Abstract
Urbanization is a global phenomenon, but its negative effects are most pronounced in developing countries. While much urbanization in the global South is unplanned, there have been occasional attempts at strategic, large-scale urban planning. One example is Abuja, Nigeria, a new city with origins in a 1970s Master Plan. Here, we use multi-temporal remote sensing to investigate four decades of urbanization in Abuja, showing the extent to which urban development has matched original intentions. Seven Landsat images from 1975 to 2014 were selected to correspond with Master Plan milestones and turning points in Nigeria’s socio-political development. Land cover classification and change detection results show built-up land increasing rapidly, from 1,167 ha in 1975 to 18,623 ha in 2014, mostly converted from grassland, often via a pioneer bare soil class. Comparing image analysis against the Master Plan shows that, in the early years, Abuja’s development matched broad planning intentions fairly closely. Later, though, unplanned development proliferated, and the city’s resemblance to the Master Plan diminished progressively. Level of adherence to the Master Plan varied widely according to the system of government. Notably, after long-term military rule was replaced by a democratic government around the turn of the millennium, unplanned development increased sharply.
1. Introduction
The current rate of urbanization worldwide is unprecedented, with these rapidly growing urban environments having significant human and environmental consequences. In 1900, approximately 5% of the world’s population lived in cities [1], increasing to 55% in 2018 and forecast to be 68% by 2050 [2]. Much of the world’s future urban and population growths will occur in developing countries, with Africa and Asia urbanizing at a faster rate than the rest of the world. By 2050, the global urban population is expected to increase by 2.5 billion, with 90% of this increase in Africa and Asia; China, India and Nigeria alone are forecast to account for 37% of the global urban population increase [3]. Urbanization impacts are often felt most severely in developing countries poorly equipped to manage the challenges associated with rapid urban growth, such as environmental degradation, high unemployment, poverty and housing shortages [4].
To manage urbanization more effectively, some countries have taken the approach of building new planned cities—for example, Dodoma (Tanzania), Lilongwe (Malawi), Pyinmana (later renamed Naypydaw, Myanmar), Brasilia (Brazil), Islamabad (Pakistan), Canberra (Australia) and Washington D.C. (USA). Planned cities are often guided by some form of “Master Plan”, a comprehensive long-term planning document providing a clear framework for city design, land use, growth and development schedules. In developed nations, there has been strong criticism of the use of Master Plans, with many countries now moving to more flexible and collaborative initiatives such as strategic spatial plans, strategic urban planning, multi-functional urban projects and smart growth or “urban villages” [5,6,7,8,9]. Some of these criticisms are that Master Planning is less participatory and democratic and does not adequately address environmental concerns, such as resource depletion, climate change and environmental sustainability. However, in developing countries, Master Planning has remained popular and is still considered a valuable approach for effective urban development and management. One notable example of a planned capital city in the global South is Abuja, Nigeria.
In 1975, the Nigerian government concluded that Lagos was not capable of continuing as federal capital due to inadequate space for future development, lack of cultural diversity and non-central (within Nigeria) location [10]. The government thus commissioned planning of a new centrally located capital city that should be ethnically neutral, have sufficient natural land resources for development and provide a symbol of Nigeria’s ambition to foster unity and portray greatness [10]. In February 1976, the Federal capital development authority (FCDA) was established to plan and develop this new capital city. To achieve this, a Master Plan was developed by International Planning Associates (IPA) in 1979 [11], a policy regarded as one of the most profound decisions taken by Nigeria since independence from Great Britain in 1960 [12]. Construction began in 1980 with an intended occupancy date of 1986, later moved to 1991 (when Abuja replaced Lagos as the capital city) due to the slow pace of development. The Master Plan proposed a 20+ year implementation period, with the year 2000 set as the target for all phases of the city to be fully developed [13].
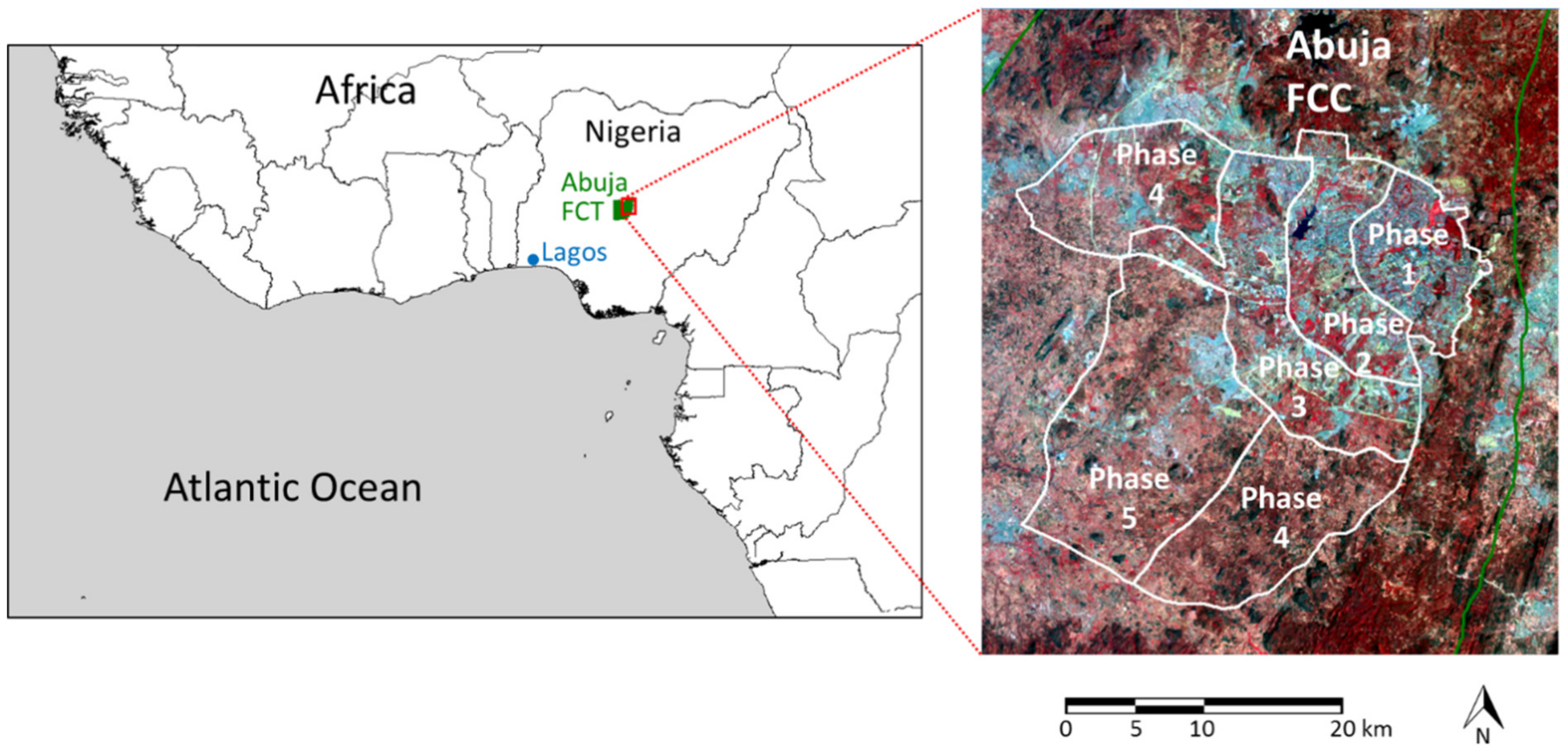
The Master Plan originally specified four phases of development radiating outwards sequentially from the main urban center in the northeast (Figure 1). This phased approach was adopted to ensure orderly growth of the city, limiting disruption and pollution associated with development and enabling targeted infrastructural development so the city is habitable, populated and functional at the conclusion of each phase [13]. The phases were intended to occur broadly sequentially, though some allowance was made for overlap between phases. While the spatial footprints of these phases were specified precisely, the development timescales were less clear. Few specific dates were given, though construction of phase one was scheduled to start in 1980 and end by 1986 (when Abuja was intended to be inaugurated as Nigeria’s capital city), and a completion of all four phases was scheduled for 2000. Prior to development, 500–600 small settlements and villages were present in the Federal capital territory (FCT) in which the Federal capital city (FCC) of Abuja was developed, with a total population around 300,000 in 1975. The Master Plan proposed these settlements and their residents be relocated from areas earmarked for development within the planned city [13], though there has been little follow-up analysis to investigate the process or success of this relocation.
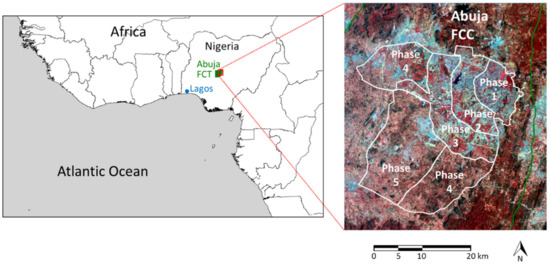
Figure 1.
Study area showing the extent of Abuja Federal capital territory (FCT) on the left, with an inset of Abuja Federal capital city (FCC) and its phase boundaries on the right. The FCC footprint is overlaid on a false color composite Landsat operational land imager (OLI) image. (FCC map adapted from data supplied by the Abuja Geographic Information System Agency, Federal Capital Development Authority and Nigeria Space Research and Development Agency; Landsat OLI image supplied by US Geological Survey).
The Master Plan specified that of the FCC’s usable land (excluding steep slopes and rock outcrops), 49% was earmarked for residential development, 32.5% for recreational purposes (including green and open space), 16.5% for light industries (including commercial activities) and 2% for government usage [13]. Since its inception, however, Abuja has experienced rapid population growth and urbanization. With an urbanization rate of 8.3% per annum, it is the fastest-growing city in Africa [14], putting considerable strain on the city’s infrastructure and limiting overall adherence to the provisions of the Master Plan [11,15]. The original population target was 1.6 million, although it is speculated this figure may be exceeded (up to an additional 1.6 million), with the additional population accommodated in other satellite towns within the FCT [13]. In the official 2006 census, the population was stated as just under 1.7 million [16], although this figure is highly contentious with other studies estimating the daytime population to be close to 7 million [15]. In 2005, the Nigerian government responded to observations that both urbanization and population growth had far outstripped projections [3] by proposing an additional, fifth phase of development covering an area of approximately 210 km2. However, details remain scant, and the proposal has never been ratified by the FCDA.
