Abstract
The Gaussian mixture model (GMM) plays an important role in image segmentation, but the difficulty of GMM for modeling asymmetric, heavy-tailed, or multimodal distributions of pixel intensities significantly limits its application. One effective way to improve the segmentation accuracy is to accurately model the statistical distributions of pixel intensities. In this study, an innovative high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation algorithm is proposed based on a flexible hierarchical GMM (HGMM). The components are first defined by the weighted sums of elements, in order to accurately model the complicated distributions of pixel intensities in object regions. The elements of components are defined by Gaussian distributions to model the distributions of pixel intensities in local regions of the object region. Following the Bayesian theorem, the segmentation model is then built by combining the HGMM and the prior distributions of parameters. Finally, a novel birth or death Markov chain Monte Carlo (BDMCMC) is designed to simulate the segmentation model, which can automatically determine the number of elements and flexibly model complex distributions of pixel intensities. Experiments were implemented on simulated and real high-resolution remote sensing images. The results show that the proposed algorithm is able to flexibly model the complicated distributions and accurately segment images.
1. Introduction
With the developments in remote sensing technology, the spatial resolution of remote sensing imagery has improved from meter level to centimeter level [1,2,3]. Accurate segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images plays an important role in obtaining detailed information of ground objects. Recently, various image segmentation algorithms have been proposed [4,5,6,7]. Among them, the statistical model-based segmentation algorithm has received extensive attention. Its major advantage is its ability to model class attributes and spatial relations of pixels in a probabilistic way [8]. For example, the label field of pixels can be modeled using the Markov random field (MRF) [9], while the probability density function (pdf) of the pixel label can be defined by the Gibbs distribution combining the labels of neighboring pixels [10,11]. Its primary concerns consist of accurately building the statistical model of the image and estimating the optimal model parameters. The former is the precondition while the latter is an essential requirement to obtain good results. In high-resolution remote sensing imagery, the statistical distribution of pixel intensities appears as randomly asymmetric, heavy tailed, or multimodal in an object region [12,13]. One effective way of obtaining highly accurate segmentation results is accurately modeling the distribution of pixel intensities. However, this process is not simple nor straightforward, and modeling complicated distributions has resulted in significant challenges in designing statistical model-based image segmentation algorithms.
In recent decades, a number of segmentation algorithms based on statistical models have been proposed [14,15]. Among them, the single distribution-based segmentation algorithm, which assumes that the statistical distribution of pixel intensities approximately satisfies the identical and independent distribution, is usually applied for remote sensing images. Wang et al. [15] proposed the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image segmentation algorithm, where the statistical distributions of pixel intensities are assumed to satisfy the identical and independent Gamma distributions. However, the algorithm fails to consider the difference of pixel intensities in the object region and the similarity of pixel intensities in the different regions. This results in the algorithm having some difficulties in modeling the complicated distributions of pixel intensities.
To resolve this problem, the finite mixture model (FMM) [16], which is defined by the weighted sums of components, has been proposed to model the statistical distribution of pixel intensities in image segmentation. The components are used to model the statistical distribution of pixel intensities in the object region. FMM can model more accurately the statistical distribution of pixel intensities. In practice, the components of FMM can be defined by various distributions to form the different mixture models. The Gaussian mixture model (GMM) with a Gaussian distribution as its component is the most widely used mixture model in image segmentation [8,17,18,19,20,21], due to its simple structure and easy implementation. Gaussian distribution is symmetric, which is why the component of GMM has difficulties in modeling the asymmetric, heavy-tailed, or multimodal distributions of pixel intensities. In order to improve the robustness of modeling complicated distributions, the student’s t-mixture model (SMM) is proposed. The student’s t-distribution can be heavy tailed by adjusting its freedom parameter. Hence, the component of SMM is more robust than GMM’s in modeling heavy-tailed distributions of pixel intensities [22,23]. However, modeling the asymmetric or multimodal distributions of pixel intensities remains difficult. To address this problem, the Gamma mixture model (GaMM) is proposed. Its component is a Gamma distribution, which becomes asymmetric and heavy tailed by changing its shape and scale parameters. GaMM is widely used to model the statistical distribution of pixel intensities in SAR image segmentation [24,25]. However, it still fails to solve the problem of modeling the multimodal distribution of pixel intensities. This means that while the said mixture models can be used in asymmetric or heavy-tailed distributions, their usage in modeling randomly asymmetric, heavy-tailed, or multimodal distributions of pixels intensities is still heavily constrained. Additionally, for high-resolution remote sensing images, such a limitation would yield terrible results.
To address this concern, some researchers have utilized the weighted sums of distributions instead of the component of FMM in modeling the statistical distribution of pixel intensities in the object region. For example, Nguyen et al. [26,27] proposed a medical image segmentation algorithm based on asymmetric GMM and a feature selection algorithm based on asymmetric SMM. However, their proposed algorithms are still sensitive to image noise and do not consider the spatial relation of pixels. Ji et al. [28] proposed a medical image segmentation algorithm based on spatially constrained asymmetric GMM. However, this algorithm is difficult to apply when segmenting high-resolution remote sensing images and cannot obtain good results. This is because the algorithm is complicated and utilizes a fixed number of distributions, which results in less flexibility in modeling complicated statistical distributions. The features of high-resolution remote sensing images are also explain this, such as the diversity of ground objects, the complexity of reflected spectrum, and the uncertainty of imaging conditions.
In order to resolve the various concerns and accurately segment high-resolution remote sensing images, a new hierarchical GMM (HGMM)-based high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation algorithm is proposed in this study. The hierarchy of HGMM presents its components and the corresponding elements for each component. The proposed algorithm has the following advantages: First, the proposed algorithm can accurately model the complicated distributions of pixel intensities in high-resolution remote sensing images. Since the components of HGMM are defined by the weighted sums of elements, the algorithm can flexibly model complicated distributions of pixel intensities in the object regions. This is a major precondition to obtaining highly accurate segmentation results. Second, the proposed algorithm considers local spatial relations of pixels by modeling the prior distribution of the component weight, and therefore has robustness against image noise. Finally, the proposed algorithm is designed using the birth or death Markov chain Monte Carlo (BDMCMC) in simulating the segmentation model, which can realize parameter sampling in different dimensions. Thus, the number of elements can be automatically determined to flexibly model the complicated distributions of pixel intensities. Experiments were conducted on simulated and high-resolution remote sensing images. The results show that the proposed algorithm has good performance for high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the proposed algorithm in detail. This section includes a discussion on the image model, the segmentation model, and optimal segmentation. Section 3 presents the experiment results of synthetic and panchromatic remote sensing images with high resolution. Section 4 presents the discussions of results, and Section 5 presents the conclusions of the proposed algorithm.
2. The Proposed Algorithm
2.1. Image Model
Let z = {zi; i = 1, …, n} be a panchromatic remote sensing image, where i is the index of pixels, n is the number of pixels, and zi is the intensity of pixel i. In statistical terms, z can be regarded as the realization of a random field Z = {Zi; i = 1, …, n}, where Zi is the random variable defined on pixel i.
