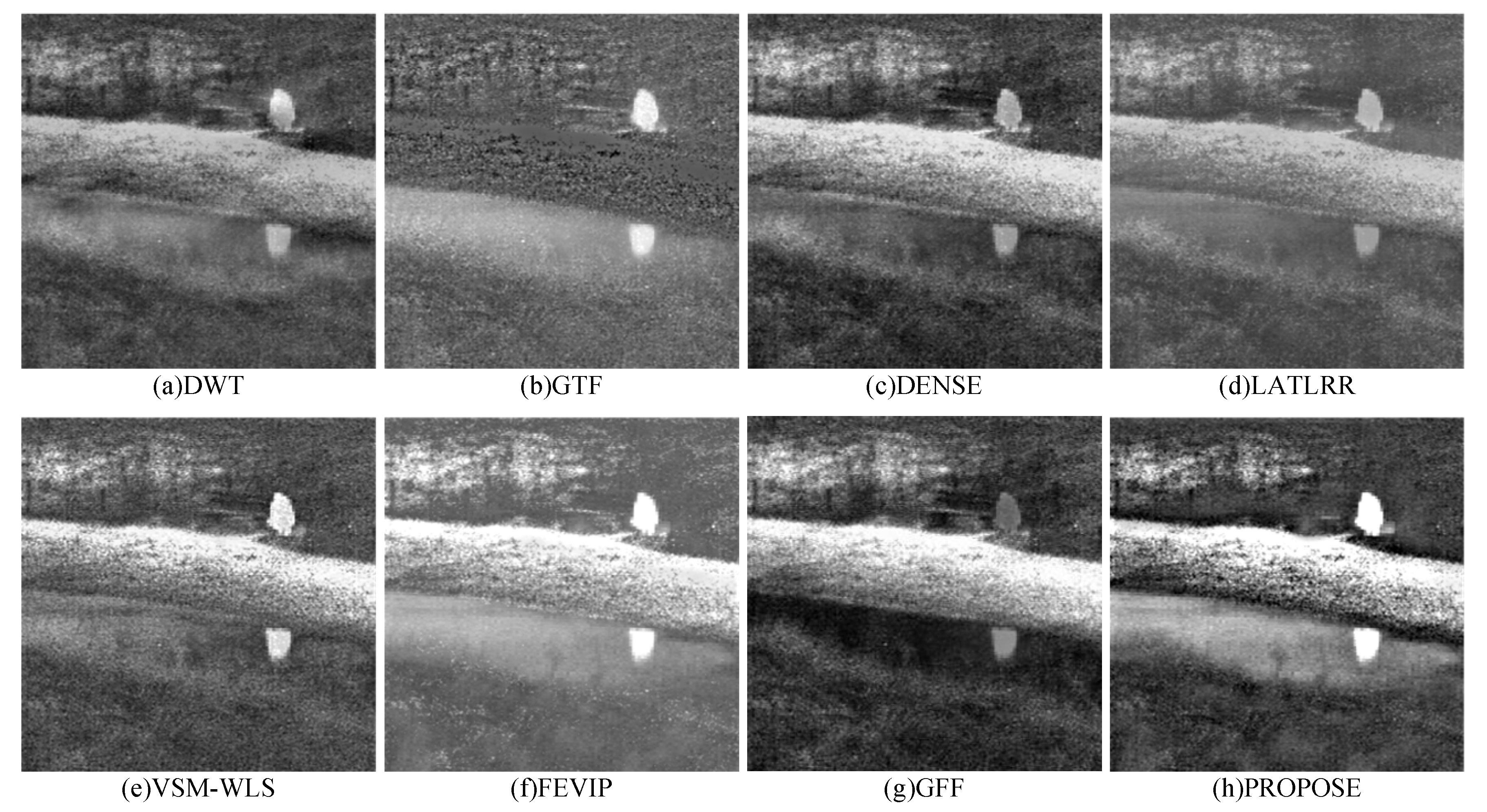
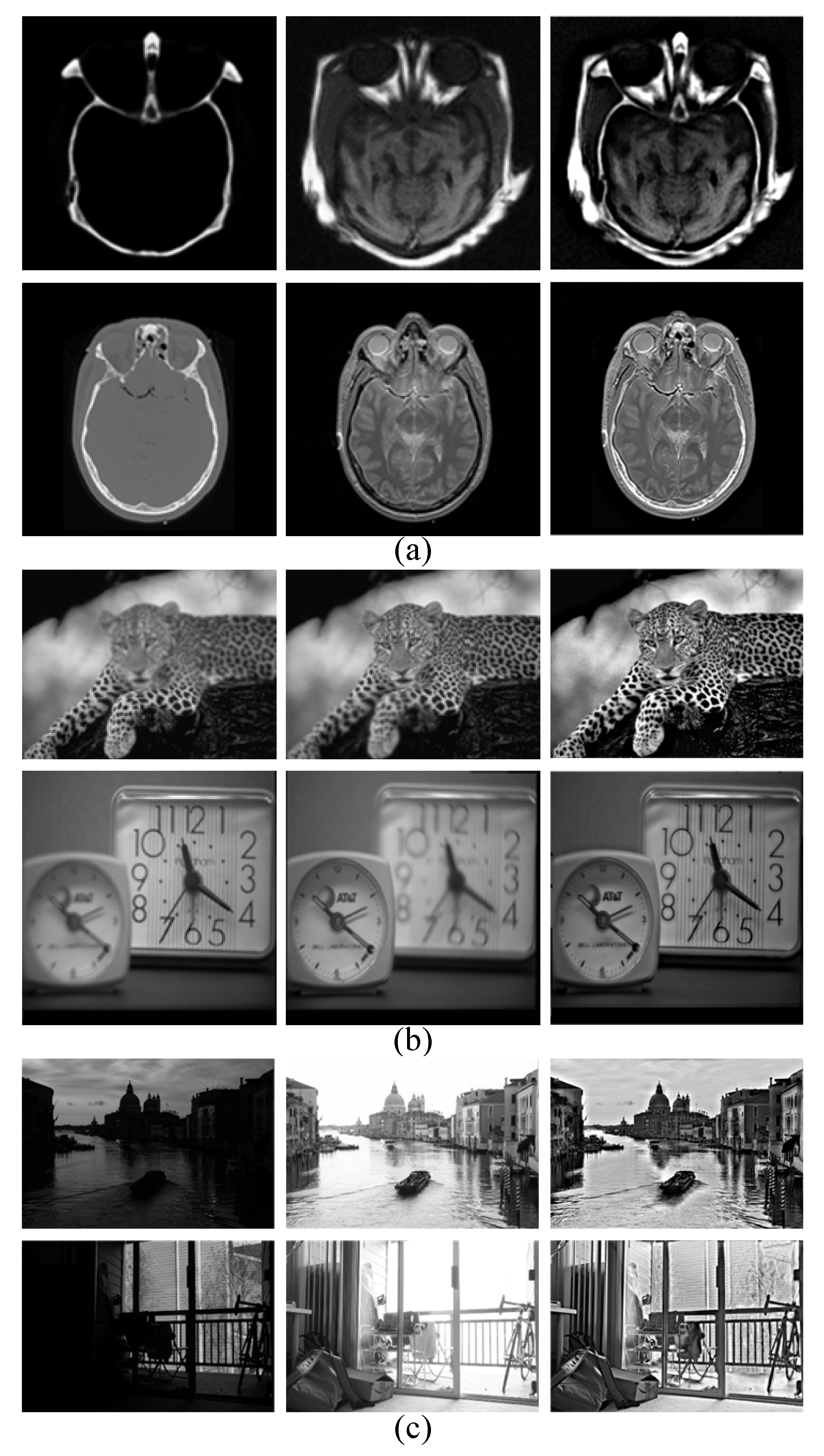
4. Experimental Results and Analyses
4.1. Experimental Settings
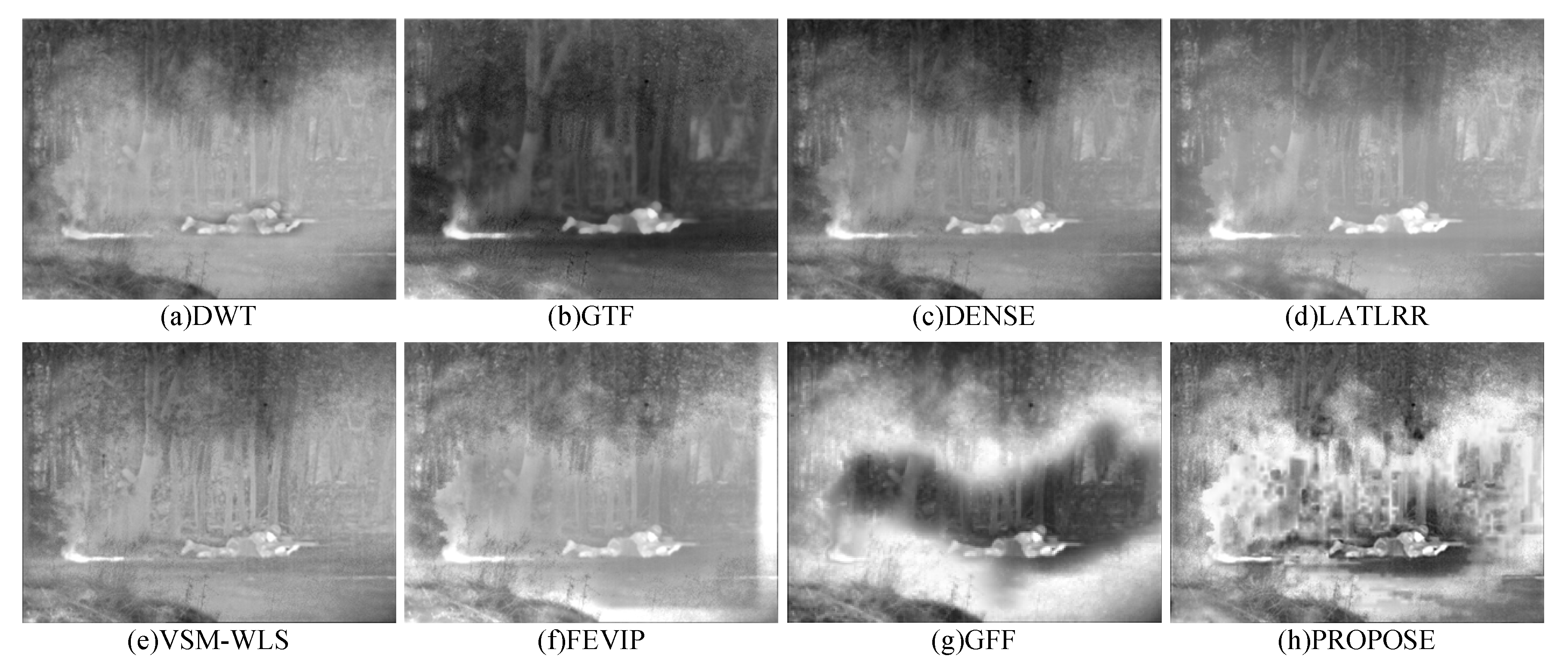
4.2. Qualitative Evaluation
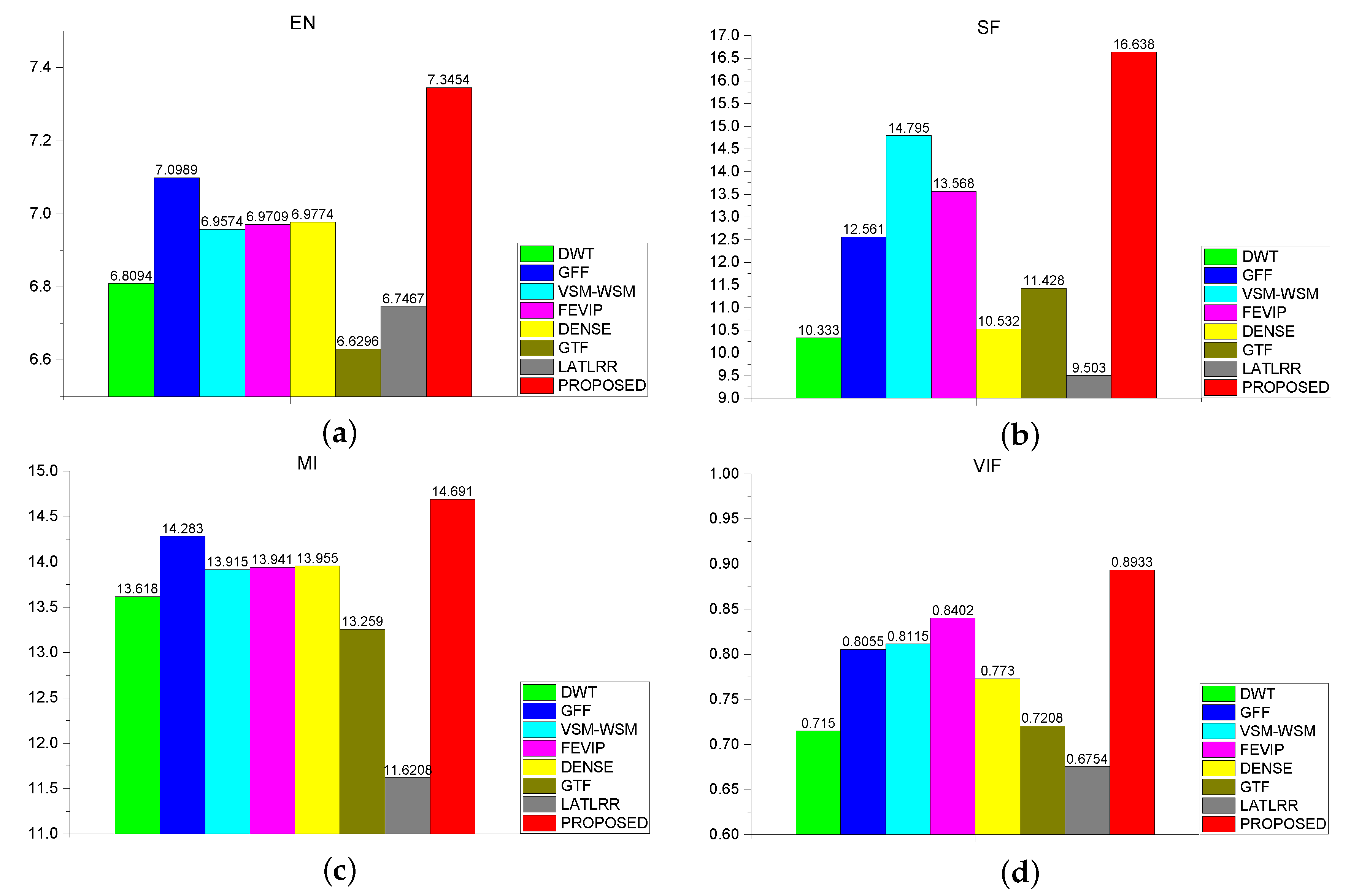
4.3. Quantitative Evaluation
4.3.1. Quantitative Metrics
4.3.2. Quantitative Evaluation Results
4.4. Computational Costs
4.5. Extension to Other-Type Image Fusion Field
4.6. Algorithm Limitation Analysis
- Optimal modality selection threshold. As can be seen from Section 3.1, the optimal modality has played a key role in the proposed algorithm. However, for different data sets, the contrast and texture features of the interesting region are different, so thresholds need to be adjusted for different data sets. In order to resolve this issue, we can experiment on many different data sets, and then the threshold empirical equation can be fitted according to the experimental results. In this way, we can automatically select thresholds for different data sets.