Given the pace of global urbanization and its negative consequences, monitoring urban area growth is critical to provide essential information for urban management and planning. To do this, a regular and reliable source of spatial information is needed, with ground survey labor-intensive and costly. Remote sensing is the only realistic solution. Satellite data has been used widely in mapping urban growth and assessing city morphology, informal settlements, and socio-economic features such as population size and poverty [17,18]. Urban remote sensing dates back to the start of the Landsat programme in 1972, when the spatial data requirements needed to delineate broad urban patterns were met with medium (79 by 57 m) spatial resolution Landsat multispectral sensor (MSS) imagery [1]. Later generations of the Landsat Thematic Mapper series (30-m spatial resolution) improved the detail and accuracy available for urban mapping to some extent [19]. However, the introduction of very high-resolution (VHR) sensors, the first being IKONOS, launched in 1999 with 4-m spatial resolution (multispectral) imagery [20,21], improved capabilities dramatically. The greater detail provided by VHR sensors offered improved discrimination of built-up and non-built-up areas and has improved the ability to analyze internal variations within urban settlements [22].
Many studies have used a diverse range of multispectral remote sensing imagery and techniques to investigate urban areas around the world. For instance, Huang et al. (2018) [23] applied deep learning on VHR multispectral imagery to increase the accuracy of land use classification in Shenzhen and Hong Kong, China. In the city of Mekelle, Ethiopia, a more traditional approach of applying a maximum likelihood classifier on Landsat multispectral imagery was adopted to assess urban expansion and land cover use changes successfully [24]. A similar approach of using Landsat imagery and spatial metrics was also adopted successfully by [25] to model the internal structure and dynamics of urban sprawl in Ghanaian cities. Furthermore, [26] also investigated the spatiotemporal patterns of urban expansion and factors influencing the expansion in Miami between 1992 and 2016 using medium resolution satellite imagery. Researchers have combined satellite imagery analysis and social media data to map urban areas [27,28]. Other studies attempted to show the impact of urban growth and land use change on different parts of the environment—for instance, the impact of urban growth on agriculture and natural land [29]. Reference [30] proposed an analytical framework for land use research, while the global consequences of land use to the environment were described by [31].
While great effort goes into the Master Plan development and implementation, there is often little later reflection on its success. Examples where Master Plans have previously been assessed include six local plans in New Zealand [32]; Islamabad, Pakistan [33]; Amman, Jordan [34]; the central district plan of Israel [35]; Guangzhou, China [36]; Lucknow, India [37]; Nanjing, China [38] and Lisbon, Portugal [39], though these have not generally exploited time-series remotely sensed imagery to aid their assessment. These studies instead focus mainly on planning policy implementations or the level of conformance of current land use to the Master Plan without interrogating the processes that led to the current situation. Most studies also fail to analyze the intention of the original Master Plan in relation to the later outcomes observed and conduct assessments over a relatively short time-frame rather than considering the full lifetime of a city’s development.
In Abuja, few studies have retrospectively examined the city’s urban growth and development [11,40,41,42], and there has been no comprehensive review of the Master Plan’s successes and failures [11]. Notably, no study has examined how Abuja has developed in relation to the original Master Plan using satellite remote sensing. This study is one of the first to assess comprehensively the success of a city Master Plan in the global South using the approach of mapping land cover changes using historical remotely sensed imagery over the full lifetime of a city. As such, the findings of this study, which examines long-term changes in Abuja and, also, comments on potential causes of these changes will have significance for urban planning and management practices in the context of rapid global urbanization.
This study aims to monitor the urbanization of Abuja since its inception in the early 1980s and assess the extent to which the Master Plan has been realized. To achieve this, a time-series of historical Landsat images is used to generate a series of land cover maps enabling changes in land cover types and coverage throughout Abuja’s Federal capital territory (FCT) between 1975 and 2014 to be quantified. Of particular interest and novelty is monitoring the development of the city over its full lifetime and in the distinction between planned (as identified in the Master Plan) and unplanned urban development. The very existence of a Master Plan implies that unplanned developments should not have occurred or, at least, should be relatively insignificant. There will also be consideration of how prevailing social and political context can influence urban development. For instance, during implementation of Abuja’s Master Plan, Nigeria’s government switched variously between democratic and military rule, potentially influencing urban development policies. Ultimately, the findings of this study will enable recommendations on how planners and policy makers can better monitor urban growth, thus tackling unwanted consequences of urbanization more effectively. To address this overall aim, four research questions are posed: (1) How have patterns of land cover in Abuja FCT evolved since the 1970s? (2) Has the Master Plan been effective in dictating the pace and pattern of urbanization in Abuja? (3) Has unplanned urban development been limited successfully? (4) Have changes in political governance influenced the nature of urban growth?
2. Study Area
This study focusses on the Federal capital city (FCC) of Abuja, Nigeria, and its surrounds. The FCC covered an area of 256 km2 (in the original Master Plan), later extended to approximately 450 km2, including an extra development phase added in 2005, with the five phases of development displayed in Figure 1. To the north and east of the urban center is a large rock outcrop that inhibits construction; thus, development was intended to be focused to the west and south. The FCC is located within the Federal capital territory (FCT), which itself covers an area of around 8000 km2, the FCT is positioned between latitude 7°25′ and 9°20′N and longitude 5°45′ and 7°39′W, with elevations ranging from approximately 100 m (in the southwest) to above 600 m (in the northeast). Abuja has two distinct seasons: the wet season between early April and late October and the dry season from November to March. The FCT is located within the Guinea-Savanna vegetation zone [43].
3. Research Data
3.1. Remotely Sensed Imagery
Seven Landsat images covering the lifetime of the Master Plan from 1975, 1986, 1990, 1999, 2002, 2008 and 2014 (Table 1), downloaded via the EarthExplorer facility (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/), were used in this study. To enable ready comparison, images were acquired from similar times of the year, minimizing seasonal effects. Image selection was influenced by the availability of cloud-free images, with January targeted since this is central in the dry season and all images selected being within one month of this target window. Image years were spaced throughout the project timescale, with certain years targeted to correspond with political and legislative change in Nigeria. For example, 1975 corresponded with the original (1976) proposal to create Abuja [44], 1986 with intended initial occupation of the city [45] and 1990 with the proposed relocation of the capital city from Lagos to Abuja [43]. The year 1999 was selected to match Nigeria’s switch from military to democratic governance, and 2002, 2008 and 2014 were selected with relatively short intervals to provide a broadly equivalent time interval to the four-year tenure of elected governments in Nigeria. Matching the imagery to key dates in Nigeria’s recent political past is important, since civilian rule has seen a marked increase in infrastructural investment in Abuja [46].

Table 1.
Multi-temporal Landsat time-series and NigeriaSat-2 imagery used to analyze urbanization in Abuja (MSS = multispectral scanner, TM = thematic mapper, ETM+ = enhanced thematic mapper plus and OLI = operational land imager; B = blue, G = green, R = red, NIR = near infrared, SWIR = shortwave infrared and P = panchromatic).
Due to the timescale over which urban development is investigated, it was necessary to use images acquired from different Landsat sensors: multispectral scanner (MSS), thematic mapper (TM), enhanced thematic mapper plus (ETM+) and operational land imager (OLI). The spectral and spatial specifications of these instruments vary, but basic multispectral image configurations were used in all cases (see Table 1 for details). Thus, the spatial resolution was 30 m for all TM, ETM+ and OLI images, with only the MSS image being at a coarser resolution (originally acquired at 79 × 57 m, and subsequently resampled to regular 60 m pixels before data supply). Spectrally, standard visible (blue, green and red); near infrared (NIR) and shortwave infrared (SWIR) bands were used, wherever available. The thermal band (TM, ETM+ and OLI), and OLI’s coastal and cirrus bands, were omitted, since these bands are not optimized for land cover features.
3.2. Urban Planning Data
The Abuja Master Plan was used as a data source for proposed land cover distributions throughout the study area, against which the remote sensing analysis results were compared. A map of the original (four) Master Plan FCC phases was obtained from the Abuja Geographic Information System (AGIS) agency and subsequently digitized. A phase-five map was obtained from the FCDA Department of Urban and Regional Planning and also digitized. To enable detailed spatial analysis, vector maps (shapefiles) showing individual districts within the FCC were obtained from AGIS. For six of these districts (Jahi, Katampe, Kaura and Utako located in phase 2 and Kabusa and Saraji in phase 3), detailed land cover and land use budget allocations (i.e., specific planned areal extents of different classes) were available, provided by the FCDA.
3.3. Land Cover Reference Data
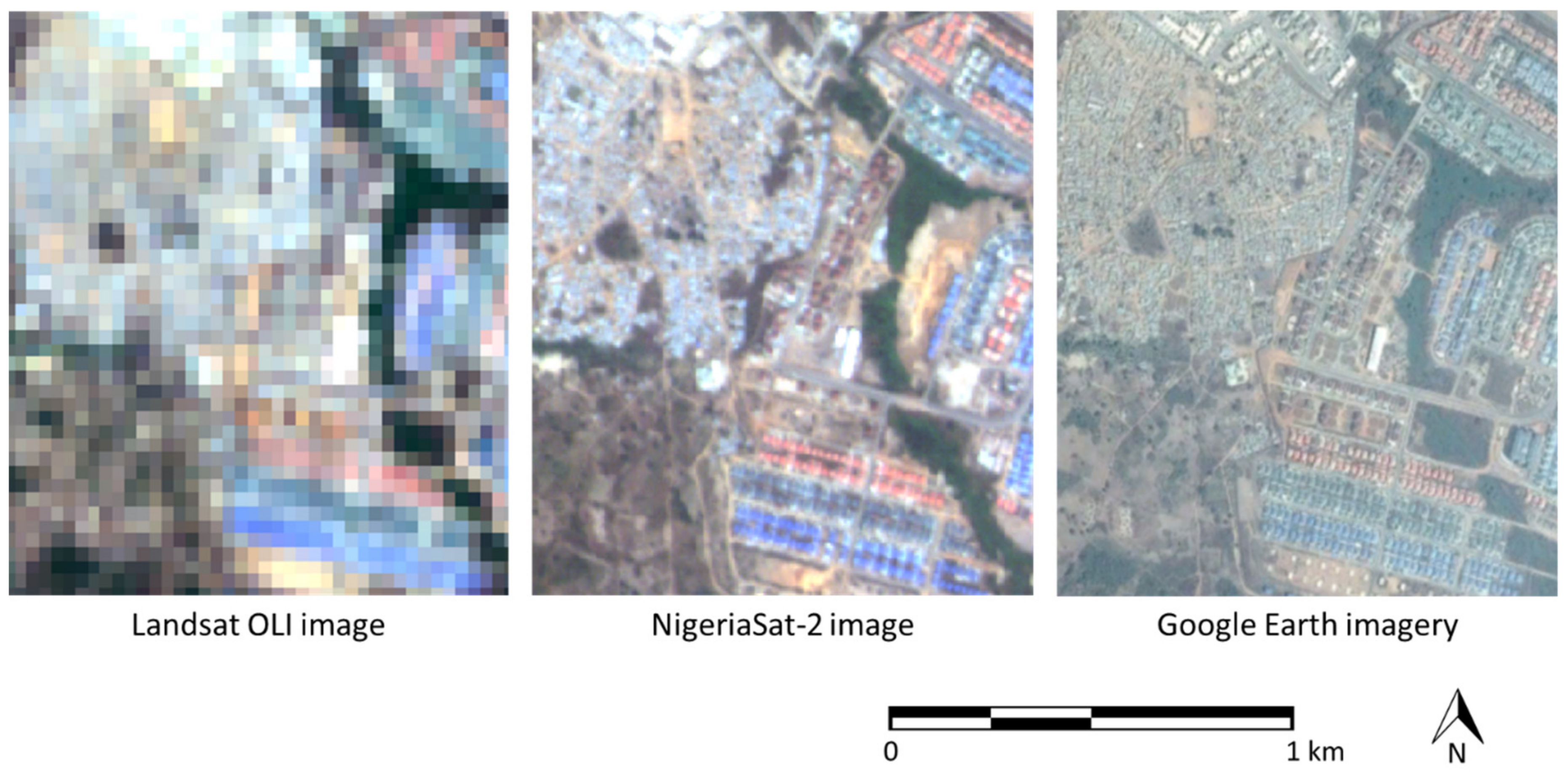
To enable independent verification of the land cover change analysis, a robust reference dataset was compiled from a range of available sources. First, a six-week field campaign was undertaken in 2015. This involved extensive land cover survey throughout the study area and interviews (relating to land cover and land use change over the years and planning policies) with the city’s planning officials and residents. Second, land cover maps covering parts of the study area (phases 1–3) were acquired from both AGIS and the FCDA. Third, VHR imagery was accessed, both through Google Earth’s historical imagery function (containing imagery dating back to 2001) [47,48] and directly from a NigeriaSat-2 image (Table 1) of Abuja acquired in January 2014 (supplied by the Nigeria Space Research and Development Agency (NASRDA)) (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Contrast between planned (east of image) and unplanned (northwest of image) urban development in Kabusa district, as represented by three different false color composite images captured in January 2014: Landsat operational land imager, NigeriaSat-2 and Google Earth imagery. (Landsat OLI image supplied by US Geological Survey, NigeriaSat-2 image supplied by Nigeria Space Research and Development Agency and Google Earth imagery © 2018 CNES/Airbus.)