In the FMM-based segmentation algorithm, the pdf of the pixel intensity zi can be expressed as:
where Ψi = {αi, Ω} is the set of model parameters for pixel i; αi = {αli; l = 1, …, k} is the set of component weights for pixel i; l is the index of the component; k is the number of components corresponding to the number of object regions; αli represents the probability that pixel i is assigned to the object region l and satisfies the conditions 0 ≤ αli ≤ 1 and ; Ω = {Ωl; l = 1, …, k} is the set of component parameters; and pli(zi|Ωl) is the pdf of the zi conditional on the set of the component parameter Ωl, which is used to mainly model the statistical distribution of the object region l.
Equation (1) is the general formulation of mixture models, where pli(zi|Ωl) can be defined by various types of distributions. For example, in GMM, its component is the Gaussian distribution with a mean μl and variance σl2, that is:
where Ωl= {μl, σl2} is the set of parameters for component l in GMM. Additionally, commonly used mixture models include SMM and GaMM [22,25], and their components are defined by the student’s t and Gamma distributions, respectively.
In this study, a new HGMM is proposed, where the components can accurately model the asymmetric, heavy-tailed, and multimodal distributions of pixel intensities in each object region. The pdf of its component can be expressed as:
where in component l, Ωl = {ml, wl, θl} is the set of parameters; ml is the number of elements and can be viewed as a random variable to flexibly model the complicated distributions; wl = {wlj; j = 1, …, ml} is the set of element weights; j is the index of elements; wlj is the weight of element j and satisfies the conditions 0 ≤ wlj ≤ 1 and ; θl = {θlj; j = 1, …, ml} is the set of element parameters; plji(zi|θlj) is the pdf of the Gaussian distribution called element; θlj = {μlj, σlj2} is the set of element parameters; and μlj and σlj2 are the mean and variance, respectively.
Combining Equations (1) and (3), the pdf of zi given Ψi can be modeled by the HGMM as:
Equation (4) shows that HGMM has a distinct hierarchy. The HGMM has three layers, and each layer can be concretely expressed as follow:
1) The basic layer consists of elements, which are used to model the distribution of local sections of the object region.
2) The second layer consists of components, which are defined by the weighted sums of elements. They are used to model the statistical distributions of pixel intensities in the object regions.
3) The last layer comprises the HGMM, which is defined by the weighted sums of components, which are used to model the statistical distribution of pixel intensities in high-resolution remote sensing imagery.
Assume that the pixel intensities are statistically independent, and the joint distribution of z given Ψ can be written as:
where Ψ = {Ψi; i = 1, …, n} is the set of model parameters, which can be further written as Ψ = {α, m, w, μ, σ2}; α = {αi; i = 1, …, n} is the set of component weights; m = {ml; l = 1, …, k} is the set of element numbers; w = {wl; l = 1, …, k} is the set of element weights; μ = {μlj; l = 1, …, k, j = 1, …, ml} is the set of means; and, σ2 = {σlj2; l = 1, …, k, j = 1, …, ml} is the set of variances.
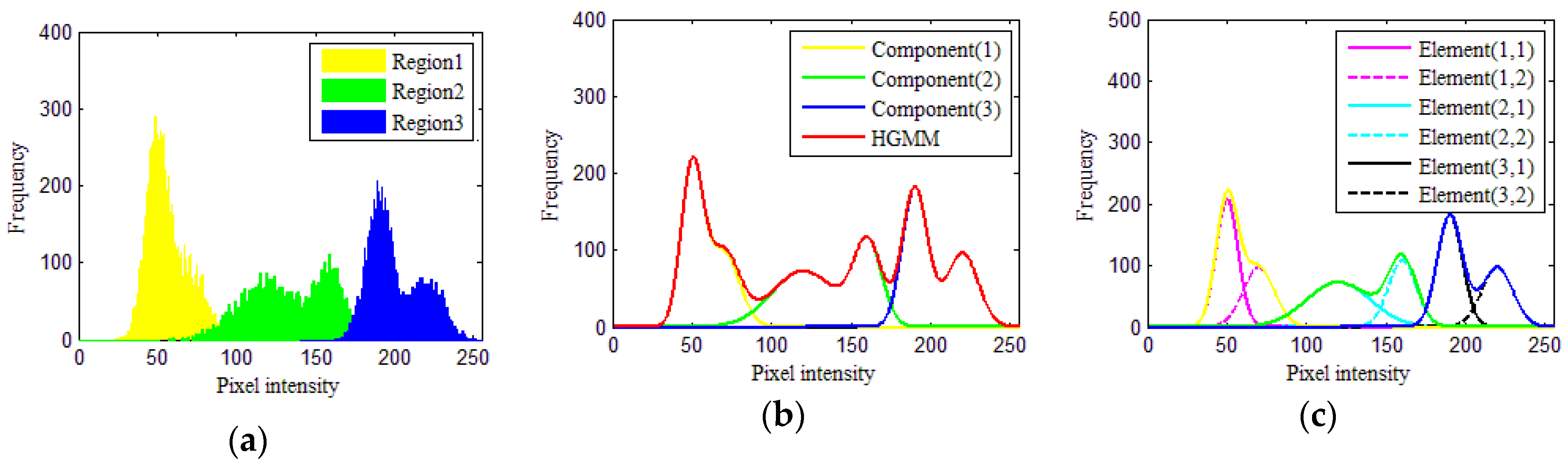
To present the modeling ability of the proposed HGMM and the role of its layers, the complex histogram and its fitting curves are shown in Figure 1. The histograms of data are shown in Figure 1a, which presents the regions in different colors: Yellow (Region 1), green (Region 2), and blue (Region 3). The yellow histogram is asymmetric; the green histogram is asymmetric, heavy tailed, and multimodal; and the blue histogram is asymmetric and multimodal. The fitting curves of the HGMM and its components are shown in Figure 1b, which shows that the HGMM with the new components can accurately fit the complex histograms. For example, the green histogram, which is asymmetric, heavy tailed, and multimodal, can accurately be fitted by the green curve. The fitting curves of the elements for each component are shown in Figure 1c, which further indicates the ability of the HGMM to fit complex histograms.

Figure 1.
(a) Histogram of data with three regions, where regions 1-3 is shown in yellow, green, and blue, respectively. (b) HGMM and its three components, where the red, yellow, green, and blue curves present p(z|Ψ), α1p1(z|Ω1), α2p2(z|Ω2), and α3p3(z|Ω3), respectively. (c) Elements of each component, where pink, cyan, and black curves are α1w11p11(z|θ11), α2w21p21(z|θ21), and α3w31p31(z|θ31), and pink, cyan, and black dotted curves are α1w12p12(z|θ12), α2w22p22(z|θ22), and α3w32p32(z|θ32), respectively.
