Development and Performance Evaluation of a Very Low-Cost UAV-Lidar System for Forestry Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
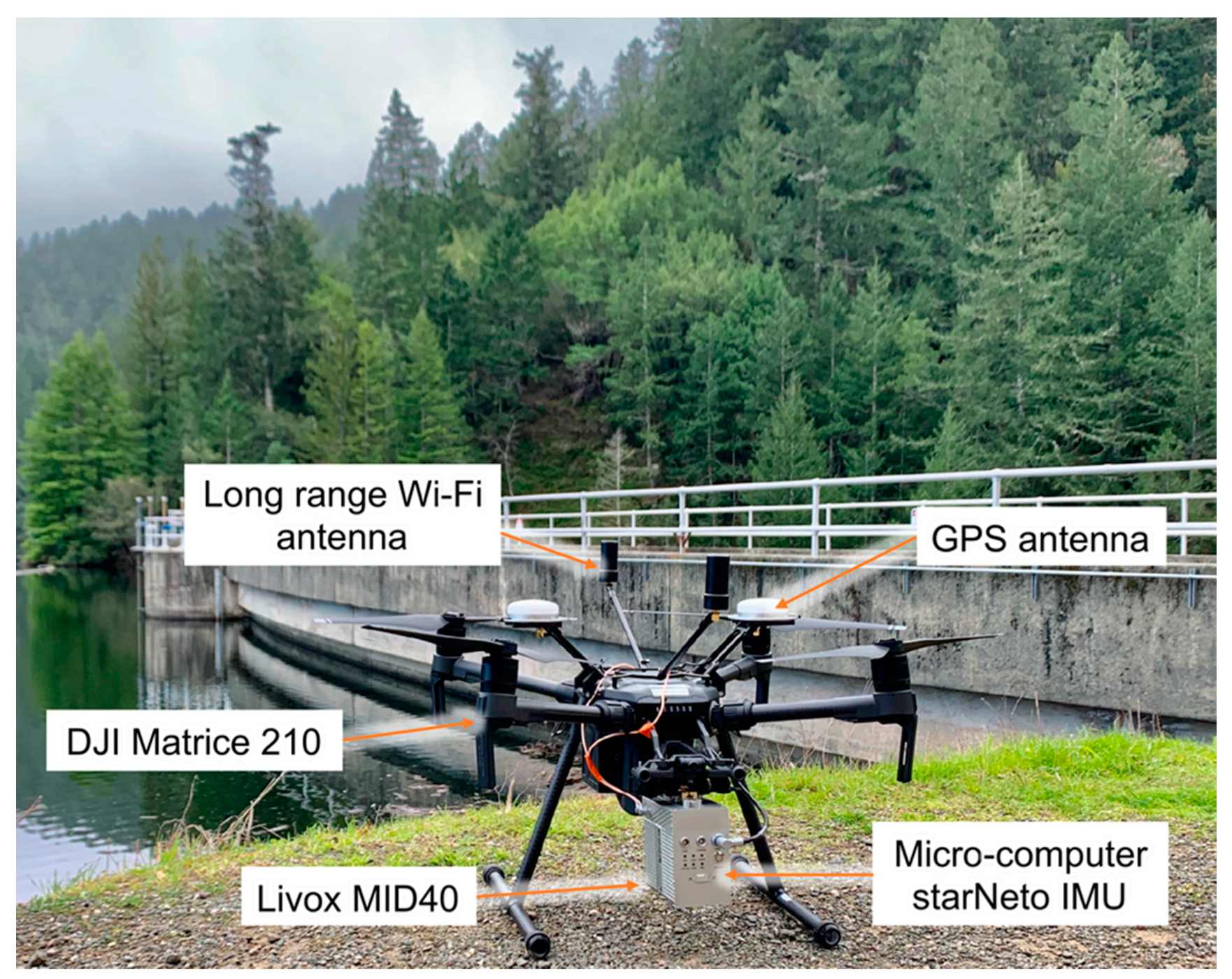
2. Development of the DJI Livox System
3. Performance Evaluation of the DJI Livox System
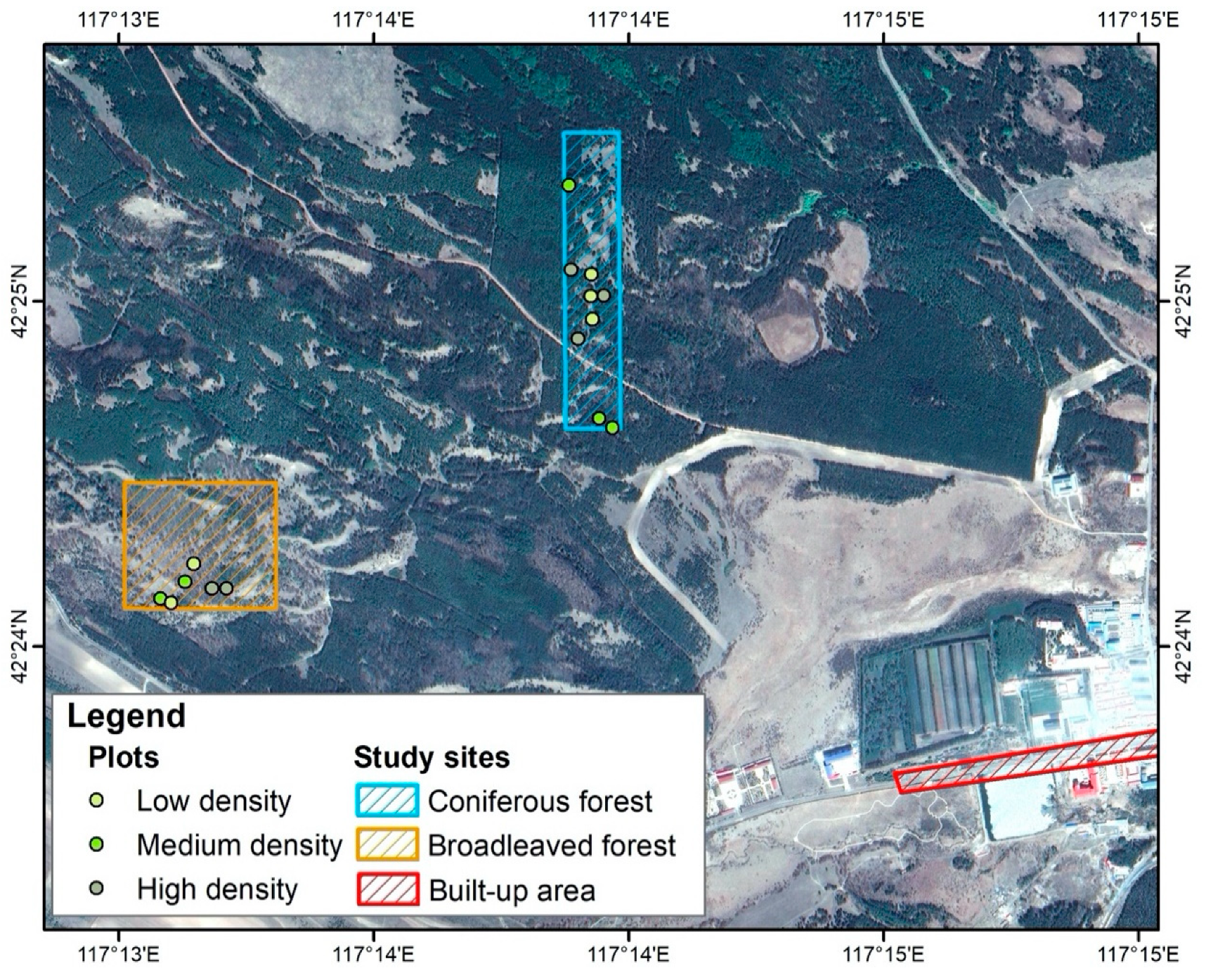
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Collection
3.2.1. Field Data
3.2.2. UAV Lidar Data Acquisition
3.3. Lidar Data Preprocessing
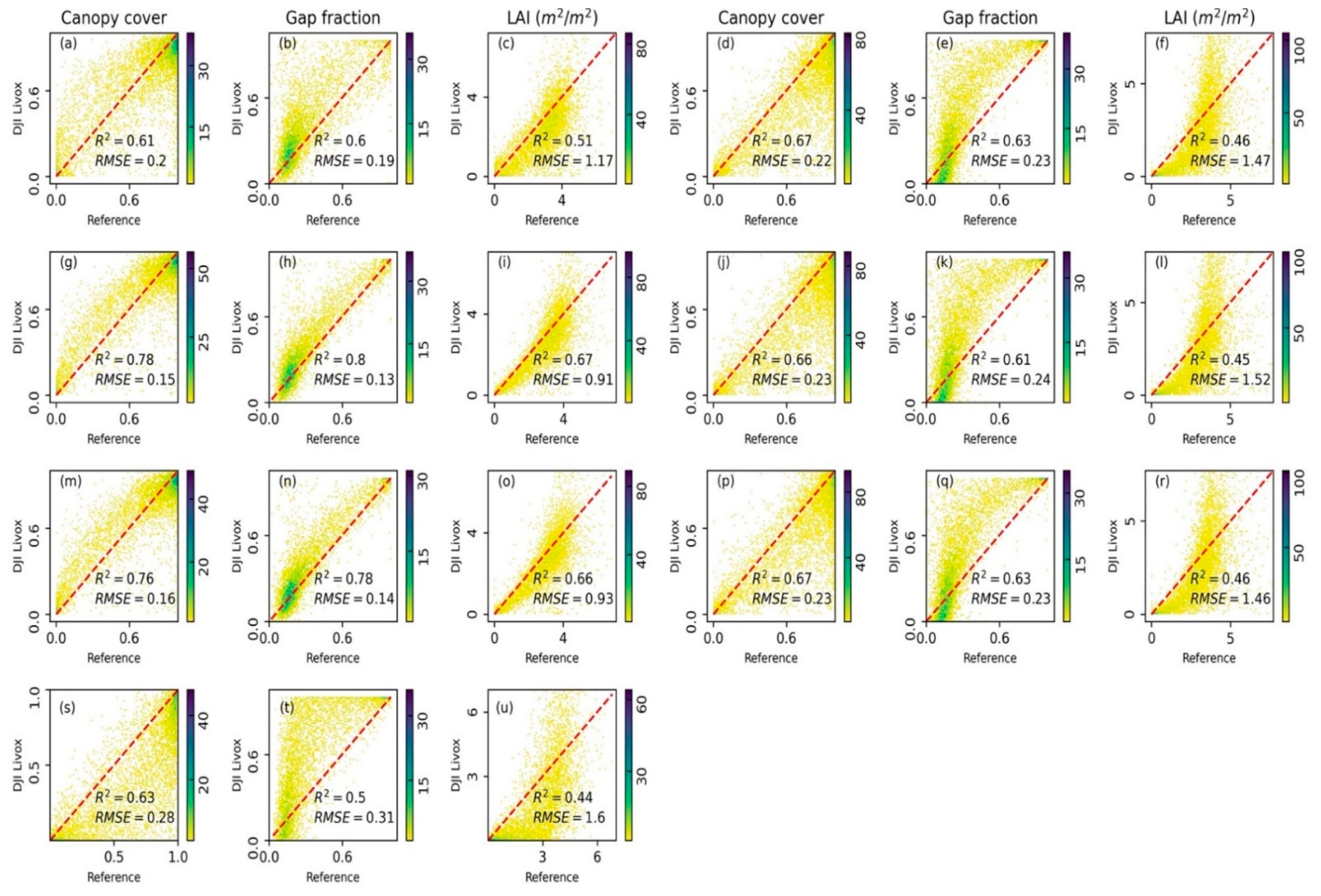
3.4. Forest Inventory Attributes Extraction
3.5. Evaluation of the DJI Livox System
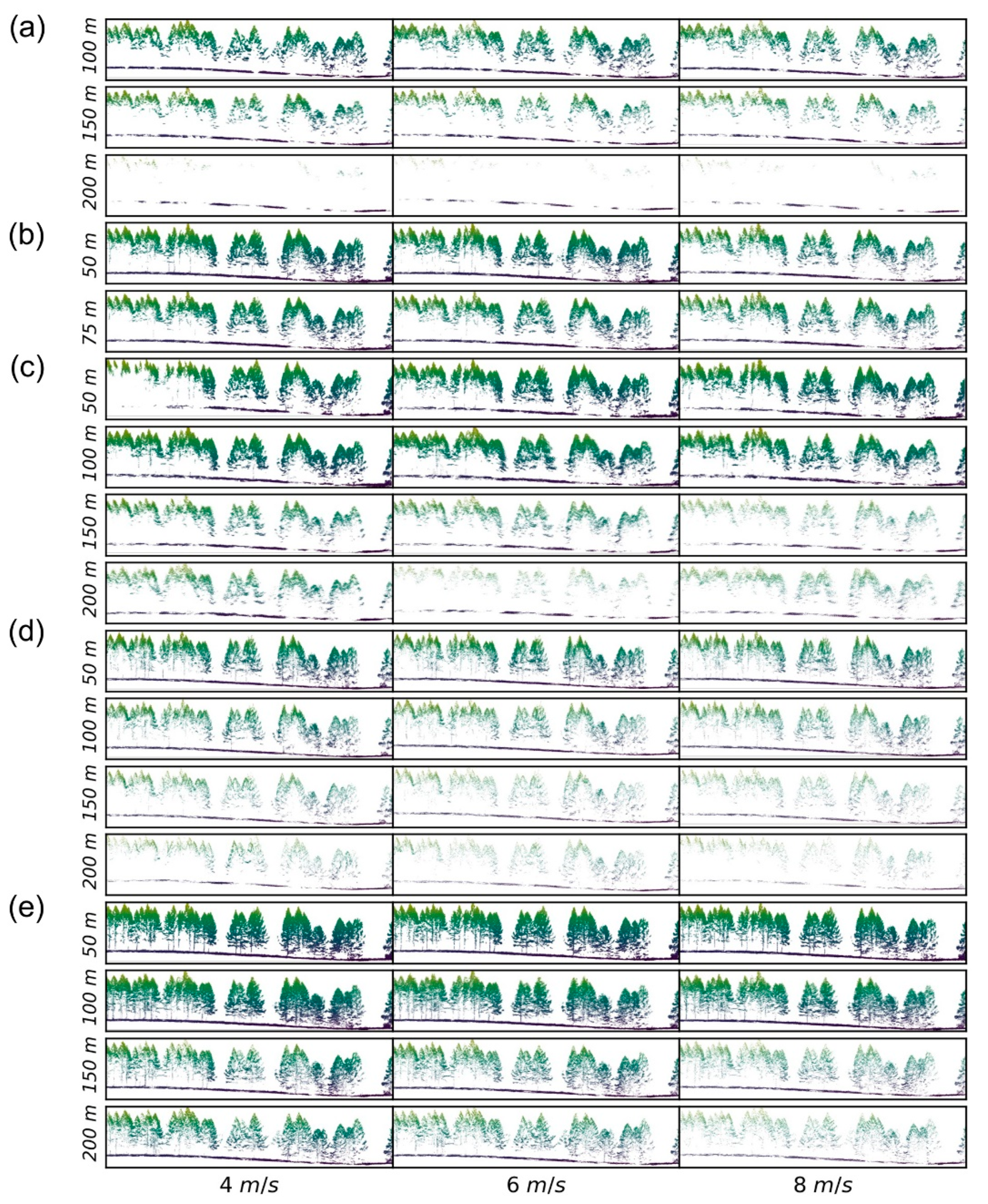
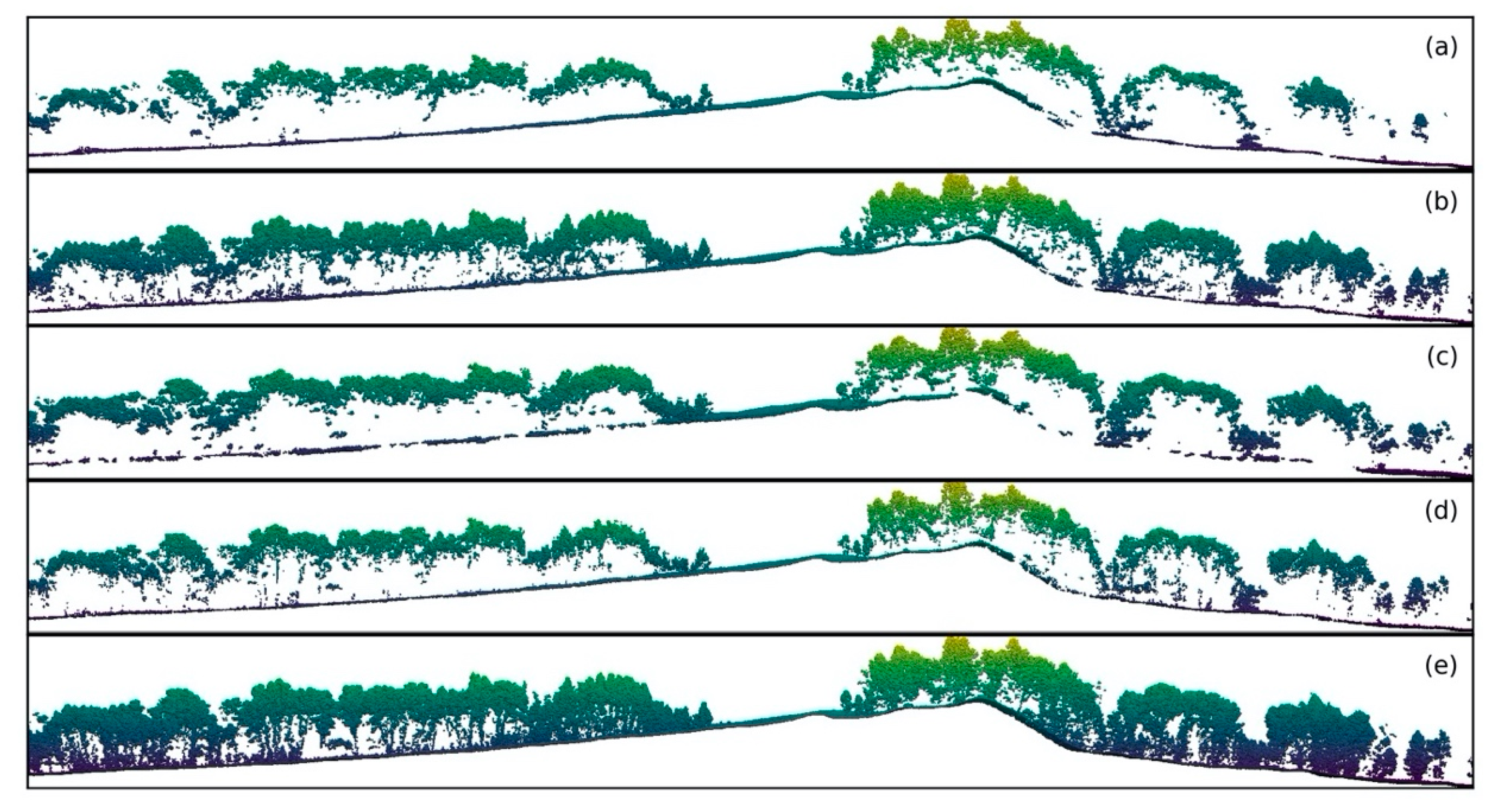
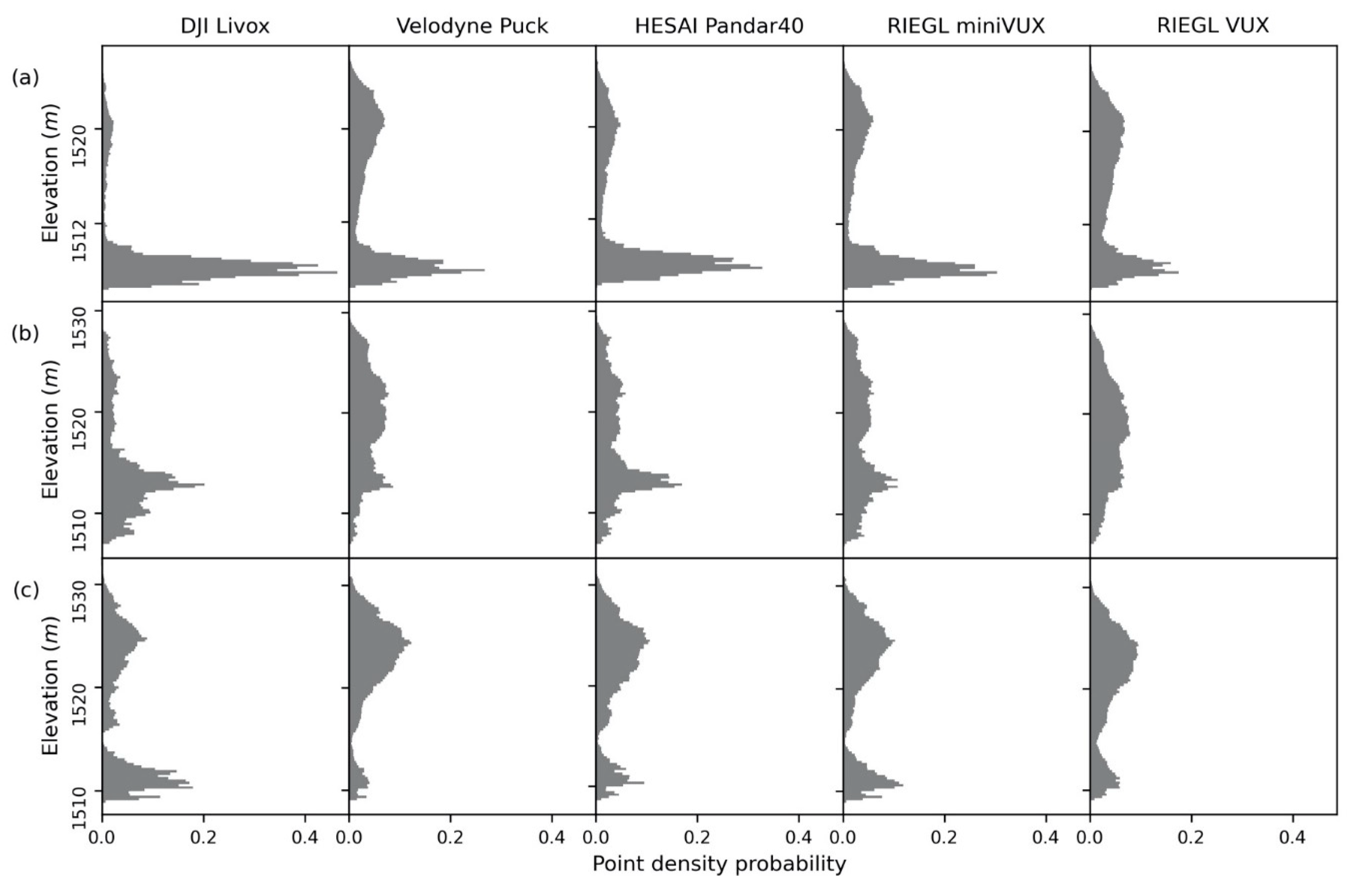
3.5.1. Lidar Data Quality Assessment
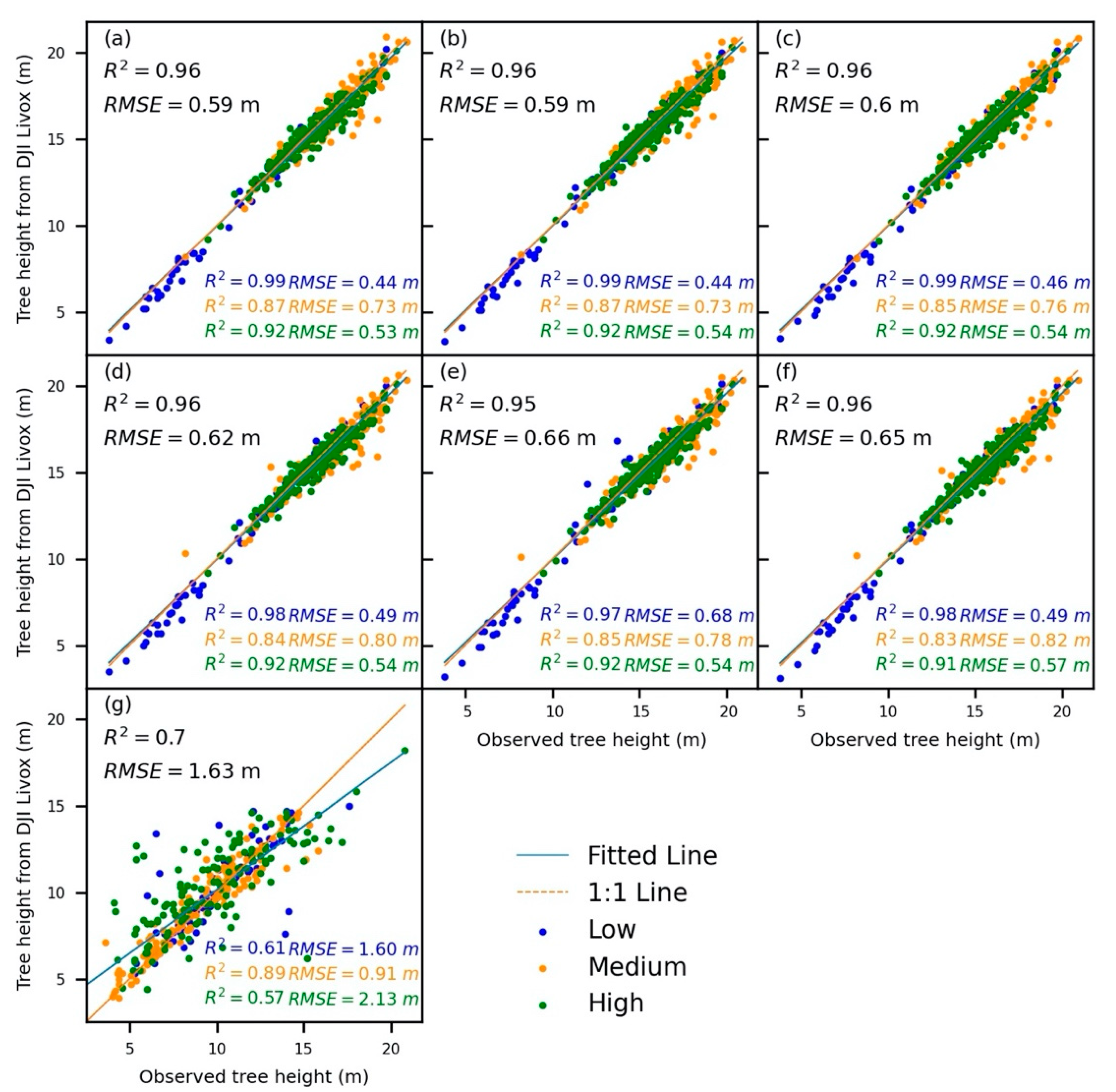
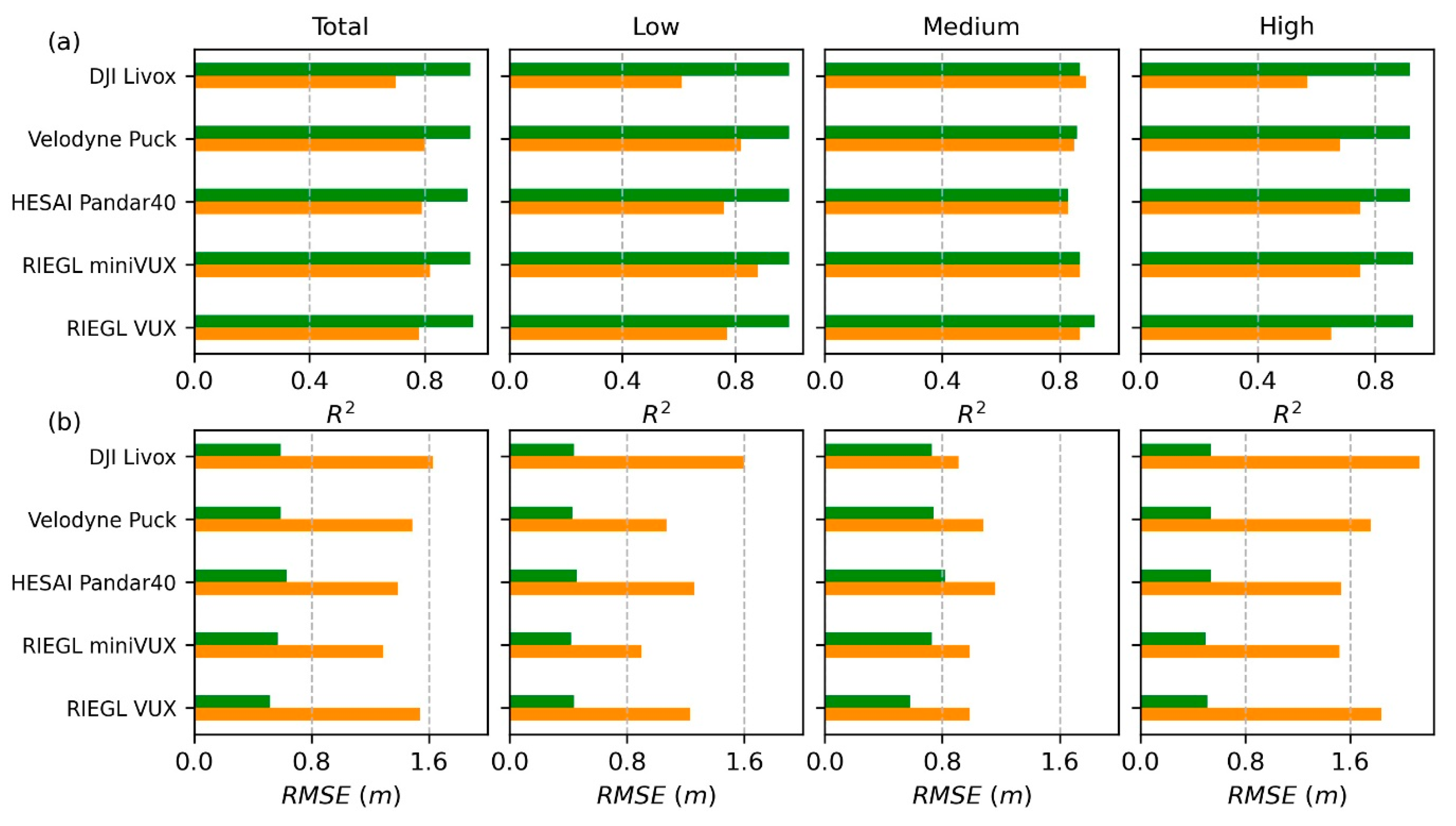
3.5.2. Accuracy Assessment of Individual Tree Attributes
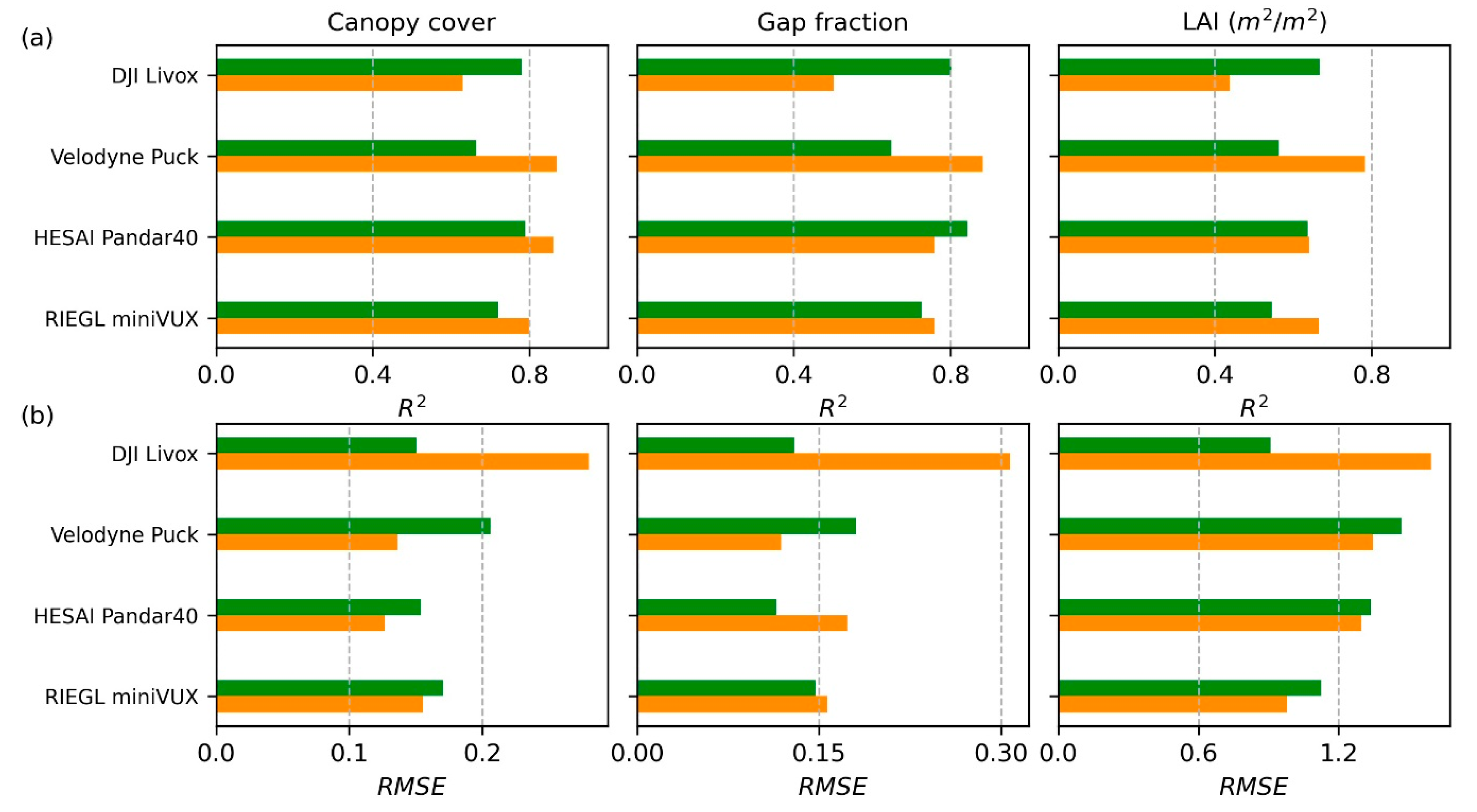
3.5.3. Comparisons with Four Other UAV Lidar Systems
4. Results
4.1. Data Quality Assessment
4.2. Accuracy Assessment of Individual Tree Height Estimates
4.3. Validation of Plot-Level Forest Inventory Attribute Estimates
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, J.; Chen, A.; Peng, C.; Zhao, S.; Ci, L. Changes in forest biomass carbon storage in China between 1949 and 1998. Science 2001, 292, 2320–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatchi, S.S.; Harris, N.L.; Brown, S.; Lefsky, M.; Mitchard, E.T.A.; Salas, W.; Zutta, B.R.; Buermann, W.; Lewis, S.L.; Hagen, S.; et al. Benchmark map of forest carbon stocks in tropical regions across three continents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9899–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.D.; Birdsey, R.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Jackson, R.B. The Structure, Distribution, and Biomass of the World’s Forests. In Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, Vol 44; Futuyma, D.J., Ed.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 44, pp. 593–622. [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante, M.M.C.; Roitman, I.; Aide, T.M.; Alencar, A.; Anderson, L.O.; Aragao, L.; Asner, G.P.; Barlow, J.; Berenguer, E.; Chambers, J.; et al. Toward an integrated monitoring framework to assess the effects of tropical forest degradation and recovery on carbon stocks and biodiversity. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Næsset, E.; Gobakken, T.; Holmgren, J.; Hyyppä, H.; Hyyppä, J.; Maltamo, M.; Nilsson, M.; Olsson, H.; Persson, Å.; Söderman, U. Laser scanning of forest resources: The Nordic experience. Scand. J. For. Res. 2004, 19, 482–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Nelson, R.F.; Naesset, E.; Orka, H.O.; Coops, N.C.; Hilker, T.; Bater, C.W.; Gobakken, T. Lidar sampling for large-area forest characterization: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.L.; Hyyppa, J.; Kaartinen, H.; Lehtomaki, M.; Pyorala, J.; Pfeifer, N.; Holopainen, M.; Brolly, G.; Pirotti, F.; Hackenberg, J.; et al. International benchmarking of terrestrial laser scanning approaches for forest inventories. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 137–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Shen, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, G.B.; Cao, F.L. Estimating forest structural attributes using UAV-LiDAR data in Ginkgo plantations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhai, Q.; Su, Y.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, M.; Guo, Q. Simple method for direct crown base height estimation of individual conifer trees using airborne LiDAR data. Opt. Express 2018, 26, A562–A578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, Q.; Tao, S.; Kelly, M.; Xu, G. Lidar with multi-temporal MODIS provide a means to upscale predictions of forest biomass. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowksi, M.K.; Guo, Q.; Collins, B.; Stephens, S.; Kelly, M. Predicting surface fuel models and fuel metrics using Lidar and CIR imagery in a dense, mountainous forest. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Q.; Su, Y.; Hu, T.; Guan, H.; Jin, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, K.; Wei, D.; Kelly, M.; et al. Lidar boosts three-dimensional ecological observations and modelling: A review and perspective. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Guo, Q.; Jin, S.; Guan, H.; Sun, X.; Ma, Q.; Hu, T.