These reference data sources were collated to create a single, comprehensive reference land cover dataset for each year of analysis (i.e., each of the Landsat image dates) and used to train and test land cover classification analysis. Ensuring close temporal alignment between reference and image data proved challenging, especially for the early image dates. While the 2014 image was very well-referenced (fieldwork and NigeriaSat-2 image), and other relatively recent images (1999, 2002 and 2009) were covered by historical Google Earth imagery and secondary land cover maps, reference data sources were more limited for earlier image dates (1975, 1986 and 1990). In these cases, the fieldwork campaign proved invaluable, eliciting personal observations and oral histories through interviews with long-term planning officials and residents able to provide detailed descriptions of past land cover distributions and changes over time [49,50].
4. Methodology
4.1. Land Cover Classification System
Classifying urban land cover from remotely sensed data is complex due to the spectral heterogeneity of urban reflectance [51,52,53,54]; therefore, defining appropriate thematic classes considering the study area characteristics and technical specifications of the imagery is important. The classification system used here was developed after careful study of the relevant literature and secondary land cover maps and following extensive field observations around the study area. The system was adapted from Anderson’s (1976) [55] widely used approach, specifically the level 1 classes. Six land cover classes were selected: bare exposed rock, bare ground, built-up land, forest, grassland and water (Table 2).

Table 2.
Land cover classification system.
4.2. Data Preprocessing
The Landsat images were downloaded as precision and terrain-corrected (L1TP) products, apart from the MSS image, which was downloaded as a systematically corrected (L1GS) product. To verify the geometric alignment of the images, each Landsat image was cross-checked against a VHR NigeriaSat-2 image (which was within 2–5 m of the ground control points (GCPs) selected) to ensure positional accuracy. All images other than the 1975 Landsat MSS image were geometrically aligned to within approximately 15 m of the NigeriaSat-2 image. The MSS image was geographically displaced by approximately 200 m; this error was consistent throughout the image. Therefore, an image to image co-registration was performed using the 1986 Landsat TM image as a reference. The 1986 image was selected as this was closest in time to the 1975 image, increasing the likelihood of common features (GCPs) being identifiable in both images.
While geometric alignment is essential for accurate change detection analysis, radiometric and atmospheric correction was less important, because the results pertained to processed land cover classifications. Although atmospheric correction is generally advised where spectral pixel (e.g., surface reflectance) values of multi-temporal images are compared, here, all images were converted from continuous original pixel values (digital numbers) to classified thematic land cover class labels. These land cover classifications were independently checked using accuracy assessment procedures and the errors presented. This essentially bypasses any direct requirement for atmospheric correction or radiometric normalization and is standard practice for post-classification comparison analysis [56,57,58,59,60].
Prior to classification, all images were cropped to an identical area covering Abuja FCC and its immediate surroundings. The Landsat MSS image contained a data artefact (a diagonal line towards the southern edge of the image—see Figure 3) which was masked and the affected area excluded from all images. The 2008 ETM+ image suffered from striping caused by the scan-line corrector fault which affected all imagery acquired by this sensor since 2003 [61]. Several methods to overcome this problem have been promoted by the USGS (https://landsat.usgs.gov/landsat-7), including web-enabled Landsat data (WELD), Erdas imagine mosaicking method, historic techniques (Phase 1 and 2) and Erdas imagine focal analysis. Here, the focal analysis approach was used to gap fill areas of data loss. An iterative approach was employed, with visual assessment used to ensure a satisfactory outcome.
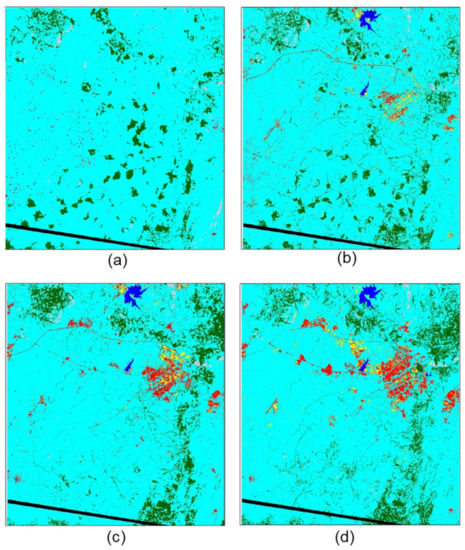
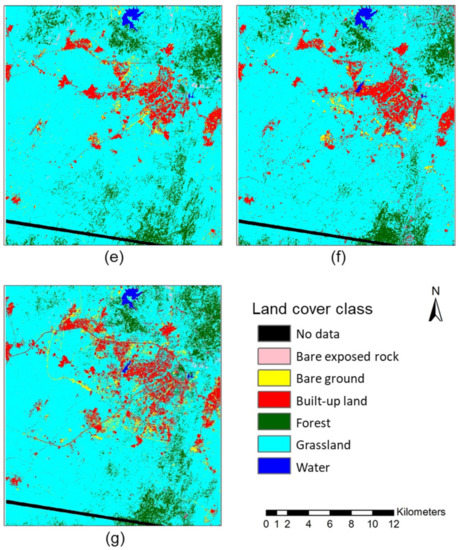
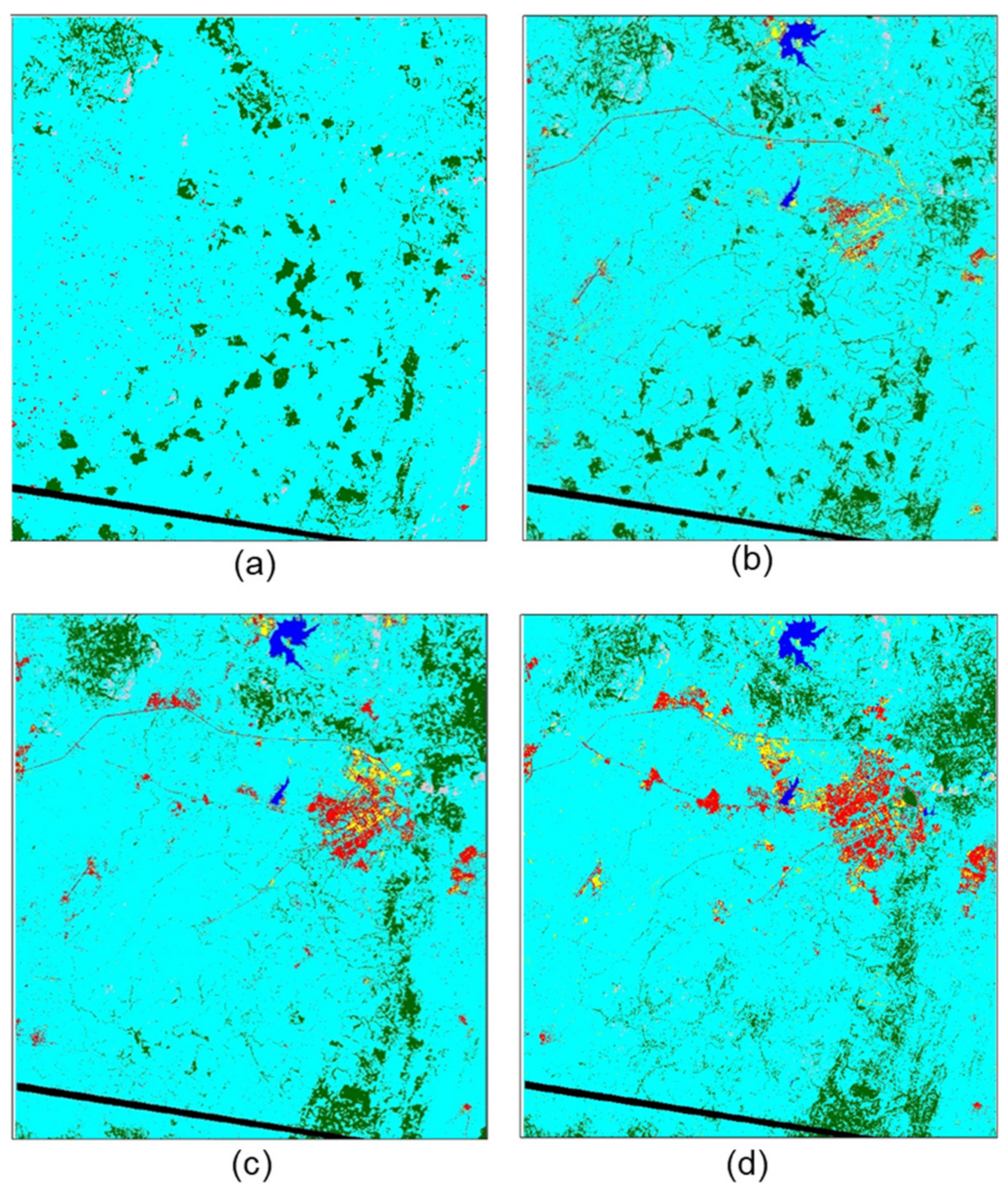
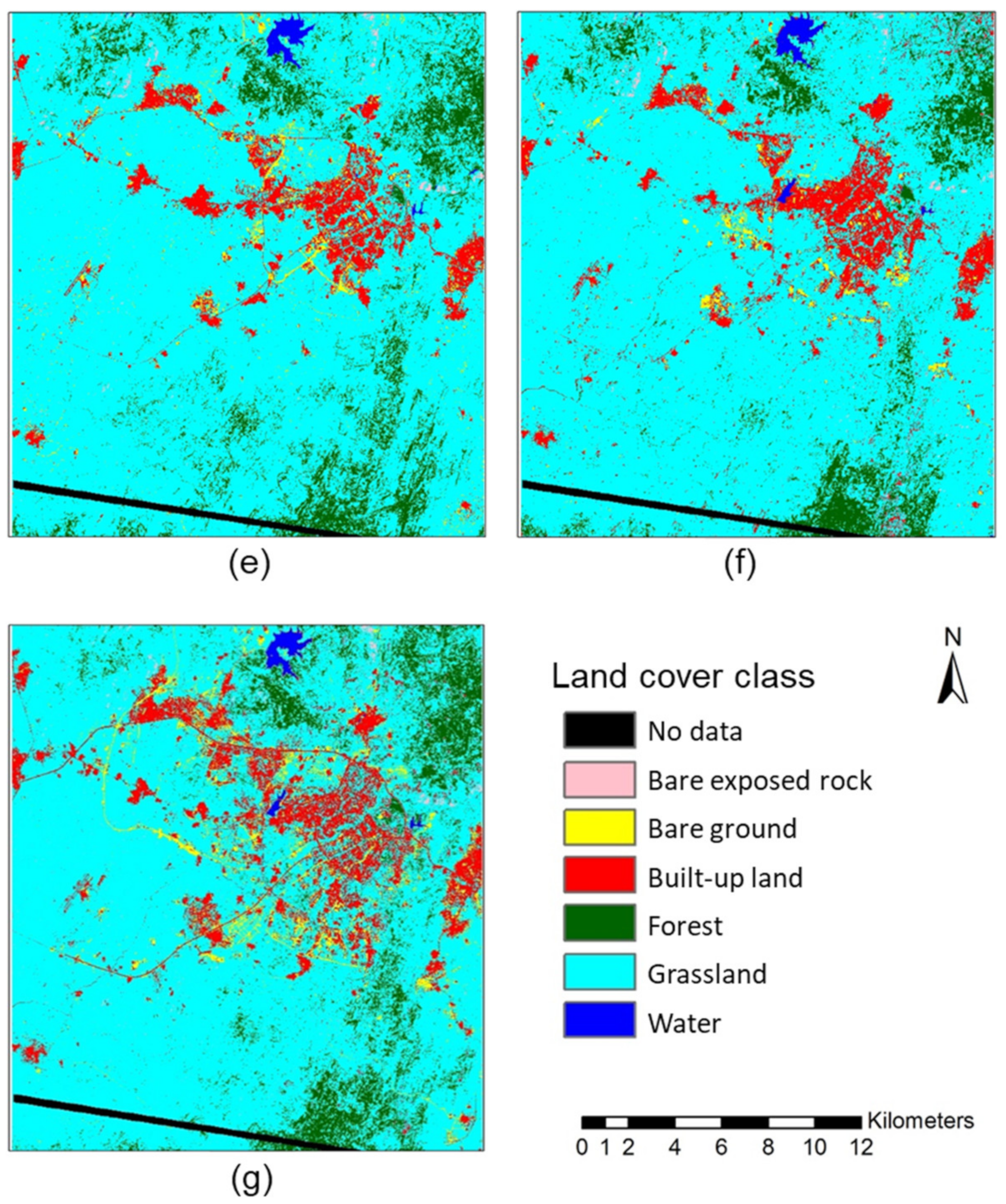
Figure 3.
Land cover classification of Abuja, Nigeria and its environs in (a) December 1975, (b) January 1986, (c) February 1990, (d) January 1999, (e) December 2002, (f) January 2008 and (g) January 2014. No data corresponds to dropped lines in the 1975 image, with the affected area masked out of all classifications to enable direct comparison.
Finally, boundary data of the Master Plan development phases were digitized from maps supplied by AGIS and FCDA, versions of which are also available in the Master Plan documents [13], to create vector coverages to enable integrated analysis with the classified images.
4.3. Image Classification
Land cover classification was conducted using the maximum likelihood (ML) approach. ML classification is widely used, well-understood and generally accurate when training data are selected appropriately [54,62,63,64,65,66]. Class training samples were chosen carefully from each image to meet the statistical requirements of the parametric ML classifier (see Supplementary Materials). Reference data (described in Section 4.4) were scrutinized to select training samples (i.e., image pixels) representing each class; these samples were sufficiently large, distributed throughout the study area and relatively evenly spread between classes to provide robust statistical representation of all classes [67,68,69]. However, class training for the 1975 Landsat MSS image proved problematic, as the coarse spatial resolution of MSS meant that identifying small features, especially built-up areas (which in 1975 tended to be small, informal settlements), was challenging. As such, the class training samples for this image tended to be relatively small (see Supplementary Materials).
Statistical separability testing was performed on training samples to ensure there was no significant spectral overlap between classes. Specifically, transformed divergence (TD) statistics were calculated for all classes and images. TD represents the degree of divergence between pairs of classes as values between 0 and 2000, where a low value suggests poor separability and the 2000 maximum indicates full separability [70]. TD results were generally high for all years of imagery, with many class pairs exhibiting full (TD = 2000) separability. The lowest values were recorded for the 1999 image, with an average TD value of 1972. Having established suitable spectrally separability, ML classification was performed [71].