2.2. Segmentation Model
In order to realize image segmentation, the posterior distribution of Ψ given z is viewed as the segmentation model. Following the Bayesian theorem [29,30], the segmentation model can be built by combining the HGMM and the prior distributions of its parameters. It can be written as:
where p(Ψ) is the prior distribution of Ψ. According to the relations among model parameters, p(Ψ) is further written as:
The prior distributions of model parameters are defined as follows:
1) p(α). In order to take the spatial relations of pixels into account, MRF [8,9] is built on the component weights. The pdf of αi can be defined by the Gibbs distribution [8] given the component weights of neighboring pixels for pixel i. Then, the prior distribution of α can be modeled as:
where A is the normalizing constant and is usually set to be 1; β is a constant controlling the smoothing strength of neighboring pixels of pixel i; Ni is the set of indexes for neighboring pixels in the square window centered at pixel i; and, i’ is the index of neighboring pixels.
2) p(m). Assume that the number of elements ml, l = 1, …, k satisfy the independent and identical truncated Poisson distribution [15] with parameter λ, which can be written as:
3) p(w|m). Given the numbers of elements ml, l = 1, …, k, the element weight vectors wl, l = 1, …, k have different dimensions. Since the Dirichlet distribution [31] is flexible in modeling the statistical distribution of multidimensional data, it can be used to model the pdf of the weight vector wl. Assume that the element weights are independent among components. Accordingly, the prior distribution of w given m can be written as:
where Γ(·) is Gamma function; δlj is the parameter of the Dirichlet distribution, which can be further written as δ = {δl; l = 1, …, k} = {δlj; j = 1, …, ml}; and, δlj.s are constants for controlling the peak position and the steepness of the distribution curves. To simplify the model solution, δlj is set to be the same, i.e., δlj = δ. Then, the symmetric Dirichlet distribution is used as the prior distribution of the element weight, which can be expressed as:
4) p(μ|m) and p(σ|m). Given the number of elements ml, μlj (σlj) are assumed to satisfy the identical and independent Gaussian distribution with a mean μμ (μσ) and variance σμ2 (σσ2), i.e., μlj ~ N(μμ, σμ2) and σlj ~ N(μσ, σσ2), where μμ(μσ) and σμ2(σσ2) are constants. The joint prior distributions of μ and σ can be written as:
2.3. Optimal Segmentation
To realize image segmentation, a new BDMCMC algorithm [15,32] is designed to simulate from the segmentation model in Equation (6), which can implement parameter sampling in various dimensions. The simulation process can be summarized as follows: Let the set of current parameters be Ψ and the set of candidate parameters be Ψ*, where t is the index of iterations. The acceptance rate a(Ψ, Ψ*) of Ψ* can be calculated using the posterior distributions of Ψ and Ψ*. If a(Ψ,Ψ*) = 1, then Ψ(t+1) = Ψ*; otherwise, Ψ(t+1) = Ψ. Four simulating operations are designed in this study, including updating the component weight, updating the element weight, updating the set of element parameters, and the birth or death an element in a component. The specific processes and the acceptance rates of each operation are described as follows:
1) Updating the component weight operation. Let the randomly selected component weight be αli, and this is then changed to αli + α*, where α*∈(−αli, 1) is the increment weight. To satisfy the constraints of the component weights for pixel i, their normalization is needed to change each component weight for pixel i. As a result, the candidate component weights for pixel i can be written as:
Then, the set of candidate component can be written as α* = {α1, …, αi−1, αi*, αi+1, …,αn}. Its acceptance rate can be obtained as:
2) Updating the element weight operation. Let the randomly selected element weight be wlj, which can then be changed to wlj + w*, where w*∈(−wlj, 1) is the increment of the weight. To satisfy the constraints of the element weight in the component l, their normalization is implemented to change each element weight for the component l. Consequently, the candidate element weight for the component l can be written as:
Then, the set of candidate element weights can be written as w* = {w1, …, wl−1, wl*, wl+1, …, wk}. Its acceptance rate can be written as:
3) Updating the parameter of the element. Let the randomly selected set of element parameters be θlj = {μlj, σlj2} and the candidate set of parameters be θlj* = {μlj*, σlj*2}, where μlj* (σlj*) is randomly generated from the Gaussian distribution with the mean μlj (σlj), and the standard deviation εμ (εσ) is set to 0.5. The set of candidate parameters in component l can be written as θl* = {θl1, …, θlj−1, θlj*, θlj+1, …, }. Then, the set of candidate element parameters can be written as θ* = {θ1, …, θl−1, θl*, θl+1, …, θk}. Its acceptance rate can be calculated as:
4) Birth or death of an element in a component. The index of component l is randomly selected from {1, …, k}, and its number of elements is ml. When adding an element in the component l, the candidate number of elements is ml* = ml + 1, and correspondingly add and , where the added mean and variance are generated by their prior distribution. The element weights satisfy the condition . Then, the candidate set of element weights can be written as:
.
The set of candidate element parameters can be written as θl*
= {θl1, …, , }. The acceptance rate of adding an element can be written as a(m, m*) = min(1, R), where R is written as:
When ml > 2, the deletion of an element can be carried out. In this case, the index of the deleted element j is randomly selected from {1, …, ml}, and correspondingly delete wlj and θlj. The new element weights of component l can then be written as {wl1, …, wlj−1, wlj+1, …., }. To satisfy the constraints of element weights, the candidate set of element weights can be written as:
The candidate set of element parameters can be written as θl* = {θl1*, …, θlj−1*, θlj*, …, } = {θl1, …, θlj−1, θlj+1, …, }. The candidate number of elements is ml* = ml −1. The acceptance rate of element deletion can be written as a(m, m*) = min(1, 1/R), given that this operation is antithetical with element addition.
In iterations, the above operations are carried out in sequence. To realize the image segmentation, the pixel label can be obtained by maximizing the component weights, which can be written as:
where ci is the label of pixel i, and c = {ci; i = 1, …, n} is the segmented result of the given image.
The proposed HGMM based segmentation algorithm is summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
HGMM segmentation algorithm.
3. Results
In this section, the segmentation experiments were implemented to test the proposed algorithm on synthetic high-resolution remote sensing images. The evaluated segmentation algorithms included hidden MRF (HMRF) [33], fuzzy C-means (FCM) [26], Gamma distribution [15], GMM [20], SMM [23], and GaMM-based segmentation algorithms. The comparison and implementation of the proposed algorithms were executed in Matlab software on an Intel Core i5 computer.
Table 2 lists the constants used in the HGMM algorithm, which can be applied in segmentation experiments of simulated and real high-resolution remote sensing images. When δ is more than 1, the Dirichlet distribution is the centralized distribution. With the value of δ increasing, the pdf of the Dirichlet distribution becomes more centralized. Hence, δ can be set to 10, which is appropriate to constrain the weight of the element. The values of εμ and εσ should be small to generate the candidate parameter around the current parameters. If the values are too large, the appropriate candidate parameters will be missed. The coefficient β∈(0, 1) controls the smoothing degree for image noise. When the value of β increases, the smoothness of the proposed algorithm becomes stronger for image noise. Hence, β was set to 0.8, which can obtain optimal results in many experiments. The value ÿ was set by the histogram of the image, and it is greater than 2, which is enough to model the complicated distributions of pixel intensities in high-resolution remote sensing images. The smaller the value ÿ is, the less the estimated parameters are. Hence, the value ÿ was set to be 3 in the experiments. For convenience, the values μμ and σμ were set by the half-interval and quarter-interval values of the intensity range, respectively. The values μσ and σσ were set by the quarter value of μμ and σμ, respectively.