- Manual parameter selection. As can be seen from Section 3.2, this paper proposes that the feature fusion strategy has the problem of manually designing parameters, which result in the algorithm not being able to run automatically. One possible solution is to match the gray-scale histogram. If there is an over-enhancement phenomenon, adjust the feedback.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ardeshir Goshtasby, A.; Nikolov, S.G. Image fusion: Advances in the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, X. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects. Inf. Fusion 2017, 42, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, C.; Van Genderen, J. Review article Multisensor image fusion in remote sensing: Concepts, methods and applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 823–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xin, B.; Deng, N.; Xing, W.; Cheng, Y. An investigation of ramie fiber cross-section image analysis methodology based on edge-enhanced image fusion. Measurement 2019, 145, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson, F.; Sveinsson, J.; Ulfarsson, M. Sentinel-2 Image Fusion Using a Deep Residual Network. Remote Sens. 2018, 18, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, G. A Novel Geometric Approach to Binary Classification Based on Scaled Convex Hulls. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2009, 20, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Li, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhao, L.; Fan, Y. Accurate segmentation of nuclei in pathological images via sparse reconstruction and deep convolutional networks. Neurocomputing 2017, 229, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Huang, W. An improved fusion algorithm for infrared and visible images based on multi-scale transform. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 74, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvejic, N.; Bull, D.; Canagarajah, N. Region-based multimodal image fusion using ICA bases. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmans, T.; Javed, S.; Zhang, H. On the Applications of Robust PCA in Image and Video Processing. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 1427–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, P.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Z. Image fusion using quaternion wavelet transform and multiple features. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 6724–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulanon, D.M.; Burks, T.F.; Alchanatis, V. Image fusion of visible and thermal images for fruit detection. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 103, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Blum, R.S. A categorization of multiscale-decomposition-based image fusion schemes with a performance study for a digital camera application. Proc. IEEE 1999, 87, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, S. Multifocus image fusion and restoration with sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Blum, R.; Blum, R.; Han, J.; Tao, D. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: A review. Inf. Fusion 2018, 40, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Ji, Y.; Xu, W. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion through Details Preservation. Sensors 2019, 19, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cui, G.; Gong, X. Fusion of visible and infrared images using global entropy and gradient constrained regularization. Infrared Phys. Technol 2017, 81, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, B.; Agrawal, S.; Panda, R.; Abraham, A. A survey on region based image fusion methods. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Song, M.; Guo, B. Image fusion based on object region detection and non-subsampled contourlet transform. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 62, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, X.; Pei, H. A fusion algorithm for infrared and visible images based on saliency analysis and non-subsampled shearlet transform. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 73, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qi, Y.; Ding, W. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on saliency detection in sparse domain. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 83, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.A.; Bouridane, A.; Kurugollu, F. Accelerating the computation of GLCM and Haralick texture features on reconfigurable hardware. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Singapore, 24–27 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Guided image filter. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, L.; Pan, X.; Zhou, J.; Qin, L.; Xu, W. Single Image Defogging Based on Multi-Channel Convolutional MSRCR. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 72492–72504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Wang, Z. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2013, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, K.R.; Srikar, V.S.; Babu, R.V. DeepFuse: A Deep Unsupervised Approach for Exposure Fusion with Extreme Exposure Image Pairs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4714–4722. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xiao, J. Infrared and visible image fusion using Latent Low-Rank Representation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1804.08992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bai, X.; Zhang, L. Infrared and Visual Image Fusion through Infrared Feature Extraction and Visual Information Preservation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 83, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Blasch, E.; Xue, Z. Objective Assessment of Multiresolution Image Fusion Algorithms for Context Enhancement in Night Vision: A Comparative Study. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F.; Xue, B. Edge preserved image fusion based on multiscale toggle contrast operator. Image Vis. Comput. 2011, 29, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskicioglu, A.M.; Fisher, P.S. Image quality measures and their performance. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 43, 2959–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Jin, L.; Li, G. Infrared and visual image fusion using LNSST and an adaptive dual-channel PCNN with triple-linking strength. Neurocomputing 2018, 310, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.; Van Aardt, J.; Ahmed, F. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023522. [Google Scholar]








| Group | Fusion Algorithm | Evaluation Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN | MI | SF | VIF | ||
| Kaptein-1654 | DWT | 6.4807 | 12.9614 | 8.3551 | 0.6842 |
| GFF | 7.0315 | 14.0630 | 9.7603 | 0.7862 | |
| VSM-WSM | 6.7426 | 13.4853 | 12.158 | 0.7933 | |
| FEVIP | 6.6648 | 13.3297 | 11.803 | 0.8394 | |
| DENSE | 6.4133 | 12.8267 | 6.9027 | 0.6976 | |
| GTF | 6.5244 | 13.0488 | 9.1600 | 0.6558 | |
| LATLRR | 6.5546 | 13.1093 | 7.6490 | 0.6651 | |
| PROPOSED | 7.0438 | 14.0877 | 14.314 | 0.9089 | |
| Bench | DWT | 7.0807 | 14.1614 | 18.0912 | 0.6409 |
| GFF | 7.4934 | 14.9868 | 23.2069 | 0.8241 | |
| VSM-WSM | 7.1646 | 14.3293 | 26.3591 | 0.6546 | |
| FEVIP | 6.9297 | 13.8594 | 21.7905 | 0.6886 | |
| DENSE | 7.3496 | 14.6993 | 21.6091 | 0.6627 | |
| GTF | 6.7781 | 13.5562 | 21.8149 | 0.7237 | |
| LATLRR | 6.8550 | 13.7101 | 15.8557 | 0.5950 | |
| PROPOSED | 7.3676 | 14.7352 | 27.5356 | 0.8357 | |