Quantitative accuracy assessment was conducted for each land cover classification. This involved generating a random sample of points in the study area (a stratified approach was used, ensuring all classes were well-represented) and, at each point, comparing the classified image pixel with the reference data. The reference data used for the accuracy assessment were independent of the reference data used for class training (i.e., the same locations were not used for both training and testing). A relatively large sample of 240 points was used for each image to ensure reliable results. Results were presented and interrogated using the standard error matrix approach [72].
Post-classification comparison was also conducted on the classified images to identify changes over time. This involved overlaying the classifications from the different years and assessing how pixels’ class associations change between image dates [60,73], and how the area coverage of each class varies. Here, more detailed spatial interrogation was also conducted on the growth of the built-up class, to identify expansions of built-up land for each time-period and to determine which other classes were converted to built-up.
4.4. Comparison with Master Plan
Following image classification and change detection analysis, spatial boundary data drawn from the Master Plan were integrated with the classified images to determine how closely urban development (as determined from the images) matched Master Plan projections. Specifically, vector coverages of the five development phases were overlaid on the land cover classifications, and the area of the built-up class was extracted. This analysis was also conducted beyond the development phase footprints to identify unplanned developments outside the planned area.
As the Master Plan contains a timeline of when and how the city should grow, this enabled comparative analysis of correspondence and deviation between the planned and observed phases of development to be performed. Additional local-scale analysis was conducted by comparing Master Plan projections of built-up areas for six Abuja districts with the image analysis results.
5. Results
5.1. Land Cover Classification
The seven land cover classifications (1975, 1986, 1990, 1999, 2002, 2008 and 2014) are presented in Figure 3. These clearly illustrate the rapid development of Abuja over this period, with built-up land displayed in red. All six classes were mapped for all except one of the Landsat images. In the earliest (1975) Landsat MSS image, only four classes were mapped: bare exposed rock, built-up land, forest and grassland. The other two classes, bare ground and water, were omitted because they were not present in the study area in 1975. Other notable features include the general dominance of the study area by the grassland; and the creation of two water bodies (reservoirs) in the northern part of the study area to supply the population in Abuja, which first became apparent in the 1986 classification (though the smaller of these is misclassified as built-up in 2002, because the reservoir was dry at this time). Interestingly, the bare ground class tends to act as a pioneer class and identify land cleared for development, with land was converted from (i) an initial class (commonly grassland but, also, sometimes forest) in the earliest image, via (ii) the bare ground class in the next image as land was cleared for development to (iii) the built-up land class in the latest image. Finally, areas of the forest in the southern part of the study area were lost rapidly after 1986, replaced by grassland. This surprise finding was investigated during the 2015 field campaign, and although unknown to planning officials at the time, it subsequently became apparent that the two main causes for this forest loss were illegal logging and agricultural clearance (A. Wakili, personal communication (interview), 3 October 2015).
Quantitative accuracy assessment was performed on all the classified images, with overall classification accuracies of 67.5% (1975), 90.8% (1986), 84.6% (1990), 86.7% (1999), 86.0% (2002), 78.8% (2008) and 83.8% (2014). Accuracies were generally high, with all classifications approaching or exceeding 85%, except the 1975 and 2008 images. The 1975 image was likely affected by its coarser spatial resolution and simpler spectral configuration compared to the other images, making class separability more difficult, especially for smaller land cover features such as dwellings and informal settlements (i.e., built-up land). The 2008 image may have been affected by the gap-filling analysis, though visually, it appears relatively accurate, with the representation of built-up land clearly showing urban development progressing between the 2002 and 2014 images. Full error matrices for all classifications are available as Supplementary Materials.
Extensive land cover conversions have taken place in the study area over the last 40 years, as illustrated by the change detection statistics presented in Table 3. The most dramatic class changes involve built-up land, which increased steadily from 1164 ha (or 0.6% of the study area) in 1975 to 18,623 ha (9.8%) in 2014, and water, which was completely absent at the start of the study but increased to 1038 (0.5%) ha in 2014 through reservoir creation. Other notable changes include a slow but steady increase in bare ground during the study period, which can be attributed to the ongoing clearance of land for new urban development. Forest areas remained relatively steady throughout the study, averaging approximately 9%–9.5% of the study area despite logging and agricultural clearance activities. These losses are offset with gains in human-made forests scattered throughout the study area (e.g., national (government-managed) parks and commercial plantations, as confirmed through fieldwork and interviews in 2015). Similarly, bare exposed rock remained relatively constant (at an average of about 1000 ha), since this land is unsuitable for urban development or land conversion. Grassland is the only class suffering significant loss of area, with this process being gradual and constant throughout the study period. In 1975, grassland covered 172,082 ha (91.1% of the study area), decreasing to 144,463 ha (76.7%) by 2014. This change occurred as grassland was converted to built-up, often via bare ground as a pioneer urban development class, and also, to water.

Table 3.