Table 2.
Setting constants of the HGMM algorithm.
The initial parameters can be generated as follows. The weights of components and elements were randomly generated that satisfy their constraint conditions. Means and variances were randomly generated by their prior distributions.
3.1. Simulated Image
Figure 2a is the template image for the standard segmentation image, in which 1–3 are the labels of the different object regions. Figure 2b is the simulated image to test the proposed algorithm. Table 3 summarizes the pixel intensities of each object region that are randomly generated by two Gaussian distributions with different parameters.

Figure 2.
The template image and the simulated image. (a) The template image, (b) the simulated image.

Table 3.
The setting parameters of the simulated image.
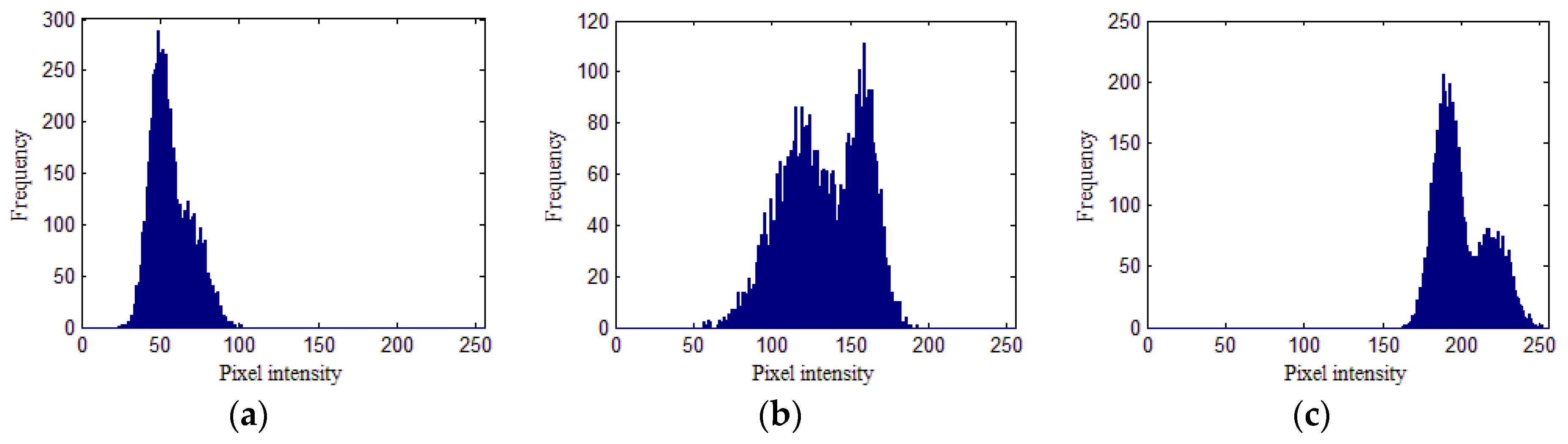
Figure 3a–c are the histograms of each region of the simulated image, where the horizontal axis is the pixel intensity, and the vertical axis is the pixel frequency. The histogram of Region 1 is asymmetric, Region 2 is heavy tailed and bimodal, and Region 3 is bimodal. Hence, the simulated image is applicable to test the modeling ability of the proposed algorithm.

Figure 3.
Histograms of each region of the simulated image: (a) Region 1, (b) Region 2, and (c) Regions 3.
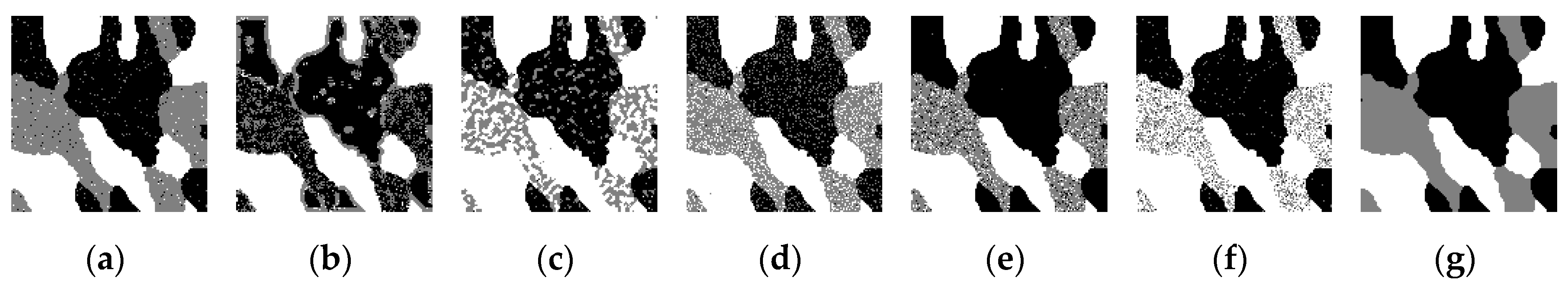
Figure 4a–g shows the segmentation results of the simulated image using the HMRF, FCM, Gamma distribution, GMM, SMM, GaMM, and HGMM-based segmentation algorithms. In Figure 4a, the HMRF algorithm is able to obtain slightly good segmentation results with few wrongly segmented pixels. In Figure Figure 4b, the FCM algorithm is unable to segment Regions 1 and 2. In Figure 4c,d, plenty of wrongly segmented pixels can be found for Regions 1 and 2. In Figure 4e,f, wrongly segmented pixels are mainly located in Region 2. In Figure 4g, the proposed algorithm is able to more accurately segment each region, and very few wrongly segmented pixels can be found.

Figure 4.
The segmentation results of the simulated image. (a) HMRF algorithm, (b) FCM algorithm, (c) Gamma distribution-based algorithm, (d) GMM algorithm, (e) SMM algorithm, (f) GaMM algorithm, and (g) the proposed algorithm.
