Spatiotemporal Variability of Surface Phytoplankton Carbon and Carbon-to-Chlorophyll a Ratio in the South China Sea Based on Satellite Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
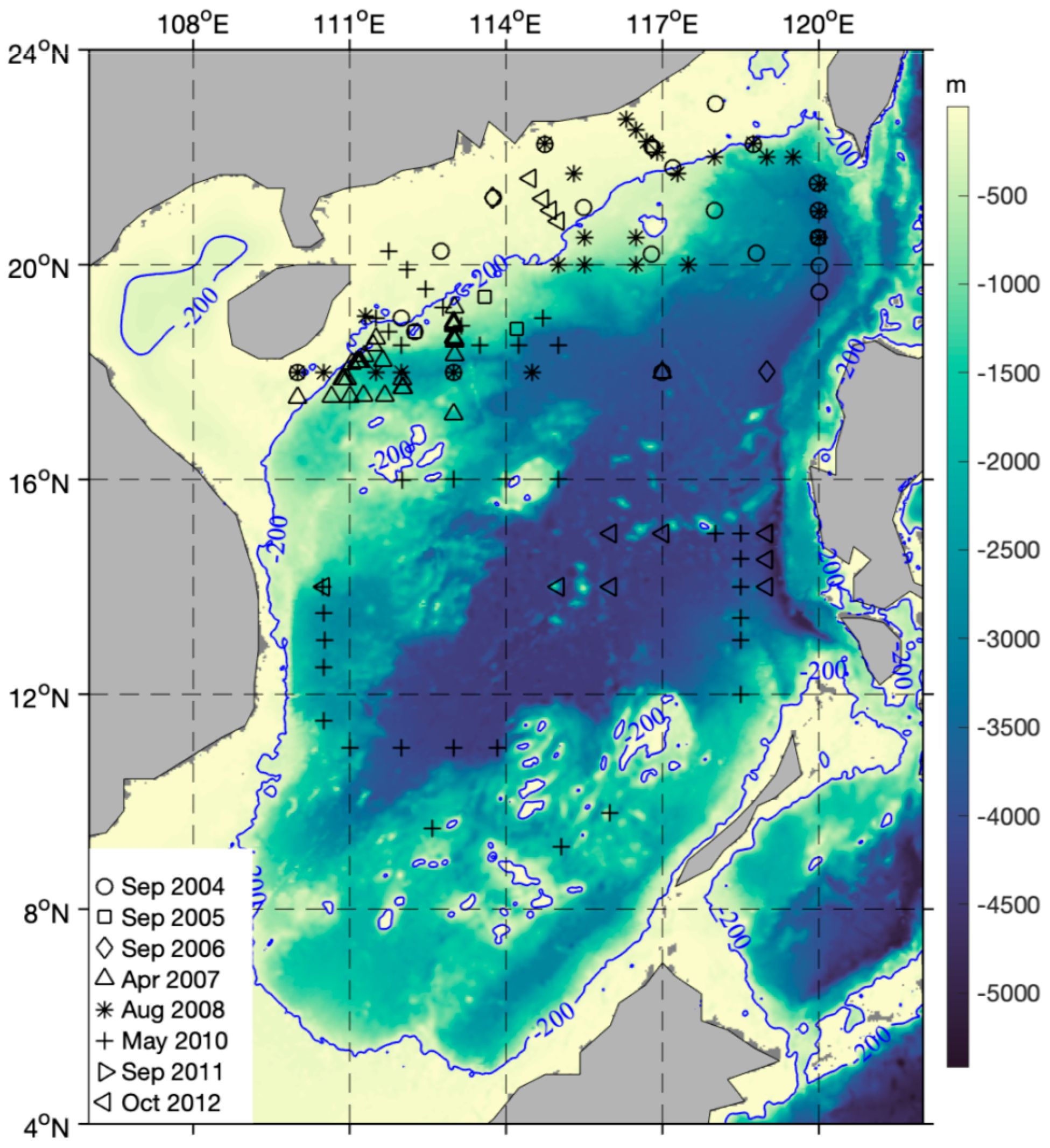
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Estimates of Phytoplankton Carbon
2.4. Algorithm to Estimate Phytoplankton Size Classes
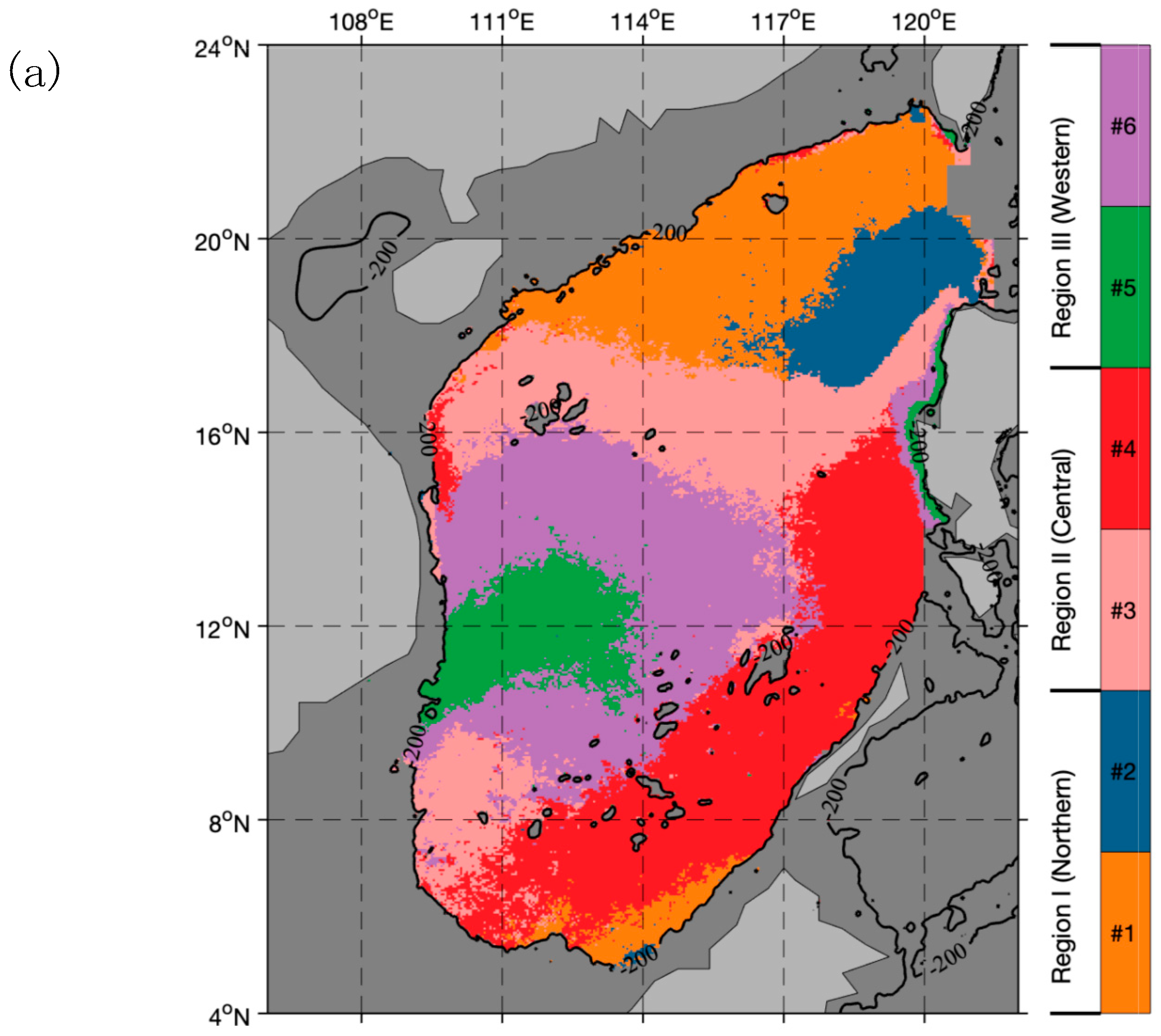
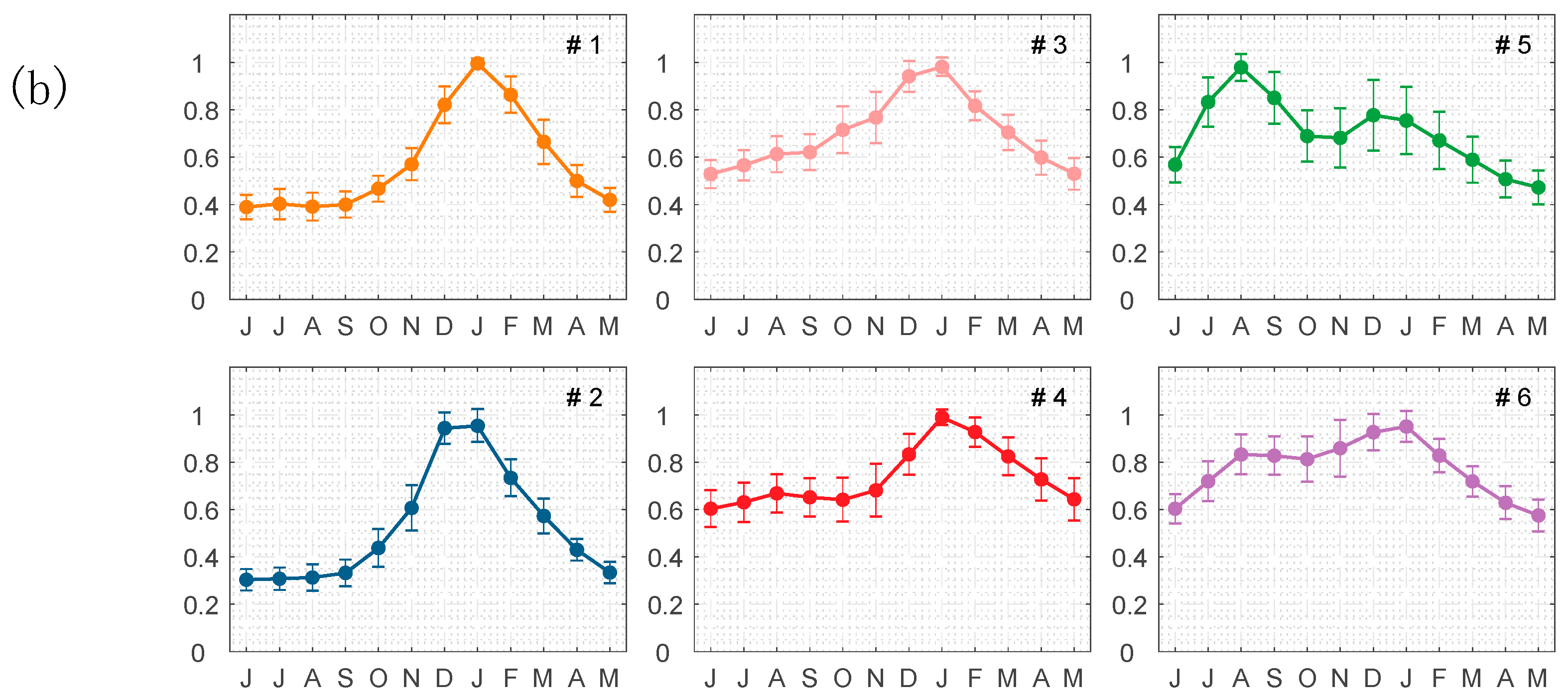
2.5. Dividing Biogeochemical Provinces in the SCS
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
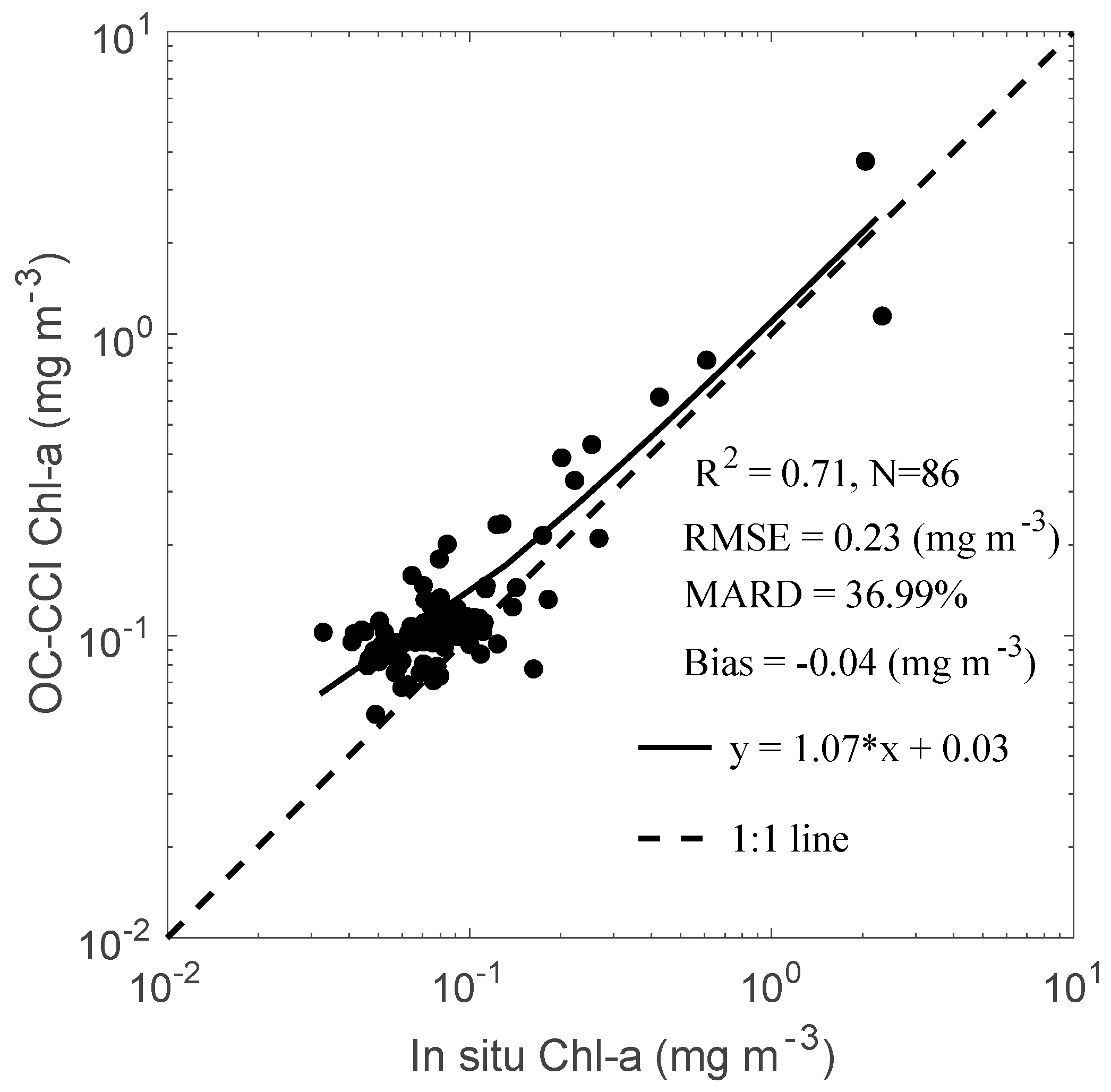
3.1. Validation of OC-CCI Product
3.2. Comparison of Phytoplankton Carbon Estimates Using Different Empirical Algorithms
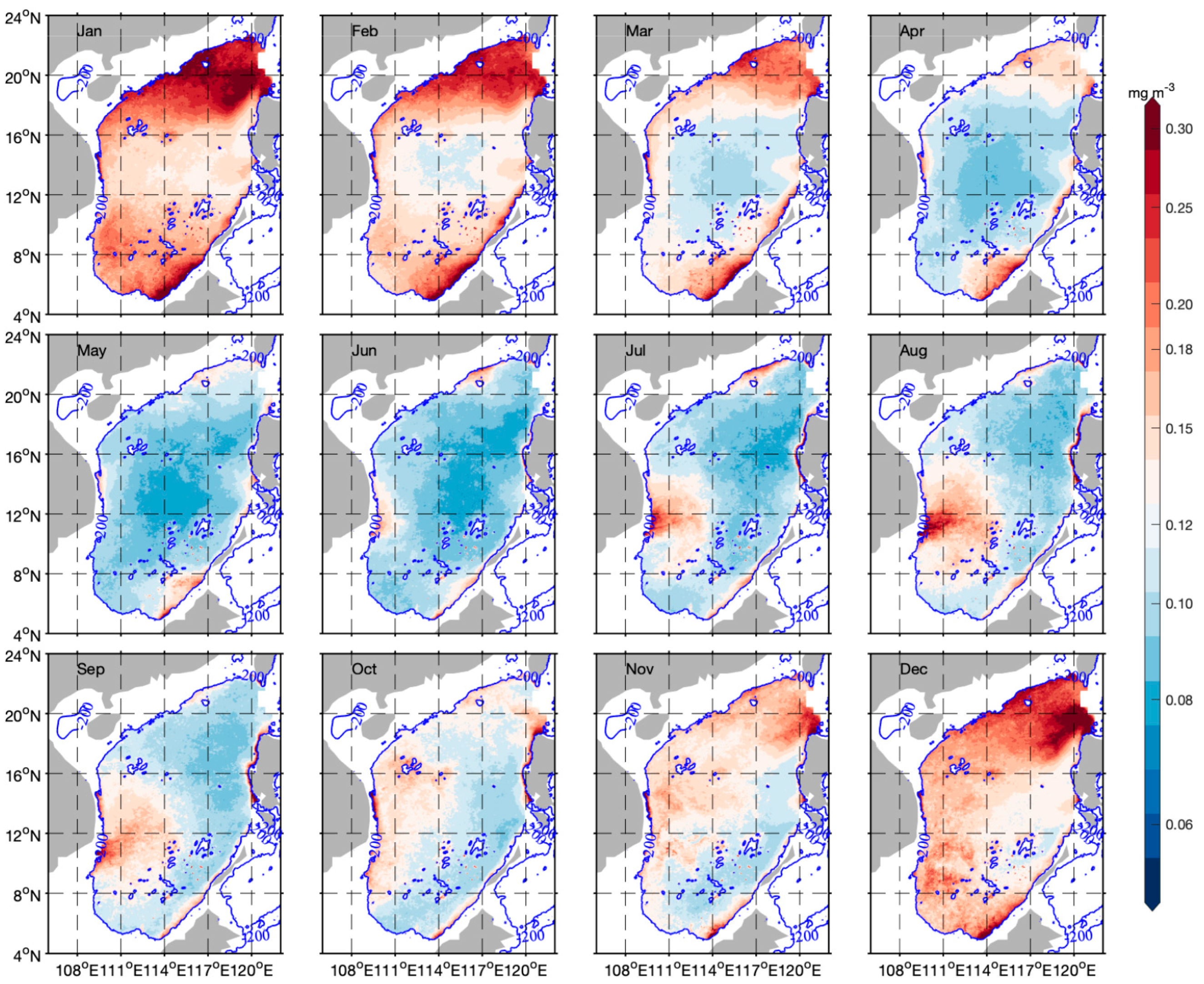
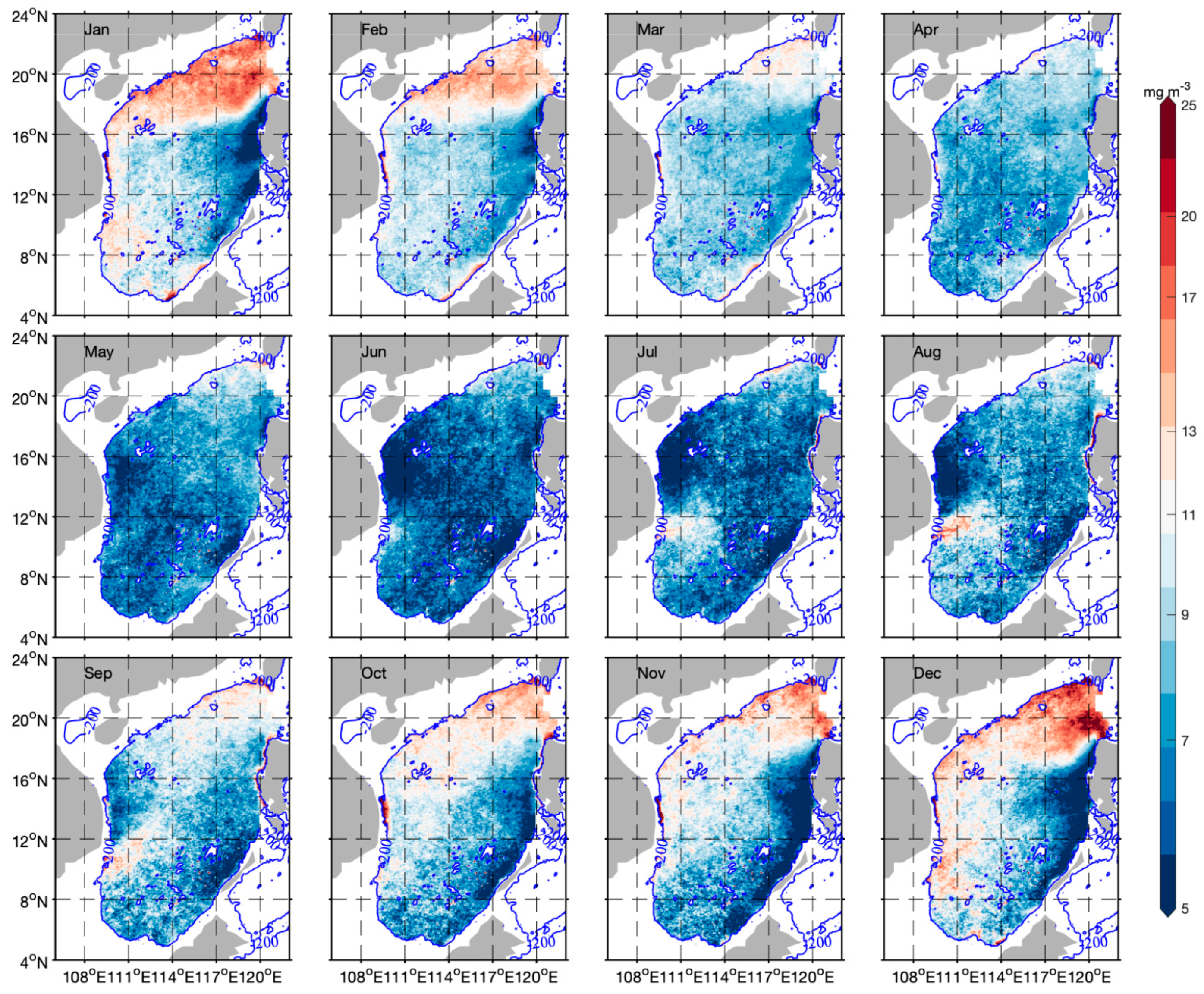
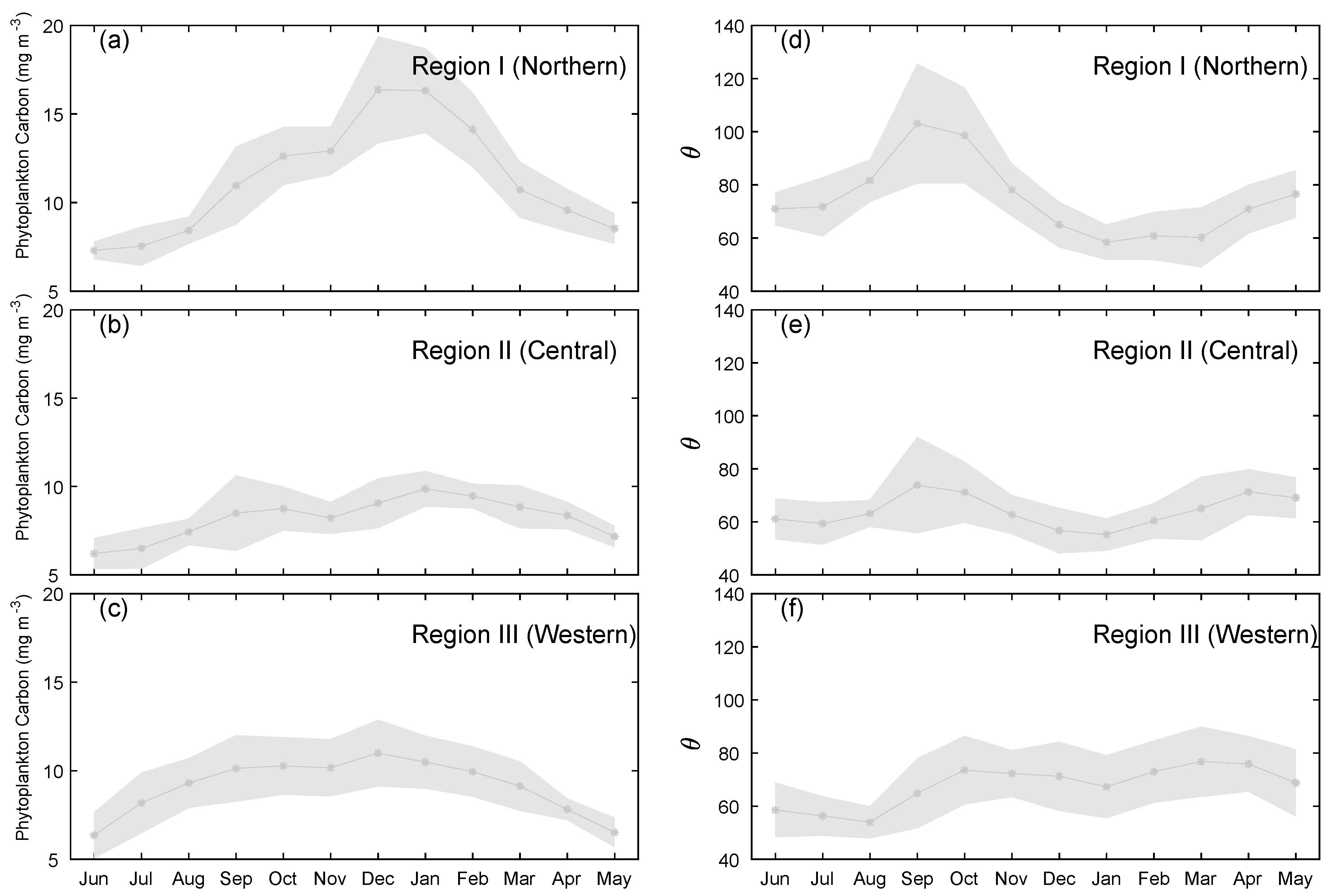
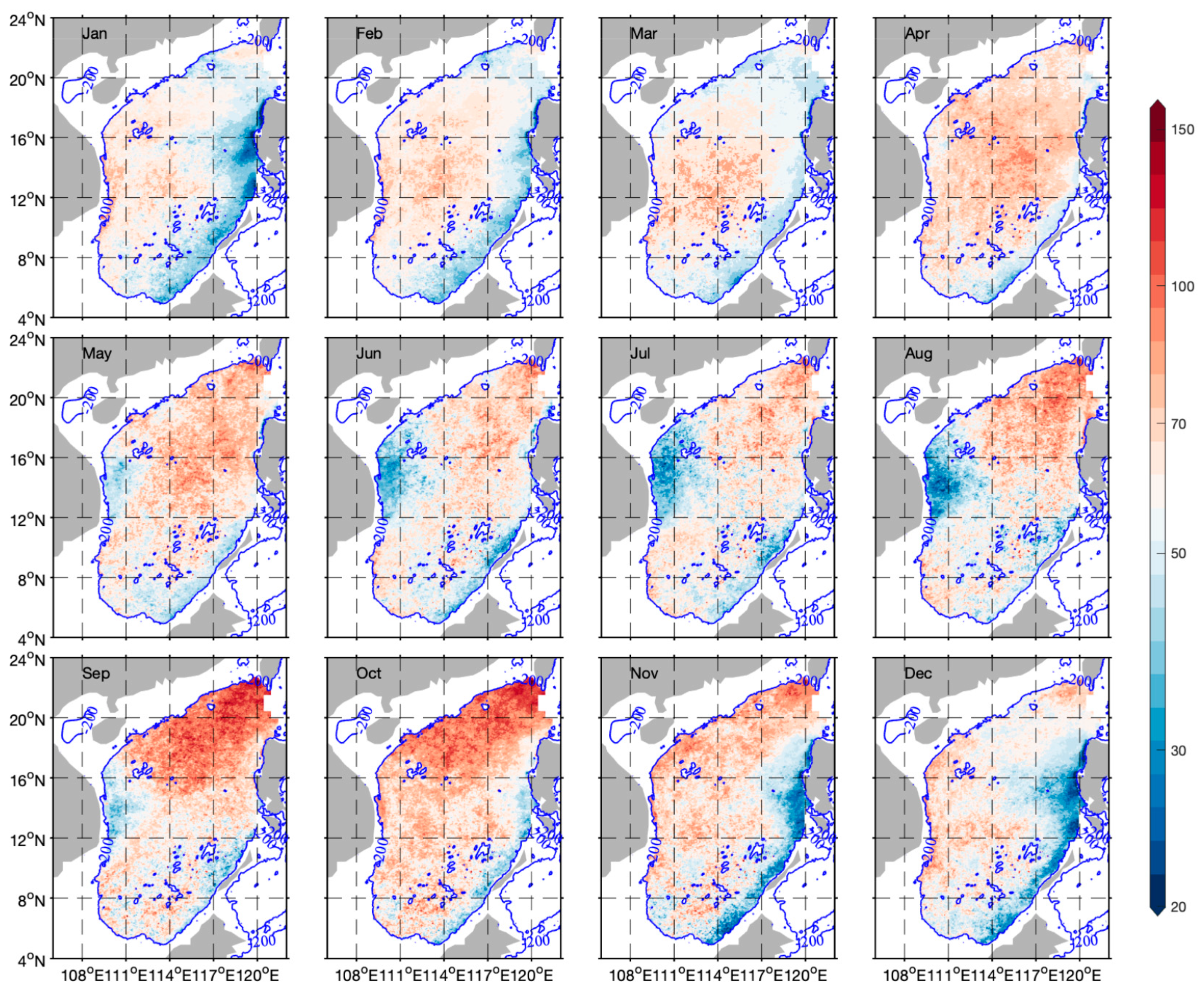
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Phytoplankton Carbon and θ
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Phytoplankton Carbon and θ
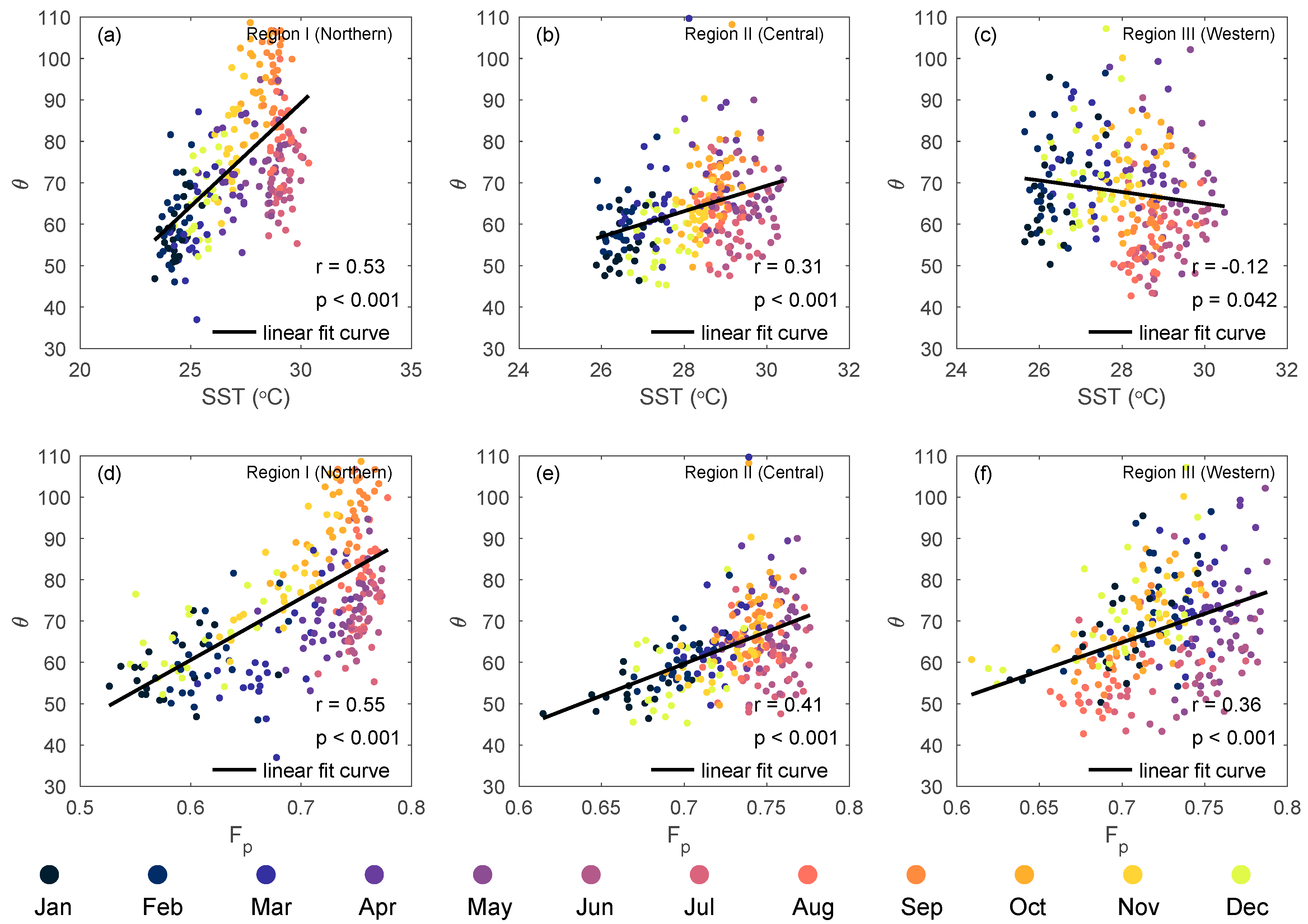
4.2. Factors Affecting θ
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Falkowski, P. OCEAN SCIENCE The power of plankton. Nature 2012, 483, S17–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, C.B.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; Falkowski, P. Primary production of the biosphere: Integrating terrestrial and oceanic components. Science 1998, 281, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Raven, J.A. Aquatic Photosynthes; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.G.; Follows, M.J. Ocean Dynamics and the Carbon Cycle Principles and Mechanisms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Mitchell, B.G.; Siegel, D.A.; Carder, K.L.; Garver, S.A.; Kahru, M.; McClain, C. Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 24937–24953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenzen, J.C. A method for the continuous measurement of in vivo chlorophyll concentration. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1966, 13, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantoura, R.F.C.; Llewellyn, C.A. The rapid determination of algal chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments and their breakdown products in natural waters by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 1983, 151, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yentsch, C.S.; Menzel, D.W. A method for the determination of phytoplankton chlorophyll and phaeophytin by fluorescence. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1963, 10, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Humphrey, G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Und Physiol. Der Pflanz. 1975, 167, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; LaRoche, J. Acclimation to sectral irradiance in algae. J. Phycol. 1991, 27, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geider, R.J. Light and temoerature dependence of the carbon to chlorophyll a ratio in microalgae and cyanobacteria: Implications for phytoplankton. New Phytol. 1987, 106, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geider, R.J.; MacIntyre, H.L.; Kana, T.M. Dynamic model of phytoplankton growth and acclimation: Responses of the balanced growth rate and the chlorophyll a:carbon ratio to light, nutrient-limitation and temperature. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 148, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laws, E.A.; Bannister, T.T. Nutrient- and light-limited growth of Thalassiosira fluviatilis in continuous culture with implications for phytoplankton growth in the ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 457–473. [Google Scholar]
- Westberry, T.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Siegel, D.A.; Boss, E. Carbon-based primary productivity modeling with vertically resolved photoacclimation. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boss, E. The beam attenuation to chlorophyll ratio: An optical index of phytoplankton physiology in the surface ocean? Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2003, 50, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boss, E.; Siegel, D.A.; Shea, D.M. Carbon-based ocean productivity and phytoplankton physiology from space. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, M.; Morel, A.; Fournier-Sicre, V.; Fell, F.; Stramski, D. Light scattering properties of marine particles in coastal and open ocean waters as related to the particle mass concentration. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Christaki, U.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Montresor, M.; Ribera d’Alcalá, M.; Vaqué, D.; Zingone, A. Plankton in the open Mediterranean Sea: A review. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1543–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morel, A. Optical modeling of the upper ocean in relation to its biogenous matter content (case I waters). J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellacicco, M.; Volpe, G.; Colella, S.; Pitarch, J.; Santoleri, R. Influence of photoacclimation on the phytoplankton