Areal coverage of each land cover class (in both ha and percentage of study area) for the 1975, 1986, 1990, 1999, 2002, 2008 and 2014 land cover classifications.
5.2. Master Plan Comparison
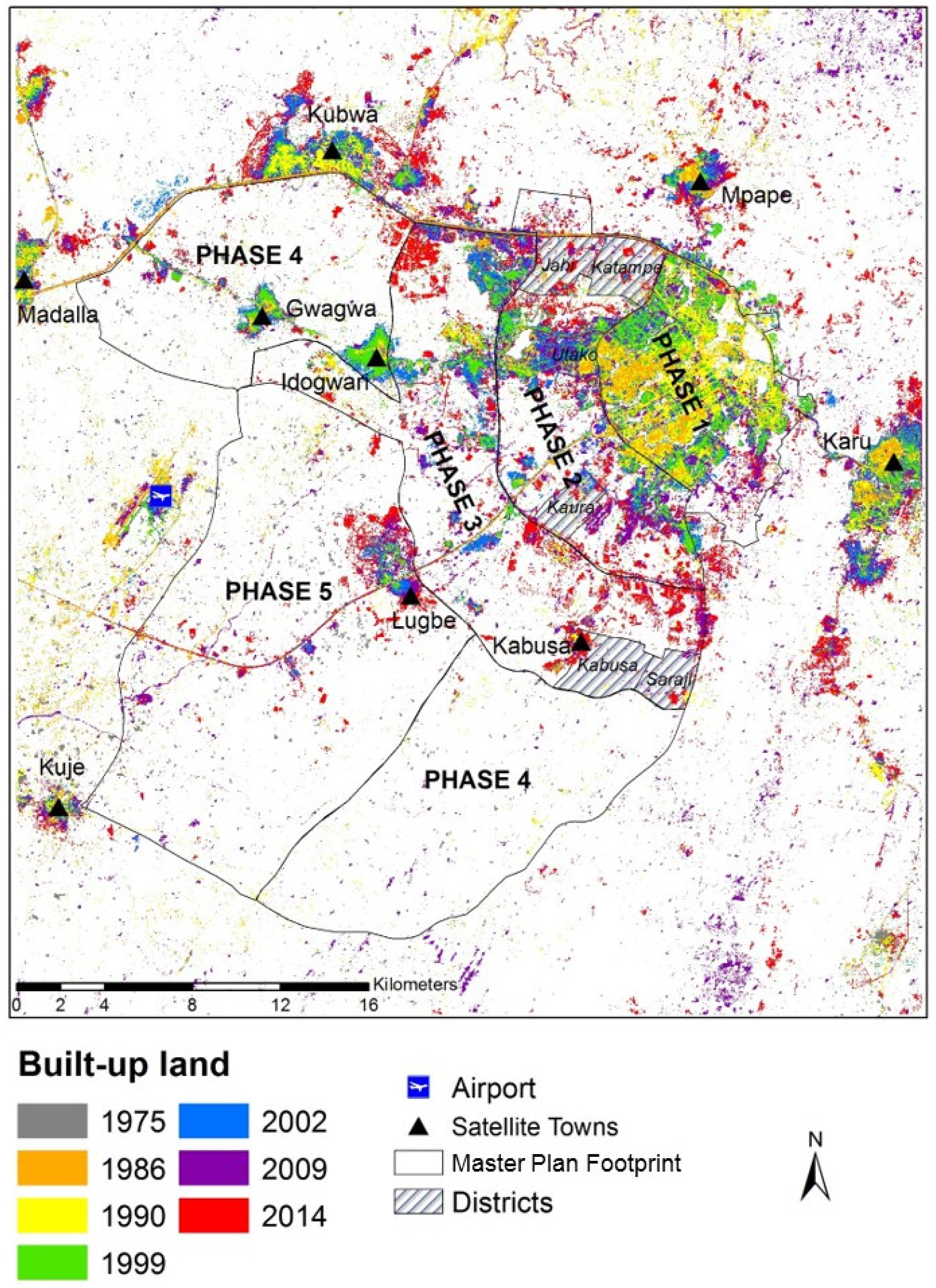
The increase in built-up land over the study period is illustrated in Figure 4, overlaid with the Master Plan development phase boundaries and with the satellite towns and airport developments indicated. It is noticeable that the central strategy of the Master Plan, whereby development commenced in the main urban center in the northeast of the FCC and radiated outwards sequentially during the development phases, was realized to an extent. Figure 4 shows early concentration of built-up land in the northeast (the orange and yellow colors representing built-up lands in 1986 and 1990, respectively), next adjoined by development extending during the middle period of the study (1999: green, 2002: blue) and, finally, occurring further out to the west from the urban core (2009: purple, 2014: red).
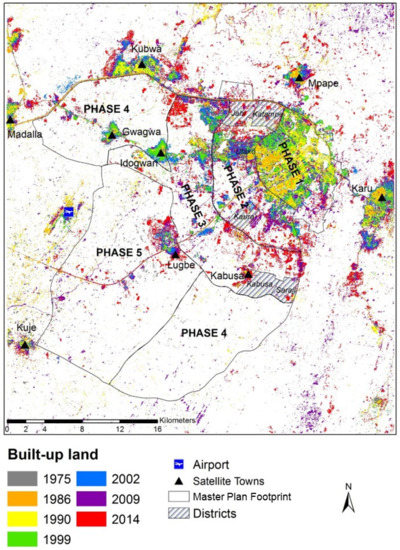
Figure 4.
Development of built-up land in the Abuja area between 1975 and 2014. Districts refers to the individual districts of Jahi, Katampe, Kaura and Utako in the Master Plan Development Phase 2 and Kabusa and Saraji in Phase 3.
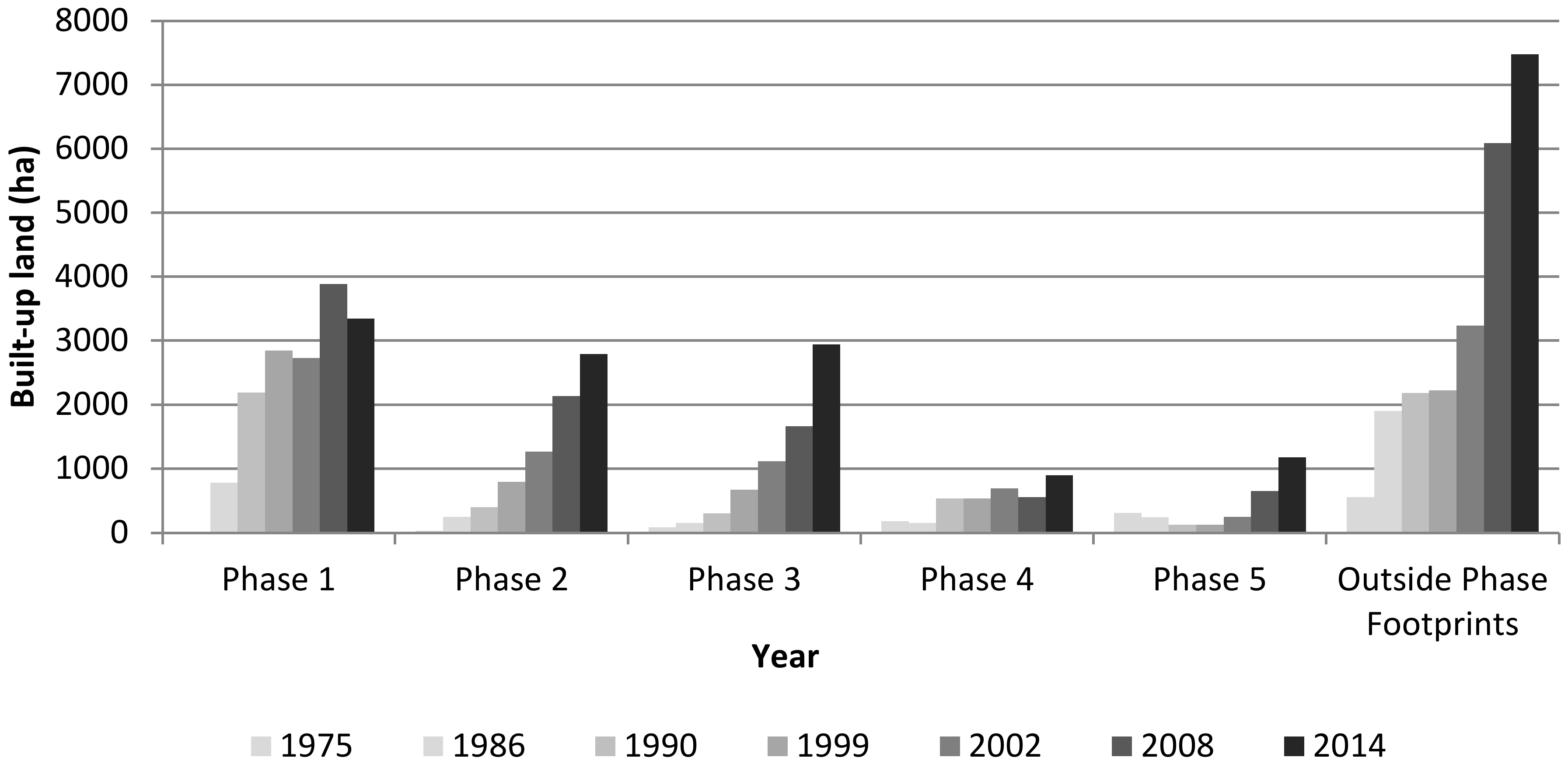
Though the general trend of urban development in Abuja matched the broad Master Plan strategy, it is clear there is significant deviation from the specific objectives outlined in the plan. Figure 5 shows the areal extent of built-up land in the individual development phase footprints taken from the time-series of land cover maps. It is clear that deviations from original plans occurred early in the development of Abuja. While phase 1 was scheduled for completion in 1986, by this time only 781 ha of built-up land existed, with continued development in this phase footprint continuing right up to at least 2014 when 3345 ha of built-up land was present. Development in phases 2, 3 and 4 occurred concurrently throughout the 1980s and 1990s, rather than sequentially, as intended. In the 2000s, the area of built-up land increased rapidly in phases 2 and 3, while that of phase 4 remained generally static. In contrast to phase 4, phase 5 seems to have been growing quickly and steadily since 2005, when it was first proposed.a
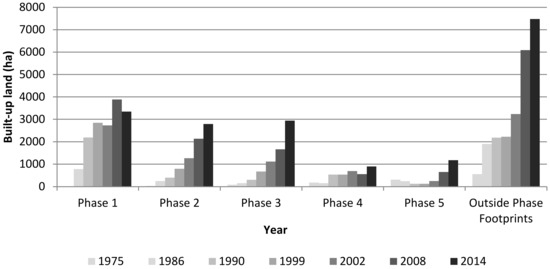
Figure 5.