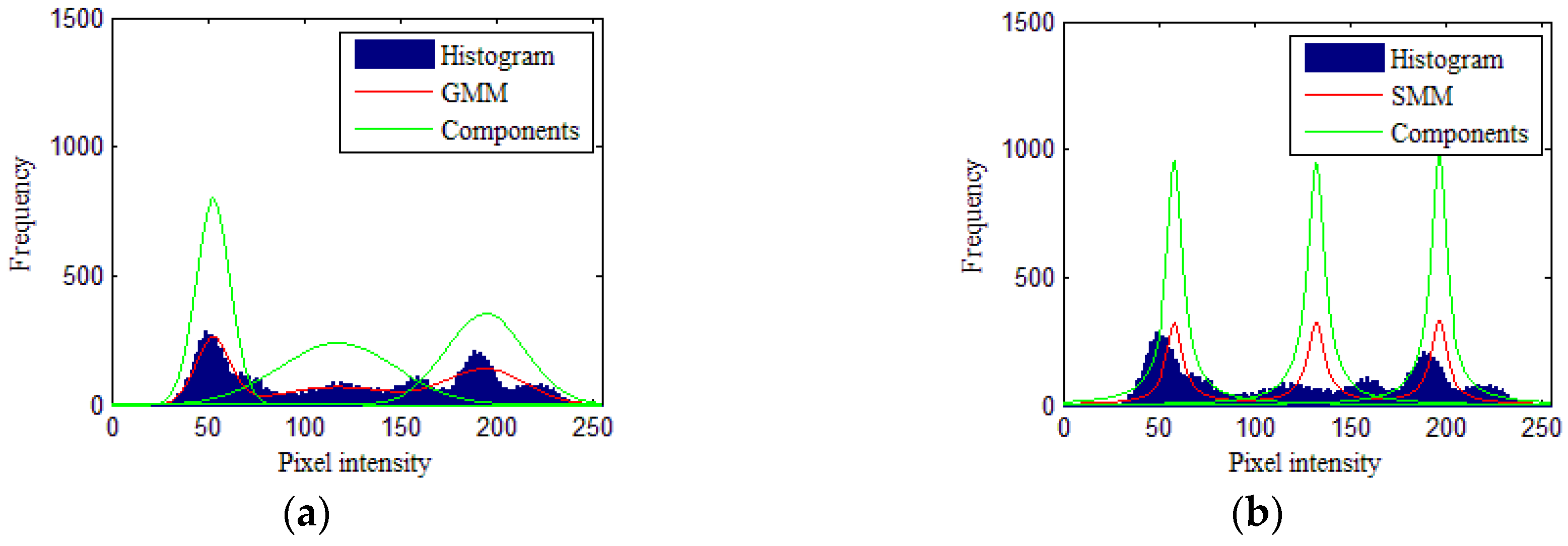
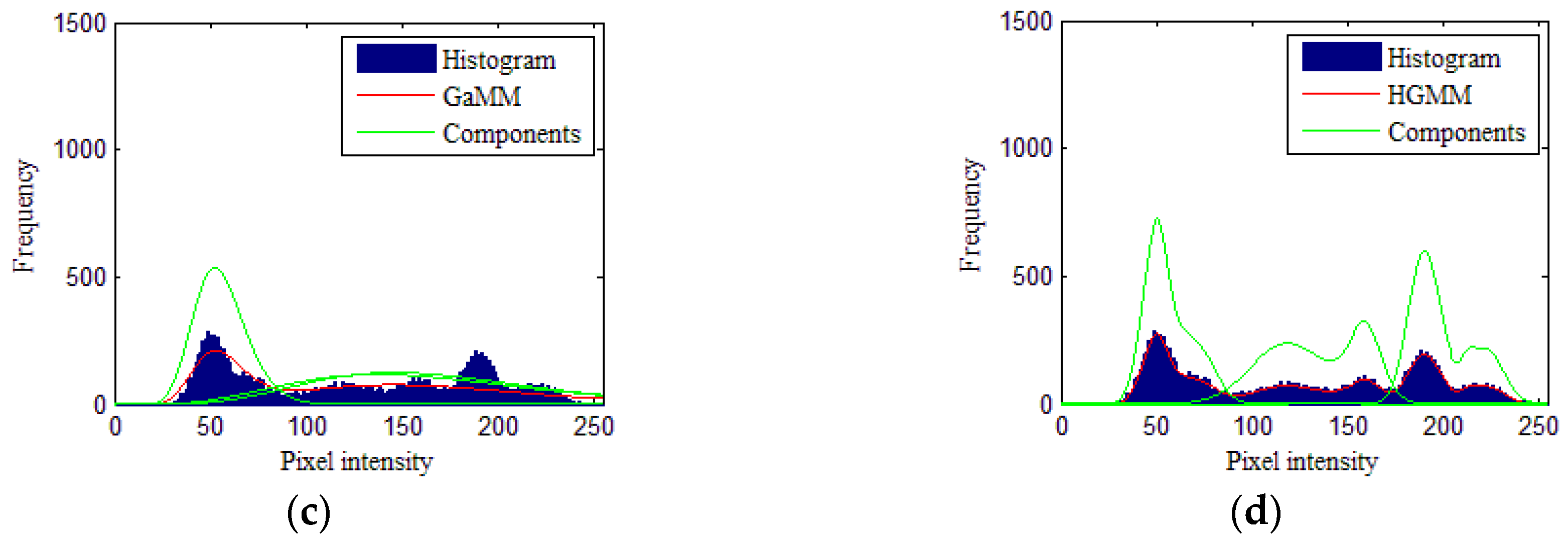
To verify the modeling ability of the proposed algorithm, a non-linear curve fit was performed on the histogram of the simulated image, as shown in Figure 5, where the blue region indicates the histogram of the simulated image. The red curves show the fitting curves of the GMM, SMM, GAMM, and HGMM in Figure 5a–d, respectively. The green curves correspondingly present the components of each mixture model. In Figure 5a–c, the fitting curves do not accurately fit the histogram of the simulated image, where the components are presented in a single distribution. In Figure 5d, the proposed HGMM can more accurately fit the complex histogram (red lines), and the component curves (green lines) are able to fit each peak of the histogram.


Figure 5.
The fitting results of the histograms of the simulated image. (a) GMM algorithm, (b) SMM algorithm, (c) GaMM algorithm, and (d) HGMM algorithm.
Table 4 lists the accuracies of the segmentation results in Figure 4, which includes the user accuracy, production accuracy, overall accuracy, and the Kappa coefficient. The accuracies were calculated using the confusion matrix, which can be obtained by comparing each segmentation result with the template image. In comparing the accuracies of the algorithms, the following results were obtained: For the HMRF algorithm, while the accuracies are above 96%, they are lower than the accuracies of the proposed algorithm. The lowest accuracies for the FCM, Gamma distribution, GMM, SMM, and GaMM-based algorithms are 28.28%, 51.13%, 76.50%, 76.50%, and 32.91%, respectively. For the proposed algorithm, the accuracies are all above 99%. The overall accuracy of the proposed algorithm is 1.64%, 33.03%, 18.69%, 12.57%, 6.7%, and 20.41% higher than the FCM, Gamma distribution, GMM, SMM, and GaMM-based algorithms, respectively. Moreover, the Kappa coefficient of the proposed algorithm is also higher.

Table 4.
Accuracy evaluation of the synthetic image.