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. The Development and Evaluation of a Backpack LiDAR System for Accurate and Efficient Forest Inventory. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hyyppä, J.; Liang, X.; Kaartinen, H.; Yu, X.; Lindberg, E.; Holmgren, J.; Qin, Y.; Mallet, C.; Ferraz, A.; et al. International Benchmarking of the Individual Tree Detection Methods for Modeling 3-D Canopy Structure for Silviculture and Forest Ecology Using Airborne Laser Scanning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5011–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magnussen, S.; Nord-Larsen, T.; Riis-Nielsen, T. Lidar supported estimators of wood volume and aboveground biomass from the Danish national forest inventory (2012–2016). Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Su, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhao, X.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Xu, G.; Lin, G.; et al. An integrated UAV-borne lidar system for 3D habitat mapping in three forest ecosystems across China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2954–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Lucieer, A.; Watson, C.; Turner, D. Development of a UAV-LiDAR System with Application to Forest Inventory. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1519–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaakkola, A.; Hyyppä, J.; Kukko, A.; Yu, X.; Kaartinen, H.; Lehtomäki, M.; Lin, Y. A low-cost multi-sensoral mobile mapping system and its feasibility for tree measurements. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggisser, M.; Hollaus, M.; Otepka, J.; Pfeifer, N. Influence of ULS acquisition characteristics on tree stem parameter estimation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 168, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Habib, A. NRLI-UAV: Non-rigid registration of sequential raw laser scans and images for low-cost UAV LiDAR point cloud quality improvement. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 158, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglhaut, J.; Cabo, C.; Puliti, S.; Piermattei, L.; O’Connor, J.; Rosette, J. Structure from Motion Photogrammetry in Forestry: A Review. Curr. For. Rep. 2019, 5, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, W. Efficient structure from motion for large-scale UAV images: A review and a comparison of SfM tools. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbody, T.R.H.; Coops, N.C.; White, J.C. Digital Aerial Photogrammetry for Updating Area-Based Forest Inventories: A Review of Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Directions. Curr. For. Rep. 2019, 5, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, X.; Ruan, H. Comparison of UAV LiDAR and Digital Aerial Photogrammetry Point Clouds for Estimating Forest Structural Attributes in Subtropical Planted Forests. Forests 2019, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moe, K.T.; Owari, T.; Furuya, N.; Hiroshima, T. Comparing Individual Tree Height Information Derived from Field Surveys, LiDAR and UAV-DAP for High-Value Timber Species in Northern Japan. Forests 2020, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kachamba, D.J.; Ørka, H.O.; Gobakken, T.; Eid, T.; Mwase, W. Biomass Estimation Using 3D Data from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery in a Tropical Woodland. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippelli, S.K.; Lefsky, M.A.; Rocca, M.E. Comparison and integration of lidar and photogrammetric point clouds for mapping pre-fire forest structure. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielcarek, M.; Kamińska, A.; Stereńczak, K. Digital Aerial Photogrammetry (DAP) and Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) as Sources of Information about Tree Height: Comparisons of the Accuracy of Remote Sensing Methods for Tree Height Estimation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliti, S.; Ørka, H.O.; Gobakken, T.; Næsset, E. Inventory of Small Forest Areas Using an Unmanned Aerial System. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9632–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayathunga, S.; Owari, T.; Tsuyuki, S. Evaluating the Performance of Photogrammetric Products Using Fixed-Wing UAV Imagery over a Mixed Conifer–Broadleaf Forest: Comparison with Airborne Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Wang, M.; Ma, M.; Lin, Y. Aboveground Tree Biomass Estimation of Sparse Subalpine Coniferous Forest with UAV Oblique Photography. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, D.; Lucieer, A.; Watson, C.; McCoull, C. Lever-arm and boresight correction, and field of view determination of a spectroradiometer mounted on an unmanned aircraft system. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 155, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tan, J.; Liu, H. Rigorous Boresight Self-Calibration of Mobile and UAV LiDAR Scanning Systems by Strip Adjustment. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filin, S. Recovery of systematic biases in laser altimetry data using natural surfaces. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaloud, J.; Lichti, D. Rigorous approach to bore-sight self-calibration in airborne laser scanning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2006, 61, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennie, C.; Lichti, D.D. Static calibration and analysis of the Velodyne HDL-64E S2 for high accuracy mobile scanning. Remote Sensing 2010, 2, 1610–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusu, R.B.; Cousins, S. 3D is here: Point Cloud Library (PCL). In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Li, W.; Yu, H.; Alvarez, O. Effects of Topographic Variability and Lidar Sampling Density on Several DEM Interpolation Methods. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Guo, Q.; Jakubowski, M.K.; Kelly, M. A New Method for Segmenting Individual Trees from the Lidar Point Cloud. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, W.; Flanagan, J. A bottom-up approach to segment individual deciduous trees using leaf-off lidar point cloud data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Su, Y.; Jin, S.; Kelly, M.; Hu, T.; Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G.; et al. The Influence of Vegetation Characteristics on Individual Tree Segmentation Methods with Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korhonen, L.; Korpela, I.; Heiskanen, J.; Maltamo, M. Airborne discrete-return LIDAR data in the estimation of vertical canopy cover, angular canopy closure and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.J.; Moskal, L.M.; Kim, S.-H. Modeling approaches to estimate effective leaf area index from aerial discrete-return LIDAR. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Su, Y.; Guo, Q. Comparison of Canopy Cover Estimations From Airborne LiDAR, Aerial Imagery, and Satellite Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4225–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlburger, G.; Pfennigbauer, M.; Schwarz, R.; Flöry, S.; Nussbaumer, L. Concept and Performance Evaluation of a Novel UAV-Borne Topo-Bathymetric LiDAR Sensor. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, H.; Su, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, G.; Li, W.; Ma, Q.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q. A marker-free method for registering multi-scan terrestrial laser scanning data in forest environments. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottfried, M.; Hollaus, M.; Glira, P.; Wieser, M.; Milenković, M. First examples from the RIEGL VUX-SYS for forestry applications. In Proceedings of the SilviLaser 2015, La Grande Motte, France, 28–30 September 2015; pp. 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Wang, Y.; Pyörälä, J.; Lehtomäki, M.; Yu, X.; Kaartinen, H.; Kukko, A.; Honkavaara, E.; Issaoui, A.E.I.; Nevalainen, O.; et al. Forest in situ observations using unmanned aerial vehicle as an alternative of terrestrial measurements. For. Ecosyst. 2019, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieser, M.; Mandlburger, G.; Hollaus, M.; Otepka, J.; Glira, P.; Pfeifer, N. A Case Study of UAS Borne Laser Scanning for Measurement of Tree Stem Diameter. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, L.; Lucieer, A.; Malenovský, Z.; Turner, D.; Vopěnka, P. Assessment of Forest Structure Using Two UAV Techniques: A Comparison of Airborne Laser Scanning and Structure from Motion (SfM) Point Clouds. Forests 2016, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chisholm, R.A.; Cui, J.; Lum, S.K.; Chen, B.M. UAV LiDAR for below-canopy forest surveys. J. Unmanned Veh. Syst. 2013, 1, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakubowski, M.K.; Guo, Q.; Kelly, M. Tradeoffs between lidar pulse density and forest measurement accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treitz, P.; Lim, K.; Woods, M.; Pitt, D.; Nesbitt, D.; Etheridge, D. LiDAR Sampling Density for Forest Resource Inventories in Ontario, Canada. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 830–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langford, J.; Niemann, O.; Frazer, G.; Wulder, M.; Nelson, T. Exploring Small Footprint Lidar Intensity Data in a Forested Environment. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 2416–2419. [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola, A.; Hyyppä, J.; Yu, X.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H.; Liang, X.; Hyyppä, H.; Wang, Y. Autonomous Collection of Forest Field Reference—The Outlook and a First Step with UAV Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalla Corte, A.P.; Rex, F.E.; Almeida, D.R.A.d.; Sanquetta, C.R.; Silva, C.A.; Moura, M.M.; Wilkinson, B.; Zambrano, A.M.A.; Cunha Neto, E.M.d.; Veras, H.F. Measuring individual tree diameter and height using GatorEye High-Density UAV-Lidar in an integrated crop-livestock-forest system. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, D.L. A comparison of spectral reflectance properties at the needle, branch, and canopy level for selected Conifer species. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Popescu, S.C. Lidar-based mapping of leaf area index and its use for validating GLOBCARBON satellite LAI product in a temperate forest of the southern USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1628–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Laser Scanner | Maximum Range (m) | FOV (°) | Range Precision (cm) | Maximum Measurement Rate (kHz) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIEGL miniVUX-1UAV | 250 | 360 | 1.0 | 100 | ~1.55 |
| RIEGL VUX-1UAV | 1050 | 330 | 0.5 | 500 | ~3.50 |
| HESAI Pandar40 | 200 | 360 | 2.0 | 720 | ~1.46 |
| Velodyne Puck LITE | 100 | 360 | 3.0 | 300 | ~0.59 |
| Velodyne HDL-32E | 100 | 360 | 2.0 | 695 | ~1.0 |
| Ibeo LUX | 150 | 110 | 4.0 | 976 | ~1.0 |
| Sick LMS511 PRO | 80 | 190 | 2.5~5.0 | 100 | ~3.7 |
| Sick LD LRS1000 | 250 | 360 | 3.8 | 10 | ~4.1 |
| Hokuyo UTM30LX | 30 | 270 | 3.0~5.0 | 25 | ~0.37 |
| Tree Density Category | Coniferous Forest Site | Broadleaved Forest Site | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (Stems/ha) | DBH (cm) | Height (m) | Density (Stems/ha) | DBH (cm) | Height (m) | |