| Kaptein-1123 | DWT | 6.9721 | 13.9442 | 8.2929 | 0.7879 |
| GFF | 6.8563 | 13.7127 | 7.0714 | 0.7057 | |
| VSM-WSM | 6.9714 | 13.9429 | 10.580 | 0.8895 | |
| FEVIP | 7.1691 | 14.3383 | 9.2726 | 0.9552 | |
| DENSE | 6.9073 | 13.8147 | 7.1428 | 0.8230 | |
| GTF | 6.9581 | 13.9162 | 6.4738 | 0.7037 | |
| LATLRR | 6.7016 | 13.4032 | 6.4051 | 0.7232 | |
| PROPOSED | 7.4212 | 14.8424 | 10.701 | 0.9851 | |
| Soldier-in-trench | DWT | 6.8856 | 13.7711 | 10.5937 | 0.8135 |
| GFF | 7.1845 | 14.8668 | 13.0178 | 0.9179 | |
| VSM-WSM | 6.9738 | 13.9477 | 13.8672 | 0.9587 | |
| FEVIP | 6.9431 | 13.8864 | 11.7221 | 0.8934 | |
| DENSE | 6.9996 | 13.9993 | 10.1163 | 0.8834 | |
| GTF | 6.6015 | 13.2031 | 12.5306 | 0.8535 | |
| LATLRR | 6.5548 | 13.1097 | 8.11250 | 0.7282 | |
| PROPOSED | 7.2061 | 14.4122 | 14.0425 | 0.9365 | |
| Airplane | DWT | 6.6942 | 13.3885 | 5.5777 | 0.7933 |
| GFF | 6.4477 | 12.8954 | 5.2579 | 0.7515 | |
| VSM-WSM | 6.6104 | 13.2210 | 5.9202 | 0.8567 | |
| FEVIP | 6.7302 | 13.4606 | 7.1918 | 0.8798 | |
| DENSE | 7.0350 | 14.0700 | 6.1090 | 0.9516 | |
| GTF | 5.8563 | 11.7127 | 4.3989 | 0.6881 | |
| LATLRR | 6.4571 | 12.9143 | 4.2604 | 0.7423 | |
| PROPOSED | 7.1444 | 14.2889 | 8.1186 | 1.0698 | |
| Soldier_behind_smoke | DWT | 6.9039 | 13.8079 | 8.5219 | 0.7425 |
| GFF | 7.5263 | 15.1527 | 11.884 | 0.9369 | |
| VSM-WSM | 6.9735 | 13.9470 | 11.831 | 0.9064 | |
| FEVIP | 7.0271 | 14.0543 | 11.626 | 0.9149 | |
| DENSE | 7.0523 | 14.1046 | 7.8967 | 0.8117 | |
| GTF | 6.6015 | 13.2030 | 10.924 | 0.8302 | |
| LATLRR | 6.9239 | 13.8479 | 7.7548 | 0.7209 | |
| PROPOSED | 7.6489 | 15.2979 | 15.063 | 0.7842 | |
| Road | DWT | 6.6485 | 13.2971 | 12.8952 | 0.5427 |
| GFF | 7.1527 | 14.3056 | 17.7289 | 0.7165 | |
| VSM-WSM | 7.2656 | 14.5313 | 22.8475 | 0.6218 | |
| FEVIP | 7.3325 | 14.6650 | 21.5730 | 0.7106 | |
| DENSE | 7.0858 | 14.1717 | 13.9473 | 0.5809 | |
| GTF | 7.0878 | 14.1756 | 14.6903 | 0.5906 | |
| LATLRR | 7.1803 | 14.3606 | 16.4928 | 0.5532 | |
| PROPOSED | 7.5860 | 15.1721 | 26.6966 | 0.7334 | |
| Fusion Algorithm | Kaptein-1654 | Bench | Kaptein-1123 | Soldier-in-Trench | Airplane | Soldier_behind_SMOKE | Road |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWT | 0.2417 | 0.0981 | 0.2085 | 0.3058 | 0.1647 | 0.2735 | 0.1009 |
| GFF | 0.2047 | 0.0628 | 0.2042 | 0.3086 | 0.1669 | 0.3046 | 0.0709 |
| VSM-WSM | 1.6626 | 0.2464 | 1.6521 | 2.8538 | 1.1455 | 2.8557 | 0.2132 |
| FEVIP | 0.0827 | 0.0467 | 0.0904 | 0.0997 | 0.0761 | 0.1074 | 0.0500 |
| DENSE | 0.4263 | 0.3906 | 0.6727 | 0.4877 | 0.6018 | 0.5047 | 0.3663 |
| GTF | 3.5350 | 0.2946 | 3.1396 | 6.2277 | 3.1988 | 3.8056 | 0.2673 |
| LATLRR | 58.971 | 13.081 | 59.234 | 108.09 | 42.076 | 110.11 | 10.999 |
| PROPOSED | 0.2054 | 0.0514 | 0.2161 | 0.3570 | 0.1534 | 0.3443 | 0.0487 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W. An Efficient Method for Infrared and Visual Images Fusion Based on Visual Attention Technique. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050781
Liu Y, Dong L, Chen Y, Xu W. An Efficient Method for Infrared and Visual Images Fusion Based on Visual Attention Technique. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(5):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050781
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yaochen, Lili Dong, Yang Chen, and Wenhai Xu. 2020. "An Efficient Method for Infrared and Visual Images Fusion Based on Visual Attention Technique" Remote Sensing 12, no. 5: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050781
APA StyleLiu, Y., Dong, L., Chen, Y., & Xu, W. (2020). An Efficient Method for Infrared and Visual Images Fusion Based on Visual Attention Technique. Remote Sensing, 12(5), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050781




