Sea-Level Change along the Emilia-Romagna Coast from Tide Gauge and Satellite Altimetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
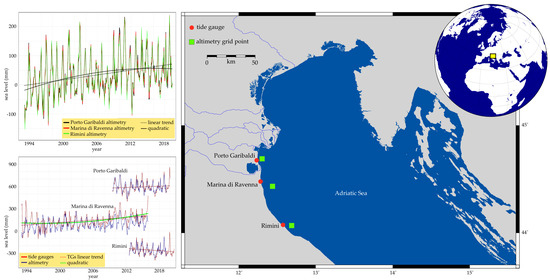
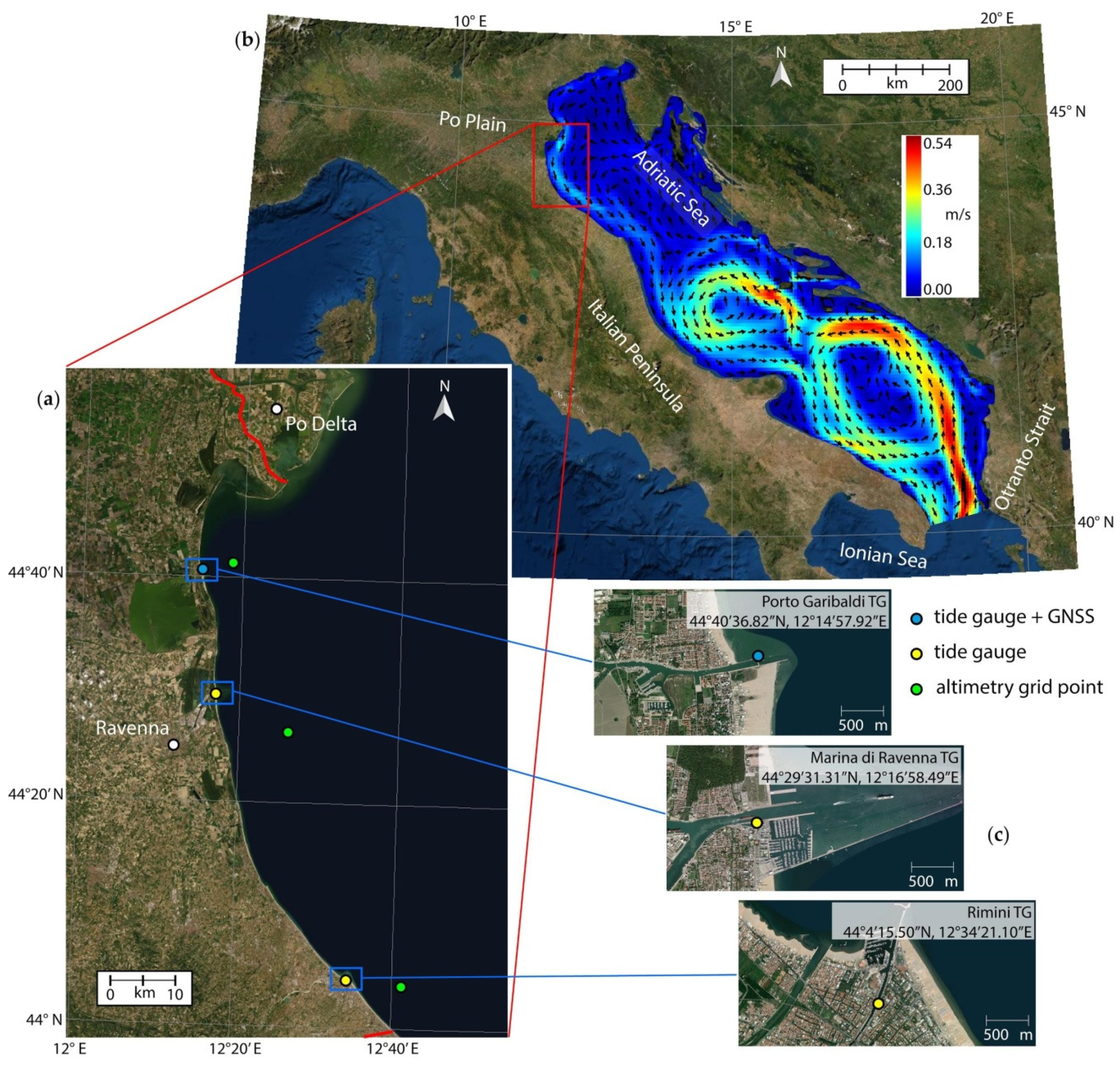
2. Study Area
3. Data
4. Analysis
5. Results
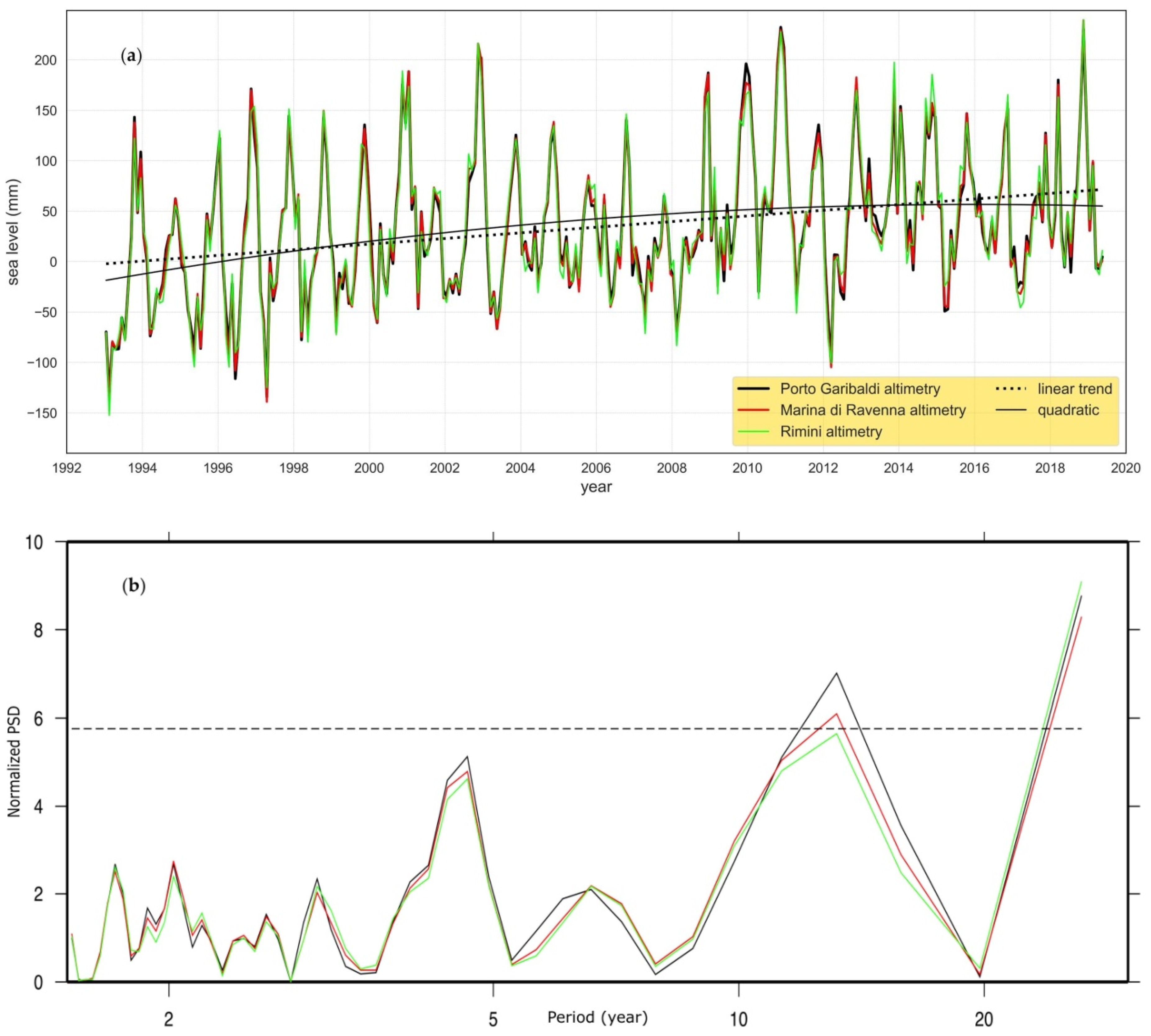
5.1. Sea-Level Assessment
5.2. Periodic Signals
6. Discussion
6.1. Sea-Level Time Series and Rates for the E-R Coast
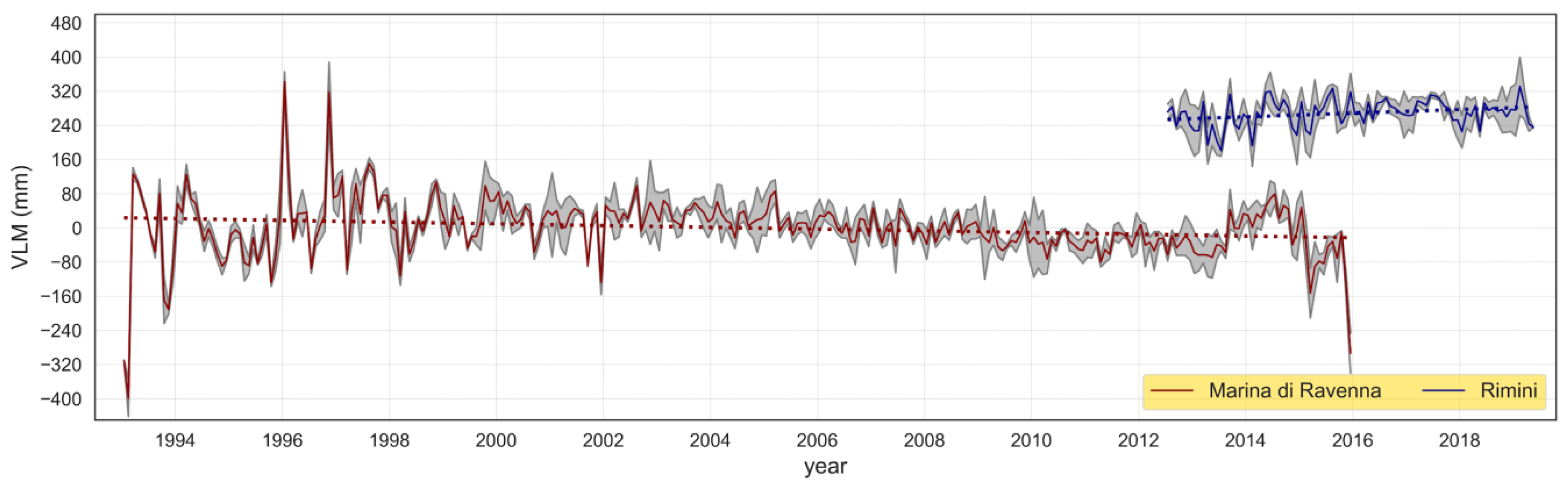
6.2. The Role of Vertical Movements in Sea-Level Determination
6.3. The Sea-Level Trend Acceleration Issue
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMO | Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation |
| ARPAE | Regional Agency for Prevention, Environment, and Energy of the Emilia-Romagna region |
| ASL | Absolute Sea Level |
| CMEMS | Copernicus Marine Environment Service |
| DAC | Dynamic Atmospheric Corrections |
| DInSAR | Differential Synthetic-Aperture Radar Interferometry |
| DUACS | Data Unification and Altimeter Combinations System |
| E-R | Emilia-Romagna |
| EAC | Eastern Adriatic Current |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| ECV | Essential Climate Variable |
| EMD | Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| ENSO | El Niño Southern Oscillation |
| ERF | Effective Radiative Forcing |
| GARI | Permanent GNSS station co-located at Porto Garibaldi tide gauge |
| GCOS | Global Climate Observing System |
| GIA | Glacial Isostatic Adjustment |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| HF | High Frequencies response of sea level to wind and pressure forcing effects |
| Hs | Significant wave Height |
| IB | Inverse Barometer effect |
| IGS | International GPS Service |
| IMF | Intrinsic Mode Function |
| InSAR | Interferometric Synthetic-Aperture Radar |
| INGV | Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia |
| IOC | Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| LSP | Lomb–Scargle Periodogram |
| NAO | North Atlantic Oscillation |
| NGL | Nevada Geodetic Laboratory |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Square regression |
| PSMSL | Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level |
| RLR | Revised Local Reference |
| RMN | Italian National Tide Gauge Network |
| RSL | Relative Sea Level |
| SA | Satellite Altimetry |
| SAPG | Closest altimetry pixel to Porto Garibaldi tide gauge |
| SARA | Closest altimetry pixel to Marina di Ravenna tide gauge |
| SARN | Closest altimetry pixel to Rimini tide gauge |
| SLE | Sea-Level Equation |
| SSH | Sea Surface Height |
| TG | Tide Gauge |
| TGPG | Tide Gauge at Porto Corsini |
| TGRA | Tide Gauge at Marina di Ravenna |
| TGRN | Tide Gauge at Rimini |
| UNFCCC | United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change |
| VLM | Vertical Land Movement |
| WAC | Western Adriatic Current |
Appendix A

| Rate (mm/year) | Type of Data Considered | |
|---|---|---|
| Antonioli et al., 2017 | 8.3 ± 0.3 | monthly mean (2000–2013) |
| Bruni et al., 2019 | 1.25 ± 0.16 | monthly mean (1873–2016), detrended for non-linear VLM |
| Cerenzia et al., 2016 | 8.5 ± 0.2 | annual mean (1897–2014) |
| 7.7 ± 0.3 | monthly mean (1970–2013) | |
| 9.8 ± 1.3 | annual mean (1990–2013) | |
| (2.2 ± 1.3) | (detrended for linear VLM) | |
| Fenoglio-Marc et al., 2012 | 6.5 ± 1.5 | monthly mean (1993–2008), IB correction, deseasoning |
| Masina and Lamberti, 2013 | 8.6 ± 0.5 | annual mean (1896–2011) |
| 3.1 ± 0.7 | annual mean (1896–1950) | |
| 10.3 ± 8.0 | annual mean (2000–2011) | |
| Tsimplis et al., 2012 | 3.1 ± 1.3 | annual mean (1897–1921) |
| 1.5 ± 1.3 | annual mean (1905–1921), normalized for Trieste | |
| 8.4 ± 1.1 | annual mean (1937–1972) | |