3.2. High-Resolution Remote Sensing Image
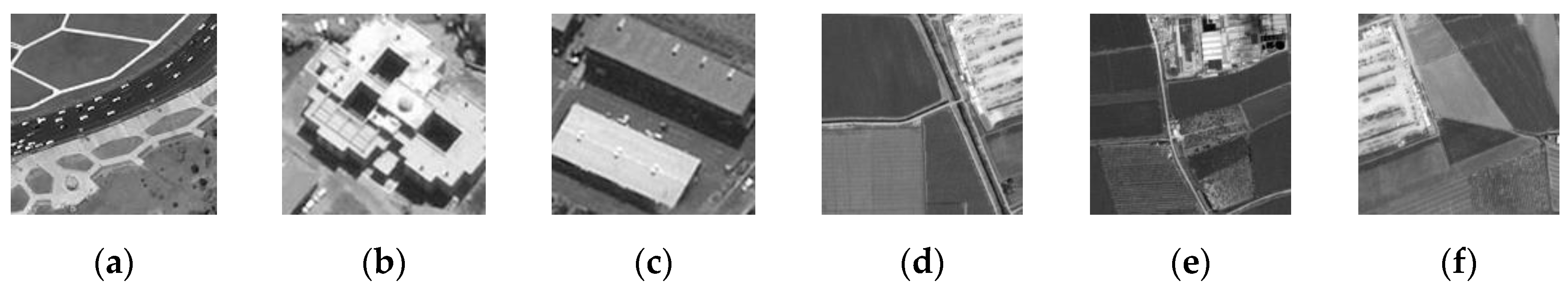
Figure 6 presents the various high-resolution remote sensing images. Figure 6a–c are 128×128 pixels at a 0.5-m resolution and are from Worldview-1. Figure 6d–f are 256×256 pixels at a 2.5-m resolution, which are from Cartosat-1. The images include buildings, farmland, road, and bare land, which means these images can effectively be used to test the proposed algorithm. The number of object regions were set to be 3, 3, 4, 3, 3, and 4 visually, which is based on the number of peaks in the histograms.

Figure 6.
The high-resolution remote sensing images. (a)–(f) images 1-6.
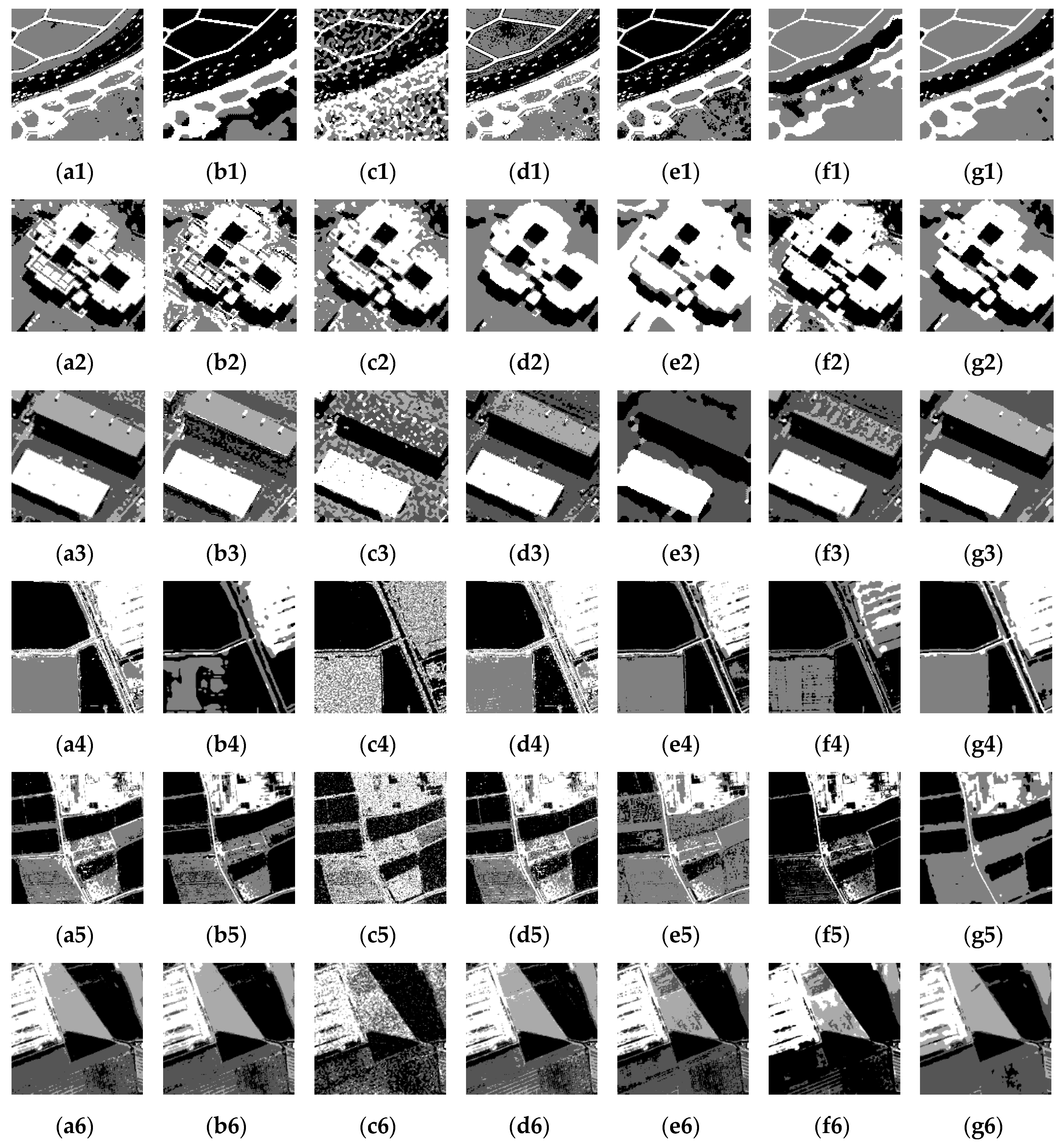
Figure 7 presents the segmentation results of high-resolution remote sensing images employing HMRF, FCM, Gamma distribution, GMM, SMMM, GaMM, and HGMM-based segmentation algorithms. In Figure 7a1–a6,b1–b6, the HMRF and FCM algorithms were unable to obtain good results, and some pixels were wrongly segmented. In Figure 7c1–c6, many pixel blocks were wrongly segmented using the Gamma distribution-based algorithm. In Figure 7d1–d6,e1–e6,f1–f6, segmentation using the GMM, SMM, and GaMM-based algorithms yielded slightly better results than the Gamma distribution-based algorithm. However, some pixels were still incorrectly segmented. Figure 7g1–g6 show that the proposed algorithm was able to obtain better results compared with the other techniques. Each region was properly segmented, with only a few pixels wrongly segmented.

Figure 7.
The high-resolution remote sensing images and their segmentation results: (a1)–(a6) HMRF algorithm, (b1)–(b6) FCM algorithm, (c1)–(c6) Gamma distribution based algorithm, (d1)–(d6) GMM algorithm, (e1)–(e6) SMM algorithm, (f1)–(f6) GaMM algorithm, and (g1)–(g6) the proposed algorithm.
