A Genetic Optimization Resampling Based Particle Filtering Algorithm for Indoor Target Tracking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basics of a Generic Particle Filter and Genetic Algorithm
2.1.1. Generic Particle Filter
2.1.2. Genetic Algorithm
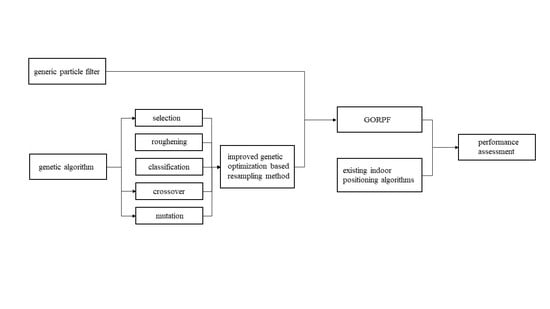
2.2. Genetic Optimization Resampling-Based Particle Filter (GORPF)
2.2.1. Improved Genetic Optimization Resampling Method
Selection
Roughening
Classification
Crossover
Mutation
2.2.2. Genetic Optimization Resampling-Based Particle Filter
2.3. Assessment of the Proposed Method
2.3.1. Test A: One-Dimensional Tracking
2.3.2. Test B: Three-Dimensional Tracking
3. Results
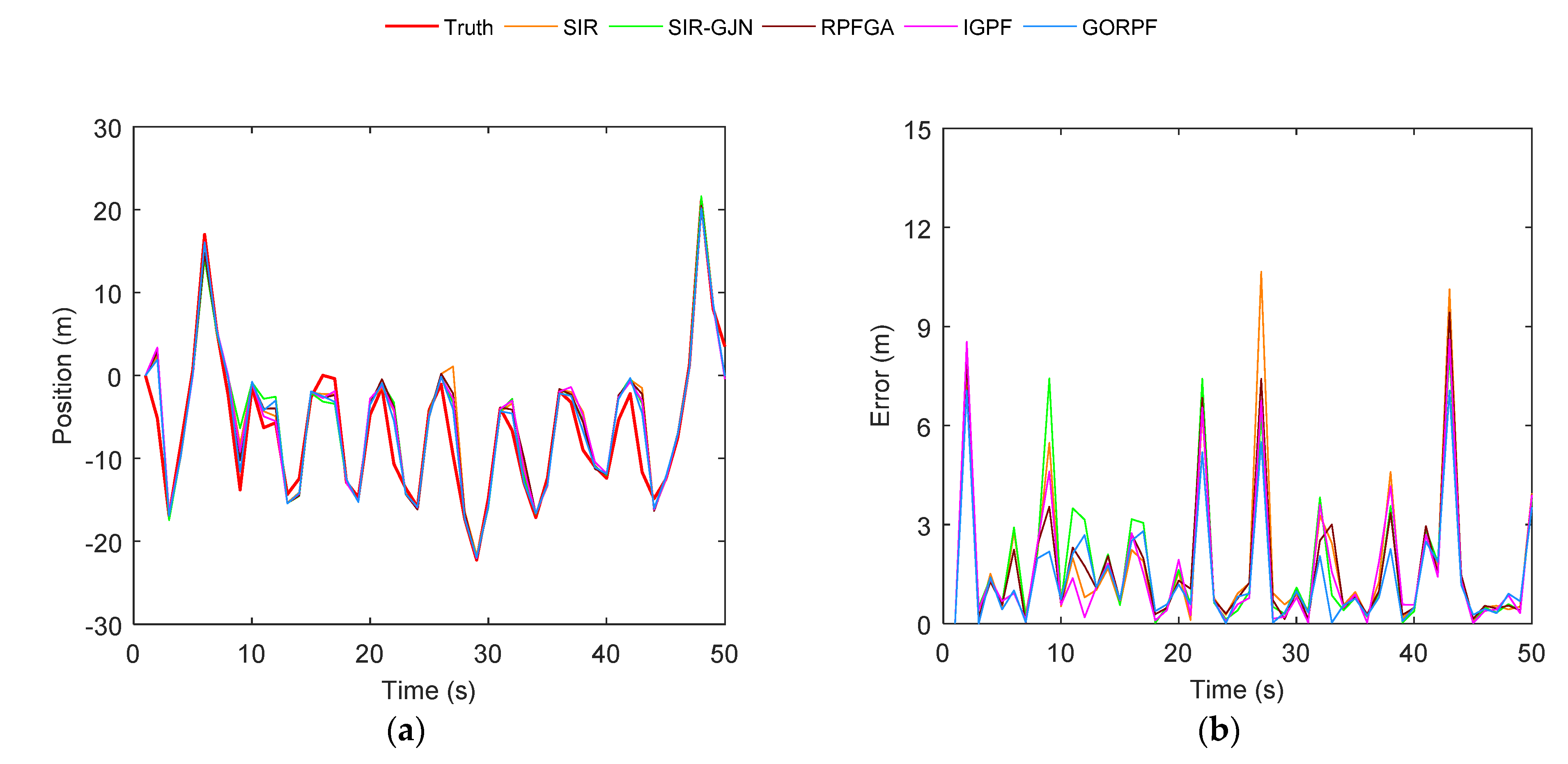
3.1. Results of Test A
3.2. Results of Test B
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, D.; Ullah, S.; Nabi, S. A generic approach toward indoor navigation and pathfinding with robust marker tracking. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julier, S.; Uhlmann, J.K. A new extension of the Kalman filter to nonlinear systems. In Proceedings of the SPIE 3068, Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition VI, Orlando, FL, USA, 28 July 1997; pp. 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merwe, R.V.D.; Doucet, A.; Freitas, N.D.; Wan, E.A. The unscented particle filter. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 17 January 2000; pp. 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Park, T.H. Extended Kalman filter (EKF) design for vehicle position tracking using reliability function of radar and lidar. Sensors 2020, 20, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Bayesian filtering: From Kalman filters to particle filters, and beyond. Statistics 2003, 182, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risfic, B.; Arulampalam, S.; Gordon, N. Beyond the Kalman Filter: Particle Filters for Tracking Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulampalam, M.S.; Maskell, S.; Gordon, N.; Clapp, T. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pak, J.M.; Ahn, C.K.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Shi, P.; Lim, M.T. Accurate and reliable human localization using composite particle/FIR filtering. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2017, 47, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenc, I.; Chong, C.C. A survey on TOA based wireless localization and NLOS mitigation techniques. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut. 2009, 11, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Dutkiewicz, E. NLOS identification and mitigation for mobile tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 1438–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Mao, Y. Wireless location technology of Gauss Particle filter under NLOS environment. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Materials Engineering, Manufacturing Technology and Control, Taiyuan, China, 27 January 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, F.; Fritsche, C.; Gustafsson, F.; Zoubir, A.M. TOA-based robust wireless geolocation and Cramér-Rao lower bound analysis in harsh LOS/NLOS environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicoli, M.; Morelli, C.; Rampa, V. A jump Markov particle filter for localization of moving terminals in multipath indoor scenarios. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 3801–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.J.; Salmond, D.J.; Smith, A.F.M. Novel approach to nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian state estimation. IEEE Proc. F Radar Signal Process. 1993, 140, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oudjane, N.; Musso, C. Progressive correction for regularized particle filters. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Information Fusion, Paris, France, 10 August 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilks, W.R.; Berzuini, C. Following a moving target—Monte Carlo inference for dynamic Bayesian models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2001, 63, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orguner, U.; Gustafsson, F. Risk sensitive particle filters for mitigating sample impoverishment. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 5001–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Sattar, T.; Sun, S. Deterministic resampling: Unbiased sampling to avoid sample impoverishment in particle filters. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.E. Genetic Algorithm in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1989; Volume 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Monte carlo filter using the genetic algorithm operators. J. Stat. Comput. Sim. 1997, 59, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hwang, J.P.; Kim, E.; Kang, H. A new evolutionary particle filter for the prevention of sample impoverishment. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2009, 13, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, X. Object tracking with an evolutionary particle filter based on self-adaptive multi-features fusion. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, L.; Sun, X.; Yin, L.; Li, H.; Luo, D. Firefly Algorithm (FA) based particle filter method for visual tracking. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2015, 126, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tan, Q.K.; Chen, J.; Ren, Z. Particle filter based on improved genetic algorithm resampling. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Nanjing, China, 12–14 August 2016; pp. 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Z. Particle filter based on particle swarm optimization resampling for vision tracking. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 8910–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddasi, S.S.; Faraji, N. A hybrid algorithm based on particle filter and genetic algorithm for target tracking. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 147, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, J.; Pearce, C.; Green, D. Binary versus real coding for genetic algorithms: A false dichotomy? ANZIAM J. 2010, 51, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanat, A.; Almohammadi, K.; Alkafaween, E.; Abunawas, E.; Hammouri, A.; Prasath, V. Choosing mutation and crossover ratios for genetic algorithms—A review with a new dynamic approach. Information 2019, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bessaou, M.; Siarry, P. A genetic algorithm with real-value coding to optimize multimodal continuous functions. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2001, 23, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraj, R.; Ravichandran, T. A review of selection methods in genetic algorithm. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 3792–3797. [Google Scholar]
- Umbarkar, A.J.; Sheth, P. Crossover operators in genetic algorithms: A review. ICTACT J. Soft Comput. 2015, 6, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.S.; Lin, T.Y.; Fung, R.F. Key design parameters and optimal design of a five-point double-toggle clamping mechanism. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 4304–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, M.; Escalera, S.; Baró, X.; Radeva, P.; Vitrià, J.; Pujol, O. Minimal design of error-correcting output codes. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2012, 33, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Eiben, A.E.; Smith, J.E. Introduction to Evolutionary Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.; Mehrotra, K.; Mohan, C.; Ranka, S. Characterization of a class of sigmoid functions with applications to neural networks. Neural. Netw. 1996, 9, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Q. Study on the facility layout in workshop based on improved adaptive genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Software Engineering, Wuhan, China, 11–13 December 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Rosenbluth, A.; Rosenbluth, M.; Teller, A.; Teller, E. Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, S.; Ranvier, S.; Zhao, X.; Kivinen, J.; Vainikainen, P. Multipath propagation characterization of ultra-wide band indoor radio channels. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Zurich, Switzerland, 5–8 September 2005; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinoglu, Z.; Gezici, S.; Guvenc, I. Ultra-Wideband Positioning Systems: Theoretical Limits, Ranging Algorithms, and Protocols; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, C.; Kohno, R. High data rate transmissions using orthogonal modified Hermite pulses in UWB communications. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Telecommunications, Papeete, Tahiti, French Polynesia, 23 February–1 March 2003; pp. 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uren, J.; Price, B. Surveying for Engineers, 5th ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.; Quan, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhou, N.; Wen, C.; Nie, Q.; Jing, F. An autonomous ultra-wide band-based attitude and position determination technique for indoor mobile laser scanning. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthukrishnan, K.; Hazas, M. Position estimation from UWB pseudorange and angle-of-arrival: A comparison of non-linear regression and Kalman filtering. In Proceedings of the Location and Context Awareness, 4th International Symposium, LoCA 2009, Tokyo, Japan, 7–8 May 2009; pp. 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Q. Particle filter with multimode sampling strategy. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, J.; Gao, H. State estimation in nonlinear system using sequential evolutionary filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3786–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberge, V.; Tarbouchi, M.; Labonte, G. Comparison of parallel genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for real-time UAV path planning. IEEE Trans Ind. Informat. 2013, 9, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| GORPF Algorithm | |
|---|---|
| Data: , , , , | |
| Result: | |
| 1. | begin |
| 2. | - Generate initial particles of the position estimate: |
| 3. | fordo |
| 4. | for do |
| 5. | - |
| 6. | - = |
| 7. | end for |
| 8. | - Calculate the sum of weight: |
| 9. | for do |
| 10. | - Weight normalization: |
| 11. | end for |
| 12. | - Calculate position estimate: |
| 13. | - Implement improved genetic optimization resampling to get |
| 14. | end for |
| 15. | end |
| is the process noise generated based on . | |
| Computer | Lenovo ideapad 500S-13ISK |
| CPU | Intel Core i5-6200U CPU @ 2.30GHz |
| RAM | 4.00 GB |
| Operating System | Windows 10 Home Version 1903, 64 bits |
| Software | MATLAB 9.1.0.441655 (R2016b) 64 bits |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 2000 (unitless) | |
| 0.2 m/s2 | |
| 0.25 m | |
| 0.2 m | |
| 0.01 m/s | |
| 0.9 (unitless) | |
| 0.6 (unitless) | |
| 0.1 (unitless) | |
| 0.01 (unitless) |
| Test Number | Test Conditions | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIR | SIR-GJN | RPFGA | IGPF | GORPF | ||
| Test 1 | 3.0117 | 2.8601 | 2.7280 | 2.6625 | 2.1999 | |
| Test 2 | 3.5766 | 3.4715 | 3.2275 | 3.1752 | 2.4809 | |
| Test 3 | 4.2175 | 4.0914 | 3.6317 | 3.6546 | 2.9284 | |
| Performance Metric | Algorithms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIR | SIR-GJN | RPFGA | IGPF | GORPF | EKF | |
| MRSE (m) | 0.2603 | 0.2436 | 0.2306 | 0.2234 | 0.2019 | 0.2677 |
| Computation time (s) | 0.1602 | 0.1766 | 0.2253 | 0.2805 | 0.3382 | 1.2861 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, N.; Lau, L.; Bai, R.; Moore, T. A Genetic Optimization Resampling Based Particle Filtering Algorithm for Indoor Target Tracking. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010132
Zhou N, Lau L, Bai R, Moore T. A Genetic Optimization Resampling Based Particle Filtering Algorithm for Indoor Target Tracking. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(1):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010132
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ning, Lawrence Lau, Ruibin Bai, and Terry Moore. 2021. "A Genetic Optimization Resampling Based Particle Filtering Algorithm for Indoor Target Tracking" Remote Sensing 13, no. 1: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010132
APA StyleZhou, N., Lau, L., Bai, R., & Moore, T. (2021). A Genetic Optimization Resampling Based Particle Filtering Algorithm for Indoor Target Tracking. Remote Sensing, 13(1), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010132