Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- (1).
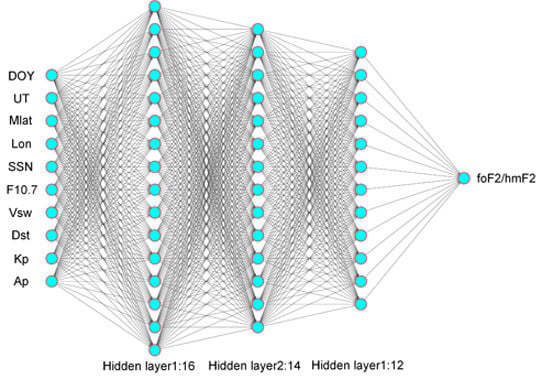
- Ten input parameters (same as the input layer in Figure 2) of ionosonde foF2 points IONOfoF2 were taken as the input information for the COSPF and IONOPF models, respectively.
- (2).
- The foF2 values were simulated by the COSPF and IONOPF models, respectively, namely, COSPFfoF2 and IONOPFfoF2; then, the difference was computed between COSPFfoF2 and IONOPFfoF2.
- (3).
- The sum of the pre-corrected ionosonde foF2 value IONOfoF2 and the above difference was regarded as the final corrected value COSMIC-foF2corr.
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Accuracy in the Solar Minimum Year
3.2. Validation of Accuracy in the Solar Moderate Year
3.3. Validation of Accuracy over the Greenwich Meridian
3.4. Validations of Global Spatiotemporal Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, X.; Bortnik, J.; Li, W.; Ma, Q.; Denton, R.; Yue, C.; Angelopoulos, V.; Thorne, R.; Darrouzet, F.; Ozhogin, P. A neural network model of three-dimensional dynamic electron density in the inner magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 9183–9197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichaipanich, N.; Hozumi, K.; Supnithi, P.; Tsugawa, T. A comparison of neural network-based predictions of foF2 with the IRI-2012 model at conjugate points in southeast asia. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2934–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athieno, R.; Jayachandran, P.; Themens, D. A neural network-based foF2 model for a single station in the polar cap. Radio Sci. 2017, 52, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumluca, A.; Tulunay, E.; Topalli, I.; Tulunay, Y. Temporal and spatial forecasting of ionospheric critical frequency using neural networks. Radio Sci. 1999, 34, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wan, W.; Liu, L.; Ning, B.; Zhao, B. Applying artificial neural network to derive long-term foF2 trends in the Asia/Pacific sector from ionosonde observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoque, M.; Jakowski, N. A new global model for the ionospheric F2 peak height for radio wave propagation. In Annales Geophysicae; Copernicus GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2012; pp. 797–809. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Ning, B.; Liu, L.; Song, G. A prediction model of short-term ionospheric foF2 based on AdaBoost. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyemi, E.O.; McKinnell, L.; Poole, A. Near-real time foF2 predictions using neural networks. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhatov, N.; Revunov, S.; Uryadov, V. Artificial neural network technique for predicting the critical frequency of the ionospheric F 2 layer. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2005, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhou, C.; Deng, Z.; Ni, B.; Zhao, Z. Predicting foF2 in the China region using the neural networks improved by the genetic algorithm. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2013, 92, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williscroft, L.A.; Poole, A.W. Neural networks, foF2, sunspot number and magnetic activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 3659–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnell, L.; Oyeyemi, E. Equatorial predictions from a new neural network based global foF2 model. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenos, T. Neural-network-based prediction techniques for single station modeling and regional mapping of the foF2 and M (3000) F2 ionospheric characteristics. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2002, 9, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKinnell, L.-A.; Friedrich, M. A neural network-based ionospheric model for the auroral zone. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyemi, E.; Poole, A.; McKinnell, L. On the global model for foF2 using neural networks. Radio Sci. 2005, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Lin, C.; Lin, C.; Tsai, H.; Solomon, S.; Sun, Y.; Lee, I.; Schreiner, W.; Kuo, Y. Artificial plasma cave in the low-latitude ionosphere results from the radio occultation inversion of the FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulasi Ram, S.; Sai Gowtam, V.; Mitra, A.; Reinisch, B. The Improved Two-Dimensional Artificial Neural Network-Based Ionospheric Model (ANNIM). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 5807–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krankowski, A.; Zakharenkova, I.; Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Shagimuratov, I.I.; Wielgosz, P. Ionospheric electron density observed by FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC over the European region and validated by ionosonde data. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 949–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNamara, L.F.; Thompson, D.C. Validation of COSMIC values of foF2 and M (3000) F2 using ground-based ionosondes. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, C.; Batista, I.; Abdu, M. Radio occultation electron density profiles from the FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC satellites over the Brazilian region: A comparison with Digisonde data. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, B.; Yue, X.a.; Mao, T. Comparison between ionospheric character parameters retrieved from FORMOSAT3 measurement and ionosonde observation over China. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 3625–3632. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.; Jakowski, N. A new global empirical NmF2 model for operational use in radio systems. Radio Sci. 2011, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilitza, D.; Reinisch, B.W.; Radicella, S.M.; Pulinets, S.; Gulyaeva, T.; Triskova, L. Improvements of the International Reference Ionosphere model for the topside electron density profile. Radio Sci. 2006, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowtam, V.S.; Ram, S.T. An Artificial Neural Network-Based Ionospheric Model to Predict NmF2 and hmF2 Using Long-Term Data Set of FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC Radio Occultation Observations: Preliminary Results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 11743–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Su, C.-L.; Ko, H.-T. A global survey of COSMIC ionospheric peak electron density and its height: A comparison with ground-based ionosonde measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Ning, B.; Liu, L.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, G. Comparison between ionospheric peak parameters retrieved from COSMIC measurement and ionosonde observation over Sanya. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Syndergaard, S.; Burns, A.G.; Solomon, S.C.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Z.; Roble, R.G.; Wu, Q.; Kuo, Y.H.; Holt, J.M. Comparison of COSMIC ionospheric measurements with ground-based observations and model predictions: Preliminary results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Razin, M.; Voosoghi, B. Regional application of multi-layer artificial neural networks in 3-D ionosphere tomography. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 58, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montana, D.J.; Davis, L. Training Feedforward Neural Networks Using Genetic Algorithms. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Detroit, MI, USA, 20–25 August 1989; pp. 762–767. [Google Scholar]
- Song, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, C.; Liu, J.; He, J. Predicting TEC in China based on the neural networks optimized by genetic algorithm. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, T. Storm time behavior of topside scale height inferred from the ionosphere–plasmasphere model driven by the F2 layer peak and GPS-TEC observations. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yue, J.; Yang, Y.; He, C.; Hu, A.; Zhang, K. Ionospheric and Thermospheric Responses to the Recent Strong Solar Flares on 6 September 2017. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 8865–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Yue, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Bi, J.; Zhang, K. Ionospheric responses to typhoons in Australia during 2005–2014 using GNSS and FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC measurements. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yue, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, Y.; Zou, B.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, K. Statistical seismo-ionospheric precursors of M7. 0+ earthquakes in Circum-Pacific seismic belt by GPS TEC measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, W.; Chang, X. Analysis of the melting glaciers in Southeast Tibet by ALOS-PALSAR data. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2019, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Schreiner, W.S.; Pedatella, N.; Anthes, R.A.; Mannucci, A.J.; Straus, P.R.; Liu, J.Y. Space weather observations by GNSS radio occultation: From FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC to FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2. Space Weather 2014, 12, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]










© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Zhao, D.; He, C.; Hu, A.; Zhang, K. Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050866
Li W, Zhao D, He C, Hu A, Zhang K. Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(5):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050866
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wang, Dongsheng Zhao, Changyong He, Andong Hu, and Kefei Zhang. 2020. "Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations" Remote Sensing 12, no. 5: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050866
APA StyleLi, W., Zhao, D., He, C., Hu, A., & Zhang, K. (2020). Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations. Remote Sensing, 12(5), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050866