Increases in built-up land in Abuja both within the boundaries of the five Master Plan development phase areas and outside the overall Master Plan footprint.
Of particular interest is the increase in built-up land outside the phase boundaries (Figure 4 and Figure 5) showing unplanned urban development. This essentially represents a direct failure of the Master Plan. This unplanned development occurred almost immediately after construction commenced in phase 1, and by 1986, when phase 1 was scheduled for completion, unplanned built-up land covered more than twice the area of built-up land within the phase 1 footprint. Unplanned development then remained largely static until 1999, from when a dramatic and sustained increase is observed (see outside phase footprints in Figure 5). The unplanned developments are mostly concentrated in the satellite towns located in and around the outskirts of the FCC and also around the airport west of Abuja (Figure 4).
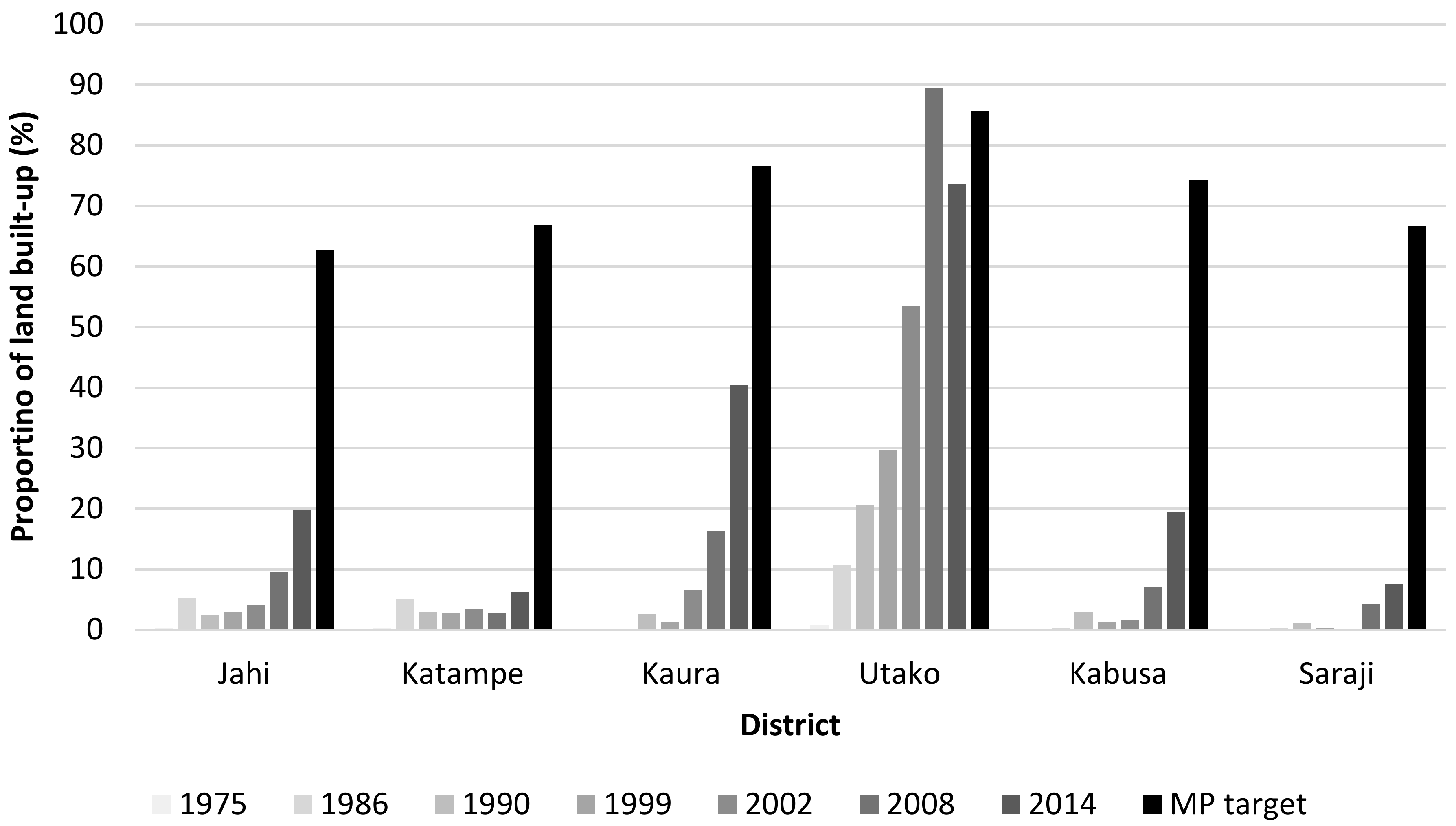
Figure 4 and Figure 5 enable broad comparison between Master Plan objectives (development phase footprints/timescales) and image-derived land cover change, but more detailed analysis is conducted for six districts of Abuja where the Master Plan set specific development targets. For Jahi, Katampe, Kaura and Utako (phase 2) and Kabusa and Saraji (phase 3), the Master Plan stated intended areal coverage of built-up land, and these values are compared against built-up land mapped from the time-series of Landsat images (Figure 6).
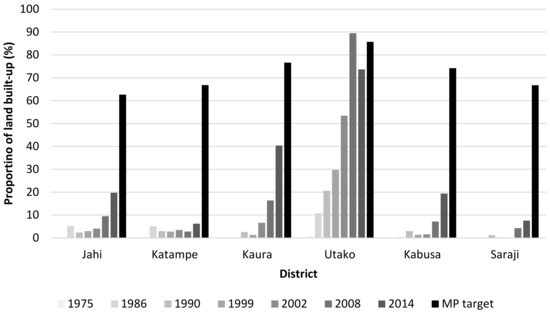
Figure 6.
Areal coverage of built-up land in individual districts over time compared to the target coverage specified originally in the Master Plan (MP). (Jahi, Katampe, Kaura and Utako in MP development Phase 2; Kabusa and Saraji in Phase 3.).
Figure 6 shows marked discrepancies between planned and actual built-up land for these individual districts. Most of the districts fall well short of projected urban development, with five of the six districts investigated barely registering any built-up land at all before 1999, the date by which the original Master Plan should have been fully implemented. Only Utako can be seen to be urbanizing progressively throughout the original timescale of the Master Plan, with the proportion of built-up land increasing steadily from 1975 (pre-plan), through 1990 (around the time of inaugurating Abuja as Nigeria’s capital), to 1999 (completion of Master Plan). Since 1999, the proportion of built-up land has increased noticeably in all six districts, though only Utako has come close to approaching its original target built-up area. Kaura has developed to about half of its target built-up area, while the other four districts fall far short of their targets. There is no noticeable trend related to development phases. The only real success story, Utako, is in the Master Plan phase 2 footprint. Overall, these district-level results, though only representing a small sample of Abuja’s districts, show a general failure to achieve detailed, local-scale Master Plan objectives, with a significant shortfall in built-up land. This does bring into question why an additional development phase was added in 2005, when so much of the original Master Plan area remained undeveloped.
6. Discussion
The first research question posed in this study was “How have patterns of land cover in Abuja FCT evolved since the 1970s?” Historical remote-sensing image analysis clearly shows a picture of rapid and ongoing urbanization, with large areas of grassland being converted to built-up land, plus the creation of two large artificial water bodies to supply the new city (Figure 3). Interestingly, the bare ground land cover class effectively acts as a pioneer class for urban development, showing where land has been cleared for construction. This offers a potential means of forecasting future urbanization. Though forest cover remained broadly static over the study area as a whole, locally there are interesting, and hitherto unknown, patterns of change. Rural forest patches were lost rapidly after 1986, caused by illegal logging and agricultural clearance (M. Hamza, personal communication (interview), 3 October 2015). Elsewhere, afforestation occurred through parkland developments and commercial plantation.
Historical Landsat imagery has proved effective for land cover classification and change analysis in this urbanizing environment. While recent generations of Landsat (OLI, ETM+, etc.) yielded the most accurate classification analysis, even the earliest MSS instrument, with its coarse spatial resolution and limited spectral band set, enabled effective identification of the major land cover classes. Thus, the Landsat archive provides a valuable resource for the retrospective monitoring of urban growth in the global South and elsewhere. The situation for ongoing and future monitoring is now perhaps even more promising, with the emergence of additional, free sources of moderate spatial resolution imagery from Europe’s Sentinels mission, plus multiple VHR image sources providing increased local area detail.
The second research question posed was “Has the Master Plan been effective in dictating the pace and pattern of urbanization in Abuja?” The Master Plan did not state the aims or goals of individual phases in the city. Rather, a general objective of having the city developed in phases, for the purpose of planned growth in incremental stages, was proposed. This was primarily to streamline the growth and construction of the city in an orderly fashion and to also reduce the impact of noise, dust and disruption that usually accompanies a continuous long-term construction program [13]. The phases were also designed to be efficient, attractive and self-sustaining at each stage of growth. The timeline of completion of each phase was not stated. Rather, phase 1 was scheduled to be completed by 1986, while the four original phases were expected to be completed by the year 2000.
While some broad intentions of the original Master Plan were followed in the early stages of Abuja’s development, the Master Plan cannot be considered a success overall. Figure 4 and Figure 5 show that planned development up to 1986 was focused mainly on the phase 1 footprint, as intended. Even so, phase 1 development was slow, and the target date for relocating the capital from Lagos to Abuja was postponed from 1986 to 1991. Thereafter, the general pattern of urban development diverged more and more from Master Plan objectives. Instead of sequential development through phases 2, 3 and 4, urbanization actually occurred more or less concurrently in these phases (Figure 5). Local, district-scale analysis (Figure 6) reinforces the general discrepancy between Master Plan intentions and actual development, with only one of six sample districts coming close to realizing built-up area projections. Ultimately, apparent failure in realizing some of the original Master Plan intentions was confirmed in 2005, when an extra development phase was devised to compensate for the lack of success in achieving the original goals. Such a failure of Master Planning can be attributed to slow but consistent disconnect between the planning phase and implementation processes over the years. This seem to be a recurring feature in the global South, as a similar conclusion was reached by [74], when investigating Master Planning as a tool for guiding urban development in Qatar. On the contrary, in the Norwegian cities of Sandefjord and Elverum, 96% and 98% of the urban expansion since 1970 was found to be in accordance with their Master Plans [75].
The third research question posed was “Has unplanned urban development been limited successfully?” The principal aim of an urban Master Plan is to control development, thus eliminating, or at least minimizing, unplanned urban sprawl. Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the Master Plan has not been wholly successful in limiting this unplanned development; indeed, far from it. Substantial parts of the study area outside the Master Plan phase footprints have been developed, including several sizeable satellite towns. One stated aim within the original Master Plan was to relocate pre-existing settlements within the FCT area, accommodating the population in the newly developed FCC. However, detail was scant on how this relocation would proceed, and it appears now that little action was taken to achieve this goal. To date, the majority of the indigenous population are yet to be provided with compensated land [76]. This inaction seems to have played a significant role in the presence, persistence and growth of unplanned urban settlements. Pre-existing settlements close to Abuja, such as Karu, Kubwa, Mpape and Kuje, have become a magnet for unplanned urbanization (Figure 4), offering informal, low-cost development options compared to the relatively high cost of urban construction within the FCC [77,78].