seasonal cycle in the Mediterranean Sea as seen by satellite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellacicco, M.; Volpe, G.; Briggs, N.; Brando, V.; Pitarch, J.; Landolfi, A.; Colella, S.; Marullo, S.; Santoleri, R. Global Distribution of Non-algal Particles from Ocean Color Data and Implications for Phytoplankton Biomass Detection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 7672–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellacicco, M.; Cornec, M.; Organelli, E.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Neukermans, G.; Volpe, G.; Barbieux, M.; Poteau, A.; Schmechtig, C.; D’Ortenzio, F.; et al. Global Variability of Optical Backscattering by Non-algal particles From a Biogeochemical-Argo Data Set. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 9767–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellacicco, M.; Pitarch, J.; Organelli, E.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Volpe, G.; Marullo, S. Improving the Retrieval of Carbon-Based Phytoplankton Biomass from Satellite Ocean Colour Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T.; Kovac, Z.; Dingle, J.; Jackson, T.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Franks, P.; Maranon, E.; Kulk, G.; Bouman, H.A. Reconciling models of primary production and photoacclimation [Invited]. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, C100–C114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halsey, K.H.; Jones, B.M. Phytoplankton strategies for photosynthetic energy allocation. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 265–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, W.W. Assimilation of SeaWiFS ocean chlorophyll data into a three-dimensional global ocean model. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 69, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zadeh, N.; Phillips, P.J.; Wittenberg, A.T.; Levy, H.; Harrison, M.J.; Hallberg, R.W.; Griffies, S.M.; Dunne, K.A.; Cooke, W.; Adcroft, A.J.; et al. GFDL’s ESM2 Global Coupled Climate–Carbon Earth System Models. Part II: Carbon System Formulation and Baseline Simulation Characteristics. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2247–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. An Exact Solution for Modeling Photoacclimation of the Carbon-to-Chlorophyll Ratio in Phytoplankton. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Stuart, V.; Nair, A.; Oka, K.; Nakane, T.; Bouman, H.; Forget, M.H.; Maass, H.; Platt, T. Carbon-to-chlorophyll ratio and growth rate of phytoplankton in the sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 383, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Le Borgne, R.; Murtugudde, R.; Busalacchi, A.J.; Behrenfeld, M. Spatial and temporal variability of the phytoplankton carbon to chlorophyll ratio in the equatorial Pacific: A basin-scale modeling study. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakobsen, H.H.; Markager, S. Carbon-to-chlorophyll ratio for phytoplankton in temperate coastal waters: Seasonal patterns and relationship to nutrients. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 1853–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Wu, H.T.; Yang, S. Hydrologic processes associated with the first transition of the Asian summer monsoon: A pilot satellite study. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyrtki, K. Physical Oceanography of the Southeast Asian Waters; Library–Scripps Digital Collection: UC San Diego, CA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Kawamura, H.; Hong, H.; Qi, Y. A Review on the Currents in the South China Sea: Seasonal Circulation, South China Sea Warm Current and Kuroshio Intrusion. J. Oceanogr. 2000, 56, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Chai, F.; Pettigrew, N.; Xu, D.; Shi, M.; Xu, J. Kuroshio intrusion and the circulation in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, X.; Chai, F.; Xue, H.; Cai, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, J. Physical-biological oceanographic coupling influencing phytoplankton and primary production in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, G.T.F.; Ku, T.-L.; Mulholland, M.; Tseng, C.-M.; Wang, D.-P. The SouthEast Asian Time-series Study (SEATS) and the biogeochemistry of the South China Sea—An overview. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Qiu, G.; Boss, E.; Wang, H. Temporal and Vertical Variations of Particulate and Dissolved Optical Properties in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, D.; Kawamura, H.; Lee, M.-A.; Van Dien, T. Seasonal and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a concentrations and water conditions in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, Y.Q.; Wang, D.X.; Wang, W.Z. Study on the features of chlorophyll a derived from SeaWiFS in the South China Sea (in Chinese). Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2005, 27, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoqi, W.; Xiaogang, X.; Jinping, W.; Na, L. A Satellite-Based Analysis on the Seasonal Variations and Inter-Relationships between Chlorophyll and Particle in the South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 37, 26–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Huang, B.Q.; Lin, L.Z.; Laws, E.A.; Wang, L.; Shang, S.L.; Zhang, T.L.; Dai, M.H. Photosynthetic parameters in the northern South China Sea in relation to phytoplankton community structure. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 4187–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xing, X.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chai, F. The variability of chlorophyll-a and its relationship with dynamic factors in the basin of the South China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 200, 103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J.; Le, F.; Cai, Y.; Ning, X. Summer phytoplankton assemblages and carbon biomass in the northern south China sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Leptoukh, G.G.; Acker, J.G.; Yu, Z.; Kempler, S.J. Seasonal Variations of Chlorophyll a Concentration in the Northern South China Sea. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.K.; Chao, S.Y.; Shaw, P.T.; Gong, G.C.; Chen, C.C.; Tang, T.Y. Monsoon-forced chlorophyll distribution and primary production in the South China Sea: Observations and a numerical study. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 1387–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, P.; Chai, F. Spatial and temporal variability in phytoplankton carbon, chlorophyll, and nitrogen in the North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Brockmann, C.; Brotas, V.; Calton, B.; Chuprin, A.; Cipollini, P.; Couto, A.B.; Dingle, J.; Doerffer, R.; et al. An Ocean-Colour Time Series for Use in Climate Studies: The Experience of the Ocean-Colour Climate Change Initiative (OC-CCI). Sensors 2019, 19, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, R. SCSPOD14, a South China Sea physical oceanographic dataset derived from in situ measurements during 1919–2014. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A.; Peterson, A.R. Optimization of a semianalytical ocean color model for global-scale applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Sathyendranath, S.; Hirata, T.; Lavender, S.J.; Barciela, R.M.; Hardman-Mountford, N.J. A three-component model of phytoplankton size class for the Atlantic Ocean. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cao, W.; Wang, G.; Hu, S. Satellite-observed variability of phytoplankton size classes associated with a cold eddy in the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Fang, W.; Fang, G. Seasonal-to-interannual variability of chlorophyll in central western South China Sea extracted from SeaWiFS. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhurst, A.R. Ecological Geography of the Sea. In Ecological Geography of the Sea, 2nd ed.; Longhurst, A.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ortenzio, F.; d’Alcala, M.R. On the trophic regimes of the Mediterranean Sea: A satellite analysis. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milligan, G.W.; Cooper, M.C. An examination of procedures for determining the number of clusters in a data set. Psychometrika 1985, 50, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, B.D.; Wigley, T.M.L.; Boyle, J.S.; Gaffen, D.J.; Hnilo, J.J.; Nychka, D.; Parker, D.E.; Taylor, K.E. Statistical significance of trends and trend differences in layer-average atmospheric temperature time series. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 7337–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadinov, T.S.; Siegel, D.A.; Maritorena, S. Retrieval of the particle size distribution from satellite ocean color observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramski, D.; Reynolds, R.A.; Kahru, M.; Mitchell, B.G. Estimation of Particulate Organic Carbon in the Ocean from Satellite Remote Sensing. Science 1999, 285, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisson, K.M.; Boss, E.; Westberry, T.K.; Behrenfeld, M.J. Evaluating satellite estimates of particulate backscatter in the global open ocean using autonomous profiling floats. Opt. Express 2019, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhou, W.; Cao, W.; Wang, G.; Zheng, W.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zeng, K.; et al. Evaluating semi-analytical algorithms for estimating inherent optical properties in the South China Sea. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13155–13176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranon, E.; Cermeno, P.; Huete-Ortega, M.; Lopez-Sandoval, D.C.; Mourino-Carballido, B.; Rodriguez-Ramos, T. Resource supply overrides temperature as a controlling factor of marine phytoplankton growth. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loisel, H.; Duforêt-Gaurier, L.; Dessailly, D.; Sathyendranath, S.; Evers-King, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Thomalla, S.; Mangin, A.; D’andon, O.H.F. A satellite view of the particulate organic carbon and its algal and non-algal carbon pools. In Ocean Optics XXIV; Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2018; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Buck, K.R.; Chavez, F.P.; Campbell, L. Basin-wide distributions of living carbon components and the inverted trophic pyramid of the central gyre of the North Atlantic Ocean, summer 1993. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1996, 10, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Shiah, F.-K.; Gong, G.-C.; Chiang, K.P. Cross-shelf variation in carbon-to-chlorophyll a ratios in the East China Sea, summer 1998. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. Size-partitioned phytoplankton carbon and carbon-to-chlorophyll ratio from ocean colour by an absorption-based bio-optical algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palacz, A.P.; Xue, H.; Armbrecht, C.; Zhang, C.; Chai, F. Seasonal and inter-annual changes in the surface chlorophyll of the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, X.; Gong, F.; Pan, D. Satellite-Based Estimation of Particulate Organic Carbon Export in the Northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 8227–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Cao, W.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Lin, J.; Zhou, W.; Yao, L. Empirical ocean color algorithm for estimating particulate organic carbon in the South China Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, W.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Li, T.; Gong, F.; Zhang, L. Satellite views of the seasonal and interannual variations of the particulate organic carbon in the northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 39, 122–134. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, P.-T.; Chao, S.-Y.; Liu, K.-K.; Pai, S.-C.; Liu, C.-T. Winter upwelling off Luzon in the northeastern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 16435–16448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, G.; Jing, Z.; Zhou, L.; Ke, Z.; Tan, Y. Distribution of picoplankton in the northeastern South China Sea with special reference to the effects of the Kuroshio intrusion and the associated mesoscale eddies. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 589, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xiu, P.; Chai, F.; Xue, H.; Wang, D.; Sun, J. Enhanced chlorophyll concentrations induced by Kuroshio intrusion fronts in the northern South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.-P. Summer upwelling in the South China Sea and its role in regional climate variations. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, D.; Wang, J.; Tan, L. Response of phytoplankton community structure and size-fractionated Chlorophyll a in an upwelling simulation experiment in the western South China Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2016, 15, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.Z.; Tang, D.L.; Luo, X. Phytoplankton size structure in the western South China Sea under the influence of a jet-eddy system. J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 187, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finenko, Z.Z.; Hoepffner, N.; Williams, R.; Piontkovski, S.A. Phytoplankton carbon to chlorophyll a ratio: Response to light, temperature and nutrient limitation. Mar. Ecol. J. 2003, 2, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Behrenfeld, M.; Le Borgne, R.; Murtugudde, R.; Boss, E. Regulation of phytoplankton carbon to chlorophyll ratio by light, nutrients and temperature in the Equatorial Pacific Ocean: A basin-scale model. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boss, E.; Lyon, P.E.; Fennel, K.; Hoge, F.E.; Koblinsky, C.J. An Optical Index of Phytoplankton Photoacclimation and Its Relation to Light-Saturated Photosynthesis in the Sea; NASA Technical Report; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.-Z.; Wang, H.; Chai, F.; Qiu, G. Physical drivers of chlorophyll variability in the open South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggert, J.D.; Murtugudde, R.G.; McClain, C.R. Processes controlling interannual variations in wintertime (Northeast Monsoon) primary productivity in the central Arabian Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 2319–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Wang, G.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, W.; Cao, W. Spatiotemporal Variability of Surface Phytoplankton Carbon and Carbon-to-Chlorophyll a Ratio in the South China Sea Based on Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010030
Xu W, Wang G, Jiang L, Cheng X, Zhou W, Cao W. Spatiotemporal Variability of Surface Phytoplankton Carbon and Carbon-to-Chlorophyll a Ratio in the South China Sea Based on Satellite Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wenlong, Guifen Wang, Long Jiang, Xuhua Cheng, Wen Zhou, and Wenxi Cao. 2021. "Spatiotemporal Variability of Surface Phytoplankton Carbon and Carbon-to-Chlorophyll a Ratio in the South China Sea Based on Satellite Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010030
APA StyleXu, W., Wang, G., Jiang, L., Cheng, X., Zhou, W., & Cao, W. (2021). Spatiotemporal Variability of Surface Phytoplankton Carbon and Carbon-to-Chlorophyll a Ratio in the South China Sea Based on Satellite Data. Remote Sensing, 13(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010030