| (7.1 ± 0.8) | (normalized for Trieste) | |
| 3.9 ± 0.6 | daily mean | |
| Zerbini et al., 2017 | 1.22 ± 0.32 | annual mean (1896–2012), IB correction, detrended for non-linear VLM |
| 1.05 ± 0.54 | annual mean (1934–2012), IB correction, detrended for non-linear VLM |
References
- Matthäus, W. On the History of Recording Tide Gauges. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. B Biol. 1972, 73, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.A.; Clark, P.U.; Cazenave, A.; Gregory, J.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Levermann, A.; Merrifield, M.A.; Milne, G.A.; Nerem, R.S.; Nunn, P.D.; et al. Sea level change. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1139–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Legeais, J.-F.; Ablain, M.; Zawadzki, L.; Zuo, H.; Johannessen, J.A.; Scharffenberg, M.G.; Fenoglio-Marc, L.; Fernandes, M.J.; Andersen, O.B.; Rudenko, S.; et al. An improved and homogeneous altimeter sea level record from the ESA Climate Change Initiative. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nerem, R.S.; Beckley, B.D.; Fasullo, J.T.; Hamlington, B.D.; Masters, D.; Mitchum, G.T. Climate-change–driven accelerated sea-level rise detected in the altimeter era. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2022–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dangendorf, S.; Hay, C.; Calafat, F.M.; Marcos, M.; Piecuch, C.G.; Berk, K.; Jensen, J. Persistent acceleration in global sea-level rise since the 1960s. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Marinova, N.; Lowe, J.A.; Brown, S.; Vellinga, P.; de Gusmão, D.; Hinkel, J.; Tol, R.S.J. Sea-level rise and its possible impacts given a ’beyond 4 °C world’ in the twenty-first century. Phil. Trans. Soc. A 2011, 369, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, B.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Zimmermann, J.; Nicholls, R.J. Future Coastal Population Growth and Exposure to Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Flooding—A Global Assessment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, O.B.; Scharroo, R. Range and geophysical corrections in coastal regions: And implications for mean sea surface determination. In Coastal Altimetry; Vignudelli, S., Kostianoy, A., Cipollini, P., Benveniste, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 103–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roblou, L.; Lamouroux, J.; Bouffard, J.; Lyard, F.; Le Hénaff, M.; Lombard, A.; Marsaleix, P.; De Mey, P.; Birol, F. Post-processing altimeter data towards coastal applications and integration into coastal models. In Coastal Altimetry; Vignudelli, S., Kostianoy, A., Cipollini, P., Benveniste, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignudelli, S.; Birol, F.; Benveniste, J.; Fu, L.-L.; Picot, N.; Raynal, M.; Roinarn, H. Satellite Altimetry Measurements of Sea Level in the Coastal Zone. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 1319–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollini, P.; Calafat, F.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Melet, A.; Prandi, P. Monitoring sea level in the coastal zone with satellite altimetry and tide gauges. Surv. Geophys. 2017, 38, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipollini, P.; Benveniste, J.; Birol, F.; Fernandes, M.J.; Obligis, E.; Passaro, M.; Strub, P.T.; Valladeau, G.; Vignudelli, S.; Wilkin, J. Satellite altimetry in coastal regions. In Satellite Altimetry over the Oceans and Land Surfaces; Stammer, D., Cazenave, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 343–380. [Google Scholar]