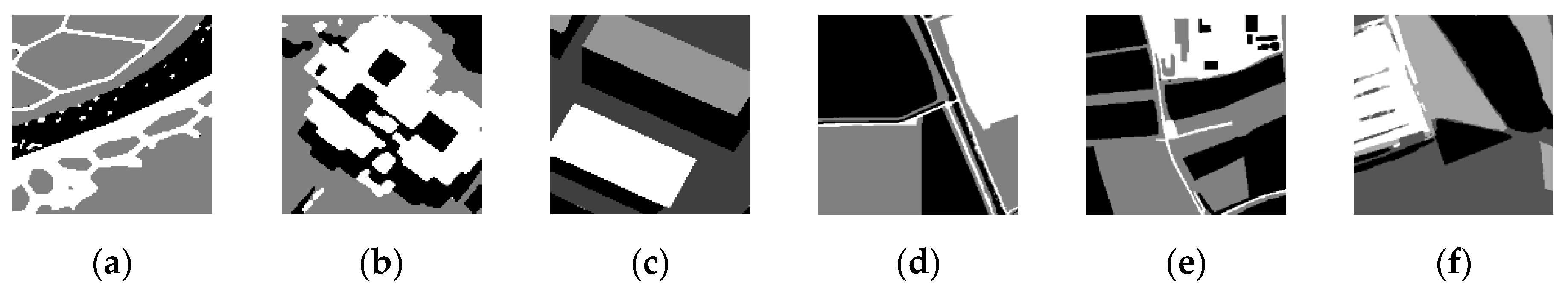
To quantitatively evaluate the above segmentation results of high-resolution remote sensing images, the segmentation accuracies were calculated and are shown in Table 5. These values were obtained using the confusion matrix generated by comparing the segmentation results (shown in Figure 7) with the template image (shown in Figure 8). The estimated accuracies of the various algorithms for each of the high-resolution images were above 85%, 53%, 62%, 82%, 66%, and 57% using the HMRF, FCM, Gamma, GMM, SMM, and GaMM algorithms, respectively. For the proposed algorithm, the accuracies were above 88%, which is comparatively higher than those from the other algorithms.

Table 5.
Accuracy evaluation of remote sensing images.

Figure 8.
The template images of high-resolution remote sensing images. (a)–(f) images 1–6.
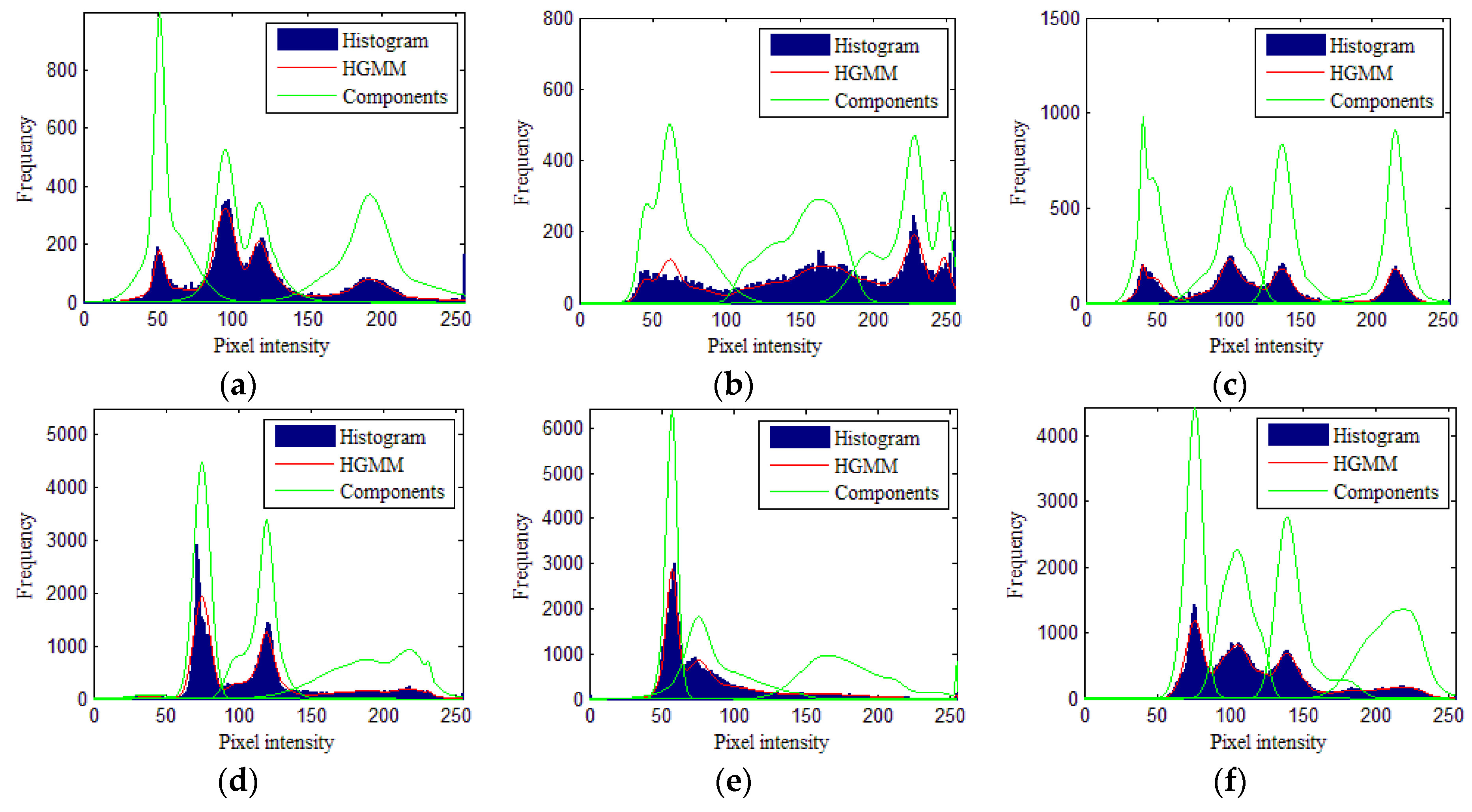
Figure 9 shows the fitting curves of the various histograms that were used to assess the modeling ability of the proposed algorithm, particularly for high-resolution remote sensing images. The histograms of high-resolution remote sensing images show asymmetric, heavy-tailed, and multimodal features. As shown in Figure 9a, the green curves are able to accurately fit each peak for the different object regions: The first curve is heavy tailed, the second curve is multimodal, and the last curve is asymmetric. Furthermore, the proposed HGMM can accurately fit the histograms, as displayed by the red curves.

Figure 9.
The fitting results of histograms of high-resolution remote sensing images using the proposed algorithm. (a)–(f) high-resolution remote sensing images 1-6.
To test the efficiency performance of the proposed algorithm, the segmentation times of the various algorithms were calculated and are summarized in Table 6. The segmentation times for the HMRF and FCM algorithms were between 70 and 130 s; between 110 and 1600 s for the GMM and SMM-based algorithms; and between 720 and 3700 s for the Gamma distribution and GaMM-based algorithms. For the proposed algorithm, the segmentation times were between 630 and 2400 s.

Table 6.
The efficiency performance of the segmentation algorithms.
4. Discussion
The results from the experiments using simulated images show that many pixels were incorrectly segmented by comparative segmentation algorithms, particularly in Region 2, while the proposed algorithm performed better visually. The comparative algorithms were not able to accurately fit the histograms for each region. For instance, in Figure 5a, the second green curve over-fits the histogram for Region 3. Since the Gaussian distribution is asymmetric, and the GMM components have difficultly fitting in asymmetric and other complex histograms, many pixels, particularly those found in Region 2, are wrongly segmented. Given that the student’s t-distribution is heavy tailed, the component of SMM is unable to accurately fit the asymmetrical, heavy-tailed, and bimodal histograms in Figure 5b. The gamma distribution is right-skewed, but the GaMM-based algorithm does not fit the bimodal histogram for each region in Figure 5b,c. Thus, many white pixels are wrongly segmented into Region 2. The component of HGMM is defined by the weight sums of two Gaussian distributions, which can accurately fit the histograms for each region in Figure 5d. Hence, the proposed algorithm is able to obtain the best results and can achieve higher accuracy than the comparative algorithms.