Affordability is a key driver of unplanned development. One significant flaw in the original Master Plan was the little regard given to the needs and means of the unskilled/low-income population. Instead, the focus was on high-quality infrastructure, including housing, which had the effect of pricing out low-income residents. As [12] observed, Abuja is a city planned without much regard to Nigeria’s poor. Many of the migrants traveling to Abuja in search of better employment opportunities fall under this category, and the inevitable consequence is unplanned urban sprawl. Current residents echo these concerns. For instance, a resident of Ndako village (located in FCC phase 3) interviewed for this study stated, “If informal settlements are not dealt with properly, the city will be a mess in 10–20 years. The planners seem relaxed at the moment. So, if this continues, the city will be in trouble.” (C. Akap, personal communication (interview), 9 October 2015).
Though population estimates for Abuja vary, it appears that the Master Plan substantially underestimated the number of people attracted to the new city. As relocation to Abuja intensified, the development of infrastructure, especially housing, could not match population growth, leading to a major expansion of unauthorized housing [79,80]. Furthermore, Abuja’s rapid and uneven urbanization has resulted in greater pressures on existing service infrastructures, such as roads, sanitation and energy supply, affecting the quality of service, especially in suburbs and satellite towns [81]. The problem of a Master Plan underestimating population growth is not unique to Abuja. A similar situation was observed in Shenzhen, China, where its Master Plan made provisions for a population of 4 million, while the 2000 census recorded 7 million inhabitants [9,82].
Overall, Abuja’s propensity for unplanned urban development is fairly typical of cities in the global South, exhibiting common problems such as urban sprawl, lack of housing, poor infrastructure and development of slums [14,45,83]. Viewing the pattern of urban development across the city as a whole, a striking picture begins to appear—that of a dual city which, at its center, is modern, planned, affluent and efficient, while, around the periphery, is unplanned, underdeveloped and spontaneous.
The fourth research question posed was “Have changes in political governance influenced the nature of urban growth?” It is clear that the pace of urbanization is not uniform over the study period, and various changes in government have tended to accelerate or slow urban development [84]. During the early part of Abuja’s establishment, up to around the year 2000, urban development was relatively slow (Figure 5). Thereafter, the area covered by built-up land increasing rapidly. This change can be linked directly to the nature and level of governmental control. In 1999, after 16 years of military rule, Nigeria switched to a democratic government. This had various consequences; in addition to a relaxation of planning legislation and control, Abuja received increased investments [46], leading to more urban development but also attracting more migrants to the area in search of better employment opportunities, further increasing demand for housing and urban infrastructure. The data supporting this is the clear difference in the growth rate of built-up land outside the Master Plan footprint (i.e., unplanned development) between 1986–1999 (military regime) and 1999–2014 (civilian regime). The total area of built-up land outside the footprint is 1901 ha in 1986 and 2220 ha in 1999, a growth rate of approximately 1% per year. By 2014, the total area of built-up land outside the footprint has grown to 7477 ha, a growth of almost 7% per year since 1999.
Over the study period, the philosophy and approach towards implementing the Master Plan has varied. For example, in the 1980s when construction of Abuja started, the policy on how to tackle indigenous inhabitants was to resettle completely all villages within five kilometers of the new FCC footprint, thereby providing a “blank canvas” [46] (p.16) for construction of the new city. However, there was a significant shift in policy in the 1990s, as the military government of the day introduced what it called an “Integration Policy” [85] that sought to upgrade pre-existing villages within the FCC. This policy, though, was short-lived, and little action was ever undertaken [77]. In 1999, after the return to civilian rule, the integration policy was abandoned, and a hybrid policy involving both resettlement and village integration was attempted. Overall, none of these initiatives proved particularly successful in solving the problem [86]; thus, unplanned settlements remain widespread and continue to expand rapidly.
In 2003, a significant attempt was made to correct and reverse the “bastardization” of the Master Plan pre-1999 [87]. This regime was credited for making determined efforts to realign the physical development of the city with the Master Plan despite political obstacles arising through past regimes’ actions and inaction [88]. During this time, many unplanned constructions and even entire settlements were demolished, though this did not solve the problem outright, as no sustainable solutions or alternatives were provided for the residents.
Another further shift in land development policy came in 2013 with the “Land Swap Initiative”, which provided large tracts of grassland for private developers on the understanding that their construction work would include development of basic infrastructure and fund the resettlement of indigenous populations living on the allocated land [89]. However, most districts earmarked for development under this initiative are yet to show any visible evidence of construction.
Evidence from Abuja suggests that political inclination and governance play a major role in the growth and management of cities, and this is perhaps especially the case throughout the global South. Thus, adherence to, or disregard of, a Master Plan may well be influenced by politics, rather than focusing first and foremost on land use need and environmental implications. A similar observation was made by [90] in a study to identify the challenges of implementing a Master Plan in Lahore, Pakistan. In that case, weak institutions and a lack of coordination between government agencies were identified as major impediments to realizing the city’s Master Plan objectives.
7. Conclusions
The fast pace of urbanization worldwide, and especially in the global South, has serious social and environmental consequences, including overpopulation, housing and infrastructure shortages; slum development and urban sprawl. Effective urban planning is essential to control development, yet this study shows that even newly planned cities may have limited success in eliminating unwanted urban sprawl. Here, the 40+ year Landsat image archive enabled the assessment of urban development over the whole lifetime of the planned city of Abuja, Nigeria. A series of seven Landsat images from the mid-1970s, covering the period from when the new city was first proposed to the modern day show rapid urbanization, with large areas of grassland being converted to built-up land, often via an intermediate bare soil class. Land cover change, as identified from image analysis, was compared against the intentions of the city’s original Master Plan, showing that early success in realizing plans soon gave way to uncontrolled and unintended development. Of particular concern is the wide-ranging failure to prevent unplanned developments in the long-term. Though it is hard to pinpoint precise reasons for the failure of the planning process, it is clear that the level of adherence to the Master Plan varied according to the system of government in place. For instance, after long-term military rule was replaced by democratic government around the turn of the millennium, unplanned developments increased sharply.
It now seems clear that Abuja’s original Master Plan included certain significant oversights when anticipating future urban infrastructure requirements. Notably, while uncertainty exists over population estimates, the city’s population is almost certainly substantially larger than that originally predicted. Additionally, insufficient consideration was given to the needs and means of unskilled/low-income residents [12], and it is this large portion of the population that has driven the growth of unplanned development since planned housing is generally unaffordable [77,78]. Throughout Abuja’s development, it appears there was little formal review of progress against the original plans. By design, urban Master Plans are largely static, but this puts them at odds with cities, which by their nature are growing and changing in ways not easily predictable [9]. Future attempts at large-scale urban planning in the global South would seem well-advised to retain greater flexibility in adapting initial plans according to regular progress reviews.
A first step towards improving urban planning in the global South and, thus, reducing unplanned urbanization and its unwanted consequences is simply to gather useful intelligence about the problem. Experience from Abuja shows that planning officials are often wholly underinformed on the reality of urban development. For instance, during this study, a senior FDCA planner stated, “A lot of changes have happened to our land use that we don’t even know here in planning” (Y. Abubakar, personal communication (interview), 6 October 2015). One potential and highly effective source of spatial intelligence for monitoring and guiding urban development is remote sensing. Landsat now provides a long-term archive of image data that can enable retrospective monitoring, and new sources of imagery such as Europe’s Sentinels mission and widely available VHR sensors provide enhanced imaging capabilities for detailed and regular monitoring. We promote the uptake of remote sensing as a key element of urban planning activities and recommend planners develop monitoring protocols to review land use change regularly using multitemporal imagery. This will enable more effective assessments of urban development activities against stated plans, including Master Plans, mitigating the occurrences and consequences of unplanned urbanization and leading to better future planning and forecasting.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/12/7/1112/s1: Table S1: Land cover class training and testing data for the 1975–2014 Landsat images of Abuja. Table S2: Error matrix for Abuja land cover classification using 1975 Landsat multispectral scanner image. Table S3: Error matrix for Abuja land cover classification using 1986 Landsat thematic mapper image. Table S4: Error matrix for Abuja land cover classification using 1990 Landsat thematic mapper image. Table S5: Error matrix for Abuja land cover classification using 1999 Landsat thematic mapper image. Table S6: Error matrix for Abuja land cover classification using 2002 Landsat-enhanced thematic mapper plus image. Table S7: Error matrix for Abuja land cover classification using 2009 Landsat-enhanced thematic mapper plus image. Table S8: Error matrix for Abuja land cover classification using 2014 Landsat operational land imager image.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.A.G. and P.A., with J.M. and C.G.M.; Formal analysis I.A.G. with P.A., C.G.M. and J.M.; Writing I.A.G., P.A. and C.G.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Federal Capital Development Authority (FCDA) and the Abuja Geographic Information System agency for providing Abuja map data and to the Nigerian National Space Research and Development Agency for its support and for providing the NigeriaSat-2 image. Our thanks go to the various local stakeholders and residents who agreed to interviews, providing valuable data on historical land use changes. In particular, Y. Abubakar, Deputy Director of the FCDA’s Department of Urban and Regional Planning, and Opara of the FCDA’s Forestry Department contributed significant insights on urban development and forest loss respectively. Thanks, finally, to Edge Hill University and the Petroleum Technology Development Fund, Nigeria for sponsorship towards I.A.G.’s doctoral studies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Maktav, D.; Erbek, F.; Jürgens, C. Remote sensing of urban areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; (ST/ESA/SER.A/420); United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision; (ST/ESA/SER.A/366); United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Liu, Q.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Lin, P.; Li, X. Monitoring urban expansion with remote sensing in China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, J.; Belil, M.; Castells, M.; Benner, C. Local and Global: The Management of Cities in the Information Age; United Nations Centre for Human Settlement, Earthscan: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, T. Urban Planning and Governance: Is there a Barcelona Model? Int. Plan. Stud. 2000, 5, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrechts, L. In pursuit of new approaches to strategic spatial planning. A European perspective. Int. Plan. Stud. 2001, 6, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, F. Strategic urban planning in Latin America: Experiences of building and managing the future. Habitat Int. 2005, 29, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, V. The planned city sweeps the poor away…: Urban planning and 21st century urbanisation. Prog. Plann. 2009, 72, 151–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikejiofor, U. Planning and the political process: Sifting some underlying issues in the development of Abuja, Nigeria’s new capital. Third World Plann. Rev. 1997, 19, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.R. Abuja city profile. Cities 2014, 41, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, L. Architecture, Power and National Identity; Routledge: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- IPA (International Planning Associates). The Master Plan for Abuja the New Federal Capital of Nigeria; Federal Capital Development Authority (FCDA): Abuja, Nigeria, 1979.