- Marti, F.; Cazenave, A.; Birol, F.; Passaro, M.; Léger, F.; Niño, F.; Almar, R.; Benveniste, J.; Legeais, J.F. Altimetry-based sea level trends along the coasts of Western Africa. Adv. Space Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodworth, P.L.; Player, R. The permanent service for mean sea level: An update to the 21st century. J. Coast. Res. 2003, 19, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Holgate, S.J.; Matthews, A.; Woodworth, P.L.; Rickards, L.J.; Tamisiea, M.E.; Bradshaw, E.; Foden, P.R.; Gordon, K.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Pugh, J. New Data System and Products at the Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level (PSMSL). Tide Gauge Data. Available online: http://www.psmsl.org/data/obtaining/ (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Zerbini, S.; Plag, H.-P.; Baker, T.; Becker, M.; Billiris, H.; Burki, B.; Kahle, H.-G.; Marsone, I.; Pezzoli, L.; Richter, B.; et al. Sea level in the Mediterranean: A first step towards separating crustal movements and absolute sea-level variations. Glob. Planet Chang. 1996, 14, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouin, M.-N.; Wöppelmann, G. Land motion estimates from GPS at tide gauges: A geophysical evaluation. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 180, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gröger, M.; Plag, H.-P. Estimations of a global sea level trend: Limitations from the structure of the PSMSL global sea level data set. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1993, 8, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, W.E.; Clark, J.A. On Postglacial Sea Level. Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 1976, 46, 647–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostanciaux, E.; Husson, L.; Choblet, G.; Robin, C.; Pedoja, K. Present-day trends of vertical ground motion along the coast lines. Earth Sci. Rev. 2012, 110, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Marcos, M. Vertical land motion as a key to understanding sea level change and variability. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 64–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mellor, G.L.; Ezer, T. Sea level variations induced by heating and cooling: An evaluation of the Boussinesq approximation in ocean models. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 20565–20577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitus, S.; Antonov, J.I.; Boyer, T.P.; Baranova, O.K.; Garcia, H.E.; Locarnini, R.A.; Mishonov, J.R.; Reagan, J.R.; Seidov, D.; Yarosh, E.S.; et al. World ocean heat content and thermosteric sea level change (0–2000 m), 1955–2010. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Cazenave, A.; Gennero, C. Contribution of climate-driven change in continental water storage to recent sea-level rise. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13158–13161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngo-Duc, T.; Laval, K.; Polcher, J.; Lombard, A.; Cazenave, A. Effects of land water storage on global mean sea level over the past half century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L09704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.F.; Dyurgerov, M.B.; Rick, U.K.; O’Neel, S.; Pfeffer, W.T.; Anderson, R.S.; Anderson, S.P.; Glazovsky, A.F. Glaciers dominate Eustatic sea-level rise in the 21st century. Science 2007, 317, 1064–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stammer, D.; Cazenave, A.; Ponte, R.M.; Tamisiea, M.E. Causes for contemporary regional sea level changes. In Annual Review of Marine Science; Carlson, C.A., Giovannoni, S.J., Eds.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 21–46. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer, M.; Glavovic, B.C.; Hinkel, J.; van de Wal, R.; Magnan, A.K.; Abd-Elgawad, A.; Cai, R.; Cifuentes-Jara, M.; DeConto, R.M.; Ghosh, T.; et al. Sea Level Rise and Implications for Low-Lying Islands, Coasts and Communities. In IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E., Mintenbeck, K., Alegrìa, A., Nicolai, M., Okem, A., et al., Eds.; in press; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/chapter/chapter-4-sea-level-rise-and-implications-for-low-lying-islands-coasts-and-communities/ (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Pinardi, N.; Bonaduce, A.; Navarra, A.; Dobricic, S.; Oddo, P. The Mean Sea Level Equation and Its Application to the Mediterranean Sea. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao, R.A.F.; Gregory, J.M.; Bouttes, N. Analysis of the regional pattern of sea level change due to ocean dynamics and density change for 1993-2099 in observations and CMIP5 AOGCMs. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2647–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, K.; Smither, K.; Johnston, P. Sea-level change, glacial rebound and mantle viscosity for northern Europe. Geophys. J. Int. 1998, 134, 102–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peltier, W.R. Global glacial isostasy and the surface of the ice-age Earth: The ICE-5G (VM2) model and GRACE. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2004, 32, 111–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, D.P.; Wahr, J.; Tamisiea, M.E.; Nerem, R.S. Ocean mass from GRACE and glacial isostatic adjustment. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, B11415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcos, M.; Tsimplis, M. Forcing of coastal sea-level rise patterns in the North Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L18604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis, D.; Ruiz, S.; Sotillo, M.G.; Álvarez-Fanjul, E.; Terradas, J. Low frequency Mediterranean sea level variability: The contribution of atmospheric pressure and wind. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 63, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Baker, T.F. Sea level drop in the Mediterranean Sea: An indicator of deep water salinity and temperature changes? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, N.; Masetti, E. Variability of the large scale general circulation of the Mediterranean Sea from observations and modelling: A review. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2000, 158, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafat, F.M.; Chambers, D.P.; Tsimplis, M.N. Mechanism of decadal sea level variability in the eastern North Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C09022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landerer, F.W.; Volkov, D.L. The anatomy of recent large sea level fluctuations in the Mediterranean Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Raicich, F.; Fenoglio-Marc, L.; Shaw, A.G.P.; Marcos, M.; Somot, S.; Bergamasco, F. Recent developments in understanding sea level rise in the Adriatic coasts. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2012, 40–41, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgate, S.J. On the decadal rates of sea level change during the twentieth century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L01602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodworth, P.L.; White, N.J.; Jevrejeva, S.; Holgate, S.J.; Church, J.A.; Gehrels, W.R. Evidence for the accelerations of sea level on multi-decade and century timescales. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozier, M.S.; Roussenov, V.; Reed, M.S.C.; Williams, R.G. Opposing decadal changes for the North Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, G.; Spada, G. Linear and non-linear sea-level variations in the Adriatic Sea from tide gauge records (1872–2012). Ann. Geophys. 2014, 57, P0658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorito, S.; Calabrese, L.; Perini, L.; Cibin, U. Uso del suolo della costa. In Il Sistema Mare-Costa dell’Emilia-Romagna; Perini, L., Calabrese, L., Eds.; Edizioni Pendragon: Bologna, Italy, 2010; pp. 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Marsico, A.; Lisco, S.; Lo Presti, V.; Antonioli, F.; Amorosi, A.; Anzidei, M.; Deiana, G.; De Falco, G.; Fontana, A.; Fontolan, G.; et al. Flooding scenario for four Italian coastal plains using three relative sea level rise models. J. Maps 2017, 13, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perini, L.; Calabrese, L.; Luciani, P.; Olivieri, M.; Galassi, G.; Spada, G. Sea-level rise along the Emilia-Romagna coast (Northern Italy) in 2100: Scenarios and impacts. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 2271–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simoncelli, S.; Fratianni, C.; Pinardi, N.; Grandi, A.; Drudi, M.; Oddo, P.; Dobricic, S. Mediterranean Sea Physical Reanalysis (CMEMS MED-Physics) [Data set]. Copernic. Monit. Environ. Mar. Serv. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambolati, G.; Teatini, P. Numerical analysis of land subsidence due to natural compaction of the Upper Adriatic Sea basin. In CENAS, Coastline Evolution of the Upper Adriatic Sea due to Sea Level Rise and Natural and Anthropogenic Land Subsidence; Gambolati, G., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishing, Water Science & Technology Library: Norwell, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 28, pp. 103–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ferranti, L.; Antonioli, F.; Anzidei, M.; Monaco, C.; Stocchi, P. The timescale and spatial extent of vertical tectonic motions in Italy: Insights from relative sea-level changes studies. J. Virtual Explor. 2010, 36, 1441–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, F.; Anzidei, M.; Lambeck, K.; Auriemma, R.; Gaddi, D.; Furlani, S.; Orrù, P.; Solinas, E.; Gaspari, A.; Karinja, S.; et al. Sea level change in Italy during Holocene from archaeological and geomorphological data. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2007, 26, 2463–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, F.; Ferranti, L.; Fontana, A.; Amorosi, A.; Bondesan, A.; Braitenberg, C.; Dutton, A.; Fontolan, G.; Furlani, S.; Lambeck, K.; et al. Holocene relative sea-level changes and vertical movements along the Italian coastline. Quat. Int. 2009, 206, 102–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Ferronato, M.; Gambolati, G.; Bertoni, W.; Gonella, M. A century of land subsidence in Ravenna, Italy. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzi, M.; Bonsignore, F.; De Nigris, N.; Paccagnella, T.; Romagnoli, C.; Unguendoli, S. Stato del Litorale Emiliano-Romagnolo al 2012. Erosione e Interventi di Difesa; I Quaderni di ARPAE: Bologna, Italy, 2016; p. 277. ISBN 978-88-87854-41-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pirazzoli, P.A. Secular trends of relative sea-level (RSL) changes indicated by tide-gauge records. J. Coast. Res. 1986, S11, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi, M.; Costantino, R.; De Nigris, N.; Morelli, M.; Romagnoli, C.; Unguendoli, S.; Vecchi, E. Stato del Litorale Emiliano-Romagnolo al 2018. Erosione e Interventi di Difesa; I Quaderni di ARPAE: Bologna, Italy; p. 259. ISBN 978-88-87854-41-1. in press.
