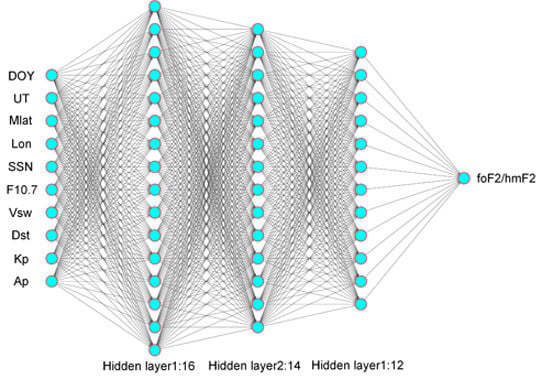
Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations
Abstract
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Zhao, D.; He, C.; Hu, A.; Zhang, K. Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050866
Li W, Zhao D, He C, Hu A, Zhang K. Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(5):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050866
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wang, Dongsheng Zhao, Changyong He, Andong Hu, and Kefei Zhang. 2020. "Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations" Remote Sensing 12, no. 5: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050866
APA StyleLi, W., Zhao, D., He, C., Hu, A., & Zhang, K. (2020). Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations. Remote Sensing, 12(5), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050866