- Myers, G.A. African Cities: Alternative Visions of Urban Theory and Practice; Zed Books Limited: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Iro, I. Demographic pressure and the application of GIS in land reforms: The case of restoration of Abuja master plan and sanitization of cadastral and land registry. In Proceedings of the Map Middle East Conference on GIS Development, Dubai Municipality, UAE, 9–11 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- NPC. Nigeria Population Census; National Bureau of Statistics: Abuja, Nigeria, 2006.
- Longley, P.A. Geographical information systems: Will developments in urban remote sensing and GIS lead to ‘better’ urban geography? Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2002, 26, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, P. Comparison of simulated IKONOS and SPOT HRV imagery for classifying urban areas. In Remotely Sensed Cities; Mesev, V., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2003; pp. 23–45. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, T.; Hay, G.J.; Weng, Q.; Resch, B. Collective sensing: Integrating geospatial technologies to understand urban systems—An overview. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1743–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, P. Remote sensing: Base mapping. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2003, 27, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wania, A.; Kemper, T.; Tiede, D.; Zeil, P. Mapping recent built-up area changes in the city of Harare with high resolution satellite imagery. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 46, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhao, B.; Song, Y. Urban land-use mapping using a deep convolutional neural network with high spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Yasuda, H.; Haregeweyn, N.; Belay, A.S.; Hadush, Z.; Gebremedhin, M.A.; Mekonnen, G. The dynamics of urban expansion and land use/land cover changes using remote sensing and spatial metrics: The case of Mekelle City of northern Ethiopia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 4107–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpienbaareh, D.; Luginaah, I. Modelling the internal structure, dynamics and trends of urban sprawl in Ghanaian cities using remote sensing, spatial metrics and spatial analysis. Afr. Geogr. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rifat, S.A.; Liu, W. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns and major explanatory factors of urban expansion in Miami Metropolitan Area during 1992–2016. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Gong, P. Mapping urban land use by using Landsat images and open social data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Hong, Y. Classifying urban land use by integrating remote sensing and social media data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1675–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellozzo, F.; Amato, F.; Murgante, B.; Clarke, K. Modelling the impact of urban growth on agriculture and natural land in Italy to 2030. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 91, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramankutty, N.; Coomes, O.T. Land-use regime shifts: An analytical framework and agenda for future land-use research. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Defries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurian, L.; Day, M.; Backhurst, M.; Berke, P.; Ericksen, N.; Crawford, J.; Chapman, S. What drives plan implementation? plans, planning agencies and developers. J. Environ. Plann. Man. 2004, 47, 555–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, S.I.; Imran, M. Planning of Islamabad and Rawalpindi: What went wrong? In Proceedings of the 42nd ISoCaRP Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 14–18 September 2006; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Beauregard, R.A.; Marpillero-Colomina, A. More than a master plan: Amman 2025. Cities 2011, 28, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, E.; Felsenstein, D.; Razin, E.; Stern, E. Assessing land use plan implementation: Bridging the performance-conformance divide. Land Use Policy 2017, 61, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Shen, T. Evaluation of plan implementation in the transitional China: A case of Guangzhou city master plan. Cities 2011, 28, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, V. Land use dynamics and peri-urban growth characteristics: Reflections on master plan and urban suitability from a sprawling north Indian city. Environ. Urban. Asia 2012, 3, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z. Master plan, plan adjustment and urban development reality under China’s market transition: A case study of Nanjing. Cities 2013, 30, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padeiro, M. Conformance in land-use planning: The determinants of decision, conversion and transgression. Land Use Policy 2016, 55, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujoh, F.; Kwabe, I.D.; Ifatimehin, O.O. Understanding urban sprawl in the federal capital city, Abuja: Towards sustainable urbanization in Nigeria. J. Geogr. Reg. Plann. 2010, 3, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ujoh, F.M.; Kwabe, I.D.; Ifatimehin, O.O. Urban expansion and vegetal cover loss in and around Nigeria’s federal capital city. J. Ecol. Nat. Environ. 2011, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zubair, O.A.; Ojigi, L.M.; Mbih, R.A. Urbanization: A catalyst for the emergence of squatter settlements and squalor in the vicinities of the federal capital city of Nigeria. J. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idoko, M.A.; Bisong, F.E. Application of geo-information for evaluation of land use change: A case study of federal capital territory-Abuja. Environ. Res. J. 2010, 4, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J. The political history of Nigeria’s new capital. J. Mod. Afr. Stud. 1984, 22, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikejiofor, U. Access to land, development control and low-income housing in Abuja, Nigeria: Policy, politics and bureaucracy. Plann. Pract. Res. 1998, 13, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adama, O. Governing from Above: Solid Waste Management in Nigeria’s New Capital City of Abuja; Universitetsservice US-AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- O’Regan, H.J.; Wilkinson, D.M.; Marston, C.G. Hominin home ranges and habitat variability: Exploring modern African analogues using remote sensing. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 9, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, C.G.; Giraudoux, P. On the synergistic use of optical and SAR time-series satellite data for small mammal disease host mapping. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianchu, X.; Fox, J.; Vogler, J.B.; Yongshou, Z.P.F.; Lixin, Y.; Jie, Q.; Leisz, S. Land-use and land-cover change and farmer vulnerability in xishuangbanna prefecture in southwestern China. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Petropoulou, C.; Hirsch, J. Urban development in the Athens metropolitan area using remote sensing data with supervised analysis and GIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. High spatial resolution spectral mixture analysis of urban reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenböck, H.; Esch, T.; Felbier, A.; Wiesner, M.; Roth, A.; Dech, S. Monitoring urbanization in mega cities from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, R.; Aplin, P.; Boyd, D.S. Mapping complex urban land cover from spaceborne imagery: The influence of spatial resolution, spectral band set and classification approach. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.R. A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensor Data; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976.
- Foody, G.M. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, P. On scales and dynamics in observing the environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 2123–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. An automated approach for updating land cover maps based on integrated change detection and classification methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 71, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, D.; Cheng, A.; Wei, H.; Stanley, D. Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 80, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewkesbury, A.P.; Comber, A.J.; Tate, N.J.; Lamb, A.; Fisher, P.F. A critical synthesis of remotely sensed optical image change detection techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Recovering missing pixels for Landsat ETM SLC-off imagery using multi-temporal regression analysis and a regularization method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M.; Campbell, N.; Trodd, N.; Wood, T. Derivation and applications of probabilistic measures of class membership from the maximum-likelihood classification. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1992, 58, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Erbek, F.S.; Özkan, C.; Taberner, M. Comparison of maximum likelihood classification method with supervised artificial neural network algorithms for land use activities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1733–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otukei, J.R.; Blaschke, T. Land cover change assessment using decision trees, support vector machines and maximum likelihood classification algorithms. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, S27–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Han, D.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Bray, M.; Islam, T. Selection of classification techniques for land use/land cover change investigation. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Gong, P. Comparison of classification algorithms and training sample sizes in urban land classification with Landsat thematic mapper imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 964–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, K.; Bhaskaran, R. Supervised classification performance of multispectral images. J. Comput. 2010, 2, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Fichera, C.R.; Modica, G.; Pollino, M. Land cover classification and change-detection analysis using multi-temporal remote sensed imagery and landscape metrics. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Zhang, N.; Wei, X.; Gu, X.; Zhao, X.; Yao, Y.; Xie, X. Land cover classification of finer resolution remote sensing data integrating temporal features from time series coarser resolution data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Stow, D. The effect of training strategies on supervised classification at different spatial resolutions. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Howarth, P. An assessment of some factors influencing multispectral land-cover classification. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1990, 56, 597–603. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, D. Correlations between urbanization and vegetation degradation across the world’s metropolises using DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2067–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Sawaya, K.E.; Loeffelholz, B.C.; Bauer, M.E. Land cover classification and change analysis of the twin cities (Minnesota) metropolitan area by multi-temporal Landsat remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A. Rapid urban development and national master planning in Arab gulf countries. Qatar as a case study. Cities 2014, 39, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglie, I.; Sandberg, S.V.L. Urban expansion in Norway-development by plan? Scand. Hous. Plan. Res. 1997, 14, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amba, K. The need for popular participation in Abuja: A Nigerian story of informal settlements. J. Place Manag. Dev. 2010, 3, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COHRE. The Myth of the Abuja Master Plan: Forced Evictions as Urban. Planning in Abuja; Centre for Housing Right and Evictions: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jibril, I. Squatter resettlement/relocation programme in Abuja, Nigeria and the issue of land title security. In Proceedings of the FIG Working Week, Eilat, Israel, 3–8 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Morah, E.U. Housing in Nigeria’s new capital at Abuja: Achievements and problems. In UBC Planning Papers: Comparative Urban & Regional Studies, (CS 23); University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mabogunje, A. Abuja; the Promise, the Performance and the Prospects. The Review of Abuja Master Plan; Fountain Publications: Ibadan, Nigeria, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ebehikalu, N.O.; Dawam, P.D.; Kasim, U. A study of the state of infrastructure in the Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. J. Resour. Develop. Manag. 2016, 18, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann, J. Globalization and the emerging culture of planning. Prog. Plann. 2005, 64, 183–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, A.; Mohammed, B.; Wilson, D.C.; Cheeseman, C.R. Solid waste management in Abuja, Nigeria. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikoku, G. The city as public space: Abuja-the capital city of Nigeria. FORUM 2004, 6, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Space for Change. Abuja Land Swap Initiative: The Challenges Within. Available online: https://spacesforchange.org/abuja-land-swap-initiative-the-challenges-within/ (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Gusah, S. Community land trusts: A model for integrating Abuja’s urban villages within the city master plan. In CHANGING CITIES: Climate, Youth, and Land Market in Urban Areas; Herzer, L.E., Ed.; Wilson Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 141–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kalgo, M.; Ayileka, O. The review of Abuja master plan. In Proceedings of the International Workshop for the Review of Abuja Master Plan, Abuja, Nigeria, 29 November–2 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Olujimi, J. Evolving a planning strategy for managing urban sprawl in Nigeria. J. Hum. Ecol. 2009, 25, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premium Times. Land swap policy will address resettlement of Abuja indigenes—FCTA. Available online: http://www.premiumtimesng.com/regional/173558-land-swap-policy-will-address-%E2%80%8Bre%E2%80%8Bsettlement-abuja-indigenes-fcta.html/ (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Hameed, R.; Nadeem, O. Challenges of implementing urban master plans: The Lahore experience. Proc. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2006, 17, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).