- Vecchi, E.; Aguzzi, M.; Albertazzi, C.; De Nigris, N.; Gandolfi, S.; Morelli, M.; Tavasci, L. Third beach nourishment project with submarine sands along Emilia-Romagna coast: Geomatic methods and first monitoring results. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2020, 31, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, A.; Anderlini, L.; Palano, M.; Albano, M.; Pezzo, G.; Antoncecchi, I.; Chiarabba, C.; Serpelloni, E.; Stramondo, S. Application and analysis of geodetic protocols for monitoring subsidence phenomena along on-shore hydrocarbon reservoirs. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 69, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerenzia, I.; Putero, D.; Bonsignore, F.; Galassi, G.; Olivieri, M.; Spada, G. Historical and recent sea level rise and land subsidence in Marina di Ravenna, northern Italy. Ann. Geophys. 2016, 59, p0546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavola, P.; Armaroli, C.; Chiggiato, J.; Valentini, A.; Deserti, M.; Perini, L.; Luciani, P. Impact of storms along the coastline of Emilia-Romagna: The morphological signature on the Ravenna coastline (Italy). J. Coast. Res. 2007, SI50, 540–544. [Google Scholar]
- Sedrati, M.; Ciavola, P.; Reyns, J.; Armaroli, C.; Sipka, V. Morphodynamics of a Microtidal Protected Beach during Low Wave-energy Conditions. J. Coast. Res. 2009, SI56, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Orlić, M.; Gačić, M.; La Violette, P.E. The currents and circulation of the Adriatic Sea. Oceanol. Acta 1992, 15, 109–124. [Google Scholar]
- Artegiani, A.; Bregant, D.; Paschini, E.; Pinardi, N.; Raicich, F.; Russo, A. The Adriatic Sea general circulation. Part I: Air-sea interactions and water mass structure. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 14, 1492–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artegiani, A.; Paschini, E.; Russo, A.; Bregant, D.; Raicich, F.; Pinardi, N. The Adriatic Sea general circulation. Part II: Baroclinic circulation structure. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 27, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zore, M. On gradient currents in the Adriatic Sea. Acta Adriat. 1956, 8, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Poulain, P.-M. Adriatic Sea surface circulation as derived from drifter data between 1990 and 1999. J. Mar. Syst. 2001, 29, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio-Marc, L.; Braitenberg, C.; Turini, L. Sea level variability and trends in the Adriatic Sea in 1993-2008 from tide gauges and satellite altimetry. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2012, 40–41, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignudelli, S.; De Biasio, F.; Scozzari, A.; Zecchetto, S.; Papa, A. Sea Level Trends and Variability in the Adriatic Sea and Around Venice. In Fiducial Reference Measurements for Altimetry. International Association of Geodesy Symposia; Mertikas, S., Pail, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, B.; Abdallah, A.M.; Alam El-Din, K.; Nagy, H.; Shaltout, M. Inter-Annual Variability and Trends of Sea Level and Sea Surface Temperature in the Mediterranean Sea over the Last 25 years. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 3787–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GPS. Available online: https://www.sonel.org/-GPS-.html?lang=en (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Devoti, R.; D′Agostino, N.; Serpelloni, E.; Pietrantonio, G.; Riguzzi, F.; Avallone, A.; Cavaliere, A.; Cheloni, D.; Cecere, G.; D′Ambrosio, C.; et al. A Combined Velocity Field of the Mediterranean Region. Ann. Geophys. 2017, 60, S0215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zerbini, S.; Raicich, F.; Prati, C.M.; Bruni, S.; Del Conte, S.; Errico, M.; Santi, E. Sea-level change in the Northern Mediterranean Sea from long-period tide gauge time series. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 167, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, S.; Zerbini, S.; Raicich, F.; Errico, M. Rescue of the 1873-1922 high and low waters of the Porto Corsini/Marina di Ravenna (northern Adriatic, Italy) tide gauge. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1227–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrinelli, A.; Bencivelli, S.; Lovo, S.; Crocetto, N.; Perfetti, N.; Ricchieri, F.; Russo, P. La stazione Mareografica Integrata di Porto Garibaldi. In Proceedings of the Atti 13a Conferenza Nazionale ASITA, Bari, Italy, 1–4 December 2009; pp. 1565–1570. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO/IOC. Manual on sea-level measurement and interpretation. In IOC Manuals and Guides; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1985; Volume 14, p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus-Marine environment monitoring service Website. Available online: https://marine.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Global Climate Observing System (GCOS). Systematic Observation Requirements for Satellite-Based Data Products for Climate (2011 Update)—Supplemental Details to the Satellite-Based Component of the “Implementation Plan for the Global Observing System for Climate in Support of the UNFCCC (2010 update)”, GCOS-154 (WMO). Available online: https://library.wmo.int/opac/doc_num.php?explnum_id=3710 (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Pascual, A.; Faugere, Y.; Larnicol, G.; Le Traon, P.Y. Improved description of the ocean mesoscale variability by combining four satellite altimeters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L02611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dibarboure, G.; Pujol, M.-I.; Briol, F.; Larnicol, G.; Picot, N.; Mertz, F.; Escudier, P.; Ablain, M. Jason-2 in DUACS: Updated System Description, First Tandem Results and Impact on Processing and Products. Mar. Geod. 2011, 34, 214–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AVISO altimetry Website. Available online: https://www.aviso.altimetry.fr/ (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Wunsch, C.; Stammer, D. Atmospheric loading and the oceanic “inverted barometer” effect. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrere, L.; Lyard, F. Modeling the barotropic response of the global ocean to atmospheric wind and pressure forcing—Comparison with observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) (2017): ERA5: Fifth Generation of ECMWF Atmospheric Reanalyses of the Global Climate. Copernicus Climate Change Service Climate Data Store (CDS). Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/home (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Spada, G.; Galassi, G. New estimates of secular sea level rise from tide gauge data and GIA modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1067–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomb, N.R. Least-squares frequency analysis of unequally spaced data. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1976, 39, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scargle, J.D. Studies in astronomical time series analysis. II—Statistical aspects of spectral analysis of unevenly spaced data." Astrophys. J. 1982, 263, 835–853. [Google Scholar]