| Low | 565 | 17.76 ± 6.79 | 15.59 ± 1.90 | 624 | 12.34 ± 5.45 | 9.30 ± 3.11 |
| Medium | 858 | 23.19 ± 6.43 | 13.27 ± 3.95 | 1128 | 12.59 ± 5.38 | 9.67 ± 2.58 |
| High | 1130 | 19.46 ± 3.85 | 16.87 ± 2.00 | 2096 | 10.84 ± 5.30 | 9.09 ± 2.79 |
| UAV Lidar System | Coniferous Forest | Broadleaved Forest | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flight Height (m) | Flight Speed (m/s) | Scan Rate (Hz) | Flight Height (m) | Flight Speed (m/s) | Scan Rate (Hz) | |
| DJI Livox | 100, 150, 200 | 4, 6, 8 | 100 | 150 | 6 | 100 |
| Velodyne Puck | 50, 75 | 4, 6, 8 | 300 | 75 | 6 | 300 |
| HESAI Pandar40 | 50, 100, 150, 200 | 4, 6, 8 | 720 | 150 | 6 | 720 |
| RIEGL miniVUX | 50, 100, 150, 200 | 4, 6, 8 | 100 | 150 | 6 | 100 |
| RIEGL VUX | 50, 100, 150, 200 | 4, 6, 8 | 400 | 150 | 6 | 400 |
| Mean Bias (cm) | Standard Deviation of Bias (cm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal precision | 3.72 | 2.53 |
| Vertical precision | 4.75 | 3.57 |
| Relative horizontal accuracy | 12.10 | 13.25 |
| Relative vertical accuracy | 21.80 | 9.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Sun, X.; Su, Y.; Guan, H.; Sun, Q.; Kelly, M.; Guo, Q. Development and Performance Evaluation of a Very Low-Cost UAV-Lidar System for Forestry Applications. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010077
Hu T, Sun X, Su Y, Guan H, Sun Q, Kelly M, Guo Q. Development and Performance Evaluation of a Very Low-Cost UAV-Lidar System for Forestry Applications. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(1):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010077
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Tianyu, Xiliang Sun, Yanjun Su, Hongcan Guan, Qianhui Sun, Maggi Kelly, and Qinghua Guo. 2021. "Development and Performance Evaluation of a Very Low-Cost UAV-Lidar System for Forestry Applications" Remote Sensing 13, no. 1: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010077
APA StyleHu, T., Sun, X., Su, Y., Guan, H., Sun, Q., Kelly, M., & Guo, Q. (2021). Development and Performance Evaluation of a Very Low-Cost UAV-Lidar System for Forestry Applications. Remote Sensing, 13(1), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010077