In the experiment of high-resolution remote sensing images, the comparative algorithms were not able to segment the high-resolution image, even when the difference of the pixel intensity was clearly noticeable (such as farmlands). The proposed algorithm obtained better segmentation results and produced much higher segmentation accuracy compared with the other algorithms because it was able to accurately fit each histogram of the remote sensing images. The proposed algorithm has the capability of accurately modeling complicated distributions of pixel intensities and is able to obtain better segmentation, particularly for high-resolution remote sensing images.
The results of the efficiency performance evaluation show that the HMRF and FCM algorithms had the fastest segmentation times. However, the HMRF and FCM algorithms are sensitive to the initial parameter and easily obtain the local solution. The gamma distribution and GaMM-based algorithms are slower because of the H-M algorithm sampling parameters in a number of iterations, while the GMM and SMM-based algorithms showed better segmentation efficiency than the Gamma distribution and GaMM-based algorithms. The proposed algorithm registered a slightly faster segmentation time than the Gamma distribution and GaMM-based algorithms but was slower than the GMM and SMM-based algorithms. This is because the BDMCMC algorithm is used for sampling parameters in numerous iterations. Additionally, with the size of the image increasing, the segmentation time also increases. Though the efficiency of the proposed algorithm is worse, its accuracy is better than the other compared algorithms.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposed a novel HGMM-based high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation algorithm. First, to accurately model the asymmetric, heavy-tailed, and multimodal distributions of pixel intensities, HGMM is defined to build the statistical model of high-resolution remote sensing images. Instead of a single distribution as a component, the components of HGMM are defined by the weighted sums of elements, which can accurately model the complicated distributions of pixel intensities in object regions. Accurately modeling the distribution of pixel intensities can more fully utilize the information of the pixel intensity, which is an effective way to obtain good segmentation. Second, the number of elements is viewed as a random variable to flexibly model the statistical distribution of pixel intensities. The prior distribution of the component weight is defined by the Gibbs distribution, which considers the locally spatial relations of pixels to improve the robustness to image noise. Finally, a new BDMCMC is designed to simulate the segmentation model. The algorithm can optimize the model parameters and determine the number of elements.
The experimental results showed that the proposed algorithm is able to model complex distributions of pixel intensities and shows a better modeling ability than traditional statistical model-based algorithms for high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation. Hence, the proposed algorithm can obtain better results. However, one limitation of the proposed algorithm is that the number of components is fixed by the user, which is a common problem in current segmentation algorithms. Another limitation is that the constants of prior distributions are set using prior knowledge and experiments. Additionally, the proposed algorithm has comparatively low segmentation efficiency due to its usage of BDMCMC algorithm sampling parameters. In the future, the above problem will be resolved. In order to improve the efficiency, the sampling processes can be modified to prevent the numbers of candidate parameters from being rejected. Moreover, some constants or coefficients can be estimated or defined by maximizing the posterior distribution, such as β.
Author Contributions
Methodology, X.S., Y.L., and Q.Z.; Writing—review and editing, X.S., and Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41301479 and 41271435.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the reviewers for their valuable suggestions to improve the quality of this paper. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41301479 and 41271435. Special thanks to the professional English editing service from EditX.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Xiao, P.F.; Feng, X.Z.; Wang, J.G.; Wang, Z. Hybrid region merging method for segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 98, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.F.; Zhang, S.W. Local and global evaluation for remote sensing image segmentation. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinias, I.; Panagiotakis, C.; Tziritas, G. MRF-based segmentation and unsupervised classification for building and road detection in peri-urban areas of high-resolution satellite images. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 122, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Q.; Lin, Z.L.; Acton, S.T. Learning automata for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2016, 74, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.F. A novel region-merging approach guided by priority for high resolution image segmentation. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Xue, D.H.; Lv, Z.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Asoke, K.N. Unsupervised change detection using fast fuzzy clustering for landslide mapping from very high-resolution images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Wu, Q.M.J. Fast and robust spatially constrained Gaussian mixture model for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2013, 23, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z. Markov Random Field Modeling in Image Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte, M. A label field fusion Bayesian model and its penalized maximum rand estimator for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1610–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Si, B.; Herrmann, J.M.; Feng, X.S. Local autoencoding for parameter estimation in a hidden Potts-Markov random field. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 324–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouveyron, C.; Brunet-Saumard, C. Model-based clustering of high-dimensional data: A review. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2014, 71, 52–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Chova, L.; Tuia, D.; Moser, G.; Camps-Valls, G. Multimodal classification of remote sensing images: A review and future directions. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterington, D.M.; Smith, A.F.M.; Markov, U.E. Statistical Analysis of Finite Mixture Distributions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.H. Segmentation of high-resolution SAR image with unknown number of classes based on regular tessellation and RJMCMC algorithm. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 1290–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclachlan, G.J.; Peel, D. Finite Mixture Models; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Permuter, H.; Francos, J.; Jermyn, I. A study of Gaussian mixture models of color and texture features for image classification and segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2006, 39, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikou, C.; Galatsanos, N.P.; Likas, A.C. A class-adaptive spatially variant mixture model for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2001, 20, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yong, X.; Zheng, Y. A robust modified Gaussian mixture model with rough set for image segmentation. Neurocomputing 2017, 266, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, C. Superpixel segmentation using Gaussian mixture model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4105–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Wu, Q.M.J. Robust Student’ s-t mixture model with spatial constraints and its application in medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2012, 31, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wen, C.; Wang, H. Fast and robust image segmentation with active contours and Student’s-t mixture model. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 63, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziou, D.; Bouguila, N.; Allili, M.S.; El-Zaart, A. Finite gamma mixture modelling using minimum message length inference: Application to SAR image analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 771–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.H.; Li, X.L.; Li, Y. Multilook SAR image segmentation with an unknown number of clusters using a Gamma mixture model and hierarchical clustering. Sensors 2017, 17, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Wu, Q.M.J.; Mukherjee, D.; Zhang, H. Bounded asymmetric mixture model for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; IEEE: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Wu, Q.M.J.; Zhang, H. Asymmetric mixture model with simultaneous feature selection and model detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Cao, G.; Zheng, Y. A rough set bounded spatially constrained asymmetric Gaussian mixture model for image segmentation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comer, M.L.; Delp, E.J. The EM/MPM algorithm for segmentation of textured images: Analysis and further experimental results. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congdon, P. Bayesian Statistical Modelling. Biometrics 2007, 63, 976–977. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Wu, Q.M.J. Dirichlet Gaussian mixture model: Application to image segmentation. Image Vis. Comput. 2011, 29, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M. Bayesian analysis of mixture models with an unknown number of components-an alternative to reversible jump methods. Ann. Stat. 2000, 28, 40–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzis, S.P.; Varvarigou, T.A. A fuzzy clustering approach toward hidden Markov random field models for enhanced spatially constrained image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2008, 16, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).