- Ruf, T. The Lomb-Scargle Periodogram in Biological Rhythm Research: Analysis of Incomplete and Unequally Spaced time series. Biol. Rhythm Res. 1999, 30, 178–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudet, L. Application of Empirical Mode Decomposition to the Detection of Sudden Ionospheric Disturbances by Monitoring the Signal of a Distant Very Low Frequency Transmitter. Creative Commons Version. 2009. Available online: https://sidstation.loudet.org/emd-en.xhtml (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Chambers, J.M. Linear models. In Statistical Models in S; Chambers, J.M., Hastie, T.J., Eds.; Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hollander, M.; Wolfe, D.A. Kendall and Spearman tests. In Nonparametric Statistical Methods; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1973; pp. 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Sea Level Research Group, University of Colorado. Available online: http://sealevel.colorado.edu (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Meyssignac, B.; Calafat, F.M.; Somot, S.; Rupolo, V.; Stocchi, P.; Cazenave, A. Two-dimensional reconstruction of the Mediterranean sea level over 1970-2006 from tide gauge data and regional ocean circulation model outputs. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 77, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibić, I.; Šepić, J.; Pasarić, M.; Orlić, M. The Adriatic Sea: A Long-Standing Laboratory for Sea Level Studies. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 3765–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Lichter, M. Statistical analysis of recent Mediterranean Sea-Level data. Geomorphology 2009, 107, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasarić, M.; Orlić, M. Response of the Adriatic Sea Level to the planetary-scale atmospheric forcing. In Sea Level Changes-Determination and Effects, Geophysical Monograph; Woodworth, P.L., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; Volume 69, pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaduce, A.; Pinardi, N.; Oddo, P.; Spada, G.; Larnicol, G. Sea-level variability in the Mediterranean Sea from altimetry and tide gauges. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 2851–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Woodworth, P.L. The global distribution of the seasonal sea level cycle calculated from coastal tide gauge data. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 16031–16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, P.; Bonaduce, A.; Pinardi, N.; Guarnieri, A. Sensitivity of the Mediterranean sea level to atmospheric pressure and free surface elevation numerical formulation in NEMO. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 3001–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Calafat, F.M.; Marcos, M.; Jordà, G.; Gomis, D.; Fenoglio-Marc, L.; Struglia, M.V.; Josey, S.; Chambers, D.P. The effect of the NAO on sea level and on mass changes in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, J.R. An Introduction to Error Analysis: The Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements; University Science Books: Mill Valley, CA, USA, 1997; p. 327. [Google Scholar]
- Masina, M.; Lamberti, A. A nonstationary analysis for the Northern Adriatic extreme sea levels. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 3999–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, F.; Anzidei, M.; Amorosi, A.; Lo Presti, V.; Mastronuzzi, G.; Deiana, G.; De Falco, G.; Fontana, A.; Fontolan, G.; Lisco, S.; et al. Sea-level rise and potential drowning of the Italian coastal plains: Flooding risk scenarios for 2100. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 158, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peltier, W.R.; Tushingham, A.M. Global sea level rise and the greenhouse effect—Might they be connected? Science 1989, 244, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prandi, P.; Cazenave, A.; Becker, M. Is coastal mean sea level rising faster than the global mean? A comparison between tide gauges and satellite altimetry over 1993-2007. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L05602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carminati, E.; Di Donato, G. Separating natural and anthropogenic vertical movements in fast subsiding areas: The Po plain (N. Italy) case. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbini, S.; (Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Bologna, Bologna, Emilia-Romagna, Italy). Personal communication, 2020.
- ARPAE. Rilievo Della Subsidenza Nella Pianura Emiliano-Romagnola—Seconda Fase. Relazione Finale; ARPAE: Bologna, Italy, 2018; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti, L.; Tapponnier, P.; King, G.C.P.; Meyer, B.; Manighetti, I. Growth folding and active thrusting in the Montello region, Veneto, northern Italy. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 739–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio-Marc, L.; Dietz, C.; Groten, E. Vertical land motion in the Mediterranean Sea from altimetry and tide gauge stations. Mar. Geod. 2004, 27, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Vigo, I.; Chao, B.F.; Martinez, M.C. Vertical crustal motion along the Mediterranean and Black Sea coast derived from ocean altimetry and tide gauge data. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2007, 64, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Marcos, M. Coastal sea level rise in southern Europe and the nonclimate contribution of vertical land motion. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C01007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nerem, R.S.; Mitchum, G.T. Estimates of vertical crustal motion derived from differences of TOPEX/POSEIDON and tide gauge sea level measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, C.; Kuo, C.; Mitrovica, J.X. Glacial Isostatic Adjustment in the Great Lakes region inferred by tide gauges and satellite altimetry. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2002AGUSM.U42A..14S/abstract (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Larsen, C.F.; Echelmeyer, K.A.; Freymueller, J.T.; Motyka, R.J. Tide gauge records of uplift along the northern Pacific-North American plate boundary, 1937 to 2001. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 2216–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, Y.; Scholz, C.H. Vertical deformation of the Japanese islands, 1996-1999. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 2257–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Shum, C.; Braun, A.; Mitrovica, J.X. Vertical crustal motion determined by satellite altimetry and tide gauge data in Fennoscandia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L01608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, R.; Beckley, B.; Lemoine, F. Vertical crustal motion derived from satellite altimetry and tide gauges, and comparison with DORIS measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 45, 1510–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santamarìa-Gomez, A.; Gravelle, M.; Wöppelmann, G. Long-term vertical land motion from double-differenced tide gauge and satellite altimetry data. J. Geod. 2014, 88, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinherenbrink, M.; Riva, R.; Frederikse, T. A comparison of methods to estimate vertical land motion trends from GNSS and altimetry at tide gauge stations. Ocean Sci. 2018, 14, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, P.J. An Assessment of the Utility of Satellite Altimetry and Tide Gauge Data (ALT-TG) as a Proxy for Estimating Vertical Land Motion. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 35, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlington, B.D.; Frederikse, T.; Nerem, R.S.; Fasullo, J.T.; Adhikari, S. Investigating the Acceleration of Regional Sea Level Rise During the Satellite Altimeter Era. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasullo, J.T.; Nerem, R.S.; Hamlington, B. Is the detection of accelerated sea level rise imminent? Sci. Rep. 2016, 31245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazenave, A.; Cabanes, C.; Dominh, K.; Mangiarotti, S. Recent sea level change in the Mediterranean Sea revealed by Topex/Poseidon satellite altimetry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 1607–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio-Marc, L. Analysis and representation of regional sea-level variability from altimetry and atmospheric-oceanic data. Geophys. J. Int. 2001, 145, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigo, I.; García, D.; Chao, B.F. Change of sea level trend in Mediterranean and Black Seas. J. Mar. Res. 2005, 63, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Criado-Aldeanueva, F.; Del Río, J.; Vera, J.G.-L. Steric and mass-induced Mediterranean sea level trends from 14 years of altimetry data. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 60, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth, P. A search for accelerations in records of European mean sea level. Int. J. Climatol. 1990, 10, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, B.C. Global sea level rise. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1991, 96, 6981–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jevrejeva, S.; Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Holgate, S. Nonlinear trends and multiyear cycles in sea level records. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C09012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meloni, M.; Bouffard, J.; Doglioli, A.M.; Petrenko, A.A.; Valladeau, G. Toward science-oriented validations of coastal altimetry: Application to the Ligurian Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poitevin, C.; Wöppelmann, G.; Raucoules, D.; Le Cozannet, G.; Marcos, M.; Testut, L. Vertical land motion and relative sea level changes along the coastline of Brest (France) from combined space-borne geodetic methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biasio, F.; Baldin, G.; Vignudelli, S. Revisiting Vertical Land Motion and Sea Level Trends in the Northeastern Adriatic Sea Using Satellite Altimetry and Tide Gauge Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchettin, D.; Bruni, S.; Raicich, F.; Lionello, P.; Adloff, F.; Androsov, A.; Antonioli, F.; Artale, V.; Carminati, E.; Ferrarin, C.; et al. Review article: Sea-level rise in Venice: Historic and future trends. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| SA Rate (mm/year) | SA Acceleration (mm/year2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Porto Garibaldi (January 1993–May 2019) | 2.8 ± 0.5 *** | −0.3 ± 0.1 * |
| Marina di Ravenna (January 1993–May 2019) | 2.8 ± 0.5 *** | −0.3 ± 0.1 * |
| Rimini (January 1993–May 2019) | 2.9 ± 0.5 *** | −0.3 ± 0.1 * |
| TG Rate (mm/year) | TG (IB-Corrected) Rate (mm/year) | |
|---|---|---|
| Porto Garibaldi (July 2009–December 2019) | 1.4 ± 2.8 | 2.8 ± 2.2 |
| Marina di Ravenna (January 1993–December 2015) | 5.8 ± 0.8 *** | 5.5 ± 0.8 *** |
| Rimini (July 2012–September 2020) | −7.7 ± 3.6 * | −5.1 ± 3.0 ° |
| SA Rate (mm/year) | TG (IB-Corrected) Rate (mm/year) | |
|---|---|---|
| Porto Garibaldi (July 2009–May 2019) | −3.1 ± 2.0 | 1.2 ± 2.3 |
| Marina di Ravenna (January 1993–December 2015) | 3.5 ± 0.6 *** | 5.5 ± 0.8 *** |
| Rimini (July 2012–May 2019) | −3.3 ± 3.2 | −7.6 ± 3.7 * |
| 1992–2000 (mm/year) | 2002–2006 (mm/year) | 2006–2011 (mm/year) | 2011–2016 (mm/year) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porto Garibaldi | 7.5–10 | 7.5–10 | 2.5–5 | 2.5–5 |
| Marina di Ravenna | 7.5–10 | 7.5–10 | 5–7.5 | 2.5–5 |
| Rimini | 5–7.5 | 5–7.5 | 5–7.5 | 0–2.5 |
| U | N | S | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porto Garibaldi (July 2009–May 2019) | −4.3 ± 3.1 *** | −1.7 ± 2.3 | −0.2 ± 2.1 |
| Marina di Ravenna (January 1993–December 2015) | −2 ± 1 | NA | NA |
| Rimini (July 2012–May 2019) | 4.3 ± 4.9 | NA | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meli, M.; Olivieri, M.; Romagnoli, C. Sea-Level Change along the Emilia-Romagna Coast from Tide Gauge and Satellite Altimetry. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010097
Meli M, Olivieri M, Romagnoli C. Sea-Level Change along the Emilia-Romagna Coast from Tide Gauge and Satellite Altimetry. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010097
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeli, Matteo, Marco Olivieri, and Claudia Romagnoli. 2021. "Sea-Level Change along the Emilia-Romagna Coast from Tide Gauge and Satellite Altimetry" Remote Sensing 13, no. 1: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010097
APA StyleMeli, M., Olivieri, M., & Romagnoli, C. (2021). Sea-Level Change along the Emilia-Romagna Coast from Tide Gauge and Satellite Altimetry. Remote Sensing, 13(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010097